Text
The true post-cyberpunk hero is a noir forensic accountant

I'm touring my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me in TOMORROW (Apr 17) in CHICAGO, then Torino (Apr 21) Marin County (Apr 27), Winnipeg (May 2), Calgary (May 3), Vancouver (May 4), and beyond!

I was reared on cyberpunk fiction, I ended up spending 25 years at my EFF day-job working at the weird edge of tech and human rights, even as I wrote sf that tried to fuse my love of cyberpunk with my urgent, lifelong struggle over who computers do things for and who they do them to.
That makes me an official "post-cyberpunk" writer (TM). Don't take my word for it: I'm in the canon:
https://tachyonpublications.com/product/rewired-the-post-cyberpunk-anthology-2/
One of the editors of that "post-cyberpunk" anthology was John Kessel, who is, not coincidentally, the first writer to expose me to the power of literary criticism to change the way I felt about a novel, both as a writer and a reader:
https://locusmag.com/2012/05/cory-doctorow-a-prose-by-any-other-name/
It was Kessel's 2004 Foundation essay, "Creating the Innocent Killer: Ender's Game, Intention, and Morality," that helped me understand litcrit. Kessel expertly surfaces the subtext of Card's Ender's Game and connects it to Card's politics. In so doing, he completely reframed how I felt about a book I'd read several times and had considered a favorite:
https://johnjosephkessel.wixsite.com/kessel-website/creating-the-innocent-killer
This is a head-spinning experience for a reader, but it's even wilder to experience it as a writer. Thankfully, the majority of literary criticism about my work has been positive, but even then, discovering something that's clearly present in one of my novels, but which I didn't consciously include, is a (very pleasant!) mind-fuck.
A recent example: Blair Fix's review of my 2023 novel Red Team Blues which he calls "an anti-finance finance thriller":
https://economicsfromthetopdown.com/2023/05/13/red-team-blues-cory-doctorows-anti-finance-thriller/
Fix – a radical economist – perfectly captures the correspondence between my hero, the forensic accountant Martin Hench, and the heroes of noir detective novels. Namely, that a noir detective is a kind of unlicensed policeman, going to the places the cops can't go, asking the questions the cops can't ask, and thus solving the crimes the cops can't solve. What makes this noir is what happens next: the private dick realizes that these were places the cops didn't want to go, questions the cops didn't want to ask and crimes the cops didn't want to solve ("It's Chinatown, Jake").
Marty Hench – a forensic accountant who finds the money that has been disappeared through the cells in cleverly constructed spreadsheets – is an unlicensed tax inspector. He's finding the money the IRS can't find – only to be reminded, time and again, that this is money the IRS chooses not to find.
This is how the tax authorities work, after all. Anyone who followed the coverage of the big finance leaks knows that the most shocking revelation they contain is how stupid the ruses of the ultra-wealthy are. The IRS could prevent that tax-fraud, they just choose not to. Not for nothing, I call the Martin Hench books "Panama Papers fanfic."
I've read plenty of noir fiction and I'm a long-term finance-leaks obsessive, but until I read Fix's article, it never occurred to me that a forensic accountant was actually squarely within the noir tradition. Hench's perfect noir fit is either a happy accident or the result of a subconscious intuition that I didn't know I had until Fix put his finger on it.
The second Hench novel is The Bezzle. It's been out since February, and I'm still touring with it (Chicago tonight! Then Turin, Marin County, Winnipeg, Calgary, Vancouver, etc). It's paying off – the book's a national bestseller.
Writing in his newsletter, Henry Farrell connects Fix's observation to one of his own, about the nature of "hackers" and their role in cyberpunk (and post-cyberpunk) fiction:
https://www.programmablemutter.com/p/the-accountant-as-cyberpunk-hero
Farrell cites Bruce Schneier's 2023 book, A Hacker’s Mind: How the Powerful Bend Society’s Rules and How to Bend Them Back:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/06/trickster-makes-the-world/
Schneier, a security expert, broadens the category of "hacker" to include anyone who studies systems with an eye to finding and exploiting their defects. Under this definition, the more fearsome hackers are "working for a hedge fund, finding a loophole in financial regulations that lets her siphon extra profits out of the system." Hackers work in corporate offices, or as government lobbyists.
As Henry says, hacking isn't intrinsically countercultural ("Most of the hacking you might care about is done by boring seeming people in boring seeming clothes"). Hacking reinforces – rather than undermining power asymmetries ("The rich have far more resources to figure out how to gimmick the rules"). We are mostly not the hackers – we are the hacked.
