#textile history
Text

Vogue Arabia featured traditional hand embroidery from different regions of Palestine in solidarity with Palestine
#free palestine#palestine#Vogue#vogue arabia#fashion#fashion history#textiles#textile history#mine#Gaza#free Gaza#Middle East#mena#couture#high fashion#haute couture#Art#Art history
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
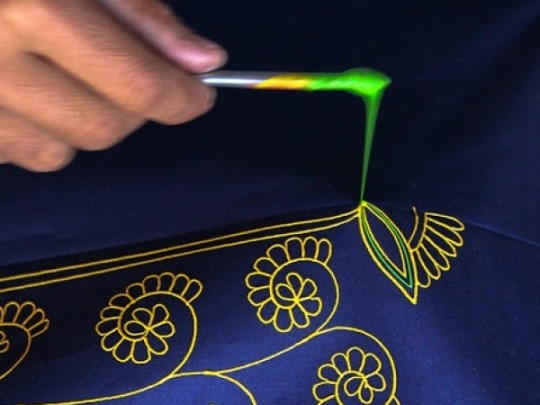
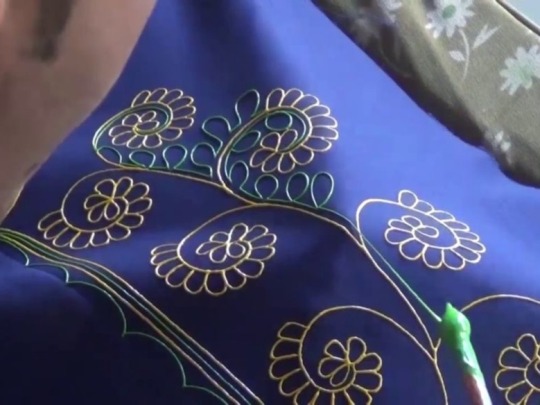
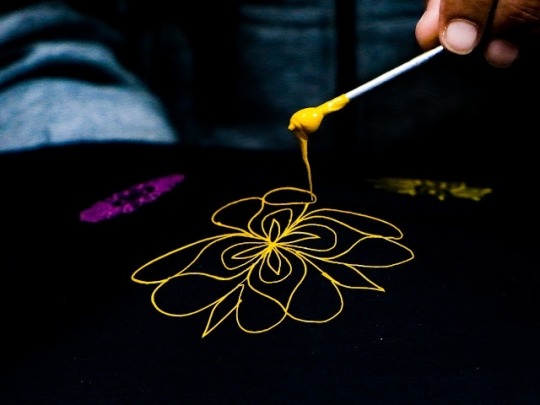
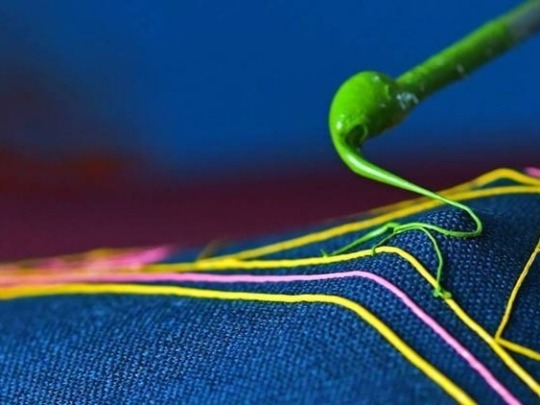
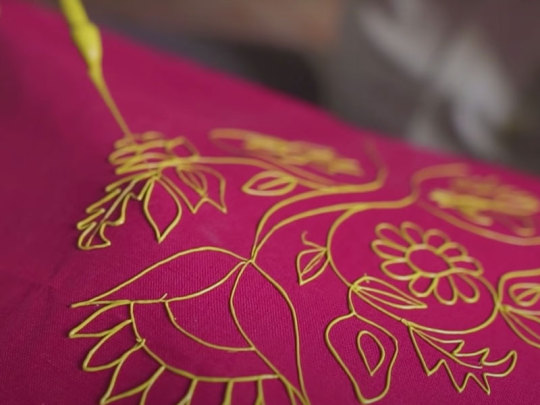
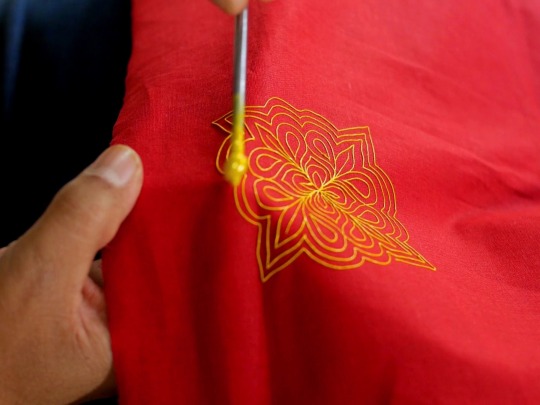
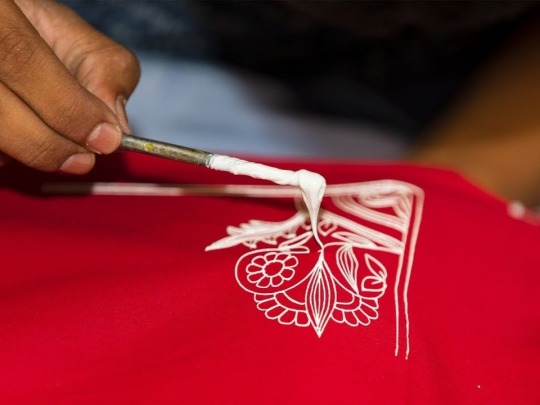
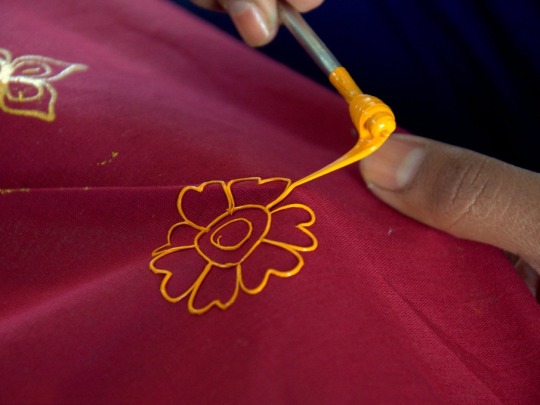

