#ecology and conservation
Text
I'm livid. Attenborough played a large part in me deciding to follow ecology and conservation as a career path! The episode that's being withdrawn is about the destruction and rewilding of British natural habitats, which the general public need to see! Pandering to right-wing morons, who do nothing but bury their heads in the sand and pretend that they've got nothing to do with it, is not how we're going to fix it! The world is suffering biodiversity loss on a huge scale and more awareness means more likelihood of people coming together to find solutions! I've never been so disappointed with the BBC...
#bbc#david attenborough#stem awareness#biodiversity#biodiversity loss#citizen science#ecology and conservation#rewilding#British natural habitats#habitat restoration#habitat loss#fuck tories
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
If you aren't following the news here in the Pacific Northwest, this is a very, very big deal. Our native salmon numbers have been plummeting over the past century and change. First it was due to overfishing by commercial canneries, then the dams went in and slowed the rivers down and blocked the salmons' migratory paths. More recently climate change is warming the water even more than the slower river flows have, and salmon can easily die of overheating in temperatures we would consider comfortable.
Removing the dams will allow the Klamath River and its tributaries to return to their natural states, making them more hospitable to salmon and other native wildlife (the reservoirs created by the dams were full of non-native fish stocked there over the years.) Not only will this help the salmon thrive, but it makes the entire ecosystem in the region more resilient. The nutrients that salmon bring back from their years in the ocean, stored within their flesh and bones, works its way through the surrounding forest and can be traced in plants several miles from the river.
This is also a victory for the Yurok, Karuk, and other indigenous people who have relied on the Klamath for many generations. The salmon aren't just a crucial source of food, but also deeply ingrained in indigenous cultures. It's a small step toward righting one of the many wrongs that indigenous people in the Americas have suffered for centuries.
#salmon#dam removal#fish#animals#wildlife#dams#Klamath River#Klamath dams#restoration ecology#indigenous rights#Yurok Tribe#Karuk Tribe#nature#ecology#environment#conservation#PNW#Pacific Northwest
13K notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
A sponge city is a new urban construction model for flood management, strengthening ecological infrastructure and drainage systems, proposed by Chinese researchers in early 2000 and accepted by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the State Council as urbanism policy in 2014. It can alleviate urban flooding, water resources shortage, and the urban heat island effect and improve the ecological environment and biodiversity by absorbing and capturing rain water and utilizing it to reduce floods. (x)
Sponge cities are part of a worldwide movement that goes by various names: green infrastructure in Europe, low-impact development in the United States, water-sensitive urban design in Australia, natural infrastructure in Peru, nature-based solutions in Canada. In contrast to industrial management, in which people confine water with levees, channels, and asphalt and rush it off the land as quickly as possible, these newer approaches seek to restore water’s natural tendency to linger in places like wetlands and floodplains. — The architect making friends with flooding

#ecology#ecology and conservation#nature#architecture#urban planning#water#video#photography#links#reference#Youtube#my post
1 note
·
View note
Text
Yo this rules and is genuinely uplifting
16K notes
·
View notes
Text

#green memes for ecological fiends#zoology#ecology#bird#hawks#environmental science#biodiversity#conservation biology#conservation#wildlife
28K notes
·
View notes
Text


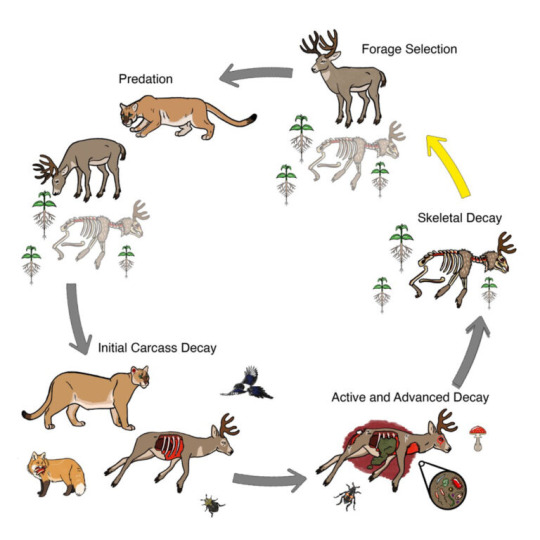

the mountain lions are unwittingly practicing witchcraft to improve their hunting chances and leaving patches of terra preta behind
21K notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey. You.
Check out this weird fish.

