#japanese language
Text
背負う
しょう
to carry on one's back
Note: if you look this up in the dictionary the pronunciation is せおう but according to my sources when you pronounce it it should be しょう
リュックを背負ってください。
リュック を しょって ください。
Please put on your backpack.

#日本語#japanese#japanese language#japanese langblr#japanese studyblr#langblr#studyblr#単語#語彙#japanese vocabulary#tokidokitokyo#tdtstudy
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey I need your help!
So I have memorized hiragana and katakana months ago already, but I have been stuck there since then because I have no idea what I should do next. I know some random kanji that I have memorized while looking for lyrics of some of まふまふ songs, but other than that I know little kanji or vocabulary in general; therefore, even though I can read hiragana and katakana I still can't comprehend what I am reading (tried reading posts on social media, level 0 books, etc etc)
So, does anybody have a specific roadmap with specific resources or smth cause I am really stuck?
31 notes
·
View notes
Text

#studyblr#study blog#langblr#langblog#japanese langblr#japanese language#japanese#studyinspo#study motivation#study aesthetic#language#language learning#japan#japan travel#student#studyspo#studyabroad
16 notes
·
View notes
Note
have you seen the commentary from the p5r artbook going around? the shuake part of my dash is losing it a bit at the implication that their wishes were mutual!!! that seems to be what some people are getting from the commentary at least… amy insights?

Hi! I have been through the artbook. It's great, isn't it? :D
The image above is called "One Ending", and the creator caption (by illustrator Akane Kabayashi) reads:
When I think about how Akechi's wish was to play chess after school with the protagonist, I almost want to call him out with "You liked him after all, didn't you!"
Look at that. We're told about Akechi's wish, and what it included. We're as good as told outright that he likes Joker—and this isn't the only time, there's also this:


—There are a whole lot of things we can imagine, based on how the protagonist was depicted as someone special to Akechi.
Those are more or less the exact emotions represented during Akechi's confidant. (Mumon Usuda, chief designer)
"someone special" here is 特別な存在 tokubetsuna sonzai—literally "a special presence". It means a special person, and more than that; it describes someone you find compelling, someone you can't look away from, someone who becomes one of your most important people, the centre of your world. It's another term that is often romantic, but isn't necessarily romantic.
(In the same way, I think Kabayashi's suki jan! is more tongue-in-cheek than it is a cast-iron confirmation that Akechi was canonly in love with Joker. The language there is teasing, it's ambiguous, it's baity; Kabayashi is joking. This is a rank 6—as they say, if you know, you know. But it is of course ultimately up to all of you.)
There's another mention of this image, down in the creator interview:

Out of all the Maruki ending illustrations, it was Akechi's that stuck with me the most. It made such an impression to see them opening up as friends, having a fun, peaceful time together like high school students should. (Mumon Usuda, chief designer)
What really strikes me in all of this is the emphasis the creators put on the fact that this is Akechi's illustration, Akechi's wish. Because I've thought for a while that we know Akechi has a wish. You can see him struggling with his refusals to Maruki in the first week of January. And you can hear his wish spoken—when Maruki repeats it back to him, during the boss fight, on 2/3:
Maruki
{F1 81}君たちとなら、君も過ちのない道を歩めるかも知れないじゃないか!
{F1 81}-kun-tachi to nara, kimi mo ayamachi no nai michi o ayumeru kamoshirenai ja nai ka!
If you're with {F1 81}―kun and his friends, you could begin to atone for what you've done!
Think about it! With [Amamiya]-kun and his friends beside you, you could choose a path with no mistakes as well!
So this wish has several parts. First, there's that kimi mo, "you also"; it's tempting to read this as Maruki also wanting his new world to erase his past mistakes. Second, there's the first part, "if you're with [Amamiya]-kun and his friends". Where to even start here?
Being with Joker and the others is a prerequisite for the second half of Akechi's wish. It doesn't just coexist, it enables the rest of it. Just like his words in the engine room, "I wonder why we couldn't have met a few years earlier, [Ren]..."
Remember, Akechi's whole arc is about his rejection of trust and friendship, and his insistence on doing everything himself. This is precisely what Futaba calls him out on—"you trusted no one", or "you played life in single-player mode". This is what he unlearns at the climax of the engine room, when he realises he isn't prepared to let the others die—and follows through to save them.
Akechi is nothing without others, and he knows it. Without their support, which he believes he has no right to, he has no hope of living a better life, even were he to be given the chance—and he knows that, too. He has learned, and he has grown—and yet he knows the things he needs and wants so badly are forever inaccessible.
And his wish is about all the Phantom Thieves, not just Joker. There are many tiny references to this end—not least the original Japanese rank 10 line for his confidant, where he sacrifices himself for all of you. Joker is his compelling presence, his someone special, but he's formed small bonds with the others too, God help him.
and then there's the crime thing
The localisation frames Akechi's wish in terms of atonement, but that's not what's on offer. You cannot, after all, atone for things you never did. We see Akechi's wish put into practice, in the Maruki ending, where he appears with his friends beside him, wholly innocent and with unstained hands. And we see it in the first week of January, after he has finally met Maruki and spoken to him:

Akechi: Ah, that reminds me—there was one more thing I wanted to tell you.
Akechi: About the reality Maruki's put us in...
Akechi: It seems that Okumura and Wakaba are both considered alive by all accounts.
[Ren: They're not dead anymore? / What do you mean?]
Akechi: They aren't mere illusions, or cognitive beings—they truly are alive and existing in this world.
Akechi: In fact, their deaths seem to have never taken place at all in this reality.
[Ren: What happened to Shido?]
Akechi: Shido was the only one arrested on the crime of attempting to overthrow the government...
Akechi: It seems the Phantom Thieves were causing a stir in this society as well, but there's no record of your arrest now.
Akechi: Basically, in this reality, you and I haven't committed any crimes.
While Akechi still remembers his crimes, they never took place. They have been undone, and only his lingering memory—and Joker's, at this point—speaks to them. He objects to this on countless levels, he summons all the strength he has to refuse it, but don't make the mistake of thinking that means he doesn't want it. This is Akechi's wish in action.
People are often very certain that Akechi's resolve in the third semester is like iron—that he rejects Maruki's offers right away, is never tempted, never wavers. But that can't be true. We know he's afraid to die. We know about the bad end where you don't complete the Palace, where Akechi says nothing and stares at the floor, seemingly blaming himself internally while all the others blame themselves aloud, for being unable to say no to Maruki's temptations. We know how he responds to this assertion of Maruki's—Maruki, who has perfectly summed up what we know all the other PTs wanted, and who (even if Word of God hadn't just confirmed Akechi's wish) we have, honestly, no reason to doubt.
Because Akechi never refutes this wish that Maruki describes. He never says he doesn't want it. He just rejects it—like all the others, who so desperately want what Maruki could give them. Futaba's mother, Haru's father. Akechi's life, and his innocence. And the people who might have been his friends, if he could dare, one day, to ask.
Akechi is tested just like the others, and the price he pays for his defiance is perhaps the highest of all.
and finally

