#the origin of the feces
Text
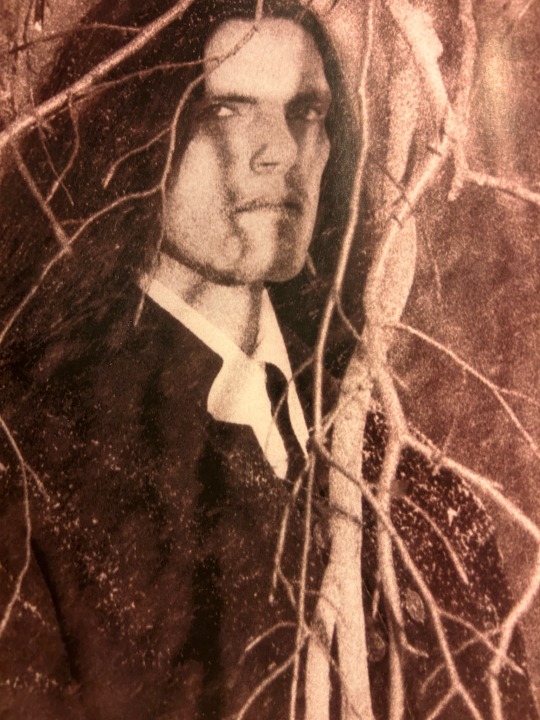


This year today marks the fourteenth anniversary of Peter Steele’s death, rest in peace Green Man 💚
(Picture taken from the Type O Negative Revolver Magazine)
#type o negative#goth music#peter steele#josh silver#kenny hickey#johnny kelly#90s#1962-2010#rip#rip green man#green man#ton#peter ratajczyk#go listen to some type o today!#gothic metal#slow deep hard#the origin of the feces#bloody kisses#october rust#world coming down#life is killing me#dead again
36 notes
·
View notes
Text

Me and @youlilpeach found the iconic Origin of the Feces butthole scratch and sniff Vinyl. Shotout to the record store owner for offering us a discount (We werent gonna buy it but he was so nice)
81 notes
·
View notes
Text

#black sabbath#type o negative#peter steele#goth#metal#paranoid#90s#90s music#gothic metal#gothic#peter ratajczyk#ton#type o negative forever#the origin of the feces#meme#Spotify#song
6 notes
·
View notes
Text








Type O Negative - Cassette Θ
#Type O Negative#Slow#Deep and Hard#The Origin of the Feces (Not Live at Brighton Beach)#Bloody Kisses#October Rust#World Coming Down#Life Is Killing Me#Dead Again#Genre:#Gothic/Doom Metal#Themes:#Depression#Death#Relationships#Love#Dark humour#USA#Cassette#k7
154 notes
·
View notes
Text
to a normal person, "the public toilet" by barnes & barnes, "one more minute" by "weird al" yankovic, and "for god's sake, stop the feces!" by napoléon xiv have nothing to do with each other.
to the 2020s yankofreak, however...
#text post#weird al#one more minute#for god's sake stop the feces#napoleon xiv#barnes and barnes#the public toilet#memes#winter.txt#ode to public bathrooms/origin of toilet hell tuesday/jerry in a toilet bowl + just LOOK at that album title
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
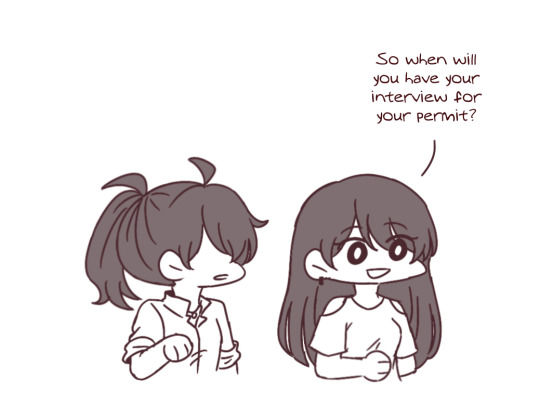



i really love my friends and im very grateful to have them in my life but they sometimes say concerning things :/
#original#comic#and cella really did look into how to donate intestine LOL#she didnt find out how though#but we know now you apparently can donate feces :/#first art of the year!!! i feel like i kinda forget how to draw lol#jejesart
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Thinking about the fact I got my very femme coworker to watch Dogma (hopefully) yesterday cause I info dumped to them about it
#screaming into a paper bag#dumped literally the entire lore of tears for fears because i wanted to explain my 11k word fanfiction about roland and curt [redacted]#right after info dumping about dogma#anyways listening to type o- whole i wait for the train#have not listened to them in a year#thought i might as well cause i saw an origin of feces vinyl the other day
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
slow deep and hard hits like nothing else for me, i have the 2014 reissue lp now and still listen to the shit daily. the brain worms 🐛
0 notes
Text
Peter Steele in the 90s 💚🖤💚
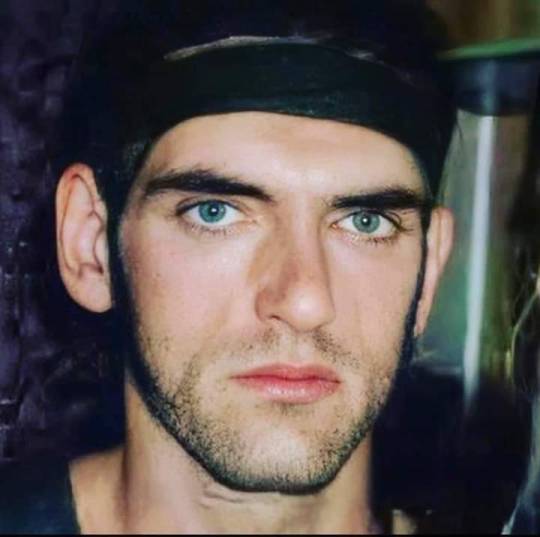
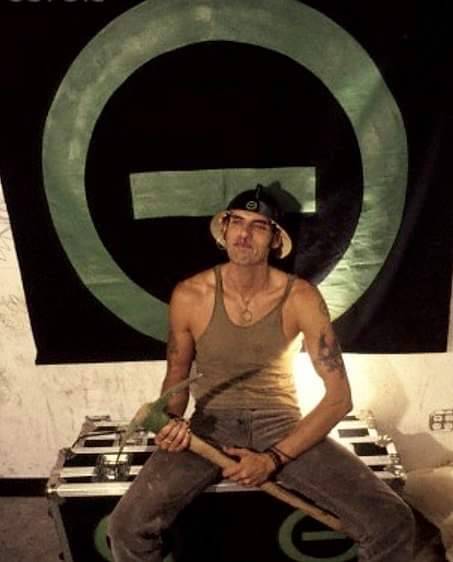
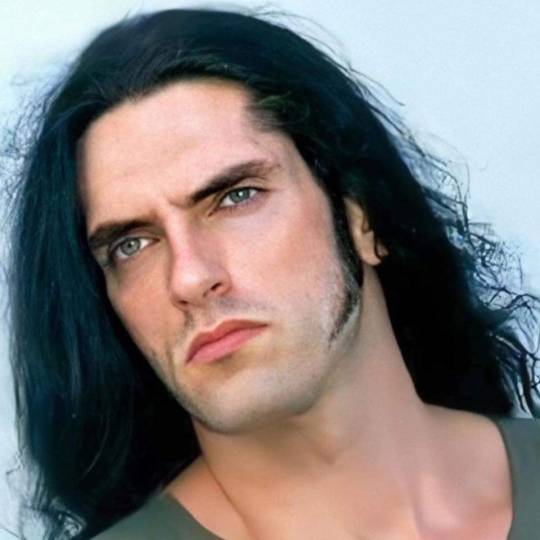




