#Literary analysis
Text
Warning signs of fascist themes in history media
Fascism is a reactionary, authoritarian and nationalist ideology that opposes peace, democracy, and human rights. Fascists are sometimes attracted to history because they use it to promote violence and myths of racial superiority. Fascist ideas can be found in certain books, movies, social media, Youtube channels and more.
Here I'm going to talk about general patterns to help you recognize fascist shit when you see it, examples I've seen in Roman history studies, and suggestions for what you can do about it.
Fascist themes
I have focused on themes rather than specific dogwhistles, arguments, or symbols, because fascist rhetoric often disguises itself to appear more palatable, and varies across countries. Themes are also useful for analyzing books, podcasts, and other media where political bias isn't always obvious. For specific fascist code-words and symbols, see the links at the end of this post.
Not every item on this list will appear for every fascist, and not every person who does one of these things is a fascist. But any of them should warn you to be on alert.
1. Fascism is reactionary.
Fascism rejects the modern, changing world. Fascists feel like the "natural order" or "old way of life" is threatened and must be preserved. They may call themselves conservatives or traditionalists, but their methods and goals are more radical and disruptive than traditional conservatism.
Fascists often feel like they have been attacked, humiliated, or left out of their rightful place in society. They resent groups of people they believe are getting undeserved benefits or respect. These groups are usually minorities such as immigrants, Jews, queer people, women or racial minorities. The fascist may believe these groups are involved in a conspiracy to undermine or corrupt "decent" people, or to abuse children.
Be especially alert for antisemitism, which accounts for a large number of hate crimes, and has been a key part of most fascist movements.
The fascist portrays modern society as weak, corrupt, degenerate, or oppressive to people like himself.
In history media, this may appear as nostalgia for the past, "reject modernity, return to tradition," and romanticizing a primitive or traditional aesthetic. It can also show up as whitewashing the "heroic" culture and vilifying other cultures, or erasing the existence of minorities from history altogether. The fascist may downplay historical injustices like slavery and the exclusion of women from the workforce.
2. Fascism is authoritarian.
The "natural order" of the fascist is hierarchical, with some people mattering more than others. Those on the bottom of society are there because they deserve it, and their struggles and feelings don't matter. If they demand equal rights, assistance programs or respect, they are seen as entitled, lazy, whiny, and arrogant. Naturally, the fascist assumes his place is at or near the top of the hierarchy.
The fascist usually opposes ambiguity and crossing boundaries - mixed race couples, cultural exchange, women in mostly-male jobs, trans and gender-nonconforming people - because these undermine the artificial divisions in the fascist hierarchy.
A powerful central authority is seen as necessary to fix society. To be good requires obedience; to disagree makes you a traitor.
If the fascist has a leader, that leader is idolized and unquestioned. The fascist leader is typically charismatic, masculine, and "tough on crime." The fascist denies any wrongdoing from the leader, minimizes or tries to justify it.
Opposition to democracy, because democracy requires dissent. The legislature is de-legitimized as representing the people's will, and elections are called fraudulent without evidence. The fascist sees rule of law as a hindrance to "reforming" society. (This separates the fascist from the "mainstream" conservative, who usually cares more about upholding the status quo.)
Many fascists will project authoritarianism onto their opponents because they assume those opponents also view the world this way, just with a different group on top.
In history media this may appear as glorifying anti-democratic leaders, justifying violence as necessary, or denying that shameful events like the Holocaust happened. The fascist is also likely to portray democracy, defense attorneys, and civil rights activists as obstacles to doing "what needs to be done."
3. Fascism is nationalistic.
Fascists usually identify strongly with a certain nation, culture, or race. Different kinds of people are seen as inherently different in moral character, intellectual ability, or skills. You are encouraged to derive your worth from this group identity and to treat other people based on theirs.
This group is elevated at the expense of individual human rights. The fascist only values freedom of speech, freedom of association, and the rights of the accused for himself and his allies. People who are inferior or who disagree are not granted those same rights.
This offers a sense of identity and pride for people whose identity is feels unstable or threatened. It preys upon the lonely, the disillusioned, the failures. Historically, most fascist support comes from middle-class people who feel insecure about their place in the world, and angered by the rise of groups they see as beneath them.
4. Fascism is anti-intellectual.
Although fascists are attracted to history, they are usually more interested in using history as a prop for their mythic struggle of good and evil than in learning what history actually was.
Fascists will readily cherry-pick events and stories that feel glorious, exciting or romantic, or which feed their belief of being victimized. They will ignore or distort information that contradicts this, like historical multiculturalism and facts that make the "glorious race/empire" look bad.
The fascist may also combine myths, occult symbols, or historical details with no connection to each other, looking for a "deep underlying truth" that academics have missed (because it doesn't exist).
Fascists often try to discredit scientists, historians and the humanities. They may accuse "ivory-tower intellectuals" of being wrong, worthless, elitist or out of touch, or even creating a conspiracy to hide the truth. By framing intellectuals as the enemy, the fascist gives himself an excuse not to listen to them or doubt his fantasy of superiority.
When fascists present their own intellectuals, these intellectuals usually fixate on denouncing modern society and supporting fascist ideology, not on new discoveries or creativity. In the fascist mindset, all important truths are already known, all cultural and moral questions are already solved. Art can only conform to accepted standards, not challenge standards or create anything new.
Self-contradiction and hypocrisy. Fascist ideology appeals to people's feelings, not their logic. The enemy is both strong (to present a credible threat) and weak (so they can be held in contempt). The genocide didn't happen - and if it did, it wasn't really that bad. It's wrong for others to offend us, but we are justified in harassing or attacking them.
Intolerance of disagreement and dissent. The fascist mistakes feeling uncomfortable for being harmed, and thus any statements that make him feel uncomfortable, must be attacks from bad people. Critics must be shamed, mocked, harassed into silence, or expelled. Changing your mind is a sign of weakness.
Black and white morality / intolerance of nuance. The fascist has already decided that some people are right, period, and others are wrong, period. There is no room for morally complicated situations or mutual responsibility.
In-group jargon and redefining words. The fascist may refer to his opponents as slurs, say "pedophile" when he means "gay people," or invent new slang, dogwhistles and acronyms. This word-shuffling builds a sense of connection with other fascists, helps to dehumanize the enemy, and allows fascists to deny that they're bad people because they're not using specific bad words. (A fascist may complain about "Zionists" when he means "Jews," use Norse runes instead of swastikas, or say he's "proud of his heritage" instead of a white supremacist.)
In history media, look for dogwhistles, narratives with clear "good guys" and "bad guys," claims of a conspiracy among intellectuals or bankers, and contradictions. Does the text try to persuade you with evidence and logic, or with emotional appeals? Does it downplay or erase facts that would undermine the author's argument?
5. Fascism is violent.
Glorification of violence and war. Fascists believe that violence against their enemies is both necessary and justified to "defend their way of life," or protect society. They exult in shows of physical strength and aggression, and see physical weakness as pathetic. Weapons may be glorified and fetishized as well.
This can also extend to sexual violence and domination. The woman is an accessory to macho fantasies: an object of conquest, a prize to be flaunted and defended, a symbol of the man's own success and competence. A man who feels humiliated or threatened by a woman, perhaps because she rejected or outranked him, may threaten rape to "put her in her place."
The cult of heroic death. To overcome people's natural instinct to live, fascism glorifies veterans and martyrs, and encourages people to identify with and fight for the nation/race. Courage and strength are equated with violence. The costs of war are ignored - homelessness, starvation, massacres, grief, lifelong trauma and disability for many - even on the "winning" side.
Opposition to peace. Pacifists and neutral parties are considered traitors. Compromise is seen as giving in to the enemy. "You are either with us or against us."
Fascist justice centers on punishment, enforcing obedience and purging "bad people" rather than rehabilitation, education, or providing adequate social services.
In history media, look for an emphasis on the military, weapons, symbols of power, brutality, conquest, and sexual violence. Are these things equated with masculinity, power or success? Are we encouraged to identify with the conqueror instead of the conquered? Does the narrative mention people who opposed the war, or are they erased or lumped in with traitors?
6. Fascism is mean-spirited.
You probably noticed resentment, insecurity, anger and contempt in the previous sections. Fascism appeals to these emotions within people, and tells them that their unhappiness is other people's fault.
In fascist communities and blogs you will often see these same negative feelings, and externalized blame. Less overt fascist spaces may seem supportive, friendly, or just like hobbyists having fun, and this draws vulnerable people in. But it's juxtaposed with a deep disrespect for those who are seen as inferior.
Fascist jokes and memes are usually predicated on smugness (at being part of a "superior" race or nation), contempt (for "lesser" people), anger, or violent fantasies. They have a mean streak and may appear ironic ("It's just a joke, lighten up"), for the sake of plausible deniability.
The fascist does not merely hate that the "Other" exists (although they often do) - they resent being expected to treat others with respect, empathy and equality. They may demonize empathy by calling others "special snowflakes" who are trying to enforce "political correctness" or restrict freedom of speech. These are deflections so the fascist can avoid admitting how unreasonable and hurtful his behavior actually is.
Pay attention to how specific communities and media make you feel. Do you feel like you're becoming angrier or more fearful of the world over time? Do you feel less respect for certain kinds of people than you used to, or see the world's problems as those people's fault? If so, those spaces and media may be unhealthy for you, and could be promoting prejudice.
Example red flags I've seen in Roman history studies
Exulting over the Roman empire's size.
War being portrayed as exciting, heroic or brave.
Arguing that conquest (especially Caesar's conquest of Gaul) was justified.
Praising the emperors Vespasian, Titus or Hadrian uncritically - all of whom were involved in brutal oppression of Jewish people.
Arguing that Roman slavery was "not that bad" compared to other forms of slavery.
Unironically calling non-Romans barbarians, savages, or primitive.
Erasure of Rome's cultural and ethnic diversity, the role of women in politics, and queer history.
Portraying the end of free elections, debate, and political opposition as a good thing, particularly under Julius Caesar or Augustus.
Attributing the fall of Rome to "moral decline" or "degeneracy."
Attraction to symbols of power and famous military leaders - legions, centurion armor, idolizing Caesar, even the word "fascism" comes from the Latin fasces.
Falsely claiming that the Nazi salute originated with the Romans. (It's a neoclassical invention.)
Now, just because you see these red flags doesn't automatically mean the person is a fascist. Sometimes people use a word or meme without realizing its implications, and older works often say things that would be offensive today. That's another reason why I focused on general themes.
Look at the underlying patterns in what a person or work is saying, and think about what they want you to believe. As a whole, does it seem reactionary, authoritarian, nationalist, anti-intellectual, pro-violence, and/or mean-spirited? Conversely, if the person or work seems to value open-mindedness, democracy, education, peace, empathy, feminism, and multiculturalism, and if they treat those who disagree with them with respect, those are all good signs.
How should you respond?
A full guide to fighting fascism is beyond the scope of this post. I suggest contacting human rights groups in your area for the best ways to counter fascism in general.
For media with fascist themes or by fascist creators:
Do not share, recommend, or give it a wider audience. Even if it's "just a funny meme," spreading it can give fascists more followers, and make them more confident to attempt violence.
Do not spend money that will support fascist creators, organizers, or groups if you can avoid it. Don't buy their books, anime, hockey team apparel, whatever. Boycott them and tell people why.
Call it what it is. Fascist, racist, white supremacist, or whatever label applies. Don't use euphemisms for the sake of politeness - that only helps fascism appear respectable.
Post or share critical reviews that explain why the media is fascist. This will help others learn to recognize and call out fascism, too.
Sometimes people are attracted to controversial works just to be contrarian or to see what the controversy is about. You might decide it's more effective to avoid naming fascist works and giving them more publicity, and instead to call out the fascist ideas in them, to educate others. This is the approach I took in this post, but which method is better depends on the situation.
Don't use "fascist" for any bigot, conservative, or person you dislike. This waters the word down and makes it less likely to be taken seriously when a real hate group is threatening people. Fascism is a particularly violent, extreme, and anti-democratic type of bigotry. But when you DO see fascism, name and shame it.
If it's on social media or a blog, do not respond to it directly. Make a new post instead debunking it. This will avoid giving the fascists a broader audience, and they're less likely to notice and threaten you. Block and report them; try to get their communities removed from the platform. On a large enough scale, this helps prevent fascist groups from organizing and expanding their membership.
Read, watch, and promote non-fascist media and sources, like I do in my book reviews and favorites page. Bonus points if you can find sources for historical diversity and multiculturalism!
Further resources
This is an updated version of my older post, based on my notes from Umberto Eco's Ur-Fascism and Stuart Hood's Fascism: A Graphic Guide. I also found Miriam Griffin's A Companion to Julius Caesar anthology useful for understanding how fascism and other political movements have co-opted Roman history for their own purposes.
The Alt-Right Playbook video series deconstructs fascist and alt-right arguments, and explains how they gain traction in politics, particularly in the USA.
Subtler signs of fascism: What are dogwhistles? / List of dogwhistles (incomplete) / List of hate symbols / Early Warning Signs of Fascism
Art Spiegelman's graphic novel Maus is a memoir of the Holocaust from the viewpoint of an Auschwitz survivor and his son. It is much darker and more visceral than the preceding books, but also valuable for demonstrating what fascism looks like "on the ground" when it gains power, and the consequences if we do not fight against it.
If you or someone you love has gotten involved with hate groups, Life After Hate offers support and counseling. Also check out QAnon Casualties - Resources, even if the group isn't QAnon. Your past doesn't have to define your future.
For good sources on Roman history, I have a page of recommended media, including links to resources on queer history, Black history, disability studies, women in classical antiquity, and my tips for evaluating whether a history book is reliable.
I am not a historian or political theorist. If I got something wrong or if you have additional helpful info, please don't hesitate to say so!
#warning: this is like 2800 words#as usual i'm not a historian just an amateur trying to help raise awareness#correct me if i got anything wrong#good luck. i love you all <3#fascism#media literacy#critical thinking#literary analysis#jlrrt essays#things to whack racists with
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Review of 'The Time Machine' by H.G. Wells

