#psychological disorder
Text


Simple journaling yg mana waktu itu lagi hype ngobrolin dunia mental health. Bahkan lagi nonton drakor its ok not to be okay yg nyeritain banyak soal psikologi, mental health, trauma, dan kecenderungan kepribadian anti simpati + nyeleneh dari peran utama cewek versus kepribadian kalem baik hati dari peran utama cowok. Lubh the k-drama🤍
1 note
·
View note
Text
I talk to many people who say things like "oh I have trauma but I don't have PTSD", but then when I talk to them a little more I realize that they most likely do, they just can't recognize it as such due to how lacking PTSD awareness is, even beyond the whole "it's not just a veteran's disorder" thing.
The main reason they think they don't have PTSD usually has to do with flashbacks and nightmares, either they have one but not the other or have neither. But here's the thing, those are only two symptoms out of the 23-odd recognized symptoms. Flashbacks and nightmares are two of the five symptoms under Criterion B (Intrusion), which you only need one of for a diagnosis. The other three symptoms are unwanted upsetting memories, emotional distress after being reminded of trauma and physical reactivity after being reminded of trauma (i.e. shaking, sweating, heart racing, feeling sick, nauseous or faint, etc). Therefore you can have both flashbacks and nightmares, one but not the other, or neither and still have PTSD.
In fact, a lot of the reasons people give me for why they don't think they have PTSD are literally a part of the diagnostic criteria.
"Oh, I can barely remember most parts of my trauma anyway." Criterion D (Negative Alterations in Cognition and Mood) includes inability to recall key features of the trauma.
"Oh but I don't get upset about my trauma that often because I avoid thinking of it or being around things that remind me of it most of the time." Criterion C (Avoidance) includes avoiding trauma-related thoughts or feelings and avoiding trauma-related external reminders, and you literally cannot get diagnosed if you don't have at least one of those two symptoms.
"Oh I just have trouble getting to sleep or staying asleep, but I don't have nightmares." Criterion E (Alterations in Arousal and Reactivity) includes difficulting sleeping outside of nightmares.
"But I didn't have many/any trauma symptoms until a long time after the trauma happened." There's literally an entire specification for that.
Really it just shows how despite being one of the most well-known mental illnesses, people really don't know much about PTSD. If you have trauma, I ask you to at least look at the criteria before you decide you don't have PTSD. Hell, even if you don't have trauma, look at the criteria anyway because there are so many symptoms in there that just are not talked about.
PTSD awareness is not just about flashbacks and nightmares.
#ptsd#post traumatic stress disorder#cptsd#complex post traumatic stress disorder#complex ptsd#trauma#actually ptsd#actually cptsd#mental illness#mental health#mental health awareness#ptsd awareness#cptsd awareness#neurodivergent#ptsd thoughts#awareness#important#mentally ill#actually mentally ill#psychology
48K notes
·
View notes
Text

Understanding Psychological Disorders: A Guide by Shri Balmukand Apex Hospital
Psychological disorders, often referred to as mental health disorders, are conditions that affect a person's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. They can range from mild to severe and can impact every aspect of a person's life. At Shri Balmukand Apex Hospital, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive care and support for individuals dealing with psychological disorders. Our team of experienced psychologists and psychiatrists work tirelessly to diagnose, treat, and manage these conditions, helping individuals regain control of their lives.
1 note
·
View note
Text

#aspd thoughts#aspd feels#aspd things#actually aspd#aspd traits#psychology#life quote#quotes#mental health#quoteoftheday#bipolar#bipolar girl#bipolar disorder#dark humor#dark#art
26K notes
·
View notes
Text

Story from the Washington Post here, non-paywall version here.
Washington Post stop blocking linksharing and shit challenge.
"The young woman was catatonic, stuck at the nurses’ station — unmoving, unblinking and unknowing of where or who she was.
Her name was April Burrell.
