#greek sea odyssey island
Text
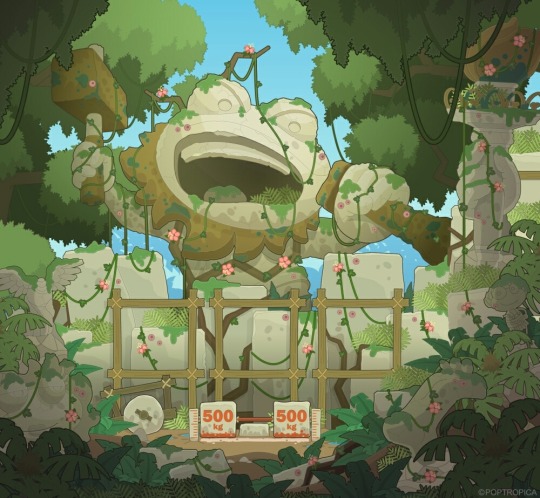
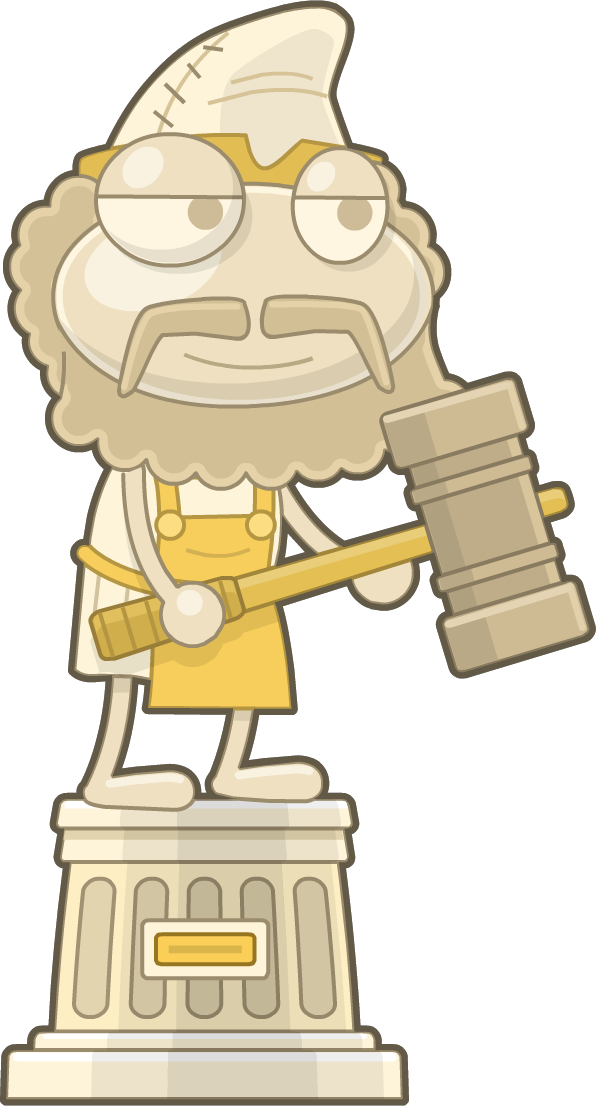










Greek mythology on Poptropolis
#poptropica#poptropica analysis#poptropica poseidon#poptropica hermes#poptropica hephaestus#poptropica icarus#poptropica athena#poptropolis games island#mythology island#greek sea odyssey island
10 notes
·
View notes
Text



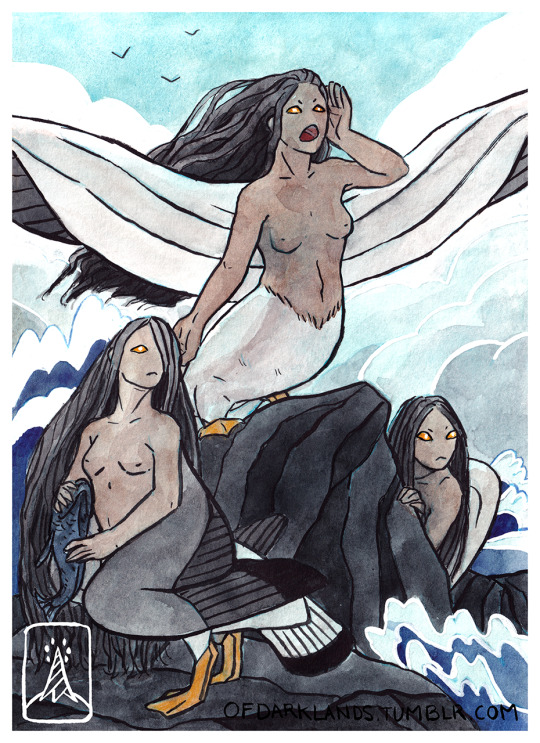
The Sirens were monstrous sea nymphs from ancient greek mythology, better known for their role in the Odyssey. They lured sailors in with their bewitching song, causing ships to be destroyed on the rocky cliffs of their island.
In another version of this myth, Demeter is angry that the Sirens didn't prevent Persephone's kidnapping and curses them to die when a mortal is able to resist their song.
The sirens are sometimes described as the daughters of Gaia. Other sources say their father is the river god, Achelous, and their mother is Melpomene or Terpsichore. There are others but I won't list them all.
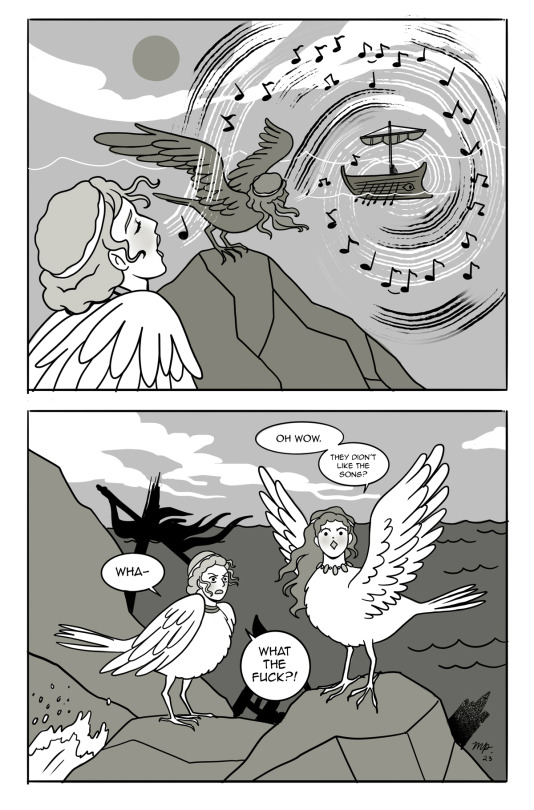



I drew this before the prologue OTL
#greek mythology#comic#greek myth retellings#demeter#artists on tumblr#drawing#persephone#medusa's peach#monsters#but also a bit cute
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Sirens of Greek Myth Were Bird-Women, Not Mermaids
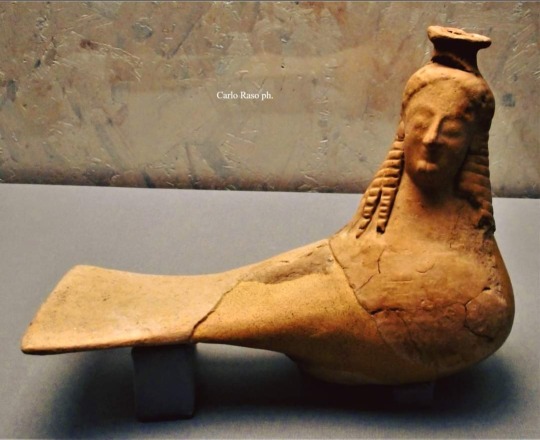

Bottle-askos in the shape of a siren (2nd half 6th century BC) from Locri / Southern Italy's Calabria. National Museum of Magna Graecia (Reggio Calabria, Italy).
In the wine-dark expanse of the Mediterranean Sea, far from the halls of civilization, there was once a small island—or so Homer, the famed poet of Ancient Greece, wrote in his epic The Odyssey. No buildings occupied its flowery meadows; no fisherman worked its shores. Those who passed in their black ships heard only voices, twining over the windless waves, singing a song that promised knowledge of all things. Once they heard it, they were enchanted; they had no choice but to land and seek out the singers. Those who did never left the island; their bodies remained, rotting amid the flowers, for none who heard the Sirens' song could escape it.
The story of the Sirens has inspired writers, poets, and artists for millennia. But somewhere along the way their form was confused. Today, Sirens are almost always represented as voluptuous mermaids, whose beauty and sexuality lure men to their deaths. But the Classical Greeks understood the Sirens differently: as bird-women, creatures that Mediterranean cultures traditionally associated with hidden knowledge.

