#fair labor standards act
Text
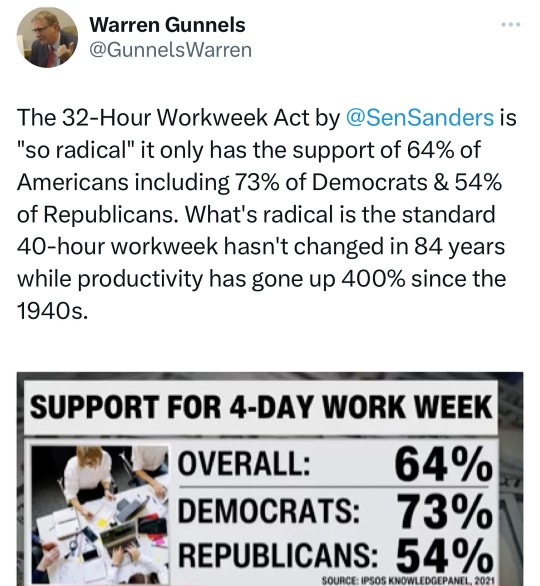

#bernie sanders#work week reduction#32-hour work week#overtime pay#productivity#technology#fair labor standards act#international examples#france#norway#denmark#germany#well-being#stress#fatigue#republican senator bill cassidy#small enterprises#job losses#consumer prices#japan#economic output#labor dynamics#artificial intelligence#automation#workforce composition
63 notes
·
View notes
Photo

(via Chick-Fil-A Restaurant Required To Pay Workers In Legal Tender, Not Chicken Tenders - Wonkette)
In July of this year, a Chik-Fil-A franchisee in Hendersonville, South Carolina, tried to save some money by asking "volunteers" to come work at their store directing customers to their new Drive Thru Express in exchange for chicken dinners.
"We are looking for volunteers for our new Drive Thru Express! Earn 5 free entrees per shift (1 hr) worked," a Facebook post read, "Message us for details."
then
Now, instead of saving a few bucks, franchise owner Joel Benson will be required to pay all of his "volunteers" in actual, non-edible money. The Labor Department ordered him this week to pay $235 in back pay to seven workers — on top of, we can assume, the five chicken entrees they were given at the time — as paying them in chicken was a violation of the Fair Labor Standards Act. Imagine that!
and
In addition to the backpay, this particular Chick-Fil-A is also being fined $6,450 in civil penalties for violating child labor laws by allowing three minors to operate a trash compactor, which is also illegal. While people under 18 can work, there are laws regulating what kind of work they are allowed to do, and operating a trash compactor is not one of the things they are allowed to do.
don’t go there - this entire company sucks in every way
220 notes
·
View notes
Text
#talkin#tik tok#food#recipes#nikki.mov#unions#labor unions#child labor#fair labor standards act#maternity leave#capitalism#class solidarity
86 notes
·
View notes
Text

I am still convinced that the American people, since 1932, continue to insist on two requisites of private enterprise, and the relationship of Government to it. The first is complete honesty at the top in looking after the use of other people's money, and in apportioning and paying individual and corporate taxes according to ability to pay. The second is sincere respect for the need of all at the bottom to get work — and through work to get a really fair share of the good things of life, and a chance to save and rise.
—Franklin D Roosevelt, Fireside Chat following Passage of the Fair Labor Standards Act, June 24, 1938
[Scott Horton]
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
So, for the past several weeks I have been speaking with my management team (in person) about how I would love to finish up the training that was cut short but all of my shifts have been dedicated to my regular duties and how I needed time scheduled during a shift that I could dedicate to training.
For the past couple of weeks I have been receiving (written) messages from management about the importance of completing our training modules. These messages have included deadlines for our training.
Meanwhile I have continued to speak to management about how I would love to complete my training but just need time.
Yesterday the deadline passed.
Today I received a message from management that if I did not complete the training before I clocked in for my next shift I would not be allowed to work.
So maybe it's my fault for not conducting my end of the conversation in written form where everything could be recorded for prosperity. Well, lesson learned.