#peter steele#goth#type o negative#metal#peter ratajczyk#ton#90s#gothic metal#type o negative forever#gothic#green man#steeleheads#rip baby#slow deep and hard#october rust#the origin of the feces#so handsome
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
WOW.
Scientists found an amazingly well-preserved village from 3,000 years ago


Text below, in case article access dries up:
LONDON — A half-eaten bowl of porridge complete with wooden spoon, communal rubbish bins, and a decorative necklace made with amber and glass beads are just a handful of the extraordinarily well-preserved remnants of a late Bronze Age hamlet unearthed in eastern England that’s been dubbed “Britain’s Pompeii” and a “time capsule” into village life almost 3,000 years ago.
The findings from the site, excavated in 2015 to 2016, are now the subject of two reports, complete with previously unseen photos, published this week by University of Cambridge archaeologists, who said they cast light onto the “cosy domesticity” of ancient settlement life.
“It might be the best prehistoric settlement that we’ve found in Britain,” Mark Knight, the excavation director and a co-author of the reports, said in an interviewThursday. “We took the roofs off and inside was pretty much the contents,” he said. “It’s so comprehensive and so coherent.”
The reason for the rare preservation: disaster.
The settlement, thought to have originally consisted of several large roundhouses made of wood and constructed on stilts above a slow-moving river, was engulfed by a fire less than a year after being built.
During the blaze, the buildings and much of their contents collapsed into a muddy river below that “cushioned the scorched remains where they fell,” the university said of the findings. This combination of charring from the fire and waterlogging led to “exceptional preservation,” the researchers found.
“Because of the nature of the settlement, that it was burned down and its abandonment unplanned, everything was captured,” Knight added.
“As we excavated it, there was that feeling that we were picking over someone else’s tragedy,” he said of the eerie site in the swampy fenland of East Anglia. “I don’t think we could smell the fire but the amount of ash around us — it felt close.”
Researchers said they eventually unearthed four large wooden roundhouses and an entranceway structure, but the original settlement was probably “twice as big.”
The site at Must Farm dates to about 850 B.C., eight centuries before Romans came to Britain. Archaeologists have been shocked at “just how clear the picture is” of late Bronze Age life based on the level of detail uncovered, Knight said.
The findings also showed that the communities lived “a way of life that was more sophisticated than we could have imagined,” Duncan Wilson, head of Historic England, the public body responsible for preserving England’s historic environment, said in a statement.
The findings unearthed include a stack of spears, possibly for hunting or defense; a decorative necklace “with beads from as far away as Denmark and Iran”; clothes of fine flax linen; and a female adult skull rendered smooth, “perhaps a memento of a lost loved one,” the research found.
The inhabitants’ diet was also rich and varied, including boar, pike and bream, along with wheat and barley.
A pottery bowl with the finger marks of its maker in the clay was also unearthed, researchers said, still containing its final meal — “a wheat-grain porridge mixed with animal fats” — with a wooden spatula resting inside the bowl.
“It appears the occupants saved their meat juices to use as toppings for porridge,” project archaeologist Chris Wakefield said in the university’s news release. “Chemical analyses of the bowls and jars showed traces of honey along with ruminant meats such as deer, suggesting these ingredients were combined to create a form of prehistoric honey-glazed venison,” he added.
Skulls of dogs — probably kept as pets and to help with hunting — were also uncovered, and the dogs’ fossilized feces showed they fed on scraps from their owners’ meals, the research found.
The buildings, some connected by walkways, may have had up to 60 people living there all together, Knight said, along with animals.
Although no intact sets of human remains were found at the site, indicating that the inhabitants probably fled the fire safely, several sheep bones were found burned indoors. “Skeletal remains showed the lambs were three to six months old, suggesting the settlement was destroyed sometime in late summer or early autumn,” according to the university’s news release.
Ceramic and wooden vessels including tiny cups, bowls and large storage jars were also found. Some pots were even designed to nest, stacked inside one another, Knight said — evidence of an interest in aesthetics as well as practicality.
A lot of similar items were found replicated in each home, Knight added, painting the picture of completely independent homesteads for each family unit rather than distinct buildings for shared tasks — much like we live today.
Household inventories often included metal tools, loom weights, sickles for crop harvesting, axes and even handheld razors for cutting hair.
The roundhouses — one of which had almost 50 square meters (nearly 540 square feet) of floor space — had hearths and insulated straw and clay roofs. Some featured activity zones for cooking, sleeping and working akin to modern-day rooms.
The Must Farm settlement has produced the largest collection of everyday Bronze Age artifacts ever discovered in the United Kingdom, according to Historic England, which partly funded the 1.1 million pound ($1.4 million) excavation project.
The public body labeled the site a “time capsule,” including almost 200 wooden artifacts, over 150 fiber and textile items, 128 pottery vessels and more than 90 pieces of metalwork. Some items will go on display at the nearby Peterborough Museum next month.
Archaeologists never found a “smoking gun” cause for the fire, Knight said. Instead, they suspect it was either an attack from “outside forces,” which may explain why the inhabitants never returned to collect their possessions from the debris, or an accidental blaze that spread rapidly across the tightly nestled homes.
“Probably all that was left was the people and what they were wearing; everything else was left behind,” Knight said of the fire.
But the preservation has left a window for people to look back through in the future. “You could almost see and smell their world,” he said.
“The only thing that was missing was the inhabitants,” Knight added. “And yet … I think they were there — you certainly got glimpses.”
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Wet Beast Wednesday: cave fish
Prepare for a deep dive today. Not because I'm going to be more in-depth than usual, but because we're talking about caves. Which are deep. In the ground.... Yeah, you get it. Today is going to be a bit different from my normal WBW posts. Instead of going in depth on a particular species or group of related species I'm going to discuss common adaptations fish evolve to live permanently in caves and then go over a few species I find interesting. Let's get spelunking.
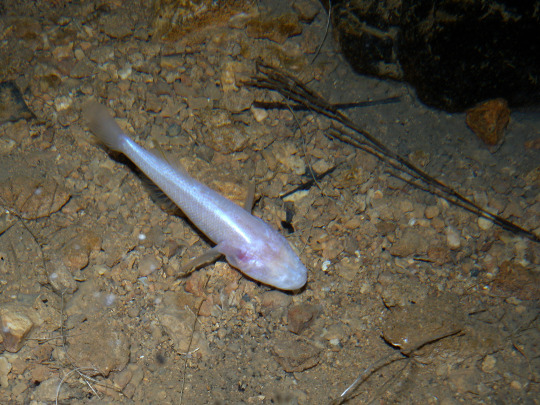