For Henry, Marty Hench is a hacker (the rare hacker that works for the good guys), even though "he doesn’t wear mirrorshades or get wasted chatting to bartenders with Soviet military-surplus mechanical arms." He's a gun for hire, that most traditional of cyberpunk heroes, and while he doesn't stand against the system, he's not for it, either.
Henry's pinning down something I've been circling around for nearly 30 years: the idea that though "the street finds its own use for things," Wall Street and Madison Avenue are among the streets that might find those uses:
https://craphound.com/nonfic/street.html
Henry also connects Martin Hench to Marcus Yallow, the hero of my YA Little Brother series. I have tried to make this connection myself, opining that while Marcus is a character who is fighting to save an internet that he loves, Marty is living in the ashes of the internet he lost:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/07/dont-curb-your-enthusiasm/
But Henry's Marty-as-hacker notion surfaces a far more interesting connection between the two characters. Marcus is a vehicle for conveying the excitement and power of hacking to young readers, while Marty is a vessel for older readers who know the stark terror of being hacked, by the sadistic wolves who're coming for all of us:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I44L1pzi4gk
Both Marcus and Marty are explainers, as am I. Some people say that exposition makes for bad narrative. Those people are wrong:
https://maryrobinettekowal.com/journal/my-favorite-bit/my-favorite-bit-cory-doctorow-talks-about-the-bezzle/
"Explaining" makes for great fiction. As Maria Farrell writes in her Crooked Timber review of The Bezzle, the secret sauce of some of the best novels is "information about how things work. Things like locks, rifles, security systems":
https://crookedtimber.org/2024/03/06/the-bezzle/
Where these things are integrated into the story's "reason and urgency," they become "specialist knowledge [that] cuts new paths to move through the world." Hacking, in other words.
This is a theme Paul Di Filippo picked up on in his review of The Bezzle for Locus:
https://locusmag.com/2024/04/paul-di-filippo-reviews-the-bezzle-by-cory-doctorow/
Heinlein was always known—and always came across in his writings—as The Man Who Knew How the World Worked. Doctorow delivers the same sense of putting yourself in the hands of a fellow who has peered behind Oz’s curtain. When he fills you in lucidly about some arcane bit of economics or computer tech or social media scam, you feel, first, that you understand it completely and, second, that you can trust Doctorow’s analysis and insights.
Knowledge is power, and so expository fiction that delivers news you can use is novel that makes you more powerful – powerful enough to resist the hackers who want to hack you.
Henry and I were both friends of Aaron Swartz, and the Little Brother books are closely connected to Aaron, who helped me with Homeland, the second volume, and wrote a great afterword for it (Schneier wrote an afterword for the first book). That book – and Aaron's afterword – has radicalized a gratifying number of principled technologists. I know, because I meet them when I tour, and because they send me emails. I like to think that these hackers are part of Aaron's legacy.
Henry argues that the Hench books are "purpose-designed to inspire a thousand Max Schrems – people who are probably past their teenage years, have some grounding in the relevant professions, and really want to see things change."
(Schrems is the Austrian privacy activist who, as a law student, set in motion the events that led to the passage of the EU's General Data Privacy Regulation:)
https://pluralistic.net/2020/05/15/out-here-everything-hurts/#noyb
Henry points out that William Gibson's Neuromancer doesn't mention the word "internet" – rather, Gibson coined the term cyberspace, which, as Henry says, is "more ‘capitalism’ than ‘computerized information'… If you really want to penetrate the system, you need to really grasp what money is and what it does."
Maria also wrote one of my all-time favorite reviews of Red Team Blues, also for Crooked Timber:
https://crookedtimber.org/2023/05/11/when-crypto-meant-cryptography/
In it, she compares Hench to Dickens' Bleak House, but for the modern tech world:
You put the book down feeling it’s not just a fascinating, enjoyable novel, but a document of how Silicon Valley’s very own 1% live and a teeming, energy-emitting snapshot of a critical moment on Earth.
All my life, I've written to find out what's going on in my own head. It's a remarkably effective technique. But it's only recently that I've come to appreciate that reading what other people write about my writing can reveal things that I can't see.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/17/panama-papers-fanfic/#the-1337est-h4x0rs