[The Maruki ending illustrations are] of Maruki's world, where everyone's wishes are granted and they seem happy. The scene shows their actualised wishes, which were never granted in the real world. (Mumon Usuda, chief designer)
We shouldn't forget the price Akechi pays for his impossible wish. Sure, the vision of himself being altered like Sumire clearly haunts him, and I'm sure it made the choice easier—but I don't think it made it that easy. Instead of taking the dream Maruki offered him, Akechi chose to face up to what he'd done, and who he'd become; at the very end, in the third semester and in the engine room, he always makes the right choice.
And that choice was taken away from him. Agency over his life and death, his own acts, and who he would even be—Joker and Maruki take it all away from him and make him a puppet, just like Shido.
Maruki's ending isn't pretty.
revision history
Click here for the latest version.
v1.0 (2024/03/29)—first published.
#asks#persona 5#p5 meta#things i translate#japanese language#word of god#shuake#goro akechi#takuto maruki
531 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’ve been having trouble putting this idea into words so you’ll have to bear with me, but I was struck when I saw a Japanese news program interviewing foreign tourists in Japan, and some australian women were dubbed over with a stereotypically feminine speech register (lots of のs and わs), and my first thought was “they weren’t speaking that femininely in english”.
A friend of mine from the UK recently mentioned that he noticed that australia has a generally more masculine culture than england - he felt that everyone is a bit more masculine here, including women. This kind of confirmed to me that my impressions of the dubbing were right - the tourists were speaking in a relatively (internationally) more masculine way. Yet their dub made them sound so much more feminine.
It made me wonder. When translating something, do you translate the manner of speaking “directly”, or “relatively” in terms of cultural norms? Maybe this graph will help me explain the question.
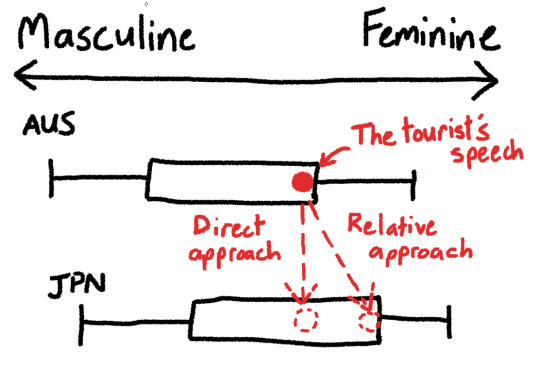
A direct appoach in this case might appear to a Japanese person to result in an unexpectedly masculine register, but preserves how the speaker's cultural upbringing has influenced their speech.
The news program translators chose the relative approach - I think I would prefer the direct approach. I think I prefer it because I believe translation should be a rewriting of the original utterance as if the speaker was originally speaking the target language, and the direct approach compliments that way of thinking the best.
Actually now that I type that, I’m second guessing myself. Does it? It does, if for the purposes of the “rewrite it as if they spoke japanese” thought experiment, we suppose the speaker magically learned japanese seconds before making the utterance, but what if we suppose the speaker magically grew up learning japanese - then maybe they would conform to the relative cultural values. But also, maybe they would never have said such a thing in the first place - their original utterance was informed by their upbringing and cultural values, so how could you possibly know what they would have said if they had known japanese from birth? Maybe my initial instinct was right after all?
If you work in translation, I’m very interested to hear if you have come across this problem and how you deal with it 🙏
Further reading: I think this question also ties into this problem I’ve been struggling to answer for a while.
632 notes
·
View notes
Text





2K notes
·
View notes
Text
接続詞(せつぞくし)
conjunctions - words that are used to link phrases together
情報を加える // Adding information:
しかも besides
そのうえ moreover, on top of that
さらに moreover, on top of that
そればかりか not only that, but also...
そればかりでなく not only that, but also...
情報を対比する // Putting into contrast:
それに対して in contrast
一方 whereas
他の可能性・選択肢を言う // Giving alternatives:
あるいは or perhaps (presenting another possibility)
それとも or (presenting another option within a question)
結論を出す// Drawing a conclusion:
そのため for that reason
したがって therefore
そこで for that reason (I went ahead and did...)
すると thereupon (having done that triggered sth. to happen)
このように with this (adjusting a conclusion to the arguments given beforehand)
こうして in this way
理由を言う // Giving a reason:
なぜなら...からだ the reason is
というのは...からだ the reason is
逆説を表現する // Expressing a contradiction:
だが however, yet, nevertheless (contradicting what one would have expected)
ところが even so (spilling a surprising truth)
それなのに despite this, still
それでも but still (despite a certain fact, nothing changes)
説明を補う // Amending one's explanation:
つまり that is, in other words (saying the same thing using different words)
いわば so to speak (making a comparison)
要するに to sum up, in short
説明を修正する // Revising one's explanation:
ただし however (adding an exception to the information stated beforehand)
ただ only, however
もっとも however (obviating any expectations that might arise through the previous statement)
なお in addition, note that (adding supplementary information)
話題を変える // Changing the subject:
さて well, now, then (common in business letters after the introductory sentence; is often ignored in tranlations)
ところで by the way
#文法#grammar#conjunctions#japanese grammar#jlpt n2#japanese langblr#japanese language#language#japan#japanese#japanese vocabulary#langblr#linguistics#studyblr#study blog#studyspo#study motivation#study aesthetic#study notes#learning japanese#nihongo#日本語#日本語の勉強#light academia#light acadamia aesthetic
666 notes
·
View notes
Text




learning japanese update: i’ve been practicing writing down sentences and trying to understand the sentence structure. linguistically, japanese and turkish have similarities, so i can say that it’s been going well and i’m having sooo much fun!!
#langblr#lunlunstudies#learning japanese#japanese learning#language lessons#second language#japanese language#language learning#language#langblog#studying#studyblr#studyspo#studystudystudy#study motivation
407 notes
·
View notes
Text
神無月 (kan-na-zuki) "October" (archaic)

神 = god
無 = not
月 = month
The modern Japanese word for October is 十月 (literally "10th Month), however in the old-fashioned calendar is was known as 神無月, or "the month with no gods".
In October, all the gods in Japan (there are believed to be 8 million of them) go to Izumo Shrine in Shimane Prefecture for a meeting, thus leaving most of Japan with no gods.