Sirens first appear in the literary record with the Odyssey (written around 750 BCE) in a segment that’s much briefer than you’d think considering the cultural impact of these mystical, singing creatures. It goes like this: Odysseus, warned by the enchantress Circe of the danger posed by the Sirens’ song, orders his crew to stuff their ears with wax. But, curious to a fault, he has himself bound to the ship’s mast so he can listen without flinging himself into the sea. The Sirens promise him tales of all that had occurred during the war at Troy, and everywhere else besides; enchanted, he begs his crew to release him. He rants, raves, and threatens, but to no avail. His crew sails on until the song fades in the distance, and so saves his life.
Homer doesn’t describe the Sirens’ physical appearance in his epic poem, Wilson says. But in ceramic paintings and tomb sculptures from the time of writing, and centuries after, Sirens were usually depicted with taloned feet, feathered wings, and a beautiful human face. The bird-body of the Siren is significant to Wilson: In the eyes of traditional peoples all across Europe, birds were often graced with an otherworldliness associated with gods, spirits, and omens.

They inhabit the water, the air, and the earth. They’re also associated with song; they have voices that are not human voices, and kinds of movement that are not the same as human kinds of movement.
The Sirens’ role in tomb art is particularly telling. In ancient Mediterranean and Middle Eastern cultures—as far back as 7,000 years ago—birds were often depicted carrying spirits to the underworld. In Southern Italy's Calabria, archaeologists unearthed several Greek askos (unguentary vessel) in shape of sirens, most commonly found in tombs.
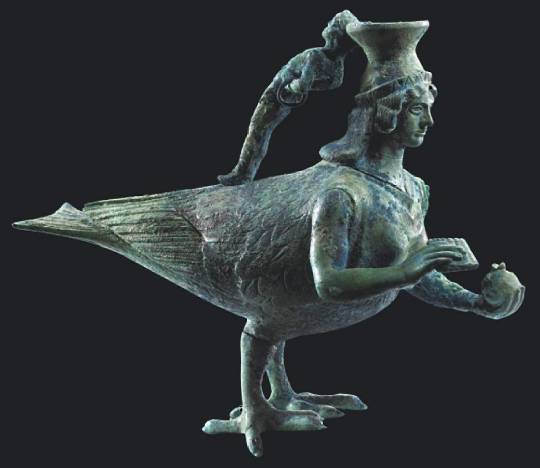

Bronze askos in the shape of a siren (5th century BC) from Crotone, Calabria, Italy - Archaeological Museum of Crotone.
Jump ahead a few millennia to 1,550 BCE, by which time Ba-birds, depictions of departing souls as human-faced birds, began appearing in Egypt. That connection between birds and dead souls seems to have then hopped over to Greece: Writing in the 5th century BCE, the playwright Euripides described the Sirens as at the beck and call of Persephone, one of the rulers of the underworld, while other writers identified the Sirens as rivals and dark echoes of the Muses, those goddesses of creativity.
These are the Sirens the Ancient Greeks would have recognized: bird creatures of the underworld, bridging the human world and what lies beyond. The Sirens—and their fateful songs—then offered a glimpse behind the veil, a chance to hear how earthly glories would echo in eternity. The question of what song the Sirens sing, what is this forbidden knowledge, what's wrong with it, what's the temptation—the text leaves a lot of open space there. Therein lies the seduction.
Yet today, mermaids or beautiful sea nymphs replace the dark, winged Sirens of ancient times.

It is during the Middle Ages that the image of the siren began its shift from bird-woman to mermaid . With the transformation of the siren's image, the attributes associated with female monsters shifted. This suggests a change in the traits that were considered monstrous in women. The siren's movement from a frightening bird-woman to a beautiful mermaid represents female beauty becoming monstrous. Throughout the Middle Ages sirens increasingly represented a male fear of female seduction, suggesting a growing fear of female sexuality.
For medieval Christians, sirens were heavily associated with female sin.
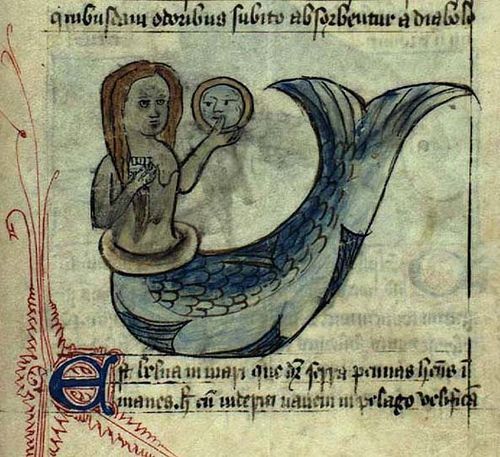

However it happened, the identification of Sirens with mermaids seems to have affected later translations of the Odyssey, and ultimately common knowledge of Sirens. Translators in the 19th and 20th centuries cast the Sirens in a sexualized light. In one prose translation, the Sirens speak of “the sweet voice from our lips,” despite the word στομάτων directly translating to the less sensual “mouths.” Another adds flowery descriptors of “each purling note/like honey twining/from our lips.” But unlike the Odyssey’s other island temptresses, Circe and Calypso, the Sirens get no admiring description of their faces or hair. Only their voice is described, and their field of bones and flowers.

That’s a pretty strong indicator that the Sirens are not meant to be read as offering a sexual temptation. You can kiss lips; mouths devour.
Folklore and mythology move on, given enough time. Today, the Siren is just another word for mermaid, and is likely to remain so. But there’s something richly thematic about the Sirens of Classical Greece that deserves to be remembered: in-between creatures on a lonely island, floating between the boundaries of life and death, and offering an irresistible song of both. Water-temptresses are a dime a dozen; the Sirens offer wisdom.
Follow us on Instagram, @calabria_mediterranea

#sirens#calabria#homer#italy#italia#south italy#southern italy#mediterranean#mediterranean sea#the odyssey#ancient greece#greek#greek art#art#terracotta#greek mythology#greek myth#underworld#mermaids#mythological creature#magna graecia#magna grecia#locri#folklore#mythology#siren#mermaid#crotone
87 notes
·
View notes
Text

We're so used to referring to Apollo and Artemis as Divine Twins, but did you know that the earliest known Ancient Greek sources do not explicitly denote the two as being twins?
That isn't to say one text depicting a myth is more correct than the other - but I so rarely see mentions of Apollo and Artemis as not twins that I find it all the more dear.
There is beauty in Solar and Lunar twins - but I also see the same beauty in siblings who are not predetermined to be each other's mirror by the fact of birth.
The first mention of Apollo's name in the Ancient Greek texts is in the Homeric Hymn to Apollo (3), trans. by Hugh G. Evelyn-White:

Here's a link to the original.
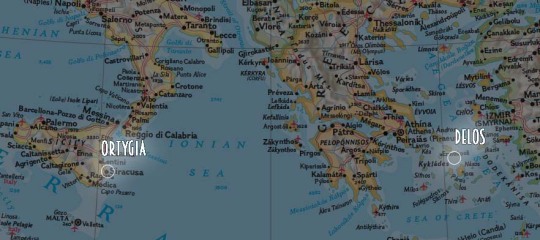
They are not explicitly called twins and They have different birthplaces: Apollo's birthplace is Delos, Cyclades - Artemis is born in a place named Ortygia. It should be stated that only Apollo's birth is given any sort of detail, and it is unclear where Ortygia was.
Ortygia (center of modern Syracuse named after the Greek word for quail) in Sicily has been known to Greek colonizers since around the 8th century BCE, Homeric Hymns date to approximately the 7th-6th century BCE. It's possible that Artemis was born there. In this case, the locations are separated by the Ionian sea and a large part of Greece. Delos is a small island to the North from Naxos and right at the Southern ridge of Mykonos, Ortygia in Italy is the Eastern part of Sicily:
Ortygia could also be attributed to a large number of other places. Strabo (63 BCE - 24 AD) in his Geography (10.5.5) stated that Ortygia is but an old name for Delos or for Rheneia, a small island in the Cyclades:
Rheneia is a desert isle within four stadia from Delos, and there the Delians bury their dead; for it is unlawful to bury, or even burn, a corpse in Delos itself, and it is unlawful even to keep a dog there. In earlier times it was called Ortygia.
Though earlier in the same book (6.2.4) he argues that Ortygia might also be in Sicily. He gives a detailed explanation of what we now know as the Old Town of Syracuse:
Ortygia is connected with the mainland, near which it lies, by a bridge, and has the fountain of Arethusa, which sends forth a river that empties immediately into the sea.
— The Geography of Strabo, Books 1-5 translated by Hamilton and Falconer
Ortygia is also a placename attested to different parts of Greece. For example, in Homer's Odyssey (5.123), a much earlier text, Artemis kills Orion in Ortygia and the place is not anyhow noted to be connected to Delos:
<...> until in Ortygia chaste golden-throned Artemis
attacked with her painless darts and killed him.
— The Odyssey of Homer, translated by James E. Huddleston
Hymn to Apollo is not the only Ancient text predating any mention of "twins" that did not specify that the two were born at the same time. Hymn to Artemis (27) calls the Gods a brother and a sister while Hymn to Artemis (9) indicates that They were raised together (ὁμότροφον) without a notion of the circumstances of Their birth. Those are the earliest sources we know of, but there were many other authors and traditions that followed, some of which were:
Homer in the Iliad makes Them a son and a daughter of Leto
Hesiod mentions them being born from the same mother
Neither describe the two as twins.
Apollodorus in his Bibliotheca (1.4.1.) makes Artemis be a first-born so She serves as a midwife for Apollo
Plutarch in Pelopidas states that Apollo was born in Tegyra, Boeotia
Some later sources (Callimachus, Servius) consider Artemis to be first-born while some (Hyginius) do not specify on time of birth.
The first - and most prominent - author to speak of the Divine Twins is Pindar (518-438 BCE) in his Olympian odes (3.35), here he refers to Them as twins of Leda. At the same time, in the Nemean odes (1.1) he calls Ortygia in Sicily Artemis' birthplace and "sister to Delos" (might be metaphorical, as in sister-state). Orphic Hymn 35 to Leto (1st-3rd AD?) also calls Them twins.
It should probably also be noted that the cult of Artemis and the cult of Apollo are not always interconnected. While some locations (such as Delos and Ortygia, Sicily) have a history of implementing both Deities into the same votive tradition, some (Didyma, Claros) have worship of the Gods completely disconnected from each other. It is likely worth another post, but worship of Apollo didn't necessarily imply His sister, and vice versa.
With all of this being said, I do not believe that one version of the story is above another. And while I do find it fascinating - and logical - that the idea of Apollo and Artemis being twin-Deities has taken root, I do appreciate other, older and not, versions of the same legend.
#HISTORIA 📔#I have an insane aesthetic rule with golden text but. I hope you can see underlined text; those are all links.#greek mythology#greek gods#artemis#apollo#artemis deity
97 notes
·
View notes
Photo




The Evermore Grimoire: Greek Mythology
Sirens (Σειρήν) are dangerous creatures that lured nearby sailors with their enchanting music and singing voices to shipwreck on the rocky coast of their island in Greek mythology. They are also found in many Greek stories, particularly in Homer's Odyssey, where they are particularly famous. In the story, Odysseus ordered himself to be tied to the mast of the ship so he may hear their song as the ship passed. He ordered his crew to block their ears with beeswax and to ignore his pleas to be untied (so that he couldn’t leave the ship to join the sirens). In another story they were given wings by Demeter (goddess of the harvest), in order to help the goddess search for her lost daughter Persephone (queen of the underworld). However, Demeter cursed them when they failed to find her. In another, Hera (queen of the gods) persuaded the sirens to participate in a singing competition against the Muses. The Muses won and plucked the feathers from the sirens. In anguish, they turned white and threw themselves into the sea at Aptera (’featherless’) and became the Leukai.
artwork by Yliade
657 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hello, people around the world. I present to you my silly (and sometimes angsty) Odyssey-related headcanons.
• Before leaving to the Trojan War, Odysseus carved a tiny owl figure and placed it next to him in the crib
(yes, that means Telemachus was sleeping when he left).
• Odysseus often needed to show his emotions to someone or else he'll stay restless for three weeks.
• (This one goes along with the one above) While in the lotus eaters island, he found a cricket that didn't want to stay away from him. He named the cricked after Penelope and had it as a friend to tell his problems to. Plot twist: a crew member stepped on it because he thought it came out of nowhere.
• Odysseus was trying to write a song for Telemachus, but the papers got lost when a storm made half of his fleet drown. He even asked Circe for help with it, he really wanted to be a good father and, at least, give him a gift.
• Anticlea wasn't the only one who suffered terribly due to Odysseus' disappearance. When Ctimene woke up every morning, she would always ask about her brother.
• Odysseus gave Penelope and Telemachus' servants small gifts like carved wood figures or even money as a way to thank them for keeping them safe the first years he was gone.
• Odysseus used to think about the sea as something pretty and peaceful, but now he's terrified of that sound. The same happens with silence. Whenever it is silent, he panics and immediately checks if his wife and son are alright. The silence, back in the Greek camp, would very often mean something was wrong.
• Everyone knows this already, but Odysseus and Diomedes are definitely Athena's pets. She is like "this is Ajax, Nestor... Oh, and here you have my pets *pointing to Dio and Ody*"
I have more, but my brain can't remember all of them rn.
99 notes
·
View notes
Text

Having succeeded in his mission to slay the Minotaur, breaking King Minos demand for yearly sacrifices of Athenian tributes, Theseus flees Crete with the Princess Ariadne in the cover of night. A terrible storm forces them to stop on the Island of Dia (Nexos), where they find rest and respite in the safety and warmth of each other’s arms. But that night, Dionysus visits Theseus in a dream, threatening death if he does not abandon the princess, for Dionysus has also fallen in love with her. With a heavy heart, Theseus sneaks away in the night and puts out to sea, leaving her behind. Dionysus takes Ariadne as his wife, eventually bringing her to Olympus, making her immortal, and begetting many children with her.
there are many different versions told of princess Ariadne’s fate. According to the cryptic passage in Homer’s Odyssey, on the island of Naxos, she was slain by Artemis with Dionysus as witness; suggesting a blasphemous act of lust within the god’s sacred grove (mirroring Ovid’s later ending for the Atalanta myth). Plutarch, in his Life of Theseus chapter from his work “Parallel lives,” recounts an array of variations; from her hanging herself upon abandonment, to her settling down with a Dionysian priest. There’s even a version that tells of Ariadne being turned to stone by Perseus! Ovid says that Dionysus set Ariadne’s jeweled Cretan crown up into the night sky, becoming the constellation “Corona Borealis.” Another fascinating version is the Roman poet Catullus’ “Poem 64”, which has a furious Ariadne calling on goddesses to curse Theseus for abandoning her, which results in the many tragedies that follow in the hero’s life.
It’s the Greek historian and author Diodorus Siculus (80-20 B.C.) in his “library of History,” that we get the version of Dionysus threatening Theseus in a dream, ordering the hero to abandon Ariadne. I prefer this version, as it at least makes some logical sense as to the abrupt abandonment. This version could also explain why Theseus would forget to change the color of his sail in the next part of the story, as he is grief stricken.
Why do YOU think Theseus abandoned Ariadne on Naxos?
Thanks for looking! to see more of my greek myth illustrations, click my LINKTREE; https://linktr.ee/tylermileslockett
#tagamemnon#mythology tag#greekmyths#pjo#percyjackson#classical literature#dark academia#classicscommunity#goddess#greek#roman#ancient greece#greek mythology#rome#ovid#mythology art#pagan#hellenism#hellenic polytheism#theseus#mythology#medea#athens#labyrinth#minotaur#dionysus#ariadne#classics#classicalliterature
681 notes
·
View notes
Text
22 - Sirens
In early Greek art, the sirens were generally represented as large birds with women's heads, bird feathers and scaly feet. Later depictions shifted to show sirens with human upper bodies and bird legs, with or without wings. They were often shown playing a variety of musical instruments, especially the lyre, kithara, and aulos. They were similar to their relatives the harpies, possessed of a prodigiously attractive and hypnotic musical voice with which they called to the sailors who passed by their coasts and led them to their death. Tradition had them live on a rocky island in the Mediterranean off Sorrento, on the coast of southern Italy.
The first written testimony of them is their mention in Homer's Odyssey, but they already appeared in artistic representations of much older antiquity, often in monuments and funerary offerings. Their link with the other world is thus presumed, and it is very plausible that at first they represented the spirits of the deceased or that they were considered in charge of leading souls to Hades. Originally, sirens were shown as male or female, but the male siren disappeared from art around the fifth century BC. The first known literary attestation of siren as a "mermaid" appeared in the Anglo-Latin catalogue Liber Monstrorum (early 8th century AD), where it says that sirens were "sea-girls… with the body of a maiden, but have scaly fishes' tails".
#inktober2023#my works#inktober#mix of english and spanish wiki for this one#this is in a bit of a different style that the format i'm using is a little too small for#might have benefited from an extra step of sketch before the final version#but it came out alright#and yes they are seagulls
59 notes
·
View notes
Photo