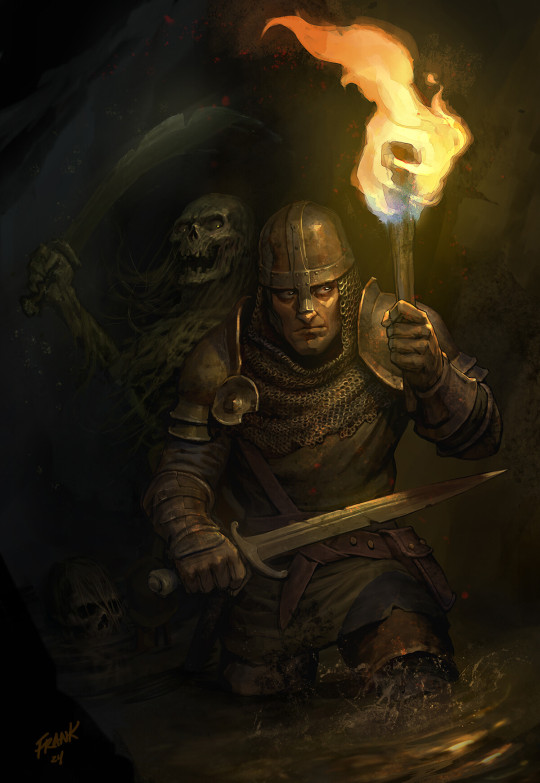
Image:
Frédéric Poirot (modified)
https://www.flickr.com/photos/fredarmitage/1057613629 CC BY-SA 2.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/
143 notes
·
View notes
Text
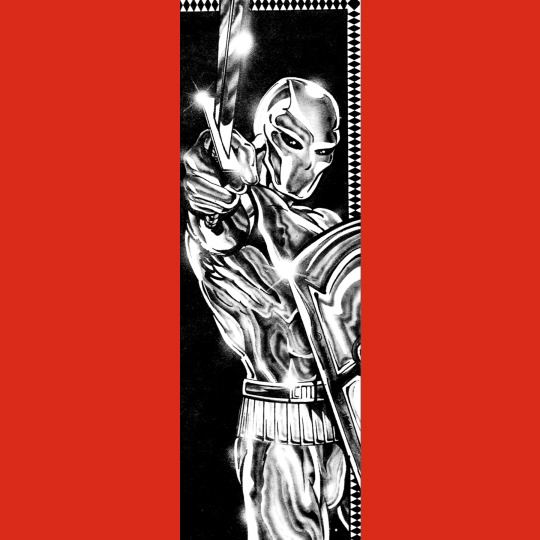






Shadows of Evil (1984) is the biggest adventure in the Role Aids line, clocking in at 80 pages plus map pull-outs. There is some source material at the front of the book for roleplaying in the Celtic world (or, I guess, the post-Roman Celtic world, more accurately) and a set of powers and items designed as a supplement for the D&D Druid class (reprinted from an earlier article in Dragon Magazine). This focus on Celts is a little jarring, as the Boris Vallejo cover is pretty generic looking fantasy, and, aside of some narrative trappings, the adventures don’t have much Celtic flavor.
There are two linked adventures. The first concerns a, well, a weird place. It was a site of worship for Dark Druids, then a Roman fort and now it is a manor that doubles as an abbey for some good Druids that seem rather Christian, really. They’ve been corrupted, though and in order to set things right, an evil artifact of great power must be retrieved. The second adventure requires the destruction of the artifact lest its use bring about the return of an evil pre-Celtic deity. To do so, the player have to travel to an evil citadel…owned by a witch-king…and throw the thing…into a pit of fire. Which seems a lot more Lord of the Rings than Celtic mythology. All of this is further undercut by pretty standard dungeon design populated by a prosaic complement of D&D monsters. I actually like the dungeons and how generic they are, but they feel real weird in the Celtic context.
Nice art throughout by Robin Wood. Very different, I think, from her work in Swordthrust.
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
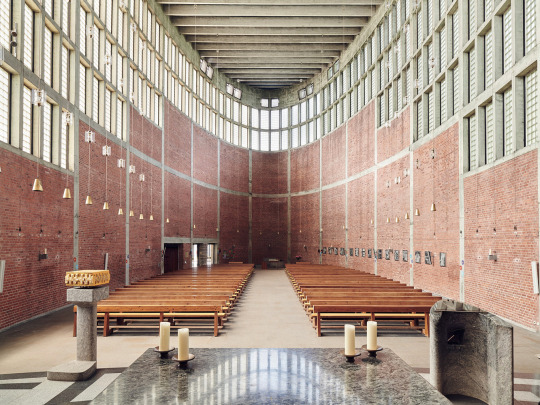

