#automation
Text

Whispering secret data.
#lab#machine#automation#robotics#cyberpunk#retro#scifi#stuck#laboratory#farm#android#cyborg#data#secret#whisper#illustration#drawing#digitalartwork#digitaldrawing#digitalart#digitalillustration#90s#cables#machinelearning#connection#ring#runner#net#flesh
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
#holland roden#kim dokja#automation#hijack#femininity#feminized husband#giantess#vogue#weheartit#kelly gale#Diane Guerrero#john Hancock#dm me for my content#bubbline
133 notes
·
View notes
Text

Häagen-Bot.
And more robots.
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
Accessibility tip:
If you want to automate your home a bit, but you don't want any "smart" tech, you can just buy remote controlled power sockets instead
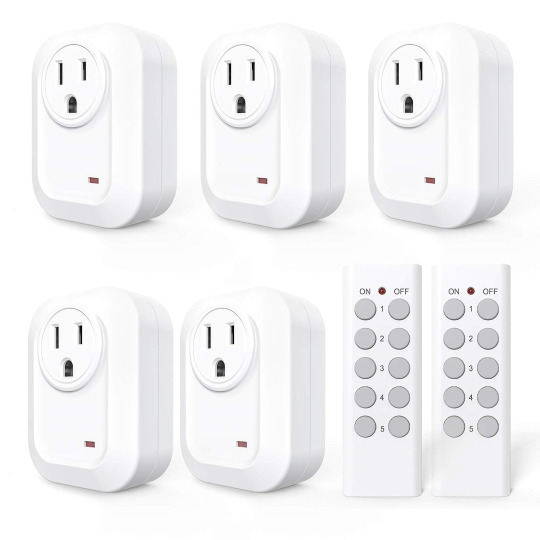

They are a lot cheaper and easier to set up and use than some home automation smart tech nonsense
They don't need an app (but some models come with optional apps and there are apps that are compatible with most of these)
Many of them use the 433mhz frequency to communicate, which makes most models compatible with each other, even if they are from different manufacturers
The tech has been around for a long time and will be around for a long time to come
You don't have to put any fucking corporate listening devices like an amazon echo in your home
Models for outdoors exist as well
#accessibility#automation#tech#a set like the one pictured above usually costs around $20-$30#I got like 7 of these bad boys and 3 remotes#I can control basically everything in my room with these remotes#I got one remote on my office chair one on my nightstand and one by my door#this always makes me feel a bit like I am in Arnold's room from Hey Arnold!
29K notes
·
View notes
Text
The real reason the studios are excited about AI is the same as every stock analyst and CEO who’s considering buying an AI enterprise license: they want to fire workers and reallocate their salaries to their shareholders

The studios fought like hell for the right to fire their writers and replace them with chatbots, but that doesn’t mean that the chatbots could do the writers’ jobs.
Think of the bosses who fired their human switchboard operators and replaced them with automated systems that didn’t solve callers’ problems, but rather, merely satisficed them: rather than satisfying callers, they merely suffice.
Studio bosses didn’t think that AI scriptwriters would produce the next Citizen Kane. Instead, they were betting that once an AI could produce a screenplay that wasn’t completely unwatchable, the financial markets would put pressure on every studio to switch to a slurry of satisficing crap, and that we, the obedient “consumers,” would shrug and accept it.
Despite their mustache-twirling and patrician chiding, the real reason the studios are excited about AI is the same as every stock analyst and CEO who’s considering buying an AI enterprise license: they want to fire workers and reallocate their salaries to their shareholders.
-How the Writers Guild sunk AI's ship: No one's gonna buy enterprise AI licenses if they can't fire their workers

Image:
Cryteria (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#labor#unions#ai#tescreal#ai hype#critihype#automation#luddism#writers strike#writers guild#union strong#class war
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
Someone needs to work for Ok Go
source
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
#mazda rx7#jdm#trevor spitta#art#japan#automotive#coupe#pickup#sedan#adirondack nationals#car show#automobile#automatically generated text#automation#cars#convertible#suv#sports cars#classic car#fast cars#vintage cars#electric cars#classic cars#today on tumblr#trending now#for you#fyp#trending#tumblr#for you page
359 notes
·
View notes
Note
If management finds a way to automate jobs during a strike, is that scabbing?
Peripherally.
The automation itself is more part of the general category of management strategies to restructure workflow and production methods in order to reduce the need for, and thus the power of, labor. This dates back to the origins of Taylorism itself in the 1890s as an effort to “steal the brains from underneath the cap of labor” and through to the emergence of Human Relations and Industrial Psychology in the early 20th century as a means to better control workers. So I think you could see in as essentially equivalent to classic speed-up and stretch-out efforts to maintain production at as low a cost as possible during a strike, and thus break the union.
However, the dirty truth of automation is that there is no clean way to fully substitute machinery for labor. Due to the inherent limitations of technology at any stage of development, you need labor to repair and maintain and monitor automated systems, you need labor to install and operate the machines, you need labor to design and program and manufacture the machines. (This is one reason why the job-killing predictions around automation often fall flat, because the supposedly superior new technology often requires a significant increase in human labor to service the new technology when it breaks. For example, this is why automation in fast food has proven to be so difficult and partial than expected: it turns out that self-checkout machines are actually very expensive to operate in terms of skilled manpower.) And to the extent that a given automation contract or project is being undertaken during a strike in order to break that strike, that’s absolutely scabbing.
#labor#labor history#trade unions#unions#strikes#automation#Taylorism#political economy#economic history#scabbing#labor studies
131 notes
·
View notes
Text
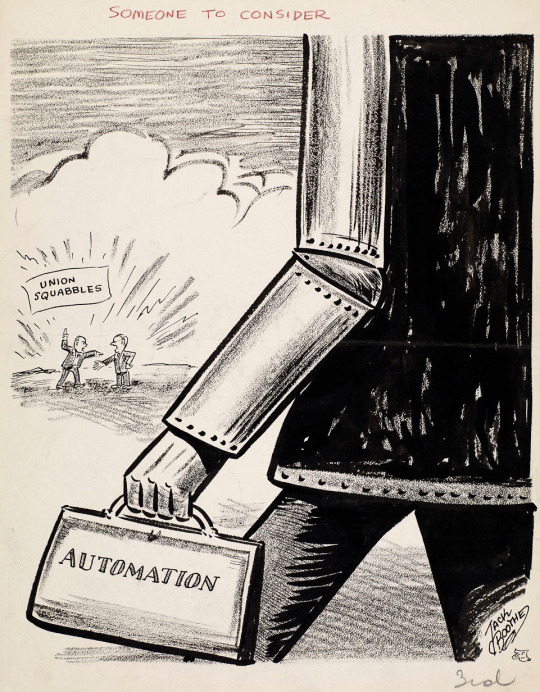
Jack Boothe cartoon from the Hamilton Spectator of Hamilton, Ontario, April 7, 1960.
(Library and Archives Canada)
157 notes
·
View notes
Text

