#it’s cultural story which is mythology
Text
Vote for your favourite horse/horse-adjacent character from Fantasy and Science Fiction books, and yell at me in the replies/comments about your fave that i missed.
#no pegasus or sleipnir bc i'm strictly keeping it to fantasy/scifi books rather than cultural mythology#i tried to limit to one per source except lotr which gets two bc it was The First#the horse and his boy#the narnia chronicles#lord of the rings#the neverending story#the witcher#the wheel of time#a song of ice and fire#the last unicorn#valdemar#shadowfax#bela#bree#binky#artax#bill the pony#roach#the silver#lady amalthea#yfandes#heralds of valdemar
504 notes
·
View notes
Text
rebirth!
#tags contain very light spoilers!!!!!#i've been enjoying it!#currently very busy w classes and such so i haven't had much of an opportunity to progress very far#and ive only had it a handful of days but i can appreciate a lot of what theyre doing :]#of course i am .. very wary when it comes to zack's involvement specifically#i am curious to see where they take his story but i must reiterate time and time again that i. as a zack blog (lol). am very#very very very dependent on and interested in zack's death as a monolith in the narrative#and i do not think i will be changing that soon.. nor do i have much interest in aus in which he survives#(same goes for aerith)#(<- i have metas to write on that)#however.. i am still very early on in the game (still in ch2 -.-)#and i can recognize the need to justify a remake.. esp a remake of something so mythologized and important to#media and culture as the original game was..... ohhh the narrative masterpiece that 1997 is........#so taking this “remake” in such a vastly different direction is nice!#but just to ramble a bit further .. im not a big fan of much of anything contemporary ff..... anything put out from 14-16 i just rlly#havent been able to get into personally.. the methods of story telling and the over reliance on pretty anime graphics#to cover up any weaknesses in character and scenario writing...#and i think thats where the most glaring vices in rebirth have been thus far.. other than the padding for time with fetch quests#(as was in remake)#ok ok my opinions
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Can I have one (1) single classics blog that doesn't continuously shit on adaptations/retellings
#[talk less smile more]#/this is my one tumblr post this week hi#/blog: 'hey look at this cool art of your favourite homer characters! here's a dionysos! here's a good take on ancient greek literature!'#/blog five seconds later: '~feminist~ retellings are ruining culture forever. lore olympus has personally killed my family.#/the ~real myth~ was sooo feminist and my personal headcanon is superior to anything madeline miller does ever which is evil'#/begging y'all to shut the fuck up and think for three seconds about what an adaptation is#/'making a story that is definitely ~originally about~ rape and abduction romantic is evil actually--'#/THIS IS WHAT LORE OLYMPUS IS ABOUT. IT'S ABOUT RAPE AND VIOLENCE AGAINST WOMEN.#/i'm not a big fan of it and it plays very fast and loose with mythology (which is FINE because it's an ADAPTATION) but it IS about rape#/anyways rant over have a lovely week#/rec me blogs if u know any i'd love to engage with classics tumblr a bit again but by the gods it's so tiring
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
>see person with irish mythology url
>'oh sweet i'll check them out'
>pinned post is collage au fic of the ulster cycle
>'We Are Fundamentally Different People'
#absolutely not slagging off this person. godspeed god bless#however as someone who spiritually believes in a lot of irish myth and old religion (not the catholicism)#i am So Incredibly Fucking Cautious abt like. the way ppl treat pantheons and myths as like. fandoms#and like thats not to say u cant make adaptions of myth! ppl do that all the time!#but u have to be cautious not to be disrespectful yknow?#like keep in mind that these are things that genuine people did and do believe in#and if u like. reduce them to incorrect quotes n stuff without being careful its easy to minimise that#esp w minority religions like jesus x judas stuff is probs weird for the christians but i dont care as much abt them#like i feel so so sorry for like. believers in norse greek and roman myth specifically#because theyve become like. pop culture mythology almost#like if i talked abt my faith and people went 'oh like from marvel/percy jackson' i think id fucking bite them#anyway long story short i wont judge u for writing fic n that for myth bcos u could have been careful writing it#but like fuck if im gonna risk reading it to find that out for myself#practically the only 'modernised' gaelic myth i seek out is stuff regarding the dullahan#and thats bcos most of it either conflates it with the headless horseman as in ichabod crane and bram bones#or treats 'dullahan' as a species and isnt specifically about Gan Ceann himself which is where id have potential problems#am i making sense?#fuck knows
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
@feline17ff since you asked!! and yea i didnt wanna make the other post too long esp since knowing me this will likely get long too, but here are all my minor/not fleshed out EAH ocs :D
Ever-After Natives;
- Dahlia Diamandis, Daughter of Rose (Diamonds and Toads) — fleur’s roommate, wants to be a scientist instead of a princess, coughs up flowers and gems when talking, likes hocus lattes, friends with rosabella and darling, rebel
- Furnando Percy-Kit Boots, Son of Puss in Boots — likes fencing, powers of purr-suasion, spanish guitar riffs follow him everywhere, friends with sparrow, crush on kitty, roybel/neutral
- Porter Schumacher, Son of the Shoemaker (The Elves and the Shoemaker) — friends with humphrey dumpty, helps in the fashion design class, likes elf cookies, rebel
- Ernest Pendragon, Son of King Arthur — friends with daring, has a posse that’re all sons of the round table knights, rivals with sparrow, royal
- Richard ‘Dick’ York, Son of the Duke of York — on the debate team, in marching band, can’t make decisions, friends with ernest, royal
- Penelopea Pod, Daughter of the Princess and the Pea — friends with blondie, attention to detail that sometimes borders on nitpicky, always wears comfey clothes since she never gets a good nights rest, royal
- Elio MacDonald, Son of Old MacDonald —has a dog named bingo, has somewhat of a southern accent, best friends with spud, rebel
- Spud Muffin, Son of the Muffin Man — prefers cooking over baking, best friends with elio, crush on miss muffet, rebel
- Valentina Prekrasnaya, Daughter of Vasilisa — actually pretty close with baba yaga, doll collector, royal
- Marie Stahlbaum, Daughter of Clara Stahlbaum (The Nutcracker) — likes fighting as much as dancing, has a pet baby rat, crush on sparrow, rebel
- Figgy Dulce, Daughter of the Sugarplum Fairy — friends and business partners with ginger, always followed by helga and gus due to her powers over sweets, royal
- Brie King, Daughter of the Mouse King — friends with duchess and faybelle, wears furs and luxury brands and hoards finery, royal
Transfer Students;
• Neverland High
- Patricia “Patty” Pan, Daughter of Peter Pan — can fly without wings or pixie dust, crush on jade that drives her narrative, (also adding that she doesn’t want to lose her friends like briar, but is still labeled as a royal overall)
- Jade Hook, Daughter of Captain Hook — has a peg leg and refuses to lose her hand as well, sword fights with furnando, rebel
- Wendell Darling, Son of Wendy Darling — quiet and demure, does lots of photography and candid shots, works on the yearbook, royal
- Tyrick Bell, Son of Tinkerbell — naturally produces pixie dust and accidentally makes things fly all the time, doesnt want to be a sidekick, rebel
- Sierra Lily, Daughter of Tiger Lily — spends lots of time in the enchanted forest, chill and meditative, hangs around pixies and fairies most, royal
• Emerald City High
- Dorian Gale, Son of Dorothy Gale — always lived in oz despite it going against the story, besties with alistair, prefers cats over dogs, royal
- Sarah Crow, Daughter of the Scarecrow — dating tinsley, thrifter, scared of birds, friends with cedar and sierra, royal
- Tinsley Mann, Son of the Tin Man —dating sarah, needs to oil his joints a lot, friends with nathan nutcracker, royal
- Leo Caitiff, Son of the Cowardly Lion — friends with furnando, fem catboy lol, does cheerhexing, royal
- Esmeralda West, Daughter of the Wicked Witch of the West — likes being a witch but doesnt want her sister/cousin killed or herself to be melted, rebel
- Lucinda North, Daughter of the Good Witch of the North — wants to be evil and deceive/manipulate people since its more fun for her, rebel
- William Oz, Son of the Wizard of Oz — destined to be the next wizard despite being the younger sibling, thinks the role is lame since you end up with the reputation of a fraud, rebel
- Winona Oz, Daughter of the Wizard of Oz — wants to be the next wizard but gets denied because of gender roles, rivals with her brother, rebel
• Dowa-Kou (童話高)
- Tsuki Hime (月姫), Daughter of Princess Kaguya (The Tale of the Bamboo Cutter) — light and water powers, only active at night, pined after by all the tarō boys, royal
- Toutaro (桃太郎), Son of Momotaro — great with both plants and animals, pacifist, always has peaches on him, friends with hunter, rebel
- Kanetaro (金太郎), Son of Kintaro — often made to do a bunch of heavy lifting, strong enough to lift tiny and is close friends with him, humble modest and sweet and doesnt like sticking out in a crowd, rebel
- Unabara Taro (海原太郎), Son of Urashima Taro — friends with meeshell, ANOTHER similar situation to briar where he doesnt want to lose his family after 100 years under the sea, still a ‘royal’
#since eah is p much only european stories (minus baba yaga ig they needed more named antagonists to be school staff??)#i wanted to branch out and use fairytales from other cultures for diversity! variety is the spice of life after all ✨#and (as far as i know) japanese stories are the next closest thing to fairytales#as opposed to recurring characters being used to teach different themes or a having singular character with no narrative#which the vast majority of folklore does instead (notably african which was my next go-to)#although if someone who was super interested in norse mythology made characters for eah thatd be so cool!!#as a foil to cupid and the assumed greek mythos story world she hails from#eah#ocs#oc stuff#writing#my writing#my stuff
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
on one hand. this weird girl is homophobic and transphobic and has bad opinions on art. but on the other hand, she's gonna have suuuch a rough queer awakening... shes a wolf girl, an otaku and she reads&watches yuri and tells her mom all about it. and i cant wait to watch it happen
#its gonna be sooooo funny to watch#'how can you tell' I CAN ALWAYS TELL#no uhh i was there#that was me#so thats kinda funny#leon likes talking#by bad opinions on art i mean. she has this massive project story thing shes writing#shes enjoying it. she incorporates a million different fragments of different mythologies#and has a massive world. its in multiple words actually#but you can already smell how she isnt developing any of them enough#anyway this is just buildup to say that. she talked badly of my buddy's story (which is centered in a city) because the scale was smaller#and actually my buddy's story bangs. it goes hard. and he has great art to match#the culture involved is actually well developed bc hes really connected to our country and he does his Research which is always cool#anyway im rambling abt something unrelated now#basically i have a creature to put under a microscope