Church St Theresia (1959-62) in Linz, Austria, by Rudolf Schwarz. Photo by Jamie McGregor Smith.
49 notes
·
View notes
Text
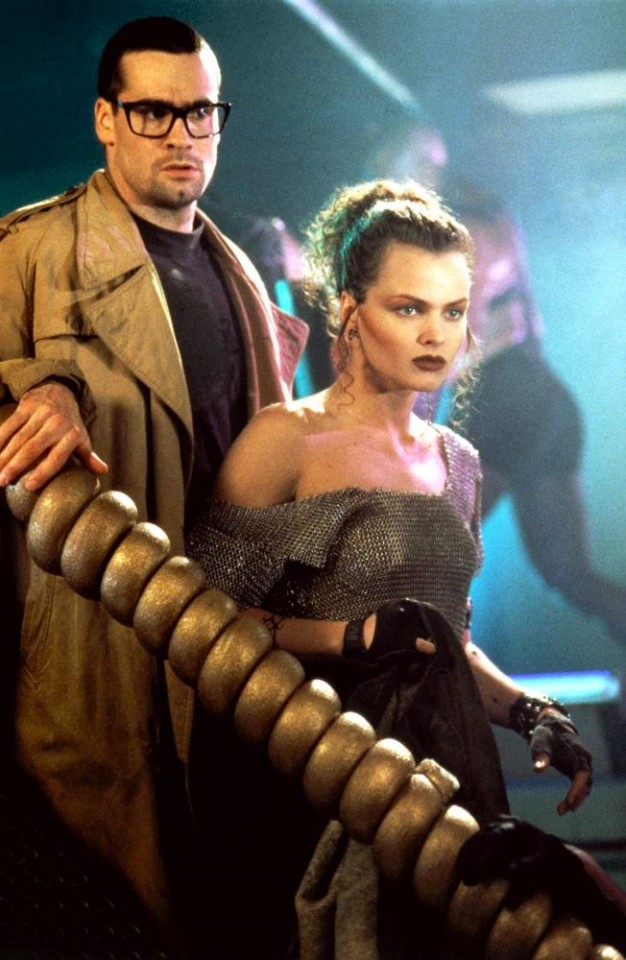

Henry Rollins & Dina Meyer, Johnny Mnemonic (1995)
176 notes
·
View notes
Text
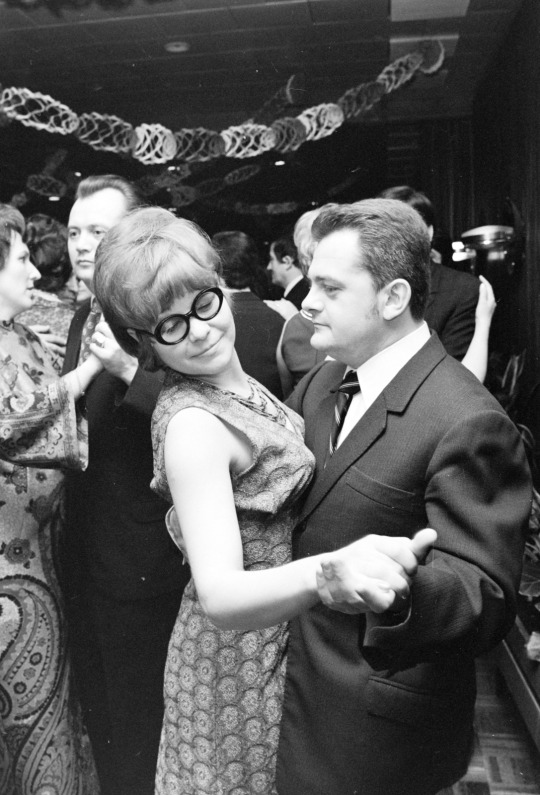