Before she became a patient, April had been an outgoing, straight-A student majoring in accounting at the University of Maryland Eastern Shore. But after a traumatic event when she was 21, April suddenly developed psychosis and became lost in a constant state of visual and auditory hallucinations. The former high school valedictorian could no longer communicate, bathe or take care of herself.
April was diagnosed with a severe form of schizophrenia, an often devastating mental illness that affects approximately 1 percent of the global population and can drastically impair how patients behave and perceive reality.
“She was the first person I ever saw as a patient,” said Sander Markx, director of precision psychiatry at Columbia University, who was still a medical student in 2000 when he first encountered April. “She is, to this day, the sickest patient I’ve ever seen.” ...
It would be nearly two decades before their paths crossed again. But in 2018, another chance encounter led to several medical discoveries...
Markx and his colleagues discovered that although April’s illness was clinically indistinguishable from schizophrenia, she also had lupus, an underlying and treatable autoimmune condition that was attacking her brain.
After months of targeted treatments [for lupus] — and more than two decades trapped in her mind — April woke up.
The awakening of April — and the successful treatment of other people with similar conditions — now stand to transform care for some of psychiatry’s sickest patients, many of whom are languishing in mental institutions.
Researchers working with the New York state mental health-care system have identified about 200 patients with autoimmune diseases, some institutionalized for years, who may be helped by the discovery.
And scientists around the world, including Germany and Britain, are conducting similar research, finding that underlying autoimmune and inflammatory processes may be more common in patients with a variety of psychiatric syndromes than previously believed.
Although the current research probably will help only a small subset of patients, the impact of the work is already beginning to reshape the practice of psychiatry and the way many cases of mental illness are diagnosed and treated.
“These are the forgotten souls,” said Markx. “We’re not just improving the lives of these people, but we’re bringing them back from a place that I didn’t think they could come back from.” ...
Waking up after two decades
The medical team set to work counteracting April’s rampaging immune system and started April on an intensive immunotherapy treatment for neuropsychiatric lupus...
The regimen is grueling, requiring a month-long break between each of the six rounds to allow the immune system to recover. But April started showing signs of improvement almost immediately...
A joyful reunion
“I’ve always wanted my sister to get back to who she was,” Guy Burrell said.
In 2020, April was deemed mentally competent to discharge herself from the psychiatric hospital where she had lived for nearly two decades, and she moved to a rehabilitation center...
Because of visiting restrictions related to covid, the family’s face-to-face reunion with April was delayed until last year. April’s brother, sister-in-law and their kids were finally able to visit her at a rehabilitation center, and the occasion was tearful and joyous.
“When she came in there, you would’ve thought she was a brand-new person,” Guy Burrell said. “She knew all of us, remembered different stuff from back when she was a child.” ...
The family felt as if they’d witnessed a miracle.
“She was hugging me, she was holding my hand,” Guy Burrell said. “You might as well have thrown a parade because we were so happy, because we hadn’t seen her like that in, like, forever.”
“It was like she came home,” Markx said. “We never thought that was possible.”
...After April’s unexpected recovery, the medical team put out an alert to the hospital system to identify any patients with antibody markers for autoimmune disease. A few months later, Anca Askanase, a rheumatologist and director of the Columbia Lupus Center,who had been on April’s treatment team, approached Markx. “I think we found our girl,” she said.
Bringing back Devine
When Devine Cruz was 9, she began to hear voices. At first, the voices fought with one another. But as she grew older, the voices would talk about her, [and over the years, things got worse].
For more than a decade, the young woman moved in and out of hospitals for treatment. Her symptoms included visual and auditory hallucinations, as well as delusions that prevented her from living a normal life.
Devine was eventually diagnosed with schizoaffective disorder, which can result in symptoms of both schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. She also was diagnosed with intellectual disability.
She was on a laundry list of drugs — two antipsychotic medications, lithium, clonazepam, Ativan and benztropine — that came with a litany of side effects but didn’t resolve all her symptoms...