The huge shimenawa (sacred rope) at Izumo Shrine.
#Japanese#kanji#Japan#Japanesecalligraphy#書道#October#十月#神無月#japanese language#japanese culture#japanese calligraphy#japanese art#calligraphy#japanese langblr
923 notes
·
View notes
Text
Japanese Reading Resources for Absolute Beginners
A question I encounter often is "How much Japanese should I study before I can begin reading in Japanese?"
From my experience as a learner and reader myself and from managing a Japanese book club for other learners I can honestly say that you can start way earlier than you probably think!
There are many resources that only require knowing hiragana. Those texts usually teach vocabulary through pictures and only use basic grammar.
Some are even simpler than that: The Japan Foundation's Hiragana Books are great for those, who are still remembering hiragana characters. Every short book introduces only 1-2 new characters, so it's a great reading exercise for those who've just started.

The free graded reader 「どうぞ、どうも」 by the NPO Tagengo Tadoku only uses the words 「どうぞ」 and 「どうも」 to write an entire story. Again, this makes for a great exercise in reading hiragana and understanding context. Another "level 0" recommendation by the same NPO would definitely be 「しろい?くろい?」. This book uses the full range of hiragana characters but the grammar is simple and all used vocabulary is illustrated.


Another site with great resources for absolute beginners is Nihongo Tadoku Dōjō. If you have memorized both hiragana and katakana and know how the particles を and で work you will be able to read this text about stationary (ぶんぼうぐ) and understand everything by looking at the pictures!
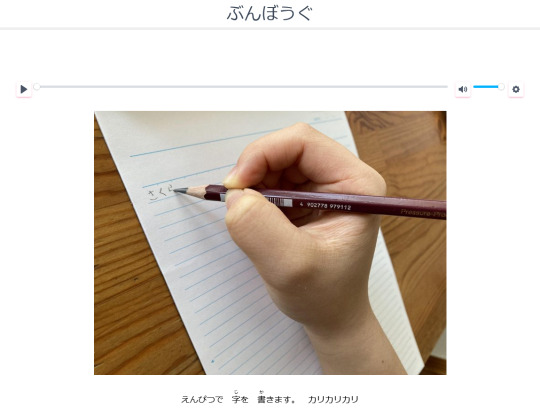
The resources linked so far can all be accessed completely free on the linked websites. If you have the money to spare, please also have a look at the box 「スタート」 from the series reberubetsu nihongo tadoku raiburarī published by the NPO Tagengo Tadoku and ASK (affiliate link). This box includes 8 little books in very simple Japanese.