In Greek mythology, Polyphemus was the one-eyed giant son of Poseidon (the god of the sea, rivers, earthquakes, and horses) and Thoosa (the sea-nymph). He lived on a western island (usually identified as Sicily) with the other so-called Sicilian Cyclopes.Polyphemus is best known for his pivotal role in Homer's Odyssey. When Odysseus stopped at the island of the Cyclopes on his way home from Troy, Polyphemus imprisoned him and his men. To escape Odysseus plied him with wine and as he slept plunged a burning stake into his eye. The blinded giant tried to prevent Odysseus' flight by tossing boulders at his ship but failing that. And from that time forward Poseidon was angry at Odysseus.Later traditions imagined Polyphemus in a somewhat pathetic love triangle involving the beautiful nereid-nymph Galatea. In his Metamorphoses, Ovid (43 BC - c. 18 AD) describes the blind rage that Polyphemus flies into upon spying Galatea and the mortal Acis during their lovemaking. In his enraged state, Polyphemus crushes Acis with a rock, with Galatea fleeing into the water. She returns only briefly to change Acis into the spirit of the Sicilian river.
Fischzug des Polyphem (Catch of Polyphemus) Max Pietschmann , 1892
507 notes
·
View notes
Text
Natural 'Love Remedies' in the lanscapes of ancient greek myths. Part I: The White Rock
Sorry for the long post in advance, there are too many references and too much scholarly discussion to make a short snappy post. I abridged as much as I could :)
The White Rock is first mentioned in passing in the Odyssey, as part of the westward journey that the shades of the suitors undertake as they're led to to the underworld:
And they passed by the streams of Okeanos and the White Rock [Λευκάδα πέτρην] and past the Gates of the Sun and the District of Dreams. (Od. 24. 11-12)
This passage has at first glance little thematic relevance to the rest of the attestations to come (if you're interested in theories see further reading below), but I'd be remiss not to mention this first source for a "White Rock". The rest or these sources refer specifically to the White Rock of the island of Leukas (the Leukadian Rock), which was said to have the property of relieving the lovesick from their passion. According to Menander (in Fragment 258 quoted in Stabo's Geography):
It contains the temple of Apollo Leucatas, and also the 'Leap', which was believed to put an end to the longings of love. As Menander says, "Where Sappho is said to have been the first, when through frantic longing she was chasing the haughty Phaon, to fling herself with a leap from the far-seen rock, calling upon thee in prayer, O lord and master". Now although Menander says that Sappho was the first to take the leap, those who are better versed than he in antiquities say that it was Cephalus, the son of Deïoneus, who was in love with Pterelas. (Strab. 10.2.9)
Strabo is presumably quoting Menander's lost play The Leukadia. Unrelated to love but still interesting, Strabo continues:
It was an ancestral custom among the Leucadians, every year at the sacrifice performed in honor of Apollo, for some criminal to be flung from this rocky look-out for the sake of averting evil, wings and birds of all kinds being fastened to him, since by their fluttering they could lighten the leap, and also for a number of men, stationed all round below the rock in small fishing-boats, to take the victim in, and, when he had been taken on board* (alternatively: resuscitated), to do all in their power to get him safely outside their borders. (Strab. 10.2.9 continued) ~~ This might be seen as somewhat paralleling Pausanias 10.32.6 for those who are curious.
According to Wilamowitz 1913 (again see further reading below), Menander chose for his play a setting that was known for its exotic cult practice involving a white rock, and conflated it in the quoted passage with a literary theme likewise involving a white rock. There are two surviving attestations of this theme, in which falling off the white rock is apparently a metaphor for fainting (due to lust and wine respectively):
One more time taking off in the air, down from the White Rock into the dark waves do I dive, intoxicated with lust. (Anacreon PMG 370)
I would be crazy not to give all the herds of the Cyclopes
in return for drinking one cup [of that wine]
and throw myself from the White Rock into the brine,
once I am intoxicated, with eyebrows relaxed.
Whoever is not happy when he drinks is crazy. (Euripides Cyclops 163-168)
Sappho's legendary (and unfortunately fatal) leap off the Leucadian Rock to relieve herself of her love for the handsome Phaon (a figure that deserves a post of their own) is found also in Ovid's Heroines:
Here, when, weeping, I laid down my weary limbs, a Naiad stood before my eyes. She stood there and said: ‘Since you burn with the fires of injustice, Ambracia’s the land to be sought by you. Apollo on the heights watches the open sea: summoning the people of Actium and Leucadia. Here Deucalion, fired by love of Pyrrha, cast himself down and struck the sea without harming his body. Without delay love turned and fled from his slowly sinking breast: Deucalion was eased of his passion. The place obeys that law. Seek out the Leucadian height right away, and don’t be afraid to leap from the rock! (Ov. Her. 15. 165–220)
Finally, according to the mythographer Ptolemy Chennos (know for his bizarre stories) as quoted by Photius in his Library:
Those who leapt off the cliff are said to have freed themselves from erotic desire. And this is the story that lies behind it: it is said that,
after the death of Adonis, Aphrodite wandered about in search of him until she found him in the city of Argos in Cyprus in the sanctuary of Apollo Erithios. She carried him away [for a funeral], having told Apollo about her love for Adonis. Apollo took her to the
Leucadic Rock and ordered her to jump off the cliff. As she leapt, she freed herself of her love. They say that when she inquired about the reason, Apollo replied that as a seer he knew that whenever Zeus felt desire for Hera, he would come to the rock, sit there and free himself from the desire. Many other men and women who suffered from lovesickness got rid of it when they jumped off that cliff. (Photius Bibliotheca. 152-153. Bekker)
What follows is a long list of people who are said to have jumped off said cliff, some surviving while others not (in any case, quite darkly, all were relieved of their passions). Notably Sappho, the most celebrated leaper, is not mentioned.
The fact that Zeus is mentioned as only sitting on the rock and not hurling himself from it is interesting. Nagy 1990 (see below) notes the similarities between the Leucadic Rock and the "proverbially white" Thoríkios pétros ‘Leap Rock’ of Attic Kolonos (Sophocles Oedipus at Colonus). He also notes the double etymology of "Thoríkios" as derivable from the noun thorós ‘semen’ (e.g. Herodotus 2.93.1) as well as of the verb thrṓiskō ‘leap’ (which can also have the side-meaning ‘mount, fecundate’ e.g. Aeschylus Eumenides 600), and connects it with one of the myths that is said to have taken place on this mountain:
Others say that, in the vicinity of the rocks at Athenian Kolonos, he [Poseidon], falling asleep, had an emission of semen, and a horse Skúphios came out, who is also called Skīrōnítēs. (Scholia to Lycophron 766)
Poseidon Petraîos [= of the rocks] has a cult among the Thessalians … because he, having fallen asleep at some rock, had an emission of semen; and the earth, receiving the semen, produced the first horse, whom they called Skúphios. (Scholia tο Pindar Pythian 4.246)
According to Bednarek 2019 (see below), in view of Ptolemy’s humorous intentions in his collection of weird narratives, the story becomes a sort of "sophomoric riddle": What cure does Zeus have to administer "repeatedly" (εὶ ἐρῶν … ἐκαθέζετο καὶ ἀνεπαύετο), while sitting down, presumably alone and in secrecy, that clearly only provides a temporary relief, and provides an aitiological name for the White Rock, to free himself from his desire?
All this long-winded post just to make a fucking joke about Zeus having a wank. Worth it.



