#Augmented and virtual reality
Text
3 Questions: Technology roadmapping in teaching and industry
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/3-questions-technology-roadmapping-in-teaching-and-industry/
3 Questions: Technology roadmapping in teaching and industry
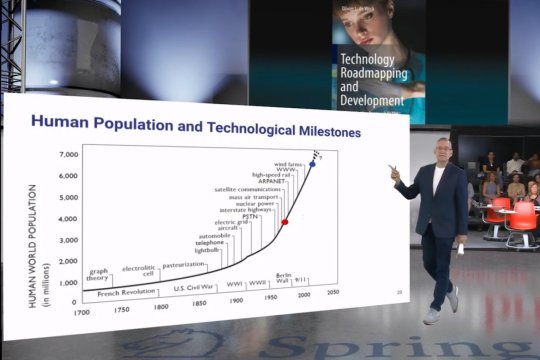

Innovation is rarely accidental. Behind every new invention and product, including the device you are using to read this story, is years of research, investment, and planning. Organizations that want to reach these milestones in the fastest and most efficient way possible use technology roadmaps.
Olivier de Weck, the Apollo Program Professor of Astronautics and professor of engineering systems, taps into his expertise in systems design and engineering to help company leaders develop their own path to progress. His work has led to an MIT graduate course, two MIT Professional Education classes, and the textbook “Technology Roadmapping and Development: A Quantitative Approach to the Management of Technology.” Recently, his textbook was honored with the Most Promising New Textbook Award from the Textbook and Academic Authors Association. The textbook not only serves as a guide to students but also to company leaders. Aerospace design and manufacturer Airbus, defense technology laboratory Draper, and package delivery giant UPS have implemented de Weck’s methods. Here, De Weck describes the value of technology roadmapping.
Q: What is technology roadmapping, and why is it important?
A: A technology roadmap is a planning tool. It connects current products, services, and missions to future endeavors, and identifies the specific technologies needed to achieve them.
Let’s say an organization wants to build a spacecraft to explore an asteroid in the farthest reaches of our solar system. It will need a new kind of electric thruster technology so that it can travel to the asteroid faster and more efficiently than what is currently possible. A technology roadmap details several factors, such as the level of performance needed to meet the goal and how to measure progress. The guide also links various responsibilities within an organization, including strategy, product development, research and development (R&D), and finance, so everyone understands the technologies that are being funded and how they will benefit the company.
Technology roadmapping has been in use for over five decades. For a long time, it was taught in business schools in a more general and qualitative way, but the practice has evolved over the years. The technology roadmapping I teach and write about uses quantitative engineering analysis and connects it to strategic thinking. From 2017 to 2018, I used and refined this approach for Airbus, which has a $1 billion R&D budget. Together, we developed over 40 technology roadmaps, which included a plan to build ZEROe, a commercial aircraft that will run on hydrogen fuel, by 2035.
Q: Are technology roadmaps used widely in industry today, and what gaps in knowledge/processes does your approach address?
A: Colleagues from the University of Cambridge and the Fraunhofer Institute in Germany and I recently conducted an industry-wide survey about technology roadmapping. Of the 200 companies that participated, 62 percent said they use technology roadmaps to make strategic investment decisions and 32 percent update them yearly. Yet only 11 percent of firms plan technologies 10 years out. This is a bit concerning because technology does not move as fast as many people believe. Using Airbus’s ZEROe aircraft as an example, it is important to think 10 or even 20 years ahead, not just within three to five years.
My approach to technology roadmapping uses a method I call Advanced Technology Roadmap Architecture (ATRA). It provides a step-by-step methodology to create a technology roadmap that is more rigorous and has a longer time horizon than traditional roadmaps. ATRA asks four essential questions: Where are we today, where could we go, where should we go, and where we are going? Instead of technologies, I want people to think of these questions as a guide to their retirement investing. You could invest in some high-risk mutual funds, low-risk bonds, or an index fund that will follow the market. You would pick investments that reflect your future goals and risk tolerances. ATRA works in the same way. It enables organizations to select the right mix of R&D based on different scenarios and different risk tolerances.
Q: Can you share how you designed your book and the courses, including 16.887/EM.427, to help students understand and apply technology roadmapping?