The stories of H.G.Wells are rich and captivating worlds where he makes the unfathomable seem plausible. Wells uses concepts from the sciences readily in his writing as a base of reality. His protagonists tend to be inquisitive types that posit questions about the state of the world, often giving and testing their hypotheses along a surreal adventure. In The Time Machine our protagonist is simply and ambiguously labeled the Time Traveler. He has just transformed physics forever by creating a vehicle that can fold and traverse spacetime. Now he aims to demonstrate to his civilized friends his unbelievable achievement. In a way this demonstration is both a primer for them and a reassurance for himself that he is not in a fantasy.
“Can an instantaneous cube exist?”
This is a question the Time Traveler asks his dinner party audience in order to introduce the concept of Time as the 4th dimension. He claims you need “duration” for anything to truly exist. If a cube only exists for an imperceptible instant then did it really exist? It’s a question that provokes a bunch of thoughts. How long is an instant? If an instant is measurable then the cube did exist for a time, no? But without the evidence of creation or decay of the cube how can we be certain that it existed? This question is a seemingly untestable hypothetical.
“But you are wrong to say that we cannot move about in Time. For instance, if I am recalling an incident very vividly I go back to the instant of its occurrence: I become absent-minded, as you say. I jump back for a moment. Of course we have no means of staying back for any length of Time, any more than a savage or an animal has of staying six feet above the ground. But a civilized man is better off than the savage in this respect. He can go up against gravitation in a balloon, and why should he not hope that ultimately he may be able to stop or accelerate his drift along the Time-Dimension, or even turn about and travel the other way?"
The idea of memories being a way to time travel brings into thought a swell of philosophy. Is time really just a figment of consciousness. A way for humans to make sense of the world, to traverse it, to learn from it. Many scientists seem to think so (1). A mind altering realization that I can’t truly grasp fully. But what if in a way thinking of time as just a construct of the mind might reveal an ultimate interpretation of this extraordinary tale that’s being told. I’m sure it’s read that way by some.
Also, ‘if ever a creature could figure out time travel it’s humans’, believes the Time Traveler. His distinction between “civilized” man and a “savage” is problematic to say the least, but we’ll revisit that later because it has major bearing on how our protagonist sees the world.
Distinguishing the 4th dimension of Time as another measure of existence (like the 3 Euclidian measures of height, length and width) is a way for the reader, and the dinner party audience, to conceptualize it as a plane that we can move along. Today scientists still haven’t cracked the code of time travel and some contest Time being the 4th dimension at all. (2)(3)
“The peculiar risk lay in the possibility of my finding some substance in the space which I, or the machine, occupied. So long as I travelled at a high velocity through time, this scarcely mattered: I was, so to speak, attenuated— was slipping like a vapour through the interstices of intervening substances! But to come to a stop involved the jamming of myself, molecule by molecule, into whatever lay in my way: meant bringing my atoms into such intimate contact with those of the obstacle that a profound chemical reaction-possibly a far-reaching explosion-would result, and blow myself and my apparatus out of all possible dimensions into the Unknown. This possibility had occurred to me again and again while I was making the machine”
Here the Time Traveler is describing his first, future time warp. Imagine flying through time and seeing your home, and world as you knew it, vanish. It reads as an incredibly disorienting experience. And this possibility of stopping at the wrong time and fusing with some obstruction in his position seems like a massive red flag. The logic that Wells presents shows how deep he went in imagining what time travel would be like. He intuitively analyzed many of the potential pitfalls that could occur.
“What might appear when that hazy curtain was altogether withdrawn? What might not have happened to men? What if cruelty had grown into a common passion? What if in this interval the race had lost its manliness and had developed into something inhuman, unsympathetic, and overwhelmingly powerful? I might seem some old-world savage animal, only the more dreadful and disgusting for our common likeness, a foul creature to be incontinently slain.”
And here begins the traveler’s speculative musings on the futurity of man. I enjoy this aspect of the story in particular because of my own fascination with humanity’s future. Here he contemplates what we might turn into. Projecting forward, knowing that our species has a long history of warring against each other, it would be a safe bet that that would continue. It has for some time. But is it intrinsic to what our species is? One read of this quote is that the Traveler thinks cruelty is currently uncommon, and that we might devolve into being cruel creatures. Wells and the Time Traveler are from England. They grew up as citizens of a colonial power, used to a culture of cruel conquest. They are also used to thinking that to maintain their civilization some other peoples need to be on the sacrificial end. This dichotomic mentality deems all other lives expendable on their route to control, and maybe this line of thinking from the Time Traveler is an example of that mentality bleeding over into his predictions. When I read that last sentence of the quote I couldn’t help but think about the British colonist’s warped rationale for incontinently slaying the indigenous peoples of Australia or N. America. A bit of projection maybe?
Now he’ll actually stop at a time, far different than his own. A moment in time where mother nature’s diversity has been restored, while humanity is “upon the wane.”
“You see I had always anticipated that the people of the year Eight Hundred and Two Thousand odd would be incredibly in front of us in knowledge, art, everything. Then one of them suddenly asked me a question that showed him to be on the intellectual level of one of our five-year-old children- asked me, in fact, if I had come from the sun in a thunderstorm! … A flow of disappointment rushed across my mind. For a moment I felt that I had built the Time Machine in vain.”
The anticipation of a progressive revolution speaks to his belief in humanity’s continued evolution (whatever that means). It can be coming from a societally egoistic perspective or a self-ego perspective, being that the Time Traveler can see himself as a revolutionary inventor. Thinking that we will always be progressing doesn’t take into account the pitfalls that come from our expansion.
I think that Wells actually does a nice job in creating this character that doesn’t get lost in himself too much, and tends to stick to ideas about the world. He rolls with the punches of having some of his hypotheses turn out wrong. He is human of course and does have brief episodes of existential dread, but the plot is more important than character to this story. In a way it is more captivating that way. The protagonist can be an amorphous entity for the reader to plop themselves into to experience the imaginary world of time travel.
Meeting the Eloi people in this moment shatters the glass of that societal ego. Our traveler was so looking forward to ascertaining the future’s wisdom. My interpretation is that The Time Machine is unwittingly prophetic in distinct ways. And that the future’s wisdom is revealed. More to come.
“For the first time I began to realise an odd consequence of the social effort in which we are at present engaged. And yet, come to think, it is a logical consequence enough. Strength is the outcome of need; security sets a premium on feebleness. The work of ameliorating the conditions of life-the true civilising process that makes life more and more secure-had gone steadily on to a climax. One triumph of a united humanity over Nature had followed another. Things that are now mere dreams had become projects deliberately put in hand and carried forward. And the harvest was what I saw!”
“Social triumphs, too, had been effected. I saw mankind housed in splendid shelters, gloriously clothed, and as yet I had found them engaged in no toil. There were no signs of struggle, neither social nor economical struggle. The shop, the advertisement, traffic, all that commerce which constitutes the body of our world, was gone. It was natural on that golden evening that I should jump at the idea of a social paradise.”
He finds a world where the small population of Eloi are thought to be our last descendants. There is very little modern architecture left, and even less not fully claimed back by vegetation. Wondering why there are so few people left and why no one is doing any work, he speculates that it might be the logical order of a fully realized civilized world. A utopia of sorts where life is so easy that we have adjusted to a life of physical and mental sloth. The idea of the exponentially increasing civilizing process is a prevalent idea in present day thought. First it assumes that civility = collective good, when practically speaking only a subset of our population benefits from this modernity while the other part either toils to maintain it or gets excluded from it. Which brings up another variable when projecting forward, which is; what happens to class and human exploitation. The trend of modernity, industrialization, civilization or whatever you want to call it hasn’t necessarily been in effort to make life easier in those respects. Some technologies and medicines have of course had positive effects, but toil and hardship has stayed steadfast (4). You can even argue that there were many ‘primitive’ societies that lived more sustainably and with less toil than us (5). What I’m ultimately saying is that “ameliorating the conditions of life” can be helped of course by developments in our understanding about the world (such as in medical science and tech), but that one of those developments has to be an egalitarian and democratic society. At least if we want to shoot for utopia.
Anyway, this timeline of history doesn’t entirely hold up as the Time Traveler searches for more clues.
“Very simple was my explanation, and plausible enough—as most wrong theories are!"
We cannot fully affirm the Time Traveler’s conjecture anymore because he has proven himself fallible. Yet he does make some convincing arguments for certain aspects of the changed world. These must be considered. I like that he’s not an all knowing narrator. He is trying his best to have educated hypotheses about this confusing new age.
“Even in our own time certain tendencies and desires, once necessary to survival, are a constant source of failure. Physical courage and the love of battle, for instance, are no great help—may even be hindrances—to a civilised man.”
Here I agree with him that our proclivity for battle is a negative. I feel linking “physical courage and the love of battle” either doesn’t translate well to today (and I’m not understanding) or they are distinctly separate tendencies. You can be courageous and put your body on the line for the greater good of humanity; hence it wouldn’t be a hinderance. That can be through battle or it can be through other means like protest. And once again the Time Traveler makes a distinction here between civilized man and humanity in general. His use of vocabulary like “savage” and “civilized” throughout the novella depict a man who sees himself as a distinct version of humanity or an entirely different being in general. One that’s superior to other peoples. This thinking is in line with 19th century European views and informs their creation of the defunct classification of race (6).
“The Time Machine was gone! At once, like a lash across the face, came the possibility of losing my own age, of being left helpless in this strange new world.”
After a day getting acquainted with his surroundings he gets this heart stopper. Coming to the conclusion that his invention must have been moved deliberately, he begins his search for the culprit. It couldn’t have been the “indolent” Eloi. He befriends one of them that he names Weena and she joins the traveler on his explorations.
“But, gradually, the truth dawned on me: that Man had not remained one species, but had differentiated into two distinct animals: that my graceful children of the Upper World were not the sole descendants of our generation, but that this bleached, ob-scene, nocturnal Thing, which had flashed before me, was also heir to all the ages.”
His first encounter with the Morlocks, the Eloi’s underground counterparts.
“At first, proceeding from the problems of our own age, it seemed clear as daylight to me that the gradual widening of the present merely temporary and social difference between the Capitalist and the Labourer, was the key to the whole position.”
I had to stop and think about this one. Could it be possible for a class divide of peoples that stretches on for millennia to actually produce distinct creatures? I think 800,000 years is long enough for a species to evolve some changed features, especially moving down into a subterranean environment. Still, the people that lived there would have to have been forced to live there by the upper worlders. In a Capitalist vs laborer dynamic we know from history that uprisings would likely occur amongst the subjugated class which would make it difficult for the dynamic to stay so divided. Especially if the Eloi ancestors were dependent on the labor that the Morlock ancestors were producing, as the traveler hypothesizes. As long as humans have been organizing together there have been some who selfishly try to extract a bigger piece of the pie at the expense of others; at the expense of equality. I think Wells recognizes an existing class divide and extrapolates out from there to create a semi-logical science fiction future. From a capitalist’s perspective having a labor force trapped underground, unable to complain or taint the image of your exclusive eden, seems ideal. This imagery is extremely reminiscent of another classic short story called The Ones Who Walk Away from Omelas by Ursula K. Le Guin (7). Wells’ conceives of many possible variables that might’ve shaped his world, but leaves room for a reader to interpret. I want to take some of his prophetic descriptions and offer up my own reading after the following quote.
“I think I have said how much hotter than our own was the weather of this Golden Age. I cannot account for it. It may be that the sun was hotter, or the earth nearer the sun.”
Well Wells, maybe it was hotter because of human induced climate change. There are plenty of anecdotes in the story that describe humanity as the main arbiter of earth’s future changes. We all tend to acknowledge that as a matter of fact. The agricultural and industrial revolutions proved that we, more than any other species, shape the landscape of the world. But having the hindsight of 21st century knowledge really informs how I see The Time Machine. In the story humanity has decreased in numbers drastically, has devolved in its intellectual capacity, and our infrastructures have collapsed. Humans no longer are “progressing” in the modern sense where progress gets unnecessarily linked with expansion, extraction, and exploitation. Perhaps they are just living sustainably like any other creature. I know a small mention about the climate being hotter doesn’t explicitly point to climate change being the culprit for the Eloi’s reality. Still, could it be that the big existential crisis of our time was never remedied and this led to mass degradation of human society? Some of our smartest minds tend to think this is what’s coming for us (8). Maybe the forces of change ran half of humanity underground and that’s what birthed the Morlocks. Maybe traversing time in The Time Machine was in effort to glimpse into our unassured future.
“However great their intellectual degradation, the Eloi had kept too much of the human form not to claim my sympathy, and to make me perforce a sharer in their degradation and their Fear.”
A great example of the simplistic inclination we have to sympathize with who/what-ever looks most like us. It’s not to say it’s not practical because instinctually we gravitate towards our families who of course resemble us the most. But to overlook the science in favor of habit and familiarity has put humanity at odds with itself and the ecosystem. No matter the race, nationality, or however we choose to divide, the science says that we are all practically the same, with the same basic needs and desires. The same is true of us and the rest of the biosphere full of carbon based life forms. Disassociating ourselves from that collective has given us the illusion of invincibility. The repercussions will be severe.
“I felt the intensest wretchedness for the horrible death of little Weena. It seemed an overwhelming calamity. Now, in this old familiar room, it is more like the sorrow of a dream than an actual loss.”
Finally after many dramatic happenings (that I can keep listing but I genuinely recommend you read) the Time Traveler has found his machine and is able to return to a more familiar time. Recounting his experience is almost like thinking on a dream. His friends will hardly believe the tale and maybe some part of himself doesn’t either. Remember, if time is truly a construction of a conscious mind then maybe the time machine was merely a device that allowed the traveler to explore their own minds imagination of a prospective future. An experience akin to a deep psychedelic trip or lucid dreaming. In that case he might have thought that progress was inevitable but subconsciously knew that civilization “must inevitably fall back upon and destroy its makers in the end.” Surely some will think he’s just mad. I choose to believe the traveler’s account and take the revelation as what’s possibly to come on our current path.
“No. I cannot expect you to believe it. Take it as a lie—or a prophecy. Say I dreamed it in the workshop. Consider I have been speculating upon the destinies of our race until I have hatched this fiction. Treat my assertion of its truth as a mere stroke of art to enhance its interest. And taking it as a story, what do you think of it?"
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/is-time-an-illusion/
https://medium.com/@imshub13/why-time-is-not-the-fourth-dimension-c520161ea6d9
https://phys.org/news/2012-04-physicists-abolish-fourth-dimension-space.html
https://books.google.com/books?id=eHT43wfyw-sC&lpg=PA1&ots=edPFq4SIKR&dq=ancient%20hours%20working%20lives&lr&pg=PA13#v=onepage&q=ancient%20hours%20working%20lives&f=false
https://groups.csail.mit.edu/mac/users/rauch/worktime/hours_workweek.html
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4326670/
https://www.ceremade.dauphine.fr/~ekeland/lectures/Mathematical%20Models%20in%20Social%20Sciences/ursula-k-le-guin-the-ones-who-walk-away-from-omelas.pdf
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/article/climate-change-predictions-2070
Please follow me on Substack
#book review#story review#h.g. wells#science fiction#science#time travel#time machine#the time machine#literary quotes#literary analysis#literary fiction
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
Rereading the Lord of the Rings series recently, and it's so fascinating to me how much the series is a denial of the typical juvenile power-fantasy that is associated with the fantasy genre.
Like, the power-fantasy is the temptation the Ring uses against people It tempts Boromir with becoming the "one true king" that could save his people with fantastic power. It tempts Sam with being the savior of Middle Earth and turning the ruin that is Mordor into a great garden. It tempts Gandalf and Galadriel with being the messianic figure of legend who brings salvation to Middle Earth and great glory to herself.
The things the Ring tempts people with are becoming the typical protagonists of fantasy stories that we expect to see. and over and over we see that accepting that role, that fantasy of being the benevolent all-powerful hero, is a bad thing. LotR is about how power, even power wielded with benevolent intent, is corrupting.
And its so fascinating how so much of modern fantasy buys into the very fantasy LotR denies. Most modern fantasy is about being that Heroic power-fantasy. About good amassing power to rival evil. But LotR dares not to. It dares to be honest that there is no world where anyone amasses that power and remains good.
I guess that's one of the reasons its so compelling.
#Lord of the Rings#LotR#lotr#literature#fantasy#literary analysis#analysis#Galadriel#Gandalf#The One Ring#Sauron#Sam#Samwise Gamgee#Boromir#Gandalf the Grey#Gandalf the White
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
There is no easy way out of learning to be literate when it comes to fiction.
You cannot say "An author is never what they write".
You cannot say "An author is always what they write".
Authors who are completely normal people with healthy understandings of every dark topic in our work can write extremely fucked up shit about topics including bigotry, rape, you name it. If you think writing about those topics at all is "glorifying" it, then you will falsely believe those authors are horrible people.
But horrible people can actually be authors - and sometimes they hide their horribleness in ways you can't recognize. Sometimes they don't - sometimes they are just fully and openly bigoted.
But if you can't tell the difference between "A story that has fucked up shit in it because those things fit the mood, motifs, message, or genre" vs "A story with fucked up shit in it because the author thinks those things are morally good", you are going to fucking struggle in life and you will in fact be very susceptible to bigoted propaganda.
And no, I won't sit here and say it's always easy to tell the difference. But with practice, you can in fact tell the difference between a story where the author is writing about the main character being ravaged and raped in a sexy way because it's a safe way to explore that fantasy, VS, an author who clearly just thinks women should be raped and subjugated because that's their actual worldview.
That can involve examining the individual piece of media, other things that author has written, who the author is, etc.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
I've been thinking about the fact that some readers of Sense and Sensibility don't believe Willoughby truly loved Marianne, even though everyone in the book believes it and the narrator makes it clear how much he cared for her, at the end. And I think this reading of him takes away from one of the messages of the book, which is that love is not enough.
Willoughby loves Marianne, but that's not enough to stop him from hurting her, it's not enough to make him give up his cushy lifestyle and marry her, and it wouldn't have been enough to keep him happy with her long-term. Marianne loves Willoughby, but it wouldn't have been enough for her to be happy with him long-term either.
Edward loves Elinor, but that's not a good enough reason to break his promise to Lucy, because integrity and honor and responsibility are just as important to him. Brandon loves Marianne, but that's not reason enough to court her, because he knows her feelings lie elsewhere and she doesn't respect and esteem him yet.
Love is important to all these characters, and is a vital part in making the marriages that they ultimately end up in strong and happy, but it's not the only thing that makes them work.
Of course, Sense and Sensibility is hardly the only Austen novel to make the point that you need more than love or romance or passion to make a relationship work. But I think it's interesting how we get to see this play out in the villain of the novel. Willoughby does some truly horrific things, but his character shows that even really bad guys are capable of feeling love and guilt and remorse. But none of these feelings are ultimately strong enough to change him. Because love is not enough.
760 notes
·
View notes
Text
Critical Role's Cameraman
So, Critical Role (@criticalrole) just released their newest opening title sequence, an animated sequence in the same style of Your Turn To Roll and I would be remis as a film nerd to not pick apart every detail.
What fascinates me about this introduction, however, is the camera movement and shot composition. Allow me to explain.
I DONT THINK THERE ARE SPOILERS AHEAD, BUT JUST TO BE SAFE