Cool, huh? It's got no bones and it's older than T rex. Wanna learn more? Check out Consider Nature:
#animals#science#biology#nature#conservation#wildlife#environment#fish#fishing#ecology#considernature
5K notes
·
View notes
Photo

Plant native plants, y’all!
#lawns#gardens#home and garden#gardening#native plants#ecology#environment#conservation#nature#outdoors
14K notes
·
View notes
Text
In the Willamette Valley of Oregon, the long study of a butterfly once thought extinct has led to a chain reaction of conservation in a long-cultivated region.
The conservation work, along with helping other species, has been so successful that the Fender’s blue butterfly is slated to be downlisted from Endangered to Threatened on the Endangered Species List—only the second time an insect has made such a recovery.
[Note: "the second time" is as of the article publication in November 2022.]
To live out its nectar-drinking existence in the upland prairie ecosystem in northwest Oregon, Fender’s blue relies on the help of other species, including humans, but also ants, and a particular species of lupine.
After Fender’s blue was rediscovered in the 1980s, 50 years after being declared extinct, scientists realized that the net had to be cast wide to ensure its continued survival; work which is now restoring these upland ecosystems to their pre-colonial state, welcoming indigenous knowledge back onto the land, and spreading the Kincaid lupine around the Willamette Valley.
First collected in 1929 [more like "first formally documented by Western scientists"], Fender’s blue disappeared for decades. By the time it was rediscovered only 3,400 or so were estimated to exist, while much of the Willamette Valley that was its home had been turned over to farming on the lowland prairie, and grazing on the slopes and buttes.

Pictured: Female and male Fender’s blue butterflies.
Now its numbers have quadrupled, largely due to a recovery plan enacted by the Fish and Wildlife Service that targeted the revival at scale of Kincaid’s lupine, a perennial flower of equal rarity. Grown en-masse by inmates of correctional facility programs that teach green-thumb skills for when they rejoin society, these finicky flowers have also exploded in numbers.
[Note: Okay, I looked it up, and this is NOT a new kind of shitty greenwashing prison labor. This is in partnership with the Sustainability in Prisons Project, which honestly sounds like pretty good/genuine organization/program to me. These programs specifically offer incarcerated people college credits and professional training/certifications, and many of the courses are written and/or taught by incarcerated individuals, in addition to the substantial mental health benefits (see x, x, x) associated with contact with nature.]
The lupines needed the kind of upland prairie that’s now hard to find in the valley where they once flourished because of the native Kalapuya people’s regular cultural burning of the meadows.
While it sounds counterintuitive to burn a meadow to increase numbers of flowers and butterflies, grasses and forbs [a.k.a. herbs] become too dense in the absence of such disturbances, while their fine soil building eventually creates ideal terrain for woody shrubs, trees, and thus the end of the grassland altogether.
Fender’s blue caterpillars produce a little bit of nectar, which nearby ants eat. This has led over evolutionary time to a co-dependent relationship, where the ants actively protect the caterpillars. High grasses and woody shrubs however prevent the ants from finding the caterpillars, who are then preyed on by other insects.
Now the Confederated Tribes of Grand Ronde are being welcomed back onto these prairie landscapes to apply their [traditional burning practices], after the FWS discovered that actively managing the grasslands by removing invasive species and keeping the grass short allowed the lupines to flourish.
By restoring the lupines with sweat and fire, the butterflies have returned. There are now more than 10,000 found on the buttes of the Willamette Valley."
-via Good News Network, November 28, 2022
#butterflies#butterfly#endangered species#conservation#ecosystem restoration#ecosystem#ecology#environment#older news but still v relevant!#fire#fire ecology#indigenous#traditional knowledge#indigenous knowledge#lupine#wild flowers#plants#botany#lepidoptera#lepidopterology#entomology#insects#good news#hope
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
“I loathe that word ‘pristine.’ There have been no pristine systems on this planet for thousands of years,” says Kawika Winter, an Indigenous biocultural ecologist at the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa. “Humans and nature can co-exist, and both can thrive.”
For example, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) in April, a team of researchers from over a dozen institutions reported that humans have been reshaping at least three-quarters of the planet’s land for as long as 12,000 years. In fact, they found, many landscapes with high biodiversity considered to be “wild” today are more strongly linked to past human land use than to contemporary practices that emphasize leaving land untouched. This insight contradicts the idea that humans can only have a neutral or negative effect on the landscape.
Anthropologists and other scholars have critiqued the idea of pristine wilderness for over half a century. Today new findings are driving a second wave of research into how humans have shaped the planet, propelled by increasingly powerful scientific techniques, as well as the compounding crises of climate change and biodiversity loss. The conclusions have added to ongoing debates in the conservation world—though not without controversy. In particular, many discussions hinge on whether Indigenous and preindustrial approaches to the natural world could contribute to a more sustainable future, if applied more widely.
3K notes
·
View notes
Photo









