#writing systems
Text
Lingthusiasm Episode 88: No such thing as the oldest language
It's easy to find claims that certain languages are old or even the oldest, but which one is actually true? Fortunately, there's an easy (though unsatisfying) answer: none of them! Like how humans are all descended from other humans, even though some of us may have longer or shorter family trees found in written records, all human languages are shaped by contact with other languages. We don't even know whether the oldest language(s) was/were spoken or signed, or even whether there was a singular common ancestor language or several.
In this episode, your hosts Gretchen McCulloch and Lauren Gawne get enthusiastic about what people mean when we talk about a language as being old. We talk about how classifying languages as old or classical is often a political or cultural decision, how the materials that are used to write a language influence whether it gets preserved (from clay to bark), and how people talk about creoles and signed languages in terms of oldness and newness. And finally, how a language doesn't need to be justified in terms of its age for whether it's interesting or worthy of respect.
Read the transcript here.
Here are the links mentioned in the episode:
Lingthusiasm episode 'Tracing languages back before recorded history'
'My Big Fat Greek Wedding- Give me any word and I show you the Greek root' on YouTube
Glottolog entry for 'classical'
Wikipedia entry for 'Complaint tablet to Ea-nāṣir'
Wikipedia entry for 'Bath curse tablets'
Wikipedia entry for 'Cuneiform'
Wikipedia entry for 'Mesopotamian writing systems'
Wikipedia entry for 'Home Sign'
Lingthusiasm episode 'Villages, gifs, and children: Researching signed languages in real-world contexts with Lynn Hou'
Wikipedia entry for 'Al-Sayyid Bedouin Sign Language'
Wikipedia entry for 'Kata Kolok' (also known as Benkala Sign Language)
True Biz by Sara Nović on Goodreads
Gretchen's thread about reading True Biz
You can listen to this episode via Lingthusiasm.com, Soundcloud, RSS, Apple Podcasts/iTunes, Spotify, YouTube, or wherever you get your podcasts. You can also download an mp3 via the Soundcloud page for offline listening.
To receive an email whenever a new episode drops, sign up for the Lingthusiasm mailing list.
You can help keep Lingthusiasm ad-free, get access to bonus content, and more perks by supporting us on Patreon.
Lingthusiasm is on Bluesky, Twitter, Instagram, Facebook, Mastodon, and Tumblr. Email us at contact [at] lingthusiasm [dot] com
Gretchen is on Bluesky as @GretchenMcC and blogs at All Things Linguistic.
Lauren is on Bluesky as @superlinguo and blogs at Superlinguo.
Lingthusiasm is created by Gretchen McCulloch and Lauren Gawne. Our senior producer is Claire Gawne, our production editor is Sarah Dopierala, our production assistant is Martha Tsutsui Billins, and our editorial assistant is Jon Kruk. Our music is ‘Ancient City’ by The Triangles.
This episode of Lingthusiasm is made available under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial Share Alike license (CC 4.0 BY-NC-SA).
#linguistics#language#lingthusiasm#episodes#podcast#podcasts#episode 88#language history#oldest language#classical languages#ancient languages#sign language#home sign#cuneiform#writing technology#writing systems#SoundCloud
120 notes
·
View notes
Text
Problem with Discord's new (and old) font(s) and its treatment of non-Latin text
Before getting into it, I'm gonna say that I'm not going to criticize its aesthetics or "readability". These feedbacks are rarely helpful from the designer's perspective especially coming from people who don't know much about what goes into designing a typeface, and because readability is really, really subjective.
I was happy to hear that discord was changing its font, especially when I found out that they are adding support for Vietnamese. Previously, discord used Whitney, a humanist sans serif font with Latin, Greek, and Cyrillic support. Unfortunately, Whitney doesn't support all Latin characters in Unicode, and crucially it doesn't support Vietnamese characters.
Text font not supporting a script is usually not a problem, the fallback font will take care of it for you. The problem occurs when there's partial support. Vietnamese uses Latin, but it also has a ton of precomposed vowels with diacritics. This is what Vietnamese looks like on my phone, where the font change hasn't taken effect yet:

here's the same text with unsupported characters highlighted in red:
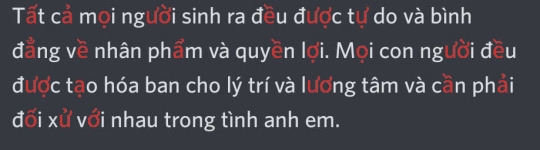
It might not look that weird because the fallback font on my phone happened to be somewhat similar in style to Whitney, but depending on the device it may be completely unreadable. I submitted a feedback a while ago asking them to address this issue
This is why when I heard that discord was changing its font to add Vietnamese characters, I was excited. This is what the same text looks like in gg sans.
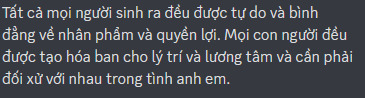
All characters harmonious!
However, after receiving the update I was disappointed because the new font now no longer supports Greek and Cyrillic. This alone is not really a big problem, because Greek, Cyrillic and Latin characters rarely occur in the same word. Although it is disappointing that they are no longer harmonious, it's not that big of a problem. The problem though, is that they decided to include Δ, Ω, μ, π (capital delta, capital omega, lowercase mu, and lowercase pi) into the font.
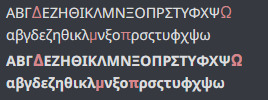
Depending on the device and rendering settings, it might look like it fits well with the fallback font, being almost unnoticeable, or so noticeable that it's hard to read. These four glyphs are often included in typefaces that only support Latin as they are often included in Latin lettersets because of their use in mathematics and science, so I thought it was simply an odd oversight.
Then I found out about this:
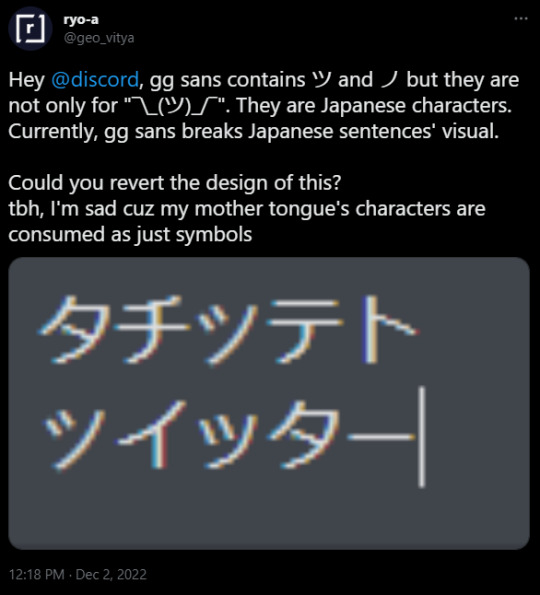
(As of 2022/12/3 9:22 pm UTC+9 I couldn't recreate this. It may be because of css setting or because they've already fixed it. I'm hoping it is the latter)
They decided to include katakana characters to be only used in the shrug emoticon.
I was massively disappointed when I heard this news because it means they did not care at all about global accessibility when making the new font. I was under the impression that they were doing it at least partially to address this issue. I was under the impression that maybe they've heard us complain and complain about the font only having partial support for Vietnamese. Maybe they've realized the core problem. But no, it's clear that they still don't know what the problem is.
Maybe I should have realized it sooner. Did you know, Discord limits the amount of diacritics that can be attached to a single character, even though in a lot of non-Latin writing systems diacritics are crucial because they represent vowels, consonant clusters, et cetera?
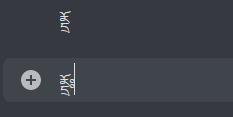
Moreover, did you know that Discord has a limit on how many diacritics you can have in a single message? This means if you have a copy pasta in abugida writing systems such as Devanagari, Thai, Khmer, Lao, Bengali, Burmese, et cetera, the vowel diacritics are just going to disappear after a while, rendering the text unreadable?