A: My time at Airbus allowed me to implement and battle-test technology roadmapping and ATRA. When I returned to MIT in 2019, I had already drafted chapters of the book and MIT students provided great feedback, which allowed me to refine and improve the book to the point where it would be useful and understandable to future MIT engineering and business students, industry practitioners, and C-level executives.
An important feature of both my textbook and class that may not be obvious is my focus on history. With innovation moving as fast as it is, it is easy to claim a never-been-done-before technology. That is often not the case — for example, one student did a technology roadmap of virtual reality headsets. He realized that people were doing virtual reality in the 1960s and 70s. It was super crude, clunky, and the resolution was poor. Still, there is a 60-year history that needs to be understood and acknowledged. My students and I have created a library of nearly 100 roadmaps on wide-ranging technologies, including superconducting nuclear fusion, lab-grown meat, and bioplastics. Each one traces an innovation’s history.
#Aeronautical and astronautical engineering#aerospace#aircraft#amp#Analysis#approach#architecture#Asteroid#Augmented and virtual reality#billion#book#Books and authors#Business#c-level#classes#Companies#course#courses#defense#Design#details#development#easy#education#engineering#Engineering systems#executives#Faculty#finance#focus
0 notes
Text
As per a report by Allied Market Research, the global augmented and virtual reality market is predicted to garner a revenue of $856.2 billion by 2031. The market accounted for $27.6 billion in 2021 and is anticipated to rise at a CAGR of 41.1% during the 2022-2031 period.
#Augmented and Virtual Reality Market#Augmented and Virtual RealitY#Augmented and VR#Augmented and Virtual Reality Market trends
0 notes
Text
Augmented and Virtual Reality : Shaping Future 2023
For a long time, the concept of Augmented and Virtual Reality has been the talk of the town It s incredible that people still
0 notes
Photo

Communicating across time
TeleAbsence, a project from the MIT Media Lab, probes and imitates the way humans process feelings of belonging, love, and loss.
https://news.mit.edu/2023/communicating-across-time-teleabsence-0811
#Arts#Augmented and virtual reality#Communications#Students#Technology and society#Graduate#postdoctoral#Media Lab#Visual arts#Art#Culture and Technology#Center for Art#Science and Technology#School of Architecture and Planning#Ken Shulman | Arts at MIT#MIT News
0 notes
Text
Top 5 In-Demand Tech Skills to Land You a Job in 2022
With new capabilities and demand coming up each now and then, there are a bunch of stuff you ought to study and sell. To assist these making an attempt to take the bounce of faith, we have organized a listing of the most demanded capabilities in 2022.
Top 5 In-Demand Tech Skills to Land You a Job in 2022
5 first-rate tech capabilities to land a job
It’s all about consistency and difficult work!
Talking to any skilled man or woman in the tech industry, you would recognize that it’s the enterprise that by no means settles. Any ability that you analyze nowadays may turn out to be out of date 20 years later and you will have to study new…

View On WordPress
#Augmented and Virtual Reality#Block Chain#Cybersecurity#Data Mining#Tech Skills#Top 5 In-Demand Tech Skills to Land You a Job in 2022
0 notes
Text
The (open) web is good, actually

I'll be at the Studio City branch of the LA Public Library tonight (Monday, November 13) at 1830hPT to launch my new novel, The Lost Cause. There'll be a reading, a talk, a surprise guest (!!) and a signing, with books on sale. Tell your friends! Come on down!

The great irony of the platformization of the internet is that platforms are intermediaries, and the original promise of the internet that got so many of us excited about it was disintermediation – getting rid of the middlemen that act as gatekeepers between community members, creators and audiences, buyers and sellers, etc.
The platformized internet is ripe for rent seeking: where the platform captures an ever-larger share of the value generated by its users, making the service worst for both, while lock-in stops people from looking elsewhere. Every sector of the modern economy is less competitive, thanks to monopolistic tactics like mergers and acquisitions and predatory pricing. But with tech, the options for making things worse are infinitely divisible, thanks to the flexibility of digital systems, which means that product managers can keep subdividing the Jenga blocks they pulling out of the services we rely on. Combine platforms with monopolies with digital flexibility and you get enshittification:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/21/potemkin-ai/#hey-guys
An enshittified, platformized internet is bad for lots of reasons – it concentrates decisions about who may speak and what may be said into just a few hands; it creates a rich-get-richer dynamic that creates a new oligarchy, with all the corruption and instability that comes with elite capture; it makes life materially worse for workers, users, and communities.