So, we open with a hand, this is a close up, I don't think that is unobvious.
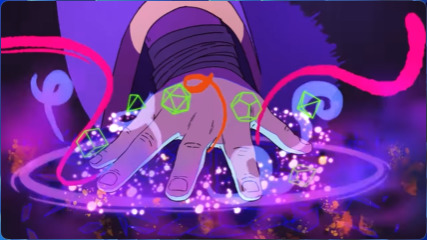
But this stops being a close up rather quickly, before it starts moving away. The shot just gives the hand context, and suddenly you aren't in an extreme close up of a hand, you are in a medium shot of a very large person. Then the camera pans backwards, and you can see villains and places spring up, although the perspective on Matt remains weird. Is he a few metres from you, or a hundred? How big is the Game Master here? There's a sense of mystery, of incomprehension. This is setting up some cosmic horror shenaniganry.

Then, we get Fearne. This is a wide camera motion, swivelling around her in a tracking shot that focuses on her face, and those eyes. It is like a reverse panorama, where Fearne is taking in the world, the world is observing Fearne.

But I want you to take note of the leaves here, because they are used to form a connection between her and Orym. The transition uses them, while it isn't a direct wipe transition (the leaf just flies close to mask an abrupt cut), it is framed as one. The name of that isn't important, though, what's important is the leaves. By being in both shots, they emphasise the relationship between the two characters. But where for Fearn they show off her sense of wonder, for Orym, they take on a very different meaning.

Notice, however, how still this shot is. There is no sense of danger here. This is a scene of a warrior with a sword and two people passing on from this world. But it's calm. Because this is a memory. Orym might not be at peace with the death, but the memory isn't a violent one, it's a memory of his family's lives.
Cut to a close up. Orym creates a gust of wind.

And cut to the next shot.

I will not lie, Bertrand is my favourite character across all of Critical Role, so this shot of him made me smile, but it isn't the point here. The point is Imogen's introduction.