Affected portion underlined in red. I assume these are done to prevent zalgo, which really shouldn't be done by Discord itself, not to mention that typical "zalgo" diacritics are usually IPA diacritics with actual use, which can often stack in a zalgo-like fashion.
Did you know that Discord enforces strict text line height, even though some writing systems need more horizontal space than latin to be legible? Anything outside of the bounds are cut off and rendered invisible.
Anyway, do you remember when I said I wasn't going to talk about aesthetics and readability? I kind of lied. I am going to talk about them.
A lot of people seem to be saying that the new font is bad and that it's significantly less readable than the previous font. I have doubts about whether this is actually because of the font itself or because they're simply not used to it yet. My guess would be the latter. However, that doesn't mean the solution is to make these people shut up and wait till they get used to it.
There is no universal solution for readability and legibility. The truth is that different people have different needs, and this is no different when it comes to typefaces. Ideally, discord should provide an option to change fonts. Many platforms do. They've been refusing to implement it because, I dunno, brand image?
There is also a bigger problem with how UI designers design in general. They only design around Latin in mind, even though different writing systems use space differently. Many Brahmic scripts use ligatures and diacritics stacking above or below the main character. If you care about non-Latin scripts not appearing illegible, make it so that UI elements can accommodate for that, or something.
I'm bad at writing conclusions, so there you have it. Me rambling about a thing that I care about that apparently everyone else should too.
419 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ranking my favourite natural writing systems by sexual appeal
1. Burmese: မြန်မာအက္ခရာ
2. Tibetan: བོད་སྐད
3. Mkhedruli (Georgian): მხედრული
4. Baybayin (Tagalog): ᜊᜌ᜔ᜊᜌᜒᜈ᜔
5. Devanagari (Sanskrit and Hindi): देवनागरी
6. Hebrew: אָלֶף־בֵּית עִבְרִי
7. Arabic: كتابة عربية
8. Javanese: ꦧꦱꦗꦮ
9. Thai: ภาษาไทย
10. Bengali: বর্ণমালা
11. Sinhalese (Sri Lankan): සිංහල (yes this is the language with the ඞ character)
12. Greek: ελληνικά
13. Katakana (Japanese): カタカナ
14. Hangeul (Korean): 한글
15. Hiragana (Japanese): ひらがな
16. Amharic (Ethiopian): ኢትዮጵያ
17. Kanji (Japanese): 漢字
18. Syriac (Aramaic): ܫܢܐ ܣܘܪܝܝܐ
19. Akkadian: 𒀝𒅗𒁺𒌑
20. Mandarin (Sorry, it’s the only Chinese language I’m semi-familiar with, I’m basic): 官话
21. Cyrillic (Slavic): кириллица
I LIKE ALL OF THESE, I JUST LIKE SOME EVEN MORE THAN OTHERS
#linguistics#writing systems#burmese#tibetan#georgian#baybayin#devanagari#sanskrit#hindi#hebrew#arabic#javanese#thai#bengali#Hebrew and Burmese are the ones I’d write English in
30 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey, guys! Want to vote on the best 6th-10th Century script (writing system) that I, Gecko, personally like?
Of course you do! Writing systems are SO COOL!
And here's a bit about each of the contenders:
Arabic (Naskh Script)
Derived from the Aramaic Script, which grew out of Phoenician, Arabic has a variety of forms. The Naskh script is the one I find the most beautiful, with it's extreme variation on character length and height. I also love the use of multiples colours for Ḥarakāt (vowel marks and other diacritics). Add in the elegant curves and solid lines, and Naskh Script becomes one of the most stylish scripts around.

Latin (Insular Script)
Derived from Greek, the Latin alphabet is usually a competent and pleasant mix of lines and curves, uprights and descenders. Insular script plays with these qualities, and the result is electric! many of the uprights (t, d, f) are gone. New descenders are added (r, s, f). Horizontal lines take a new prominence. Line weight is increased, and the curves become more angular. Something old to us becomes new again.

Chinese (Semi-Cursive Script)
There are many ways to write Hanzi (Chinese characters), and Semi-Cursive Script manages to combine the best qualities of most of them! The expressive curves and flow of a cursive script. The solid shapes and readability of Regular Script. One of the joys of Hanzi is the visual interest of so many unique characters; which share components, but use them differently. Semi-Cursive keeps much of that interest, while also providing a dynamic energy and movement.

Sogdian (Cursive Script)
Derived from the Syriac script, which grew out of the Aramaic Script, the Sogdian Alphabet was developed by traders who met most of the major cultures of the Old World, and let all of those cultures affect their language and writing. Sogdian can be written write to left, like most Aramaic scripts, but also top to bottom, like the Chinese Scripts of their main trade partner. Curvy cursive lines, and characters of wildly varying length, give this script a interesting sense of flow.
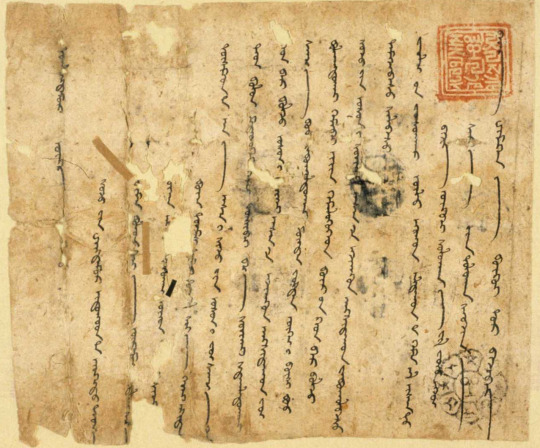
Hebrew (Ktav Ashuri Script with Palestinian Vocalization)
Another offshoot of the (Imperial) Aramaic Script, the Hebrew Alphabet has a really interesting, heavy, square, solid feel. In contrast, Palestinian Voicing (an extinct form of writing vowels where all of them were above the consonants) is really light, stacked on top their vowels in little floaty towers. It's a cool combination!

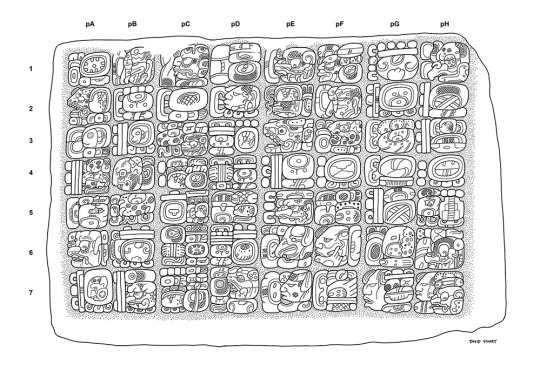
Maya (Classical Maya Script)
The most famous script of the Americas, Maya has one of the most unique reading orders of any script. Characters are written in blocks, which are then read in a zigzag (right, and then down-left) pattern. Full of heads (both animal and human), torches, seeds, and other half-identifiable shapes, Maya texts are works of art, and the more you study them, the more beautiful they become.
Nubian (Old Nubian Script)
Derived from Greek with additional letters from Coptic (Egyptian) and Meroitic (a previous Nubian culture). Lines above letters are used to skip parts of words deemed unnecessary. The mixture of rectangles and triangles, heavy and light line weights - it reminds me of telegrams, or early typewriter text. I love it!