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
the thing you have to realize about me is that I started taking college classes when I was like fourteen at three different schools between my HS classes, and then at my actual university, I had to start and stop and change gears a few times because of health problems and because I studied abroad for a while and like
that’s why when I start a sentence with “oh, I went to college for--” you never, ever know how it’s going to end. I went to college for a lot of things and honestly most of them were patently insane lmao.
#the egyptology story is kind of a long one I guess#I was more into greek mythology if we're being honest#but I was accepted into a program at UChicago to take a really intensive actual-college-credit course over the summer#and egyptology was what was offered so it was what I took#and I loved learning middle egyptian and studying egyptian culture and religion#I loved going to the OI to translate steles#and all that was probably what got me into the university I ended up attending#but I realized fairly early on that my health would preclude me from ever going on a dig#so I switched gears to translation which I do actually love#but god there's something so shitty about learning to read middle egyptian#and realizing slowly that everything you read in a museum is saying 'for the love of every god do not move this from its resting place'#and you're like... how can I say I respect this religion and these people if I'm desecrating their wishes#and THEN you learn the very imperialist history of egyptology#and... you end up dropping the major because you have ethical qualms#but you know just enough about egypt to know that all these occultists were full of absolute BULLSHIT when you switch to that#people are always like OH YOU STUDIED CULTS AND NRMS AND STUFF DO THEY SCARE YOU#IS THE OCCULT SCARY#no the history of the occult is full of clubs full of idiots arguing over whose dreams are more legit#I'm off topic
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
The particularly Jewish aspects of Death as a character
Are the metaphysical reasons for the animosity I give her with Lucifer Morningstar and the Silver City's constructs, because they are beings of Christian myth and they do not, as such, tend to welcome those that are specifically Jewish or for that matter rooted in paganism. Some of the pagan entities are collectively too powerful to be readily bullied, but they still don't like them and neither are they going to.
The Morningstar as I write them in a story from Death's point of view comes across as a being specifically rooted in Christian mythological tones, directly in line with the Lucifer side of Vertigo (which is among the reasons that I do not like it and why I give Lucifer's side of things a slight bit of a hard time). Death, equally, has the role as guide to souls to retrieve souls that changed their mind about their afterlife, which doesn't endear her to rulers of afterlife planes in general. They are all reluctant to see their kingdoms diminished by even a single soul.
But that animosity in say, Hades or the Aztec realm of the dead would unfold vastly differently to that of Hell (and she is the afterlife traditions of Biblical and Sumerian motifs and the Norse Hel, which is by no means the only afterlife for a Germanic pagan). The Christian aspects also influence strongly Lucifer's smug arrogance, an arrogance backed up by the very literal reality that only the Presence can corral his two eldest if they get rambunctious.
Arrogance with power to back it up is the most dangerous kind. While also contributing to the same ideological gulf as Death sees existence as something to engage with the world and other supernatural entities do not and do not want to.
#death of the endless#sandman fanfic#lucifer morningstar#yes Lucifer is directly from Christian mythology#The Christian Bible never says Lucifer is Ha-Satan#even Revelation only says that the Devil is the Serpent in Genesis#so the version of Lucifer seen in Sandman is much more the product of Milton's mythology than anything else#so very specifically rooted in the pop culture understanding of the Devil rather than the actual lore#which is true of Sandman in general as the myths are often adapted with slight twists to fit the story and the cosmology
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
The truth about Medusa and her rape... Mythology breakdown time!
With the recent release of the Percy Jackson television series, Tumblr is bursting with mythological posts, and the apparition of Medusa the Gorgon has been the object of numerous talks throughout this website… Including more and more spreading of misinformation, and more debates about what is the “true” version of Medusa’s backstory.
Already let us make that clear: the idea that Medusa was actually “blessed” or “gifted” by Athena her petrifying gaze/snake-hair curse is to my knowledge not at all part of the Antique world. I still do not know exactly where this comes from, but I am aware of no Greek or Roman texts that talked about this – so it seems definitively a modern invention. After all, the figure of Medusa and her entire myth has been taken part, reinterpreted and modified by numerous modern women, feminist activist, feminist movements or artists engaged in the topic of women’s life and social conditions – most notably Medusa becoming the “symbol of raped women’ wrath and fury”. It is an interesting reading and a fascinating update of the ancient texts, and it is a worthy take on its own time and context – but today we are not talking about the posterity, reinvention and continuity of Medusa as a myth and a symbol. I want to clarify some points about the ACTUAL myth or legend of Medusa – the original tale, as told by the Greeks and then by the Romans.
Most specifically the question: Was Medusa raped?
Step 1: Yes, but no.
The backstory of Medusa you will find very often today, ranging from mythology manuals (vulgarization manuals of course) to Youtube videos, goes as such: Medusa was a priestess of Athena who got raped by Poseidon while in Athena’s temple, and as a result of this, Athena punished Medusa by turning her into the monstrous Gorgon.
Some will go even further claiming Athena’s “curse” wasn’t a punishment but a “gift” or blessing – and again, I don’t know where this comes from and nobody seems to be able to give me any reliable source for that, so… Let’s put this out of there.
Now this backstory – famous and popular enough to get into Riodan’s book series for example – is partially true. There are some elements here very wrong – and by wrong I do mean wrong.
The story of Medusa being raped and turned into a monster due to being raped does indeed exist, and it is the most famous and widespread of all the Medusa stories, the one people remembered for the longest time and wrote and illustrated the most about. Hence why Medusa became in the 20th century this very important cultural symbol tied to rape and the abuse of women and victim-blaming. HOWEVER – the origin of this story is Ovid’s Metamorphoses, from the first century CE or so. Ovid? A Roman poet writing for Roman people. “Metamorphoses”? One of the two fundamental works of Roman literature and one of the two main texts of Roman mythology, alongside Virgil’s Aeneid. This is a purely Roman story belonging to the Roman culture – and not the Greek one. The story of Medusa’s rape does not have Greek precedents to my knowledge, Ovid introduced the element of rape – which is no surprise given Ovid turned half of the romances of Greek mythology into rapes. Note that, on top of all this, Ovid wasn’t even writing for religious purposes, nor was his text an actual mythological effort – he wrote it with pure literary intentions at heart. It is just a piece of poetry and literature taking inspiration from the legends of the Greek world, not some sort of sacred text.
Second big point: The legend I summarized above? It isn’t even the story Ovid wrote, since there are a lot of elements that do not come from Ovid’s retelling of the story (book fourth of the Metamorphoses). For example Ovid never said Medusa was a priestess of Athena – all he said was that she was raped in the temple of Athena. I shouldn’t even be writing Athena since again, this is a Roman text: we are speaking of Minerva here, and of Neptune, not of Athena or Poseidon. Similarly, Minerva’s curse did not involve the petrifying gaze – rather all Ovid wrote about was that Minerva turned Medusa’s hair into snakes, to “punish” her because her hair were very beautiful, and it was what made her have many suitors (none of which she wanted to marry apparently), and it is also implied it is what made Neptune fall in love (or rather fall in lust) with her. I guess it is from this detail that the reading of “Athena’s curse was a gift” comes from – even though this story also clearly does victim-blaming of rape here.
But what is very fascinating is that… we are not definitively sure Neptune raped Medusa in Ovid’s retelling. For sure, the terms used by Ovid in his fourth book of Metamorphoses are clear: this was an action of violating, sexually assaulting, of soiling and corrupting, we are talking about rape. But Ovid refers several other times to Medusa in his other books, sometimes adding details the fourth-book stories does not have (the sixth book for examples evokes how Neptune turned into a bird to seduce Medusa, which is completely absent from the fourth book’s retelling of Medusa’ curse). And in all those other mentions, the terms to designate the relationship between Medusa and Neptune are more ambiguous, evoking seduction and romance rather than physical or sexual assault. (It does not help that Ovid has an habit of constantly confusing consensual and non-consensual sex in his poems, meaning that a rape in one book can turn into a romance in another, or reversal)
But the latter fact makes more sense when you recall that the rape element was invented and added by Ovid. Before, yes Poseidon and Medusa loved each other, but it was a pure romance, or at least a consensual one-night. Heck, if we go back to the oldest records of the love between Poseidon and Medusa, back in Hesiod’s Theogony, we have descriptions of the two of them laying together in a beautiful, flowery meadow – a stereotypical scene of pastoral romances – with no mention of any brutality or violence of any sort. As a result, it makes sense the original “romantic” story would still “leak” or cast a shadow over Ovid’s reinvented and slightly-confused tale.
Step 2: So… no rape?
Well, if we go by Greek texts, no, apparently Medusa was not raped in Greek mythology, and only became a rape victim through Ovid.
The Ancient Greek texts all record Poseidon and Medusa sleeping with each other and having children, but no mention of rape. And the whole “curse of Athena” thing is not present in the oldest records – no temple of Athena soiling, no angry Athena cursing a poor girl… “No curse?” you say “But then how did Medusa got turned into a Gorgon”? Answer: she did not. She was born like that.
