#sanskrit
Text
Ms. Coll. 390, Item 2676, is a picture book, containing drawings and miniature paintings of birds and animals, mythological beings, scenes of daily life, court scenes, and more. Many of the pictures are unfinished, upside-down or overpainted, suggesting a work in progress or a sketchbook. It is written in Sanskrit, circa 1700-1850.
🔗:
#manuscript#sanskrit#south asia#18th century#19th century#drawings#art#history of art#indian art#india#animals#birds#painting#sketchbook#picture book#book history#rare books
310 notes
·
View notes
Photo
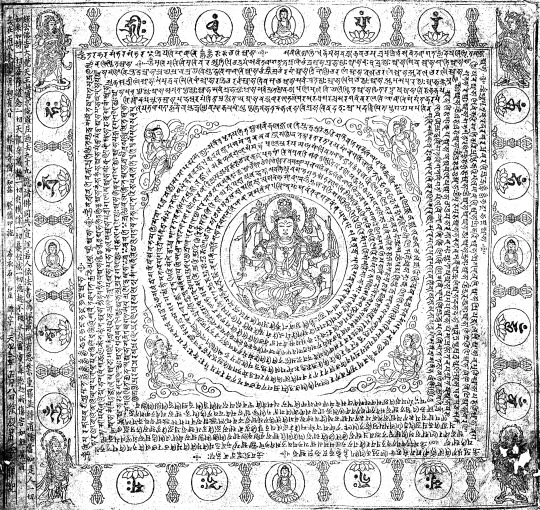
Pratisara Mantra, 927 CE, found near Luoyang, China
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

वात्मानं बोध
Awaken to your true nature.
484 notes
·
View notes
Link

“A 27-year-old PhD scholar finally cracked the riddle which has defeated Sanskrit experts since the 5th Century BC—by decoding a rule taught by “the father of linguistics” Pāṇini.
The discovery makes it possible to ‘derive’ any Sanskrit word—to construct millions of grammatically correct words including ‘mantra’ and ‘guru’—using Pāṇini’s revered ‘language machine’ which is widely considered to be one of the great intellectual achievements in history.
Leading Sanskrit scholars have described the discovery as ‘revolutionary’—and it now means that Pāṇini’s grammar can be taught to computers for the first time...
Pāṇini’s system—4,000 rules detailed in his greatest work, the Aṣṭādhyāyī which is thought to have been written around 500 BC—is meant to work like a machine. Feed in the base and suffix of a word and it should turn them into grammatically correct words and sentences through a step-by-step process.
However, until now, there had been a huge problem. Scientists say that, often, two or more of Pāṇini’s rules are simultaneously applicable at the same step, leaving scholars to agonize over which one to choose...
Thought to have lived in a region in what is now north-west Pakistan and south-east Afghanistan, Pāṇini taught a ‘metarule’ to help decide which rule should be applied in the event of a conflict...
Traditionally, scientists have interpreted Pāṇini’s metarule as meaning: in the event of a conflict between two rules of equal strength, the rule that comes later in the grammar’s serial order wins.
Rajpopat rejects this, arguing instead that Pāṇini meant that between rules applicable to the left and right sides of a word respectively. Pāṇini wanted us to choose the rule applicable to the right side. Employing this interpretation, Rajpopat found Pāṇini’s language machine produced grammatically correct words with almost no exceptions...
“This discovery will revolutionize the study of Sanskrit at a time when interest in the language is on the rise.”
Sanskrit is an ancient and classical Indo-European language from South Asia. It is the sacred language of Hinduism, but also the medium through which much of India’s greatest science, philosophy, poetry, and other secular literature have been communicated for centuries.
While only spoken in India by an estimated 25,000 people today, Sanskrit has influenced many other languages and cultures around the world.
Rajpopat, who was born in Mumbai and learned Sanskrit in high school, explained, “Some of the most ancient wisdom of India has been produced in Sanskrit and we still don’t fully understand what our ancestors achieved.
“I hope this discovery will infuse students in India with confidence, pride, and hope that they too can achieve great things.”
He said that a major implication of his discovery is that now we have the algorithm that runs Pāṇini’s grammar, we could potentially teach this grammar to computers.
“Computer scientists working on Natural language processing gave up on rule-based approaches over 50 years ago. So teaching computers how to combine the speaker’s intention with Pāṇini’s rule-based grammar to produce human speech would be a major milestone in the history of human interaction with machines, as well as in India’s intellectual history.”” -via Good News Network, 12/16/22
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
About Vedic Scriptures
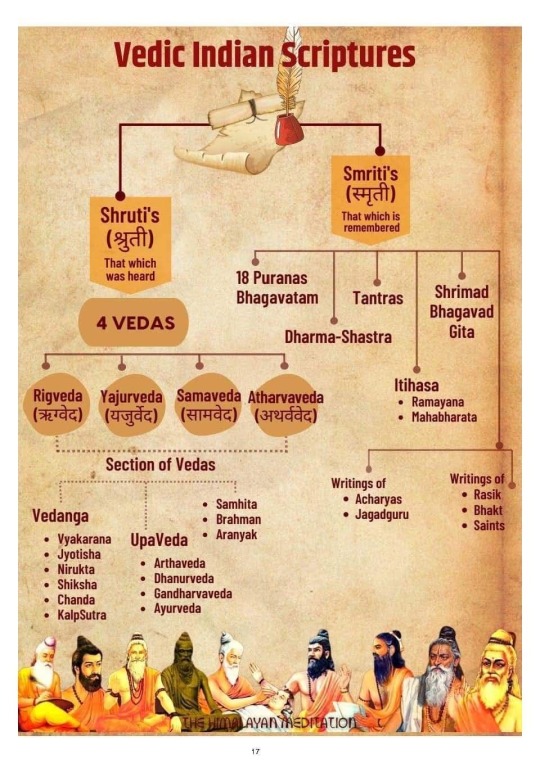