She also had lupus, which she had been diagnosed with when she was about 14, although doctors had never made a connection between the disease and her mental health...
Last August, the medical team prescribed monthly immunosuppressive infusions of corticosteroids and chemotherapy drugs, a regime similar to what April had been given a few years prior. By October, there were already dramatic signs of improvement.
“She was like ‘Yeah, I gotta go,’” Markx said. “‘Like, I’ve been missing out.’”
After several treatments, Devine began developing awareness that the voices in her head were different from real voices, a sign that she was reconnecting with reality. She finished her sixth and final round of infusions in January.
In March, she was well enough to meet with a reporter. “I feel like I’m already better,” Devine said during a conversation in Markx’s office at the New York State Psychiatric Institute, where she was treated. “I feel myself being a person that I was supposed to be my whole entire life.” ...
Her recovery is remarkable for several reasons, her doctors said. The voices and visions have stopped. And she no longer meets the diagnostic criteria for either schizoaffective disorder or intellectual disability, Markx said...
Today, Devine lives with her mother and is leading a more active and engaged life. She helps her mother cook, goes to the grocery store and navigates public transportation to keep her appointments. She is even babysitting her siblings’ young children — listening to music, taking them to the park or watching “Frozen 2” — responsibilities her family never would have entrusted her with before her recovery.
Expanding the search for more patients
While it is likely that only a subset of people diagnosed with schizophrenia and psychotic disorders have an underlying autoimmune condition, Markx and other doctors believe there are probably many more patients whose psychiatric conditions are caused or exacerbated by autoimmune issues...
The cases of April and Devine also helped inspire the development of the SNF Center for Precision Psychiatry and Mental Health at Columbia, which was named for the Stavros Niarchos Foundation, which awarded it a $75 million grant in April. The goal of the center is to develop new treatments based on specific genetic and autoimmune causes of psychiatric illness, said Joseph Gogos, co-director of the SNF Center.
Markx said he has begun care and treatment on about 40 patients since the SNF Center opened. The SNF Center is working with the New York State Office of Mental Health, which oversees one of the largest public mental health systems in America, to conduct whole genome sequencing and autoimmunity screening on inpatients at long-term facilities.
For “the most disabled, the sickest of the sick, even if we can help just a small fraction of them, by doing these detailed analyses, that’s worth something,” said Thomas Smith, chief medical officer for the New York State Office of Mental Health. “You’re helping save someone’s life, get them out of the hospital, have them live in the community, go home.”
Discussions are underway to extend the search to the 20,000 outpatients in the New York state system as well. Serious psychiatric disorders, like schizophrenia, are more likely to be undertreated in underprivileged groups. And autoimmune disorders like lupus disproportionately affect women and people of color with more severity.
Changing psychiatric care
How many people ultimately will be helped by the research remains a subject of debate in the scientific community. But the research has spurred excitement about the potential to better understand what is going on in the brain during serious mental illness...
Emerging research has implicated inflammation and immunological dysfunction as potential players in a variety of neuropsychiatric conditions, including schizophrenia, depression and autism.
“It opens new treatment possibilities to patients that used to be treated very differently,” said Ludger Tebartz van Elst, a professor of psychiatry and psychotherapy at University Medical Clinic Freiburg in Germany.
In one study, published last year in Molecular Psychiatry, Tebartz van Elst and his colleagues identified 91 psychiatric patients with suspected autoimmune diseases, and reported that immunotherapies benefited the majority of them.
Belinda Lennox, head of the psychiatry department at the University of Oxford, is enrolling patients in clinical trials to test the effectiveness of immunotherapy for autoimmune psychosis patients.
As a result of the research, screenings for immunological markers in psychotic patients are already routine in Germany, where psychiatrists regularly collect samples from cerebrospinal fluid.