Party time, 1974. From the Budapest Municipal Photography Company archive.
119 notes
·
View notes
Text

'Spring.'
Postcard by Mela Koehler (Austrian, 1885–1960).
Published by Wenau Brabant.
Image and text information courtesy MFA Boston.
49 notes
·
View notes
Text

XIX century Library at Marienburg Castle, Germany
882 notes
·
View notes
Text
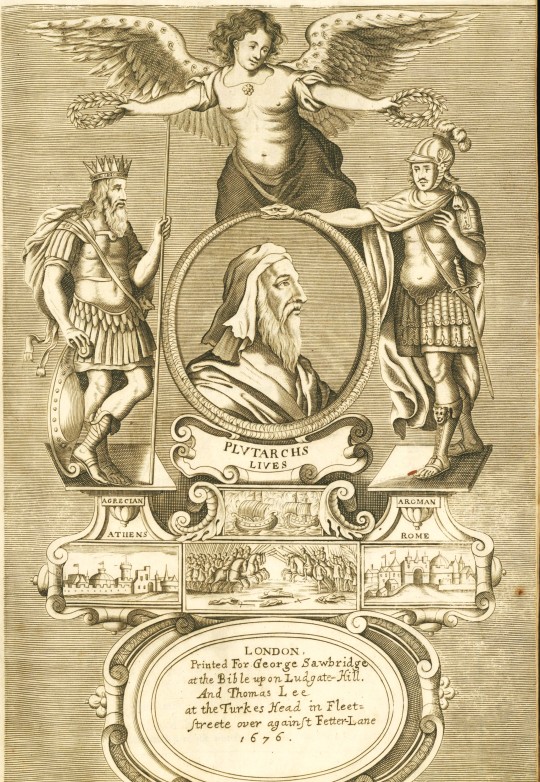










Classic Profiles
This is a 1676 edition of The Lives of the Noble Grecians and Romans, compared together by the 1st-century BCE Greek philosopher and historian Plutarch of Chaeronea, printed by the printer to the University of Cambridge John Hayes for the bookseller George Sawbridge. Originally written in Greek, Plutarch's Lives appeared in print for the first time as a Latin translation in 1470, and this English translation by Sir Thomas North was first published in 1579 from a French by James Amiot (Jacques Amyot). The text is a collection biographies of famous Greeks and Romans, including Alexander the Great, Pericles, Tiberius Gracchus, and Cicero. These figures left an indelible mark on history, their lives and achievements shaping the world as we know it.
Sir Thomas North (1535 – c. 1604) was an English translator and lawyer significantly contributing to English literature. His translation of Plutarch's Lives served as the primary source text for William Shakespeare's Roman plays, a testament to his work's enduring influence. This translation is regarded as one of the earliest examples of exceptional English prose. It was followed by another edition in 1595, which included updated biographies. A third edition of North's Plutarch was published in 1603, including even more translated Parallel Lives and a supplement of other biographies.
Jacques Amyot (1513-1593), a French scholar, writer, and translator, made substantial contributions to the field of translation and literature. His work on the translation of Plutarch's Lives (1559-1565) was instrumental in shaping the literary landscape of his time and laid the foundation for future translations and interpretations of Plutarch's work.
The first edition of this book was dedicated to Queen Elizabeth I. This dedication reflects the book's significance and provides a glimpse into the political and cultural landscape of the time, adding another layer of depth to the reader's understanding. Plutarch’s Lives helped shape the understanding of the classical Greek democracies and oligarchies of the Roman Republic and the role attributed to their founders—among them the legendary Lycurgus of Sparta and the Athenian lawgiver Solon.
-Melissa, Special Collections Classics Intern
View other Classics posts
42 notes
·
View notes
Text
The true post-cyberpunk hero is a noir forensic accountant

I'm touring my new, nationally bestselling novel The Bezzle! Catch me in TOMORROW (Apr 17) in CHICAGO, then Torino (Apr 21) Marin County (Apr 27), Winnipeg (May 2), Calgary (May 3), Vancouver (May 4), and beyond!