But there are many other ways in which the enshitternet is worse than the old good internet. Today, I want to talk about how the enshitternet affects openness and all that entails. An open internet is one whose workings are transparent (think of "open source"), but it's also an internet founded on access – the ability to know what has gone before, to recall what has been said, and to revisit the context in which it was said.
At last week's Museum Computer Network conference, Aaron Straup Cope gave a talk on museums and technology called "Wishful Thinking – A critical discussion of 'extended reality' technologies in the cultural heritage sector" that beautifully addressed these questions of recall and revisiting:
https://www.aaronland.info/weblog/2023/11/11/therapy/#wishful
Cope is a museums technologist who's worked on lots of critical digital projects over the years, and in this talk, he addresses himself to the difference between the excitement of the galleries, libraries, archives and museums (GLAM) sector over the possibilities of the web, and why he doesn't feel the same excitement over the metaverse, and its various guises – XR, VR, MR and AR.
The biggest reason to be excited about the web was – and is – the openness of disintermediation. The internet was inspired by the end-to-end principle, the idea that the network's first duty was to transmit data from willing senders to willing receivers, as efficiently and reliably as possible. That principle made it possible for whole swathes of people to connect with one another. As Cope writes, openness "was not, and has never been, a guarantee of a receptive audience or even any audience at all." But because it was "easy and cheap enough to put something on the web," you could "leave it there long enough for others to find it."
That dynamic nurtured an environment where people could have "time to warm up to ideas." This is in sharp contrast to the social media world, where "[anything] not immediately successful or viral … was a waste of time and effort… not worth doing." The social media bias towards a river of content that can't be easily reversed is one in which the only ideas that get to spread are those the algorithm boosts.
This is an important way to understand the role of algorithms in the context of the spread of ideas – that without recall or revisiting, we just don't see stuff, including stuff that might challenge our thinking and change our minds. This is a much more materialistic and grounded way to talk about algorithms and ideas than the idea that Big Data and AI make algorithms so persuasive that they can control our minds:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/06/attention-rents/#consumer-welfare-queens
As bad as this is in the social media context, it's even worse in the context of apps, which can't be linked into, bookmarked, or archived. All of this made apps an ominous sign right from the beginning:
https://memex.craphound.com/2010/04/01/why-i-wont-buy-an-ipad-and-think-you-shouldnt-either/
Apps interact with law in precisely the way that web-pages don't. "An app is just a web-page wrapped in enough IP to make it a crime to defend yourself against corporate predation":
https://pluralistic.net/2023/08/27/an-audacious-plan-to-halt-the-internets-enshittification-and-throw-it-into-reverse/
Apps are "closed" in every sense. You can't see what's on an app without installing the app and "agreeing" to its terms of service. You can't reverse-engineer an app (to add a privacy blocker, or to change how it presents information) without risking criminal and civil liability. You can't bookmark anything the app won't let you bookmark, and you can't preserve anything the app won't let you preserve.
