#Writing Disability with Cy Cyborg
Text
Tips for writing and drawing Wheelchair using characters: Your character's wheelchair can tell us a lot about them
When you first start learning character design, you'll often be told something to the effect of "use your character's outfit to tell us more about them" - and this same principles can be applied to a disabled character's mobility aids.
Mobility aids like wheelchairs, to many disabled people, are a part of us. They can be an extension to a person's body and chances are, if you're going to be using this piece of equipment every day for the foreseeable future (or at least for a good amount of time for the foreseeable future), it's going to start reflecting some aspects of your personality, your interests, your passions, especially when you remember, a lot of people get their wheelchairs custom built for them.
You can use your character's wheelchair to tell us a lot about them without ever needing to show/describe them directly.
Let me show you two examples:
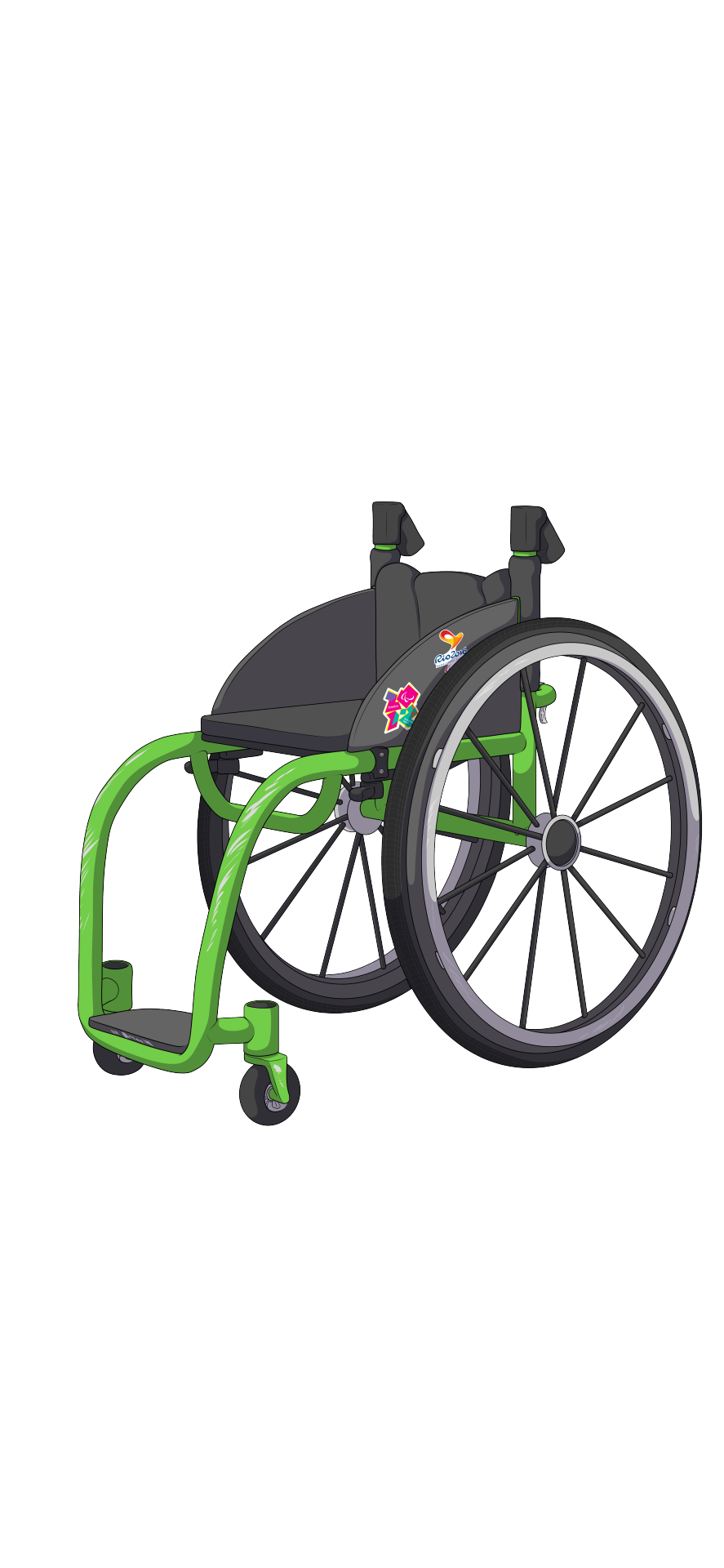
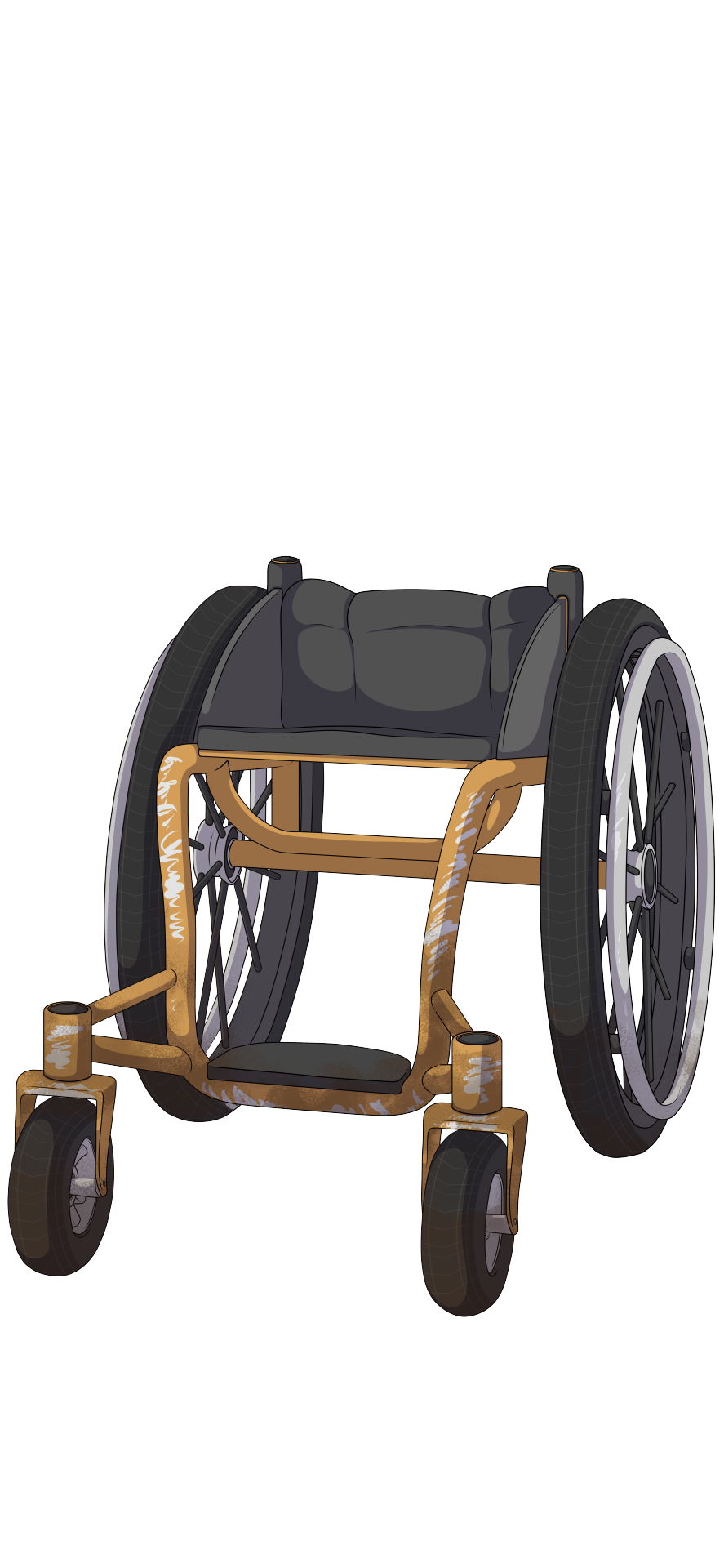