Khmer (Angkorian Khmer Script)
Derived from the Pallava Script, which derived from the Brahmi Script, Khmer is probably my favourite script to write. The curves feel so good! The spirals so pleasing! You write consonant clusters by writing little letters below the main one! A joy to create, and a joy to look at.

Japanese (Cursive Script)
See these wiggles? They're Chinese characters. Elegant, looking like poetry no matter what they're saying, Cursive Japanese is art. It's also ridiculous. 3 different characters, each with multiple strokes, indicated by wiggling the brush as you draw a line! Most cursive scripts are like this, but the contrast between the square solidness of Regular Script and the flow of Cursive is one of the more extreme. What a delight!

Sanskrit (Siddham Script)
I had SO MANY options for Sanskrit (Brahmi) Scripts, you guys. SO MANY! But in north-west India, during the period I study, this version of Siddham is the prettiest. Look at the curves! Those aren't just decorative, each curvy line that goes above or below the text is a vowel. Consonant clusters are shown by combining the characters together in one spot. The lines at the top haven't yet started connecting, like they do in modern Devanagari, but there's already a sense of it's existence. Such a cool script!

#long post#gecko's polls#calligraphy#scripts#writing systems#arabic#hebrew#khmer#maya#latin#nubian#sanskrit#sogdian#chinese#japanese
227 notes
·
View notes
Text
30.01.24 Origin of Japanese kana

Answer and Translation
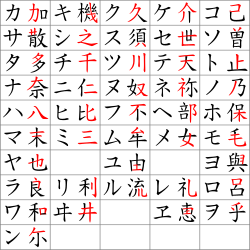
Both hiragana and katakana are symbols that express a sound and were born out of a kanji [Chinese character]. Do you understand which kana was born from which kanji? First, fill in the katakana with the same pronunciation as the hiragana, then search for the original respective kanji.
1. こ(己)・ コ(己)
2. ん(无)・ ン(尓)
3. に(仁)・ 二(仁)
4. ち(知)・ チ(千)
5. は(波)・ ハ(八)
As a general rule, hiragana developed from the cursive script aka "grass script" (sōsho・草書) of the characters of the historical writing system man’yōgana (万葉仮名), while the corresponding katakana are composed of components of man’yōgana characters ⬇️

20 notes
·
View notes
Text

What if we kissed in front of the trilingual cuneiform inscription of Xerxes I at Van Fortress in Turkey
#langblr#linguistics#cuneiform#ancient languages#writing systems#language#language blog#languageblr#language meme#language memes#linguistics humor#language learning#linguistics memes#linguistics blog#lingblr#studyblr#language lover#lingblog#languages#linguistics tumblr#linguistics jokes#ancient history#xerxes i#turkey#turkiye#trilingual
344 notes
·
View notes
Photo
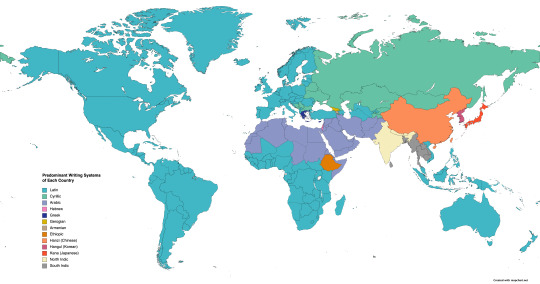
Predominant Writing Systems of Each Country
179 notes
·
View notes
Text
Has anyone ever experimented with creating a conlang that utilizes a 3D alphabet? This could open up a lot of possibilities when it comes to writing, where different dimensional orientations of the letter could be read in different emotional tones or voices, and you could branch off sentences into different physical spaces if you need to go on a tangent (as a substitute to parenthesis). This could also open up wild 3D crosswords, where an A could make different sounds depending on its orientation, so intersecting words wouldn’t rely on the letter itself, but they would have to rely on the letter locked in that specific dimensional orientation.
Or what if there were letters that relied on a 3rd dimension, but not to be viewed in different angles? What if humanity reset, and written language was developed by pressing hands into concrete in different positions as well as depths? Kind of like pressing still sign language into concrete, but depth would indicate different tones or expressions or something. Then this could evolve over time into having stroke opacity play a huge part in future writing with ink.
Maybe both of these writing systems could open up a whole new form of crossword puzzles! And don’t even get me started on word searches.
22 notes
·
View notes
Text