Although is Bertrand not actually the point? Because take a look at how Imogen is shown here. Do you notice anything?
She's shown in the exact same way. Imogen is shown doing the exact same thing that those who have died have done. And she can see them ahead of her. The camera panning back shows a wider perspective here, showing her as she tries to run, tries to get away from the same path as Bertrand.
The wind from Orym's blade that came to this scene gets across a consistent element: Memory. This is a dream. But dreams can become nightmares.
As Imogen loses her footing, the camera gives some of its wildest movements yet. It tumbles around her, then looks up.

The camera stops moving when it sees the red moon, because now the viewer has something to orientate themselves around. There is a constant point, and we can see Imogen falling down. And getting closer, and closer, and closer, until.



These are the three frames in order, there is nothing in between.
Imogen crashes into the screen, and we get an abrupt impact frame (that's the black and white one) then Ashton. This is so cool to watch, in my opinion, but it is quite possibly the opposite of smooth in camera work. So why is it so cool? Motion.
The motion is in towards Imogen and out away from Ashton. They are both falling, just in different directions. And the impact frame both helps smooth over and accentuate the abrupt transition.
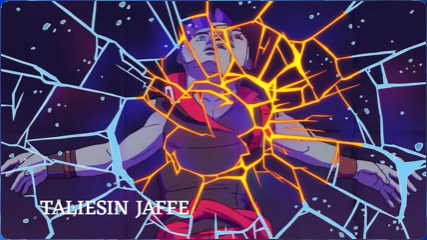
The camera around Ashton is a tracking shot. They are falling, but they remain the exact same in the screen (shrinking slightly). The rest of the world moves. And when Ashton lands, the screen cracks. The tracking shot is used to show Ashton's disassociation with their surroundings. Not in a "I feel nothing" type of way, but in a "it's me vs the world" type of way.

Then, there is an abrupt cut away. Nothing hides or smooths this at all, because Ashton's memory isn't smooth, and neither is Ashton. Remember the disassociating thing I mentioned, now it changes again to someone who gets lost in his thoughts. Medium.com calls this an "anxiety stare" and as someone who does that on the regular, I can attest to this abruptness being exactly what that feels like.

I'm not going to talk too much about the ship, but just be aware that there is a Dutch angle (the horison is diagonal) here to heighten the stress of it.

Likewise with this shot, there isn't much to talk about. The slow outward zoom and triangular composition are neat, and the tiered reactions (bottom row reacts, then middle, then Fearne) are amusing, but other than that, not much.

Then we meet Laudna, playing with Pate and giving him life. That's a neat little shot, I wonder if there's a metaphor there.

Oh.
This is a super cool visual because it establishes exactly who this character is in two seconds. But I also want to point out the symmetry of this. The hair becomes the blood which becomes the hair again, and then the tree.

Laudna is introduced as big and scary and imposing, and that is very intentionally undercut by making her look small.

Being small means you are less likely to be the focal character, so shrinking Laudna takes away her agency. Only to give it back through Imogen, and when the camera pans back outwards, Laudna is the same size, but the colours and the surroundings make her feel less alone, and as a weird result of that, less small.

And last but not least in this moment, there is the delayed drop of the hands. Laudna finally feels safe and finally breathes a sigh of relief.

That, however, imediately match cuts to this. FCG's vision. The red tinting has obvious implications that I don't need to explain, but the match cut heavily implies a connection between this group and the Bells Hells. There is a fear that this might happen again made clear by a single transition.


Here's something else. FCG doesn't move. At least, the camera doesn't treat them as moving. It's a slow panning out as if nothing is happening. It's the disassociation vibe that you get from Ashton's falling shots now repurposed to someone who isn't in control of their own actions. This is what FCG is afraid of, this is the important pieces of his character. This is FCG.

And just like Laudna, FCG finally gains agency when surrounded by their friends who hug them, and FCG finally moves.

Chetney Pock O'Pea, outlaw of the RTA, alpha of his own heart. A fundamentally chaotic character who takes rules as suggestions to be intentionally ignored. A man who's first instinct upon meeting you is to consider how you could be killed. And he is introduced whittling, with a steady camera and warm light illuminating his face. This is a peaceful side of Chetney, there is a duality to him.


Speaking of which, notice how Chetney draws back from the light as he transforms. His eyes begin to glow, but they don't illuminate him, until this:

Chetney is now backlit by the cold light of the moon itself (There's a neat reveal of Ruidus caused by the pan, but that's only tangentially relevant). Notice how much further you are from him here than in his first shot. But notice how much of him is visible, and how much of the screen he takes up. It's the same, this is still the same character. It's a true Doctor Jeckyl and Mr Hyde character. This isn't split personality, but a character who can be a different person in each form, while still remaining Chetney at all times.

There is more in this video. I encourage you to watch it, but unfortunately, Tumblr has a limit on how many images I can include, so I will leave you with this final shot. A group of heroes looking up at a threat that is so much bigger than them, a threat that is literally controlling the light. But the Bells Hells are closer to the camera, they take up more of the screen. The battle isn't lost, instead, it is just starting.
#rants#literary analysis#literature analysis#media analysis#critrole#critical role#bells hells#imogen temult#laudna#ashton greymoore#fcg#orym of the air ashari#fearne calloway#chetney pock o'pea#its Thursday night#critical role bells hells
516 notes
·
View notes
Text