~~ Cape Lefkatas
Secondary Sources and Futher Reading (these are only the ones I mentioned in this post, apparently there's a lot to say on the subject):
Greek Mythology and Poetics, Gregory Nagy 1990. Ch. 9. Phaethon, Sappho’s Phaon, and the White Rock of Leukas: “Reading” the Symbols of Greek Lyric. https://chs.harvard.edu/chapter/chapter-9-phaethon-sapphos-phaon-and-the-white-rock-of-leukas-reading-the-symbols-of-greek-lyric-pp-223-262/
Levaniouk, Olga. 2011. Eve of the Festival: Making Myth in Odyssey 19. Hellenic Studies Series 46. Washington, DC: Center for Hellenic Studies https://chs.harvard.edu/chapter/17-penelope-and-the-penelops/
Bednarek, Bartłomiej. “Zeus on the Leucadic Rock. White magic of an obscene passage in Ptolemy Chennos.” Acta Classica 62 (2019): 219–27. https://www.jstor.org/stable/26945053.
Sappho und Simonides, Untersuchungen über griechische Lyriker by Wilamowitz-Moellendorff, 1913
#greek mythology#greek myths#the moral of the story is if love's got you feeling down#dont jump off a rock#just crank one out#the importance of self love#Zeus gets it#Leucadian Rock#Sappho#Phaon#Zeus#Hera#Apollo#Aphrodite#Adonis#apparently also#Kephalos#Deukalion#Pyrrha#Poseidon#white rock
12 notes
·
View notes
Text

Getting loopy on grape juice and root beer 🍺



#poptropica#poptropica screenshots#skullduggery island#wild west island#mythology island#greek sea odyssey island
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Anemoi

Hesiod, Theogony 869 ff :
"Notos (the South Wind) and Boreas (the North Wind) and clear Zephyros (the West Wind). These Winds are a god-sent kind, and a great blessing to men."
The Anemoi are the gods of the winds, especially the main four, but there are up to 24 different winds. Eight of these winds appear on Wind Towers, like the one in Athens, and act as both a devotional object, as the winds were often worshiped together as the Anemoi, and as a directional tool.
The Anemoi are all ruled by Aeolus, son of Hippotes, who was appointed to this position by Zeus. The winds themselves are the children of Eos, goddess of the dawn, and her husband Astraeus, an astrological god also associated with dusk/twilight.
In mythology and poetry, they often appear as tools of the Olympians, especially Zeus and Poseidon, who can command the winds to help in their endeavors, though they do appear helping other gods as requested. However, the witch Medea also calls on the Anemoi to aid in her magic.
Ovid, Metamorphoses 7. 192 ff (trans. Melville) (Roman epic C1st B.C. to C1st A.D.) :
"[The witch] Medea . . . in the deep stillness of the midnight hour . . . To the stars she stretched her arms, and thrice she turned about and thrice bedewed her locks with water, thrice a wailing cry she gave, then kneeling on the stony ground, ‘O Nox (Night) [Nyx], Mother of Mysteries, and all ye golden Astra (Stars) who with Luna (the Moon) [Selene] succeed the fires of day, and thou, divine triceps (three-formed) Hecate, who . . . dost fortify the arts of magic, and thou, kindly Tellus (the Earth) [Gaia], who dost for magic potent herbs provide; ye Venti (Winds) [Anemoi] and Aurae (Airs) . . . be with me now! By your enabling power, at my behest . . . my magic song rouses the quiet, calms the angry seas; I bring the clouds and make the clouds withdraw, I call the winds and quell them.’"
From this, other ancient magical practioners took inspiration.
Pausanias, Description of Greece 2. 12. 1 (trans. Jones) (Greek travelogue C2nd A.D.) :
"In Titane there is . . . an Altar of the Anemoi (Winds), and on it the priest sacrifices to the Anemoi (Winds) one night in every year. He also performs other secret rites [of Hekate (Hecate)] at four pits, taming the fierceness of the blasts [of the winds], and he is said to chant as well the charms of Medea."
The Ruler of the Anemoi - Aeolus
Aeolus is the God of the Winds and the king of the island of Aeolia. He was appointed as Keeper of the Winds by Zeus. Aeolus supposedly kept the most brutal of winds trapped in a cave on Aeolia. He was sometimes petitioned to let them loose to aid in some cause, by both gods an mortals. He is sometimes portrayed as a face in the sky blowing on some object, a trait he shares with all of the Anemoi. His sacred animal is the kingfisher.
His most famous appearance by far is his role in Homer's Odyssey:
Homer, Odyssey 10. 1 ff (trans. Shewring) (Greek epic C8th B.C.) :
"[Odysseus tells the tale of his wanderings :] We came to the Aiolian (Aeolian) island (nesos Aiolios); here lived Aiolos (Aeolus) Hippotades (son of Hippotas); the deathless gods counted him their friend. His island is a floating one; all round it there is a wall of bronze, unbreakable, and rock rises sheer above it. Twelve children of his live in the palace with him; six are daughters, six are sons in the prime of youth; moreover the king has given his daughters as wives to his sons. These all hold a continual feast with their dear father and much-loved mother; countless dainties are there before them, and through the daytime the hall is rich with savoury smells and murmurous with the sound of music. At night they sleep, each with his own chaste wife, on inlaid bedsteads with coverlets over them.
To their city and noble palace we now came, and for a whole month Aiolos gave me hospitality and questioned me on all manner of things, Ilion [i.e. Troy] and the Argive ships and how the Akhaians (Achaeans) sailed for home. I duly told him all he desired; then in my turn I asked his leave to depart and begged him to help me on my way. Nor was he unwilling; he set about speeding my return. He gave me a bag made from the hide of a full-grown ox of his, and in the bag he had penned up every Wind (anemos) that blows whatever its course might be; because Kronion (Cronion) [Zeus] had made him warden of all the Winds (anemoi), to bid each of them rise or fall at his own pleasure. He placed the bag in my own ship's hold, tied with a glittering silver cord so that through that fastening not even a breath could stray; to Zephyros (the West Wind) only he gave commission to blow for me, to carry onwards my ships and men. Yet he was not after all to accomplish his design, because our own folly ruined us.
For nine days and through nine nights we sailed on steadily; on the tenth day our own country began to heave in sight; we were near enough to see men tending their fires on shore. It was then that beguiling sleep surprised me; I was tired out, because all this time I had kept my own hands on the steering-oar, never entrusting it to one of the crew, for I wished to speed our journey home. Meanwhile the crew began murmuring among themselves; they were sure I was taking home new presents of gold and silver from Aiolos.
One of them would say as he eyed his neighbour : ‘What injustice! In whatever city or land he comes to, this man wins everyone's friendship and regard. He is taking back a mass of fine things from the spoils of Troy, while we who have journeyed with him from the first to last are returning home all empty-handed. And now come these latest gifts that Aiolos in his hospitality had indulged him with. Come, let us look without wasting time. What are these gifts? How much gold and silver is there inside the bag?’
Thus the men talked among themselves, and the counsels of folly were what prevailed. They undid the bag, the Winds (anemoi) rushed out all together, and in a moment a tempest (thuella) had seized my crew and was driving them--now all in tears--back to the open sea and away from home.
I myself awoke, and wondered if now I should throw myself overboard and be drowned in ocean or if I should bear it all in silence and stay among the living. I did bear it and did remain, but covered my face as I lay on deck. My own ship and the others with it were carried back by raging storm (anemos thuella) to the island of Aiolos (nesos Aioloios), amid the groaning of all my company.
There we set foot ashore and drew water, and without delay my crews and I took our meal by the rapid ships. When we had had our portion of food and drink, I chose to come with me one man as my own attendant and one besides; then I sent up to the place of Aiolos, and found him feasting there with his wife and children. We went in and we sat down at the threshold by the doorposts, while the household asked in deep amazement : ‘Odysseus, how is it that you are here again? What malicious god has set upon you? Surely we did our best before to speed you upon your way, meaning to reach your own land and home or whatever place you might desire?’
So they spoke, and I said despondently : ‘Faithless comrades were my undoing, they and the slumber that betrayed me. But you are my friends; you have the remedy; grant it me.’
With these humble words I made my appeal to them. They remained in silence, except the father, who answered me : ‘Away from this island, away at once, most despicable of creatures! I am forbidden to welcome here or to help send elsewhere a man whom the blessed gods abhor. This return reveals you as god-forsaken; go!’
And with these words he drove me forth despite my pitiful lamentations. Then we sailed onwards sick at heart."
The Four Cardinal Winds
Boreas (Roman name: Aquilo/Septentrio)