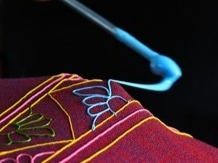








Rogan is an technique of cloth printing practiced in the Gujarat, Peshawar and Sindh regions of India and Pakistan. The word rogan has roots in both Persian and Sanskrit, meaning oil. In this craft, paint is made from boiled castor oil or linseed oil and vegetable dyes is laid down on fabric using a stylus.
The process of applying this oil based paint to fabric was developed among the Khatri community in Gujarat and the techniques of preparing and applying dyes was passed down in the family. As rogan printed cloth tended to be less expensive than other heavily embroidered garments but could still produce the illusion of embroidery, it was the wedding garment of choice for women from poorer families. The craft nearly died out in the late 20th century with the availability of cheaper and machine-made textiles. However, it is currently being revived mostly due to the efforts of the artist Abdulgafur Khatri and his family, who work tirelessly to spread awareness about Rogan art and teach it to young people, mostly young women from poor families in order to empower them by providing a means of livelihood as well as keeping the art of rogan alive.
1 / 2 / 3 / 4 / 5 / 6 / 7 / 8 / 9 / 10 / 11 | textile series
#ots#textiles#indian textiles#textile history#textile art#art printing#rogan art#gujarat#india#pakistan#south asia#desi tumblr#desiblr#sindh#peshawar#desi tag
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo
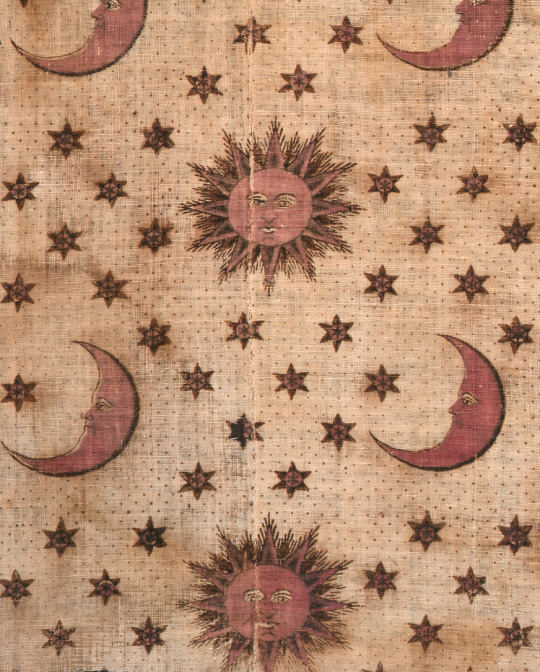

Textile fragment: English, c. 1800-1820 from the Winterthur Museum.
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
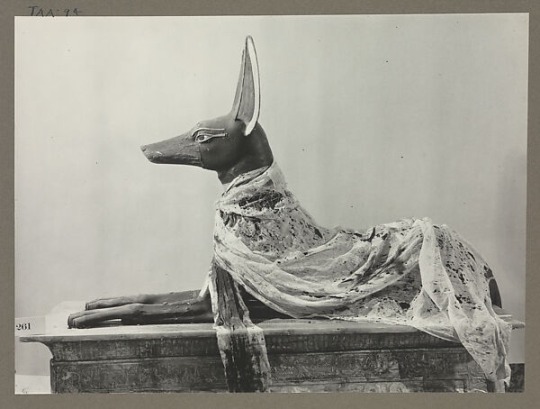
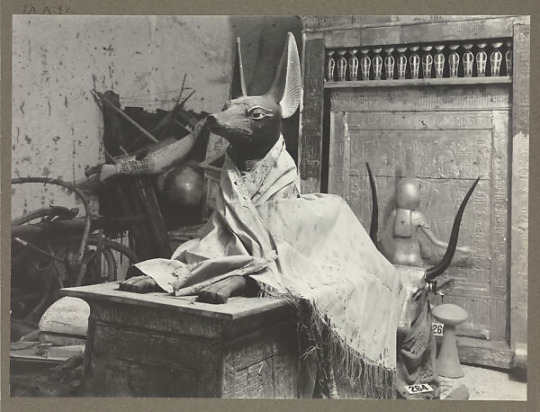