From A to Finis
This week we came across a rather elegant finis, and it turns out it is probably the least interesting part of the book! (We promise to post more on this gem soon!) It is found in a 1799 book containing specimens and analysis of writing systems from around the world. This final page contains information about Rejang, an Indonesian language.
Fry, Edmund. Pantographia : containing accurate copies of all the known alphabets in the world; together with an English explanation of the peculiar force or power of each letter: to which are added, specimens of all well-authenticated oral languages; forming a comprehensive digest of phonology. London : Printed by Cooper and Wilson, for John and Arthur Arch, Gracechurch-Street; John White, Fleet-Street, John Edwards, Pall-Mall; and John Debrett, Piccadilly, MDCCXCIX [1799].
67 notes
·
View notes
Text
Transcript Episode 88: No such thing as the oldest language
This is a transcript for Lingthusiasm episode ‘No such thing as the oldest language. It’s been lightly edited for readability. Listen to the episode here or wherever you get your podcasts. Links to studies mentioned and further reading can be found on the episode show notes page.
[Music]
Gretchen: Welcome to Lingthusiasm, a podcast that’s enthusiastic about linguistics! I’m Gretchen McCulloch.
Lauren: I’m Lauren Gawne. Today, we’re getting enthusiastic about old languages. But first, our most recent bonus episode was deleted scenes with three of our interviews from this year.
Gretchen: We had deleted scenes from our liveshow Q&A with Kirby Conrod about language and gender. We talked about reflexive pronouns, multiple pronouns in fiction, and talking about people who use multiple pronoun sets.
Lauren: We also have an excerpt from our interview with Itxaso Rodríguez-Ordóñez about Basque because it’s famous among linguists for having ergativity.
Gretchen: We wanted to know “What do Basque people themselves think about ergativity?” It turns out, there are jokes and cartoons about it, which Itxaso was able to share with us.
Lauren: Amazing and charming.
Gretchen: Finally, we have an excerpt from my conversation with authors Ada Palmer and Jo Walton about swearing in science fiction and fantasy. This excerpt talks about acronyms both of the swear-y and non-swear-y kind.
Lauren: You can get this bonus episode as well as a whole bunch more at patreon.com/lingthusiasm.
Gretchen: Also, yeah, maybe this is a good time to remember that we have over 80 bonus episodes.
Lauren: We have bonus episodes about the time a researcher smuggled a bunny into a classroom to do linguistics on children.
Gretchen: We also have a bonus episode about “The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog” and more phrases that contain all the letters of the alphabet – plus, what people do with phrases like this in languages that don’t have alphabets.
Lauren: We also have an entire bonus episode that’s just about the linguistics of numbers.
Gretchen: If you wish you had more lingthusiasm episodes to listen to right now, or if you just wanna help us keep making this podcast long into the future, we really appreciate everyone who becomes a patron.
Lauren: You can find all of that at patreon.com/lingthusiasm.
[Music]
Gretchen: Hey, Lauren, I’ve got big news.
Lauren: Yeah?
Gretchen: Did you know I’m from the oldest family lineage in the world?
Lauren: Wow! You sound like you are part of some prestigious, ancient, royal – I can only assume royal with that level of knowledge about your family lineage.
Gretchen: Well, you know, I have some family members who are really into genealogy. I’ve been looking at some family trees. And I have come to the conclusion that my family is the oldest family in the world.
Lauren: You know, I have grandparents, and they have grandparents, and I assume they had grandparents, and I guess my family goes all the way back as well. We didn’t come out of nowhere. I might not know all their names. I don’t think we were ever rulers of any nation state as far as I’m aware. But I dunno if you are from the oldest family lineage because I think everyone is.
Gretchen: Well, this is not a mutually exclusive statement. I can be from the oldest family lineage, and you can be from the oldest family lineage, and everyone listening to this podcast can be all from the oldest family lineage in the world because we’re all descended from the earliest humans.
Lauren: This is a good point.
Gretchen: Psych!
Lauren: I think it’s definitely worth remembering the difference between the very fact that we are all from the same humans – and the difference between that and knowing names of specific individuals back to a certain point.
Gretchen: I should clarify – I am not royalty. I do not actually know the names all the way back because at a certain point writing stops existing and, at some point before that, people stopped recording my ancestors. I don’t know when it stops.
Lauren: But there’s definitely a tradition in certain royal families and stuff of being able to claim that you can trace your family back to, you know, maybe –
Gretchen: Like Apollo or something.
Lauren: Oh, gosh, like, mythical characters, okay. I was thinking of just tracing them back a thousand years, but I guess –
Gretchen: Tracing them back to Adam and Eve or tracing them back to Helen of Troy or Apollo or these sorts of things. I feel like – at least I’ve heard of this. I think that talking about human ancestral lineages helps us make sense of the types of claims that people also make about languages being the oldest language.
Lauren: I feel like I’ve heard this before – different languages making claim to being the oldest language.
Gretchen: I’ve heard it quite a lot. I did a bit of research, and I looked up a list of some languages that people have claimed to be the oldest.
Lauren: Okay, what did you find?
Gretchen: A lot of things that can’t all be true at the same time.
Lauren: Or can all be true because all languages are descended from some early human capacity for human language.
Gretchen: Right. There’s different geographical hot spots, you know, people making claims about Egyptian, about Sanskrit, Greek, Chinese, Aramaic, Farsi, Tamil, Korean, Basque – speaking of Basque episodes. Sometimes, people look at reconstructed languages like Proto-Indo-European, which is, you know, the old thing that the modern-day Indo-European Languages are descended from. But part of the issue here is that, at least for spoken languages – and we’re gonna get to sign languages – but at least for spoken languages, babies can’t raise themselves.
Lauren: Unfortunately, I, personally, have to say after the last few years.
Gretchen: Deeply inconveniently –
Lauren: Yeah.
Gretchen: – for adult sleep schedules. If you have a baby with typical hearing, and they’re being raised in a community or even by one person, they’re gonna acquire language from the people that are raising it.
Lauren: Absolutely – in much the same way we all have people giving us genetic input, we also have people giving us linguistic input and continuing on that transmission of human language.
Gretchen: Exactly. When the languages claim to be “old,” that’s often more of a political claim or a religious claim or a heritage claim than it is a linguistic claim because we think that languages probably have a common ancestor. Certainly, all languages are learnable by all humans. If you raise a baby in a given environment, they’ll grow up with the language that’s around them. The human capacity for language seems to be common across all of us. We just don’t know what that tens-of-thousands-year-old early language looked like.
Lauren: In much the same way we lose track of earlier ancestors when we get earlier than written records. We talked about this in the reconstructing old languages episode that there’s just a point where you can’t go back further because there’s just not enough information to say exactly how Proto-Indo-European might have, at some earlier point, been related to, say, the Sino-Tibetan languages or the Niger-Congo family.
Gretchen: Right. We also talked about this in the writing systems episode where writing systems had been invented about 4,000, 5,000, 6,000 years ago, but human language probably emerged sometime between 50,000 and 150,000 years ago, which is so much older. That’s 10-times-to-30-times older than that. We don’t know because sounds and signs leave impressions on the air waves that vanish very quickly and don’t leave fossils until writing starts being developed much later.
Lauren: Very inconvenient.
Gretchen: Absolutely the first thing I would do with a time machine.
Lauren: All of those languages that you mentioned as people laying claim to them being the oldest, they come from all kinds of different language families. Although, I have to say, a very Indo-European, Western skew there, which probably reflects the corners of the internet that you have access to.
Gretchen: This reflects the people that are making claims like this on the English-speaking internet that I’m looking at and the modern-day nation states and religious traditions and cultural traditions that are making claims to certain types of legitimacy via having access to old texts or having access to uninterrupted transmission of stories and legends and mythologies that give them those sorts of claims. There’s no reason to think that a whole bunch of languages on the North and South American continents are not also equally old as all the other languages, but people aren’t doing nation state building with them, and so they don’t tend to show up on those lists.
Lauren: Yeah. A lot of nation state building, a lot of religion happening there as well. I think about how yoga is – I love a bit of yoga, and I think it’s really lovely that all the yoga terms are still given to you in this older Sanskritic language, but it definitely is done sometimes with this claim to legitimacy and prestige in the same way that having something in Latin for the Catholic Church gives that same kind of vibe.
Gretchen: I think about this scene from the movie My Big Fat Greek Wedding where you have the daughter, who’s the one that’s getting married. She’s in the car as a teen with her parents. It’s this scene where the parents are being a bit cringe-y in the way that teens often experience their parents to be. The dad is saying, “Name a word. I will tell you how it comes from Greek,” because he’s got this big Greek pride thing going.
Lauren: This a classic Greek-American migrant pride happening.
Gretchen: Right. He says, “arachnophobia,” and he’s explaining how the roots come from Greek, and that one’s true. Then the daughter’s friend, who’s in the back seat, is rolling her eyes and saying, “Well, what about ‘kimono’?”
Lauren: Ah, “kimono” the Japanese robe?
Gretchen: Yes. The Dad’s like, “Oh, no, it’s from Greek. Here’s this connection that I have found.”
Lauren: I like his linguistic ad-libbing skills.
Gretchen: It’s certainly a great improvisational performance skill. The movie is clearly designed to put the viewer in sympathy with the young girls in the back seat who are teasing him, and the daughter’s face-palming at this claim, which is one of the reasons why it’s one of my favourite examples of people making up fake etymologies in media because you don’t leave the movie thinking, “Oh, I never realised ‘kimono’ was from Greek.” You leave that movie being like, “Ah, here’s this dad who has over-exaggerated pride in his heritage that doesn’t allow for other people’s heritage to also have words that come from them.” It’s a claim that he's making for personal reasons and for heritage reasons that doesn’t have linguistic founding, but none of these claims have linguistic founding.
Lauren: The dad has come kind of close to a linguistic truth though, which is that linguists talk about languages having features that can be either conservative or innovative. Modern Greek has a lot of the same sound features as Ancient Greek, which is probably helped by that consistent writing system. A writing system definitely helps transmission stay stable because you can point back to older texts. English has probably slowed down a lot in its change because of the writing system as well.
Gretchen: Genuinely, English has borrowed a lot of words from Greek – as well as a lot of other languages that are not Greek. This gets to both Greek and Sanskrit and Chinese having these eras that are talked about as “classical” or as “old,” which is an era that the present-day people, or some slightly earlier group of people, looked back on and thought, “Yeah, those people were doing some cool stuff. We’re gonna call it ‘classical’ because we liked it in history.”
Lauren: I do love the idea that Chaucer had no idea that he was moving on from Old English to Middle English because there wasn’t a Modern English yet.
Gretchen: How could you describe yourself as “Middle English” – that’s sort of like the “late-stage capitalism” that implies that we’re towards the end of something. Like, we don’t know, folks.
Lauren: I don’t think English always does self-deprecating well. English has a lot of belief in its superiority as a language. I think we can say that about the ideology behind English. But I do love that English didn’t go for “Classical English.” Imagine if we said Beowulf was written in “Classical English.”
Gretchen: We could have, yeah. We could have.
Lauren: We just went with, “Ah, that’s old. I don’t understand it. It’s got cases. It’s got all these extra affixes. It’s old. It’s a bit stuffy.”
Gretchen: That may have been because they were comparing it already to Classical Latin and Classical Greek, which was even more antique. The English speakers were looking elsewhere for their golden age. I don’t think people often claim that English is the oldest language because English speakers are seeing the history of their society located in this Greco-Latin tradition.