Let this be a living example that knowing the beliefs of any individual who wrote any piece of text- be it literature, articles, or posts- can and should drastically alter your perception on what the text is actually communicating, even if that knowledge has, on its face, changed none of the actual printed words. This is how application of real-world context works, and this is how it applies to any recorded medium.
It reminds me heavily of a quote from video essayist Jacob Geller, regarding the 1938 film Olympia- "It's different when Nazis do it".
Olympia is a film that, on its face, simply depicts an artistic documentation of the 1936 Berlin Olympics. But within the context of its production taking place during the Nazi regime, with its director being a well known Nazi propagandist... The way the movie fixates on the power and elegance of the human form and Ancient Greek statues quickly shifts from being completely innocuous appreciation to the worship of what is perceived as the ideal forms of the "Aryan race". Suddenly, you understand the movie not to be a pretty inoffensive documentation of a historical event, but a propaganda piece.
Understanding the time period in which something was made, as well as the setting it was produced in/for, and whatever ideologies an artist may hold and experiences they've had is absolutely critical to getting a full understanding of anyone's work. There are some things that are near completely anodyne on their face, but the revelation of what the author thinks and feels about other people and the world around them totally redefines every word on the page.
This image is such a prime example of why context matters. This opinion, laid bare, stripped of context, is both inoffensive and nonsensical. No one's ever thought it to be lame to create your own nickname... But on its own, that's a harmless kind of wrong.
... But with the addition of them being marked as Anti-Trans (red) on Shinigami Eyes, a browser extension dedicated to crowdsourcing keeping track of Trans Friendly and Transphobic creators... Suddenly, "Nicknames" doesn't mean "Nicknames" anymore. Suddenly, you realize that "Nicknames" is code for "Chosen Names of Trans People". Suddenly this isn't about thinking choosing your own nickname is lame, this is about thinking that trans people shouldn't have the right to name themselves. Suddenly it's about invalidating identities, thinking they're worth mocking. Thinking that people who identify as trans are "just trying to be cool", and that they're not actually what they say they are, because you don't get to choose your gender nickname, that's something already decided for you.
Suddenly, you realize, it's not about "being lame".
It's about Transphobic Violence.
This is why you cannot ignore when an artist, author, essayist, developer, musician- so on and so forth- is bigoted. This is why you can't ignore the context behind their upbringing. This is why you can't ignore the context behind their lived experience, their ideals, their goals, their message. Yes, it may appear innocent on its face. Yes, it may look fine stripped from the context of it being written by an inevitably flawed human being. But what's really being said here? What do those words mean... To the one who wrote them?
Context redefines Text.
Even if the words didn't change.
#this post is a bit random. not apologizing. it was just such a perfect encapsulation#i am still tagging this as homestuck because this is ultimately EXACTLY how i feel about hussie + their works. you must understand this.#its so applicable to hussie + homestuck + analysis of homestuck that it is fucking painful. PLEASE understand this. PLEASEEEE#homestuck#homestuck meta#homestuck analysis#andrew hussie#context#literary analysis#essay writing#cw nazi#cw transphobia#nekro.pdf#nekro.txt
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
emma is the villain of tgwdlm
I need to talk about this oh my god
because it's told from the hive's perspective. paul is the protagonist because he is the one who resists them but must ultimately come to accept that they're right. emma is the one who must be beaten through force.
the difference between the hero and the villain is that the hero must change, while the villain cannot. (I'm not speaking in universals here, just generalizations of how the narrative structures work that tgwdlm uses in parody.) the hero and the villain both hold a belief that represents the thematic evil; by the end of the story, the hero must undergo apotheosis, which is to say, ultimate unity with the thematic good. once this is achieved, he can defeat the villain, who represents the thematic evil completely and is incapable of change.
to the hive, "good" is unquestioning conformity to the group's ideals, specifically, singing and dancing in sync with everybody else. "evil" is refusing to sing and dance along when, clearly, you want to.
paul is the perfect protagonist because he resists song and dance, but largely because it makes him uncomfortable. getting out of your comfort zone is necessary for change! it's a good thing to let yourself go through something uncomfortable in order to come out the other side better and stronger for it. (that much is true; however, sometimes discomfort is a legitimate sign that you should stay away from something.) paul has never really tried singing or dancing, and deep down, is afraid that if he tried it, he might like it. exactly the sort of person who can be converted and used as a shining example of the hive's righteousness.
emma must be the villain because her refusal to fall in line is a choice. she can sing, she can dance, she was in brigadoon in high school and she fuckin killed it, she is even taught a whole ass song with choreography by the hive on their first morning in hatchetfield (emma's comment about how they have to sing "all the time, apparently!" and zoey's implied presence at the theater when the meteor hit - because she was with sam, and sam was there - strongly suggests that nora and zoey were zombified all morning and she had no idea). it's stated by hidgens and suggested by nora and zoey that getting a human to sing/dance along with them is supposed to be a sort of mesmerizing tactic that the hive uses to start synchronizing a person to the hive mind, but emma refuses. she sings and she dances, just like they want, but she chooses to actively hate it the whole time, on principle. she can't be convinced; they have to swarm her, surround her on all sides. let it out is meant to win paul to their side; inevitable is just to gloat.
in the bar scene in hidgens' bunker, emma says that she must be the villain to paul's hero because she was in the musical that got him to hate musicals. on the one hand, she had it backwards; she's the villain because according to the hive, the all-encompassing narrative power, he's not supposed to hate musicals. on the other hand, she's kind of right: paul is the protagonist because he is the guy who didn't like musicals, while emma is the villain because she has the capacity to like musicals as well as experience in them, but has chosen to reject them.
who is the hero and who is the villain all depends on who is telling the story. and the hive is telling this story. don't forget that.
#starkid#team starkid#the guy who didn't like musicals#tgwdlm#media analysis#literary analysis#hero's journey#tgwdlm emma#tgwdlm paul#emma perkins#paul matthews#lauren lopez#jon matteson#nick lang#matt lang#jeff blim
299 notes
·
View notes
Text
As much as I love Disco Elysium, I think I was not prepared for Sacred and Terrible Air. Of course, I was expecting to know more about the world of Elysium as a whole, and Robert Kurvitz is a very good writer, but the thesis of the novel (and how it makes its points) flash-banged me.
Disco Elysium this is not, and it wasn’t supposed to be, but I think I can understand better now what the team at ZA/UM was getting at with this specific setting, and these specific narrative angles. Kinda messy, because it’s been a week since I finished it, but here are some things I’d like to highlight:
1. The pedophilia. I surely wasn’t expecting this to be such a central theme of the novel, but a lot of its main points revolve around it. The most interesting use of this, as a narrative device, is how the girlfriend of Jesper basically accuses him of being a pedophile because he cannot relate to the adults around him. He’s still obsessed with a girl he met when he was 13 years old, and fetishizes a scrunchie he stole from her bag two decades ago. Yeah, I guess Jesper, well into his thirties, is still in love with a 13 year old girl. His girlfriend is almost half his age, and they started dating when she was 15 years old and a lingerie model (!). Zigi mentions how pedophilia was a bougie disease, and well… That idea went right into my thought cabinet (I call it “Bougie Babies for Sale).
Still processing it.
Now, let’s go back to the rest of the main characters. With all this in mind, a pedophilic overtone covers their interest in these four missing girls, but Jasper is the only one who acts on it, sort of. Khan remains in a sort of arrested development (he still uses a shirt he had when he was 13), foregoing normal adult relationships, and Tereesz joins the police as an investigator with the idea of still finding them some day (essentially letting these eternally prepubescent girls define his entire existence), leading him to a very dark path. I wonder if the brutality they afford to the “actual” pedophiles in the story (Vidkun Hird and the Linoleum Salesman) comes from the realization that they are not that different?
2. Obviously, though, this fetishization of the Lund sisters is also a fetishization of the past. The novel states it in the first few pages; they disappeared twenty years ago, in a time that most conservative people remember as the “good old days”. Basically their version of the American Fifties. Now, being obsessed with the past is a running theme in both SaTA and DE, but the angle here is different.
I already said it: the past is not remembered, is fetishized with an almost sexual yearning by a lot of the male characters of the book. They want to be consumed by it (and lucky them! It will) and do nothing more than serve it. It reminds me of a poem by Yamil Nardil Sadek, which, translated to the best of my ability, goes like:
She awaits me
sitting on the bed,
wearing leather,
and armed to the teeth,
the Memory.
Yeah, that sums up Sacred and Terrible Air pretty well. Everyone is being consumed by the past, bite by bite, and enjoying it. Vidkun Hird, by the mythologized version of his tribe’s history; Sarjan Ambartsumjan, by a miniature ship model that requires constant, devoted thought or else it will disappear, the three main characters by the memory of that summer with the Lund girls. Even the Linoleum Salesman is being haunted and consumed, of sorts, by his sickness and dementia that only sometimes let him take a peek of the past. Beyond that, there are very few characters that do not spend time being followed by relentless ghosts. Literally, in the case of Zigi. Which brings me to…
3. The Pale. It was a really cool concept in Disco Elysium, and it’s an existential nightmare in Sacred and Terrible Air. It always was, really. But here it lets you take a look into it in a way that’s applicable in real life. The Pale is a metaphor for many things, but actually for a single one: A world where our current Capitalist reality facilitates both apathy and yearning for better days, often idealized in our collective pasts.
My favorite scene, one that was incredibly puzzling but so obvious in retrospect, is a beautiful speech by the ghost (?) of Ignus Nilsen to Zigi. I will just paste it here:
“I said terrible things, yes! I stood on a white horse, in a blizzard, and gave speeches. In the mountains, on the construction site… I swung my sword, with silver sunbeams on the hilt. And all around me fluttered white flags, crests of crowned horns made with silver thread, a pentagon between the prongs of the horns, the branches raised to heaven. Everyone who came here with me became happy, Zigi! Communism is powerful! Believe in Communism, it’s a burst of enthusiasm! I promise! It’s beautiful when you believe in a person, but without it…!”
“Without it, there is nothing.”
“Nothing. It was a blizzard, but it was bright, it was morning. Communism is white, it sparkles! Communism is the morning, it is a jubilation!”
The Pale begins to recede dangerously around the entroponaut.
The fucking Pale recedes with talk of Communism! At first it might appear a little heavy handed (yeah, Communism, by itself, could save the world). But then I got into how Communism could be a solution to the antipathy and chronic nostalgia that sustain Capitalism, and then it hit me. Nilsen, a literal ghost from the past, is talking about a future that could have been. That he wanted to accomplish. That people, probably, can still achieve. The Pale is not eternal, it can be pushed back. Because the Pale seems to subsist on the past, it abhors any talk of the future. A better future. That’s how we solve things, and for a central thesis, is not bad at all.
With that being said, and because I’m just rambling here while pretending I’m working, there are also some things that I just didn’t understand, but maybe it was because of the translation. The original novel is written in a very poetic style, and some of that is still here, but I still need to untangle…
1. The Man. It is said that the day the Lund girls disappeared, they were joined by a mysterious Man that nobody seemed to remember correctly. A character even suspects that she was remembering wrong. Now, the Pale erases people and memories retroactively, so maybe it had something to do with it, but… Who was that? Is there any theory about that Man, or I just missed something? Some scenes and narrations were tough to parse for me (my primary language is not English).
2. Was Malin Lund pregnant? That flash with the fetus was sudden and weird.
3. What was the significance of the three meat piroshkis? They mention that it was unusual that the girls bought them (and if you do the math, you can realize early on that they were not planning to get back home. That purchase didn’t leave them enough money for the bus fare back), but that’s it. Were they for the Man? Also, the narration mentions that Lund girls’ picnic basket contained “the kind of things girls like to eat”, so maybe they were planning to see the boys and bring them the kind of things boys eat? I’m overthinking that? The chapter actually titled “Three Meat Piroshkis” just left me even more confused.
4. I don’t understand how Khan’s pen works at all. The one he brought to the school reunion. That was the part I re-read the most.
Anyway, even with that, I loved Sacred and Terrible Air. Definitely one of the most enthralling reads I had, with or without the background of Disco Elysium. I’d still like an official translation that could potentially solve the issues I had, but for now, a Top 10 Book for me.
Go for it now.
221 notes
·
View notes
Text
For the record, and I will die on this hill, the actual message of Jurassic Park - including the book and the movie - is that we don't have any control, not even over ourselves.
This works in multiple ways, but especially in a meta way:
crichton was originally trying to write a story against unregulated genetic technology. no one, ever, has this takeaway. so he did not have control over how people take his story.