Take a look at these two wheelchairs. they're similar in shape and build, but still pretty different to each other. Can you make some guesses about their users based only on what's shown here?
intended answers below:
Please note, the following points are all generalisations and the real world is rarely this simple. This is to demonstrate how to use disability aids to contribute to your character's design, not how to make assumptions about real people in real life.
So here are some similarities between the chairs:
Both wheelchairs have ridged frames, this means the wheelchair can't be folded in any way. These kinds of chairs can imply a few different things depending on the person. They are typically lighter, sturdier and more durable, and indicate the person probably will be using the wheelchair for a long time and/or has the money to get something built to last (or lives in a place where cost not an issue due to universal/subsidised access to healthcare). They are also typically better to travel with when flying, as they are less likely to be broken by airport security/staff.
Both wheelchairs also lack anti-tip wheels, which are a third set of wheels that extend from the back of the chair. Them not being present could indicate the person is likely pretty confident in their ability to use the chair without worrying about tipping out. It could also indicate they are in an environment where the anti-tips could be more of a hazard than a help, such as on rough terrain.
So lets look at some specifics for the green wheelchair:
Take a look at the wheels. The front wheels are pretty small and appear to be solid, while the back wheels appear to be quite narrow (compared to the orange chair anyway). This indicates the user likely lives somewhere with decent accessibility like a (well funded) city where they are unlikely to encounter unpaved/dirt roads/grass. Small front wheels and thin back wheels are good for manoeuvrability and a smooth ride over even terrain, but they will get stuck as soon as bumps appear, so this probably isn't an issue for this person.
While its a bit hard to tell unless you have seen other similar wheelchairs, this wheelchair is very long in the front, meaning the footplate and front wheels are further away from the seat than most. There could be a few reasons for this. One either indicates the person has very long legs, or a lack of motion in their knees, making it harder to bend their legs. This is moves the chair's centre of gravity forward by a decent amount, making it harder to tip back, which could indicate the person's legs are very light. You tend to see this most often in the wheelchairs of bilateral leg amputees, who are at a greater risk of tipping backwards due to a lack of weight at the front of the chair (even if they wear their prosthetics).
The colour of the chair is bright. This could simply be the character's favourite colour, or maybe this colour has some significance to them?
There are stickers on the side of the chair relating to the Paralympics. This could indicate the person is a fan, or perhaps had some involvement in the games?
The wheelchair has handles on the back, but they are able to be folded down. This is a popular feature for people who are independent enough to go out on their own, but still want to have the option for some help. folding down the handles also deters random strangers from grabbing at you (an unfortunately common experience for wheelchair users).
There is some mild paint scratching to the front of the wheelchair, but nothing too noticable. This is typical of older chairs and people who are a little rough on their chairs. Maybe they've had a few stacks and falls throughout the years, probably going a decent speed.
Ok, now let's look at the orange chair
This wheelchair has very large, inflatable front wheels, and very thick back wheels. This will make the chair slower and less manoeuvrable on flat/even surfaces, but much, much easier to push on rough terrain. This is supported by the amount of mud on the wheelchair.
The seat on this wheelchair tilts upwards slightly. This is called a bucket (or according to an old basketball teammate of mine, a dump-truck lol). This is a feature you typically see in wheelchairs made for people with spinal injuries who are unable to move their legs and engage their lower bodies or core to help keep them stable.
The back of this chair is very low, indicating that if this wheelchair user has a spinal injury, it's probably pretty low on their spine, likely fairly close to the hips, making the person a low-level paraplegic. Higher-level paraplegics and quadriplegics usually need a higher back to help support them and keep them from flopping over, since all the muscles below their place where their spine broke either doesn't work, or is significantly weaker. Higher backs though can get in the way of pushing and reduce mobility, so people who need less support will likely opt for a lower back rest.
This wheelchair has no handles, which indicates the user is probably very independent and doesn't need a lot of help getting around.
The paint on this wheelchair is very scratched up, showing the person is very tough on their wheelchair and doesn't care to get the paint touched up.
This wheelchair has no breaks. This is very common on chairs with larger tiers as they don't tend to be as effective, but also on many outdoor wheelchairs, for two reasons. One is because they are made for rough terrain, so chances are, you aren't going to go far without a big push to get you moving. The second reason is that to get over large bumps and obsticals in a wheelchair, it can be helpful to do very large pushes using the top and front of the wheel. When pushing a normal chair, most people will only use the top section of the wheel to push since it's closest, but these big pushes that use the front of the wheel make it easier to push, since you can benefit from downwards momentum. However, this is also where the breaks are located on most wheelchairs, which can create a hazard. I've lost entire fingernails by them getting snagged on the breaks when pushing this way. So if you live somewhere where the breaks are not going to be helpful to you often, it makes sense to not get them.
And here are the characters who own these wheelchairs
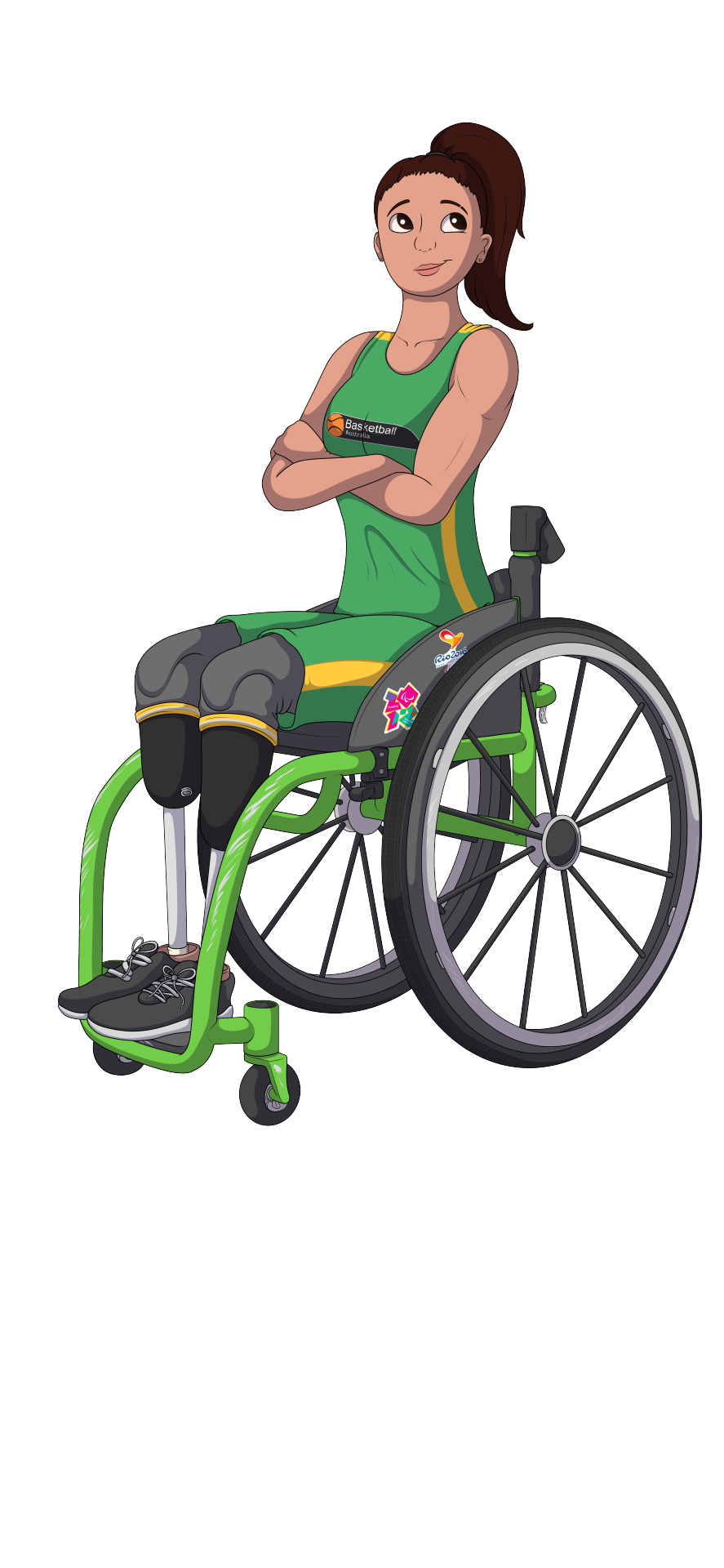


The owner of the green wheelchair is an amalgamation of a few people I knew from when I played wheelchair basketball. They're a bilateral leg amputee, and judging by their outfit (The Official National Wheelchair Basketball uniform for Australia), they're an elite athlete. This wheelchair is not the one they play sport in, but it still needs to be durable enough to withstand the rough treatment of airport staff when traveling, as well as heavy day-to-day use that comes with being an active person. While it needs to be rough, the person also seemed to want to prioritise speed and manoeuvrability, and likely doesn't need to worry about rough terrain too much, so they probably live in a major city.
The owner of the orange chair was inspired by a family friend of mine. They live on a farm, and need a chair that can handle life in those conditions, rough terrain and all. This comes at the cost of speed and manoeuvrability on smoother terrain, but honestly, anyone who's lived in the country knows you won't find many of those around there anyway, so that's not too big of a sacrifice. They are paraplegic, are very confident in their ability to use their wheelchair, and probably doesn't need help too often, but still benefit from some extra stability support from the raised seat on their chair.
Conclusion
Once again, these are generalisations, and in real life there are always exceptions, but I hope this helped demonstrate what I meant when I said you can use your character's wheelchair to tell us more info about them if you're smart about it.
I originally planned to do a whole series of these, showing a wider variety of wheelchairs and the people who they belong to, but I guess I kind of forgot because they've been sitting, abandoned on my hard drive for the last 2 years 😅. If that's something you folks would be interested in seeing though, let me know, I'd happily revive the series lol.
#Writing Disability with Cy Cyborg#id in alt text#long post#writing disability#disability#disabilities#disabled#physical disability#wheelchair user#physically disabled#wheelchair#character design#character illustration#character concept#Designing Disabled Characters#writers on tumblr#writing#writing community#writblr#writerblr#writing advice#writing tips#writing resources#art reference#artists on tumblr#artblr#illustrator#visibly disabled#disabled and proud
4K notes
·
View notes
Text

Chapter 5 of my fic is up on Ao3!
This chapter took me way too long to finish, so I'm thinking I might take a breather and skip next week's upload. We'll see how it goes lol.
As for the artwork for this chapter, it's nothing too out-there, but I decided to try some new stuff for the background and lighting/shading, and I think it looks quite nice. It's not something I'd use in all my art, but it's good for drawings like this and my comic that I want to be able to do quickly.

[ID 1: An image of Valori, a dark red dragoness with bright red eyes, wearing dark, metal armour, looking back at the viewer. In the background is a forrest of trees with blue leaves at nighttime. In the top left corner is a logo that reads "The Legend of Cynder, The Flame of Darkwick" /End ID 1]
[ID 2: A copy of the first image, just with the logo removed. /End ID 2]
#Cy Cyborg Draws#disabled artist#queer artist#writing#writeblr#my art#digital art#Ao3#ao3 fanfic#fanfic#fanfiction#ao3fic#spyro oc#spyro the dragon#the legend of spyro#spyro fanart#spyro#legend of spyro#cynder the dragon#dragon#dragon art#armored dragon
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Stop Using Slurs in Children Stories!
I bet that caught your attention. You might be thinking, what stories use the N-word, or the F-word, well...none that I found. However, there are two slur words that are often used in writing mainly in children's literature because I don’t think enough people know them to be slurs. Those words are cripple and savage.
Before I begin, I need to address a few things. First, I'll only use these words in full for educational purposes so nothing gets confusing. Secondly, I’m not hating on any of these authors. I genuinely think these people might not know cripple and savage are slurs. However, I still need examples of what I’m talking about to explain how common these words are used in writing as well as explaining why it’s a bad idea to use them, so I’m using these authors, not as targets but as examples based on the books I have.
Both of these words (cripple and savage) have a lot of history behind them, and while I strongly suggest, not using them, if for some reason, they have to be used, you need to hire a sensitivity reader who’s a part of the communities that has been affected by said words before you publish your story.
Cripple:
Before I begin, please understand I’ve consulted with a disabled person who’s well knowledgeable in this topic to help smooth out my points. I’m not apart of the physically disabled community. As I’ve been told there’s a big debate going on within the disabled community in regards to if mental disabled people are allowed to use the word cripple or not. This is beyond my understanding of the word, and the community so when I mention the word cripple, I’ll be referring it to the physical disabled community and not the mental one. Everything I’m about to say has already been said by the physically disabled community. I’m not adding anything new or talking over them. If you would like to know more about the language of disability, please read Cy-Cyborg’s article on the matter: https://writingwithcycyborg.blogspot.com/2024/02/LanguageOfDisability.html
Cripple is a world that’s defined one of three ways, to either describe someone who can’t function properly, to describe a situation that’s overwhelming, or to describe an object that isn’t working.
Example one: DragonFire: Sphere of Eternity (book 1)

“I mean, this morning, no offence, you were crippled.” (Describing a person.)
Example two: “The economy was crippled.” (Describing a situation)
Example three: DragonFire: Age of Legend (book 3) (describing an object)

The word cripple, even when it was used in a medical sense has always been a word to punch down and insult the physically disabled community. It was used to attack them and point out their disabilities. It became a common replacement for the word injured because it has a more of a punch. Instead of calling someone “severely injured” use cripple instead, it’s shorter and a lot punchier of a word. Over time it became part of normal vocabulary to use it while describing something as severe, despite it still being used as an insult at the same time. Let’s look at an example of how it’s being used to describe an injury in Robert Vane's A Dragons Chains: Book one of the Remembered War

“I moved my three non-crippled legs…” In this example, the dragon has an injured leg. Why did the author use the word cripple instead of injured? I think it’s because of shock value. Is it cheap shock value? Yes, but shock value for the reader is still shock value. Tell me, what’s the difference would be if the author replaced the word cripple with injured? “I moved my three non-injured legs...” Does using the word cripple add to the sense of urgency? Add to the sense of how injured that character's leg is? Or was it merely just a place for shock value?
But how often is this word used? Let’s take a quick look at the DragonFire series. There are currently four books in this series at the time of writing, and the word crippled is used twelve times throughout four books. Knowing it’s a slur...that’s a lot.
Some of the examples in which it was used are in things such as DragonFire: Fallen Star (book 2) where it reads:

Or
“...he yelled, his scythed tail coiling round, only for the far less crippled dragon to kick him off.” DragonFire: Order of Enishra (book 4)
It’s not just the DragonFire series which does this, other examples include, The Last Monster on Earth by LJ Davies

Which uses it four times in one book with examples such as “Lock these two in the truck with the cripple…”
Warriors: Forest of Secrets (book 3) has this line. “As Fireheart said goodbye to Yellowfang and went back to hunting, he felt a new surge of determination to bring Tigerclaw’s guilt into the open. For the sake of Redtail, murdered; for Ravenpaw, driven from the Clan; for Cinderpaw, crippled...”
And even Wings of Fire, one of my favourite book series uses it.