Harry Burton, Photo, 1926
Textile Draped over Anubis Figure, ca. 1300s BCE
Egyptian, New Kingdom
#ancient egypt#egyptian art#egyptian history#egyptian culture#ancient art#antiquities#ancient artifacts#artifacts#Egyptian artifacts#Anubis#god anubis#textile history#textiles#aesthetic#beauty#harry burton#ancient culture#ancient people#ancient history#art history#aesthetictumblr#tumblraesthetic#tumblrpic#tumblrpictures#tumblr art#tumblrstyle#artists on tumblr
296 notes
·
View notes
Note
How did cotton win over linen anyway?
In short, colonialism, slavery and the industrial revolution. In length:
Cotton doesn't grow in Europe so before the Modern Era, cotton was rare and used in small quantities for specific purposes (lining doublets for example). The thing with cotton is, that's it can be printed with dye very easily. The colors are bright and they don't fade easily. With wool and silk fabrics, which were the more traditional fabrics for outer wear in Europe (silk for upper classes of course), patterns usually needed to be embroidered or woven to the cloth to last, which was very expensive. Wool is extremely hard to print to anything detailed that would stay even with modern technology. Silk can be printed easily today with screen printing, but before late 18th century the technique wasn't known in western world (it was invented in China a millenium ago) and the available methods didn't yeld good results.
So when in the late 17th century European trading companies were establishing trading posts in India, a huge producer of cotton fabrics, suddenly cotton was much more available in Europe. Indian calico cotton, which was sturdy and cheap and was painted or printed with colorful and intricate floral patters, chintz, especially caught on and became very fashionable. The popular Orientalism of the time also contributed to it becoming fasionable, chintz was seen as "exotic" and therefore appealing.
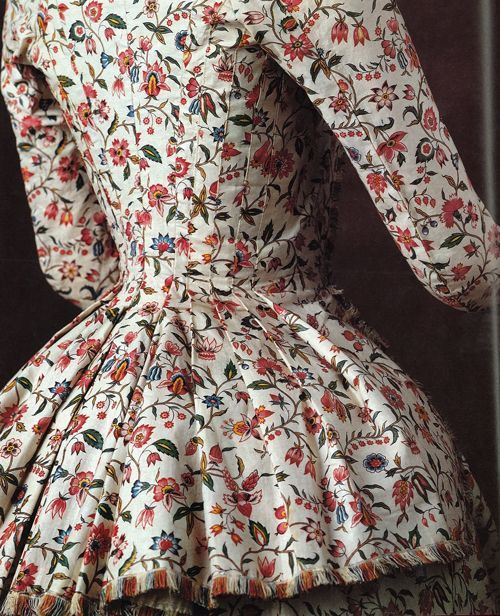

Here's a typical calico jacket from late 18th century. The ones in European markets often had white background, but red background was also fairly common.
The problem with this was that this was not great for the business of the European fabric producers, especially silk producers in France and wool producers in England, who before were dominating the European textile market and didn't like that they now had competition. So European countries imposed trade restrictions for Indian cotton, England banning cotton almost fully in 1721. Since the introduction of Indian cottons, there had been attempts to recreate it in Europe with little success. They didn't have nearly advanced enough fabric printing and cotton weaving techniques to match the level of Indian calico. Cotton trade with India didn't end though. The European trading companies would export Indian cottons to West African market to fund the trans-Atlantic slave trade that was growing quickly. European cottons were also imported to Africa. At first they didn't have great demand as they were so lacking compared to Indian cotton, but by the mid 1700s quality of English cotton had improved enough to be competitive.
Inventions in industrial textile machinery, specifically spinning jenny in 1780s and water frame in 1770s, would finally give England the advantages they needed to conquer the cotton market. These inventions allowed producing very cheap but good quality cotton and fabric printing, which would finally produce decent imitations of Indian calico in large quantities. Around the same time in mid 1700s, The East Indian Company had taken over Bengal and soon following most of the Indian sub-continent, effectively putting it under British colonial rule (but with a corporate rule dystopian twist). So when industrialized English cotton took over the market, The East India Company would suppress Indian textile industry to utilize Indian raw cotton production for English textile industry and then import cotton textiles back to India. In 1750s India's exports were mainly fine cotton and silk, but during the next century Indian export would become mostly raw materials. They effectively de-industrialized India to industrialize England further.
India, most notably Bengal area, had been an international textile hub for millennia, producing the finest cottons and silks with extremely advance techniques. Loosing cotton textile industry devastated Indian local economies and eradicated many traditional textile craft skills. Perhaps the most glaring example is that of Dhaka muslin. Named after the city in Bengal it was produced in, it was extremely fine and thin cotton requiring very complicated and time consuming spinning process, painstakingly meticulous hand-weaving process and a very specific breed of cotton. It was basically transparent as seen depicted in this Mughal painting from early 17th century.
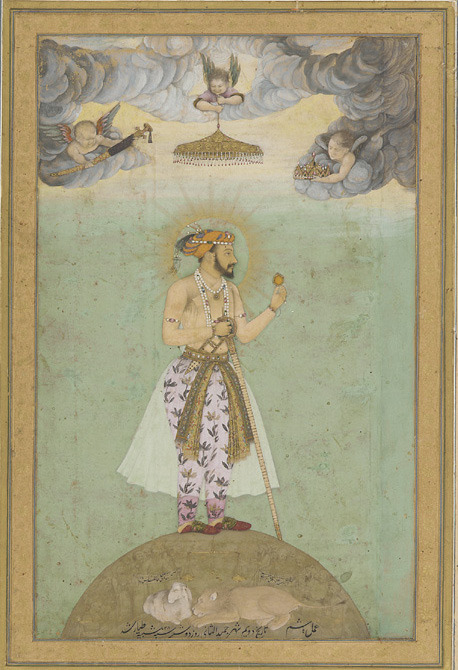

It was used by e.g. the ancient Greeks, Mughal emperors and, while the methods and it's production was systematically being destroyed by the British to squash competition, it became super fashionable in Europe. It was extremely expensive, even more so than silk, which is probably why it became so popular among the rich. In 1780s Marie Antoinette famously and scandalously wore chemise a la reine made from multiple layers of Dhaka muslin. In 1790s, when the empire silhouette took over, it became even more popular, continuing to the very early 1800s, till Dhaka muslin production fully collapsed and the knowledge and skill to produce it were lost. But earlier this year, after years lasting research to revive the Dhaka muslin funded by Bangladeshi government, they actually recreated it after finding the right right cotton plant and gathering spinners and weavers skilled in traditional craft to train with it. (It's super cool and I'm making a whole post about it (it has been in the making for months now) so I won't extend this post more.)
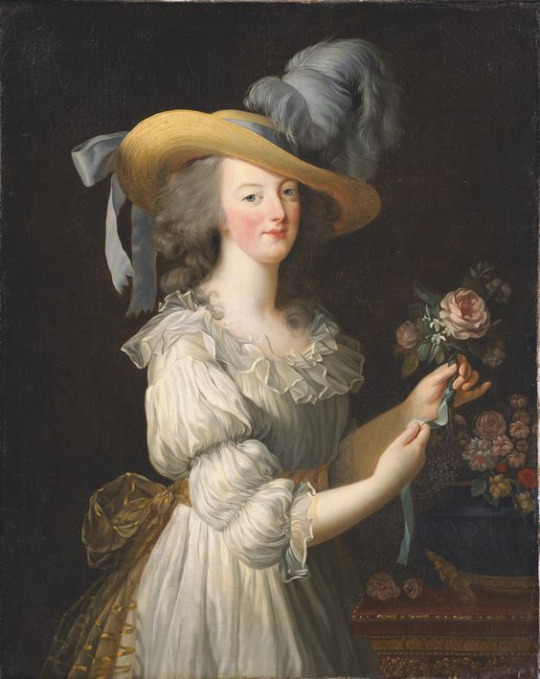