spielberg was doing that, but also "wow look at dinosaurs, look at how birdie and alive they are". some people have that takeaway. most people don't. so spielberg also does not have control over this story.
(remember guys, death to the author, it doesn't matter that this is what they were trying to say. also crichton sucks so who cares about him.)
most people see the story as "dinosaurs are inherently monstrous and we can't possibly live alongside them." this is not what the story says, at all. the story itself cannot control how people see it.
people who are keen observers of the story see how it is really saying unregulated capitalism leads to bad results - nedry is really the cause of many of the problems and its because he was overworked and underpaid. But this is not the intent of the authors, nor really what the narrative points to (as @thagomizersshow pointed out). So that message falls incredibly flat and has many holes. So not only is that not really the message, it is also not something people with decent meta analysis skills can control.
Throughout the story, it is constantly pointed out how little control people have of their surroundings. Hammond is the obvious example, but every character has moments where they wish they could act differently and can't, because they don't have control.
The theme of chaos runs throughout the entire story, not just because of Malcolm, though obviously he pushes it
Even the dinosaurs don't have control, and that's why they freak out - they want freedom, they want their own lives, but they can't have them. Their lack of control even to the extent that we have in nature leads to their own deteriorating mental states and eventual erratic behavior
all the characters - human and otherwise - are at the mercy of forces of nature beyond their control, throughout. the weather, the island itself, but the humans are at the mercy of the dinosaurs, and the dinosaurs are at the mercy of the humans.
in the end, the characters' choices at the climax are inherently limited by other characters' choices at the start, showcasing how little choice we actually have access to (and thus how little control)
yes, as far as we can tell, living beings have free will and are able to make choices. but what choices we have access to are extremely dependent on both ourselves as organisms and our environments that we live in. We do not have control over anything, not even ourselves.
And that is the message Jurassic Park carries, even if few people ever see it. Because it is so inherent to our lives that we ignore it.
After all... how much of the narratives we have in society imply we all can control ourselves completely?
And how much will that all break down when we admit we can't?
852 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why all the ducks? 🦆
Good Omens has always been my favorite book. I've seen some posts from people wondering about the prevalence of ducks. I wanted to share my interpretation of why the ducks keep popping up* so that other people can appreciate how clever the writing in my favorite book is.
The word duck is in the book a lot. Aside from the actual ducks in the duck pond, there are several references to popular expression about ducks. Notably all the duck quotes are botched or incorrect in some way, so the reader has to know what the correct expressions actually are in order for the joke to work. For example:
Crowley forgetting the phrase "like water off a duck's back":
"Ducks!" [Crowley] shouted.
"What?"
"That's what water slides off!"
Aziraphale took a deep breath.
The same phrase is referenced later:
whenever she tried to think about him beyond a superficial level her thoughts slipped away like a duck off water.
And we have "like a duck to water" to describe Aziraphale's dancing
while he had initially taken to it like a duck to merchant banking, after a while he had become quite good at it
The English language has a lot of expressions about ducks and the book expects the reader to be familiar with them. The one that I think is significantly conspicuously absent from the book is "If it looks like a duck and it quacks like a duck, then it's a duck." I think that the point of the other duck expressions is to evoke this one, since it's the whole thesis of the book.
Good Omens is about humanism and self determination. Adam isn't human, but he is shaped like a human so grows into being a human. He looks like a human and quacks like a human. He is a human. His parents are his parents. His hellhound is a cute dog. And he chooses to keep it that way. Aziraphale and Crowley get so used to being human shaped they'd prefer to keep doing that. They don't have to be enemies and can determine their own fate, just like Anathema and Newt and all their other mirrors. So by choosing humanity and embracing what I guess you could call human performativity, they all get to be what they want to be.
So I think that's the significance of the ducks.
*despite Crowley dunking them
625 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wille's Crisis : an essay about Kris (1934) and Young Royals (2021)
While watching Young Royals’ third season, I couldn’t get Karin Boye’s novel Kris out of my head. As a fan of Young Royals that feels very chill and very normal about it, I have hence written a five page brain-dump on how Malin Forst and Wilhelm’s characters and worlds are intertwined. (Small disclamers : I’m quoting Amanda Doxtater’s 2020 english translation of the novel and I’m french-canadian, so english is my second language.)
Who is Karin Boye ?
Karin Boye (1900-1940) was a leading figure in Swedish modernist literature and poetry. In 1920, at the age of 20, she studied one year in Stockholm to become a primary school teacher and after graduation, continued teaching, writing, militant engagement and several years of study in related fields. Among all of her works, the most explicitly autobiographical is her autofictive novel Kris (1934). This powerful novel explores the homosexuality and crisis of religious faith of a young woman named Malin Forst.
Malin Forst & Wilhelm
During her studies in teaching, Karin’s 20-years-old alter-ego Malin goes through an existential crisis. She feels completely paralyzed by her guilt due to her selfish inaction in the face of universal suffering, her lack of trust in institutions (educational, medical, etc.) and, worst of all, her doubts about her relationship with God. Kris also deals with Malin’s relationship to her own sexuality with the meeting of a classmate, Siv, to whom she will become passionately obsessed without ever talking to her.
We meet 16-years-old Wilhelm as a first year student at Hillerska. His failures as a royal figure and his complicated relationships to his loved ones make him feel powerless and guilty. He is thrown off balance by his doubts of the monarchic system, but most importantly, by his doubts of his life’s role model, Erik. Young Royals also deals with Wilhelm’s relationship to his own sexuality with the meeting of a classmate, Simon… Are we seeing the parallels here ?
While Malin’s torments lead her to shut down, Wilhelm screams. But both feel paralysed and don’t know how to exist out of the system they grew up in. And it’s the meeting of a same-sex student that leads them to a freer path.
« I want to see Siv. I want to be where Siv is. »
Previously, Malin considered the fusion of the will of the human with the will of God to be the most important of aspirations. Without this reference point, she has no will nor desire… until she meets another student, Siv. Her simple presence rekindles for the first time in the novel a desire, burning and forbidden: “I want to see Siv. I want to be where Siv is.” … And here is how this whole essay has come to exist. While watching season three, I joked endearingly with my friends about the way that Wille’s only hobby is to be with Simon, but I felt sad for him. Until I understood he’s on the first part of his self-discovery journey. His first true desire that stems from inside of him and wasn’t imposed by the system is “I want to see Simon. I want to be where Simon is.”
Interestingly enough, Siv and Simon both become a new manifestation of something that Malin and Wilhelm have lost. We, the reader, meet Malin when she is ‘grieving’ her old relationship to God and deconstructing her understanding of God as a single entity. Amazed by Siv’s ‘perfection’, Malin raises her to a kind of divine position with great powers. Wilhelm, for his part, feels at home with Simon because of the way he makes Wilhelm’s entire being comes alive, weightless and playful… A feeling of joy, innocence and safety he’s only ever felt with Erik before.
Anxious and desperate, Malin and Wilhelm are latching to their comfort person, making them their whole word in a way that has to change for them to grow up. After realizing Siv’s feeling for a fellow male classmate, Malin is shaken : “Only now could she see that she had embarken upon the false path of mistaking a person for what is highest and most beautiful.” Not only does this quote mirror Wilhelm letting go of his idealised conception of Erik, it is also mirrorring his realisation that Simon is not a perfectly stable and unbreakable anchor on which he can blindly rely on : “I have to take responsibilities for my own problem. I can’t drag him down with me.”
Don’t give it a name
An important part of Malin’s journey is relinquishing the power she gives to words, especially regarding God and her sexuality. Throughout the novel, she refuses to name the emotion she feels for Siv. On the day of her meeting with Siv, Malin thinks: “You, lips, I implore you to clamp so hard upon the unsayable, that not a word slips out to assert its malicious pettiness and obfuscation ! Be still, thoughts, don’t interrupt, for you have no idea what this is ! (...) Don’t give it a name, let it be just as it is, here in my blood and my eyes, life and sap ! The wonder of new creation need not be named.”
Wilhelm’s complicated relationship to words is shown in the way that he shouts his love for Simon from every rooftop, but does not wish to label his sexual orientation. In season three, he says the word queer for the first time and his voice is seeped with discomfort. He is not claiming this word as part of his identity and rather feels constricted by it, probably in the same way that every other label put on him has made him suffocate.
Furthermore, both Malin and Wilhelm wish to express themselves and experience the world, not through the restrictive lens of language, but through the sensory world. In Kris, after seeing Siv for the first time, Malin’s five senses awaken. A dialogue takes place between the sense of sight and hearing, reminding me of the way that Wilhelm and Simon’s intimacy is developped through the gentle touch of noses, the sounds of breathing, the glow of golden light and fingers lingering slightly above the other’s body… ‘Sight’ says “I’m confused. I no longer know whether I am sight or not. I envelop things and follow them as if I were touch, I hold my breath in quiet anticipation as if I were hearing, I breathe in, like one intoxicated, as if I were smell, and I drink in long, deep, draughts as if I were taste. (...) Could I be standing at threshold of some new creation ?” To which ‘hearing’ responds “ (...) Admit it - isn’t revelation through the senses at the same time the revelation of what lies beyond the senses, of what creates the senses, of the limitless feelings of eternal love ? (...)”
Checkmate
Kris’s narration drastically changes points of view in unexpected moments, moving from the pov of human characters to the pov of abstract entities. The two most important are BLACK and WHITE, two sources of cosmic powers playing a chess game whose game board is humanity.
On the one hand, WHITE represents the norm, also illustrated by threats from nature such as stormy and dangerous waters, cold, humidity and darkness, but also under the traits of the dominant society, whose rules and norms protect human beings while maintaining them in a position of submission and obedience. WHITE uses the anxious desire of his pawns (humans) as a weapon to subject them to the norm. And at first, Wille is WHITE’s perfect pawn : an anxious mess who becomes more and more obediant as season three progresses and whose ‘protectors’ are also the ones leading to his demise. Little (most likely accidental) nods to that parralel : Wille looses to Alexander while playing the white pieces in season two and interrupts his conversation with Simon to scream “The water is cold today !” at his guards on their first date.
One the other hand, BLACK is a chaotic power of life associated with desire, burning fire and passion destabilizing the established order. In the context of Kris, the norm is heterosexuality, while fire is the forbidden desire: homosexuality. This parallel is evident when Malin describes in this way the physical sensations caused by Siv’s sight: “There was no holy, burning voice within her. All that burned within her was a thirst for the forbidden after a single look cast in that direction” And based on that, I absolutely refuse to believe that Lisa put the hallway scene after a BONFIRE by accident.
I also don’t think the placement of the chess game during August’s confession to his friends is a coincidence. First, the board is oriented in a way where August sits at the junction between the black and white pieces, showcasing how the character is in a crucial moment in his journey : will he stay in WHITE’s cruches for ever or will he find the strenght to save himself ? And second, August puts a black king on the edge of the table. Not only does it foreshadow that Kronprins Wille is on his way out, it also indicates that it was a rebel and homosexual ‘power’ that guided him in his quest for self-determination, just as it was for Malin Forst.
I natt gick Gud under or how to make the lake scene destroy me even more
The poem in prose I natt gick Gud under (Last night God succumbed) stands out from the other chapters of the novel Kris, as it recounts the most decisive transformation of the main character Malin Forst. BLACK places Malin naked and at peace on the shore of a sea where she throws the words she denies. Finally at a safe distance from WHITE’s icy waters, she liberates herself from her paralysis to embrace her true feelings.
Last night God succumbed.
Perhaps it was just the hollow shell of name that went under.
But that shell of a name drew with it the power of death. I cast it off.
I see objects as they are, unwitting of the name attributed to them. I cast off their names.
I stand utterly new, on the shore of a sea. Conscience is no longer mine. I cast it off.
The will to life has made me naked. The will to life has made me see. I shall meet whatever comes with naked, open eyes.
Lisa describes the lake scene as almost religious. As he’s swimming naked in the lake, Wilhelm is shedding his crown prince shell. Leaving the waters, he is reborn. When he is standing on the shore of the lake in his white clothes, Lisa says “that is when Wilhelm grows up.” And for me, he’s ready to meet whatever comes with naked, open eyes.
Thank you ! Thank you to whoever read this far. Kris is a very complex book that, despite having read twice, I still don’t fully understand, so if you have anything new to add to this reflection, you are welcome to do so !
#lisa i hope you're still lurking#wilmon#young royals#wilhelm x simon#young royals analysis#karin boye#young royals s3#literary analysis#lake scene#lisa ambjörn
152 notes
·
View notes
Text