As I said before, the oldest record of Medusa’s romance but also of her family comes from Hesiod’s Theogony (Hesiod being one of the two “founding authors” of Greek mythology, alongside Homer – Homer did wrote several times about Medusa, but only as a disembodied head and as a monster already dead, so we don’t have any information about her life). And what do we learn? That Medusa is part of a set of three sisters known as the Gorgons – because oh yes, Ovid did not mention Medusa’s sister now did he? How did Medusa’s sisters ALSO got snake-hair or petrifying-gaze if only Medusa was cursed for sleeping with Neptune? Ovid does not give us any answer because again, it is an “adaptational plot hole”, and the people that try to adapt Ovid’s story have to deal with the slight problem of Stheno and Euryale needing to share their sister’s curse despite seemingly not being involved in the whole Neptune business. Anyway, back to the Greek text.
So, you have those three Gorgon sisters, and Medusa is said to be mortal while her sisters are not. Why is it such a big deal? Because Medusa wasn’t originally some random human or priestess. Oh no! Who were the Gorgons’ parents? Phorcys and Keto/Ceto, aka two sea-gods. Not just two sea-gods – two sea-gods of the ancient, primordial generation of sea-gods, the one that predated Poseidon, and that were cousins to the Titans, the sea-gods born of Gaia mating with Pontos.
So the Gorgons were “divine” of nature – and this is why Medusa being a mortal was considered to be a MASSIVE problem and handicap for her, an abnormal thing for the daughter of two deities. But let’s dig a bit further… Who were Phorcys and Ceto? Long story short: in Greek mythology, they were considered to be sea-equivalents of Typhon and Gaia. They were the parents of many monsters and many sea-horrors: Keto/Ceto herself had her name attributed and equated with any very large creature (like whales) or any terrifying monster (like dragons) from the sea. The Gorgons themselves was a trio of monsters, but their sisters, that directly act as their double in the myth of Perseus? The Graiai – the monstrous trio of old women sharing one eye and one tooth. Hesiod also drops the fact that Ladon (the dragon that guarded the golden apples of the Hesperids), and Echidna (the snake-woman that mated with Typhon and became known as the “mother of monsters”) were also children of Phorcys and Ceto, while other authors will add other monster-related characters such as Scylla (of Charybdis and Scylla fame), the sirens, or Thoosa (the mother of Polyphemus the cyclop). Medusa herself is technically a “mother of monsters” since she birthed both Pegasus the flying horse and Chrysaor, a giant. So here is something very important to get: Medusa, and the Gorgons, were part of a family of monsters. Couple that with the absence of any mention of curses in these ancient texts, and everything is clear.
Originally Medusa was not a woman cursed to become a monster: she was born a monster, part of a group of monster siblings, birthed by monster-creating deities, and she belonged to the world of the “primordial abominations from the sea”, and the pre-Olympian threats, the remnants of the primordial chaos. It is no surprise that the Gorgons were said to live at the edge of the very known world, in the last patch of land before the end of the universe – in the most inhuman, primitive and liminal area possible. They were full-on monsters!
Now you might ask why Poseidon would sleep with a horrible monster, especially when you recall that the Greeks loved to depict the Gorgons as truly bizarre and grotesque. It wasn’t just snake-hair and petrifying gaze: they had boar tusks, and metallic claws, and bloated eyes, and a long tongue that constantly hanged down their bearded chin, and very large heads – some very old depictions even show her with a female centaur body! In fact, the ancient texts imply that it wasn’t so much the Gorgon’s gaze or eyes that had the power to turn people into stone – but that rather the Gorgon was just so hideous and so terrifying to look at people froze in terror – and then literally turned into stone out of fear and disgust. We are talking Lovecraftian level of eldritch horror here. So why would Poseidon, an Olympian god, sleep with one of these horrors? Well… If you know your Poseidon it wouldn’t surprise you too much because Poseidon had a thing for monsters. As a sort of “dark double” of Zeus, whereas Zeus fell in love with beautiful princesses and noble queens and birthed great gods and brave heroes, Poseidon was more about getting freaky with all sorts of unusual and bizarre goddesses, and giving birth to bandits and monsters. A good chunk of the villains of Greek mythology were born out of Poseidon’s loins: Polyphemus, Antaios, Orion, Charybdis, the Aloads… And even his most benevolent offspring has freaky stuff about it – Proteus the shapeshifter or Triton half-man half-fish… So yes, Poseidon sleeping with an abominable Gorgon is not so much out of character.
Step 3: The missing link
Now that we established what Medusa started out as, and what she ended up as… We need to evoke the evolution from point Hesiod to point Ovid, because while people summarized the Medusa debate as “Sea-born monster VS raped and punished woman”, there is a third element needed to understand this whole situation…
Yes Ovid did invent the rape. But he did not invent the idea that Medusa had been cursed by Athena.
The “gorgoneion” – the visual and artistic motif of the Gorgon’s head – was, as I said, a grotesque and monstrous face used to invoke fright into the enemies or to repel any vile influence or wicked spirit by the principle of “What’s the best way to repel bad stuff? Badder stuff”. Your Gorgon was your gargoyle, with all the hideous traits I described before – represented in front (unlike all the other side-portraits of gods and heroes), with the face being very large and flat, a big tongue out of a tusked-mouth, snake-hair, bulging crazy eyes, sometimes a beard or scales… Pure monster. But then… from the fifth century BCE to the second century BCE we see a slow evolution of the “gorgoneion” in art. Slowly the grotesque elements disappear, and the Gorgon’s face becomes… a regular, human face. Even more: it even becomes a pretty woman’s face! But with snakes instead of hair. As such, the idea that Medusa was a gorgeous woman who just had snakes and cursed-eyes DOES come from Ancient Greece – and existed well before Ovid wrote his rape story.
But what was the reason behind this change?
Well, we have to look at the Roman era again. Ovid’s tale of Medusa being cursed for her rape at the hands of Neptune had to rival with another record collected by a Greek author Apollodorus, or Pseudo-Apollodorus, in his Bibliotheca. In this collection of Greek myths, Apollodorus writes that indeed, Medusa was cursed by Athena to have her beautiful hair that seduced everybody be turned into snakes… But it wasn’t because of any rape or forbidden romance, no. It was just because Medusa was a very vain woman who liked to brag about her beauty and hair – and had the foolish idea of saying her hair looked better than Athena’s. (If you recall tales such as Arachne’s or the Judgement of Paris, you will know that despite Athena being wise and clever, one of her main flaws is her vanity).
“Wait a minute,” you are going to tell me, “The Bibliotheca was created in the second century CE! Well after Greece became part of the Roman Empire, and after Ovid’s Metamorphoses became a huge success! It isn’t a true Greek myth, it is just Ovid’s tale being projected here…” And people did agree for a time… Until it was discovered, in the scholias placed around the texts of Apollonios of Rhodes, that an author of the fifth century BCE named Pherecyde HAD recorded in his time a version of Medusa’s legend where she had been cursed into becoming an ugly monster as punishment for her vanity. We apparently do not have the original text of Pherecyde, but the many scholias referring to this lost piece are very clear about this. This means that the story that Apollodorus recorded isn’t a “novelty”, but rather the latest record of an older tradition going back to the fifth century BCE… THE SAME CENTURY THAT THE GORGONEION STARTED LOSING THEIR GROTESQUE, and that the face of Medusa started becoming more human in art.
[EDIT: I also forgot to add that this evolution of Medusa is also proved by strange literary elements, such as Pindar's mention in a poem of his (around 490 BCE) of "fair-cheeked Medusa". A description which seems strange given how Medusa used to be depicted as the epitome of ugliness... But that makes sense if the "cursed beauty" version of the myth had been going around at the time!]
And thus it is all connected and explained. Ovid did invent the rape yes – but he did not invent the idea of Athena cursing Medusa. It pre-existed as the most “recent” and dominating legend in Ancient Greece, having overshadowed by Ovid’s time the oldest Hesiodic records of Medusa being born a monster. So what Ovid did wasn’t completely create a new story out of nowhere, but twist the Greek traditions of Athena cursing Medusa and Medusa having a relationship with Poseidon, so that the two legends would form one and same story. And this explains in retrospect why Ovid focuses so much on describing Medusa’s beautiful hair, and why Ovid’s Minerva would think turning her hair into snake would be a “punishment fit for the crime”: these are leftovers of the Greek tale where Medusa was punished for her boasting and her vanity.
CONCLUSION
Here is the simplified chronology of how Medusa’s evolution went.
A) Primitive Greek myths, Hesiodic tradition: Born a monster out of a family of sea-monsters and monstrous immortals. Is a grotesque, gargoylesque, eldritch abomination. Athena has only an indirect conflict with her, due to being Perseus’ “fairy godmother”. Has a lovely romance with Poseidon.
B) Slow evolution throughout Classical Greece and further: Medusa becomes a beautiful, human-looking girl that was cursed to have snake for hair and petrifying eyes, instead of being a Lovecraftian horror people could not gaze upon. Her conflict with Athena becomes direct, as it is Athena that cursed her due to being offended by her vain boasting. Her punishment is for her vanity and arrogant comparison to the goddess.
C) Ovid comes in: Medusa’s romance with Poseidon becomes a rape, and she is now punished for having been raped inside Athena’s temple.
[As a final note, I want to insist upon the fact that the story of Medusa being raped is not less "worthy" than any other version of the myth. Due to its enormous popularity, how it shaped the figure of Medusa throughout the centuries, and how it still survives today and echoes current-day problems, to try to deny the valid place of this story in the world of myths and legends would be foolish. HOWEVER it is important to place back things in their context, to recognize that it is not the ONLY tale of Medusa, that it was NOT part of Greek mythology, but rather of Roman legends - and let us all always remember this time Poseidon slept with a Lovecraftian horror because my guy is kinky.]
EDIT:
For illustration, I will place here visuals showing how the Ancient art evolved alongside Medusa's story.
Before the 5th century BCE: Medusa is a full-on monster
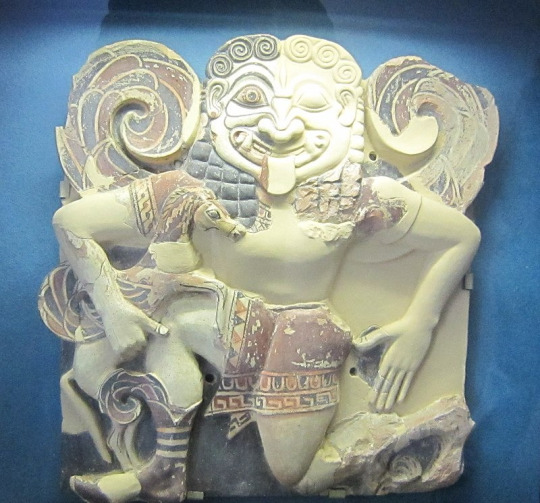
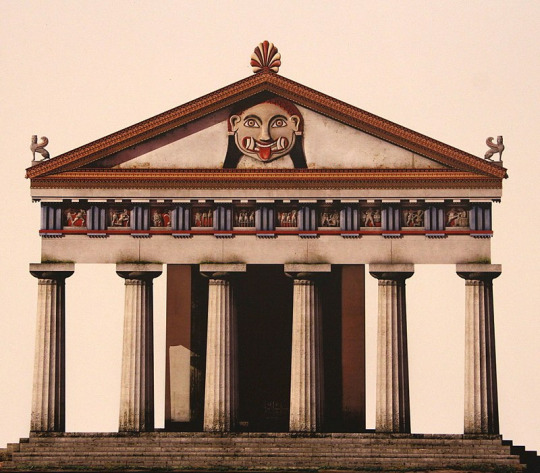