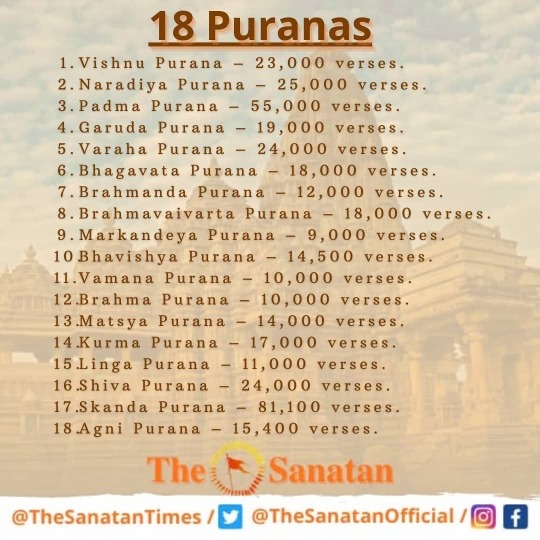
#vedic literature#hinduism#hindublr#sanatan dharma#ancient india#vedic culture#mantra#bharat#ancient indian history#puranas#sanskrit#languages#krishna#dharma#karma#hindu culture
168 notes
·
View notes
Text
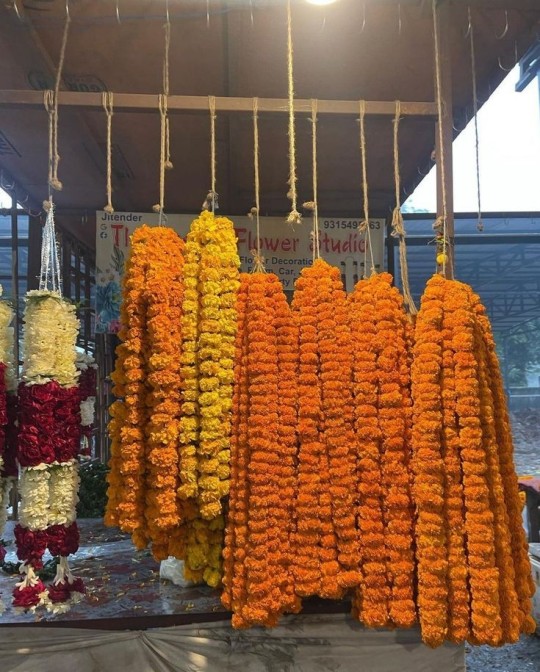