Here’s a question for you. Is it ok to use that word if the impact is meant to be insulting? In the Wings of Fire example, Queen Scarlet defeats Dune in combat, and is about to kidnap the main characters. Dune, still breathing can barley move upon which Scarlet killed him. Scarlet is one of those pure evil types of characters, this is something I could see her saying, but let’s take a step back and put your eyes in the eyes of a disabled child.
Here you are, a disabled child. You already know what the word cripple is, and it’s been used against you (don’t act like this doesn’t happen). You read Wings of Fire and you come across that sentence. What is the intent behind that sentence in the eyes of a disabled child? Are you supposed to be scared of Scarlet? Angry? Or are you upset, because even in a fantasy book with talking dragons, you can’t escape from real life or that word?
Some of you might say, “What if only the villains use that word?” While I can see Queen Scarlet calling Peril a stupid retarded motherfucker. It’s not something you want in a children's story, so why does cripple get a past?
I hope you’re getting the picture, it’s a very commonly used word, one which the disabled community has begged able-bodied people not to use. The word injured gets the same point across and it doesn’t have a history of it being a derogatory term. While replacing the word cripple with injured or severely injured isn’t a perfect fix, it’s at least getting rid of the other word which is a start at least.
Now before I continue with the other slur, I can hear some of you say you’re aware disabled people are using cripple to describe themselves. Why can’t able-bodied people use it? Here’s the thing. Not everyone in the disabled community is doing this, and it’s not a monolith. The word cripple has been used as an attack against the disabled community for decades. It targets them, puts them down, and it’s only used against them. You only use the term to refer to something as injured so there's no reason to use it on an able-bodied person. The community in which it was used against is taking that word and trying to empower it amongst themselves. You’re not gonna complain if someone who’s black uses the N-word, so why are you upset when disabled people use the word cripple to describe themselves but are saying you can’t? That word belongs to them and their community, not yours. Also, one more thing before I go, not everyone in the disabled community uses this word or wants to hear it. There have been plenty of disabled people who are fine using that word to describe themselves but won’t say it around others if other disabled people express they don’t want to hear it. So be mindful if you’re gonna use it and please hire a sensitivity reader.
Savage:
This word...I have a lot of history with it because it’s a word that’s used against my community, (indigenous) people. And yet, just like the word cripple, it’s used all the time and while it’s a very common occurrence where indigenous voices aren’t heard, we’ve been telling everyone to just drop this word. Unlike the word cripple, we aren’t trying to claim this word, we just want it gone.
The definition of this word is an easy one to understand. It’s to describe a person, object, or an action as barbaric, wild, aggressive, unintelligent, or barely even human.
Example one: “They’re savages, savages, barely even human” Disney, Pocahontas (1995). (Used against people)
Example two:DragonFire: Age of Legend (book 3) by LJ Davies

“I opened my muzzled to respond, but another savage roar drew our attention…” (Used as an action)
Example three:

(Used against a group of people)
Example four: “Savage weaponry” (Use to describe an object)
I’m gonna be using the series DragonFire a lot for my examples, because out of all the books I got, that series uses the word 19 times throughout books one, two, and three. It was used twelve times in book three and I guess someone told LJ Davies about this problem because it doesn’t appear in book four. But it DOES appear in the spin-off series “Tales of DragonFire: Rebellion” twice, and THIRTEEN TIMES in “The Last Monster on Earth”. Overall, that's THIRTY-FOUR TIMES in the course of five books, all meant for children.
LJ Davies isn’t my only example. Chester Young, used it nine times throughout books 1 and 2 of the Celestial Heir books Rowan Silver, used it once in Eyes of Silver: Dragons and Skylines (book 2) And Robert Vane, used it once in the Remembered War series in book 4
Let’s start by showing off some examples and the impact they have and please note, that this might be something you’re just not experienced with. So just like with the disabled child, try to imagine yourself as an indigenous child. You’re fully aware of the word savage, it’s been used against you, and your people. So when you read a text like “Trade with the savages...they wouldn’t understand the concept!”

It feels awfully familiar to lines you read in your history books about your people. Keep in mind, that you wanted to read a story about dragons so you could get away from real life.

(From the Last Monster on Earth by LJ Davies)
I know the United States called the Native Americans savage monsters while stealing their land, it was used as a way to justify their actions, make the natives appear barley even human or in most cases, not human at all, let’s not forget, for a good majority of the building of the United States, those founding fathers didn’t see anyone other than themselves as humans. Reading text, asking how people became savage monsters overnight should remind you how people labelled indigenous people in the past and still do today.
"To confirm the princess’s words, yes, there is an army out there whose numbers vastly exceed our own. Nevertheless, they are a crude mockery of the noble kind they once were, and they are now nothing but savages….There was a series of grunts and nods at that statement...” (DragonFire: Age of Legend, book 3)
I think, this text is a great example of what I’ve been trying to say. In this text, the character who is speaking and the grunts and nods are all dragons with human-like intelligence. They're a stand-in for us. The Elder (who spoke in said text) has been seen and viewed as one of the good guys. He calls his kind noble, and he’s working with a princess, (let’s not forget our history books on how the royal family treated indigenous people). He calls his attackers “nothing but savages”. In translation, their monsters, who are no longer noble or righteous. There’s an agreement with his statement, as if what he says is right and we should be agreeing with him.
In that sentence, understanding everyone is of human intelligence and is a stand-in for humans. We have an old white knight, calling the enemy savages while the royal family are the heroes who are trying to protect their land from those filthy, disgusting, savages. You can kind of see why I’m saying we really shouldn’t be using this word.

“Yellowfang will be allowed to stay here until she has recovered her strength. We are warriors, not savages…” Warriors: Into the Wild (book 1)
Savages...indigenous people, they aren’t warriors, they would’ve killed Yellowfang, and left her to rot in the wilds, Thunderclan is better than those monsters. Am I making my point clear enough when it comes to the history of this word, who it’s targeted against and how it comes across when reading in children's media?
You might’ve noticed I’ve mainly been using examples when it refers to a group of people, not necessarily showing off how commonly it’s used as either an action or an object because honestly...those are just kind of dumb. A savage roar? What does that mean?

Ah yes, because we really needed the use of the word “savagely” to get the point across that Misuk just destroyed a person's skull. The “turning his head into a bloody pulp” wasn’t enough on its own. Without the use of the word savagely how else could we get the aggression and power across? When savage is used as an action it’s mostly because said character loses control of their humanity. They become savage when they attack and the end result is a bloody mess because that’s the only way indigenous, I mean, monsters, I mean barbarians, I mean savage people know how to fight. You often see these kinds of moments when the good guy who’d never hurt a fly loses control and unleashes hell, they turn into something that’s not themselves, they turned into a savage and these moments are meant to be shown as shocking as the character forgets who they are for a couple of seconds.
Indigenous people were savages, with savage strength, and a savage kind of culture. They scalp people, beat them to a bloody pulp, and ate your children. Those monsters needed to be killed. Whenever you use the word savage, it circles back to a group of minorities who were just trying to survive. This word has been used so much, that I don’t think many people realise the history behind it, which is why I said I’m not hating anyone who uses it, but please try to get a sensitivity reader. Get disabled and indigenous sensitivity readers, even if there’s no indigenous or disabled representation in your books, the words you use, still affect us and it’s a good thing to be aware of the words of which you speak and write.
Please be aware of these words, especially if you’re writing stories meant for children because the more children see these words, the more normal they’ll think it is and the more often they’ll start repeating it. I think there’s a time and place for these words, but saying them as an excuse to make something more shocking, isn’t the time or place.
#writing#writeblr#book#books#disability#disabled#writers on tumblr#dragon#writers#write#writers and poets#writerscommunity#creative writing#book writing#on writing#writing advice#writer#cw: c slur#c slur#s slur#disability in media#dragonfire sphere of eternity#dragonfire#lj davies#erin hunter warriors#Tail of revenge Celestial Heir#Chester Young#A Dragons Chains#A Dragons Chains The Remembered War#robert vane
40 notes
·
View notes
Note
About the post on writing disabled characters with a readmore from a "deactivated" account - the number of popular posts I've seen with their username marked deactivated and the same user (not deactivated) later in the thread lead me to develop the unsubstantiated theory that that's how posts that were deleted on their original blog are listed. At least sometimes. cy-cyborg dot tumblr dot com at least still exists and appears to be from someone who provides advice on writing disabled characters. (Not sure what that indicates for why the post is still readable from some directions but not all, though.)
huh. I have seen similar things and assumed OP deleted and subsequently either OP or an impersonator created a new Tumblr with the same name, but we could both be guessing right about some instances and not others, idk.
this hellsite, y'all
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trainer Quest #14
Framing Question(s): How are these episodes
connected? As teachers can we use popular culture
to engage these abstract topics of violence &
vulnerability?
These two episodes are related because they both contain people that possess immortal powers. Both the characters abilities are also challenged either by injury (the Legend of Korra), or by a weird talk show host, as seen in the Steven Universe episode. They both start to feel discouraged and incapable but then are able to overcome their obstacles and find their strength again. As teachers we can definitely use popular culture, such as tv shows, to engage these abstract topics of violence and vulnerability. By using popular culture to introduce and discuss these topics with our students its helps these issues appear more relevant to the students. It will help keep them engaged because its something they enjoy doing, watching tv.
In Kafer’s reading, it starts off by saying “Donna Haraway insists that the cyborg is about both pleasure and responsibility” but then Kafer goes on to absolutely destroy Haraway by saying “Pushing the figure from a disability perspective entails bringing a disability consciousness to the cyborg, attending to the specific benefits and dangers it harbors for disabled people. This shift requires an acknowledgment that human/machine interfaces are not always beneficial or pleasurable; an awareness that many disabled people lack access to the cy- bertechnologies so highly praised in cyborg writing; an accounting for the ways in which cybertechnologies rely on disabling labor practices across the globe; and a realization that not all disabled people are interested in technological cures or fixes. Each of these elements takes cyborgology away from its traditional use of disability as metaphor, and toward an un- derstanding of disability in political and social context. In so doing, they also-and ironically-bring cyborg theory closer to the promise of Har- away's manifesto, a promise of a fully situated cyborg that refuses easy celebrations of human/technology connections.” I really enjoyed this part of the reading because I love watching people get dragged and called out on their bullsh*t.
PROMPT: Doodle an animated cartoon to relax.
Sorry mine’s so bad, its not easy to draw on a laptop tracker pad...

1 note
·
View note
Text
This is just a not-so friendly reminder to non-disabled people, especially authors, people in fandoms or in media analysis circles: Cripple/crippled is not just a fancy way of faying "badly injured". it's not an adjective you can just throw in to spice up your sentence because you used "injured" or "disabled" too many times in that paragraph, or because you feel like it gives your writing some extra "oomph".
Cripple is a slur.
A slur the physically disabled community has been asking people not to use for DECADES, since at least the 1970's (50 years). It's a slur with centuries of abuse behind it, centuries of being used to justify physically disabled people as less-than, centuries of demonisation, mistreatment, ostracization, and murder.
Some people within the physical disability community are reclaiming it, that's where movements like cripplepunk (also known as crip-punk or C-punk) come from. That's fine, I'm not talking about that. I love the cripplepunk movement and everything it stands for: being unapologetic about our disabilities and not changing ourselves for the comfort or convenience of able-bodied folks. But the people who use it in that context understand the history of the word, they know how it was used to hurt us, and they understand that not everyone in the physically disabled community is comfortable with the use of the word, especially those who were around when someone being labelled as "crippled" was seen as a valid reason to treat them as less than human. They understand the impact of the word.
But If you, as an able bodied person, casually uses "cripple" in your work, at best you are showing your disabled audience that you haven't been listening to us, at worst, you show you don't care about weather we feel safe in the spaces you have created.
And for able-bodied authors specifically, even if your character is physically disabled, I'd still recommend avoiding it unless you're prepared to do a LOT of sensitivity readings from multiple sensitivity readers. I've been physically disabled since I was 1 year old, I learned to walk for the first time in prosthetics and have been using a wheelchair since I was in school, I have no memory of life as an able-bodied person, and even I don't feel comfortable using the word cripple in my work.
It's a loaded word, with a lot of implications and a LOT of very dark, and for some people, very recent history. It's not a sentence enhancer to just throw in willy-nilly. Please.
#Writing Disability with Cy Cyborg#disabled#disability#disability history#ableism#physically disabled#cripple punk#cpunk#actually disabled#physical disability#visibly disabled#visible disability#writing disability#writing#writing community#writeblr#writers of tumblr#authors of tumblr#media analysis#write#c slur#language
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Writing and drawing amputee characters: Not every amputee wears prosthetics (and that's ok)
Not every amputee wears prosthetics, and not doing so is not a sign that they've "given up".
It's a bit of a trope that I've noticed that when an amputee, leg amputees in particular, don't wear prosthetics in media its often used as a sign that they've given up hope/stopped trying/ are depressed etc. If/when they start feeling better, they'll start wearing their prosthetics again, usually accompanied by triumphant or inspiring music (if it's a movie). The most famous example of this is in Forest Gump, Where Dan spends most of the movie after loosing his legs wishing he'd died instead. He does eventually come around, and him finally moving from his wheelchair to prosthetics is meant to highlight this.