Despite being built on the same underlying open frameworks – HTTP, HTML, etc – as the web, apps have the opposite technological viewpoint to the web. Apps' technopolitics are at war with the web's technopolitics. The web is built around recall – the ability to see things, go back to things, save things. The web has the technopolitics of a museum:
https://www.aaronland.info/weblog/2014/09/11/brand/#dconstruct
By comparison, apps have the politics of a product, and most often, that product is a rent-seeking, lock-in-hunting product that wants to take you hostage by holding something you love hostage – your data, perhaps, or your friends:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2021/08/facebooks-secret-war-switching-costs
When Anil Dash described "The Web We Lost" in 2012, he was describing a web with the technopolitics of a museum:
where tagging was combined with permissive licenses to make it easy for people to find and reuse each others' stuff;
where it was easy to find out who linked to you in realtime even though most of us were posting to our own sites, which they controlled;
where a link from one site to another meant one person found another person's contribution worthy;
where privacy-invasive bids to capture the web were greeted with outright hostility;
where every service that helped you post things that mattered to you was expected to make it easy for you take that data back if you changed services;
where inlining or referencing material from someone else's site meant following a technical standard, not inking a business-development deal;
https://www.anildash.com/2012/12/13/the_web_we_lost/
Ten years later, Dash's "broken tech/content culture cycle" described the web we live on now:
https://www.anildash.com/2022/02/09/the-stupid-tech-content-culture-cycle/
found your platform by promising to facilitate your users' growth;
order your technologists and designers to prioritize growth above all other factors and fire anyone who doesn't deliver;
grow without regard to the norms of your platform's users;
plaster over the growth-driven influx of abusive and vile material by assigning it to your "most marginalized, least resourced team";
deliver a half-assed moderation scheme that drives good users off the service and leaves no one behind but griefers, edgelords and trolls;
steadfastly refuse to contemplate why the marginalized users who made your platform attractive before being chased away have all left;
flail about in a panic over illegal content, do deals with large media brands, seize control over your most popular users' output;
"surface great content" by algorithmically promoting things that look like whatever's successful, guaranteeing that nothing new will take hold;
overpay your top performers for exclusivity deals, utterly neglect any pipeline for nurturing new performers;
abuse your creators the same ways that big media companies have for decades, but insist that it's different because you're a tech company;
ignore workers who warn that your product is a danger to society, dismiss them as "millennials" (defined as "anyone born after 1970 or who has a student loan")
when your platform is (inevitably) implicated in a murder, have a "town hall" overseen by a crisis communications firm;
pay the creator who inspired the murder to go exclusive on your platform;
dismiss the murder and fascist rhetoric as "growing pains";
when truly ghastly stuff happens on your platform, give your Trust and Safety team a 5% budget increase;
chase growth based on "emotionally engaging content" without specifying whether the emotions should be positive;
respond to ex-employees' call-outs with transient feelings of guilt followed by dismissals of "cancel culture":
fund your platforms' most toxic users and call it "free speech";
whenever anyone disagrees with any of your decisions, dismiss them as being "anti-free speech";
start increasing how much your platform takes out of your creators' paychecks;
force out internal dissenters, dismiss external critics as being in conspiracy with your corporate rivals;
once regulation becomes inevitable, form a cartel with the other large firms in your sector and insist that the problem is a "bad algorithm";
"claim full victim status," and quit your job, complaining about the toll that running a big platform took on your mental wellbeing.
https://pluralistic.net/2022/02/18/broken-records/#dashes
The web wasn't inevitable – indeed, it was wildly improbable. Tim Berners Lee's decision to make a new platform that was patent-free, open and transparent was a complete opposite approach to the strategy of the media companies of the day. They were building walled gardens and silos – the dialup equivalent to apps – organized as "branded communities." The way I experienced it, the web succeeded because it was so antithetical to the dominant vision for the future of the internet that the big companies couldn't even be bothered to try to kill it until it was too late.
Companies have been trying to correct that mistake ever since. After three or four attempts to replace the web with various garbage systems all called "MSN," Microsoft moved on to trying to lock the internet inside a proprietary browser. Years later, Facebook had far more success in an attempt to kill HTML with React. And of course, apps have gobbled up so much of the old, good internet.
Which brings us to Cope's views on museums and the metaverse. There's nothing intrinsically proprietary about virtual worlds and all their permutations. VRML is a quarter of a century old – just five years younger than Snow Crash:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VRML
But the current enthusiasm for virtual worlds isn't merely a function of the interesting, cool and fun experiences you can have in them. Rather, it's a bid to kill off whatever is left of the old, good web and put everything inside a walled garden. Facebook's metaverse "is more of the same but with a technical footprint so expensive and so demanding that it all but ensures it will only be within the means of a very few companies to operate."
Facebook's VR headsets have forward-facing cameras, turning every users into a walking surveillance camera. Facebook put those cameras there for "pass through" – so they can paint the screens inside the headset with the scene around you – but "who here believes that Facebook doesn't have other motives for enabling an always-on camera capturing the world around you?"