I love hozier's "I slithered here from Eden just to sit outside your door" BUT "banke maala preet ki tere tan pe jhar jhar jaun" I'd become a garland of love and fall on your body and "tu hi toh jannat meri, tu hi mera junoon, tu hi toh mannat meri, tu rooh ka sukoon" you are the heaven for me, you're my passion, you are my prayers, you are my soul's bliss and "tere naam se ji lu, tere naam se mar jaaun" I'd live by your name, I'd die by your name and "hawaoon mein lipta hua main, guzar jaunga tumko chu ke, agar man ho toh rok lena, thahar jaunga inn labon pe" I'm tangled with the breeze, I'll pass away after touching you, if your heart wants it, then I'll stay with you on your lips



Hindi is the language of love and longing
#india#desi dark academia#indian academia#sanskrit#indian aesthetic#indian poets#desi women#indian girl#south asian#scholary academia#desi aesthetic#desiblr#desi tag#desi tumblr#desi academia#bollywood aesthetic
809 notes
·
View notes
Text

Sun, the word for the blinding nuclear fusion reactor in the sky, stems from the same Proto-Indo-European word as French soleil, Swedish sol, Welsh haul, Irish súil, and Ancient Greek hēlios, whence the prefix helio-. They grew apart by the ravages of time. Here's how.
#historical linguistics#linguistics#language#etymology#lingblr#sanskrit#celtic languages#romance languages#germanic languages#ancient greek
322 notes
·
View notes
Text
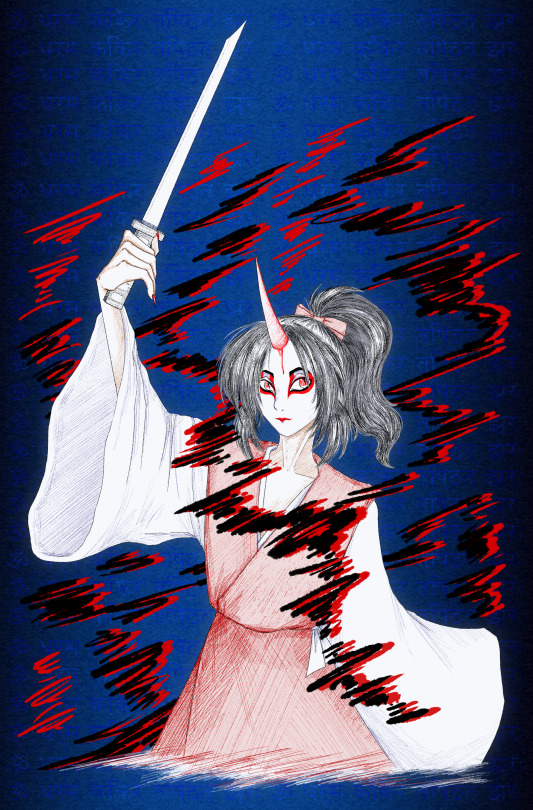