All these texts for absolute beginners will get you started reading in Japanese with very little knowledge of characters and vocabulary.
Reading in Japanese is a skill that requires practice. But once you get used to it, it can be such a valuable tool to reinforce new vocabulary and grammar. So please don't wait until you're "ready" before you start reading - start early at your own level!
#my book reviews#reading in japanese#study japanese#learning japanese#日本語#japanese books#やさしい日本語#free graded readers#free tadoku graded readers#nihongo tadoku dōjō#absolute beginner level#japanese langblr#japanese language#japanese reading comprehension#japanese free reading resources#japanese reading resources
646 notes
·
View notes
Text
Inarizaki's Kansai Dialect
Japanese Dialects are split into Eastern and Western, with the Standard Japanese dialect being Eastern (Kanto region) and Kansai region dialect being Western (eg. cities of Osaka and Kyoto, and of course Hyogo prefecture- where Inarizaki is from). The pitch, tone, and stressing of the sounds is different from standard Tokyo Japanese so you should be able to hear the difference in how the Inarizaki members speak even if you don't know any Japanese.
just in case yall didn't know, Suna is the only member on the team that does not use Kansai dialect as he was scouted from Aichi prefecture, so he basically just speaks in the standard dialect
Some linguistics of the dialect that may or may not be heard in the show:
"ya" ending vs the standard "da" ending.
Kore kirai ya. vs Kore kirai da. (I hate this.)
the use of the "h" sound instead of "s"
Han vs standard san (honorific suffix, not really used anymore)
Negation suffix "-hen" instead of the standard "-nai".
Taichou kanri dekitehen koto, homen na. vs Taichou kanri dekitenai koto, homen na. (Don't compliment him when he's obviously not taking care of himself.)
verb "oru" vs the standard "iru".
Dareka ga mitoru yo, Shin-chan. vs Dareka ga miteiru yo, Shin-chan.
(Someone's always watching, Shin-chan.)
verb "temau" vs standard "teshimau"
Naitemau yaro! vs Naiteshimau darou! (You're gonna make me cry!)
Negation "suru" verb becomes "sen" instead of "shinai".
Ki ni sen dee. vs Ki ni shinai yo. (Don't worry about it.)
Some words that are different in Kansai dialect:
Honto becomes Honma (really)
Sodane becomes Seyade (thats right)
Nande becomes Nandeyanen (why)
Totemo becomes Meccha (very)
ii becomes ee (good)
"aho" means stupid in Japanese, but apparently in the Kansai dialect calling someone an "aho" is actually a compliment?! (even though it has the same definition)
Overall, I could watch the Karasuno vs Inarizaki episodes a hundred times just to listen to Inarizaki's dialect and how different it sounds to the rest of the characters in the entire show.
Although Karasuno speaks in the standard dialect (which isn't very strange since Miyagi is a suburb close enough to the Kanto region), theres a few lines here and there where one of them says something using the Tohoku dialect (the dialect that would be used often in the rest of Tohoku, such as Aomori).
But that can be a separate post for another day!
(I especially like Kita's voice, thank you Nojima Kenji.)
#haikyuu#inarizaki#japanese linguistics#japaneselanguage#japanese#kansai#kita shinsuke#miya atsumu#miya osamu#miya twins#suna rintarou#aran ojiro#ojiro aran#akagi michinari#anime#anime and manga#linguistics#dialect#kenji nojima#japanese language#karasuno#tokyo
215 notes
·
View notes
Text
かっちり
① tightly; exactly; precisely
② close-fitting (e.g. suit); firm (body); lean
計画をかっちりと立ておく。
けいかく を かっちり と たて おく。
Make sure you have a plan solidly in place.

#日本語#japanese#japanese language#japanese langblr#japanese studyblr#langblr#studyblr#単語#語彙#japanese vocabulary#tokidokitokyo#tdtstudy
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
japanese learners/japanese speakers, is there any solid dictionary that i can use to look up words? like larousse for french, is there any websites/dictionaries for japanese?
#japanese#japanese language#japanese learning#im thinking of getting into it for real#so i thought i could start by learning vocab but i need solid stuff#i can look it up online sure but are they true? are they really giving / showing me what i wanna know?#i don't wanna triple check for each word i want to look up or learn#so help is muuuuch appreaciate it#also i think learning vocab is the least scary way to learn japanese alphabets so this is actually the main reason why im asking +#+ for a solid dictionary#thank youuu#blablabla
209 notes
·
View notes
Text


sunday studies 🕊️🍵📗
#studyblr#study blog#langblr#langblog#japanese langblr#japanese language#japanese#studyinspo#study motivation#study aesthetic#study desk#exam study#student blog#learning japanese#language blog#language learning#student life#studying
552 notes
·
View notes
Text
shido's palace: those posters
And you know the ones I mean:

Shido, we can see right up your nose. But let's talk about the text on these. First, the really big bit on the left:
獅童正義
shidou masayoshi
Look at the kanji there. His given name is twice the size of his family name. Plus, his given name doesn't have the furigana (tiny text to tell you how to read it) that you can see against his family name—despite it being easily misread as a common noun.
Because, as eny fule kno, Shido's given name is spelled the same way as 正義 seigi, meaning "justice". This will be important later. The game lampshades this, by the way, in gossip chats around the election:

"Shido-san really lives up to what his name means. He's like justice personified." Okay, gossiping person, you do you.
united future
At the bottom, in tinytext next to his spooky Illuminati-esque Whole World In His Hands logo that isn't megalomaniacal at all, we have the name of his new splinter party:
未来連合
mirai rengou
United Future
未来 mirai means future; 連合 rengou means a bloc, a coalition, an alliance or union. 連合ヨーロッパ rengou yooroppa, "a federal Europe"; 連合国 rengoukoku, "the Allied powers". So we get "United Future", perhaps less catchily "The Alliance for the Future", which is very much the sort of name new Japanese political parties tend to have.
what about that other bit
Hahaha, you mean this little thing?