I wrote a message back that I would LOVE to complete this training but, "I am hesitant to do my training off the clock as -- under the Fair Labor Standards Act -- all training that is related to work duties counts as hours worked and must be compensated."
They told me that I would be paid for work done off the clock.
Cool! How will you keep track of hours worked off the clock? I asked.
Then, and ONLY THEN did they tell me that I could log the days and times that I worked on my training and submit it for compensation.
And you can bet that I'll be auditing my paycheck.
Know your rights, people.
Be cordial, be respectful, be firm, know your rights, and keep records.
#employee rights#worker’s rights#USA workers rights#United States labor laws#labor laws#labor day#the deadline was Labor Day ironically.#know your rights#fair labor standards act
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

1 note
·
View note
Text
Final Independent Contractor Rule: Implications for Health Care
This morning, the Department of Labor issued a final rule interpreting who is and who is not, an independent contractor v. an employee. Contract work in health care has boomed since the pandemic, though even pre-pandemic, the use of contractors (physicians, nurses, therapists, etc.) was on the increase. The final rule is available here: 2024-00067
The new rule makes it harder for companies to…
View On WordPress
#1099#Agency#Compliance#Contract Work#Department of Labor#DOL#Employee#employer#Fair Labor Standards Act#Final Rule#Independent Contractor#Industry Outlook#Labor#litigation#Locum Tenens#Management#Money#Nurses#Policy#Post-Acute#staffing#Staffing Agencies#Strategy#Trends#W-2#wage and hour#wages#Washington
0 notes
Text
A Depression-era law allowing employers to pay them less is widely seen as unfair. But that view isn’t unanimous in the disability community.
0 notes
Text
How Does the Fair Labor Standards Act Protect Employees?
In 1938, the Fair Labor Standards Act was passed which protects employees’ rights to fair wages. Also known as the FLSA, this law protects employees by placing regulations on interstate commerce employment. It oversees things like child labor, minimum wage, and overtime pay; and has standards for both salaried employees and those paid by the hour.
What is the Fair Labor Standards Act?
The FLSA is a federal law that oversees wage regulations for both full and part time employees whether they are employed by a private company or government employer. It regulates things such as the minimum wage, child labor, recordkeeping, and overtime. Federal minimum wage was increased to $7.25 in 2009 and has not been raised since. Generally, if employees work more than forty hours per workweek, they should be paid ‘time and a half’ which is 1.5 times their regular rate of pay.
Who is Protected By the FLSA?
The Fair Labor Standards Act protects employees of public agencies, interstate commerce, production of commercial goods, domestic service, hospitals, schools, and other education facilities. Independent contractors and volunteers are not legally considered employees, and as such, are not protected by the standards and regulations of the FLSA. Employees who are eligible for overtime compensation are required to complete a record of their attendance and times worked.
Primary Areas of Coverage in FLSA
Minimum Wage – The FLSA maintains the federal minimum wage. As of 2009, the minimum wage has been $7.25 per hour. While states are free to set their own minimum wage rates, the only states with a minimum wage lower than the federal rate are Georgia and Wyoming. Both states pay a minimum wage of $5.15 per hour, although employers who are subject to FLSA regulations are required to pay no less than the federal minimum.
Overtime – If an employee is sixteen or older, they may work as many hours as their employer allows. However, if an employee works more than forty hours in a workweek, they may be entitled to overtime pay. Overtime pay must be at least one and a half times the normal hourly rate of pay for the employee.
Hours Worked – The FLSA oversees all time that an employee is doing their job either on site, on duty, or at a designated location.
Recordkeeping – The FLSA requires that employers keep accurate records of employee timecards and payroll. They must also have an official poster of FLSA requirements displayed for employees.
Child Labor – The FLSA maintains regulations that ensure that work does not interfere with a child’s education or best interests. It also limits the types of jobs that children can work and the conditions they can work under.
FLSA Minimum Wage Protections
Though the FLSA maintains a federal minimum wage of $7.25 per hour, many states have instituted their own laws that set their own minimum wage. The FLSA does not govern state law outside of provisions that are in line with preexisting FLSA requirements.