What came of that Konngara sketch I posted earlier.
By the way, if anyone here's good with sanskrit and vajrayana tradition tantras... Help me figure this out.
The text in the back is supposed to be the mantra adressing Konngara-douji/Kiṃkara (オン ダラマ コンガラ チシュタ サラ). The problem is, I can't seem to find it in its original sanskrit anywhere on the internet, and its katakana and latin transliterations aren't even consistent between websites that mention it. The text I've put in (ॐ धर्म किंकर तिष्ठत् झ्रः) is the least worst we've come up with. The last word is almost certainly incorrect. Does anyone know where to find the original mantra?
#own post#own art#art#touhou#touhou project#touhou pc98#highly responsive to prayers#konngara#linguistics#sanskrit#tagging those two so that people help me figure something out#details under the cut
53 notes
·
View notes
Text
A look at the etymology of the "arithmonyms" from the Locked Tomb series by Tamsyn Muir, arranged by difficulty level.
Easy:
-Deuteros = Ancient Greek δεύτερος (deúteros) "second"
-Dve = Pan-Slavic две/dvě "two"
-Tettares = Ancient Greek (Attic) τέττᾰρες (téttares) "four"
-Chatur = Sanskrit चतुर् (catur) "four"
-Pent = Ancient Greek πέντε (pénte) "five"
-Quinque = Latin quīnque "five"
-Sextus = Latin sextus "sixth"
-Hect = Ancient Greek ἕκτος (héktos) "sixth"
-Sex = Latin sex "six"
-Septimus = Latin septimus "seventh"
-Asht = Sanskrit अष्ट (aṣṭa) "eight"
-Oct = Latin octō "eight" or Ancient greek ὀκτώ (oktṓ) "eight"
-Nav = Sanskrit नव (nava) "nine"
Intermediate:
-Dyas = Ancient Greek (late medieval pronunciation) δῠᾰ́ς (duás) "the number two, couple, pair, diad"
-Tern = Latin ternī "three each, three at a time"
-Trinit = Latin trīnitās "the number three, triad, trinity"
-Tetra = Ancient Greek τετρᾰ́ς (tetrás) "the number four, the fourth day", or τετρα- (tetra-), prefixed form of τέττᾰρες (téttares) "four"
-Quinn = Latin quīnī "five each, five at a time", or quīn-, prefixed form of quīnque "five"
-Shodash = Sanskrit षोडश (ṣoḍaśa) "sixteen"
-Ebdoma = Ancient Greek (Koine pronunciation) ἑβδομάς (hebdomás) "a group of seven"
-Nonagesimus = Latin nōnāgēsimus "ninetieth"
-Novenarius = Latin novēnārius "containing or consisting of nine things"
-Novenary = Latin novēnārius (see above)
Advanced:
-Tridentarius = Neo-Latin tridēntārius "like a trident", from Latin tridēns "three teeth"
-Zeta = Sixth letter of the Greek Alphabet (although in Ancient Greek numerals it actually represents the number 7, because the original sixth letter was the now disused digamma)
-Heptane = Neo-Greek-Latin compound heptane, "saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon C7H16" (more literally "pertaining to the number seven, seven-like")
-Nonius = Latin Nōnius, a first name derived from the Nōnia plebeian family, ultimately from nōnus "ninth"
-Nova = Latin novem "nine" and/or nova "new" (it's been suggested that the Proto-Indo-European root *h₁néwn̥ "nine" is derived from the root *néwos "new")
Expert:
-Octakiseron = Ancient Greek ὀκτᾰ́κῐς (oktákis) "eight times" + unclear suffix, could have been constructed by analogy with -τερον (-teron, as in δεύτερον (deúteron) "second") and -μερον (-meron, as in ἑξαήμερον (hexaḗmeron) "six days"); alternatively based on or reinforced by the French diminutive suffix -eron, an extension of the diminutive -on (itself a merger of several Latin and Frankish suffixes), built by analogy with words like quarteron "quadroon" (from quartier "quarter, district" + -on); yet another possibility is Ancient Greek εἴρων (eírōn) "one who says less than they think, dissembler, pretender"
-Noniusvianus = not clear, perhaps a portmenteau of Latin Nōnius (see above) and noviēs "nine times", with an adjectival ending -(i)ānus.
-Nigenad = perhaps based on Proto-West Germanic *nigundō "ninth" (variant of the more common *neundō), or one of its descendants (Dutch negende, Middle English nyghend, West Frisian njoggende…); possibly reinforced by Old English nigonfeald "ninefold"
#the locked tomb#gideon the ninth#harrow the ninth#nona the ninth#arithmonym#etymology#tamsyn muir#linguistics#latin#greek#sanskrit#numbers#germanic#indo european#slavic#worldbuilding
231 notes
·
View notes
Text