Marie Antoinette in the famous painting with wearing Dhaka muslin in 1783, and empress Joséphine Bonaparte in 1801 also wearing Dhaka muslin.
While the trans-Atlantic slave trade was partly funded by the cotton trade and industrial English cotton, the slave trade would also be used to bolster the emerging English cotton industry by forcing African slaves to work in the cotton plantations of Southern US. This produced even more (and cheaper (again slave labor)) raw material, which allowed the quick upward scaling of the cotton factories in Britain. Cotton was what really kicked off the industrial revolution, and it started in England, because they colonized their biggest competitor India and therefore were able to take hold of the whole cotton market and fund rapid industrialization.
Eventually the availability of cotton, increase in ready-made clothing and the luxurious reputation of cotton lead to cotton underwear replacing linen underwear (and eventually sheets) (the far superior option for the reasons I talked about here) in early Victorian Era. Before Victorian era underwear was very practical, just simple rectangles and triangles sewn together. It was just meant to protect the outer clothing and the skin, and it wasn't seen anyway, so why put the relatively scarce resources into making it pretty? Well, by the mid 1800s England was basically fully industrialized and resource were not scarce anymore. Middle class was increasing during the Victorian Era and, after the hard won battles of the workers movement, the conditions of workers was improving a bit. That combined with decrease in prices of clothing, most people were able to partake in fashion. This of course led to the upper classes finding new ways to separate themselves from lower classes. One of these things was getting fancy underwear. Fine cotton kept the fancy reputation it had gained first as an exotic new commodity in late 17th century and then in Regency Era as the extremely expensive fabric of queens and empresses. Cotton also is softer than linen, and therefore was seen as more luxurious against skin. So cotton shifts became the fancier shifts. At the same time cotton drawers were becoming common additional underwear for women.
It wouldn't stay as an upper class thing, because as said cotton was cheap and available. Ready-made clothing also helped spread the fancier cotton underwear, as then you could buy fairly cheaply pretty underwear and you didn't even have to put extra effort into it's decoration. At the same time cotton industry was massive and powerful and very much eager to promote cotton underwear as it would make a very steady and long lasting demand for cotton.
In conclusion, cotton has a dark and bloody history and it didn't become the standard underwear fabric for very good reasons.
Here's couple of excellent sources regarding the history of cotton industry:
The European Response to Indian Cottons, Prasannan Parthasarathi
INDIAN COTTON MILLS AND THE BRITISH ECONOMIC POLICY, 1854-1894, Rajib Lochan Sahoo
#i have fixed the wording in the beginning so it doesn't sound like i'm saying cotton in general dyed better than wool or silk#answers#fashion history#historical fashion#history#textile history#dress history#historical clothing#indian history#colonial history#indian textiles#cotton#slavery
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Irish dress history sources online:
A list of sources for Irish dress history research that free to access on the internet:
Primary and period sources:
Text Sources:
Corpus of Electronic Texts (CELT): a database of historical texts from or about Ireland. Most have both their original text and, where applicable, an English translation. Authors include: Francisco de Cuellar, Luke Gernon, John Dymmok, Thomas Gainsford, Fynes Moryson, Edmund Spenser, Laurent Vital, Tadhg Dall Ó hUiginn
Images:
The Edwin Rae Collection: A collection of photographs of Irish carvings dating 1300-1600 taken by art historian Edwin Rae in the mid-20th c. Includes tomb effigies and other figural art.
National Library of Ireland: Has a nice collection of 18th-20th c. Irish art and photographs. Search their catalog or browse their flickr.
Irish Script on Screen: A collection of scans of medieval Irish manuscripts, including The Book of Ballymote.
The Book of Kells: Scans of the whole thing.
The Image of Irelande, with a Discoverie of Woodkarne by John Derricke published 1581. A piece of anti-Irish propaganda that should be used with caution. Illustrations. Complete text.
Secondary sources:
Irish History from Contemporary Sources (1509-1610) by Constantia Maxwell published 1923. Contains a nice collection of primary source quotes, but it sometimes modernizes the 16th c. English in ways that are detrimental to the accuracy, like changing 'cote' to 'coat'. The original text for many of them can be found on CELT, archive.org, or google books.
An Historical Essay on the Dress of the Ancient and Modern Irish By Joseph Cooper Walker published 1788. Makes admirable use of primary sources, but because of Walker's assumption that Irish dress didn't change for the entirety of the Middle Ages, it is significantly flawed in a lot of its conclusions. Mostly only useful now for historiography. I discussed the images in this book here.
Chapter 18: Dress and Personal Adornment from A Smaller Social History of Ancient Ireland by P. W. Joyce published 1906. Suffers from similar problems to An Historical Essay on the Dress of the Ancient and Modern Irish.
Consumption and Material Culture in Sixteenth-Century Ireland Susan Flavin's 2011 doctoral thesis. A valuable source on the kinds of materials that were available in 16th c Ireland.
A Descriptive Catalogue of the Antiquities in the Museum of the Royal Irish Academy Volumes 1 and 2 by William Wilde, published 1863. Obviously outdated, and some of Wilde's conclusions are wrong, because archaeologists didn't know how to date things in the 19th century, but his descriptions of the individual artifacts are worthwhile. Frustratingly, this is still the best catalog available to the public for the National Museum of Ireland Archaeology. Idk why the NMI doesn't have an online catalog, a lot museums do nowadays.
Volume I: Articles of stone, earthen, vegetable and animal materials; and of copper and bronze
Volume 2: A Descriptive Catalogue of the Antiquities of Gold in the Museum of the Royal Irish Academy
A Horsehair Woven Band from County Antrim, Ireland: Clues to the
Past from a Later Bronze Age Masterwork by Elizabeth Wincott Heckett 1998
Jewellery, art and symbolism in Medieval Irish society by Mary Deevy in Art and Symbolism in Medieval Europe- Papers of the 'Medieval Europe Brugge 1997' Conference (page 77 of PDF)
Looking the part: dress and civic status and ethnicity in early-modern Ireland by Brid McGrath 2018
Irish Mantles, English Nationalism: Apparel and National Identity in Early Modern English and Irish Texts by John R Ziegler 2013
Dress and ornament in early medieval Ireland - exploring the evidence by Maureen Doyle 2014
Dress and accessories in the early Irish tale, ‘The Wooing of Becfhola’ by Niamh Whitfield 2006
A tenth century cloth from Bogstown Co. Meath by Elizabeth Wincott Heckett 2004
Tertiary Sources:
Medieval Ireland: An Encyclopedia edited by Sean Duffy published 2005
Re-Examining the Evidence: A Study of Medieval Irish Women's Dress from 750 to 900 CE by Alexandra McConnell
#resources#dress history#irish dress#irish history#early medieval#bronze age#textile history#late medieval#16th century#historical dress
80 notes
·
View notes
Text
My Guild sends out a weekly newsletter and sometimes they include articles that I think you guys might enjoy, this is one of those times :3
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
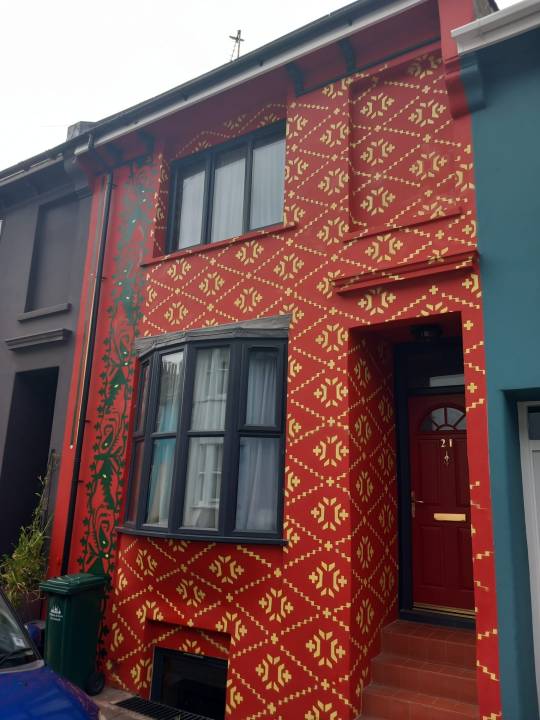