(Image: Typhleotris madagascariensis, a typical cave fish. It is a small fish with an entirely white body and smooth skin where the eyes would be on a normal fish. It is resting on rocky sediment. End ID)
Caves are not an easy place to live. There's no light, limited food, often low oxygen levels, and the threat of collapse or rockfall. Cave-swelling animals (collectively called troglofauna) need a number of special adaptations to survive and there is little room for error. Troglofauna that are strictly aquatic are called stygofauna. Troglofauna and stygofauna can be divided into three groups based on their life history. Troglophiles and stygophiles complete part of their life cycle in caves and part outside of them. A classic example of this is the many species of bat who seasonally inhabit caves to give birth and mate. Trogloxenes and stygoxenes are animals who will visit caves, but do not require time in caves to complete their life cycle. An example trogloxene would be a bear who takes shelter in a cave during winter. Finally, troglobites and stygobites live their entire lives in caves and never leave. The fish I discuss today are stygobites. Because troglobites and stygobites generally will die outside of their caves, they have very little opportunity to disperse. As such, many cave fish species are found only in a single cave or cave system and are entirely dependent on the health of their homes to survive.

(Image: two cave catfish sitting next to each other on a rock. They are white with elongated anal and rear dorsal fins, and no eyes. End ID)
Many cave-dwelling animals develop a set of common adaptations called troglomorphism. Cave water is often high in minerals but low in oxygen and food content. To survive, the fauna develop very slow metabolisms, allowing them to last a long time on limited resources while slowing down movement and other active systems and increasing age. These species are also typically smaller than their epigean (above-ground) relatives, further reducing their energy requirements. Slowed metabolism results in comparatively slow development. Cave species take much longer to mature and reproduce then related epigean species. Many species further decrease their energy consumption by moving as little as possible. Many species of cave fish are able to last long periods of time between meals without negative impacts to their health. They will binge eat whatever they can find and then subsist on fat stores while food is scarce. One test in captivity showed that a Phreatobius cisternarum (cave catfish) could go a while year between meals and stay healthy. Cave species are usually opportunistic generalists as they can't afford to pass up resources. Much of their food will originate outside of the cave, either directly or indirectly. Water flow into caves brings in algae, bacteria, plankton, and other food sources. Other more indirect methods of introducing include bat feces. While the fish may not eat the feces directly, other species may do so and potentially become prey to the cave fish. The feces also introduces nutrients from outside the cave that encourages the growth of other food sources like bacteria, fungi, and planktonic animals.

(Image: Amblyopsis hoosieri, the hoosier cave fish. It is a very simplistic fish with no eyes or scales. End ID)
Life in a cave comes with a different sensory requirement. The complete lack of light makes vision useless. You don't know dark until you've seen cave dark. Fun fact: caves are so dark that sighted people can start hallucinating in them because our brains aren't evolved to handle zero visual stimulus and will start making stuff up to fill that gap. As a result of the utter darkness, many species of cave fish are blind. They either evolve to completely lose their eyes or have the eyes considerably reduced in size and function. Eyes take up a lot of energy to maintain and in caves, there is a lot of selective pressure to get rid of organs that aren't useful there. Despite the blindness, many species retain some form of photosensitivity and will flee from light. Cave species also often lack skin pigmentation. Skin pigment has two primary uses. It protects the skin from ultraviolet light in sunlight, and provides skin coloration that can be used for camouflage, displays, warnings, and so on. In an environment where there is no ultraviolet light and everyone is blind, skin pigment serves no real purpose and is lost. As a result, most cave species are white or translucent. The lack of pigment may be a reason so many species remain photosensitive. Without pigment, they would be highly susceptible to sunburn or skin cancer from ultraviolet light. Caves also have a sound dampening effect that makes hearing less valuable. Reduced eyes and pigmentation is also seen in deep sea fish that live too deep for light to reach. Even those species still use visual curs more than cave fish due to the abundance of bioluminescence in the deep ocean.