Draupadī and the Dharma of Women
"Strī" translates from Sanskrit as "woman", while "dharma" is a complex principle with manifold meanings, in this context bearing the significance of "duty"; in simple terms, it refers to an individual conduct that contributes to harmony in a greater framework, be it societal or cosmological.
Draupadī is lauded in the Critical Edition of the Mbh several times as being the epitome of strī-dharma, of the dharma of women. (2.62.20; 2.63.25-30; 2.64). Interestingly, she is most intensely praised as such after she angrily (yet elegantly!) questions the men of the royal court and demands justice, being anything but meek and demure. I would argue that this showcases that in the Mahābhārata voicing oneself and standing up for oneself are considered responsibilities belonging to the dharma of women.
To nuance this even more, Eknath Easwaran, an eminent translator of the Bhagavadgītā, highlights that, etymologically, the term "dharma" can be traced back to the root 'dhri', which means 'to support, hold up, or bear'; "dharma" therefore translates as "that which supports", and Draupadī's conduct therefore supports both society and cosmology.
In the Sanskrit Mbh, Kṛṣṇa does not appear in the sabhā (royal hall) at the time of Draupadī's attempted disrobing, and no direct mention of him is made during this episode. In a conversation with Dr. Brian Black, a Mbh researcher whom I had the honour to have as my MA supervisor, we talked about the implication of this, which is that Draupadī's adherence to strī-dharma appears to be that which shields her. A question that could arise here could be whether there is a contradiction between the Critical Edition and modern renderings of the Mahābhārata, with Draupadī being shielded by her dharma as opposed to by Kṛṣṇa.
For me there is no contradiction.
Kṛṣṇa in the Bhagavadgītā establishes himself as 'the eternal dharma' (14.27); and so, Kṛṣṇa is all dharmas, including strī-dharma. We tend to associate Kṛṣṇa with a fully-fledged incarnation; but he is beyond that. I would maintain that, as the divine principle, he exists in Draupadī's consciousness and in her actions as dharma (and not only!). The latter renditions, for me, in which he is physically there, only bring forth in tangible projections the internal process extending Draupadī's consciousness.
You can find me on IG: @musingsonthemahabharata.
Painting: Jadurani Dasi, 1986.
#mahabharata#mahabharat#draupadi#krishna#draupadi's disrobing#hindu art#mahabharatam#panchali#hindu mythology#hinduism#hindu#hindu philosophy#itihasa#sanskrit#phd#phd scholar#dharma#stri dharma#bhagavadgita#bhagavad gita#bhakti#vishnu
73 notes
·
View notes
Text



excerpt from an audio-translation I worked on with a colleague of mine; we translated Draupadī's imposing speech as rendered in modern Mahābhārat retellings. Draupadī utters this speech after she is dragged to the royal hall by her hair, and is assaulted & sexually harassed by the men of the Kuru dynasty. she renounces her status as a wife; in the Sanskrit Mbh, symbolically, by refusing to tie her hair again, while in modern renderings, explicitly, by directly renouncing her husbands who passively watched her humiliation.
in this sequence, Draupadī curses the Kurus. the curse bears similarities across the Sanskrit & modern tellings; that just as she bled in the sabhā (royal court / hall), so will all the men bleed on the battlefield, and just as she wept with her hair untied, so will their women cry before their corpses with their hair dishevelled (tied hair was the marking of a wife / bride, untied hair, of a widow).
photo: Pooja Sharma as Draupadī. Pooja is my Draupadī.
#mahabharata#mahabharat#mahabharatam#mahabharata art#pooja sharma#mahabharat star plus#sabha#draupadi's disrobing#draupadi#yajnaseni#hinduism#hindu mythology#itihasa#sanskrit#goddess#shakti#kauravas#kuru dynasty#krishna#sanatana dharma#religion
111 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey, guys! Want to vote on the best 6th-10th Century script (writing system) that I, Gecko, personally like?
Of course you do! Writing systems are SO COOL!
And here's a bit about each of the contenders:
Arabic (Naskh Script)
Derived from the Aramaic Script, which grew out of Phoenician, Arabic has a variety of forms. The Naskh script is the one I find the most beautiful, with it's extreme variation on character length and height. I also love the use of multiples colours for Ḥarakāt (vowel marks and other diacritics). Add in the elegant curves and solid lines, and Naskh Script becomes one of the most stylish scripts around.