Brighton & Hove News, 28 July 2023:
'A Brighton family have literally stopped traffic with a new mural inspired by a sari pattern on their new home.
Poppy Jaman and Jaan Madan moved to Southampton Street in Hanover in January, and immediately knew they wanted to make a splash when decorating the outside.
She said: “One of the reasons we wanted to move to the centre of Brighton is that it’s so colourful.
“We were inspired by murals in Washington where there’s a whole area where there’s murals which have been created out of adversity.
“That inspired the idea of making a statement with our home. I wanted to not just paint something that I love. If you just love something that’s enough, but I also wanted to say here’s a bit of my identity.
“I collect saris and Jamdani is a signature saris of Bangladesh. It’s got a colonial past to it.

📷 X
The mural is inspired by the Jamdani weave saree, the signature saree of Dhaka, Bangladesh, which dates back at least as far back as 300BC.
Between the 16th and 19th centuries, Jamdani fabric – so fine it was known as ‘woven air’ – was one of the most highly coveted commodities in Mughal courts and further afield. However, by the mid-19th century, Jamdani had become almost extinct.
Poppy has written more about her relationship with the Jamdani design and its colonial history here.'
#sari#mural#brighton#mughal#textiles#textile history#jamdani#dhaka#bangladesh#colonial history#indian history#weave#woven fabric#pattern#surface pattern#surface pattern design#pattern design#textile design#surface decoration#street art#uk#england#british asian#saree#traditional crafts#traditional textiles#traditional clothing#bengali#weaving
124 notes
·
View notes
Text