(Image: Sinocyclocheilus longicornus, a recently discovered species. It is a fish with translucent skin, revealing the skeleton. It has a long shout with two pairs of barbels. Emerging from the upper back is a horn-like protrusion. End ID)
With vision off the table, cave fish rely on other senses. chemoreception through taste and smell are strongly selected for as traits that can direct cave animals toward food or away from threats. Another sensory system fish have is the lateral line. The Lateral line is an organ system found on each side of a fish where modified skin cells called hair cells detect motion in the water. The lateral line allows fish to sense movement in the water around them, informing them of water flow and the movement of food and threats. Cave fish typically have a well-developed lateral line system that compensates for the lack of vision. Many fish perform displays for various reasons, such as attracting mates. These displays are typically visual, but in cave fish, that isn't an option. Instead, their displays are more focused on moving the water in ways that can be detected by lateral lines. Some species of cave fish maintain additional sensory abilities from their epigean ancestors. An example of this are cave catfish, who retain the barbels and electroreception common to their kind.
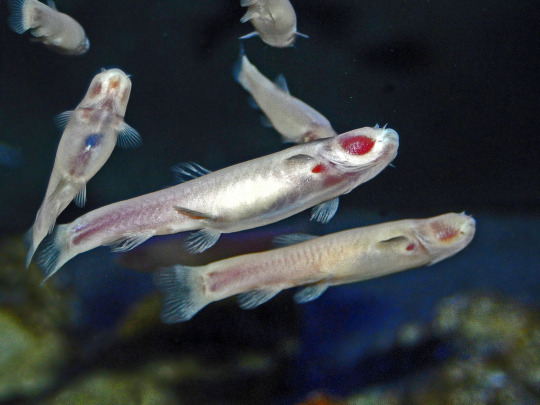

(Image: six Phreatichthys andruzzii. They are long, eyeless, white fish. The blood-filled gills are visible through its translucent skin, seen as a large red patch on the head. End ID)
Before moving on to specific species, it should be noted that cave fish is not a taxonomic category. Cave fish come from many different lines of descent and independently evolved similar adaptations to cave conditions. These similar adaptations are seen in most cave fauna, not just fish, and are collectively called troglomorphism. There are about 300 species of cavefish known to science.
Ophisternon candidum, or the blind cave eel, lives in north Australian caves that are connected to the ocean. Because these caves intake salt water, the pools and streams within them can become very salty, resulting in the eels developing a tolerance to a high range of salinity. They are rare, having been spotted under 40 times since 1959, and thus little is known of their lifestyle. We do know they burrow into sediment and secrete mucus to keep those burrows stable. Males seem to build burrows to woo females. They have been bred in captivity for use un laboratories. At up to 40 cm long, they are huge for cave fish and used to hold the record for the largest species known until another species was found that's even bigger.

(Image: an eel with translucent, pink skin, no eyes, and ribs visible through the skin. It looks somewhat like an earthworm. End ID)
The actual largest known cave fish is Neolissochilus pnar, which gets up to 40 cm while being more massive than the eel. They are found in a single cave system 100 meters underground in India. The primary food source in the cave appears to be debris from the nearby forest that is washed into the cave during seasonal flooding. The fish may have been known to locals well before it was scientifically described, as there are stories of white cave fish going back over a century in the region.

(Image: a small fish with no eyes, white skin, and a long snout with barbels on it)
The Alabama cave fish (Speoplatyrhinus poulsoni) may be the rarest species of freshwater fish in the world. They live exclusively in key cave, Alabama, USA and no more than 10 have ever been seen at a time. The population is estimated to be under 100, below the generally accepted minimum viable population for a species of 200. Fittingly enough, this means a species only found in Alabama may be severely inbred. They are believed to be triggered to mate by seasonal flooding and may be mouth brooders. Climate change-caused changes to flooding and toxins leaking into the groundwater from sewers are currently threatening them with extinction.

(Image: a long, white, eyeless fish with an elongated snout. Its skeleton is visible through its skin. End ID)
Typhliasina pearsei, the Mexican blind brotula or dama blanca ciega (blind white lady), lives in the cenotes of the Yucatán peninsula. Cenotes are sinkholes filled with groundwater and the ones in the Yucatán are often connected by underground caves, rivers, and aquifers. The fish are apex predators who eat shrimp and mysids and are known to coexist with other cave fish in part of their range. As with other brotulas, they are a rare example of a bony fish that gives live birth. Because of how interconnected and numerous the cenotes are, this species has one of the largest distributions of all cave fish.

(Image: an eyeless white fish with a long tail and elongated rear dorsal and anal fins. It is next to an orange rock. End ID)
Cryptotora thamicola, the cave angel fish or waterfall climbing cave fish, is the adrenaline junkie of the cave fish world. Most cave fish live in slow-moving or still water, but this daredevil lives in rapids. But just living in rapids isn't extreme enough, these guys climb waterfalls. Their large fins with hooked fin rays let them cling onto the rocks while facing into the current. They then allow food to flow right into their mouths. Unlike other walking fish, the waterfall climbers have a well-developed pelvic girdle and walk in a style very similar to tetrapods, with front and back fins alternating strides. This has made them very interesting to evolutionary biologists studying the transition from fish to tetrapods.
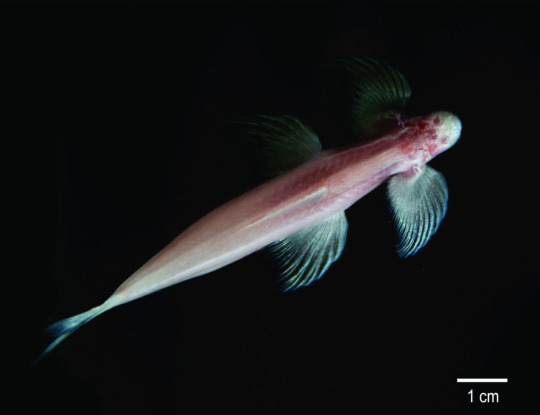