Latin (Insular Script)
Derived from Greek, the Latin alphabet is usually a competent and pleasant mix of lines and curves, uprights and descenders. Insular script plays with these qualities, and the result is electric! many of the uprights (t, d, f) are gone. New descenders are added (r, s, f). Horizontal lines take a new prominence. Line weight is increased, and the curves become more angular. Something old to us becomes new again.

Chinese (Semi-Cursive Script)
There are many ways to write Hanzi (Chinese characters), and Semi-Cursive Script manages to combine the best qualities of most of them! The expressive curves and flow of a cursive script. The solid shapes and readability of Regular Script. One of the joys of Hanzi is the visual interest of so many unique characters; which share components, but use them differently. Semi-Cursive keeps much of that interest, while also providing a dynamic energy and movement.

Sogdian (Cursive Script)
Derived from the Syriac script, which grew out of the Aramaic Script, the Sogdian Alphabet was developed by traders who met most of the major cultures of the Old World, and let all of those cultures affect their language and writing. Sogdian can be written write to left, like most Aramaic scripts, but also top to bottom, like the Chinese Scripts of their main trade partner. Curvy cursive lines, and characters of wildly varying length, give this script a interesting sense of flow.
Hebrew (Ktav Ashuri Script with Palestinian Vocalization)
Another offshoot of the (Imperial) Aramaic Script, the Hebrew Alphabet has a really interesting, heavy, square, solid feel. In contrast, Palestinian Voicing (an extinct form of writing vowels where all of them were above the consonants) is really light, stacked on top their vowels in little floaty towers. It's a cool combination!

Maya (Classical Maya Script)
The most famous script of the Americas, Maya has one of the most unique reading orders of any script. Characters are written in blocks, which are then read in a zigzag (right, and then down-left) pattern. Full of heads (both animal and human), torches, seeds, and other half-identifiable shapes, Maya texts are works of art, and the more you study them, the more beautiful they become.
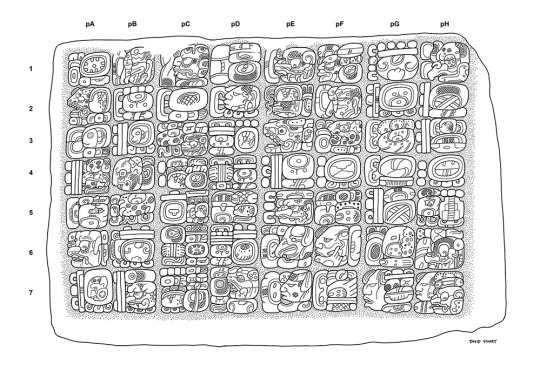
Nubian (Old Nubian Script)
Derived from Greek with additional letters from Coptic (Egyptian) and Meroitic (a previous Nubian culture). Lines above letters are used to skip parts of words deemed unnecessary. The mixture of rectangles and triangles, heavy and light line weights - it reminds me of telegrams, or early typewriter text. I love it!

Khmer (Angkorian Khmer Script)
Derived from the Pallava Script, which derived from the Brahmi Script, Khmer is probably my favourite script to write. The curves feel so good! The spirals so pleasing! You write consonant clusters by writing little letters below the main one! A joy to create, and a joy to look at.

Japanese (Cursive Script)
See these wiggles? They're Chinese characters. Elegant, looking like poetry no matter what they're saying, Cursive Japanese is art. It's also ridiculous. 3 different characters, each with multiple strokes, indicated by wiggling the brush as you draw a line! Most cursive scripts are like this, but the contrast between the square solidness of Regular Script and the flow of Cursive is one of the more extreme. What a delight!