(May 12, 2023) We are raising money for a crowd funded research project investigating the cause of blueberry hermit crabs in Okinawa, Japan using trash found on the beach as “homes” instead of natural shells. These hermit crabs are endemic to the southern islands of Japan, and they act as coastal environmental engineers. They are endangered on several islands, and we want to try and understand why they are resorting to beach trash for shells. Please consider sharing this post and donating to the project. The fundraising will be active for the next 45 days (until June 26).
You can find all project details here: https://experiment.com/projects/blueberry-hermit-crabs-with-beach-trash-homes
We suspect that areas with high rates of tourism lead to beach combers collecting natural shells leaving nothing for the hermit crabs to use. It’s possible that overfishing of turbo snails which would naturally provide shells for the crabs may also be a factor. We will survey many sites across several islands in Okinawa to try and determine a cause of this behavior.
We will be working closely with national geographic photographer Shawn Miller (photo credits above) and several researchers in Japan. Additionally, we will complete extensive beach clean ups in the areas we study. Thank you so much for reading!
#conservation#hermit crabs#ecology#biology#research#beach combers#plastic waste#save our shells#make the switch for nature#national geographic#shawn miller#beach trash#beach clean ups#blueberry hermit crab#science experiments#marine science#marine biology#activism#nature#beach#travel#environment
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
I attended my first in-person conference on Tuesday, the British Ecological Society Aquatic Group annual meeting at Lancaster University! It was quite a small conference, but really enjoyable! So many incredibly interesting talks, ranging from global warming and ocean acidification to using meeting sponges to assess community diversity through eDNA!
Despite the grey, drizzly weather, it was a great experience, and I definitely have a few more papers to read and connections to make!
Lancaster uni also had a lovely campus with pretty architecture and lots of little green spaces! There was a gorgeous coffee shop on campus (who do amazing vegan hot chocolate!) called Coastal and co. If you're ever on campus, I highly recommend them! :)
Please enjoy this little photo I took outside of where the conference was! You can just about see the coffee shop I mentioned in the back!

#phd life#marine ecology#ecological modelling#marine biology#ecology and conservation#marine ecosystems#phd research#phdblr#phd#academic conferences#British Ecological Society#aquatic ecology#aquaculture#university journey#uk universities#lancaster#Lancaster University#building confidence#working with social anxiety
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
A study that just came out demonstrates that outdoor cats are known to prey on over two thousands species of wild animal, from mammals to birds to insects. That includes 347 species that are endangered, threatened or otherwise of concern, and they've been a key factor of the permanent extinction of over 60 species. And while cats may not always bring home what they catch, chances are if your cat is allowed to roam unsupervised outside, they're killing your local wildlife.
Why is this so important? Worldwide, wild animal populations have decreased in number by 69% in the past fifty years; that means that in my lifetime (born in 1978), the sheer number of wild animals in the world has been decreased by over half. Even "common" wild species are less numerous than before. While habitat population is the single biggest cause of species endangerment and extinction overall, outdoor and indoor/outdoor cats are a significant cause as well. In fact, they are the single biggest cause of human-caused mortality in wild birds.
Most importantly, it's very, very simple to fix this problem: keep your cats indoors, and spay and neuter them. If your cat is bored, they need more enrichment, and there are plenty of ways to make your home more exciting for them, from bringing home cardboard boxes for them to explore, to playing with them more often. If you want your cat to get some outdoor enrichment, leash train them (yes, it can be done!) If you have the space and resources, build them a catio where they can be safe from outdoor dangers like predators and cars, while also keeping local wildlife safe from them.
If you just give into their whining and pawing at the door, then they know that that's what they have to do to get their way; I know it's a tough transition, but it's worth it in the end for everyone involved. Cats are domesticated, which means they are not native anywhere in the world; there are exactly zero ecosystems in which they belong, save for the safety of your home. It is your responsibility to give them an enriching environment without taking the shortcut of letting them go wreak havoc outside.
#cats#outdoor cats#feral cats#nature#wildlife#animals#ecology#environment#conservation#science#scicomm#birds#endangered species#extinction#domesticated animals#domestication#biology#animal behavior#animal welfare
8K notes
·
View notes
Text
(via @southriverforest on Instagram)
The City of Atlanta is refusing to count the 116k signatures on the Cop City Referendum petition, denying Atlanta citizens the right to vote on Cop City and the destruction of Weelaunee forest. On Monday, February 5th 2024 Atlanta will be voting on an ordinance for making referendum a clear and fair practice