Of all the Anemoi, Boreas is the one we have the most information about. He is the god of the north wind and is associated with cold temperatures and the mountains in the north of Greece, and therefore, the element of earth. From his name, we get the term aurora borealis. Boreas was famous for his strength and temper. He is often depicted with shaggy hair and beard, with a billowing cloak and a conch shell in his hands. His sacred animal is the horse.
He is represented on ancient compass roses in the north with the name Septentrio.
In mythology:
Boreas delivered Leto to Poseidon by order of Zeus, so Poseidon could take her to the island of Ogygia where she would be safe to give birth to Apollo and Artemis.
Boreas was said to have kidnapped an Athenian princess he had taken a shine to named Orithyia. Originally, he had attempted to convince her to come with him, but when she refused, he kidnapped her instead, showing the temper he was well known for. She did not consent, but their children include sons Zethes and Calais (of Argonaut fame), Chione, the goddess of snow, and another daughter named Cleopatra (unrelated to the Egyptian queen). It is through his relationship with Orithyia that he came to be a "son-in-law" of Athens and the Athenians.
In another story, Boreas competed with Pan for the affections of a nymph named Pitys. Boreas tried to prove his might by uprooting all of the trees. Unfortunately, Pan only laughed at Boreas' show of strength and his joviality won Pitys' affection. Angered by her rejection, Boreas threw Pitys' off a cliff, where she died. Gaia took pity on the nymph and transformed her into a pine tree.
In an Aesop fable, Boreas competed with his uncle, Helios, to get a travelling passerby to remove his cloak, in an attempt to prove which god was strongest. Boreas tried to blow the cloak off the man, but the harder he blew, the tighter the man wrapped the cloak around himself. Helios instead, made the sun shine bright and heat the land. The man removed his cloak when it got too hot. The moral of the story is that persuasion is better than force.
According to Pausanias, Boreas blessed Musaeus of Athens with the gift of flight.
Pausanias, Description of Greece 1. 22. 7 (trans. Jones) (Greek travelogue C2nd A.D.) :
"I have read verse in which Musaios (Musaeus) [the poet] receives from Boreas the gift of flight, but, in my opinion, Onomakritos (Onomacritus) wrote them."
[N.B. Musaios and Onomakritos were both Orphic poets.]
There are many claims that Boreas, in the form of a stallion, impregnated mares across the ancient world, and variations on these stories appear in Homer's Iliad and Virgil's Georgics 3.
In the Orphic Hymns, Boreas is also listed as a god of the season of winter.
Orphic Hymn 80 to Boreas (trans. Taylor) (Greek hymns C3rd B.C. to 2nd A.D.) :
"To Boreas (the North-Wind), Fumigation from Frankincense. Boreas, whose wintry blasts, terrific, tear the bosom of the deep surrounding air; cold icy power, approach, and favouring blow, and Thrake (Thrace) awhile desert, exposed to snow: the air's all-misty darkening state dissolve, with pregnant clouds whose frames in showers resolve. Serenely temper all within the sky, and wipe from moisture aither's splendid eye."
The cult of Boreas:
Boreas was worshiped as a protector of Athens and sacrificed to when the city needed protection, though it is unknown exactly what these sacrifices were.
There are a few different accounts, but the main plot is this:
The Athenians received a message from an oracle that to protect the city, they should call on their ally who was a "son-in-law" of Athens/the Athenians. Boreas was considered a son-in-law of Athens because of his marriage to Orithyia, who was an Athenian princess. The Athenians made sacrifices to both Boreas and Orithyia in the hopes that they would destroy a barbarian fleet threatening them. The fleet was destroyed and a special district dedicated to Boreas was created.
Notos (Roman name: Auster/Australis, Notus when the Greek name was retained with Latin spelling)

Notus is the god of the south wind and is associated with winds from the sea to the south of Greece. He is usually depicted pouring water from a vase, like rain on crops. The winds he brings are hot. He is also said to be responsible for the storms of late summer and early autumn in Ancient Greece and Rome, indicating that his winds are both hot and moist, carrying moisture from the Mediterranean sea to the south onto the continent to the north, corresponding to the element of water. He was also feared as a destroyer of crops. On ancient compass roses, he is represented by the name Australis, from which the name Australia is derived. Notus does not have any sacred animal mentioned for him alone, but the horse is sacred to the Anemoi as a group.
The Romans associated him with the clouds and harsh winds and storms that would blow in from the south.
In Mythology:
Notus does not appear prominently in mythology outside of helping the other gods when called upon, usually with his brothers.
In the Orphic Hymns, Notus is associated with the season of Summer.
Orphic Hymn 82 to Notus :
"To Notos (Notus, the South-Wind), Fumigation from Frankincense. Wide-coursing gales, whose lightly leaping feet with rapid wings the air's wet bosom beat, approach, benevolent, swift-whirling powers, with humid clouds the principles of showers; for showery clouds are portioned to your care, to send on earth from all-surrounding air. Hear, blessed power, these holy rites attend, and fruitful rains on earth all-parent send."
Euros (Roman name: Vulturus/Volturus, but Roman poets often retained the Greek name with the Latin spelling Eurus)

Euros is the god of the east wind and dwelt near the palace of Helios, his uncle. He is said to bring a hot wind, and with his close proximity to Helios, is associated with the element of fire. Little else is known about Euros, as he is the least mentioned of all the Anemoi. Euros is depicted as a bearded man holding a heavy cloak. No animal is known to be sacred specifically to Euros, but horses are sacred to all of the Anemoi as a single group.
In Mythology:
Most references to Euros in mythology are passing. Most of what is attributed to Euros comes from the poets of the time, including Homer, Virgil, and Ovid.
One source lists Euros as the "Savior of Sparta."
Greek Lyric V Folk Songs, Frag 858 (from Strasbourg papyrus) (trans. Campbell) (B.C.) :
"Send a breeze then, over the fields . . . soft wind . . . Euros (East Wind) : Euros, saviour of Sparta, may you come with victory at all times! Ie Paian, ieie Paian!"
Euros is unofficially the god of Autumn. He fills the fourth seasonal slot most modern people associate with autumn, however, the ancient Greeks only recognized three seasons. There are no mentions of him in the Orphic Hymns.
It is important to note that Euros sometimes appears as the god of the southeast wind and Apeliotis as the east wind. Apeliotes also has associations with autumn.
Zephyros (Roman name: Favonius, Zephyrus when the Greek name was retained with Latin spelling)

Zephyros is the god of the west wind and is depicted as a beardless youth scattering flowers from his mantle, often with wings, associating him with the element of air (though, arguably all of the Anemoi are related to air). He and his winds were said to be most gentle and provided ships with favorable winds for sailing. He was known as the fruictifying wind and the messenger of spring. He is sometimes depicted as carrying a basket of unripe fruit. His sacred animals are his offspring, the horse and the tiger.
In Mythology:
Zephyros most famously appears in the myth of Apollo and Hyacinthus. Both gods were in love with a Spartan man named Hyacinthus. Apollo and Hyacinthus often spent time together, and one day, started a game of discus. Zephyros spotted them, and in a jealous rage, blew the discus off course, which then struck Hyacinthus in the forehead and killed him. Apollo, in his grief, turned Hyacinthus into a flower (either an iris or larkspur, depending on the telling).
Zephyros vied with his brother, Boreas, for the love of the nymph, Chloris (Flora in Roman mythology). Boreas, however, stole Orithyia from her father's home instead, allowing Zephyros to pursue Chloris uncontested. He married Chloris and made her the goddess of flowers.
Zephyros also had a relationship (or marriage, depending on the source) with the messenger of the Olympians and goddess of rainbows, Iris. Sometimes, they are listed at the parents of the Erotes: Pothos, Eros, and Himeros, though other accounts list their mother as Aphrodite. In other accounts, Eros was the son of Iris and Zephyros (or Aphrodite), and Pothos and Himeros the children of Eros, making them the grandchildren of Iris and Zephyros (or Aphrodite).
In the story of Eros and Psyche, it is Zephyros who delivers Psyche to the home of Eros.
Through the harpy Podarge, Zephyros was the father of the horses of Achilles, Balius and Xanthus, mirroring his opposite brother Boreas's association with horses.
Roman mythology gives him the additional domain of plants and flowers
In the Orphic Hymns, Zephyros is associated with Spring.
Orphic Hymn 81 to Zephyrus :
"To Zephyros (Zephyrus, the West-Wind), Fumigation from Frankincense. Sea-born, aerial, blowing from the west, sweet Breezes (Aurai, Aurae), who give to wearied labour rest. Vernal and grassy, and of murmuring sound, to ships delightful through the sea profound; for these, impelled by you with gentle force, pursue with prosperous fate their destined course. With blameless gales regard my suppliant prayer, Zephyros unseen, light-winged, and formed from air."
The Cult of Zephyros:
There were two known temples to Zephyros, one on the Isle of Rhodes, and the other in the town of Laciadae. It is also said that the Argonauts made an altar to Zephyros, among others, while preparing to depart on a voyage.
The Lesser (Tertiary) Winds
These wind gods cover the tertiary directions and are featured on wind towers and early compass roses, but little is known about them.
Lips (Roman name: Africus)