Lauren: Yeah, I think that’s a good explanation for it. I do wonder if maybe the attitude that we now have towards Shakespearean English, if maybe that will become “Classical English” when we’re a bit further on, and Shakespeare becomes even less accessible.
Gretchen: Right. And if Shakespeare becomes the text that everyone is referring to because it’s this quote-unquote “classic” text but calling something a “classical era” reflects on the subsequent era and what they thought about the older one more so than the era itself.
Lauren: Having this ability to distinguish between an “old” or a “classical” and a “modern” version of a language requires that writing tradition, whereas the majority of human languages, for the majority of human history, have happily existed and transmitted knowledge without a writing system. These writing systems make us very focused on pinning down. I super appreciate the website Glottolog, which catalogues languages and all the names they’re known by. We have a lot of languages that are “classical,” like “Classical Chinese” or “Classical Quechua.” We have some “early” – so “Early Irish.”
Gretchen: I think I’ve also heard of “Old Irish.”
Lauren: We have “Old Chinese” and “Old Japanese” in Glottolog, but I’ve definitely also heard them referred to as “classical,” so slightly different vibes there. Of course, you have things like “Ancient Hebrew,” which, older than old, very prestigious. I particularly like the precision with which some names get given to different languages over time. Glottolog has an “Old Modern Welsh,” which is nice and specific. I particularly appreciate the “Imperial-Middle-Modern Aramaic.”
Gretchen: “Imperial-Middle-Modern Aramaic.” That also gets to languages being named and being spread through empire and conquest and wars, which is also part of that historical tradition that people look back to.
Lauren: For sure. That’s part of the narrative building around languages. A lot of what is maintained about a language is religious documents or documents of imperial rule. That means that that imperial form might have been a particular register. Imagine if all that we had about English was the tax forms that we have.
Gretchen: Oh, god, that would be really boring.
Lauren: You would have a very different idea of what English is compared to how it’s spoken day-to-day. That’s what makes this understanding of old languages just from a written record really challenging.
Gretchen: When I think about trying to understand the history of languages just from the written record, I’m reminded of this classic joke – I dunno if you’ve heard this one – where you’re walking down the street one night, and you see someone standing under a streetlight looking at their feet and trying to search for something. You go, “Oh, what are you looking for?” And the person says, “Oh, my contact lens. It fell out. I’m trying to find it.” And you say, “Oh, did you lose it under the streetlight?” And the person goes, “No, I lost it a block over that way, but there’s no streetlight there, so it’s much easier to search here.”
Lauren: [Laughs] Hmm.
Gretchen: I guess this is a joke that doesn’t work so well now that everyone has phones with flashlights on them, and contact lenses have improved their technology and don’t pop out spontaneously like that. But when we’re looking for the history of language, it’s like looking under the streetlight because that’s where it’s easy to look. It’s not actually doing a random sample of all of the bits of history – many of which are just lost to us.
Lauren: Indeed. I like thinking about the imperial languages and the classical languages because sometimes we do get written records that help give us a glimpse into just how ordinary people were going about living their lives.
Gretchen: Oh, oh, oh, oh, oh, can we talk about the clay tablet?
Lauren: We can absolutely talk about the clay tablet that I know what you mean because you’re talking about the complaint to Ea-nāṣir, which is a clay tablet that’s written in Akkadian cuneiform. It’s considered to be the world’s oldest known written complaint.
Gretchen: This is from a customer named Nanni who’s complaining about the quality of the copper ingots that was received.
Lauren: The thing that I love about this is that there is this complaint, but also, they’re pretty sure they found Ea-nāṣir’s house because there are other complaints about the quality of the copper in this residence.
Gretchen: We really think we know who’s at fault here.
Lauren: Yeah. It seems like he was just a provider of adequate quality copper, and people really needed to go to a better place to get a better quality of copper.
Gretchen: Cuneiform is also this interesting example of searching under the streetlight for the contact lens because the language Sumerian was written in cuneiform, and then later, Akkadian, which is a Semitic language related to modern-day Arabic and Hebrew, and Hittite, which is an Indo-European language related to English and Sanskrit and a bunch of other languages. They were all using this system of stamping the ends of reeds in these pointy triangle shapes onto clay blocks. Do you know what happens to clay blocks when they’re in a house, and the house burns down?
Lauren: They just get fired and made more resilient.
Gretchen: They get made incredibly durable. If people were writing on parchment or in textiles – like in fabrics or cords or strings or on leather or wood – most of those don’t get preserved the same way because you expose them to water, and they start rotting.
Lauren: And they don’t do great with fire.
Gretchen: They really don’t do great with fire. Animals will eat them. Clay has none of these problems. We don’t even know if we know what all of the ancient writing systems are because the ones that have survived are the ones on clay or stone.
Lauren: I was so charmed when I learnt about Latin curse tablets, which are very similar to the complaints to Ea-nāṣir. These are small bits of lead that people could scratch a curse or a wish onto, and then they would throw them into some kind of sacred water. They found, like, 130 of these at Bath in Britian, but they appear to have popped up all over the Roman Empire. It’s just like these tiny insights into the pettiness of humanity as opposed to the great works of literature, or we’ve talked about how the Rosetta Stone was in these three official languages and was all about a declaration about taxation.
Gretchen: But instead, you can have “This curse is on Gaius because he stole my dog” sort of thing.
Lauren: “I have given to the goddess Sulis the six silver coins which I have lost. It is for the goddess to extract them from the names written below” – and then just lists people who owe this person cash.
Gretchen: That’s petty. I like it.
Lauren: Yeah, so annoyed.
Gretchen: I actually read a romance novel called Mortal Follies by Alexis Hall, which was set in Bath and used the ancient Bath curse tablets as a plot point.
Lauren: So charming.
Gretchen: If anyone wants to read curse tablets and also “romantasy” I think is what we’re calling the genre now.
Lauren: I feel like Jane Austen would’ve included curse tablets if she knew about them.
Gretchen: I think she was no stranger to pettiness. It’s very convenient that they wrote their curses on lead tablets, which is such an incredibly durable format. Imagine if they’d written them on cloth, and then we’d never have them for posterity.
Lauren: I feel sad for all the human pettiness that we’ve lost access to.
Gretchen: Two other old writing systems that we have access to because of the durability of the materials they were written on are oracle bone script, which is the ancestor to Chinese – another writing system that we think developed from scratch because we can see it developing thousands of years ago.
Lauren: Oracle bones written on I believe turtle bones and turtle shells.
Gretchen: Yes, hence the “bone” part – also very durable material and also used for religious purposes.
Lauren: My sympathy and thanks to the turtles.
Gretchen: Indeed. Then the early Mesoamerican writing systems, of which the oldest one is the Olmec writing system, which were written on ceramics. They show representations of drawings of things that look like a codex-shaped book made out of bark which, obviously, we don’t have. We just have ceramic drawings of the bark. Come on!
Lauren: Oh, no!
Gretchen: Ah, it’s so close!
Lauren: How cruel to point out that we’re missing information.
Gretchen: You thought you were mad about the Library of Alexandria burning down. Wait until you hear about the Olmec bark.
Lauren: Yeah, ah, that really gets you and just is a reminder of how much we can’t say about the history of human language because of what we don’t have a record of.
Gretchen: Well, you know, before we do a whole episode about things that we don’t know – because much as we can make fun of searching for the contact lens under the streetlight, we don’t know what we don’t know.
Lauren: Indeed.
Gretchen: What’s something else that people sometimes mean when they say a language is “old”?
Lauren: Well, this goes back to that conservative idea that some languages just have conservative features that haven’t changed as much. A language that has a lot of sound changes we might call very “innovative,” or they’ve “innovated” a new way of doing the tense on the verbs. You can trace it back to an older form of the language, but it looks very different at this point in time.
Gretchen: I think the example that I’m most familiar with this is Icelandic versus English. In the last thousand years or so, English has had a lot of contact from things like the Norman Conquest, which introduced a lot of French words to English, compared to Icelandic, which has had less of that. Icelanders have an easier time reading something like their sagas, which are 800 and more years old, than English speakers have reading texts like Chaucer, which are about the same age but have had a lot more linguistic changes happening because of more contact in English over the years.
Lauren: That’s one of the things that linguists who look at when a language tends to be more innovative and change, it tends to be during these periods of contact. It tends to be during periods of invasion. English had the French come up from the south, repeated Viking incursions from all around the coast. They all had an impact on the language. I find it really interesting. Icelanders are really proud of how conservative the language is and that they still can read these older stories. I think in some ways English has created this story for itself where it’s really proud of the fact that it is this language that continues to take influences from places and is really innovative. These are just part of the story that a language can tell about itself and the speakers can tell about it.
Gretchen: I think that there are reasons to be proud of any language that don’t have to rely on age as the sole arbiter of legitimacy. In some cases, it’s that rupture with the past that people use as a point of pride. I’m thinking of Haitian Creole, for example, which is descended from French. You can hear that French influence. When I’ve heard people speaking Haitian Creole, it almost sounds like they’re speaking a French dialect that I don’t quite know. But the writing system is very different. It’s much more phonetic than French is. The word for “me” in Haitian Creole is “mwa,” and it’s written M-W-A. The word for “me” in Modern French is “moi,” pronounced the same way but written M-O-I.
Lauren: Right.
Gretchen: It used to be pronounced /moɪ/. This is why you get “roy” and /ʁwa/ for “king” and stuff like this, hence the spelling. But the sound changes happened in French. When the Haitian speakers were deciding how to write their language down, they were like, “No, we’re gonna have a phonetic system. We don’t need to be beholden to the French system. We’re gonna have something that establishes our identity as something that’s distinct from French.”
Lauren: For anyone who’s tried to learn the French spelling, especially those endings that are still in the writing system but not in the pronunciation system, I think it’s fair to say French has gone through a number of sound innovations, even if it might be more conservative in other features of the grammar.
Gretchen: It’s very conservative in the writing system, but the sounds have changed a lot.
Lauren: It’s interesting you bring up Haitian Creole because creoles are the result of this intense contact between two or more languages. They often get labelled as being “new,” which is kind of the flip side of this discourse around “old” languages.
Gretchen: That’s controversial in linguistics whether to consider creoles “new” or to consider them older. What they definitely have is children being raised by people who also already had some amount of language. Babies can’t raise themselves. But they do have this situation where their speakers were prevented from learning how to read and write, learning how to access the formal varieties of language, often very violently and through horrible circumstances. A lot of creoles came about because of the slave trade, because of historical systems of oppression. The language transmission was not the same as if you were learning it from parents who’d been educated in the language, but they were still learning from people who had access to the language. There’s been a bit of a swing in creole studies more recently to say, “What if we don’t consider these completely new? What if we think about the ancestral features that they have in common with the languages they’re descended from?” which you can readily trace as well.
Lauren: Thinking in terms of which features are innovative rather than the whole language as being new. Maybe it has a very innovative way of doing the noun structure, but it still has a lot of the features of the two different – or multiple different – languages in terms of sounds, and so taking apart the different linguistic elements and not just focusing on the whole thing as being “new” or “old” and trying to apply these labels that don’t actually account for what’s happening.