I was reared on cyberpunk fiction, I ended up spending 25 years at my EFF day-job working at the weird edge of tech and human rights, even as I wrote sf that tried to fuse my love of cyberpunk with my urgent, lifelong struggle over who computers do things for and who they do them to.
That makes me an official "post-cyberpunk" writer (TM). Don't take my word for it: I'm in the canon:
https://tachyonpublications.com/product/rewired-the-post-cyberpunk-anthology-2/
One of the editors of that "post-cyberpunk" anthology was John Kessel, who is, not coincidentally, the first writer to expose me to the power of literary criticism to change the way I felt about a novel, both as a writer and a reader:
https://locusmag.com/2012/05/cory-doctorow-a-prose-by-any-other-name/
It was Kessel's 2004 Foundation essay, "Creating the Innocent Killer: Ender's Game, Intention, and Morality," that helped me understand litcrit. Kessel expertly surfaces the subtext of Card's Ender's Game and connects it to Card's politics. In so doing, he completely reframed how I felt about a book I'd read several times and had considered a favorite:
https://johnjosephkessel.wixsite.com/kessel-website/creating-the-innocent-killer
This is a head-spinning experience for a reader, but it's even wilder to experience it as a writer. Thankfully, the majority of literary criticism about my work has been positive, but even then, discovering something that's clearly present in one of my novels, but which I didn't consciously include, is a (very pleasant!) mind-fuck.
A recent example: Blair Fix's review of my 2023 novel Red Team Blues which he calls "an anti-finance finance thriller":
https://economicsfromthetopdown.com/2023/05/13/red-team-blues-cory-doctorows-anti-finance-thriller/
Fix – a radical economist – perfectly captures the correspondence between my hero, the forensic accountant Martin Hench, and the heroes of noir detective novels. Namely, that a noir detective is a kind of unlicensed policeman, going to the places the cops can't go, asking the questions the cops can't ask, and thus solving the crimes the cops can't solve. What makes this noir is what happens next: the private dick realizes that these were places the cops didn't want to go, questions the cops didn't want to ask and crimes the cops didn't want to solve ("It's Chinatown, Jake").
Marty Hench – a forensic accountant who finds the money that has been disappeared through the cells in cleverly constructed spreadsheets – is an unlicensed tax inspector. He's finding the money the IRS can't find – only to be reminded, time and again, that this is money the IRS chooses not to find.
This is how the tax authorities work, after all. Anyone who followed the coverage of the big finance leaks knows that the most shocking revelation they contain is how stupid the ruses of the ultra-wealthy are. The IRS could prevent that tax-fraud, they just choose not to. Not for nothing, I call the Martin Hench books "Panama Papers fanfic."
I've read plenty of noir fiction and I'm a long-term finance-leaks obsessive, but until I read Fix's article, it never occurred to me that a forensic accountant was actually squarely within the noir tradition. Hench's perfect noir fit is either a happy accident or the result of a subconscious intuition that I didn't know I had until Fix put his finger on it.
The second Hench novel is The Bezzle. It's been out since February, and I'm still touring with it (Chicago tonight! Then Turin, Marin County, Winnipeg, Calgary, Vancouver, etc). It's paying off – the book's a national bestseller.
Writing in his newsletter, Henry Farrell connects Fix's observation to one of his own, about the nature of "hackers" and their role in cyberpunk (and post-cyberpunk) fiction:
https://www.programmablemutter.com/p/the-accountant-as-cyberpunk-hero
Farrell cites Bruce Schneier's 2023 book, A Hacker’s Mind: How the Powerful Bend Society’s Rules and How to Bend Them Back:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/06/trickster-makes-the-world/
Schneier, a security expert, broadens the category of "hacker" to include anyone who studies systems with an eye to finding and exploiting their defects. Under this definition, the more fearsome hackers are "working for a hedge fund, finding a loophole in financial regulations that lets her siphon extra profits out of the system." Hackers work in corporate offices, or as government lobbyists.
As Henry says, hacking isn't intrinsically countercultural ("Most of the hacking you might care about is done by boring seeming people in boring seeming clothes"). Hacking reinforces – rather than undermining power asymmetries ("The rich have far more resources to figure out how to gimmick the rules"). We are mostly not the hackers – we are the hacked.
For Henry, Marty Hench is a hacker (the rare hacker that works for the good guys), even though "he doesn’t wear mirrorshades or get wasted chatting to bartenders with Soviet military-surplus mechanical arms." He's a gun for hire, that most traditional of cyberpunk heroes, and while he doesn't stand against the system, he's not for it, either.