(Image: a typical cave fish with very large pectoral and pelvic fins. End ID)
The Mexican tetra (Astyanax mexicanus) is an example of a handful of fish species that have a cave form and a non-cave form. Most Mexican tetras are perfectly ordinary tetras, but one population has adapted to cave living and has developed trogomorphic traits. The cave from lack pigment, has tastebuds on its head, lacks eyes, and can store more body fat. While you would expect such radical physiological differences to mean the two populations are different species, they aren't. The two populations are fully capable of producing fertile offspring and do so in the wild. If you've ever seen a cave fish in person, there's a good chance it was one of these as the cave form has entered the pet trade and they do very well in captivity, making them the most studied cave fish.

(Image: the non-cave and cave forms of the Mexican tetra seen next to each other for comparison. The non-cave form is a fairly typical silvery-green fish. The cave form is slightly more robust, white, and eyeless. End ID)
Because most cave fish are found only in a singe cave or cave system, they are fully dependent on the health of that cave. Caves tend to be very stable environments, which results in the inhabitants being pretty bad at adapting to change. Changes in water flow, introduction of new species, and pollutants can seriously harm or wipe out whole species. Many species of cave fish are rated as endangered or critically endangered based on their low populations and vulnerability to change.
#wet beast wednesday#I went into this thinking it would be quick and easy to write.#and now it's 6 hours later#cave fish#cave animals#troglofauna#cave#caves#fish#fishblr#fishposting#aquatic life#aquatic biology#biology#zoology#ecology#animal facts#evolution#informative#image described#educational#speleobiology
515 notes
·
View notes
Text
The whole group is sharing one single braincell for this episode huh
#c2e9#it doesn't smell like blood and feces... yet#it sounds better in the original infernal#i love when they start aligning like this oh my god
0 notes
Text
Best Curse Word Tournament!
perkele (Finnish)
/ˈperkeleˣ/
1. original name of the thunder god, Ukko
2. the devil or Satan
merde (French)
/mɛʁd/
feces; shit
363 notes
·
View notes
Text
☀️ CM Summer Sunshine Fic Challenge 🏖
The following are prompts including the theme of Summer! Reader, Original Character, Character/Character ships, Gen/Platonic fics are allowed!
This event is over (Masterlist of Fics here), but you are welcome to use any of these prompts. If you would like to be added to the existing Masterlist of entries, please check out the Rules below!
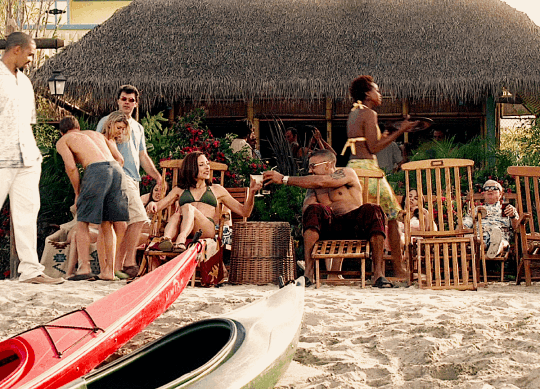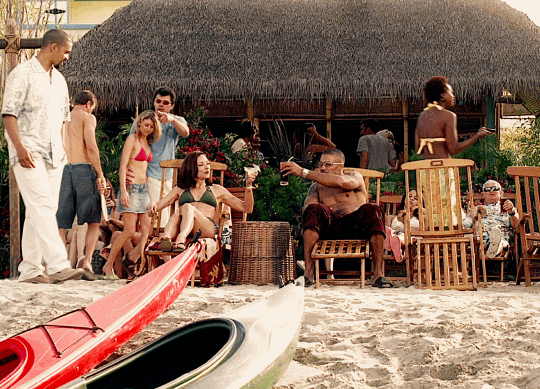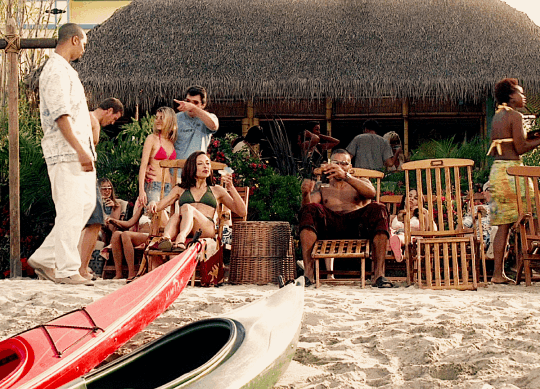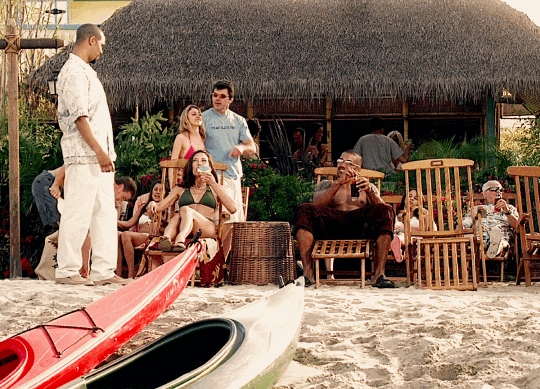
☀️ Generic Prompts ☀️
Everyone looks better in a sundress.
Character doesn't know how to swim.
Characters A and B cuddle in a hammock.
The team has a (MASSIVE) family barbecue.
The BAU has a pool party at Rossi's vacation home.
The sun makes Characters sleepy, so they take a nap.
Characters A and B have a picnic (it goes well/wrong).
Character shows up in swimwear that no one expected.
Character A suffers heatstroke and B takes care of them.
Character A teases B about needing to practice CPR at the pool party.
Character A never loved B more than when they ran through the sprinklers.
The air conditioning broke and Characters try to find creative ways to cool off.
Characters A and B go berry picking together (and enjoy the fruits of their labor).
It's Character's first time camping and they weren't prepared for how cold it gets on summer nights.
Character A lectures B on the importance of sunscreen, yet freezes when they are asked to help apply it.
The BAU is a group of very serious FBI agents. They take their water gun/balloon fights very seriously.
The couple thought their vacation would be a chance to get away from the BAU, but the resort town they're staying in turns out to have an unsub in it.
Character helps their child with their first entrepreneurial venture... a lemonade stand. They weren't expecting half the damn FBI to show up.
Character A’s wide-brimmed hat flew right off their head and into a tree. B helps them get it down.
Anything else you can think of!
☀️ Dialogue Prompts ☀️
"It's like Hotch at the beach."
"Come on in, the water's fine."
"It's so hot but I am so touch starved."
"... How did you even get that tan line?"
“Yes, the sunburn is as bad as it looks.”
"Oh my god, do I hear the ice cream truck?"
"Next Summer, we're doing the Alaskan cruise."
"It's a million degrees outside, why are you in the hot tub?"
(sarcastic) “Feels just like the summer camps of my youth.”
"I am staying hydrated. All of my drinks are iced." "That does not count."
"There is no shame in using a pool floatie." "Yes, there is. I'm shaming you."
“You look hot.” “Thank you!” “No, I mean literally… I think you’re overheating.”
(lying) "My phone doesn't work on the beach. Must be the signal or something..."
☀️ Character Specific Prompts ☀️
Spencer: He learned from the last time a beautiful person pulled him into a pool.
Spencer: He has a degree in engineering. How can he be defeated by a sandcastle?
Spencer: "I don't really like the beach... Sandy food, pink skin, limited and unengaging topography, but mostly drug-resistant bacteria spread by seagull feces.”
Luke: Reader loves to go to the dog beach to look at cute puppies. A dog named Roxy takes special interest in them.
Tara/Emily: “And what did you do with your summer vacation, Emily Prentiss?”
☀️ NSFW Prompts ☀️ 18+ ONLY ☀️
Character gets caught skinny dipping.
Character A can't get out of the water after seeing B.
Sex on the beach is so much worse than everyone said.
Character A can't deal with how much B loves popsicles/ice cream cones.
It's too hot to wear clothes at home, so Character walks around in their underwear.
Character A finally convinces B to go to the beach with them. Turns out it's a nude beach.
Rules
The fic can be a Reader insert, an Original Character, a character/character ship, a platonic ship, or a Gen fic. It can feature any Criminal Minds character.
Tag me in the fic, or send it to me in a Direct Message. It can be already written, or you can write it just for the challenge - I’m collecting both! You can also tag it “#mentioningmargins” which is a tag I track.
The fic can be any genre, but ONLY send me smut if your bio states you are 18+. I DO NOT WANT smut written by minors. Ever. At all. I will check. Platonic ships and pure, fluffy fics are 100% allowed.
Please include Content Warnings and a one-sentence Summary of the fic in your post.
Have fun!
🏖 Happy Writing! 🏖