Gretchen: It can be kind of exoticising to creoles to say, “Oh, these are completely different from all of the other ways that languages have gotten transmitted,” when what’s also going on is kids in a community who were exposed to a bunch of languages or a bunch of different linguistic inputs at a time making sense of that and coming up with, collaboratively, something with the other kids in the community that is different from what people were speaking before but still has that ancestral link.
Lauren: There are contexts in which children are raised without that access to language transmission. That is when a d/Deaf child is born into a hearing and spoken language family context, which means that they’re not getting that language.
Gretchen: Generally, the child and the parents and the family and community members do end up with some amount of ways of communicating based on the existing gestures that people do alongside a spoken language and elaborating on them, making them more complex, because you are trying to communicate somehow. There are linguistic studies about this, right?
Lauren: Ideally, in an ideal world, if you’re a d/Deaf child, you would want to have access to signed language input through, ideally, your family but also your wider educational context. Some d/Deaf children do get hearing aids. They are useful but not a perfect replication of the hearing child experience. That’s a possibility. There are some contexts where children have just developed this communication system with their hearing family in their own home context. These are known as “home sign.” There have been examples of this, and they have been studied. One of the most famous examples that has been described in a lot of detail is the example of David and his family. Susan Goldin-Meadow and her collaborators over the years have done a lot of work looking at the way David and, especially, his mother communicate with each other.
Gretchen: This is a really tough situation. I think these studies started in the early ’90s. Hopefully, people know better now and can give their d/Deaf kids access to a sign language, but given that this happened, what can we learn from the situation?
Lauren: Goldin-Meadow definitely started publishing about this in the early ’80s. So, David – who I will forever think of as a 7-to-10-year-old child – is actually a GenX-er who, if he had kids himself, they’re undergraduates now.
Gretchen: Okay. It’s good to put famous children from studies in perspective.
Lauren: Because they are – it’s like the Shirley Temple phenomenon, right. David, in my mind, is always just this kid who’s learning to communicate with his mom, but he’s a fully-grown, tax-paying adult now.
Gretchen: What was he doing when he was communicating with his mom in this immortalised-in-amber childhood years?
Lauren: What was really interesting from a thinking-about-this-human-capacity-for-language-and-communication perspective is that his mother and the family developed this way of communicating with him that grew out of their typical gestures and context and a lot of showing each other stuff.
Gretchen: Pointing to things and so on.
Lauren: Pointing – so useful in all languages and all contexts. What they found was that David was creating systematic order out of the gestures that he was getting. So, he had more systematic structure in terms of the hand shape that he was using – he created these hand shape structures and these individual signs that his mom would also use but not as consistently as him. It’s actually the child taking this really idiosyncratic, raw gesture material from his mom. Gestures in spoken language context tend to be a bit more freeform and unstructured than, say, something like a signed language, which uses the same hands but in a very different way. He wasn’t doing something that was a fully structured language, but it had more structure than what he was being given.
Gretchen: His brain was really starved for linguistic input, and he was trying to extract as many linguistic vitamins and minerals as he could from this incomplete gestural system that he was being given as the closest approximation of language. Obviously, we do wish that David, who was raised in the US I think –
Lauren: I think.
Gretchen: – had just been given access to ASL, which lots of people already were using in the US and could’ve happened where he would’ve gotten the fully-fledged, healthy balanced diet of lots of linguistic input from lots of people, but the child brain seems to want to reconstruct language out of whatever is available to it.
Lauren: This type of system, which is often called “home sign,” is not the same as a fully-fledged sign language. Children often don’t have the same level of linguistic structure. They obviously can’t communicate with people outside of the home context who don’t know the signs that they’ve created with the family. I think it’s also worth pointing out that it is more structured than you would expect it to be from the input. We’ve seen when you take children from these emerging structures, and you bring enough d/Deaf people together, you actually get a real blossoming of a full linguistic system.
Gretchen: The most famous example of this is in Nicaragua in the 1980s, where a bunch of d/Deaf children were brought together at a school for the first time. The school wasn’t trying to teach them a signed language; they were trying to do an oralist method of education, which is [grumbles] – about which the less said, the better – but the kids themselves were coming in with their home sign systems and developing them further in contact with each other. When the next generation of kids showed up, and they had access to this combined home sign system, they really turned it into a full-fledged sign language, which is now – Nicaraguan Sign Language is the national sign language in Nicaragua. These types of languages are some good candidates for “youngest” language, even if we don’t know what the “oldest” language looked like.
Lauren: The amazing thing about Nicaraguan Sign Language is there were linguists on the ground pretty much from the beginning of the school in 1980s. There is a documentation of how this language has evolved. It was the older signers coming in, communicating with the younger children coming to the school, who then created more of the structure – so being a bit like David but in this really rich communicative and linguistic environment and building this structure into the language.
Gretchen: It seems to take those two generations of linguistic input. That feels very reassuring to me which is that language is so robust that even if we lose all of our writing systems, and we lose all of our memory of writing systems, and we lose access to the memory of what language looks – like, suddenly we all wake up with amnesia or something – we would rediscover this. Even though they wouldn’t be the same languages, we’d put something back together and still be able to talk to each other.
Lauren: We know this because Nicaraguan Sign Language is not the only example we have of a recently developed language that has emerged. The Nicaraguan Sign Language is a school-based sign, but we also have what are known as “village-based” sign systems, which is where there might be a d/Deaf family, or a number of d/Deaf families in the village – or a very high percentage of d/Deaf population – and a sign language emerges that the whole village, d/Deaf and hearing, use to communicate. It’s usually “village” because it is these smaller communities where people gather and live together and have to communicate with each other all the time.
Gretchen: And if you have an island or somewhere in the mountains or somewhere were there’s a high degree of genetic d/Deafness because there’s a relatively high degree of isolation, you can have a third of the village be d/Deaf, in which case, everybody in that village is learning signs from each other at a young age. I think the famous example of that that I’ve heard of relatively nearby is Martha’s Vineyard in the US, which is an island, I think. It has a village sign language.
Lauren: Lynn Hou talked about Al-Sayyid Bedouin Sign Language in the interview she did with us, which is in a tribal group in a desert in southern Israel.
Gretchen: There’s also Kata Kolok, which is also know as Benkala Sign Language or Balinese Sign Language, which is a village sign language indigenous to two neighbouring villages in northern Bali, Indonesia. Similar situations there.
Lauren: We see this robustness of language and these “young” languages but building on this underlying human tendency to want to create linguistic structure when you bring enough people who can communicate together.
Gretchen: A really interesting example that I’ve encountered recently of what it’s like to suddenly have at least access in terms of format or modality to language, even if you don’t know what everything means yet, is in the book True Biz by Sara Novic, which is set at a school for the d/Deaf. One of the main characters is a d/Deaf girl whose cochlear implants have been malfunctioning, and so she hasn’t been raised with access to a sign language, but suddenly, she’s in this school now and is learning ASL and trying to get her cochlear implants to still work but, in the meantime, is suddenly immersed in this environment where she has full access to language instead of this piecemeal access via attempting to lip read or attempting to use these implants that haven’t been working very well for her. The author is d/Deaf and talks about a variety of different types of experiences that people can have in that context.
Lauren: I really appreciated how this book made the most of the written format to occasionally just not give you what another character was saying, and so you get this experience of being the young protagonist in the book suddenly like, “I’m only getting half of this sentence. I don’t know what’s happening. It’s very stressful.”
Gretchen: Because there’s just a bunch of blank spaces. There were also some places where there were drawings of words that were being talked about or worksheets that she was seeing with line diagrams of different signs. Despite the fact that it’s a book that’s in written English trying to convey ASL, which is not English and doesn’t have a standard way of being written, I think it’s doing a really interesting job of trying to convey that experience.
Lauren: That lack of writing system for signed languages means that a lot of the history of signing in human language history has been lost to us. There have been different signing communities at different times in history. It’s probably been a very common way of humans doing language, but we just don’t know because it’s not in the streetlight of the written record.
Gretchen: Right. We don’t even know if the first language – the “oldest” language – was a spoken language or a signed language. People have come up with arguments for both things. We just don’t know.
Lauren: Which in some ways I find very relaxing instead of constantly trying to make cases for which language is the “oldest” or which is the “newest,” you can just let go of those debates because they are all, at the end of the day, unproveable. You can just enjoy the variety of human language without it being a competition.
Gretchen: A language doesn’t have to be the oldest language or even the newest language in order to be cool. Languages are great. All languages are interesting and valid, and people should have the right to have access to them when they want them. By listening to this episode, you’re participating in part of that chain of human language transmission that stretches beyond anyone’s written record or recorded record or video record. You’re still part of it.
[Music]
Gretchen: For more Lingthusiasm and links to all the things mentioned in this episode, go to lingthusiasm.com. You can listen to us on all the podcast platforms or at lingthusiasm.com. You can get transcripts of every episode at lingthusiasm.com/transcripts. You can follow @lingthusiasm on all of the social media sites. You can get scarves with lots of linguistics patterns on them including IPA symbols, branching tree diagrams, bouba and kiki, and our favourite esoteric Unicode symbols, plus other Lingthusiasm merch – like our new “Etymology isn’t Destiny” t-shirts and aesthetic IPA posters – at lingthusiasm.com/merch. Links to my social media can be found at gretchenmcculloch.com. I blog as AllThingsLinguistic.com. My book about internet language is called Because Internet.
Lauren: My social media and blog is Superlinguo. Lingthusiasm is able to keep existing thanks to the support of our patrons. If you wanna get an extra Lingthusiasm episode to listen to every month, our entire archive of bonus episodes to listen to right now, or if you just wanna help keep the show running ad-free, go to patreon.com/lingthusiasm or follow the links from our website. Patrons can also get access to our Discord chatroom to talk to other linguistics fans and be the first to find out about new merch and other announcements. Recent bonus topics include fun interview excerpts, an interview about swearing with Jo Walton and Ada Palmer, and our very special linguistics advice episode where you asked questions, and we answered them. If you can’t afford to pledge, that’s okay, too. We also really appreciate it if you can recommend Lingthusiasm to anyone in your life who’s curious about language.
Gretchen: Lingthusiasm is created and produced by Gretchen McCulloch and Lauren Gawne. Our Senior Producer is Claire Gawne, our Editorial Producer is Sarah Dopierala, our Production Assistant is Martha Tsutsui-Billins, and our Editorial Assistant is Jon Kruk. Our music is “Ancient City” by The Triangles.
Lauren: Stay lingthusiastic!
[Music]