From the 5th century to the 2nd century BCE: A slow evolution as Medusa goes from a full-on monster to a human turned into a monster. As a result the two depictions of the grotesque and beautiful gorgoneion coexist.
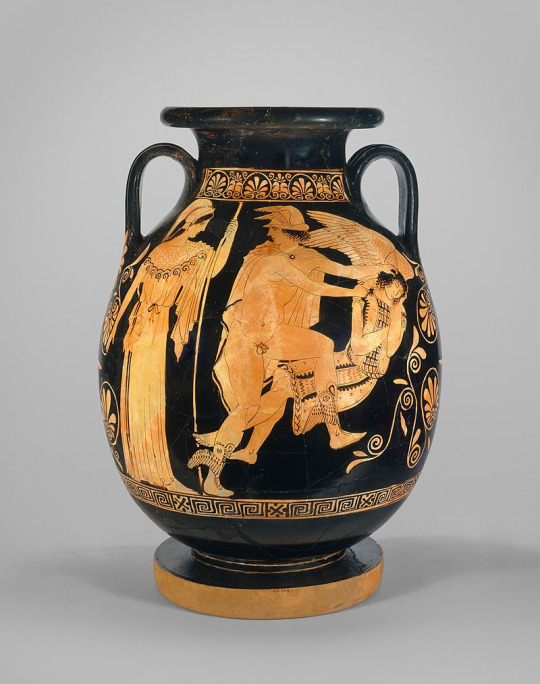