My first zine Repeating pattern is now out on Gumroad !
It's a collage of photos, hand drawn patterns and an essay I wrote about my thoughts on the history of industrial pattern design in Finland and Estonia (Particularly in Forssa and Narva). It also includes a tutorial on how to make your own repeating patterns by hand.
I plan to keep making zines on the subjects that interest me - city gardening, weaving, plant dyes... I had so much fun making this one!
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
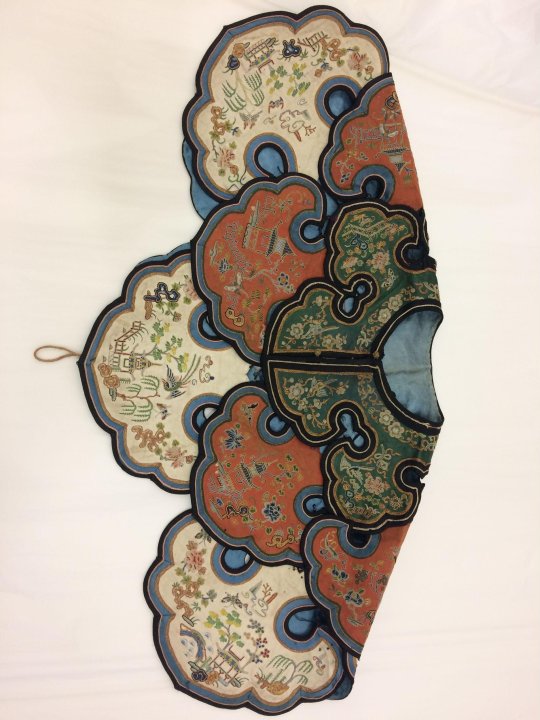
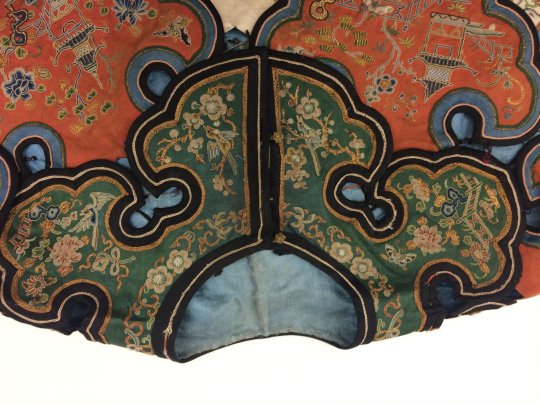
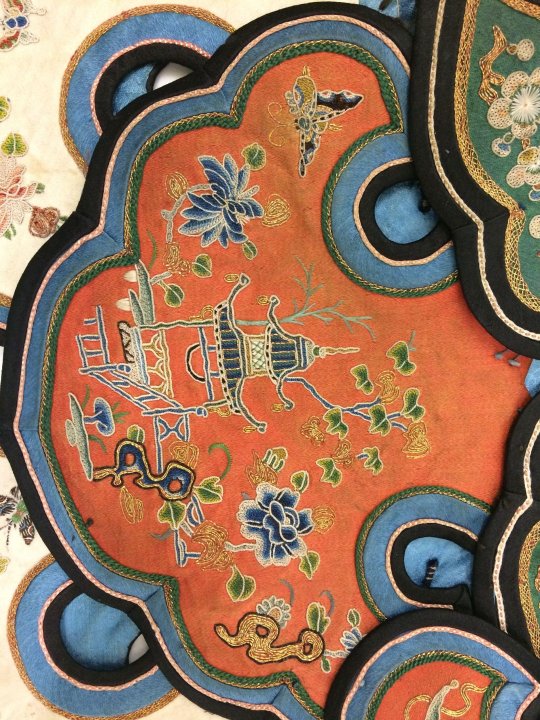
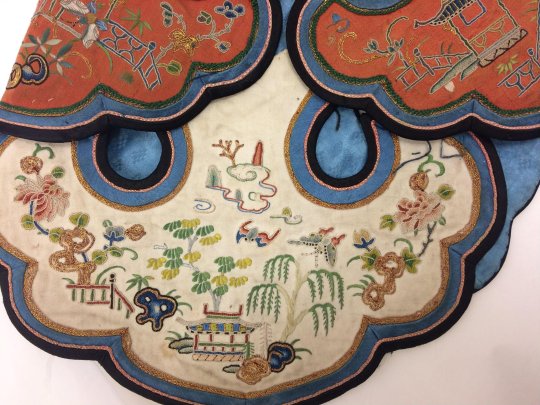
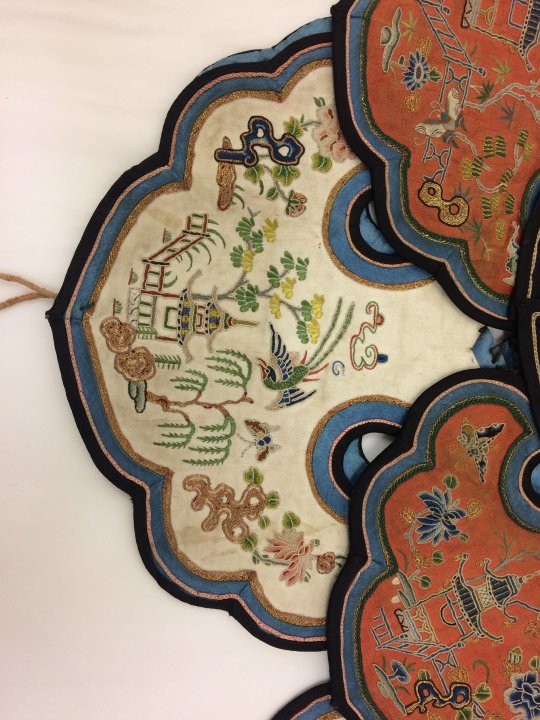








women's silk satin cloud collar in three tiers, embroidered with garden vignettes in seed stitch, satin stitch, and gold couching, and lined in blue silk. 19th century.
#china#qing dynasty#late qing dynasty#textile history#fashion#(i suppose)#museum trawling#image source: the victoria and albert museum
275 notes
·
View notes
Text

Experts have recreated the oldest-known piece of tartan ever found, which was discovered in a peat bog after being buried for centuries.
The tartan was discovered around 40 years ago in the bog in Glen Affric in the Highlands, and underwent rigorous testing by the Scottish Tartans Authority last year to confirm it was the oldest surviving piece of tartan.
The Glen Affric Tartan dates from 1500-1600 AD and went on to be exhibited at the V&A Dundee.
Manufacturer and distributor of tartan fabrics, the House of Edgar, recreated the tartan under the guidance of tartan historian Peter Macdonald to recreate the Glen Affric for people to wear.
It features the colours that dye analysis of the original tartan had confirmed – this included the use of green, yellow and red, which would have come from woad or indigo to create the green along with other natural dyes.
This, along with the determined thread count, helped The House of Edgar bring this piece of Scottish history back to life.
Emma Wilkinson, the designer for House of Edgar who worked on the project, commented: “I create new tartans every day but this project is truly special – a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity to recreate a piece of history.
“Tartan is such an iconic piece of Scotland’s identity and it has been a true pleasure to see this fabric come back to life to be enjoyed for generations to come.”
35 notes
·
View notes
Text

You know that feeling when your just happily crafting along and it’s going fine. The weather is the perfect kind of ambiance that you want (sunny, stormy, pattering if a soft rain idk you do you), the pattern is understandable and you’re generally enjoying yourself.
Then it happens. There’s a knot on your thread.