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
#language#linguistics#lingthusiasm#episodes#podcast#transcripts#podcasts#language history#Olmec Bark#cuneiform#writing systems#sign language#home sign
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
I keep thinking about the times that someone has looked at the idea of writing their language and gone '…yeah no I'm gonna fix that' or 'yeah I want a piece of that action' and made it happen, for any reason. And I'm gonna make noises about it for a little bit. Maybe highlight a couple of things.
You've got King Sejong in Korea going "OK. The script we're using now is hella complex and …Chinese. I want something that's easy enough for a farmer to learn. And maybe to pay his taxes with." And he works out hangul, neat and logical and frequent winner of Best Writing System awards if such things exist. (And then the nobles don't like it because how are they supposed to look smart if the peasants can write too?)
You've got Sequoyah, thinking the settlers he's doing business with might have at least one good idea in this whole 'talking leaves' system they're using. So he throws himself into working out a syllabary that works for the Cherokee language even when his friends and family think he's losing the plot or he's possessed or… Anything. But he hangs in there. Teaches his daughter. Proves that this is something worth it, and goes on to see the syllabary he created become official and used throughout the Cherokee Nation.
These are the best known ones. But how many are there out there?
There are systems where a missionary or someone similar's come into a place, and gone 'hm, Latin ain't cutting it for writing this' - the Cree syllabics and their extended Canadian family fall into this box, though there's at least some accounts that dispute the usual story. (Given that a lot of those sort of stories come down to 'so we can make a Bible at these people', it's fair to put a big old asterisk on them, but… they're a thing.) Getting away from that issue, though? There's local creators making a bespoke system for their language when the ones they'd picked up from outside just don't fit the sounds or grammatical patterns. Writing systems that can really belong to a language and its people.
While it's absolutely not my place to say whether something is good or bad - the only people who can do that are the language users and community the script was made for - there can't help but be a few that catch the eye. For example, I'm quite fond of the Ditema tsa Dinoko script - it's a pretty recent creation from South Africa as a script for a wide range of Bantu languages, using compact triangular blocks in a way that reflects traditional patterns from Sesotho tradition. From my outside perspective, it's an elegant script. It's just one example, though - there's many creators in Africa who have done similar things, sitting down and making a script that their language needs and that isn't being shoved on them by… yeah. Vai and N'Ko are the biggest examples but there are so many! Moving on, in Oceania, we find the Avoiuli text from Vanuatu, designed so that any one character can be drawn with one stroke in the sand… and elsewhere, the scripts being created to use with signed languages which haven't used them in the past…
If I were to try and go into all of them, it'd be a whole essay. And I'd probably miss some as I'm an outsider nerd without access to the deep literature on some of this stuff. Instead, I'll link to The World's Writing Systems as an index to browse through - unfortunately, it doesn't allow searching by how the writing system was created. But there are plenty of indigenous scripts listed there too that deserve their own deep dive. (The fact it lists con-scripts specifically made for fiction… eh.) Their icon comes from the Afaka script, for the Ndyuka creole in Suriname. A lot of the letters are quite pictorial in nature - including the 'ka' in WWS's icon. Gotta say, that's a way to make things memorable.
…anyway, that's my ramble for today. Just gonna wrap with this source which I haven't fully investigated yet, and Endangered Alphabets which isn't so much for deliberately constructed scripts but (unsurprisingly) for endangered ones in general, and as such plain deserves a link.
Now I go back to my own scribbling. Maybe I'll finish a con-script enough to show off one day. Even if one rather smaller in goals.
#writing#writing systems#language#constructed scripts#conscript#long post#i like words :3#just a ramble
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
2023 Lexember 27-30
More animals. Today's first random word is kyuk [kjuk], 'to herd (flock of animals, etc.)' The glyph has two components - on the left, kling 'sheep,' which is the semantic determiner / radical, and on the right kuk, the phonetic determiner, which rhymes with kyuk.