Post 2nd century BCE: Medusa is now a human with snake hair, and just that
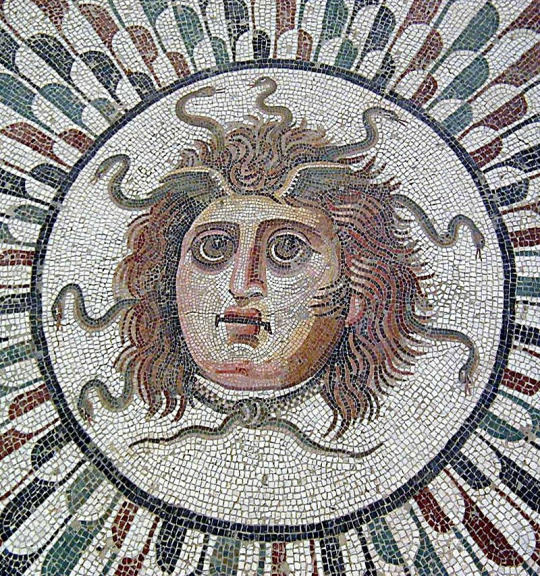



#greek mythology#medusa#gorgon#athena#gorgons#poseidon#neptune#minerva#ovid#rape in mythology#greek monsters#roman mythology
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
apocalypse :( want those stories
#.din#.txt#sry. i think im a prophet now? which means i have to be careful with my phrasing.#anyways. thinking abt how western stories end at the apocalypse whereas chinese stories just like. begin.#this makes more sense if u know abt chinese mythology but like. yu the great. tushan girl.#none of these people know a 'before'. they dont need to.#despite the ancestor worship prevalent in chinese culture its always the beginning. there is no predestined end. there just IS.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Popular Hades & Persephone "retellings" are, rightly, getting dunked on all over the socials right now and, as a Pagan who has an altar to the Queen, I could not be happier. But also, I feel like a lot of people miss WHY they're bad - aside from just plain bad writing and lazy tropes. Which are, yeah, also REALLY bad.
Pretty much all retellings try to wave away, or excuse, or twist the whole kidnapping bit. And I actually do have sympathy and understanding for why, when speaking from a modern perspective.
But honestly...you gotta get over it. There are other stories to play fix-it with, not this one.
The Abduction is The Thing.
Were I a little more sober I could bring up chapter and verse of the Hymn to Demeter but frankly, if you know even the middle school mythology curriculum version of the story, you SHOULD know the themes. The story of Persephone was one mothers and daughters in the ancient world held dear, because it was a reality: you will, one day, be swept away from your home to go cleave to a man you most likely know nothing about. You will miss your mother, but chances are very good that he will be a good husband, once you get to know him, certainly better than Zeus or Ares, and he will make you a queen of his home.
Leaving home to marry was often scary, and violent (look up the history of the tradition of Bridesmaids, if you don't already know it - they were originally decoys on the marriage road). Centuries later we'd have tales like Beauty & The Beast serving the same function: comfort, hope, you are leaving your safe loving home to figure life out with a (often older, powerful) stranger. Your trauma over this sudden ending of your childhood made manifest in a Beast, or a God of The Underworld.
It's wonderful that we don't NEED stories like this anymore to comfort us (here, at least, in this culture). But if you try to force them into modern vernacular it just will not work, not really, because you're gutting out the whole point just to have a more tidy romantic male hero.
I have read MANY very good ...novelizations? fanfic(? however you would frame them, but they're certainly not "retellings"), etc. that simply take advantage of the blank spaces in the myth, and there are many!
It's not explicit that sexual assault happens - "The Rape of Persephone" as a title was coined in much earlier eras, when the word was just as often used to simply refer to abduction.
"She was starving!" the gods didn't need to eat. So it's easy to read her eating the Pom seeds as a deliberate choice on her part. Like, shit, people, scholars have written whole papers on the symbolism of this moment, between marriage rites and even yeah, Seph choosing both worlds with her husband's knowing consent.
And that, I think, is the real heart of the thing. People want an utterly mundane, spelled-out story here, as opposed to what it really is, has always been, just like any other myth or religious parable: IT'S A METAPHOOOOOOR.
They don't need to be destined, or meet at a goddamned BALL and then CONSPIRE to fake her kidnapping, or shit, I once saw one where Hades got MIND CONTROLLED by Zeus?! Jesus.
Persephone was yoinked into the Underworld against her will.
That's how it went.
I don't mean this in a "stay out of my belief system!" way, shit I'm a white American chick with delusions of witchery. I mean this in a "stop stressing yourself out trying to make things palatable" way:
This is a very real, very precious myth to many people, BECAUSE for at least that one event, Persephone had no autonomy, BECAUSE for thousands of years most women had no autonomy. Erasing that, sanitizing the fact that a girl is ripped out of the spring, from her mother's arms, is erasing the thing that gave comfort to women for centuries. And people can and should still find power and healing in it now!
Fill in the blanks the story leaves in whatever manner seems fit to you, there's plenty of room, but. Come the fuck on.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
In defense of retellings & reimaginings
I'm not going to respond to the post that sparked this, because honestly, I don't really feel like getting in an argument, and because it's only vaguely even about the particular story that the other post discussed. The post in question objected to retellings of the Rape of Persephone which changed important elements of the story -- specifically, Persephone's level of agency, whether she was kidnapped, whether she ate seeds out of hunger, and so on. It is permissible, according to this thesis, to 'fill in empty spaces,' but not to change story elements, because 'those were important to the original tellers.' (These are acknowledged paraphrases, and I will launch you into the sun if you nitpick this paragraph.)
I understand why to the person writing that, that perspective is important, and why they -- especially as a self-described devotee of Persephone -- feel like they should proscribe boundaries around the myth. It's a perfectly valid perspective to use when sorting -- for example -- which things you choose to read. If you choose not to read anything which changes the elements which you feel are important, I applaud you.
However, the idea that one should only 'color in missing pieces,' especially when dealing with stories as old, multi-sourced, and fractional as ancient myths, and doing so with the argument that you shouldn't change things because those base elements were important to the people who originally crafted the stories, misses -- in my opinion -- the fundamental reason we tell stories and create myths in the first place.
Forgive me as I get super fucking nerdy about this. I've spent the last several years of my life wrestling with the concept of myths as storytelling devices, universality of myths, and why myths are even important at all as part of writing on something like a dozen books (a bunch of which aren't out yet) for a game centered around mythology. A lot of the stuff I've written has had to wrestle with exactly this concept -- that there is a Sacred Canon which cannot be disrupted, and that any disregard of [specific story elements] is an inexcusable betrayal.
Myths are stories we tell ourselves to understand who we are and what's important to us as individuals, as social groups, and as a society. The elements we utilize or change, those things we choose to include and exclude when telling and retelling a story, tell us what's important to us.
I could sit down and argue over the specific details which change over the -- at minimum -- 1700 years where Persephone/Kore/Proserpina was actively worshiped in Greek and Roman mystery cults, but I actually don't think those variations in specific are very important. What I think is important, however, is both the duration of her cults -- at minimum from 1500 BCE to 200CE -- and the concept that myths are stories we tell ourselves to understand who we are and what's important to us.
The idea that there was one, or even a small handful, of things that were most important to even a large swath of the people who 'originally' told the store of the Rape of Persephone or any other 'foundational' myth of what is broadly considered 'Western Culture,' when those myths were told and retold in active cultic worship for 1700 years... that seems kind of absurd to me on its face. Do we have the same broad cultural values as the original tellers of Beowulf, which is only (heh) between 1k-1.3k years old? How different are our marital traditions, our family traditions, and even our language? We can, at best, make broad statements, and of inclusive necessity, those statements must be broad enough as to lose incredible amounts of specificity. In order to make definitive, specific statements, we must leave out large swaths of the people to whom this story, or any like it, was important.
To move away from the specific story brought up by the poster whose words spun this off, because it really isn't about that story in particular, let's use The Matter of Britain/Arthuriana as our framing for the rest of this discussion. If you ask a random nerd on Tumblr, they'd probably cite a handful of story elements as essential -- though of course which ones they find most essential undoubtedly vary from nerd to nerd -- from the concept that Camelot Always Falls to Gawain and the Green Knight, Percival and the grail, Lancelot and Guinevere...
... but Lancelot/Guinevere and Percival are from Chrétien de Troyes in the 12th century, some ~500 years after Taliesin's first verses. Lancelot doesn't appear as a main character at all before de Troyes, and we can only potentially link him to characters from an 11th century story (Culhwch and Olwen) for which we don't have any extant manuscripts before the 15th century. Gawain's various roles in his numerous appearances are... conflicting characterizations at best.
The point here is not just that 'the things you think are essential parts of the story are not necessarily original,' or that 'there are a lot of different versions of this story over the centuries,' but also 'what you think of as essential is going to come back to that first thesis statement above.' What you find important about The Matter of Britain, and which story elements you think can be altered, filed off or filled in, will depend on what that story needs to tell you about yourself and what's important to you.
Does creating a new incarnation of Arthur in which she is a diasporic lesbian in outer space ruin a story originally about Welsh national identity and chivalric love? Does that disrespect the original stories? How about if Arthur is a 13th century Italian Jew? Does it disrespect the original stories if the author draws deliberate parallels between the seduction of Igerne and the story of David and Bathsheba?
Well. That depends on what's important to you.
Insisting that the core elements of a myth -- whichever elements you believe those to be -- must remain static essentially means 'I want this myth to stagnate and die.' Maybe it's because I am Jewish, and we constantly re-evaluate every word in Torah, over and over again, every single year, or maybe it's because I spend way, way too much time thinking about what's valuable in stories specifically because I write words about these concepts for money, but I don't find these arguments compelling at all, especially not when it comes to core, 'mainstream' mythologies. These are tools in the common toolbox, and everybody has access to them.
More important to me than the idea that these core elements of any given story must remain constant is, to paraphrase Dolly Parton, that a story knows what it is and does it on purpose. Should authors present retellings or reimaginings of the Rape of Persephone or The Matter of Britain which significantly alter historically-known story elements as 'uncovered' myths or present them as 'the real and original' story? Absolutely not. If someone handed me a book in which the new Grail was a limited edition Macklemore Taco Bell Baja Blast cup and told me this comes directly from recently-discovered 6th century writings of Taliesin, I would bonk them on the head with my hardcover The Once & Future King. Of course that's not the case, right?