Quite literally the opposite of Donna Tartt's "Death is the mother of beauty[...]Beauty is terror. Whatever we call beautiful, we quiver before it."
#the secret history#tsh#tsh donna tartt#donna tartt#richard papen#francis abernathy#camilla macaulay#charles macaulay#bunny corcoran#henry winter#poetry#poems and poetry#poem#poems#dark academia#dark acadamia quotes#dark acadamia aesthetic#chaotic academia#chaotic academic aesthetic#aesthetic#kait rokowski#literature#classical literature#classics#classic literature#literary quotes#literary analysis
156 notes
·
View notes
Text
I was listening to Godhunter by the Aviators, and it got me thinking about Jim again. But specifically about what is provably the most creative kill of the series - his final stand against Bular. It was stunning visually and really good choreography wise, but it got me thinking about another fight involving Bular. One of the very first things we see in the entire franchise.
The fight between him and Kanjigar. And why I think Kanjigar wouldn't even think of doing what Jim did in that final battle. It's fascinating how differently both trollhunters use Daylight, and I have my thoughts on it to share.
Let's start with Kanjigar. As we see in Wizards, he was a warrior long before getting chosen by the amuket, and it's safe to say he has been trained in using a sword. And so even when he fights with Daylight he treats it pretty much the same as a regular blade.