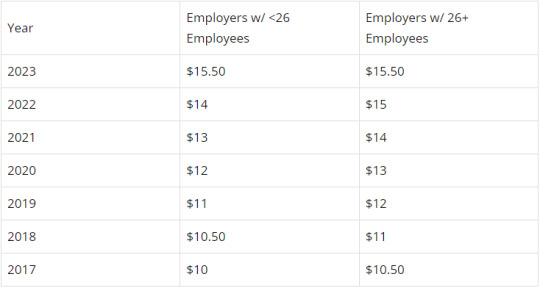
California Minimum Wage
As of January 2023, the state imposed minimum wage in California is $15.50 per hour for all employers. In the past, employers with 26 or more employees were required to pay slightly more than employers with fewer employees. California minimum wage has been rising steadily for years now:
Minimum Wage by Year
FLSA Overtime Protections
The FLSA maintains that an employer must pay covered non-exempt employees time and a half for any time worked over forty hours in a given work week. This does not include paid time off. A work week might not line up with what is considered a calendar week but is a fixed increment of 168 hours. While the work week may vary for different employees, employers are prohibited from averaging hours beyond the confines of a given work week. Furthermore, overtime pay must generally be paid out on the pay period in which it was earned.
Classifying Employees Under FLSA
It is important to know whether a worker is an employee or an independent contractor. Not only are there differences in the rights and benefits, but employers may face fines and legal action if they are caught misclassifying their workers. There are many questions that can be asked to help determine if a worker is an employee or an independent contractor:
Does the employer or the worker determine when and how the work is done?
Does the employer or the worker determine what the worker’s responsibilities are?
Does the employer or the worker provide the supplies and equipment needed?
Does the employer or the worker pay the payroll taxes?
Does the employer or the worker set the rate of pay?
Who is Exempt from Minimum Wage & Overtime Wages?
If an employee is considered nonexempt, then their employer is required to pay them overtime. If an employee is considered exempt, then their employer is not required to pay them overtime. While there are some jobs that are considered exempt in of themselves, there are three conditions that must be met to determine if an employee is considered exempt, such as:
The amount the employee is paid – Generally $35,568 or more a year
The way they are paid – Generally salary
The type of work performed – As defined by FLSA regulations
Freelance workers and independent contractors are not covered by the FLSA. Employers with less than $500,000 a year in sales as well as small farms that do not engage in interstate commerce are also exempt. Other exempt workers also include:
Executives who manage at least two people and authorize job status of others
Administrators who directly work for management and control their own work duties
Outside salespeople who work primarily offsite and on commission
Computer workers paid at least $684 weekly by salary or fee basis
Workers employed by seasonal recreation establishments
Employees of small local newspapers including delivery workers
Sailors on foreign vessels
Personal caregivers such as homecare aides and babysitters
Employees working under an apprenticeship
Record Keeping That Meets FLSA Standards
When an employer is covered by the FLSA, they must keep detailed records for their non-exempt employees. While there is no uniform standard for how these records are kept, there are specific pieces of information that need to be recorded with complete accuracy for each employee:
Full Name
Social Security Number
Date of Birth (employees under 19)
Sex
Occupation
Start of Workweek Day and Time
Daily Hours Worked
Workweek Hours Worked
How wages are paid
Pay Rate by Hour
Total Straight-time Earnings
Workweek Overtime Earnings
Wage Deductions and Additions
Wages per Pay Period
Dates of Pay Period
Date of Payment
Different types of records must be kept on file for different lengths of time. Payroll, collective bargaining agreements, and sales or purchase records must be kept for at least three years. Things like timecards, work schedules, and other methods for computing wages must be kept for at least two years. These records should be kept on site or at a central record keeping office. Employers are required to make these records open and available for Division inspection.
How FLSA Defines and Regulates Hours Worked
The law defines the word ‘employ’ as “to suffer or permit to work”. The time that an employee spends on site or on duty is considered part of their workweek. The workday begins when the employee first starts working and ends when the employee completes their work. The workday often includes more than just hours worked. There are many different classifications of hours under the FLSA and variables that determine if they are considered working hours.
Waiting – There are two different kinds of waiting time. Being engaged to wait is considered work time such as short periods of down time between tasks. Waiting to be engaged is not considered work time such as free time between jobs.