Sanskrit (Siddham Script)
I had SO MANY options for Sanskrit (Brahmi) Scripts, you guys. SO MANY! But in north-west India, during the period I study, this version of Siddham is the prettiest. Look at the curves! Those aren't just decorative, each curvy line that goes above or below the text is a vowel. Consonant clusters are shown by combining the characters together in one spot. The lines at the top haven't yet started connecting, like they do in modern Devanagari, but there's already a sense of it's existence. Such a cool script!

#long post#gecko's polls#calligraphy#scripts#writing systems#arabic#hebrew#khmer#maya#latin#nubian#sanskrit#sogdian#chinese#japanese
227 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ramayan in one picture 🚩

#ramayan#hindublr#hinduism#jai shree ram#sita ram#hanuman ji#ayodhya#ravana#sanskrit#vedic literature#valmiki ramayan
73 notes
·
View notes
Text
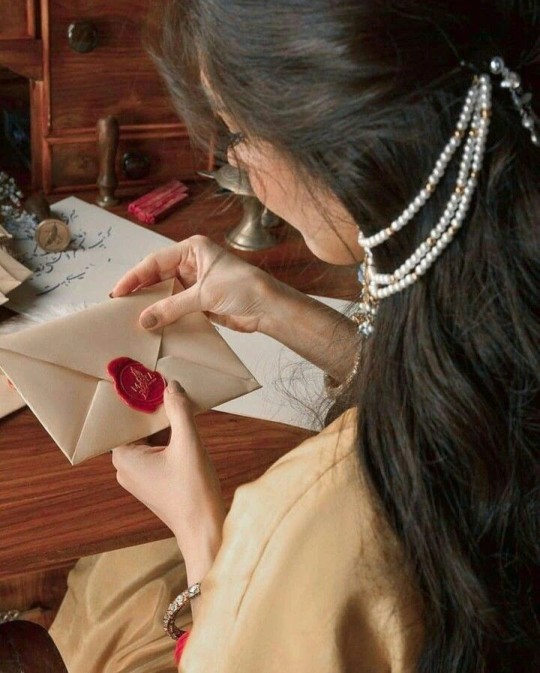