Markx is also doing similar screening with his patients. He believes highly sensitive and inexpensive blood tests to detect different antibodies should become part of the standard screening protocol for psychosis.
Also on the horizon: more targeted immunotherapy rather than current “sledgehammer approaches” that suppress the immune system on a broad level, said George Yancopoulos, the co-founder and president of the pharmaceutical company Regeneron.
“I think we’re at the dawn of a new era. This is just the beginning,” said Yancopoulos."
-via The Washington Post, June 1, 2023
#mental illness#schizophrenia#schizoaffective#psychotic disorders#psychology#neurology#autoimmune#autoimmine disease#neuroscience#medical news#medical research#catatonia#immunotherapy#immune system#clinical trials#good news#hope
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
i really dislike it when people don’t understand perfectionism.
like, it isn’t always “person who has tons of motivation and spends a ton of time making this thing *just* right”
wayyyyyy more often than not it’s:
”I know that if I try to make this thing, it won’t be perfect, so I simply won’t try.”
which definitely sounds bad, right? but when you realize that it doesn’t just apply to voluntarily making art, then you realize how perfectionism is not at all a good thing in any context.
“i know that if I try to work on this assignment right now, it won’t be good enough, so i’ll wait until the last possible moment so that I have something forcing me to do it.”
”i know that I should start going to the gym, but I won’t see any improvement right away, so I just won’t.”
”i know that i should brush my teeth tonight, but that won’t be good enough to undo the fact that i haven’t brushed them 4 days in a row, so I just won’t.”
perfectionism isn’t the uncontrollable impulse to make things “just right”. (although it can occasionally manifest as this.)
perfectionism is the absolute, psychological inability to accept the concepts of “good enough” and “better than nothing”.
#perfectionism#perfection#art#writing#making#making art#creative#creative process#lifestyle#habits#good habits#living with mental illness#mental illness#mental disorder#adhd#psychology
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
Needs to be said, probably controversial, but "bad" people deserve support for their mental health issues as well. "Bad" people should not be dehumanized and berated for their mental health issues. I dont care what they've done
#mental health#mental illness#actually mentally ill#mental health awareness#npd#aspd#cluster b#psychology#actually aspd#antisocial personality disorder#cluster b pds#personality disorder#aspd positivity
566 notes
·
View notes
Text
Parts of PTSD that no one talks about
Not knowing who to be angry at.
Being angry with yourself for letting it happen even if there was no way to stop it.
Crying and not knowing why.
Flashbacks where nothing bad is happening but it feels bad.
Denying that it ever even happened because your brain doesn't want to process it.
Wanting to go back to it so it feels "bad enough."
Intentionally triggering yourself to feel like your suffering is real.
Being angry all the time at every little thing.
Getting triggered by minor things and then being treated poorly because of your reaction to said trigger.
Hating change.
Being scared to sleep because you know you'll have nightmares.
Struggling to find hobbies that you enjoy.
Feeling like you're barely human.
Struggling to be positive about anything at all.
Feeling like you may be manipulating people around you into liking you.
Feeling like no one believes you because you barely even believe yourself.
Treating your past self as a "dead" version of you and feeling like a completely different person.
Being tired all the time, both physically and mentally.
Feeling like if you talk about it, your safety will be at risk.
Feeling the need to hide your trauma from everyone, including professionals there to help them.
Being paranoid everyone is going to hurt you.
Being physically incapable of talking about it.
Feeling like you're stuck reliving your trauma.
Having to skip classes or work days because of flashbacks.
Mourning your past self.
Wanting to hurt others so they feel what you feel.
Wondering why it had to be you and it wasn't someone else.
Chronic pain.
Clinging to "safe people."
Not being able to find a solid sense of identity.
Forcing yourself to be around people who trigger you for the sake of politeness.