On Call – An employee is considered working while on call if they are required to stay on site. Generally, if an employee is free to go about their day, they are not considered working while on call. The extent of that freedom may change whether or not the employee is considered working.
Breaks – Short breaks, often five to twenty minutes, are generally considered to be part of hours worked and are paid time. Employers may implement their own consequences for employees taking extended breaks and may be permitted to not count the extra time as time worked. Meal breaks, often thirty to sixty minutes, are usually not considered to be part of hours worked and are unpaid so long as the employee is completely free of their work responsibilities while on break.
Sleep – If an employee is on duty for shifts of twenty-four hours or longer, they may negotiate unpaid sleeping breaks with their employer. These breaks must be more than five and less than eight hours and the employer must provide a proper sleeping area. For shifts shorter than twenty-four hours, authorized sleeping breaks are considered time worked.
Training & Meetings – There are four factors that must apply in order for a meeting or training program to be unpaid: Outside of working hours, attendance is voluntary, unrelated to the employee’s job, and no work is required to be done.
Daily Commute – Regular travel time from home to work and back is not considered hours worked.
One Time Extended Commute – If an employee routinely works at one location and is required to go to another location in another city for a day, the additional commute time may be considered time worked. Employers are permitted to exclude the employee’s normal commute time from those hours.
Daily Travel – Some jobs may require travel as part of the employee’s duties such as deliveries or traveling between job sites. This travel time is considered hours worked.
Trips – If an employee is required to travel for work and is kept away overnight, this is considered travel away from home and is hours worked. Not only is working time counted, but also work hours on days off while away.
FLSA Regulations on Child Labor
There are many restrictions on the type of work that employees under eighteen years old may be permitted to perform as well as the conditions under which they are permitted to work. The FLSA does not allow minors to work jobs that they consider hazardous to the minor’s wellbeing or education. There are also restrictions governing the hours a minor is allowed to work and the breaks they must be provided. Each state also has their own laws regulating child labor that employers should be aware of.
Recent FLSA Updates
The 2018 amendments to FLSA regarding tipped employees were updated in 2020 and 2021. The new regulations forbid employers from taking any part of the employee’s tips and also updated the restrictions on when an employer can alter an employee’s pay based on earned tips.
The Joint Employer Rule was rescinded in July of 2021.
The United States Department of Labor recently began proposal of a new rule to update the regulations and guidelines for determining if a worker is an independent contractor or an employee in accordance with the FLSA. This rule was proposed in October of 2022, replacing the January 2021 rule with a more accurate and precise method for classification. The rule is considered mutually beneficial for both workers and employers, reducing the risk of employee misclassification, and increasing employer confidence and peace of mind when hiring independent contractors.
Common Violations of FLSA
Unfortunately, there are many ways in which employers can and do violate the Fair Labor Standards Act:
Misclassification – Employers may sometimes classify an employee as exempt based on their job title or type of pay rate even though the job duties and amount of pay indicate that the employee is nonexempt. It is important for employers to be mindful of all the variables of a situation and for employees to be well informed of their rights.
Not compensating off the clock work – When an employee works beyond their scheduled time, even if they are clocked out, that is still considered hours worked and the employee should be compensated. Even if the employer did not request or permit the off the clock work, they are still responsible for paying the employee.
Not compensating working breaks – When an employee is expected to be on call through their breaks, or works through their lunch, that time is considered hours worked and the employee must be compensated. In order for a break to be unpaid, the employee must not be performing any job-related duties such as cleaning, replying to emails, or interacting with clients.
Overtime waivers – If an employer has an employee sign a document waiving their right to overtime pay, that document is invalid and unenforceable.
Averaging workweeks – Sometimes, an employer may average out the number of hours an employee has worked over two or more weeks to avoid paying overtime. If an employee takes a day off one week and then works an extra eight hours the next week, the employer may average those hours out to say the employee worked forty hours each week. This may seem mathematically logical, but it is actually legally prohibited.