The thing is, it's not that it's unrealistic - in fact my last major mental health spiral was started because one of my prosthetics was being a shit and wouldn't go on properly, despite fitting perfectly at the prosthetist's the day before. I'm not going to use my legs when I'm not in a good headspace, but the problem is, this is the only time non-prosthetic using amputees ever get representation: to show how sad they are. Even if that's not what the creator/writer necessarily intended, audiences will often make that assumption on their own unless you're very careful and intentional about how you frame it, because it's what existing media has taught them to expect.
But there are lots of reasons why someone might not use prosthetics:
they might not need them: this is more common in arm amputees because of how difficult it can be to use arm prosthetic, especially above-elbow prosthetics. Most folks learn how to get on without them pretty well. In fact, most of the arm amputees I know don't have prosthetics, or only have them for specific tasks (e.g. I knew a girl who had a prosthetic hand made specifically for rowing, but that's all she used it for).
Other mobility aids just work better for them: for me, I'm faster, more manoeuvrable and can be out for longer when I'm in my wheelchair than I ever could on my prosthetics. Youtube/tik tok creator Josh Sundquist has said the same thing about his crutches, he just feels better using them than his prosthetic. This isn't the case for everyone of course, but it is for some of us. Especially people with above-knee prosthetics, in my experience.
Other disabilities make them harder to use: Some people are unable to use prosthetics due to other disabilities, or even other amputations. Yeah, as it turns out, a lot of prosthetics are only really designed for single-limb amputees. While they're usable for multi-limb amps, they're much harder to use or they might not be able to access every feature. For example, the prosthetic knee I have has the ability to monitor the walk cycle of the other leg and match it as close as possible - but that only works if you have a full leg on the other side. Likewise, my nan didn't like using her prosthetic, as she had limited movement in her shoulders that meant she physically couldn't move her arms in the right way to get her leg on without help.
Prosthetics are expensive in some parts of the world: not everyone can afford a prosthetic. My left prosthetic costs around $5,000 Australian dollars, but my right one (the above knee) cost $125,000AUD. It's the most expensive thing I own that I only got because my country pays for medical equipment for disabled folks. Some places subsidise the cost, but paying 10% of $125,000 is still $12,500. Then in some places, if you don't have insurance, you have to pay for that all by yourself. Even with insurance you still have to pay some of it depending on your cover. Arm prosthetics are even more expensive. Sure, both arms and legs do have cheaper options available, but they're often extremely difficult to use. You get what you pay for.
they aren't suitable for every type of environment: Prosthetics can be finicky and modern ones can be kind of sensitive to the elements. My home town was in a coastal lowland - this means lots of beaches and lots of swamp filled with salty/brackish water. The metals used in prosthetics don't hold up well in those conditions, and so they would rust quicker, I needed to clean them more, I needed to empty sand out of my foot ALL THE TIME (there always seemed to be more. It was like a bag of holding but it was just sand). Some prosthetics can't get wet at all. There were a few amputees who moved to the area when I was older who just didn't bother lol. It wasn't worth the extra effort needed for the maintenance.
People have allergies to the prosthetic material: This is less of a problem in the modern day, but some people are allergic to the materials their prosthetics are made from. You can usually find an alternative but depending on the type of allergy, some people are allergic to the replacements too.
Some people just don't like them.
There's nothing wrong with choosing to go without a prosthetic. There's nothing wrong with deciding they aren't for you. It doesn't make you a failure or sad or anything else. Using or not using prosthetics is a completely morally neutral thing.
Please, if you're writing amputees, consider if a prosthetic really is the best mobility aid for your character and consider having your characters go without, or at least mix it up a bit.
For example, Xari, one of the main characters in my comic, uses prosthetics unsupported and with crutches, and uses a wheelchair. They alternate between them throughout the story.
#disability#disabled#id in alt text#writing#writing disability#disability representation#authors of tumblr#write#writeblr#writers on tumblr#writerscommunity#writer#creative writing#writing tips#writing resources#writing help#writing advice#writing disability with cy cyborg
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Tips for drawing and writing amputees: The prosthetic needs something to hold onto
Prosthetics need to be able to hold on to the body.
If you're giving your amputee something similar to 99.99% of modern prosthetics, this will be done through a socket. This is a ridged cup made perfectly for the amputee that holds the prosthetic onto the body. Older prosthetics (mostly anything before the 90's) made the prosthetic socket intentionally tight in spots, which is what held it in place. Some people with sensitive skin still use this style of prosthetic but they've mainly fallen out of use in favour for suction sockets. These sockets create a vacuum seal that holds the prosthetic in place. These can work in two ways, either just by forcing excess air out of the socket and creating the seal that way, or for some legs, sucking that excess air out and into an "ankle" mechanism to offer some extra suspension and padding in the step.
Some prosthetics will also use additional measures as well as suction, such as pin-locks, where the amputee wears a sock with a screw at the bottom that clips into a mechanism at the bottom of the socket, or a prosthetic with movable panels that can be tightened via cables running through the socket.
I've used all of these except the pin lock socket, and they all have one thing in common: The sockets need as much space as possible. For prosthetics using suction in particular, this is to spread out the amount of force being applied to the leg. If all the suction is being applied to the end of the stump, it's going to get sore and could even damage the skin. If that same amount of suction is applied to a much wider area, it's going to feel less intense. Likewise, older prosthetics needed as much space to work with as possible too, as applying tight pressure to a small area as opposed to a larger surface to keep the tension isn't good for your skin or muscles in that spot.
For this reason, the sockets will take up all of the space available without limiting movement, meaning they will go all the way up to the next major joint. An amputee who lost their hand through the wrist will have a socket that goes all the way to their elbow. An amputee who lost their leg through or above the knee will have a socket that goes all the way to their hip.
Sometimes, if an amputation is particularly close to a major joint and there isn't a lot of space left between the stump and the next major joint, prosthetists will opt to immobilise the closest joint and take the socket all the way up to the next major joint. This was something I've actually discussed with my prosthetist. My left leg is amputated below the knee, but I only have a few centimetres of space below the knee. That leg occasionally needs revisions, meaning they take the very tip off of the stump to help correct issues with weird bone growth, scarring, infections etc, but if I get another revision, my leg will be too short to comfortably wear a socket, so my knee will need to be immobilised and my leg will become, functionally, an above knee amputation, despite still having the joint. This is rare, but it happens on occasion, showing that sometimes that need for space trumps even the use of a still functional joint. It's really important.
I wanted to bring this up because I see a lot of people draw sockets on their amputee's prosthetics, but they're much too tiny to be comfortable!
I did mention most prosthetics use a socket, but not all do. Some old prosthetics did not have sockets and were held in place using other methods.
This is a "prosthetic" my prosthetist found in his company's back room. He's not sure when it was made, but together we came up with an estimate of it being made around the 70's for a through-hip amputee (meaning someone who's whole leg was amputated with no stump at all)
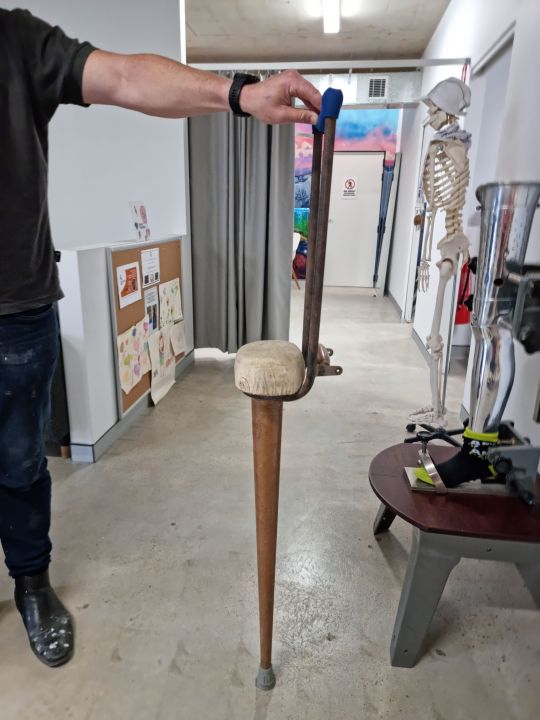

It's designed so that the user would rest their hip on the cushion and use the handle to hold it in place and move it in time with their walk. This kind of mobility aid isn't often used anymore (me nor my prosthetist have seen one out in the world), and seems to have faded in use during the 80's as sockets were invented that could better hold onto the hip and pelvis for through-hip amputees and the use of wheelchairs for amputees became less stigmatised.
There's also A new type of prosthetic has been developed called the Osseointegration prosthetic, which also doesn't use a socket either. These are very rare as they are incredibly expensive and still very risky, but these prosthetics bypass the socket and implant the prosthetic directly into the body through a rod planted inside one's stump bone. This rod has a clip at the end of the stump, so the external part of the prosthetic can be removed as needed (and replaced). The reason they are risky though is that they are EXTREMELY prone to infection. I only know one person who had this implanted successfully, but he has to be very careful to keep his leg clean or else it will get infected (and it frequently does, he's constantly on antibiotics). Everyone else I know who got it had to get it removed.
With time these implants will get safer, but we are a very, very long way off from that right now.
#Writing Disability with Cy Cyborg#disability#disabled#id in alt text#writing#writing disability#writeblr#authors of tumblr#writing advice#creative writing#on writing#writing tips#writing resources#writing help#authors on tumblr#authors#artists#artists on tumblr#artblr#drawing#art tips#art reference#amputee#amputee representation#prosthetics#disability aids#mobility aid#disability representation#disabled artist
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Tips for wring amputees: its ok if your amputee can't repair their own prosthetics
There's a trope in fiction for amputees to always be these mechanical geniuses who can make and repair their own prosthetics, endlessly tinkering away and improving them. This isn't a particularly trope, and i dont think its harmful or anything, but in reality, prosthetics are REALLY, REALLY complicated, and a lot of amputees cant do their own repairs. And thats ok. Like, prosthetic creation and repair is way, way harder than I think people expect. Well outside the skillset of your standard mechanic, handy man or craftsperson.