#actually traumatized#trauma#childhood trauma#ptsd#complex ptsd#actually ptsd#did#actually did#system#dissociative identity disorder#mental health#actually mentally ill#psychology#awareness#osdd#actually osdd#osdd system#osddid#cptsd#actually cptsd#post traumatic stress disorder#complex post traumatic stress disorder#complex trauma
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

After almost 7 months of sobriety I decided to go back to therapy.
I’ve officially been diagnosed with PTSD.
Coming to terms with this has not been easy.
Dealing with this sober has not been easy.
So I’m beginning the journey that is healing.
What a weird year it’s been.
#sobriety#sober journey#sober life#stay sober#trauma#psychological disorder#ptsd#ptsd recovery#living with ptsd#severe depression#depression#peace#happy#staystrong#healing
0 notes
Text
#dissociative episode#dissociative amnesia#dissociation#actually dissociative#actually did#dissociative system#dissociative identity disorder#other specified dissociative disorder#psychology#mental illness
248 notes
·
View notes
Text

Colin Murray Parkes, Bereavement: Studies of Grief in Adult Life
515 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hello everyone!
My name is Amina and I am a BSc Psychology with Honours student at the University of Hertfordshire. I am also the principal researcher of a study that aims to investigate whether judging category relatedness within semantic memory can be influenced by the level of typicality the items have alongside whether high versus low autistic traits have any effect on the performance of different types of processing.
I am currently taking volunteers for this online study. Any adults aged 18 to 65 can volunteer and you do not need an official Autism diagnosis to take part.
In the study, you will be given an item/ definition/ scenario at the top of your screen and will have to decide which of two following words match best to that using your keyboard. After that is completed you will be given the RAADS-14 questionnaire to complete.
It will take roughly 15 minutes to complete. However, a maximum of 30 minutes is given for the entire study to be completed including the information sheet, consent form, debrief sheet, and the “breaks” given (which are just for momentarily resting your eyes and hands), otherwise I cannot use your data. Please note that this study cannot be completed on a mobile phone or tablet, it must be done on a computer/laptop as the keyboard is required for the study’s completion.
You can completed this study at anytime until 23:59 GMT on Friday 1st of March here:
https://research.sc/participant/login/dynamic/0D915D45-8D85-44F9-9B63-376AF0C70573
This study has been approved by the Ethics Committee at the University of Hertfordshire and is also being conducted under the supervision of Dr. Nicholas Shipp.
Your participation is very important for this study and is very much appreciated.
Thank you for your time!
Many Thanks
Amina
EDIT: Study is now no longer taking participants!!! Thank you all who took part and spread the word of my study, it definitely means a lot to me 💟
#autistic traits#conceptual processing#typicality#processing#mental processing#autism spectrum disorder#psychology study#psychology research#undergraduate#student dissertation
307 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hot psychology take:
Borderline and Narcissistic Personality Disorder is *so* comorbid.
Like a 30-40% comorbidity rate. The two overlap a Lot. Mostly because of a gender differential; a lot of AMAB people are dx'd as Npd and AFABs are dx'd BPD even if they have the same symptoms.
Yet I'm seeing Borderline people like "Oh yeah I'm an EMPATH that was VICTIMIZED by a NARCISSIST" and Narcissists that are like "Oh I'm a shark chasing after prey, I don't feel anything, all I need a source."
Like no. Y'all ain't that different from one another. There is a substantial overlap in that Venn diagram. The fact that you act like this emotions vs. Non-emotional dichotomy fucking SENDS me, that's not how this works.
I'm Borderline. I don't have NPD, but I'm friends with at least two clinical Narcissists and I love them to death. I relate to them on some levels, not others. PwNPD have emotion, deep emotion, but they operate on the realization that emotional honesty is weakness and that ego is a defense. Borderlines have been punished for having identity and boundaries and therefore sacrifice it for the chance to be loved until they can't take it anymore. Both are trauma-born. Both can be manipulative. Both are statistically more often victims than perpetrators.
Cut the shit already.
-Sincerely, a Borderline dude that loves the entire Cluster B for what it is.