This is Shadow Shido's slogan. This sums up his mission, his motive, the whole reason he wants power. And what does it say?
私のために、民衆は尽くす
watashi no tame ni, minshuu wa tsukusu
The people will serve me.
What a nice thing to say! What an excellent sentiment, befitting of a public servant in a democracy! And what an unashamed piece of shit, eh? You can see why Japan is underwater in his head.
Constructions of the form X no tame ni tsukusu are quite common; my dictionary lists several. So this little phrase is a play on words in at least two ways:
First of all, it's an adaptation of a well-known phrase, 民衆のために尽くす minshuu no tame ni tsukusu, "to serve the people". Shido has taken this and inverted it: the people will serve him.
But second—remember how Shido's given name, Masayoshi, is written the same way as seigi, meaning "justice"? One of those common little example phrases in my dictionary, under tsukusu, is the following:
正義のために尽くす
seigi no tame ni tsukusu
to work for justice
This is why his given name is in massive letters on the poster: because this play on words is deliberate on his part: Shido is justice, as his name should tell you; he defines what is good and right and true—and what's good and right and true is what is in his interests. And so the people will serve him. The same way they'd serve the nation, or society, or the public good.
It's a really interesting line. And, of course, it calls to mind Akechi—supposedly a detective, in the service of justice, and yet in reality....
BTW, don't forget this is Shido's Shadow talking. How much does Shido himself, the guy walking about upstairs, delude himself about all this? That's an exercise for the reader.
revision history
Click here for the latest version.
v1.0 (2024/01/14)—first published.
726 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fake-tanuki soup or Fake tanuki-soup?
連濁(れんだく; en: rendaku)is a phonological rule in japanese that makes the first voiceless consonant of a word change into a voiced consonant when used in a compound word. For example, おり + かみ → おりがみ (ori + kami → origami) ("fold" + "paper" → "paperfolding") - the /k/ sound in かみ becomes a /g/ sound (which is the voiced version of a /k/ sound) by adding a voicing mark -> が.
What’s interesting about 連濁 is that native speakers can use it subconsciously as a sort of “order of operations” system for unfamiliar words, like PEMDAS or BIDMAS in maths. A classic example of this is the にせたぬきじる problem[1]. Native speakers can immediately and with confidence tell the difference in meaning between two compound words they have never heard before, despite the only difference being the voicing of a single consonant. Take the three words 偽 (にせ, meaning “fake” or “imitation”), たぬき (tanuki, the Japanese racoon dog), and 汁 (しる, meaning “soup” or “broth”). They can be combined into the following compound words: にせたぬきじる and にせだぬきじる (note the voicing mark, or dakuten, on the latter). Keep in mind, these two words do not exist in ordinary japanese - they’ve been created as part of a linguistics experiment.
You might think the meaning would be ambiguous in those compound words: is it (imitation tanuki)+soup or imitation+(tanuki soup)? Let’s imagine we’re referring to the former. First, we combine にせ+たぬき. There’s a rule that rendaku can’t occur if there’s already a voicing mark in the second component of the compound, but we’re safe here - たぬき has no voicing mark. Therefore, it becomes にせだぬき. Then, we combine にせだぬき+しる. Again, しる has no voicing mark in it, so we’re safe to add it in, and we get にせだぬきじる.
Conversely, let’s say we were referring to fake “tanuki-soup”. First we combine たぬき+しる. This combines safely to たぬきじる. Then we combine にせ+たぬきじる. But wait, the second component does already have a voicing mark, on じ! So we can’t add one to た. Therefore we end up with にせたぬきじる.
That’s a lot of thinking and linguistic hoops to jump through to make up 2 words, but here’s the thing: Japanese native speakers who have never heard these words before can instinctively deduce the difference in meaning with startling accuracy. They correctly determine the meaning of にせだぬきじる as “a broth made from imitation tanuki” and にせたぬきじる as “a fake version of a dish called ‘tanuki soup’”. Even more surprising is the research findings of Shigeto Kawahara, which show that children as young as 9 years old can consistently deduce the difference as well[2]. I think this shows how incredibly powerful the subconscious mind is at learning linguistic rules, and how bad the conscious mind is at learning them!
#langblr#japanese#japanese language#language acquisition#language learning#language#linguistics#learning japanese#日本語#jimmy blogthong
678 notes
·
View notes