Now in Swedish folklore there are three (3) kinds of thread knot, depending on the situation.
Number 1: the love knot (kärleksknut).

This is a kind of knot that is easily undone. Usually the thread just went over itself and made a little slip knot that you can just tug the end of. It means someone who likes you is thinking of you and it made your thread tease you about it. Might be slightly bothersome, might also make you think of them back.
Number 2: the envy knot (avundsknut).

Perfection will always attract envy. The lesson is that faults in your work is not only fine, but encouraged. Lest you should draw the gaze of the evil eye, or even worse - the gods.
An envy knot in Swedish folklore is usually caused by humans who are envious of your work. It’s the kind of knot where however you pull it it won’t release and you end up making it tighter until you just cut the thread off to make a new start after it.
Number 3: the troll knot (trollknut)

This is comparable to the other two just a knot that happens on its own. But instead of humans it’s blamed on trolls. The trolls are fickle and you can never really know what they want. But they’re hindering your progress in the project so it’s probably not your best they have in mind. Watch out.
Source: institutet för språk och folkminnen (ISOF)

#folklore#knitting#folk magic#witchcraft#folk practise#crafts#textile crafts#yarn#folktro#Sweden#Swedish#Scandinavia#svensk folktro#Sverige#textile history#textilvetenskap#handmade#yarn crafts#my post
909 notes
·
View notes
Text
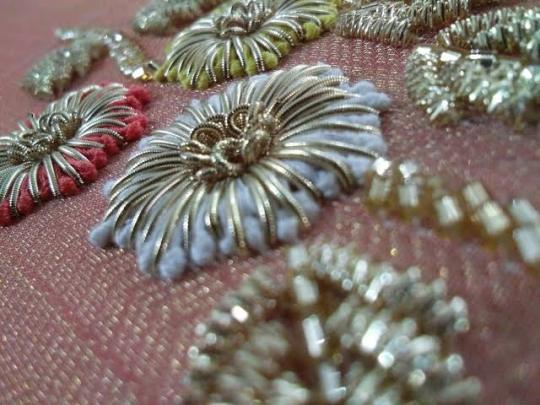
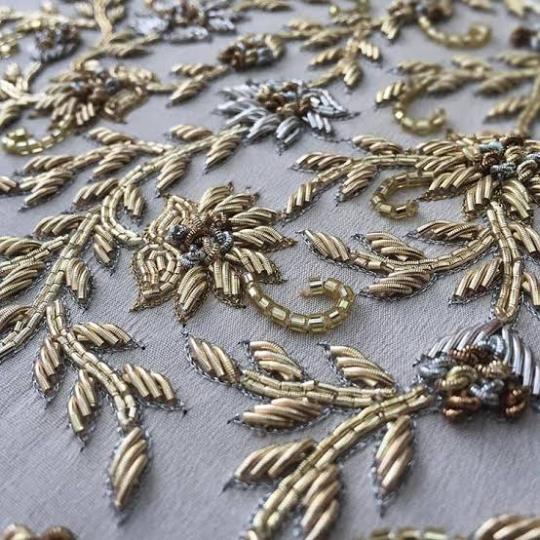