People who make and repair prosthetics are called prosthetists. To become a prosthetist, most countries around the world today require you to have completed a bachelor's degree in specifically in prosthetics and orthotics, which covers not only how to make a prosthetics (and orthodics) but a great deal of medical knowledge, physics, how different forces impact "non-standard" bodies, the additional biological wear-and-tear that comes with being an amputee and so much more. This will qualify you to do the job of fitting/making the prosthetic socket (the part that attaches to your body) and putting premade components together to make a functioning device. On top of this, many prosthetists are also expected to have artistic skills, sewing skills, good physical strength and dexterity, IT skills, and more recently, knowledge of 3D modelling and printing.
You want to make all the high-tech components the prosthetists put together to make the full prosthetic? The requirements for that vary country to country, but most will require at least some level study in the field of engineering and/or medicine, on top of what was already required for the prosthetics course.
The reason for all this is because even "basic" prosthetics are extremely finicky, and messing up one thing will have a domino effect on the rest of the body, especially in more complicated prosthetics. It can also result in people getting severally injured if anything is even slightly off. many leg amputees for example end up with spinal issues due to extremely minor issues with their prosthetic that weren't caught until years later, and by then the damage had been done.
Some amputees do learn to do basic repairs. This is most common in places like the US, where a visit to the prosthetist can cost hundred to thousands of dollars (depending on your insurance), but it's also quite common in rural parts of countries like Australia, where cost isn't an issue but access is due to vast distances between major cities. I was personally in this category; as a kid, my nearest prosthetist was 6 hours away. My prosthetist was able to teach my dad, who later taught me, how to do some of the simple repairs, but we still needed to go in every few weeks for the more complex stuff (Kids prosthetic need more adjusting than adults because they're still growing. Also I was rough on my prosthetics and broke them a lot lol).
But even after being taught how to do repairs and having my prosthetics for 20+ years, I only ever did these sorts of repairs to my below-knee prosthetic. I will not do any repairs of any kind to my above knee leg, which is much more technologically complex. Every time I tried, I made it worse to the point where the leg was unusable. I just leave those repairs to the guy who went to university to learn how to do it, and sometimes even he needs to send it off to someone with even more specialist knowledge when it's really badly messed up lol. Last time that happened Australia post lost the package. Not really relevant to this post, I just find the idea of it being sent to the wrong place by accident hilarious, it was one of my more realistic legs too so someone probably had a heart attack when they opened that package lmao.
Anyway, back on track lol.
This isn't even touching on the fact that on some more advanced prosthetics, many features are actually locked behind a security barrier only prosthetists can access. My prosthetic knee has an app on my phone I can pair it to, that allows me to change certain settings and swap between certain modes for different activities that tell the leg to change its behaviour depending on what I'm doing (e.g. a mode for running, a mode for cycling etc). but most of the more in-depth settings I can't access, only my prosthetist can, and he can only gain access to those settings with a security key given to him by the manufacturing company that requires him to provide proof of his credentials to receive it. I don't really agree with this btw, something about being locked out of my own leg's settings makes me feel a bit of an ick, but it's set up like this because people used to be able to access these settings and they would mess with things to the point their leg was virtually unusable. Because altering one setting had a domino effect on all the others, and a lot of folks weren't really paying attention to what they were messing with, all their prosthetists could do was factory reset the whole leg, which causes some issues too. Prosthetic arms are often similarly complex, as I understand it and have similar security barriers in place for more advanced arms. I don't know for sure though, so take that with a grain of salt.
All this to say these are incredibly delicate, finicky and complex pieces of equipment. There's nothing wrong with having a techy amputee character who can do their own repairs, but in reality, that is pretty rare, and its ok to have your character need to see a prosthetist or someone more knowledgeable than them. It's a part of the amputee experience I don't see reflected very often in media. In fact, the only examples I can think of in fiction (meaning not stories based on real people) where this is reflected are Full metal alchemist.

technically I think Subnautica Below Zero also mentions prosthetists are a thing in that world, but its a very "blink and you'll miss it" kind of thing...in fact I did miss it until my last playthrough lol.
#Writing Disability with Cy Cyborg#long post#id in alt text#amputee#writing disability#disability#disabilities#disabled#actually disabled#writing advice#writing#writeblr#writers on tumblr#writerscommunity#disability representation#authors of tumblr#prosthetics#disability aids#mobility aids#amputee life#amputee problems#full metal alchemist#automail#amputee representation
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
The Jaws Effect and what it means for media representation
The Jaws Effect is the name of a phenomenon that described the panic and fear that sprang up around sharks, fuelled by Steven Spielberg's movie, Jaws. While the fear of sharks and other marine predators had always been a thing, Jaws launched the fear of sharks, and Great White Sharks in particular, to new (and mostly unfounded) heights. Most people will never encounter a real-life shark and so their only knowledge about the creatures come from movies and other forms of entertainment. Entertainment that largely portrayed them as mindless, unfeeling killing machines. After Jaws, sharks became a staple in the creature-feature genre of movies, which only perpetuated the idea of sharks as dangerous monsters even further, reigniting and reconfirming the beliefs the public held about them in the process. These ideas about sharks are, of course, not true, but the misconception and fear has had a real, observable impacts on shark populations, shark conservation efforts and even laws and legislations surrounding sharks and shark conservation around the world.
Ok but Cy, this is a blog about disability and disabled representation, what do sharks have to do with anything you talk about? Well, Because The Jaws Effect is just one of many examples that shows how massive of an impact representation in the media can have, for better or for worse, especially when talking about subjects the public generally knows very little about.
This conversation is not unique to disability representation, nearly every person I've seen who's talked about how to write and design characters from any minority brings it up eventually, but the media we consume, the movies we watch, the books we read can all have big impacts on people's perceptions on those topics. When talking about disability specifically, it's an unfortunate reality that not many people know all that much about us, and so, much like sharks, for many, their only real exposure to disabled people is through the media they consume.
If you don't know anyone in a wheelchair, and your only knowledge of life as a wheelchair user comes from books and movies like Me Before You, of course you're going to (spoiler) come away thinking that life in a wheelchair is horrible and death is better than living like that. If you don't know any DID Systems and your only exposure to a condition like that is through movies like Split (and honestly, a number of other horror movies and crime shows) of course you'll think people with DID are unstable monsters who could become violent any moment. If your only exposure to autistic people is Music, then it's not shocking that you might think Autistic people are "trapped in their own minds," completely unaware of the world around them and lacking any kind of agency. As much as I'd like to be able to say these are "just movies" or "just books," and that if we don't like them, we can just not watch them, they all had an impact on the real world and real people's perceptions of the disabilities they depicted, as do the many, many smaller examples of bad representation.
This is why I personally spend so much time focused on the portrayal of disability in the media, why so much of my content is focused on creating resources for creators to represent us better, and why I think writers, artists and other types of creators should care about the representation they include.
Unfortunately, people believing misinformation and stereotypes, while annoying, isn't the worst of the impacts bad rep can have. If a stereotype is prevalent enough, and enough people believe it, it can both put us in harms way and cause us to loose access to things we desperately need and things designed to help us. One really common example of this is when movies and TV shows show a character getting up out of their wheelchair, and use this as proof that the person is faking being disabled. However, in reality, there are many disabilities that might mean someone has to use a wheelchair, even if they can still walk a little bit or stand up. The stereotype of someone standing up from their chair being a fake, especially when it's reinforced over and over again in the media, leads non-disabled people to believe that anyone who stands up from their wheelchair is faking, and results in a lot of real disabled people being harassed and denied things like access to disabled parking, toilets and other accessible spaces. There were even a few cases of people reporting those they see get out of their wheelchairs to Centrelink (The Australian "welfare" department, for those not familiar) as frauds, and while these investigations don't usually go far before someone realises what's happened, it has, on occasion, resulted in people loosing the income they depend on to survive, even temporarily.
But the impact of representation, of course, can go both ways.
I was in high school when the first How To Train Your Dragon movie came out, and at the time, I didn't really like people being able to see that I was a leg amputee because I was sick of kids in particular staring, pointing at me, asking their parents "what's wrong with them?" or asking me directly, "what's wrong with your legs?". I wore long skirts and big, bulky tracksuit pants to keep my legs covered, something that became dangerous in the hot Australian summer, but I didn't care.
But the impact of How to Train Your Dragon came in two ways. The first, was that it was one of the first times I'd seen an amputee (or rather, multiple amputees) who didn't keep their prosthetics covered or hidden, and it gave me the little boost in confidence I needed to do that myself and wear clothing that was more comfortable and functional. And second, the comments from children changed, albeit slightly, but enough that it was noticeable. The questions and comments went from "what's wrong with you?" to "oh cool, your legs are like Hiccup's!" I even had one little girl ask me once if I had a pet night fury. They went from being scared of me and my legs, or at the very least concerned for me, to genuinely curious and impressed. While reactions like that did become less and less common over time, they didn't fully go away either. Even today, I occasionally get young kids asking me why I have legs like hiccup. A friend of mine who was born with one arm shorter than the other and without fingers on that side had a similar experience with the movie Finding Nemo. Her disability was a bit more complex than what I described here, and she always found it hard to explain "what happened" to small children, however, after Finding Nemo came out, she was able to simply tell kids "this is my lucky fin, like what nemo has!" and that was enough to take her from someone "scary" to these kids to someone like their favourite characters.
Of course, it's much easier to see the impact positive representation can have on people's perceptions when we're talking about kids media, but it's not exclusive to it either.
When it comes to a minority like the disabled community who are so thoroughly misunderstood by the wider public, misinformation can and does spread easily. What people see and read in the media they consume plays a big roll in how people perceive the real people attached to the stereotypes. We often hear people say "Fiction imitates life" but the reverse can and often is also true, life can imitate and be influenced by fiction, and those of us creating should be mindful of this, especially when we're talking about a group of vulnerable people.
[Thumbnail ID: An illustration of a Great White Shark swimming near the rocky bottom of the ocean, surrounded by silver fish. In the bottom left corner of the image is "The Jaws Effect and what it means for media representation" in big, white bubble text. /End ID]
#Writing disability with Cy Cyborg#Disability 101#Long Post#Disability#Disabled#Disability Representation#Writing Disability#Writing#Writeblr#Authors#Creators#Writing Advice#Disabled Characters#Disability History#On Writing#Disability in Media
761 notes
·
View notes
Text
How The Owl House did amputee representation right before Eda ever lost her arm - Disability in Media

[ID: A screenshot of Eda from The Owl House, an old woman with pale skin, very large, grey hair and pointed ears in a red dress. Beside the screenshot on a dark pink background is text that reads "Disability in media, How the Owl House got amputee representation right before eda ever lost her arm." /End ID]
Dana Terrace's The Owl House has some of the best disability rep I’ve seen on a Disney channel show in a long time, with Eda, the main character’s mentor, being one of many stand-out examples.
Plenty of people have discussed how Eda’s curse and the loss of her magic can work as an allegory for disability and how refreshing it is to see a story (especially one aimed at a younger audience) who’s focus is not on her “overcoming” it, but learning to accept it as a part of her and go from there. Eda’s story tackles a lot of subjects that are often mishandled in other examples of disability representation, from the subject of parents who refuse to accept, to glass siblings and much, much more, The Owl House handles all these topics beautifully.
But one thing that dawned on me during my most recent re-watch of The Owl House is how well Eda (and later Lilith) worked as amputee representation, long before Eda actually lost her arm.
One of the side effects of Eda and Lilith’s curse is that sometimes their body parts, mainly their limbs, can fall off. It doesn’t hurt them, and Eda is seen removing them intentionally at multiple times in the series, but they can always be reattached.

[ID: an image of Eda holding her sister Lilith's hand. Lilith is a pale woman with long, black hair, wearing grey clothes. She is looking at her other arm suprised, as her hand is missing. Luz, a Latina girl with short brown hair and a purple hoodie is looking on, smiling. /End ID]
While most likely unintentional, the way the show depicts this with Eda in particular is exactly what I wish more people would do with their prosthetic-using amputee characters.
Eda detaches her limbs, especially her legs, when they’re inconvenient or when she’s relaxing.

[ID: an image of Eda laying on the couch in a bathrobe, her hair in a towel. She has taken her legs off, throwing them to the other side of the seat. /End ID]
The fact that this is mostly played for laughs is actually a good thing in my opinion (though obviously, the show’s overall tone is part of that), as it shows the audience who are mostly children and teens, that in a world of weird and downright scary (from the perspective of the characters) things, this isn't one of them. It’s just a thing she and Lilith can do, and it can even be funny.