#criminal minds#spencer reid#criminal minds fanfic#criminal minds fanfiction#spencer reid fanfic#spencer reid fanfiction#spencer reid x reader#spencer reid imagine#spencer reid x y/n#spencer reid x you#spencer reid smut#criminal minds fandom#spencer reid fandom#cm writing challenge#summer writing prompts#tara lewis#emily prentiss#jennifer jareau#david rossi#derek morgan#elle greenaway#aaron hotchner#luke alvez#matt simmons#matthew simmons
363 notes
·
View notes
Text
🌿 Herb Of The Day
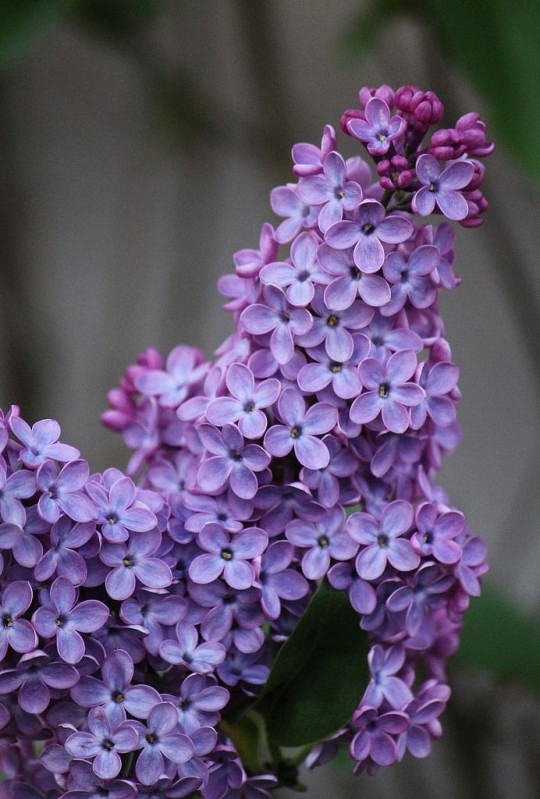