Dabka or Dapka is a detailed type of needlework from Rajasthan in India. It is usually done at the final stage of the production process to add finishing touch embellishments.
At least three to four worker workers are required for a detailed and fine work at the same time on the same piece. First a thick cotton cord is stitched on the pattern to be embroidered. Then on this cord prefabricated metal thread is looped on with an ordinary stitching needle. The patterns mostly made are of flowers, leaves, or birds. Skilled embroiders can even do french knots with the smallest size.
1 / 2 / 3 / 4 / 5 / 6 / 7 / 8 / 9 / 10 / 11 | textile series
#textiles#ots#rajasthan#india#textile art#desi fashion#desi tumblr#desiblr#indian fashion#folk art#textile history
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
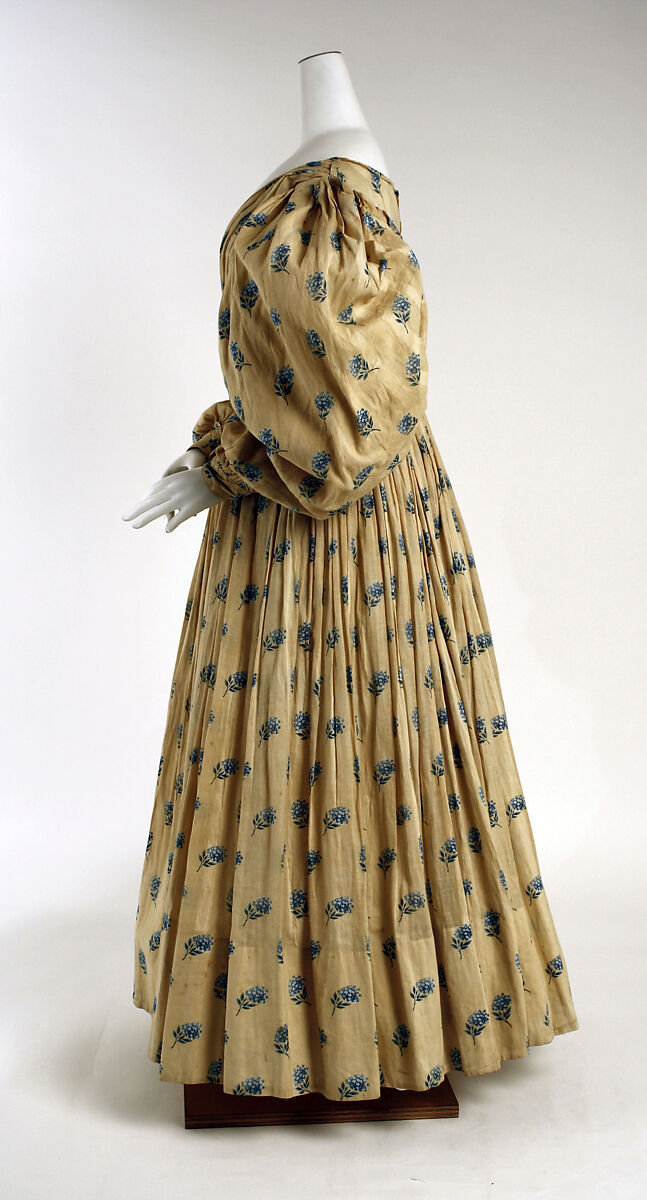
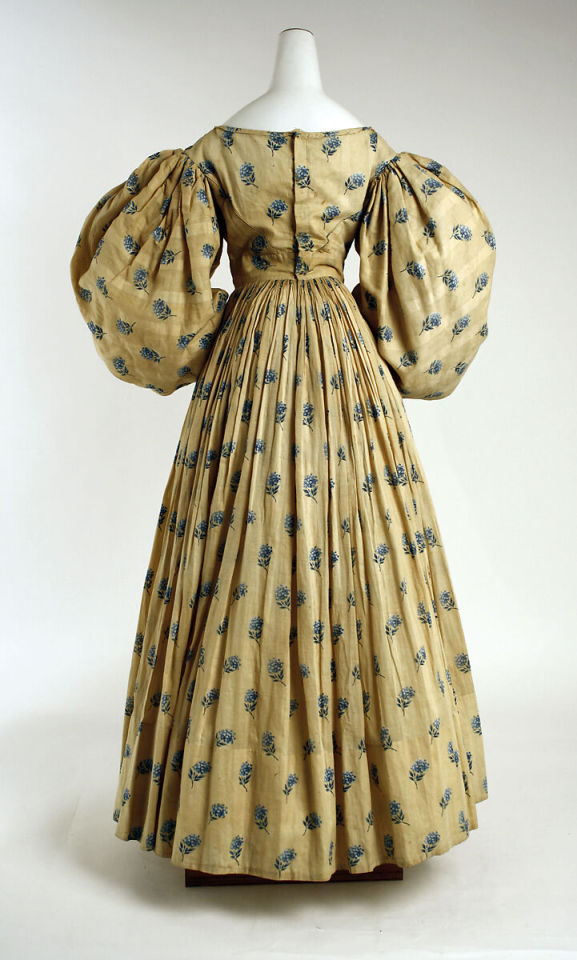





Linen dress, British, 1829 (via The Metropolitan Museum of Art)
#so obsessed with late georgian fashion right now and this one is STUNNING#historical fashion#historical dress#georgian era#georgian fashion#1820s#textile history
115 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dress History Corner Navigation
Welcome to the corner of the interned where I nerd about (mostly) Western dress history! This is the post I will update with all my more structured and researched articles. I have the same navigation on my blog, but it's only for the browser so I figured it would be useful to have navigation that work for the app too.
Some basics
An Introductory Timeline Of Western Women's Fashion
How I do my research into dress history
Dress History
Lacing in Western Fashion History
Dress Etiquette Thorough Western History
When Did It Become Acceptable For Western Women To Wear Pants?
When Did Skirts Stop Being Acceptable For Western Men To Wear?
Is Lingerie Going Backwards - A Rebuttal
The history of showing your boobs for fashion
Victorian Era
A summary of different kinds of corsets
Historical Finnish Clothing of Modern Period
Victorian Dress For Every Occasion - 1890s Edition
1890s Day Dresses
American Civil War era (1861-65) ball gown
Regency
Debunking the common narrative about Beau Brummel - The whole modern men's fashion is not the fault of One Guy
Gender non-conforming Regency styles
18th century
The Colonial History of How Cotton Became the Most Important Fabric
Mantua And It's Variants
Northern Italian countryside fashion in late 18th century.
Working Class Clothing In Late 18th Century France
Early Modern Era
Deep Dive into 15th and 16th Century Working Class Fashion in Western Europe
Medieval Era
Late 14th to Early 15th Century Bohemian and German Men's Fashion
Construction of Men's Hose
Codpiece
Construction of the French hood
Iron Age
Viking and Crusader Age Finnish men's dress
Historical Sewing
Sewing Medieval Bathhouse Dress
Historical Costuming
History of the Fantasy Corset
Met Gala 2022 Costume Commentary
Pride and Prejudice 2005 Costume Analysis
Ranking Men's Costumes in Renaissance Period Dramas - Part I: The Bad
Ranking Men's Costumes in Renaissance Period Dramas - Part II: The Good
Textiles
Hemp's properties
Sustainability
How to see through the greenwashing propaganda of the fashion industry - Case study 1: Shein
The Real Cost of the Fashion Industry
Architectural History
History of Sauna and Steam Baths
Historical Queer Figures
Julie d'Aubigny
History
Palestinian History Between Great Powers
European History Is Not White
Tag Navigation
#answers
#resources
Primary sources
#primary sources
#extant garment
#photograph
#painting
#illustration
#fashion plate
Pinterest Boards
Victorian Fashion
#i actually don't currently have the exact same navigation on the blog but i will once i get around updating it lol#fashion history#dress history#history#historical sewing#historical costuming#textiles#textile history#architectural history#architecture#historical resources#navigation#nav
211 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey people interested in textile and fashion history.
Do you know about the Barbara Johnson album?
It is an album put together between the years 1746-1823 by Barbara Johnson, and basically whenever she bought cloth of any kind she preserved a small bit in the book along the description of what she had made from that specific cloth. She also included some fashion plates in the pages.
It's in the V&A and they have done a good job of digitizing it, you can zoom in super close to the pages to look at the textile.
54 notes
·
View notes