Henry's pinning down something I've been circling around for nearly 30 years: the idea that though "the street finds its own use for things," Wall Street and Madison Avenue are among the streets that might find those uses:
https://craphound.com/nonfic/street.html
Henry also connects Martin Hench to Marcus Yallow, the hero of my YA Little Brother series. I have tried to make this connection myself, opining that while Marcus is a character who is fighting to save an internet that he loves, Marty is living in the ashes of the internet he lost:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/07/dont-curb-your-enthusiasm/
But Henry's Marty-as-hacker notion surfaces a far more interesting connection between the two characters. Marcus is a vehicle for conveying the excitement and power of hacking to young readers, while Marty is a vessel for older readers who know the stark terror of being hacked, by the sadistic wolves who're coming for all of us:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I44L1pzi4gk
Both Marcus and Marty are explainers, as am I. Some people say that exposition makes for bad narrative. Those people are wrong:
https://maryrobinettekowal.com/journal/my-favorite-bit/my-favorite-bit-cory-doctorow-talks-about-the-bezzle/
"Explaining" makes for great fiction. As Maria Farrell writes in her Crooked Timber review of The Bezzle, the secret sauce of some of the best novels is "information about how things work. Things like locks, rifles, security systems":
https://crookedtimber.org/2024/03/06/the-bezzle/
Where these things are integrated into the story's "reason and urgency," they become "specialist knowledge [that] cuts new paths to move through the world." Hacking, in other words.
This is a theme Paul Di Filippo picked up on in his review of The Bezzle for Locus:
https://locusmag.com/2024/04/paul-di-filippo-reviews-the-bezzle-by-cory-doctorow/
Heinlein was always known—and always came across in his writings—as The Man Who Knew How the World Worked. Doctorow delivers the same sense of putting yourself in the hands of a fellow who has peered behind Oz’s curtain. When he fills you in lucidly about some arcane bit of economics or computer tech or social media scam, you feel, first, that you understand it completely and, second, that you can trust Doctorow’s analysis and insights.
Knowledge is power, and so expository fiction that delivers news you can use is novel that makes you more powerful – powerful enough to resist the hackers who want to hack you.
Henry and I were both friends of Aaron Swartz, and the Little Brother books are closely connected to Aaron, who helped me with Homeland, the second volume, and wrote a great afterword for it (Schneier wrote an afterword for the first book). That book – and Aaron's afterword – has radicalized a gratifying number of principled technologists. I know, because I meet them when I tour, and because they send me emails. I like to think that these hackers are part of Aaron's legacy.
Henry argues that the Hench books are "purpose-designed to inspire a thousand Max Schrems – people who are probably past their teenage years, have some grounding in the relevant professions, and really want to see things change."
(Schrems is the Austrian privacy activist who, as a law student, set in motion the events that led to the passage of the EU's General Data Privacy Regulation:)
https://pluralistic.net/2020/05/15/out-here-everything-hurts/#noyb
Henry points out that William Gibson's Neuromancer doesn't mention the word "internet" – rather, Gibson coined the term cyberspace, which, as Henry says, is "more ‘capitalism’ than ‘computerized information'… If you really want to penetrate the system, you need to really grasp what money is and what it does."
Maria also wrote one of my all-time favorite reviews of Red Team Blues, also for Crooked Timber:
https://crookedtimber.org/2023/05/11/when-crypto-meant-cryptography/
In it, she compares Hench to Dickens' Bleak House, but for the modern tech world:
You put the book down feeling it’s not just a fascinating, enjoyable novel, but a document of how Silicon Valley’s very own 1% live and a teeming, energy-emitting snapshot of a critical moment on Earth.
All my life, I've written to find out what's going on in my own head. It's a remarkably effective technique. But it's only recently that I've come to appreciate that reading what other people write about my writing can reveal things that I can't see.

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2024/04/17/panama-papers-fanfic/#the-1337est-h4x0rs

Image:
Frédéric Poirot (modified)
https://www.flickr.com/photos/fredarmitage/1057613629 CC BY-SA 2.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/
143 notes
·
View notes
Text
Power plant in Hirschfelde (Zittau), Germany.
(Europeana)
69 notes
·
View notes
Text

1971 poster for 2001: A Space Odyssey.
84 notes
·
View notes