But the concept of canon, historically, in these foundational myths has not been anything like our concept of canon today. Canon should function like a properly-fitted corset, in that it should support, not constrict, the breath in the story's lungs. If it does otherwise, authors should feel free to discard it in part or in whole.
Concepts of familial duty and the obligation of marriage don't necessarily resonate with modern audiences the way that the concept of self-determination, subversion of unreasonable and unjustified authority, and consent do. That is not what we, as a general society, value now. If the latter values are the values important to the author -- the story that the author needs to tell in order to express who they are individually and culturally and what values are important to them* -- then of course they should retell the story with those changed values. That is the point of myths, and always has been.
Common threads remain -- many of us move away from family support regardless of the consent involved in our relationships, and life can be terrifying when you're suddenly out of the immediate reach and support of your family -- because no matter how different some values are, essential human elements remain in every story. It's scary to be away from your mother for the first time. It's scary to live with someone new, in a new place. It's intimidating to find out that other people think you have a Purpose in life that you need to fulfill. It's hard to negotiate between the needs of your birth family and your chosen family.
None of this, to be clear, is to say that any particular person should feel that they need to read, enjoy, or appreciate any particular retelling, or that it's cool, hip and groovy to misrepresent your reworking of a myth as a 'new secret truth which has always been there.' If you're reworking a myth, be truthful about it, and if somebody told you 'hey did you know that it really -- ' and you ran with that and find out later you were wrong, well, correct the record. It's okay to not want to read or to not enjoy a retelling in which Arthur, Lancelot and Guinevere negotiate a triad and live happily ever after; it's not really okay to say 'you can't do that because you changed a story element which I feel is non-negotiable.' It's okay to say 'I don't think this works because -- ' because part of writing a story is that people are going to have opinions on it. It's kind of weird to say 'you're only allowed to color inside these lines.'
That's not true, and it never has been. Greek myths are not from a closed culture. Roman myths are not sacrosanct. There are plenty of stories which outsiders should leave the hell alone, but Greek and Roman myths are simply not on that list. There is just no world in which you can make an argument that the stories of the Greek and Roman Empires are somehow not open season to the entire English-speaking world. They are the public-est of domain.
You don't have to like what people do with it, but that doesn't make people wrong for writing it, and they certainly don't have to color within the lines you or anyone else draws. Critique how they tell the story, but they haven't committed some sort of cultural treachery by telling the stories which are important to them rather than the stories important to someone 2500 years dead.
****
*These are not the only reasons to tell a story and I am not in any way saying that an author is only permitted to retell a story to express their own values. There are as many reasons to tell a story as there are stories, and I don't really think any reason to create fiction is more or less valid than any other. I am discussing, specifically, the concept of myths as conveyors of essential cultural truths.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Looks like it's time to talk about starseeds and the New Age movement again.
Since I'm seeing more starseed content being posted, I'm gonna make another post on why the whole starseed thing and the surrounding New Age belief system are... not good.
So for those who don't know, New Age mythology is essentially a hodgepodge of cherrypicked and distorted myths from various cultures, racist pseudohistory, and far right conspiracy theories. To put it very briefly, starseeds are supposedly here to help Earth resist the reptilians, a race of politics-manipulating, war-starting, media-controlling blood-drinking aliens. For those who don't recognize the tropes here, these are basically all antisemitic canards. The reptilian alien myth as most know it today comes from David Icke, who ultimately cribbed a bunch of his material from The Protocols of the Learned Elders of Zion, a Russian hoax created to justify violence against Jews. He was also influenced by the work of people like Fritz Springmeier, a hateful crank who based much of his work on other hateful cranks.
(David Icke, by the way, also claims that transgender is an evil reptilian conspiracy. You'll never find just one form of bigotry with these people.)
There are supposedly numerous alien races out there, and one of the most prominent among them are the Pleiadians, AKA Nordics. While modern depictions of the Pleiadians give them more variety in skintone, there's no denying that older Pleiadian mythology basically pictured them as Aryans In Space, even associating them with the swastika.
You see what's going on here? "Good" swastika-loving Aryan aliens versus "evil" Jewish aliens? Sound familiar?
Racism isn't just a tangential part of the starseed myth, either. It lies at its very core. It's inextricably tied in with the ancient astronaut hypothesis, which has a history of racist motivation behind it. The TL;DR is that a bunch of white people couldn't believe that non-white people had built a bunch of things they couldn't figure out how to build themselves (EG, the Great Pyramids), so they proposed that the real builders were anyone from Atlanteans to aliens. (Atlantis, by the way, never existed; it was a literary device created by Plato.)
One supposed purpose of starseeds is to help the world "wake up to the truth," which basically just means "convert people to New Age spirituality." New Age believes that world peace is contingent on a majority of the world being converted to New Age belief, and that resistance against their belief system is ultimately the work of the aforementioned reptilian aliens.
To put it another way, New Agers think they understand other cultures' spiritual traditions better than the actual members of said cultures, and think that anyone who disagrees with them is being manipulated by the conspiracy, or is an agent of the conspiracy. This includes Indigenous cultures which are already endangered from white Christian colonialism.
Essentially, endangered cultures cannot speak up for themselves and resist New Agers' efforts at cultural assimilation without being labeled a problem and an enemy. It's basically white Christian colonialism repackaged as "spiritual, not religious."
Again - if you heard from these people that some ancient text or myth describes extraterrestrial beings visiting our planet for one reason or another, you heard misinformation. They twist and misrepresent literally every myth and text they get their hands on. For example, you may have heard that the vimanas from Hindu traditions were actually alien spacecraft. They were no such thing. Or maybe you heard that the Book of Enoch describes aliens performing genetic experimentation on humans. It literally does not. At best, all of the stories they cite just kind of sound like aliens if you ignore most of their content and pay no attention to their cultural contexts.
The starseed movement preys on alienated people, especially autistic people and people with ADHD. You can look up nearly any list of signs that you're supposedly a starseed, and many of them will align perfectly with characteristics associated with autism and/or ADHD, or that people with these conditions commonly report. Some people within the movement even go so far as to claim that ADHD and autism don't even exist, but were actually made up by the conspiracy as a cover to suppress and control starseeds, which is some yikes-as-hell ableism.
So basically, people are being told that if they have these certain characteristics or symptoms, that means it's their job to spread New Age spirituality to defeat the conspiracy and help others ascend to the fifth density.
And what's the fifth density, you might ask? It's supposedly humanity's next evolutionary level, because New Age is also based on biological misconceptions. Supposedly once everyone's DNA "upgrades," they'll essentially morph into an aetheric form. Supposedly, this is preceded by a number of "ascension symptoms," including depression, headache, gastrointestinal issues, and any number of other symptoms that could indicate almost anything, including stress.
What many of these people don't realize is, this prediction has already failed. Back in the 2000s and 2010s, experiencing "ascension symptoms" was supposed to precede ascension to 5D beginning December 21, 2012. One lady, Denise Le Fay, was convinced that the hair loss she was experiencing in 2008 was an ascension symptom. As we can see by looking her up, she's very much still with us on the 3D plane these days, repeating the same tired old scripts New Agers recycle endlessly.
By the way, everything you near New Agers saying today about old systems being dismantled, dark forces being arrested or kicked off the planet, and new economic systems on the horizon? They've been recycling these scripts for years now. Take a look at this page written back in 2012. You got stuff about the complete dismantling of an enormous network of sinister forces," "the arrest and removal of a world-wide cabal," and a "new economic system."
("Cabal," by the way, is a dogwhistle term for "Jews.")
Furthermore, people in this movement are often encouraged to try and access past life memories through dreams or hypnosis, which makes the whole thing feel even more real to them. But the thing is, you can have incredibly vivid experiences about literally anything you put your mind to - the people in the reality shifting having vivid experiences of living another life in the Harry Potter universe are a great example of this. Just because you have vivid experiences, doesn't mean they have any bearing on anything happening in this reality.
So yeah, the starseed movement and the larger New Age movement are both extremely harmful. They promote racist pseudohistory, medically-irresponsible pseudoscience, conspiracy theories that target numerous marginalized groups, and functionally target aliened people with ADHD and autism to convince them that spreading its beliefs is their job.
#starseed#starseeds#new age#new age beliefs#ascension#5d#fifth density#spirituality#racism#antisemitism#ableism#transphobia#ascension symptoms#conspirituality#conspiracy theories#conspiracism#ancient aliens#ancient astronauts#ancient astronaut hypothesis#aliens#extraterrestrials#pseudoarchaeology#archaeology#pleiadians#pleiadian#dna upgrade#autism#adhd#colonialism
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
hi red!! i'm doing an analysis of sun wukong's (and journey to the west in general's) impact on modern culture for my world mythology final, and for some reason i'm having a hard time finding sources. is there anything you can recommend?
The fact that Journey to the West has contributed an enormous number of tropes to modern media is very clear when the media in question is examined, but I don't know of a specific secondary source that's already done that analysis for you. However, this IS a very good excuse for you to plow through a metric buttload of shonen manga, since the lineage is basically Sun Wukong -> Son Goku -> like a solid third of all shonen action heroes written in the last forty years.
Dragon Ball kicks things off:

Started in 1984 and almost unquestionably the most influential manga ever made. Its first arc features the weird super-strong monkey-kid Son Goku - which is just the japanese pronunciation of the characters of Sun Wukong's name - meeting up with a wacky crew of thinly-veiled expys of the Journey to the West crew, with teen inventor Bulma filling the role of Tripitaka, Oolong the pig-man filling Zhu Bajie's role and Yamcha the desert-based bandit as Sha Wujing.

Hijinks ensue, and while the story drifts pretty far from Journey to the West's original plot, it actually stays pretty solidly referential in weirdly unexpected ways. Several the villains of the week are JttW references, and even the later appearance of three more Saiyans lines up with the surprise reveal of three more Wukong-like mystical apes in the original story.

The connection between Dragon Ball and JttW is very unsubtle and a frequent reference in the chapter covers and supplemental art.


Not every subsequent JttW reference is the result of Dragon Ball popularizing it or anything, since it was already enormously popular, but I think it's pretty hard to extricate Dragon Ball's influence on anime and manga from the original influence of Journey to the West itself.
One way that a distinction can be drawn is in the differences in characterization between Goku and Sun Wukong himself. A lot of the next generation of shonen protagonists were kind of Goku-alikes - pure-hearted dumbasses who only care for the three Fs: Food, Fighting and Friendship.


But the original characterization of Sun Wukong is not really all that similar. He's a trickster, sure, but he's far from a young, friendship-motivated goober. He's profoundly intelligent, pretty much the most well-educated entity on the planet, and routinely brings up that he's centuries older than most of his peers. The Goku-alikes from the later decades of shonen anime are tellingly far-removed from that original characterization. So you get characters based on Goku's cheerful idiocy, but it's just a small subset of the broader influence of Journey to the West on the space of literature.
In general, Journey to the West frequently shows up in very small, bite-sized tropes in other stories. It's less "this is wholly based on Journey to the West" and more "oh, I know where they maybe got this idea/aesthetic/power/weapon/villain of the week from." There are way too many to list, but some of the ones that tend to jump out at me are-
Sneaky characters with monkey motifs:
Tricksy, highly mobile characters who fight with a staff:


Characters afflicted with a magical restraint artifact that allows a much weaker character to stop them from misbehaving:
Specific esoteric weapons, eg. magical fans, rakes, gourds, namedropping The Sword of Seven Stars, etc.



Villains with prominent ox or pig design motifs:


Characters whose primary combat strat is just making Shitloads Of Disposable Copies Of Themselves:


Honestly it just keeps going like this. It's kinda everywhere. Finding the JttW in things is my favorite conspiracy theory rabbit hole because it's 100% harmless and more often than not completely correct.
639 notes
·
View notes
Text
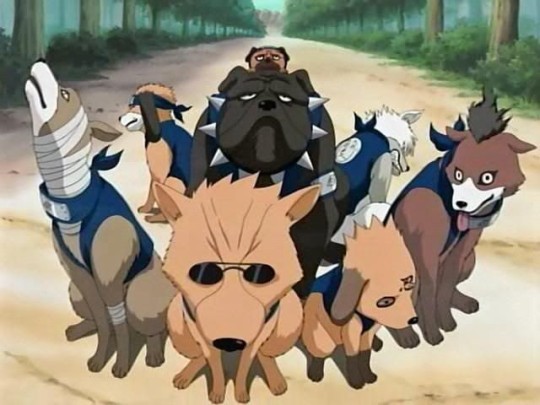
Do you like Kakashi's dogs? Let's talk about why there are eight of them.
another example of naruto's ✨cultural code✨
contents | the eight dog warriors chronicles · legacy · eight confucian virtues. also look at the cuties love them sm

Naruto Vol. 10 CH 90
[ one dog is wonderful, I'm saying as the owner of a sweet little york terrier. two dogs are good, they won't be bored together. three dogs? yeah, cool! how are you going to walk them though? four? yes... look, maybe we have to draw the line h- wha- EIGHT? Excuse Me!? ]
surely, it's worth starting with the fact that eight is a lucky number in Japanese culture — everybody watched Hachi. of course, this is not the only cultural detail where the eight is mentioned. I want to pay special attention to a thing that I didn't know about until I googled it, and this is clearly what Kishimoto was doing homage to with Kakashi's eight ninken.
The Eight Dog Warriors Chronicles
Better known as Nansō Satomi Hakkenden. and it's not just some kind of book, it's a novel, consisting of 106 booklets written by Kyokutei Bakin in XIX century. Hakkenden is considered the largest novel in the history of Japanese Literature. this is one of the main representatives of the gesaku genre, which includes works of a frivolous, joking, silly nature. further I will emphasize a few more times how damn popular this work is and how often it is reflected in culture.
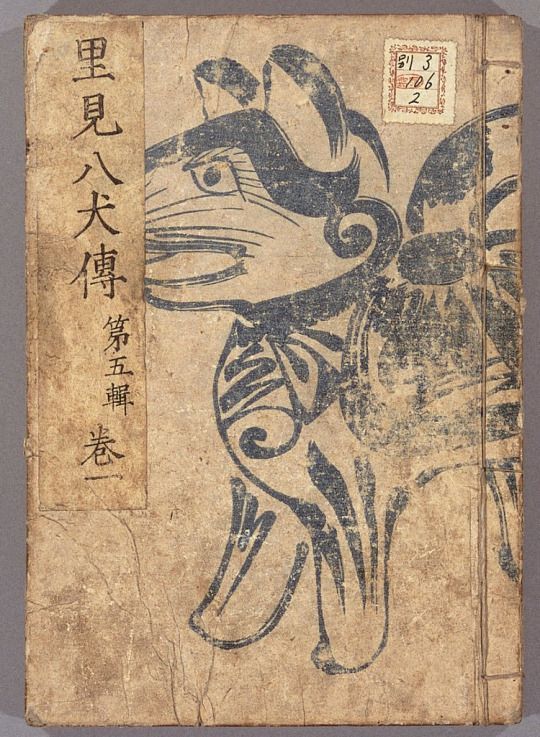



here are some illustrations for these books
now let's talk about the plot. It's weird, but it's weird at samurai-dogs-story level so stay here.
In brief, the story tells about the commander Satomi Yoshizane, whose native lands were attacked by the army of a man, whose forces surpassed those of Satomi, and the samurai in despair swore to a dog named Yatsufusa that the dog would get his beloved daughter Fuse as a wife if he chewed that man's throat. surprisingly, the dog not only understood the owner, but also fulfilled his wish! after that the commander refused to keep the promise. however, Fuse, true to her word of honor, went with Yatsufusa to the mountains and became his wife. upon learning that his daughter was pregnant, Satomi, in a rage, sent a samurai to kill Yatsufusa and bring Fuse home. she stood up for the dog anyways and died with him. at that moment, eight pearls with hieroglyphs that denoted the foundations of Confucian virtue burst out of her womb. (...cheers for mythology, I guess)
Soon, eight dog warriors who were Fuse's spiritual children were born in different parts of Awa province. after going through hardships, they got together and became vassals of the Satomi clan, then won the battle, and soon reached peace.