(Kuk refers to a kind of ornate post or pillar which has no exact equivalent in English culture - it can serve as a street sign, a boundary marker, or a commemorative whatever.)
Speaking of sheep, sheep make noise and in Tepat that noise is mey [mej], written like so:

Inside the sheep are two little curlicues, representing puffs of air. They also represent sound and speaking. When you make noise, air comes out of your mouth, right? In ancient Tepatic art, these marks were written in front of figures who were speaking, or over blocks of text that were quotes.
In this glyph, they represent the idea of a sheep speaking, and hence saying mey.
This convention is found in some other onomatopoeic glyphs. (Here comes yet another dog!) A dog "speaking" says ngan [ŋan] as in the glyph below. (As a bonus, on the right is a fun abbreviated ligature of the two glyphs.)

The sound of birds chirping is lin-lin, and is spelled with air on a bird (and once again, there is a ligature):

14 notes
·
View notes
Text

These are Ahiru characters and when the system was first found it was believed that they may have predated the use of the Chinese writing system in Japan.
Nothing's been proven there, but it's a fun set of characters to write in and comes off as a pseudo-Korean. (might predate the Korean writing system, might be based on the Korean system. Nobody has been able to prove or disprove anything, but there is a long standing belief that there was something that predated the Chinese system)
#japanese#langblr#writing systems#ahiru characters#阿比留文字#Japan#Japanese langblr#Japanese language#日本語
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's a big day for Dragonlanging today! Today, we're going to start work on the RUNES part of Tongues and Runes, which means we're going to be working on the writing system of Ndăkaga!
As it stands now with our poll, it looks like we'll be going with an Ogham-inspired aesthetic with a central line through the characters, probably looking something like this:

For this first writing episode, we'll be talking about what kind of writing system we are creating and start to find good words to get the initial pictographs all of the symbols will be based on.
So anyway, join me in about 3 1/2 hours at 3:30pm US Central Time to help me out with script creation.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
What makes a good writing system? I have been thinking quite a bit about this so here’s a list.
When mesopotamia got clay tablets, cuneiform was rotated to be easier to write. Arabic was originally inscribed in stone, which is why it’s left to right, but came to be written on paper, which is why it’s flowy and calligraphic. It’s gotta be easy to write on the first medium it was written on and any subsequent mediums.
All featural writing systems are cool. Hangul, Zbalermorna, Pitman Shorthand, Ditema tsa Dinoko! Mostly, it’s achieved by rotation, which as a dyslexic person I absolutely hate, but Pitman Shorthand used stroke heaviness, and Ditema tsa Dinoko used curved vs straight, parallel vs perpendicular, etc. (Ditema tsa Dinoko is my favorite writing system)
When the writing system denotes multiple levels of language at once. Combining phonology and morphology? This is how you get Я, لا, and all of Ithkuil. Phonology and semantics? Egyptian hieroglyphics, Mayan hieroglyphics, aUI. . . Japanese is a prime example of phonological/syntactic information (hiragana) coexisting with semantic information (kanji). Latin is phonetic but has a rich system of pragmatics: capitals, italics, question marks and exclamation points.
24 notes
·
View notes