If you can make it to Atlanta or if you're registered to vote, please show up and vote yes on Ordinance 34482.
#stop cop city#atlanta#environmentalism#politics#weelaunee forest#cop city#atlanta southern river forest#Instagram#tortuguita#ecology#enviornment#biology#conservation
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
If you learn and put into practice a SINGLE thing from my blog, it should be this: the most important work YOU can do to prevent mass extinction is not "Buy Different Product" or "Buy Product Differently."
Instead, it involves going outside and looking at the land immediately surrounding you physically and understanding that you have been appointed its protector, and then learning working contacting messaging organizing planting teaching informing organizing organizing organizing to take care of it.
There are old ladies with no email address in your community that are handing out more native plants than you knew existed, there are nature preserves and wildlife parks literally like on their knees begging for volunteers, you have neighbors and friends and acquaintances and family that you can teach and inform, there is at this very moment someone else in your community that would LOVE to start a community garden.
Learn to grow native plants and you can literally just hand them out to strangers for free and everyone loves it
I started volunteering at a nature center and now I have more contacts than I know what to do with. literally just look up anyone working in ecology or conservation in your area and email the crap outta them.
you can organize with members of your community to protect a vacant lot or a random pond or to put in foot paths or get rid of invasive species in a park or anything
8K notes
·
View notes
Text
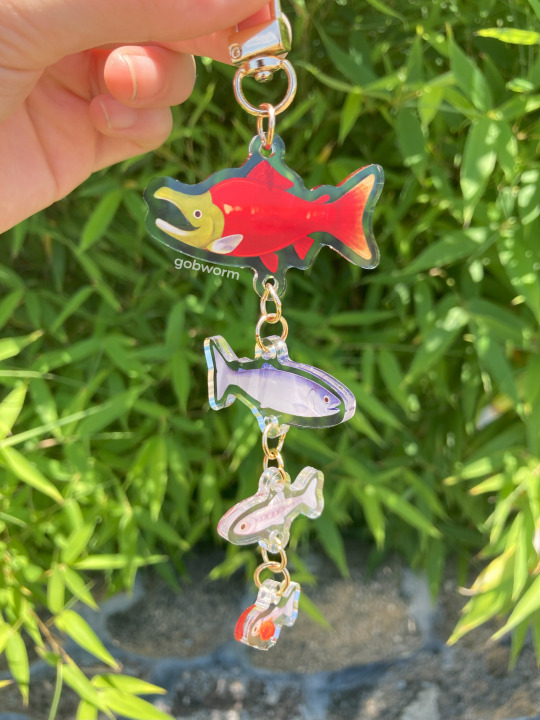
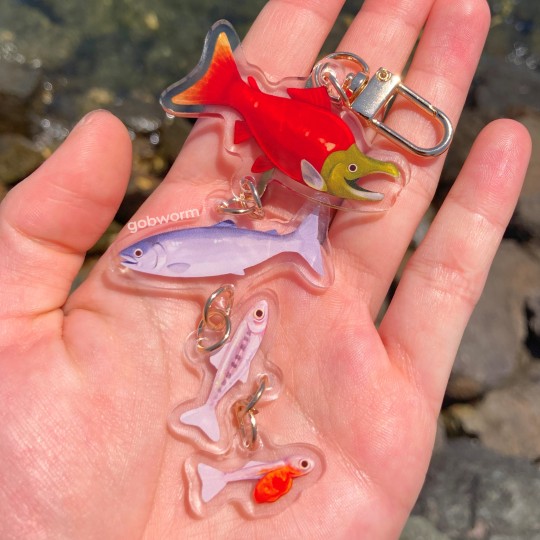
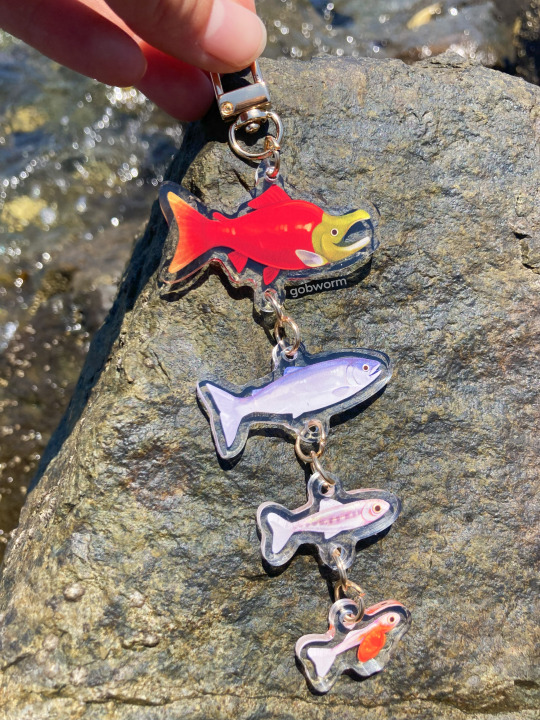



salmon life cycle charms!
buy them here!
#salmon#fish#fish biology#ichthyology#fishblr#sea creatures#marine life#marine biology#life cycle#biology#zoology#ecology#conservation#acrylic charms#small business#acrylic keychain#etsy shop#shop small#art business#digital art#artists on tumblr
3K notes
·
View notes