Apple's VisionPro VR headset is "a near-perfect surveillance device," and "the only thing to save this device is the trust that Apple has marketed its brand on over the last few years." Cope notes that "a brand promise is about as fleeting a guarantee as you can get." I'll go further: Apple is already a surveillance company:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/14/luxury-surveillance/#liar-liar
The technopolitics of the metaverse are the opposite of the technopolitics of the museum – even moreso than apps. Museums that shift their scarce technology budgets to virtual worlds stand a good chance of making something no one wants to use, and that's the best case scenario. The worst case is that museums make a successful project inside a walled garden, one where recall is subject to corporate whim, and help lure their patrons away from the recall-friendly internet to the captured, intermediated metaverse.
It's true that the early web benefited from a lot of hype, just as the metaverse is enjoying today. But the similarity ends there: the metaverse is designed for enclosure, the web for openness. Recall is a historical force for "the right to assembly… access to basic literacy… a public library." The web was "an unexpected gift with the ability to change the order of things; a gift that merits being protected, preserved and promoted both internally and externally." Museums were right to jump on the web bandwagon, because of its technopolitics. The metaverse, with its very different technopolitics, is hostile to the very idea of museums.
In joining forces with metaverse companies, museums strike a Faustian bargain, "because we believe that these places are where our audiences have gone."
The GLAM sector is devoted to access, to recall, and to revisiting. Unlike the self-style free speech warriors whom Dash calls out for self-serving neglect of their communities, the GLAM sector is about preservation and access, the true heart of free expression. When a handful of giant companies organize all our discourse, the ability to be heard is contingent on pleasing the ever-shifting tastes of the algorithm. This is the problem with the idea that "freedom of speech isn't freedom of reach" – if a platform won't let people who want to hear from you see what you have to say, they are indeed compromising freedom of speech:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/10/e2e/#the-censors-pen
Likewise, "censorship" is not limited to "things that governments do." As Ada Palmer so wonderfully describes it in her brilliant "Why We Censor: from the Inquisition to the Internet" speech, censorship is like arsenic, with trace elements of it all around us:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uMMJb3AxA0s
A community's decision to ban certain offensive conduct or words on pain of expulsion or sanction is censorship – but not to the same degree that, say, a government ban on expressing certain points of view is. However, there are many kinds of private censorship that rise to the same level as state censorship in their impact on public discourse (think of Moms For Liberty and their book-bannings).
It's not a coincidence that Palmer – a historian – would have views on censorship and free speech that intersect with Cope, a museum worker. One of the most brilliant moments in Palmer's speech is where she describes how censorship under the Inquistion was not state censorship – the Inquisition was a multinational, nongovernmental body that was often in conflict with state power.
Not all intermediaries are bad for speech or access. The "disintermediation" that excited early web boosters was about escaping from otherwise inescapable middlemen – the people who figured out how to control and charge for the things we did with one another.
When I was a kid, I loved the writing of Crad Kilodney, a short story writer who sold his own self-published books on Toronto street-corners while wearing a sign that said "VERY FAMOUS CANADIAN AUTHOR, BUY MY BOOKS" (he also had a sign that read, simply, "MARGARET ATWOOD"). Kilodney was a force of nature, who wrote, edited, typeset, printed, bound, and sold his own books:
https://www.theglobeandmail.com/arts/books/article-late-street-poet-and-publishing-scourge-crad-kilodney-left-behind-a/
But there are plenty of writers out there that I want to hear from who lack the skill or the will to do all of that. Editors, publishers, distributors, booksellers – all the intermediaries who sit between a writer and their readers – are not bad. They're good, actually. The problem isn't intermediation – it's capture.
For generations, hucksters have conned would-be writers by telling them that publishing won't buy their books because "the gatekeepers" lack the discernment to publish "quality" work. Friends of mine in publishing laughed at the idea that they would deliberately sideline a book they could figure out how to sell – that's just not how it worked.