[ID: An image of Luz and Eda dressed as pirates. Eda is sitting on the ground, her legs detached and off screen somewhere. /End ID]
It does startle Luz and Lilith on a few occasions, but that’s more because they didn’t know the curse could do that, but once they’re introduced to it, it’s never really brought up as a big deal again.
I’d love to see more amputee characters who do this with their prosthetics. So often media is almost afraid to have amputees take their prosthetics off on camera or on the page. For some folks, our prosthetics are like a part of our bodies, but that doesn’t mean we never take them off. Show your leg amputee flop on the couch and throw their legs across the room. Have them go without on occasion, not because they have to, but because they just don’t feel like putting them on.
Likewise, the owl house creators never shy away from showing Eda when her limbs aren’t all attached. A lot of media, and kid’s shows in particular, will avoid having an amputee character’s stump visible if they ever do take their prosthetics off - treating that part of the character’s body the same way they treat gore or nudity. I’ve talked before how this actually does have a real impact on how kids in particular react to amputees - I’ve legitimately had kids I worked with cry when I took my prosthetics off, then immediately calm down when they see there’s nothing "scary" under my socks.
As much as I love How To Train Your Dragon, it’s very guilty of this. Hiccup looses his leg at the end of the first movie, and wakes up with his prosthetic already attached. The Netflix series has a few instances where he has his prosthetic off, but the camera almost always avoids showing it until he can cover it up again, or is super zoomed-out so you wouldn’t be able to “see anything”. To their credit, they do get better with this in the last movie (though it's still always covered), but for the majority of the series, they are very reluctant to have any shots where hiccup’s leg is in view without the prosthetic (unless they’re very far away).

[ID: a screenshot of Hiccup from How To Train Your Dragon 3, a white man with short brown hair, and one leg missing, wearing armour made of black dragon scales and no prosthetic. He is holding onto toothless's head, a black dragon. /End ID]
Ironically, Eda does (permanently) loose an arm at the end of season 2, but I don’t really have much to say about her as amputee representation on that front, since she’s absent for a lot of Season 3, and when we do see her again, everything is so hectic, the story doesn’t really have any time to focus on her missing limb (which is reasonable). I will say, I do appreciate that they kept the amputation when she's in her owl-beast form in the finale, but there's honestly not much more to say about it. We do see her again in the epilogue after she’s had some time to settle into the amputation, wearing a hook prosthetic, but it’s, once again, too quick to really say anything from a representation standpoint. There's a few little nit-picky things I could bring up, like the fact they seemed to change the type on amputation she had (when she looses it, we see the split was very close to the elbow, but in the epilogue she has most of her forearm again) but those read to me more like animation mistakes or an odd prosthetic/clothing designs rather than a representation issue - and as someone who's worked in animation, given the stress the team was under for the finale, I'm not really worried about it. Like I said, it's more nit-picky than anything.

[ID: A screenshot of Eda, her hair tied back and wearing a red robe and a hook for her right hand. /End ID]
Despite all that though, I still think Eda is still good amputee representation, but mostly because of how they depict her curse’s side effects rather than her actual amputation. She’s honestly one of the only characters that I think you could refer to as “amputee coded” (outside of maybe Teen Titan’s Cyborg), and I genuinely wish more creators would treat their actual amputee characters the same way the Owl House treats Eda in that regard.
#Writing disability with Cy Cyborg#Writing Disability#Disability#Disabled#Disability Representation#Writing#Writeblr#Authors#Creators#Writing Advice#Disabled Characters#On Writing#Disability in Media#The Owl House#TOH#Eda#Owl House#Eda The Owl House#eda clawthorne#eda the owl lady
652 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Untrustworthy Fake: Disability Tropes

[ID: A screenshot of Willy Wonka from Charlie and the Chocolate Factory as he limps towards a crowd using a cane. In the picture, he has a brown top hat in his hand, and he's wearing a suit with a purple jacket, multicoloured bow tie and cream coloured pants. Beside him is text that reads: "Disability Tropes, The untrustworthy Fake" /End ID]
Tell me if this sounds familiar: A new character is introduced into a story with some kind of disability - usually visible but not always. Maybe they're a seemingly harmless person in a wheelchair, maybe they're a one-legged beggar on the street, or maybe they're an elderly person with a cane and a slow, heavy limp. But at some point, it's revealed it's all a ruse! The old man with a cane "falls" forward and does a flawless summersault before energetically springing back up to his feet, the wheelchair user gets to their feet as soon as they think the other character's backs are turned, the one legged beggar's crutch is knocked out of his hand, only to have his other leg pop out of his loose-fitting tunic to catch him.
All of these are real examples. Maya and The Three introduces one of it's main protagonists, Ricco, by having him pretend to be missing a leg in order to con people (something that works on the protagonist, at least at first), Buffy The Vampire Slayer had the character Spike, pretend to be in a wheelchair, until the other characters leave and he gets up, revealing it's all a ruse and Charlie and the Chocolate Factory introduces Wonka by having him slowly limp out into the courtyard of the factory, only for his cane to get stuck, causing him to "fall" and jump back up, revealing that he's actually perfectly fine. Virtually every single major crime show in the past few decades has used this trope too, from CSI to The Mentalist, Castle, Law and Order and Monk all having at least one episode featuring it in some way. Even the kids media I grew up with isn't free from it; The Suite Life of Zack & Cody sees Zach faking being dyslexic after meeting someone who actually has the condition in the episode Smarter and Smarter and the SpongeBob SquarePants episode Krabs vs Plankton has Plankton fake needing a wheelchair (among other injuries) after falling in the Krusty Krab as a ploy to sue Mr Krabs and trick the court into giving him the Kraby Patty Formula.
No matter the genre or target audience though, one thing is consistent: this trope is used as a way to show someone is dishonest and not to be trusted. When the trope is used later in the story, it's often meant to be a big reveal, to shock the audience and make them mad that they've been duped, to show the characters and us what this person (usually a villain) is willing to stoop to. Revealing the ruse early on though is very often used to establish how sleazy or even how dangerous a character is and to tell the audience that they shouldn't trust them from the get go. Gene Wilde (The actor who first played Willy Wonka) even said in several interviews that this was his intent for Wonka's character. He even went so far as to tell the director of Charlie and the Chocolate Factory that he wouldn't do the film without that scene because of how strongly he felt this trope was needed to lay the foundations for Wonka's questionable intentions and motivations. His exact words are:
"...but I wouldn't have done the film if they didn't let me come out walking as a cripple and then getting my cane stuck into a cobble stone, doing a forward somersault and then bouncing up... the director said, well what do you want to do that for? and I said because from that point on, no one will know whether I'm telling the truth or lying."
There's... a lot of problems with this trope, but that quote encapsulates one of the biggest ones. whether intentionally or not, this trope ends up framing a lot of actual disabled people as deceitful, dishonest liars.
Now I can already hear you all typing, What?! Cy that's ridiculous! No one is saying real disabled people are untrustworthy or lying about their disabilities, just people who are faking!
but the thing is, the things often used in this trope as "evidence" of someone faking a disability are things real disabled people do.
A person standing up from their wheelchair or having scuff-marks on their shoes, like in the episode Miss Red from The Mentalist isn't a sign they're faking, a lot of wheelchair users can stand and even walk! They're called ambulatory wheelchair users, and they might use a wheelchair because they can't walk far, they might not feel safe walking on all terrains, they might have unstable joints that makes standing for too long risky, they might have a heart condition like POTS that has a bigger impact when they stand up or any number of other reasons. Also even non-ambulatory wheelchair users will still have scuff marks from things like transferring and bumping into things (rather hilariously, even TV Tropes calls this episode out as being "BS" in it's listing for this trope, which it refers to as Obfuscating Disability).
A blind beggar flinching or getting scared when you pull a gun on them isn't a sign they're faking their blindness like it is in Red Dead Redemption 2. Plenty of blind people can still see a little bit, it might only be a general sense of light and darkness, it might be exceptionally blurry or just the fuzzy outlines of shapes, or they might only be able to see something directly in front of them, all of which might still be enough to cue the person into what's happening in a situation like that. Even if it's not, the sound of you pulling your gun out or other people nearby freaking out and making noise probably would tip them off.
A person needing a cane or similar mobility aid sometimes, but being able to go without briefly or do even "big movements" like Wonka's rolling somersault, doesn't mean they don't need it at all. Just like with wheelchairs, there's a lot of disabilities that require canes and similar aids some days, and not others. Some disabilities even allow people those big, often straining movements on occasion, or allow them to move without the aid for short periods of time, but not for long. Some people's disability's might even require a mobility aid like a cane as a backup, just in case something goes wrong, but that still means you need to carry it around with you, and unless it can fold down, it's easier to just use it.
Disability is a spectrum, and a lot of disabilities vary in severity and what is required of the people who have them day to day. This trope, however, helps to perpetuate the idea that someone who does any of these things (and many others) is faking, which can actively make the lives of disabled people harder and can even put them in very real danger, physically, mentally and even financially.
Just ask any ambulatory wheelchair user about how many times they've been yelled at for using accommodations they need, like disabled toilets or parking spaces. How many times they've been accused of faking and even filmed without their consent because they stood up in public, even if it was to do something like get their wheelchair unstuck or as simple as them standing to briefly reach something on a high shelf. I've caught multiple people filming me before, so have my friends and family, and it's honestly scary not knowing where those images have ended up. This doesn't just impact the person either, a friend of mine was filmed while standing up to get his daughter (who was about 4 at the time) out of the car. He was lucky to have stumbled across the video a few days later on facebook and contacted the group admins where it was posted to get it taken down, but had he not stumbled across it by chance, pictures with his home address and his car's number plate, his child's face and his face all visible would have just been floating around, all because a woman saw him stand briefly to pick up his daughter.
Many people don't stop at just saying a nasty comment or taking a photo though, a lot of people, when they suspect people are faking, will get violent. I have many friends who have been pushed, slapped in the face, spat on or had their mobility devices kicked out from under them. I've even been in a few situations myself where, had I not had people with me, I think the situation would have turned violent.
There's even been cases where those photos and videos I've mentioned before have been used against real disabled people and they've been reported to their country's welfare system as committing disability fraud. While cases like this are usually resolved *relatively* quickly, in many parts of the world, their payment will be halted while the investigation is in process, meaning they may be without any income at all because of someone else's ignorance. If you're already struggling to make ends meet (which, if you're only living off one of those payments, you probably will be), a few weeks without pay can mean the difference between having a home and being on the streets.
Not to mention that when there's so many stories about people faking a disability in the media, especially when the character is doing it to get some kind of "advantage", such as getting accommodations or some kind of disability benefit, it perpetuates the idea that people are rorting the systems put in place to help disabled people. If this idea becomes prevalent enough, the people in charge start making it harder for the people who need them to access those systems, which more often than not results in disabled people not even being able to access the very systems that are supposed to be helping them. A very, very common example of this is in education where accommodations for things like learning disabilities require you to jump through a ridiculous number of hoops, especially at higher levels, only to have some teachers and professors refuse to adhere to the adaptations anyway because they're convinced the student (and usually disabled students as a whole) is faking.
Yes, the "untrustworthy faker" is a fictional trope, and yes, it does occasionally happen in real life, but not as often as media (including things like news outlets) would have you believe. However, when the media we consume is priming people to look for signs that a disabled person is faking, it has a real impact on real disabled people's lives. "Fake-claiming" is a massive problem for people in pretty much all parts of the disabled community, and it ranges from being just annoying (e.g. such as people spamming and fake-claiming blind people online with "if you were really blind, how do you see the screen" comments) to the more serious cases I mentioned above. It's for this reason a lot of folks in the disabled community ask that people leave this trope out of their works.
#Writing disability with Cy Cyborg#Long Post#Disability#Disabled#Disability Representation#Writing Disability#Writing#Writeblr#Authors#Creators#Writing Advice#Disabled Characters#On Writing#Disability in Media#Tropes#Disability Tropes#faking disability trope
423 notes
·
View notes
Text
How your disabled character's allies react to their disability can make or break the representation in your story: Writing Disability Quick Tips