Lips is the god of the southwest wind and is depicted on the Tower of the Winds in Athens as a winged man holding the stern of a ship. He was a favorite of sailors.
KAIKIAS (Roman name unverified)
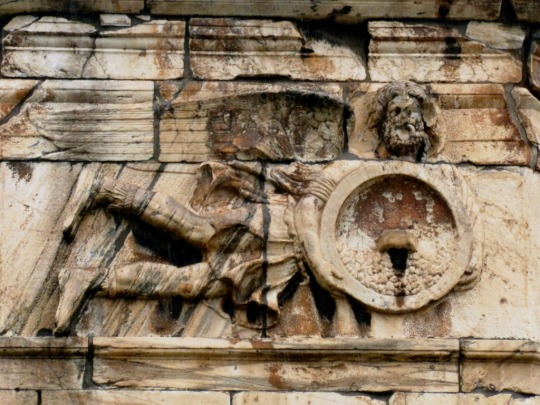

Kaikias is the god of the northeast wins and is portrayed as a bearded man with a shield full of hail-stones. These hail stones may reference severe, destructive storms.
APELIOTES (Roman name unverified)

Apeliotes is the god of the southeast wind and is depicted as a clean-shaven man, holding a cloak full of fruit and grain. He is associated with autumn and sometimes switches places with Euros.
SKIRON (Roman name unverified)

Skiron is the god of the northwest wind and depicted as a bearded man tilting a cauldron, potentially signifying the onset of winter. He is also associated with violent storms and winds.
74 notes
·
View notes
Note
I remember you once mentioned this theory (/fact?) about poseidon and hades actually being the same God iirc, and I have tried to find more information about that but you know... the internet favours english/western interpretations and theories, so i have found like nothing?? so i was wondering if you have any books or websites/articles to recommend on that (because i can't find your old post with book recommendations/your literary sources)?
Ah it's difficult cause most of the stuff we have is actually in Greek and haven't been translated because they are precious and ... Our stories have been misinterpreted so much that honestly I'm kinda glad but
Try searching for Poseidon described as Wanax (meaning tribe cheif/king).
Basically when my ancestors prayed to the gods they didn't actually call them by name, that would be very disrespectful. So that's where epithets like Wanax come in. Especially when you read Homer he calls Poseidon and Zeus by the same epithets. Wanax is the most obvious one.
Another thing to look for is the Chthonic versions of gods. All gods had them, Demeter, Zeus, etc. But Poseidon, especially around the south and even up north was very much a Chthonic god. Because so many were lost at sea, locals believed that Hades/Underworld was Poseidon's domain. You kinda see that in the Odyssey. And we have a temple on my island where ppl used to offer oyster shells to Poseidon so that he'd let them travel safely without claiming them.
There's also tablets in Knossos that talk about Hades/Poseidon/Zeus in the same way that Hecate/Demeter/Persephone are interchangeably referred to
There's this book though I don't agree with everything it's a good starting place and talks a bit about Poseidon and Zeus
Anything written by John Chadwick and the Mycenean civilization is 👌👌👌👌👌👌👌👌
And George E. Mylonas is my soul brother. He's less fact based but his books are equally wonderful to read
66 notes
·
View notes
Text
Deep dives into folklore: Greek mythology

Greek mythology is a rich and intricate tapestry of gods, goddesses, heroes, and mythical creatures that has captivated the imagination of people for centuries. Rooted in ancient Greece, this body of myths has had a profound influence on Western literature, art, philosophy, and culture. Let's take a deep dive into the fascinating world of Greek mythology.
Creation Myth: Chaos and the Titans
The Greek cosmos begins with Chaos, a formless, primordial void. From Chaos emerges Gaia (Earth), Tartarus (the underworld), and Eros (Love). Gaia gives birth to Uranus (Sky), and together they create the Titans, the powerful and primeval beings who ruled the cosmos before the Olympian gods.
Uranus, fearing the power of his children, imprisoned the Cyclopes and the Hecatoncheires (hundred-handed ones) in Tartarus. This angered Gaia, who conspired with her son Cronus to overthrow Uranus. Cronus castrated his father, and from the blood that fell to Earth, the Furies, Giants, and nymphs were born.
The Reign of the Titans
Cronus became the ruler of the cosmos, but he feared a prophecy that foretold his downfall at the hands of one of his children. To prevent this, he swallowed each of his children as they were born. However, his wife Rhea managed to save Zeus by giving Cronus a stone wrapped in swaddling clothes instead. Zeus was raised in secret on the island of Crete.
Upon reaching maturity, Zeus challenged Cronus and the Titans in a great war known as the Titanomachy. With the help of his siblings, the Cyclopes, and the Hecatoncheires, Zeus emerged victorious. The defeated Titans were imprisoned in Tartarus, and Zeus became the king of the gods.
The Olympian Gods
The Olympian gods, led by Zeus, ruled from Mount Olympus and governed various aspects of the mortal and immortal worlds. Each god and goddess had their own domain and specific attributes:
Zeus: King of the gods, god of the sky, lightning, and thunder.
Hera: Queen of the gods, goddess of marriage and childbirth.
Poseidon: God of the sea, earthquakes, and horses.
Demeter: Goddess of the harvest and fertility.
Athena: Goddess of wisdom, warfare, and crafts.
Apollo: God of the sun, music, poetry, and prophecy.
Artemis: Goddess of the hunt, wilderness, and wild animals.
Ares: God of war and bloodshed.
Aphrodite: Goddess of love and beauty.
Hephaestus: God of fire, metalworking, and craftsmanship.
Hermes: Messenger of the gods, god of commerce and travelers.
Dionysus: God of wine, pleasure, and festivity.
Heroes and Their Labors
Greek mythology is replete with heroic figures who undertake extraordinary quests and face daunting challenges. One of the most famous heroes is Heracles (Hercules), known for his twelve labors imposed as punishment for killing his wife and children in a fit of madness induced by Hera. These labors include slaying the Nemean Lion, capturing the Golden Hind, and cleaning the Augean stables.
Other notable heroes include Perseus, who slayed the Gorgon Medusa; Theseus, who defeated the Minotaur in the labyrinth; and Achilles, the hero of the Trojan War, whose only vulnerable spot was his heel.
The Trojan War
The Trojan War, a central event in Greek mythology, was fought between the Greeks and the Trojans. It was sparked by the abduction of Helen, the wife of Menelaus, by Paris, a prince of Troy. The war lasted ten years and involved famous heroes like Achilles, Hector, and Odysseus. The war is chronicled in Homer's epic poems, the "Iliad" and the "Odyssey."
The Underworld and Afterlife
Hades, the brother of Zeus and Poseidon, ruled the underworld, a realm where the souls of the deceased went after death. The ferryman Charon transported souls across the river Styx to the realm of the dead. The most famous section of the underworld is Tartarus, a place of torment for the wicked.
Mythical Creatures and Beings
Greek mythology is populated with a diverse array of mythical creatures, such as the fearsome Chimera, the multi-headed Hydra, the Sphinx, the Griffin, and the Pegasus. These creatures often played roles in the heroic quests of demigods and mortals.
Legacy and Influence
Greek mythology has left an indelible mark on Western civilization. Its themes of heroism, tragedy, and divine intervention have inspired countless works of literature, art, and philosophy. The plays of ancient Greek playwrights like Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides drew heavily from these myths. Additionally, the Renaissance saw a revival of interest in classical mythology, with artists and scholars exploring its themes in their works.
In conclusion, Greek mythology is a vast and intricate tapestry that weaves together the stories of gods, goddesses, heroes, and mythical creatures. Its enduring legacy is evident in the continued fascination with these tales and their impact on art, literature, and culture throughout the ages. The myths serve not only as captivating stories but also as windows into the ancient Greek worldview, exploring the complexities of the human experience and the relationship between mortals and the divine.
Taglist (reblog/reply to be added):
@axl-ul @crow-flower @thoughts-fromthevoid @alderwoodbooks @harleyacoincidence @tuberosumtater @sonic-spade @theonlygardenia @holymzogynybatman @nulliel-tres
#writeblr#writers of tumblr#writing#bookish#booklr#fantasy books#creative writing#book blog#ya fantasy books#ya books#deep dives into folklore#deep dives#greek mythology#greek myth retellings#greek myth art#greek myth memes#percy jackson#percy jackon and the olympians
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
References to the Odyssey in owl odyssey
Spoilers for the episode Owl Odyssey!
When I saw the episode Owl Odyssey I was taken by surprise since there were a lot of references to the actual odyssey! It's a bit of a funny coincidence since recently I've been obsessed with the musical "Epic" which is based on the Odyssey. So I'm going to be analyzing all the references I caught in Owl Odyssey. I put the "keep reading" since this post ended up super long.