-Sparrow 🧷
#hot psychology take#narcissistic personality disorder#borderline personality disorder#bpd#npd#cluster b
315 notes
·
View notes
Text
“People with ASPD and NPD are unlikely to seek help”
If you were treated like you just murdered the therapist’s entire family in front of them every time you tried I don’t think you’d seek help either
#aspd#npd#narcissist#sociopath#psychopath#bpd#hpd#cluster b#narcissistic personality disorder#antisocial personality disorder#mental illness#mental health#psychology#aspd culture is#npd stigma
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Tales From The Dystopia: Today r/systemscringe Casually Suggests Stripping Licenses From Doctors Who Provide Safe Spaces Endogenic Systems
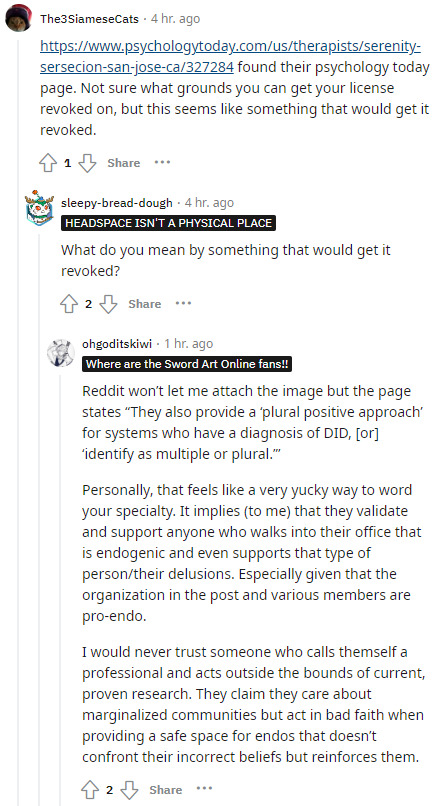
This is just... complete and utter nonsense.
First, we have research into tulpamancy affirming it as a real psychological phenomenon. We have the World Health Organization stating in the ICD-11 that someone may have multiple distinct personality states without a disorder. We have Transgender Mental Health, published by the American Psychiatric Association, stating you can be plural without trauma or a mental disorder.
Current research affirms the existence of endogenic and non-disordered plurality at every turn.
And if someone comes to a doctor experiencing healthy plurality, the last thing any doctor should do is try to gaslight them into thinking their experiences are a delusion or something that needs fixed.
I cannot overstate the pure evil of this comment: If you have a therapist who supports your plurality and provides a safe space for it, r/systemscringe wants them stripped of licenses for it and replaced by people who will treat your headmates as delusions.
We're fortunate that these people don't hold any real power or influence, because this sort of dystopian agenda is absolutely terrifying.
But even though they may not have the power to be able to enact such a thing, it's truly monstrous that they would even suggest it.
#psychiatry#psychology#syscourse#pro endo#pro endogenic#sysblr#multiplicity#plural#plurality#systems#mental health#therapy#r/systemscringe#systemscringe#fakedisordercringe#fake disorder cringe#r/fakedisordercringe#actually plural#actually a system#hate groups#hate group
155 notes
·
View notes
Text

“Heavy thoughts”
The brain of a person with PTSD is always in an exited state. In this state, a person is always ready to defend himself in extraordinary situations, but this same trait becomes a curse when stress leaves a person's life. The nervous system continues to work in the same mode, exhausting its carrier even at rest. This can be compared to a radio that is always on and can not be turned off. Often, this disease can even become an obstacle to sleep. In such situations, people sometimes start to use medications or drụgs.
Please support me with a reblog if you like this art
#my art#tbartist#post traumatic stress disorder#trauma#mental health#anxitey#psychology#bad feeling#artist on tumblr#small artist#digital art#depressing shit#stressed out#leave me alone#cyberpunk style#procreate#art story
139 notes
·
View notes