What to Do If Your Employer Violates the FLSA
Because there are employers who will violate FLSA, employees must be aware of the options available to them and the steps to take if they find themselves in such a situation. Complaints regarding FLSA violations can and should be filed with the Department of Labor’s Wage and Hour Division.
The WHD investigates violation claims by having a representative conduct interviews with the employer and various employees, research payroll and timecard documents, and gather any other information that may indicate if a violation has been committed.
The person who files the complaint does not need to be the person against whom the violation was committed. Anyone who witnesses their employer violating the FLSA may report that violation.
It is prohibited for an employer to retaliate against an employee who has filed a complaint or participated in an investigation against them.
How to File FLSA Complaint
When filing a complaint with the WHD, there are several details you will need to provide:
Your name
Your address
Your phone number
The company’s name, address, and number
Owner/employer/manager name
Your job duties
Your pay rate and method
It is good to be as detailed as possible when providing information. Your complaint is the starting point of their investigation. When filing a complaint as a third party, you may not have all of the information needed, but it is important to share as much as possible.
Contact Mesriani Law Group if You Have Experienced a FLSA Violation
The Fair Labor Standards Act exists to protect workers and their right to fair wages. All too often, employers try to circumvent the law and get away with cheating their employees out of the money they’ve earned. When these violations occur, employees have the right to file complaints against their employers. If you are facing retaliation for filing a claim with the Department of Labor or participating in an investigation against your employer, call Mesriani Law Group today for a free consultation.
Fair Labor Standards Act FAQs
What are the four main elements of the FLSA?
There are four primary areas established and enforced by the Fair Labor Standards Act. Establishing and enforcing minimum wage, overtime pay, regulations for recordkeeping, and regulations for child labor. While some jobs and employees may not be covered by the FLSA or exempt from overtime, the act generally applies to part time as well as full time workers of both private and government employers.
What are some common mistakes made under FLSA?
Whether intentional or accidental, there are employers who do not adhere to the regulations set forth by the FLSA. One of the most common mistakes employers make is misclassifying their employees. Not paying overtime properly and allowing employees to work off the clock or during their breaks without compensation are also violations that occur far too often. It is important for everyone on both sides of an employment relationship to be familiar with the law and how it applies to them.
What is not regulated under the Fair Labor Standards Act?
There are several aspects of employment that the Fair Labor Standards Act does not oversee. This includes but it not limited to things like the payment of wages in excess of FLSA requirements, lunch and rest breaks, termination letters, and final payments for terminated employees. The FLSA also does not regulate paid time off. It is important to also be aware of state laws and regulations pertaining to all employment matters.
#California Employment Law#Fair Labor Standards Act#FLSA#Employment Law#Employment Lawyers#California Attorneys
0 notes
Text
1 note
·
View note
Text
DOL Issues Guidance on Handling Telework Under FLSA, FMLA
The U.S. Department of Labor (DOL) has issued guidance on the application of the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) and Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) to employees who telework from home or from another location away from the employer’s facility.
The Field Assistance Bulletin (FAB) 2023-1, released on February 9, 2023, is directed to agency officials responsible for enforcement and provides…

View On WordPress
#business#department of labor#DOL#Employment Law#Fair Labor Standards Act#Family and Medical Leave Act#FLSA#FMLA#Labor Law#legal
0 notes
Text
Another Class Action Filed Claiming Companies Have Miscategorized Contract Growers
Latest post highlights another recent case filed claiming poultry growers are employees not independent contractors.
Image of poultry house with grass buffer strip before harvested field. Image by the Chesapeake Bay Program
The article is not a substitute for legal advice.
Earlier this year, I posted about a recently filed class action lawsuit involving contract poultry growers, arguing that they were employees of Amick Farms and not independent contractors. For anyone needing a refresher on a…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Who Needs School? Just Put 'Em To Work!
Much has been written about the history of children working and child labour laws in the United States. Federal child labor laws are broad in scope, and many states have state laws that are more restrictive, as is only right and fair. Children are children for the first 18 years of their lives, and then they are adults for the entire rest of their lives. The focus during their childhood should…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
[“Such groups suffer from a syndrome I call empowerment to the midline. We dedicate ourselves to empowering individuals, right up until the moment when someone actually begins to exercise power — defined simply as the ability to get what they want done. At that point, it’s as if they’ve stepped over an invisible line that separates the oppressed from the oppressors. Suddenly this person we’ve worked so hard to help find a voice becomes the person everyone wants to speak out against.