But today, monopolized film studios are literally annihilating beloved, high-priced, commercially viable works because they are worth slightly more as tax writeoffs than they are as movies:
https://deadline.com/2023/11/coyote-vs-acme-shelved-warner-bros-discovery-writeoff-david-zaslav-1235598676/
There's four giant studios and five giant publishers. Maybe "five" is the magic number and publishing isn't concentrated enough to drop whole novels down the memory hole for a tax deduction, but even so, publishing is trying like hell to shrink to four:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/07/random-penguins/#if-you-wanted-to-get-there-i-wouldnt-start-from-here
Even as the entertainment sector is working to both literally and figuratively destroy our libraries, the cultural heritage sector is grappling with preserving these libraries, with shrinking budgets and increased legal threats:
https://blog.archive.org/2023/03/25/the-fight-continues/
I keep meeting artists of all description who have been conditioned to be suspicious of anything with the word "open" in its name. One colleague has repeatedly told me that fighting for the "open internet" is a self-defeating rhetorical move that will scare off artists who hear "open" and think "Big Tech ripoff."
But "openness" is a necessary precondition for preservation and access, which are the necessary preconditions for recall and revisiting. Here on the last, melting fragment of the open internet, as tech- and entertainment-barons are seizing control over our attention and charging rent on our ability to talk and think together, openness is our best hope of a new, good internet. T
he cultural heritage sector wants to save our creative works. The entertainment and tech industry want to delete them and take a tax writeoff.
As a working artist, I know which side I'm on.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/13/this-is-for-everyone/#revisiting

Image:
Diego Delso (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Museo_Mimara,_Zagreb,_Croacia,_2014-04-20,_DD_01.JPG
CC BY-SA 4.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/
#pluralistic#ar#xr#vr#augmented reality#extended reality#virtual reality#museums#cultural preservation#aaron cope#Museum Computer Network#cultural heritage#glam#access#open access#revisiting#mr#mixed reality#asynchronous#this is for everyone#freedom of reach#gatekeepers#metaverse#technofeudalism#privacy#brick on the face#rent-seeking
185 notes
·
View notes
Video
“On Death” - Benjamin Franklin
#art#unreality#video#draws#weirdcore#death#augmented reality#vr#virtual reality#3d art#ghost#ghosts#ask to tag anything else#this is part of an art series i'm doing using video and found objects from my childhood home#i don't have a final title yet but for tagging purposes the working title will be#childhome#so block that if you don't wanna see a bunch of very personal experimental artwork#thank u
641 notes
·
View notes
Text
I know that the past decade of website design should've been an indicator, but it's still pretty baffling that most of these tech innovators, leading the charge in media and entertainment, are also the biggest fucking dullards with ass-backwards thinking.
Why is VR so full of basic-bitch physic engine show-offs, or virtual grocery shopping, or shitty ports of first-person games? Where's the deluge of Yugioh knockoffs (or the real deal if Konami would get a fucking clue), or hell, maybe WotC could stop retarding themselves with D&D and MtG, and give us either in VR.
Also, why is fucking Zuckerbot making digital football, instead of getting the most derranged nerds to come up with crazy 'sports' that could only be accomplished digitally? Why aren't we getting goddamn anime-tier Beyblade matches, or some other insane activity enhanced by it not being limited by physical restraints?
So fucking stupid. VRChat's done more than any of these boring turdstains with their zillions of dollars and time to waste.
128 notes
·
View notes
Text
Researchers in the emerging field of spatial computing have developed a prototype augmented reality headset that uses holographic imaging to overlay full-color, 3D moving images on the lenses of what would appear to be an ordinary pair of glasses. Unlike the bulky headsets of present-day augmented reality systems, the new approach delivers a visually satisfying 3D viewing experience in a compact, comfortable, and attractive form factor suitable for all-day wear.
“Our headset appears to the outside world just like an everyday pair of glasses, but what the wearer sees through the lenses is an enriched world overlaid with vibrant, full-color 3D computed imagery,” said Gordon Wetzstein, an associate professor of electrical engineering and an expert in the fast-emerging field of spatial computing. Wetzstein and a team of engineers introduce their device in a new paper in the journal Nature.
Continue Reading.
#Science#Technology#Electrical Engineering#Spatial Computing#Holography#Augmented Reality#Virtual Reality#AI#Artifical Intelligence#Machine Learning#Stanford
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
This tiny chip can safeguard user data while enabling efficient computing on a smartphone
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/this-tiny-chip-can-safeguard-user-data-while-enabling-efficient-computing-on-a-smartphone/
This tiny chip can safeguard user data while enabling efficient computing on a smartphone

Health-monitoring apps can help people manage chronic diseases or stay on track with fitness goals, using nothing more than a smartphone. However, these apps can be slow and energy-inefficient because the vast machine-learning models that power them must be shuttled between a smartphone and a central memory server.