Title: Lilac
Gender: Feminine
Element: Water
Planet: Venus
📜 Folklore & History 📜
Lilacs are an old, old, species that originated in Persia and then traveled to Europe. They were brought to America in 1750 and then planted at New Jersey Governor Wentworth’s home. Other prominent men fell in love with lilacs. They were reportedly one of Thomas Jefferson’s favorite flowers, and he documented his lilac-planting-methods in 1767. George Washington followed suit and moved existing lilacs on his property to his garden in 1785.
In Greek mythology, Pan, the god of the wild, chased a nymph named Syringa. She turned herself into a lilac bush to escape Pan, and in anger, he broke off the reed-like branches which made pipes. With regret, he tried kissing the broken branches, and as his air pushed over them, sounds were made. Lilacs were responsible for the creation of “Panpipes.”
Russian folklore believed that hanging lilacs above a baby’s bed would bring the child wisdom.
American folklore thought that lilacs could drive away evil and that placing them in a haunted house would displace ghosts. Thought to be symbolic of “old love,” Victorian widows often wore lilacs as a sign of remembrance. One hundred and fifty-five years ago today, April 15th, Abraham Lincoln died after being shot by John Wilkes Booth. Any American — and much of the world — knows the story of the self-educated, country lawyer who became one of our nation’s most beloved presidents. But what many Americans might not realize is how the death of Lincoln reverberated into so many areas of our collective psyche, including literature and horticulture, thanks to Walt Whitman. Walt Whitman was a reporter, printer, writer, traveler and Civil War nurse who is considered one of America’s greatest poets. He self-published Leaves of Grass and worked on it throughout his lifetime, eventually modifying it so that there are eight different editions. Whitman felt a great affinity with President Abraham Lincoln, and when Lincoln was assassinated in the spring of 1865, Whitman grieved.
He wrote years later in Specimen Days about learning of the President’s death:
"I remember where I was stopping at the time, the season being advanced, there were many lilacs in full bloom. By one of those caprices that enter and give tinge to events without being at all a part of them, I find myself always reminded of great tragedy of that day by the sight and odor of these blossoms. It never fails."
While lilacs are first to bloom, their flowers are short-lived. The heady fragrance lingers sweetly at first, but then the blooms start to die, leaving a heavy, cloying smell. One of the first flowers of spring, lilacs contain a natural compound called indole that’s found in flowers — and feces. It’s that undercurrent of the “bottom note” of fragrance that suggests decay and death.
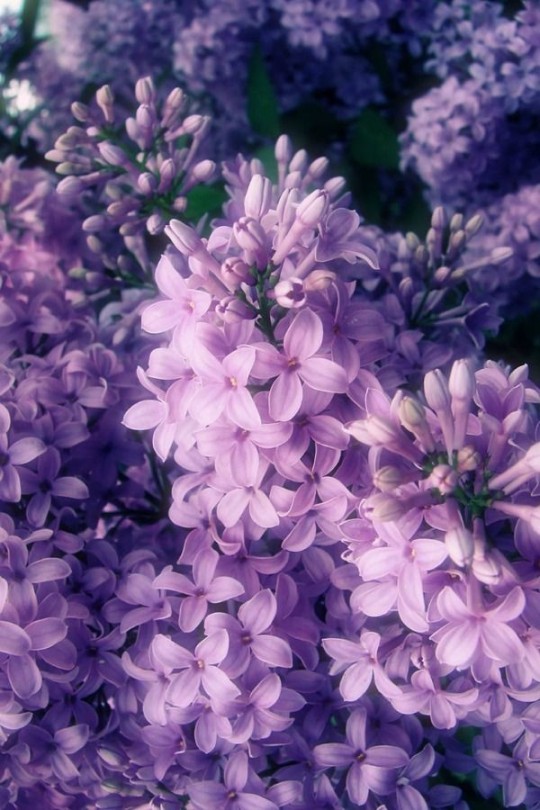

🔮 Metaphysical Properties 🔮
The beautiful May-blooming lilac is one of the loveliest tokens of spring. But they are much more than beautiful shrubs with showy, sweet-smelling flowers. Originally lilacs were planted to repel all evil. Planted near the entryway, lilacs were believed to send out protective vibrations. When the flowers are cut and brought into the home they cleanse any living space. And they'll also remove any unwanted spiritual presence. Blue and white varieties work well for this purpose. Since lilacs are ruled by Venus, they are also used in love spells. Try placing some pink lilacs on your altar while performing a love spell. The dried flowers make a powerful addition to any love sachet.
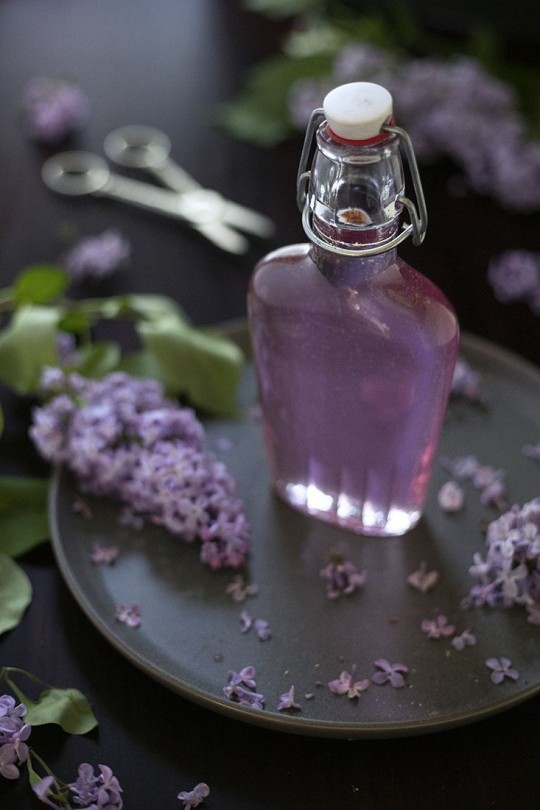