I also call this pattern empowerment to complain. We focus our nurturing and attention on anyone who takes the position of victim and complains about leadership. Anyone who takes action or sets direction is suspect. Unfortunately, this sort of empowerment is not very empowering. Nobody gets what they want, and often little or nothing gets done.
True empowerment implies action. Complaining is not enough. Taking action means taking responsibility — suggesting, offering solutions and doing the work to implement them. But in a group suffering from the empowerment to the midline syndrome, there’s no zone of action, no autonomy, no scope for creativity. The group may have done away with the inequalities of leaders and followers, of some people being the stars and others relegated to mere extras. But they’ve done so by preventing anyone from having the power to act.
Here are some of unspoken assumptions behind the empowerment to the midline syndrome in progressive and collaborative groups.
1. People who have extraordinary skills, experience, levels of commitment or other resources or who take on big responsibilities — call them leaders — are always suspect. They are fair game for attack. The result is that no one feels truly safe in the group. There is no trust. No one is able to train, to mentor or pass on skills.
2. Leaders should never receive extra benefits, perks or rewards beyond the joy of the work itself, or they are exploiting others. In collaborative groups, we are often reacting against a larger system of hierarchy, in which higher levels of responsibility confer marks of status and collateral powers. We don’t want to reproduce that sort of inequality. But we do want to allow people to earn fair rewards for their labors, marks of appreciation and respect. If a group continually sees its most experienced people drifting away or burning out, it may be a warning sign that this pattern is in force.
3. We must always sacrifice the needs, benefits and rewards of insiders to the needs of outsiders. Empowerment means always siding with the perceived victim or underdog. The group functions on power-under — people get their way by taking the position of victim. They gain social power, not by taking on responsibility, but by complaining about those who do. The complainers are not truly empowered to act, and those who do take action are undermined.
4. We refuse to acknowledge that people might have different levels of skill, experience, talent, commitment or responsibility, because to do so might affirm a hierarchy. The group is unable to make use of its members’ skills and talents. We can’t mentor and critique each other, we can’t assess what skills and forms of responsibility are needed or are operative in a group and we can’t set standards or hold one another accountable for meeting them.”]
starhawk, from the empowerment manual: a guide for collaborative groups, 2011
817 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Why Do We Have Weekends?
Ladies and gentlemen…the weekend. Why do we have it?
The short answer: unions!
In the late nineteenth century, many workers labored 7 days a week, sometimes up to a grueling 100 hours in poor conditions.
Workers were fed up. Many began to unionize and take to the streets in protest.
Violence against them at the hands of corporate union busters and law enforcement was common. Many lost their lives. But they didn’t relent.
Organized labor kept up the pressure. Workers in the mining, printing, and railroad industries eventually won 8-hour-work days. Major corporations, most notably Ford Motor Company, began to heed calls to institute 5-day work weeks.
But most workers across the country were not guaranteed these benefits.
Then came Frances Perkins — President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s Labor Secretary and the first woman cabinet secretary.
Before agreeing to the position, Perkins met with FDR to secure a guarantee that he would support her pro-labor agenda.To her surprise, FDR backed her.
In 1938, thanks to her advocacy and the momentum built by organized labor, Congress passed the Fair Labor Standards Act — which among many things ultimately established a 40-hour work week by forcing employers to pay time and a half for any hours worked beyond this limit.
And thus, created the weekend.
While many workers now enjoy weekends won by organized labor, the fight continues for those who don’t.
A rising number of contract employees, sometimes known as “gig workers,” are putting in backbreaking hours without the protections afforded to full-time workers.
Now is the time to renew the historic call of unions to make sure ALL workers are afforded the dignity — and time off from work — they deserve.
And who knows — maybe one day we’ll move to a three day weekend?
440 notes
·
View notes
Text
Companies get around paying overtime to some employees by adding "manager" to their titles.

0 notes