Engineers often speed things up using hardware that reduces the need to move so much data back and forth. While these machine-learning accelerators can streamline computation, they are susceptible to attackers who can steal secret information.
To reduce this vulnerability, researchers from MIT and the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab created a machine-learning accelerator that is resistant to the two most common types of attacks. Their chip can keep a user’s health records, financial information, or other sensitive data private while still enabling huge AI models to run efficiently on devices.
The team developed several optimizations that enable strong security while only slightly slowing the device. Moreover, the added security does not impact the accuracy of computations. This machine-learning accelerator could be particularly beneficial for demanding AI applications like augmented and virtual reality or autonomous driving.
While implementing the chip would make a device slightly more expensive and less energy-efficient, that is sometimes a worthwhile price to pay for security, says lead author Maitreyi Ashok, an electrical engineering and computer science (EECS) graduate student at MIT.
“It is important to design with security in mind from the ground up. If you are trying to add even a minimal amount of security after a system has been designed, it is prohibitively expensive. We were able to effectively balance a lot of these tradeoffs during the design phase,” says Ashok.
Her co-authors include Saurav Maji, an EECS graduate student; Xin Zhang and John Cohn of the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab; and senior author Anantha Chandrakasan, MIT’s chief innovation and strategy officer, dean of the School of Engineering, and the Vannevar Bush Professor of EECS. The research will be presented at the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference.
Side-channel susceptibility
The researchers targeted a type of machine-learning accelerator called digital in-memory compute. A digital IMC chip performs computations inside a device’s memory, where pieces of a machine-learning model are stored after being moved over from a central server.
The entire model is too big to store on the device, but by breaking it into pieces and reusing those pieces as much as possible, IMC chips reduce the amount of data that must be moved back and forth.
But IMC chips can be susceptible to hackers. In a side-channel attack, a hacker monitors the chip’s power consumption and uses statistical techniques to reverse-engineer data as the chip computes. In a bus-probing attack, the hacker can steal bits of the model and dataset by probing the communication between the accelerator and the off-chip memory.
Digital IMC speeds computation by performing millions of operations at once, but this complexity makes it tough to prevent attacks using traditional security measures, Ashok says.
She and her collaborators took a three-pronged approach to blocking side-channel and bus-probing attacks.
First, they employed a security measure where data in the IMC are split into random pieces. For instance, a bit zero might be split into three bits that still equal zero after a logical operation. The IMC never computes with all pieces in the same operation, so a side-channel attack could never reconstruct the real information.
But for this technique to work, random bits must be added to split the data. Because digital IMC performs millions of operations at once, generating so many random bits would involve too much computing. For their chip, the researchers found a way to simplify computations, making it easier to effectively split data while eliminating the need for random bits.
Second, they prevented bus-probing attacks using a lightweight cipher that encrypts the model stored in off-chip memory. This lightweight cipher only requires simple computations. In addition, they only decrypted the pieces of the model stored on the chip when necessary.
Third, to improve security, they generated the key that decrypts the cipher directly on the chip, rather than moving it back and forth with the model. They generated this unique key from random variations in the chip that are introduced during manufacturing, using what is known as a physically unclonable function.
“Maybe one wire is going to be a little bit thicker than another. We can use these variations to get zeros and ones out of a circuit. For every chip, we can get a random key that should be consistent because these random properties shouldn’t change significantly over time,” Ashok explains.
They reused the memory cells on the chip, leveraging the imperfections in these cells to generate the key. This requires less computation than generating a key from scratch.
“As security has become a critical issue in the design of edge devices, there is a need to develop a complete system stack focusing on secure operation. This work focuses on security for machine-learning workloads and describes a digital processor that uses cross-cutting optimization. It incorporates encrypted data access between memory and processor, approaches to preventing side-channel attacks using randomization, and exploiting variability to generate unique codes. Such designs are going to be critical in future mobile devices,” says Chandrakasan.
Safety testing
To test their chip, the researchers took on the role of hackers and tried to steal secret information using side-channel and bus-probing attacks.