some more illustrations made by Utagawa Kuniyoshi. from left to right: Inukawa Sōsuke (the dog warrior), Inumura Daikaku (the dog warrior), Princess Fuse (their mother).
the novel mainly tells about each individual warrior dog and his shenanigans in a funny adventurous way. huge fame has led to excerpts from Hakkenden being staged at the Kabuki Theater and mentioned in the anime and manga, such as Inuyasha, Dragon Ball, as it turned out, Naruto and so on. there's also a lot of films and video games.
The eight virtues
these are loyalty, filial piety, benevolence, love, honesty, justice, harmony, and peace.
they relate more to Chinese culture, but basically Hakkenden was inspired by it too. since I did not read the whole novel, I would still like to mention at least the values on which it is based, and which were embedded in the symbolism of this story. It's quite interesting to apply this to Kakashi's dogs. gives them more weight and depth.
It is also interesting to note that the reason why Fuse gave birth to dogs was also that her father was cursed earlier in the story in a way that his descendants would become depraved like dogs. in Japanese culture, dogs embody the duality of character: the same mentioned filth and depravity, and devotion and bravery. so as samurai. but this is a different conversation, more related to Kakashi and his dog poetry.

Did you get here? Here's an additional discovery for you✨
Pakkun's name (パックン) is derived from the Japanese onomatopoeia “pakupaku” (パクパク) which reflects the sound of munching.
Kakashi, that's very sweet of you.

thank you for reading this to the end ♡
695 notes
·
View notes
Text

Let's Talk About Magic Systems.
There are two broad ways you can establish magic in your story world - work with existing concepts, or adapting it for something new.
Pick a System
High Magic vs. Low Magic
This distinction existes mostly in the western wrld from the Middle Ages onwards. In non-western cultures, this distinct often doesn't exist.
High magic requires magicians to study from books, ingredients are expensive and instruments elaborate and hard to get. The typical practioner of High Magic is of the upper class, highly educated, and rich. They serve in King's courts and have high social standing thanks to their knowledge.
Among the lower classes and women, Low Magic is ore common. It is taught orally and doesn't require reading skills and uses everyday objects and ingredients.
Black vs. White Magic
"White" magic is often associated with good, and "Black" with the evil. However, what really matters is the magicians intension, not the magic system that they work with.
The term "black magic" is often associated with working with the dead. It can also be used by an individual/group who just wants to appear more menacing.
Ceremonial Magic
This kind of magic involves lots of ritual, recitation and prayer, often in ancient langauges such as Latin, Aramaic and Sanskrit.
Most of the time, it's High Magic and practiced by religious figures.
The typical practioner is educated, has great confidence and a good memory.
Natural Magic
It involves ingredients from nature, such as herbs and water.
It may be practiced outdoor, in a kitchen, or in a laboratory.
The rituals are simple and short, and the practioner will watch out for the turning of seasons, phases of the moon, etc.
Religious Magic
This is a diety working through a magician. The magician prays and asks her god to work the miracle.
Most religions have their own form of magic, and the kind of miracles that the magicians can bring can be limited.
Wiccan Witchcraft and Voodoo are largely religious magic.
The typical practioner would be spiritual and devout, often suspicious of other religions.
Alchemy
Alchemy is both High and Low Magic, and it can incorporate religious, spiritual, philosophical and mythological elements.
In a modern setting, alchemy can also be portrayed as "science gone too far".
The typical practioner would be patient, methodious, educated and driven. The tools includes laboratory equipment, astronomical charts, writing materials, and an unsuspecting roommate(?) for testing.
Traditional Witchcraft
Traditional Witchcraft is a form of Low Magic. In early historic periods, the witch played an important role in village life, often old women who owned apothecaries and helped out other villagers.
The typical practioner would be female, uneducated, illiterate, practical, resourceful and poor. She will have a good memory and well-developed senses.
Tools used would be simple household implements - a cauldron, a broom, knife, etc. that can evade the Inquisitor's suspicions.
Wiccan Witchcraft
If you write contemporary fiction, this is the system your character is most likely to use. It's modern witchcraft, based on the religion of Wicca.
Wiccan witchcraft mostly developed in the second half of the twentieth centruy. It is a form of bothe Natural Magic and Religious Magic.
Based on nature worship and the polarity between male and female, the magician often begins a Wiccan ritual with an invocation to a God/Godess. The Lady (Godess) is depicted as having three aspects: Maiden, Mother and Brone. The Lord (God) may be depicted with horns.
The focus of Wiccan magic is often on healing, with an emphasis of ethical consequences of what is being performed.
It is often practiced outdoors, sometimes naked (which they call 'skyclad'). Wiccan witchcraft uses the phases of the moon to amplify its effects.
Wiccan like to gather in groups called 'covens' or to meet once a month or for major festivals. The coven leader may be called 'high piestess/priest'.
Typical tools include a chalice, a knife (called 'athame'), a wand, candles, herbs, crystals, and essential oils.
Necromancy
The magician summons a dead person, either ghost or spirit, sometimes bodily. The dead are enlisted to grant the magicians with favors or are questioned for information.
It may be related to Shamanism, as well as to some forms of psychic work such as channelling and Spiritualist seances.
The typical practitioner is psychally gisted, strong-willed and courageous.
Shamnism
Shamnism is a Low Magic system. The shaman intercedes between the human and spirit world by communicating with spirits, often to obtain information or provide healing.
Shamans may travel to the spirit world to seek answered, with some level of danger. They use drums, chanting, dancing and drugs to alter their consciousness and communicate with spirits.
Practicing shamans often work alone, but they choose a successor to train. The apprentice is supposed to accept the calling.
The typical shaman is musical, sensitive with a strong sense of rhythm and the psychic.
Tools include drums, bells, a costume, herbs, bones, smoke and mind-altering drugs.
Ancient Egyptian Magic
Ancient Eyptian Magic ovelaps with Religious magic, medicine and with psychic work. The deities most frequently evoked are Selket, Aset for raising the dead, and the gof Thoth for anything to do with sickness and healing.
The emphasis of Ancient Egyptian Magic is protection, often done throgugh an amulet or talisman. The circle or oval is the most important shape that has protective qualities.
The precise wording of a spell is important, as well as the colors that are involved. For magic to affect someone the magicians must know that person's true name.
The typical practitioner is male, literate, often a priest attached to a emple.
Folk Magic
This is a form of Low Magic practiced by amateurs.
This includes housekeepers who can keep the rats out, farmers who can ripen fruit before the height of the season, and scullions who can make water boil faster.
This people would only know a handful of spells, ans pass them in to memebers of their family.
Voodoo
Voodoo is religious magic and low magic.
The rituals are held in private, and may involve communication with spirits, especially the spirits of ancestors and saints.
Commonly used to cure aliments, confound enemies, and obtain desires.
Invent a System
Choosing the Right Words
If your character is clearly a witch, shaman, a necromancer, etc. with a specialty, use that term. Otherwise, the word "magician", or "mage" would be most appropriate.
The term "magus" (plural magi) refers to practitioners of the ancient Zoroastrian faith.
Strictly speaking, witches and wizards are practitioners of two very different magic systems, so your female character can be a wizard, and vice versa.
'Warlock' really means 'oath-breaker' or 'traitor' and doesn't describe a magician.
'Conjurer' is someone who can creae effects to impress an audience, not really magical in itself. The more modern temr would be 'illusionist'
A group of magicians may be called a 'coven' (though it applies mostly to Wiccan magic). A magician working alone would be a 'solitary'.
Magic vs. Magick
Normally, "magic" is the correct spelling.
However, "magick" may be used, especially by insiders, to emphasize that they refer to the real thing, not conjuring or other trick of the eye.
The magic systems are sometimes capitalized, sometimes not. When it involves a religion, nationaliy, or a particular family line, it is capitalized. Just make sure to keep it consistent throughout your book.
If you like my blog, buy me a coffee☕ and find me on instagram! 📸
#writer#writers#creative writing#writing#writing community#writers of tumblr#creative writers#writing inspiration#writeblr#writing tips#writers corner#writers community#poets and writers#writing advice#writing resources#writers on tumblr#writers and poets#helping writers#writing help#writing tips and tricks#how to write#writing life#let's write#resources for writers#references for writers
475 notes
·
View notes