Tolerance threshold.
#lab#cyborg#android#cyberpunk#retro#monitor#tolerance#threshold#code#admin#automation#complete#artificial#intelligence#brain#mind#computer#nudesketch#femalebody#colunavertebral#silicon#robotics#cables#critical#illustration#digitalillustration#digitalart#digitalartwork#90s
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
AI ethics vs AI "safety"

They are hemorrhaging a river of cash, but that river’s source is an ocean-sized reservoir of even more cash.
To keep that reservoir full, the AI industry needs to convince fresh rounds of “investors” to give them hundreds of billions of dollars on the promise of a multi-trillion-dollar payoff.
That’s where the “AI Safety” story comes in. You know, the tech bros who run around with flashlights under their chins, intoning “ayyyyyy eyeeeee,” and warning us that their plausible sentence generators are only days away from becoming conscious and converting us all into paperclips.
It’s pure criti-hype: “Our technology is so powerful that it endangers the human race, which is why you should both invest in it and use it to replace all of your workers.”
This form of criticism is entirely distinct from the legitimate realm of “AI ethics,” whose emphasis is on how bad AI is at the things that will supposedly generate those promised trillions. Things like bias, low-quality training data, training data attacks, data ordering attacks, adversarial examples, the endless stream of confident lies, and the high degree of supervision they necessitate.
Add to that the exploitative labor pipeline, the environmental damage, and the public safety risks and a very different critique emerges —one that’s grounded in AI’s shortcomings, not the supposed risks arising from its incredible power.
-How the Writers Guild sunk AI's ship: No one's gonna buy enterprise AI licenses if they can't fire their workers

Image:
Cryteria (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:HAL9000.svg
CC BY 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/deed.en
#labor#unions#ai#tescreal#ai hype#critihype#automation#luddism#writers strike#writers guild#union strong#class war
910 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kenyan tea pickers are destroying machines brought in to replace them during violent protests that highlight the challenge faced by low-skilled workers as more agribusiness companies rely on automation to cut costs.
At least 10 tea-plucking machines have been torched in multiple flashpoints in the past year, according to local media reports. Recent demonstrations have left one protester dead and several injured, including 23 police officers and farm workers. The Kenya Tea Growers Association (KTGA) estimated the cost of damaged machinery at $1.2 million (170 million Kenyan shillings) after nine machines belonging to Ekaterra, makers of the top-selling tea brand Lipton, were destroyed in May.
In March, a local government taskforce recommended that tea companies in Kericho, the country’s largest tea-growing town, adopt a new 60:40 ratio of mechanized tea harvesting to hand-plucking. The taskforce also wants legislation passed to limit importation of tea harvesting machines. Nicholas Kirui, a member of the taskforce and former CEO of KTGA, told Semafor Africa 30,000 jobs had been lost to mechanization in Kericho county alone over the past decade.
"We did public participation in all the wards and with all the different groups, and the overwhelming sentiment we were hearing was that the machines should go," Kirui said.
In 2021, Kenya exported tea worth $1.2 billion, making it the third-largest tea exporter globally, behind China and Sri Lanka. Multinationals including Browns Investments, George Williamson and Ekaterra — which was sold by Unilever to a private equity firm in July 2022 — plant on an estimated 200,000 acres in Kericho and have all adopted mechanized harvesting.
Some machines can reportedly replace 100 workers. Ekaterra's corporate affairs director in Kenya, Sammy Kirui, told Semafor Africa that mechanization was “critical” to the company’s operations and the global competitiveness of Kenyan tea. As the government taskforce established, one machine can bring the cost of harvesting tea down to 3 cents (4 Kenyan shillings) per kilogram from 11 cents (15.32 shillings) per kilogram with hand-plucking.
Analysts partly attribute Kenya's unemployment rate — the highest in East Africa — to automation in industries, including banking and insurance. Some 13.9% of working age Kenyans (over 16) were out of work or long term unemployed in the final quarter of 2022.
354 notes
·
View notes