I love Taylor's "Can I go where you go? Can we always be this close?" BUT these are ✨ DIVINE✨"hothon se chu lo tum, mera geet amar kar do, ban jao preet meri, meri jeet amar kar do" touch my soul (me) with your lips, make my song immortal, become my love, make my victory immortal and "bin puche mera naam aur pata, rasmon ko rakh ke pare, char kadam bas char kadam, chaldo na saath mere" without asking me my name or my address, keeping the customs and traditions away, four steps, just four steps, walk with me please and "janam janam janam saath chalna yuhi, kasam tumhe kasam aake milna yahin, ek jaan hai bhale do badan ho juda, meri hoke hamesha hi rehna, kabhi na kehna alvida" lives, all my lives, walk with me like this, give me your promise to come and meet me like this, there's one soul among us even if our bodies are apart, stay mine forever, don't ever say goodbye and "barkha, bijli, baadal jhoothe, jhoothi phoolon ki saugatein, sacchi tu hai, sachha main huin, sacchi apne dil ki baatein" the rain, the thunder, the clouds are all liars, there are lies in the gifts of all the flowers, only you are true, and so are the conversations of our hearts
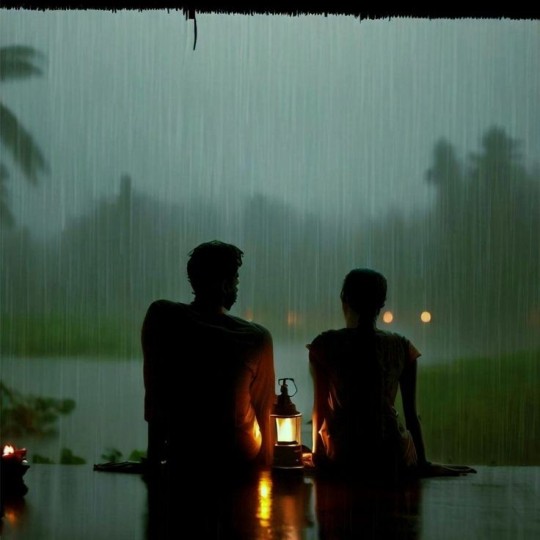
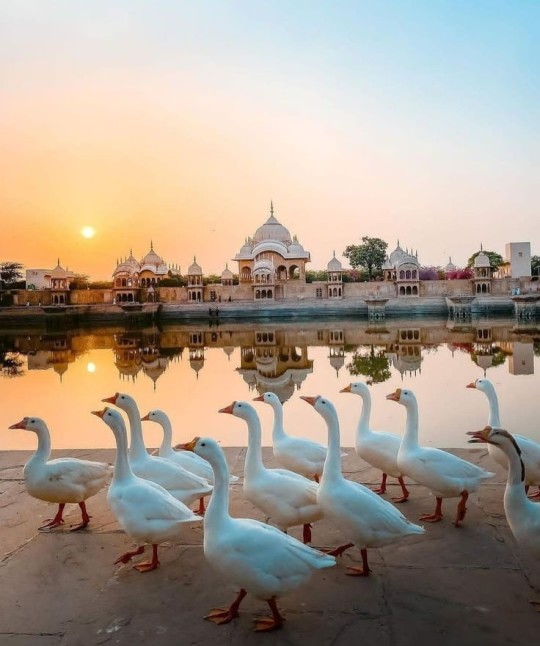
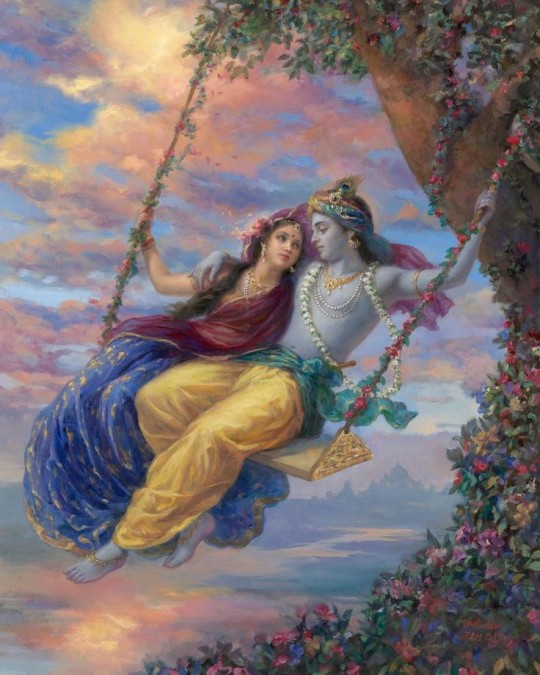



Hindi is the language of love and promise (2)
#india#desi dark academia#indian academia#sanskrit#indian aesthetic#indian poets#desi women#indian girl#south asian#scholary academia#desi music#desi academia#desi aesthetic#love language#Hindi#hindi academia#हिन्दी#Hindi is the language of love
159 notes
·
View notes
Text
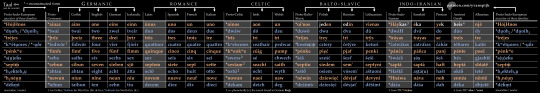
English is part of a large language family that includes French, Welsh, Polish, Persian, Greek, and Albanian. They stem from a common ancestor reconstructed as Proto-Indo-European. The cardinal numerals from 1 to 10 illustrate their relationship well. Click the image for a selection.
#historical linguistics#linguistics#language#etymology#english#latin#french#german#spanish#welsh#irish#sanskrit#persian#polish#russian#italian#gothic#proto-germanic#proto-celtic#proto-indo-iranian#proto-balto-slavic#lithuanian#ancient greek#albanian#icelandic
85 notes
·
View notes