The episode starts with Aviva, Martin, Chris, and Koki being on the spaceship Aviva made. After the Kratt bros accidently start the ship it flies off and ends up landing in the ocean which leaves Jimmy Z all alone at the Tortuga. This starts the Wild Kratts "Odyssey" as they now have to try to find their way home without any technology except Aviva's creature power disk maker and the miniaturizer.



Throughout the episode we can see that more and more animals move in, starting with the grizzly bear and they end up kicking Jimmy Z out of the Tortuga. I think the animals moving in to the Tortuga are meant to represent Antinous and the other suitors that move in to Odysseus' castle while he is trying to get home. And I guess it would make Jimmy Z Penelope since he is left to wait for the team to get back home while the creatures take over.


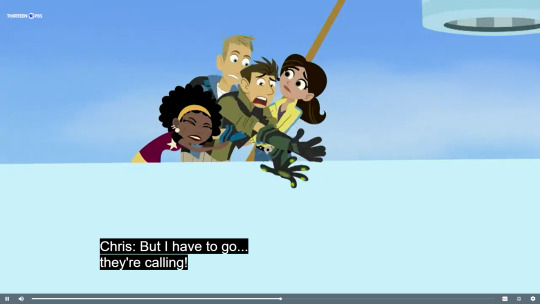


While they are on their way back home in the hot air balloon Aviva converted the ship into, Chris hears the call of some burrowing owls and is ready to jump out of the ship to get to them! I believe this is a reference to the Sirens who tried to lure Odysseus and his crew out to sea with their songs.
According to https://www.awesomestories.com/asset/view/Odysseus-and-the-Sirens
"Therefore pass these Sirens by, and stop your men's ears with wax that none of them may hear; but if you like you can listen yourself, for you may get the men to bind you as you stand upright on a cross-piece half way up the mast, and they must lash the rope's ends to the mast itself, that you may have the pleasure of listening. If you beg and pray the men to unloose you, then they must bind you faster. (See Samuel Butler’s translation of The Odyssey, Book XII, online via MIT.)"
Chris ends up asking Martin to help him out of the ropes so he can see the owls and Martin almost ends up almost helping him out of the Ropes until the crew miniaturizes Martin since they have to get home!


While miniaturized, Martin ends up meeting a Barn Owl and since nobody can hear the barn Owl he ends up naming the barn owl "Nobody". "Nobody" tries to attack Martin but Martin gets away and when he tries to tell the wild kratts crew that he was attacked they don't understand them since he keeps saying "Nobody" attacked him.






This is similar to when Odysseus is on the island with the cyclops but since he doesn't want to tell the cyclops his name he just says his name is "Nobody". When the Cyclops betrays him and attacks Odysseus, Odysseus hurts the cyclops and the cyclops calls out to their neighbors for help but the neighbors think the cyclops has gone crazy since the cyclops keeps saying he was attacked by "Nobody". Also, Chris just scooting over to check out who "Nobody" is and to see the chaos cracks me up lol.

Finally, the owl is often associated with the goddess Athena and seen as a symbol of intelligence and are effective hunters. Athena was the goddess of strategy, wisdom and warfare. Athena was also a patron of Odysseus in the Odyssey.
According to classicalwisdom.com
"Athena was a virgin warrior goddess, and was widely worshipped in the Greek world. The goddess was the embodiment also of strategy, wisdom, warfare and technical skills. Athena played a major role in the works of Homer, and is often shown as the patron of heroes such as Odysseus.
Athena was long associated with the owl. " https://classicalwisdom.com/culture/the-owl-of-athena-symbol-of-wisdom/
"Of the two Homeric poems, Athena plays a much larger role in the Odyssey. She essentially acts as the protector of Odysseus. At various points across Odysseus’ journey, it is Athena’s help and guidance that allow the cunning hero to escape to safety. Moreover, it is Athena’s request to Zeus that allows Odysseus to leave the island of Circe."
At the end of the episode, Chris uses his creature power suit to turn into an owl, fly the crew back home, and kick out all of the creatures from the tortuga. Aviva is inspired after seeing all kinds of different owls throughout their journey.





Soo that's all, 10/10 episode. :D It really lived up to the name "Owl Odyssey"! :D
#wild kratts#martin kratt#chris kratt#homer's odyssey#owls#Celeste Analyses#This episode took me by surprise!#I've been wanting to do this analysis for days
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
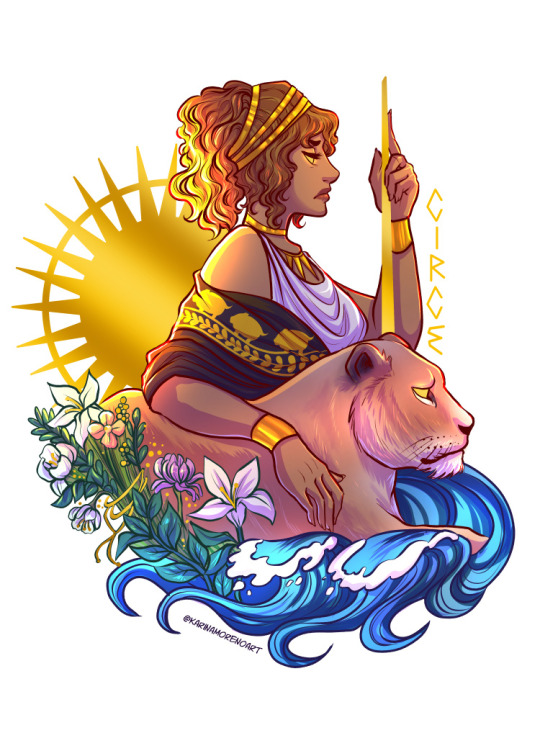
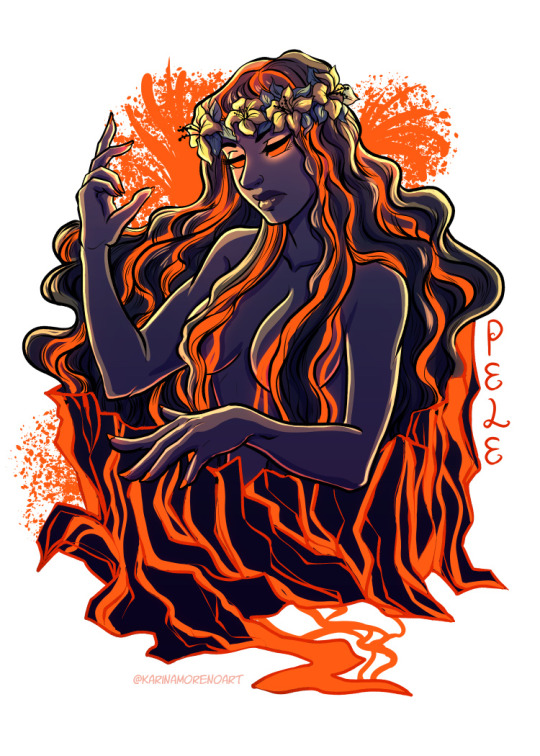





I like to reflect at the end of the year, so I wanted to showcase the first project I worked on in 2023! This is my Goddess sticker series, which you can find on my shop 💜
Goddesses:
Circe - A greek goddess born from the nymph Perse and the titan Helios. Circe has vast knowledge of potions, herbs, and animals. In Homer's Odyssey, she turns Odysseus’s men into pigs.
Ma'at - Egyptian goddess of truth, justice, balance, and order. In death, you must balance your heart against her feather to determine if you are worthy of the afterlife.
Pele - Hawaiian goddess of volcanoes, fire, and creator of the Hawaiian islands. She resides in Kīlauea, one of the most active volcanoes on earth.
Morrigan - Irish goddess of war, death, and destiny. Seeing Morrigan in battle was terrifying, as it meant impending doom on enemies. She often appears as a crow.
Sedna - Inuit goddess of the sea and marine animals. Unwilling to marry, her father threw her into the sea. When she tried to climb back on the boat, he cut off her fingers. Her fingers became marine life and she became their guardian.
10 notes
·
View notes