[ID: An image with “Writing Disability quick tips: How your character's allies react to their disability matters” written in chalk the colour of the disability pride flag, from left to right, red, yellow, white, blue and green. Beside the text are 2 poorly drawn people icons in green, one is standing with their hand up to the face of the other, who is in a wheelchair. /End ID]
Something I brought up in my big post about Toph Beifong was how the other characters reacted to Toph pointing out that things were not accessible to her and setting boundaries regarding her disability, which were ignored. I had more to say about it than I thought I did, as it turns out (when isn't that the case lol) but I feel like this is an important aspect of disability representation that is all too often over looked.
You can write the best, most accurate portrayal of a specific disability ever put to screen or page, but it won't mean much if all the other characters, specifically those we're supposed to like and empathise with, treat your character terribly for being disabled and having needs relating to said disability, especially if the story justifies their behaviour.
You see this most often with autistic characters and especially autistic-coded characters. The character in question will be given a bunch of autistic traits, most often traits relating to not understanding certain social dynamics or sarcasm, and when they get it wrong, the other characters we are supposed to like jump down their throat, tease them or outright abandon them.
Autism isn't the only disability that gets treated this way, but it is one of the more common ones that get this treatment. It doesn't matter if you do everything else right when creating an autistic character if the other "good guys" constantly call them annoying, get angry at them or laugh at them for the very traits that make them autistic, or for advocating for their needs.
Likewise, if you have a leg amputee character who is otherwise done well, but is constantly being criticised by their allies for needing to rest their legs or taking too long to get their prosthetics on, it undermines a lot of the other work you've done. Same goes for having a wheelchair user who is accused of being a bore or a stick in the mud because they point out the places their friends want to go to on a group holiday have no wheelchair access, or a deaf character who is accused of being entitled for wanting their family to learn to sign, or anything else.
This isn't to say you can never have moments like these in your stories, but its important to remember that a) people with the same disability as your character will be in your audience. If you spend a whole season of your TV show shaming your autistic character for real traits that real autistic people have, they're not exactly going to feel welcome and may not want to hang around. b) it's going to very, very heavily impact people's perceptions of your "heros" who do this, especially in they eyes of your audience members who share the character's disability or who have had similar experiences. This isn't like calling someone a mean name or being a bit of a dick when you're sleepy, it's going to take a lot to regain audience appeal for the offending character, and depending on exactly what they do and how frequently they do it, they may not even be able to come back from it at all. And finally, c) there should be a point to it outside of just shaming this character and saying the other guy is an asshole. Like I said before, you're character is criticising real people's real disabilities and the traits or problems that come with them, things that they often have no control over, it shouldn't be used as a cheap, quick way to establish a quirky enemies to lovers dynamic or show that one guy is kind of an ass before his redemption arc. If you really must have your characters do this, be mindful of when and how you use it.
#Writing disability with Cy Cyborg#Quick tips#Disability#Disabled#Disability Representation#Writing Disability#Writing#Writeblr#Authors#Creators#Writing Advice#Disabled Characters#On Writing
500 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tips for writing and drawing amputee characters: Stump Scarring
This was something I had originally intended to mention in this post but felt it deserved its own separate post.
A lot of people, when drawing and designing amputee characters, draw their characters with these big, gnarly looking scars all over the stump. I get why people do this, but in reality, most amputees have stumps that look more like this:

The only scarring that is inherent to amputation (meaning most amputees have) is a very thin line right at the tip of the stump that comes from where the stump was sewn shut. After 5-10 years though, these thin incision scars will fade to be nearly invisible in most folks other than the indent it usually leaves in the skin.
Of course, there are exceptions! My own legs are covered in heavy scarring like the pictures below.

but typically, you only see this in amputees who lost their limb in ways that required them to also need skin grafts, such as from a burn (fire or acid), gangrene, some types of rapid-onset sepsis, or particularly brutal animal attacks.
For context, I used scars from meningococcal as reference here.
I think this is another reason a lot of people, particularly in 2D comics and animation, cover their amputee character's stumps, because they think all amputees have scars like the ones in the second image and I'll be honest, that's a lot to draw when you're drawing it over and over again, but unless your amputee also needed skin grafts bcuase of their injury/illness, their stumps will look more like the first images.
Fun fact: on particularly pale skin, scars can change colour depending on temperature. scars have less circulation and the blood vessels are closer to the skin, which means if you don't have a lot of melanin, your scars can turn a grey-ish purple colour like so:
This information is brought to you by an especially pasty white person in the southern hemisphere (where it's winter atm) who's scars haven't seen the sun since june lmao.
A quick final note: If you look up "burn scars" or any other similar type of large scarring on google a lot of what you get are fresh scars, so they're going to look different than the ones here. On pale skin, large scars like the ones above start out very dark red and will fade to look more like the images here. The same is true for dark skin, typically fresh scars will be much darker in colouration and will fade to be closer to the natural skin tone with time, though on both, they will always be very visible. Some types of scarring on darker skin tones can cause the skin to become lighter, but they don't usually turn entirely light pink like I've seen some folks draw. This is why it's so important to look up references of the type of scar your character has AND how that looks on their skin tone.
And as always, listen to POC and seek out the recourses specifically made by them, especially if you're drawing characters with darker skin tones. Their lived experience will always beat my "what I found through internet research and from talking to friends"
#Writing Disability with Cy Cyborg#ID in alt text#disabled artist#queer artist#my art#artists on tumblr#artists of tumblr#digital art#writing disability#disability#disabilities#disabled#actually disabled#writing advice#writing#writeblr#writers on tumblr#writerscommunity#disability representation#authors of tumblr#disability aids#writing recourse#referance for writers#art tips#art resources#art help#art reference#art advice
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Disability Tropes: The disabling change of heart