Even after making millions of attempts, they couldn’t reconstruct any real information or extract pieces of the model or dataset. The cipher also remained unbreakable. By contrast, it took only about 5,000 samples to steal information from an unprotected chip.
The addition of security did reduce the energy efficiency of the accelerator, and it also required a larger chip area, which would make it more expensive to fabricate.
The team is planning to explore methods that could reduce the energy consumption and size of their chip in the future, which would make it easier to implement at scale.
“As it becomes too expensive, it becomes harder to convince someone that security is critical. Future work could explore these tradeoffs. Maybe we could make it a little less secure but easier to implement and less expensive,” Ashok says.
The research is funded, in part, by the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab, the National Science Foundation, and a Mathworks Engineering Fellowship.
#000#accelerators#ai#AI models#applications#approach#apps#Artificial Intelligence#attackers#Augmented and virtual reality#autonomous driving#Cells#change#channel#chips#cipher#communication#complexity#computation#computer#Computer Science#Computer science and technology#computing#conference#Critical Issue#cutting#cybersecurity#data#Design#devices
0 notes
Text
The Lawnmower Man (1992)
Accelerated cognitive growth breaks free.
#cyberpunk aesthetic#virtual reality#retro fps#augmented reality#cyberpunk#cybernetics#dystopian future#90s#90s aesthetic#sci fi#scifi#boomer shooter#cyberpunk movies#cyberpunk film#scifi movies#graphic design#escape#adventure#video games
49 notes
·
View notes
Text

youtube
#spongebob#meme#funny meme#mixed reality#virtual reality#VR#augmented reality#lol#haha#funny#memes#comedy#humor#Youtube
21 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Q&A: A high-tech take on Wagner’s “Parsifal” opera
Director and MIT Professor Jay Scheib’s production, at the Bayreuth Festival in Germany, features an apocalyptic theme and augmented reality headsets for the audience.
https://news.mit.edu/2023/high-tech-take-wagners-parsifal-opera-0803
#Music#Augmented and virtual reality#Music and theater arts#Music technology#History#Arts#Technology and society#Climate change#Ethics#Social justice#History of science#Global#School of Humanities Arts and Social Sciences#Peter Dizikes | MIT News#MIT News
0 notes
Text
The first AR laptop was just released.... to think it went from those weird ass 3DS cards to this is fucking wild????
Im fuckING LOSING IT RIGHT NOW. Everyone??? Meet fucking Spacetop??
You thought your 3DS AR Kirby cards were peak shit?? Think again.
Here's the link to the promo but if you want to hear my excited ass rant, it's below the cut lol:
Spacetop: Own Your Space (youtube)
Seeing how CNET talked about it, and actually seeing the promo made me realize this isn't some wish shit- this is actually happening. As someone who grew up obsessed with sci-fi, my heart is absolutely pounding.

No, this isn't Virtual Reality. It's Augmented Reality (AR). Meaning, despite having glasses on like a headset, your seeing the software literally floating in your living room/bathroom/local @dennys . This is totally in the starter stages, (remember when VR began popping off and it was... yeah) so don't expect it to be some perfect Star Trek shit, but it functions as intended.
Unlike VR, I am getting the impression this AR Laptop is more spatially aware and doesn't make you break your neck to look to the left. I could literally go on for years on this new technology but I'm gonna leave it here- or I'll never stop lol.
#tech#techwear#tech news#computers#laptop#techcrunch#techcore#technology#vr#ar#virtual reality#augmented reality#vr news#ar news#ai art#ai#character ai#ai art generator#chatgpt#artificial intelligence#google#apple#spacetop#sightful#tech tuesday#tech blog#old tech#microsoft#kirby series#nintendo
81 notes
·
View notes
Text

#postlarım#alıntı#aret#art#ısparta#artwork#digital art#augmented reality#virtual reality#homestuck#my art#nail art#architecture
7 notes
·
View notes
Text






















Chibi-Robo! Photo Finder (Nintendo 3DS 2014)
#video game screenshots#photo mode#virtual photography#nintendo 3ds#chibi robo#shenmue#legend of zelda#hyrule historia#franz ferdinand#egg#augmented reality
28 notes
·
View notes