Like over here. He burns himself to reach for the sword, when we know that Daylight can be teleported straight intk your palm. But it's not something Kanjigar would have had to use often because, as it's established, he is an excellent warrior. He probably is disarmed very rarely, if at all.
Not our Jim, though. He is a scrawny sixteen year old fighting giant creatures of living stone. The sword is flund from his hands constantly. And so he had to learn how to get it back in an instant or die. He is doing everything in his power to keep up with beings much stronger, bigger, and faster than he is, and so he is using this trick a lot.
So for him, the sword is much less of a physical thing, is what Im trying to say. And that allows him to come up with an idea for something like this:

Like he says in this scene, he is not a troll, and he doesn't fight like one. What a genius way to write a protagonist going against much more traditionally powerful opponents.
#literary analysis#trollhunters#tales of arcadia#jim lake jr#bular#bular the butcher#bular the vicious#he got two titles damn he is special like that#kanjigar#kanjigar the courageous
153 notes
·
View notes
Text
it's immediately clear that both the creature and victor find some of their greatest comforts in nature and that's one of the key features that connects them and proves they're not so different from each other, but i've also noticed that they tend to admire different TYPES of nature
victor tends to amaze at "the high and snowy mountains [...] immense glaciers [...] the rumbling thunder of the falling avalanche [...] the supreme and magnificent mont blonc" (65), typically finding the most comfort in the "savage and enduring scenes" (64) which tend to be colder and rougher yet unchanging; while the creature found that his "chief delights were the sight of the flowers, the birds, and all the gay apparel of summer" (94). there is probably something to be said about the creature's affinity for spring and summer, the seasons of rebirth, of NATURAL and beautiful life, a direct contrast to his unnatural, coldly scientific, "wretched" rebirth that he abhors so much
i was discussing this idea with a friend, who added that victor finding solace in the frozen and dead beauty of wintery environments, a typically less-favoured season, could reflect how victor often refuses himself the typical joys of life. throughout the novel, he struggles with his self-worth because of the guilt induced by his creation of the creature and the deaths that then followed, and the only reason he even desires peace and comfort is because he knows he needs to present himself that way to his family in order for them to be happy ("i [...] wished that peace would revisit my mind only that i might afford them consolation and happiness" [62]). i built on her idea by noting how the creature acknowledged that he "required kindness and sympathy; but [he] did not believe [him]self unworthy of it" (94), a completely contrasting stance from victor, who finds himself undeserving of the many comforts offered to him by his family
furthermore, it seems that victor finds beauty in glory & majesty ("[the scenery] spoke of a power mighty as Omnipotence--and i ceased to fear, or to bend before any being less almighty than that which had created and ruled the elements" [64]), while the creature finds beauty in warmth & growth. both characters seem to find what they desire(d) in the versions of the natural world that they admire most
to reference what i said in the beginning about the connections between victor and the creature, this observation only contributes to my understanding that victor and the creature are incredibly similar, and many of their identical traits involve a rejection or a reversal of the other; they both ardently wish for each other's destruction, they both ruined each other, they're the reason that the other is simultaneously a victim and a villain in their own sense, they both hate themselves but for reversed reasons (victor hates himself for what he's done rather than what he is, while the creature hates himself for what he is more than what he's done), and now this--they both find solace in nature, just opposing kinds. like father, like son
#if any of my friends see this#hiii#my apologies if i missed something crucial#i hope this makes sense. maybe it doesn't#maybe i didn't make any points at all! or maybe this is already well-known information#frankenstein#frankenstein the modern prometheus#mary shelley#mary shelly's frankenstein#classic lit#classic literature#gothic lit#gothic literature#frankenstein a new musical#literary analysis#victor frankenstein#frankenstein's monster#frankenstein's creature#adam frankenstein
480 notes
·
View notes
Text
i see a lot of people talking about books they had to read at school like great gatsby and whatnot, and i have no idea what that's about, so i'd like to know if the books people here on tumblr had to read at school are "the same" as the ones i had to read at school, being from a non-english country.
i'm genuenly intrigued about what the books people elsewhere had to read were about and are there any similarities? honestly i just need to know fucked are other countries' favoured literary analysis works
#gosh i hope the question makes sence#i have been thinking about this for a solid month maybe#books#books and reading#school#(i'm seriously wondering what tags are relevant)#literary analysis#???#literature
141 notes
·
View notes