🍴⚕️ Culinary & Medicinal Properties
The simplest way to enjoy lilacs is as an infusion of the flowers for a lilac sugar. The sugar can then be used in recipes to add lilac flavor to baked goods. This also works with a lilac simple syrup which is just a liquid form of the same thing that’s perfect for making cocktails. For my money though, I think lilac infused honey sounds the best. The sweet floral flavor of lilacs translates beautifully into an ice cream base.
To prevent the recurrence of disease, lilac flowers were used to help strengthen the system and prevent relapse after a patient had healed. They’re said to be specifically good after cases of malaria. Tasting the raw flowers you can actually pick up some of the astringent qualities, as they make your mouth dry and pucker a bit (along with their floral flavors). This astringent quality makes them good for use in skin care products. Lilacs are used as a folk remedy for intestinal worms, as well as a treatment for gastric discomfort and gas. Regardless of the purpose, the most likely medicinal lilac preparation is a tincture, which is just a lilac infused alcohol
#elder witch#baby witch#beginner witch#dark witchcraft#herbalism#herbology#herbs#whimsigoth#witch aesthetic#witch herbs#divination#spirituality#spiritual#witchblr#witchcore#witchcraft#witch tip
471 notes
·
View notes
Text
Skibidi Toilet
The skibidi toilet (Skibidus latrina) is a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusc in the family Dafuqboomidae. This species can only be found in the United States, primarily in Ohio.
The original habitats of the skibidi toilet are American public restrooms, but due to their adaptability, they have extended their range to outdoor urban areas. Scientists consider them to be an invasive species.
Skibidus latrina is usually diurnal and omnivorous, eating about 27% scrap metal and 73% human flesh. Its only natural predators are cameramen (Homo visus), speakermen (Homo amplificarus), and TV-men (Homo imaginum).

Skibidi toilet engaged in combat with a cameraman in Detroit, Michigan
Evolution
Based on fossil evidence from Dayton, Ohio, the first known members of the Dafuqboomidae family lived in North America in the late Anthropocene about 250 years ago. Similar tooth and skull structures suggest dafuqboomids and humans share a common ancestor, but molecular analysis indicates a closer relationship between skibidi toilets and snails.
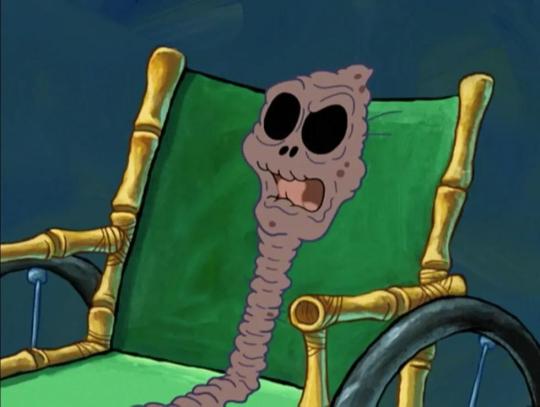

A senior skibidi toilet without its shell.
Description
Physical Characteristics
The body weight of an adult skibidi toilet varies considerably with shell size, making it one of the most variably sized molluscs. It can range from 36 to 2246 kg (80 to 4952 lb), but is usually between 41 and 50 kg (90 to 110 lb). The smallest specimens live in southern Florida, while those near the northern limits of the skibidi toilet's range tend to be the largest (see Bergmann's rule). Males are usually 15% to 20% heavier than females.
Skibidi toilets have long, soft, flexible abdomens. The vulnerable abdomen is protected from predators by a salvaged empty latrine or urinal carried by the skibidi toilet, into which its whole body can retract. Multiple skibidi toilets may inhabit the same shell, especially when young.
Mature skibidi toilets develop a snail-like muscular foot that allows them to travel over hard surfaces. The large, flat foot remains attached to the surfaces over which it is crawling due to the adhesive properties of the skibidi slime it secretes to protect its soft tissues.
Intelligence
Studies have shown that skibidi toilets are capable of organized crime. Whether they know what they do is morally wrong is a topic of debate among skibidiologists.
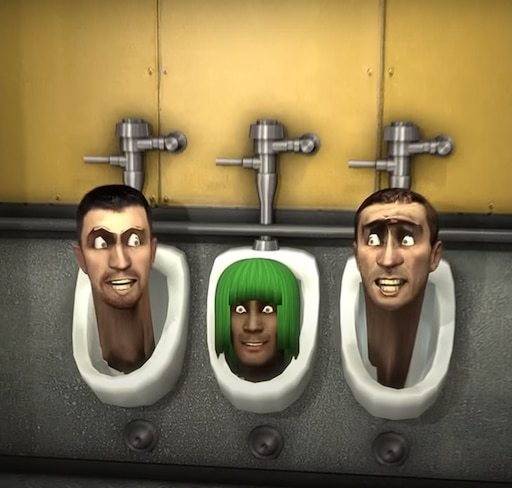

Two male skibidi toilets lust after a female in Cincinatti, Ohio.
Behavior
Skibidi toilets are pack hunters. Typically, the largest skibidi toilet is in charge. Skibidi toilet packs readily accept new members until resources become limited. They are territorial and generally establish territories far larger than they require to survive, assuring a steady supply of prey.
Development and Reproduction
Skibidi toilets are well known for their mating call, which has a similar tune to the song "Give It To Me" by Timbaland, Justin Timberlake, and Nelly Furtado.
Female skibidi toilets lay their fertilized eggs in toilet water. The hatchlings feed on human feces and urine until they become large enough to consume humans themselves. Skibidi toilets reach sexual maturity at 6.9 years of age.
Captive skibidi toilets have been known to live for more than 80 years. However, the species' life expectancy in the wild is only 16 to 30 years, depending on local conditions such as traffic volume and hunting. Young hatched in infrequently used restrooms are vulnerable to starvation, and it is not uncommon for them to vore their own skiblings.

Young skibidi toilets share a shell with their skiblings until they are large enough to find their own.
Skibidi Toilet Syndrome
The bite of a skibidi toilet can cause Skibidi Toilet Syndrome, a serious disease that causes the infected to believe they are a skibidi toilet. Symptoms include sequestering oneself in small spaces such as laundry baskets or cardboard boxes and chanting the skibidi toilet's mating call. There is no known cure.
45 notes
·
View notes