When a character in a story becomes disabled, they'll sometimes experience a trope that I like to call "the disabling change of heart". This is when the character goes through a massive change in their outlook, their personality, their goals or even roll in the story, specifically because they became (or are about to become) physically disabled. Sometimes, this will be in relatively small ways: the happy-go-lucky comedic relief character might become bitter, angry and jaded after getting into an accident that caused a spinal injury, or the severally depressed and nihilistic character might suddenly start acting more cheerful and hopeful, stating that loosing their leg has "put things into perspective and showed them what really matters". In other cases though, the impact is much larger, the heroic character you've been hearing about looses an arm thanks to the main character's actions, causing them to become consumed with anger and self-loathing which they take out on everyone else, eventually becoming an antagonist as they seek revenge for what the main character did to them. The morally grey or even villainous character is injured by their own scheme, giving themselves a permanent disability in the process, which prompts a change of heart and leads them to turn their lives around and become better people, maybe even deciding to team up with the heroes.
Now, having a character go through a personality and goal change due to a major life event, such as becoming physically disabled, isn't inherently bad. A lot of writers are told to tie major shifts in your character's development to major life events, because realistically, something like becoming newly disabled will at least impact how you view the world around you. I very frequently talk about how if I didn't loose my legs, I would have become a vastly different person, but the issues with this trope depends on how it's used and the reasons behind these developments, and whether or not the change suits the character in question.
Before we get into things, I would like to specify that in this post, I'm only going to be talking about how this trope is used with physical disabilities and other easily visible forms of disability. It does show up with characters who develop disabilities under the mentally ill and neurodivergent umbrellas, and is actually a bit more common than what I'm talking about today, but the specific ways its utilised are so different that it's more or less a separate trope, and one that deserves much more attention than I could give it here as this is already going to be a pretty long post. So for today, I'm keeping to it's use with physical and visible disabilities, and we'll talk about how this trope is used with neurodivergence and mental illness another day.
The main thing you need to be mindful of is ensuring that you, as an author, are not including your ingrained biases about disability into the reasoning behind the change. Let's look at one of the examples from before, an evil character who, after loosing their arm (because it's almost always loosing an arm for some reason) becomes a villain and wants revenge against the main character. In a story like this example, the character who became an amputee often views this new disability as something that has ruined their life. It's something that has caused them to suffer, and they want to make the main character (or whoever has "wronged" them) suffer like they did. Stories like this example portray disability as something that is not just horrible, but life-destroying, especially with villains who become all-consumed by the misery this disability has brought them. Many stories that utilise this version of the trope also often perpetuate the idea that if you become disabled, you'll have to give up all the things you love and your goals, even when this wouldn't necessarily be true for the character in question.
Let's say your character was a knight, and the main character cut off their arm in a training accident. obviously you can't be a knight with only one arm because you can't fight anymore, so they left their order. Now this character has become a villain and has found power that "makes up" for their disability, perhaps magic or some other force that doesn't exist in the real world, and are back to get revenge on the character for ruining their lives. Here's the thing though, the loss of a limb, or at least, the loss of an arm specifically, often isn't the career ender people think it is, even back then. In fact, there are many historical records of real amputees continuing to serve as knights and other similar military roles after loosing an arm or at the very least, continuing to fight in other ways. One such example was Götz of the Iron Hand, a mercenary knight who lost his arm to a cannon. Götz had fought as part of the Roman empire's military in 1498, but shortly after left to form his own mercenary company. He lost his hand in 1504 and continued his career as a mercenary with the help of an iron prosthetic capable of holding his sword and the reigns of his horse, among many other things such as writing, for another 40 years. Götz wasn't unique in this though, several suits of armour from the same time period have been found with integrated prosthetic hands, though the names of their owners are unknown. There was also Oruç Reis (aka Aruj Barbarossa), A privateer admiral who served the Ottoman Empire in and around the Mediterranean who lost his left hand - earning him one of many nicknames: Silver-Hand, thanks to the colour of his prosthetic. Oruç, like Götz, continued his career for several more years until he was eventually killed in 1518.
My point in bringing this up, is to highlight how important it is to double check that the reason your character's whole motivation for turning to villainy, isn't just based on your ideas about what a disabled person can or can not do. Actually double check it, research it, especially if it's important for your plot.
Even in the cases where the disability in question actually would stop someone from being able to do something, the incorrect assumptions can still occur and cause issues in different ways. For example, a character in a more modern setting who looses their arm due to an accident the main character was responsible for while serving in the military would be discharged, ruining the character's plan to become a general some day. This absolutely would be devastating for a character like that, and they realistically could struggle to adjust, both in terms of getting used to their disability and finding new goals for their life. They may well feel anger at the main character, however, if you are portraying just living with a disability, in the case of this example, living with an amputation as inherently "suffering" for no other reason than they are disabled, it is still perpetuating those really negative ideas about disability. I've said this a few times in other posts, but villains who are evil or even just antagonists purely because they're disabled or are trying to avoid becoming disabled is a trope all its own and one that is best avoided if you yourself aren't disabled, as even outside of spreading these negative ideas about life with a disability, it's just an overdone and overused trope.
But what about when this trope goes in the other direction? when you have an antagonistic or even just morally grey character who becomes disabled and this is the catalyst that turns them into a good guy?
For the longest time, I knew I usually disliked this version of the trope too, but I couldn't put my finger on why. With disability being the reason someone became a villain, the underlying reason it's there is often able to be boiled down to "I, the writer, think being disabled would be terrible and life like that is inherently suffering, so this character is angry about it," which is obviously an issue (the "inherently suffering" bit, not the anger). However, when a character becomes good due to becoming disabled, the reasoning is usually more along the lines of, "this is a big change in a character's life that has caused them to reconsider and revaluate things" (or at least, that's what I thought). This isn't bad, nor is it necessarily unrealistic. Hell, as I already said, I do consider my disability to be a catalyst that made me into who I am today. I also know plenty of people who, after becoming disabled later in life, did have a big change in how they viewed themselves and the world, and who consider themselves better people since becoming disabled. It's far, far from a universal experience, mind you, but it does happen. So why did this version of the trope still not sit right with me?
Well, I think there's a few reasons for it. The first being that there's a tendency for non-disabled people to think real disabled people are just incapable of evil deeds, both in the sense that they aren't physically capable of doing them (which is bad and not even always true for the reasons we already discussed), but also in the sense that there's this idea that disabled people are, for some reason, inherently more "good" and "innocent" - As if breaking your back or loosing a limb causes all evil and impure thoughts to be purged from the body. This is a result of many folks viewing disabled people as child-like, and thus attributing child-like traits (such as innocence) to them, even subconsciously. This is an incredibly common issue and something disability rights organisations are constantly pushing back against, as this mentality can cause a lot of unnecessary barriers for us. With how often I and many other disabled people are subjected to infantilization, I would be honestly shocked if it wasn't at least partially responsible for people thinking becoming disabled is a good reason to kick off a redemption arc.
This infantilization isn't unique to physically disabled people by the way, in fact it's way, way, more commonly directed at people with intellectual and developmental disabilities - or at least, people are more open about it, but as I already mentioned, how that is reflected in tropes like The Disabling Change of Heart is vastly different and deserves a post of it's own.
That's mostly just speculation on my part though, since that infantilising mindset does show up a lot in media, but not usually as part of this trope specifically.
However, it's not the only reason I wasn't a fan of it. When the disabling change of heart is used to fuel redemption arcs, I think, once again, that the disability itself being credited with causing the change directly is another factor. When this happens, it's usually because "it put things into perspective for me and showed me what really mattered."
This sounds better than our previous example on the surface, but stories that use this logic are often still portraying disability as an inherently bad and tragic thing, something so bad, in fact, that it makes all the other (legitimate) issues they thought were massive before seem so small by comparison. This is a type of inspiration porn: content made to make non-disabled people feel inspired or just better about their own situation. It's the mentality of "well my life is bad, but it could be worse, at least I'm not disabled like that!"
In a fictional story, this might look like an athlete character who dreamed of making it big so they could be famous and get out of poverty. They were a dick to anyone who got in their way but only because they were worried about not being able to make rent if they don't constantly win. One day though, they overworked themselves and got into a car accident on the way home because they were too tired, and now they're in a wheelchair and can no longer walk, which is (supposedly) absolutely tragic and way worse than anything else they were already going through. But they end up becoming a better person because it has put things into perspective for them. Yeah they were struggling to make ends meet, but at least they weren't disabled! Now that they are, they know they shouldn't have cared so much, because money doesn't matter when compared to not being able to walk, right?
As well as portraying disability in a negative light, these kinds of stories dismiss and diminish the other struggles or challenges the character is experiencing, placing the status of "not disabled" above all else.
There's also the fact that, when a lot of real people say their disabilities had positive impacts on their lives, they don't usually mean the disability itself is directly responsible for the change. There's exceptions of course but for myself personally, and most of the people I know who say they are better people because of/since becoming disabled, the disability has been more of a neutral catalyst than the actual cause of positive change. Meaning, it opened the door to allow those changes to happen, but it wasn't the direct cause. For me personally, becoming physically disabled at a young age didn't make me a nice person like people expect, I was still a little judgemental asshole for a lot of my childhood. However, because I was disabled, I had to travel a lot, initially because I needed medical treatment that my local hospital wasn't equip to provide, and later, because I started competing in disability sports. because of both of those things, I met people I never would have otherwise who made me reconsider what I'd been taught on a wide range of subjects, and made me question where those beliefs had come from in the first place. When I say my disability played a part in who I became, it wasn't because my disability itself change me, but it helped me meet people who were positive influences on me and my life. but when creatives make characters who experience arcs like this, they ignore this, again, defaulting to the "this was a bad thing that just put all my other problems into perspective" reasoning.
Some iterations of this trope also use disability as a kind of "karmic punishment" where the disability is portrayed as a rightfully deserved punishment for an evil character's deeds - usually something relating to the disability they acquired but not always. An example might look like an evil tyrant who punishes the rebels they captured by cutting off their hands. Eventually, this catches up with him, maybe the friend or a child of one of the rebels is able to capture the tyrant and cuts his hands off as payback so that he gets a taste of his own medicine, a taste of the suffering he imposed on others. Now facing at least one of the same realities of the people he subjugated, he realises the error of his ways. With some pressure from the main characters, he has a change of heart and surrenders himself, steps down to let someone else take his place, or perhaps he decides to start changing policies to be more in-line with these new morals until some other character usurps him, becoming an even bigger threat than the previous former tyrant.
Once again, stories that use a disability like this are still portraying the disability as an overall inherently bad thing, but there's the added layer at play in this example. The thing is, there are a lot of people in real-life who actually believe disability is a punishment from God. I remember one time when I was over in the US, an older lady came and sat down on the seat beside me on the bus and started asking me about my disability and specifically, how I became disabled. This isn't an unusual interaction, it happens fairly regularly whenever I use public transport, but on this particular day, the conversation suddenly shifted when I told her I became disabled when I was very young. This woman, despite the bus-driver's best efforts to get her to stop, ended up lecturing me for an hour and a half (during which time I couldn't move due to how my wheelchair was held in place) about how my disability was punishment from God for my parent's sins. She then tried to convince me to attend her church, claiming they would be able to heal me. And the thing is, this isn't an uncommon experience.
A lot of disabled people are targeted by cults using this same method: they'll convince people their disabilities are a punishment, make them believe they deserved it, that they just weren't good enough, but don't worry, if you repent and come to our specific church we can heal you. There was even a case in Australia recently that uncovered a cult called Universal Medicine, who taught that disabled people were reincarnations of evil people, and that being disabled in this life was their punishment, as well as that parents who have disabled children were being punished for other sinful behaviours. They were found to be operating a disability care service named Fabic that was being paid for by the NDIS, a subsection of the Australian government funded healthcare system that specifically aids disabled Australians by paying for and subsidising treatments, technologies (such as mobility aids) and other services relating to their disability. Fabic was found to be stealing excessive amounts of funding from their disabled clients under the guise of therapies and carer services, but was not actually helping their clients at all. Whether it's just taking advantage of them to get their money, or actually using this logic as a justification to mistreat them, this mentality of "disability is a punishment" actually gets real disabled people hurt or worse, and so seeing it come up in media, even if there is no ill-intent, can be very distressing and uncomfortable for disabled audiences.
So with all this being said, is the disabling change of heart a trope you should avoid in all it's forms and versions? No, but it does need to be handled with extreme care. I do think it should be avoided as a reason for a character becoming evil for the most part. If that really can't be avoided in your story though, at the very least, ensure that you foreshadow the change. Your happy little ray of sunshine, embodiment of sweetness and innocence type character probably isn't going to turn murderous and want revenge for an accident for example. A character who is likely to be driven to that kind of extreme of wanting revenge for their disability, so much so that they become a villain, probably already had at least a few traits that would predispose them to that line of thinking already, before becoming disabled. As for when it goes in the other direction, and you have a character becoming a good guy, avoid using the reasoning that "the disability put things into perspective for me". Instead, if you must use this version of the trope, use the character's new disability as the reason they encountered other people and situations that challenged their views, things they wouldn't have encountered otherwise. No matter the reason though, be very careful to avoid inspiration porn, and as always, try to find a sensitivity reader to give your story a once-over, just to make sure something didn't slip under your radar.
[Thumbnail ID: An illustrated image showing the same elf character twice. The picture of her on the left shows her laughing evilly, two tiny horns protruding through her brown hair. She is wearing a black dress and red shoes. On the right shows her in a yellow dress, sitting in a bright pink wheelchair with her head held eye and her eyes closed. The horns have been replaced with a glowing halo. In the centre is text that reads: "Disability Tropes: The disabling change of heart." /End ID]
#Writing disability with Cy Cyborg#Disability 101#Long Post#Disability#Disabled#Disability Representation#Writing Disability#Writing#Writeblr#Authors#Creators#Writing Advice#Disabled Characters#Disability History#Language#On Writing#Disability in Media#Tropes#Disability Tropes#The Disabling change of heart
516 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tips for Writing and Drawing Amputees: Bandaged Stumps
When writing and drawing amputee characters, unless your character only just lost their limb, they don't need to wear a bandage over their stumps.

to be clear, eda's depiction in the show was fine, since she'd only just lost her arm and went (presumably) without any medical attention, but because the show didn't have much time to show her afterwards, I've noticed a tendency of the fandom to draw her wearing the bandage permanently, so that's why I'm picking on her for my example lol.
It's a bit of a trope at this point, and I think it comes from one of a few different places:
Amputees do wear bandages on their stumps, but usually only for the first 6-12 weeks post-amputation, sometimes longer if the amputation was a result of a burn. It's possible people saw this though and assumed it was permanent.
Most amputees wear a sock made of either cotton or silicone under their prosthetics to provide them with some extra padding. These socks, called liners, often stick out from the top of the prosthetic socket and could possibly be mistaken for a bandage from a distance.
Some amputees will wear compression garments for a few months to a few years after their amputations which could also be mistaken for a bandage from a distance. These garments are designed to stop swelling and reduce phantom pain, but they aren't bandages.
Stumps get cold easier because their circulation typically isn't as good as the rest of the body, so some amputees will wear socks over them even if they aren't wearing a prosthetic to keep warm, which again could be mistaken for a bandage from a distance.
This one is funny, but in my experience unfortunately, it's the most common: people think the end of an amputee's stump is just a perpetual open wound that never heals. Meaning to avoid "gore" it needs to be covered. I've met fully grown adults who believed this until I showed up to work/uni without my prosthetics or socks on.
People are uncomfortable with seeing an uncovered stump and so put bandages over it to avoid confronting their biases.
Some combination of these points.
But yeah, unless your amputee has only just lost their limb in the last few weeks, they don't need a bandage.
The ironic thing too, is that for most amputees, bandaging a stump is nearly impossible. I've been in and out of hospital since I was 1 year old and only ever met 3 nurses and no doctors/surgeons who could successfully bandage my stump in a way that the bandage would even stay on. This is because stumps are usually tapered in shape (meaning they are wider at the top, closer to the body, and thinner at the bottom), so gravity will pull the bandage off 9 times out of 10.
On a final note: it's ok to show your amputee's stump, it's not gore, there's no blood, it just looks like a regular limb that just stops early. In fact, if you are writing/creating anything for kids or that is likely to be seen by kids, I encourage you to show your amputee's stumps at least once. I used to work on a disability awareness program for kids, and I lost count of the amount of times kids were terrified of me, because they all expected my leg to be bloody and gory. For a lot of kids, I was their first real-life exposure to an amputee, meaning they'd never even heard of people like me, or they had seen an amputee on TV, but because the show went out of its way to avoid showing the person's stump, they assumed it must have been because there was "something scary at the end" that they weren't supposed to see (kids are surprisingly perceptive, they will pick up on stuff like that without you realising). And scared kids aren't good at articulating why they're scared, and would often say really mean or hurtful things to me. I knew not to take it personally and learned how to handle those situations, but not everyone is used to dealing with kids. For a new amputee (or anyone who's less confident in their disability), the kinds of things those kids would say could be absolutely confidence destroying. I never blame the kids, it's not their fault, but the whole situation could have been avoided if they had seen people like us before they had the chance to hear the wrong info. Good representation like this can be the difference between a kid crying, making throw-up sounds and calling an amputee "disgusting monsters" (all things I've had kids do/say) and them just being like "oh ok, cool."
#Writing Disability with Cy Cyborg#writing disability#disability representation#disabled#writing advice#writeblr#authors of tumblr#writing#authors#writer#on writing#writers on tumblr#writblr#writerblr#creative writing#character design#amputee#amputee representation#artists on tumblr#designing disabled characters#oc#oc art#ocs#original character#artists#character design tips#art tips#art resources#art reference
1K notes
·
View notes