#renaissance fantasy
Text
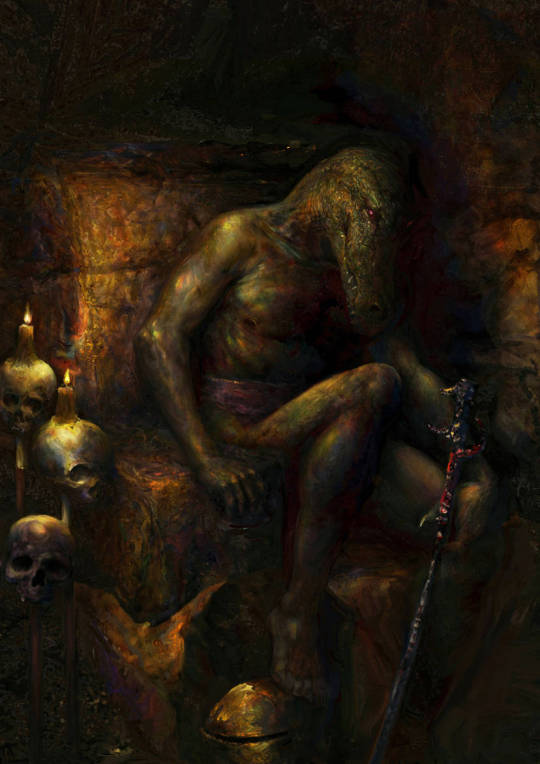
Morrowind: A portrait of Menta Na, the daedroth, with a daedric staff. Kora-Dur, Northern Vvardenfell. Year: unknown.
—I've mentioned the sudden departure of Trebonius Artorius left me with a dearth of paying clients. And since the new Archmage didn't prove to be a connoisseur of Arts—for a time I had little choice but to consider some uncanny commissions, whose source one'd do well not to mention around Temple district, lest one plans to take lodgings at Baar Dau.
#daedroth#morrowind#the elder scrolls#tes#daedra#vvardenfell#baroque#renaissance fantasy#tamriel#elder scrolls#digital painting#digital art#tesblr#morrowind mods#crpg#daedricshrine#dark fantasy#crocodilian#morrowind art#tes lore#tes art#gaming#game character#digital portrait#horror art#morrowind fanart#vivec city
100 notes
·
View notes
Note
Please tell me more about neighbourhood PMCs in renaissance Italy
It would be my pleasure! (My research into this owes a lot to the excellent Power and Imagination: City-States in Renaissance Italy by Lauro Martines.)

The first thing to note that, unlike the condottieri, these were not private military companies. Rather, the neighborhood military companies (in the sense of a military unit, rather than a profit-making entity) were self-defense organizations formed as part of a centuries-long political struggle for control over the urban commune between the signorile (the urban chivalry)/nobilita (the urban nobility) and the populo (the guilded middle class, who claimed to speak on behalf of "the people").
This conflict followed much the same logic that had given rise to the medieval commune in the first place. Legally, the communes had started as mutual defense pacts between the signorile and the cives (the free citizens of the city) against the rural feudal nobility, which had given these groups the military and political muscle to push out the marquises and viscounts and barons and claim exclusive authority over the tax system, the judicial system, and the military.
So it made sense that, once they had vanquished their enemies and established the commune as the sovereign, both sides would use the same tactic in their struggle over which of them would rule the commune that ruled the city. The signorile and nobilita formed themselves into consorteria or "tower societies," by which ancient families allied with one another (complete with dynastic marriage alliances!) to build and garrison the towers with the knights, squires, men-at-arms, and bravi of their households. These phallic castle substitutes were incredibly formidable within the context of urban warfare, as relatively small numbers of men with crossbows could rain down hell on besiegers from the upper windows and bridges between towers, even as the poor bastards on the ground tried to force the heavy doors down below.
To combat noble domination of communal government, achieve direct representation on the political councils, establish equity of taxation and regulate interest rates, and enforce legal equality between nobility and citizenry, the populo formed themselves into guilds to build alliances between merchants and artisans in the same industries. However, these amateur soldiers struggled to fight on even footing with fully-trained and well-equipped professional soldiers, and the guild militias were frequently defeated.
To solve their military dilemma, the populo engaged in political coalition-building with the oldest units of the urban commune: the neighborhoods. When the cities of medieval Italy were originally founded, they had been rather decentralized transplantations of the rural villages, where before people had any conception of a city-wide collective their primary allegiance was to their neighborhood. As can still be seen in the Palio di Siena to this day, these contrade built a strong identity based on local street gangs, the parish church, their traditional heraldry, and their traditional rivalries with the stronzi in the next contrade over. And whether they were maggiori, minori, or unguilded laborers, everyone in the city was a member of their contrade.

As Martines describes, the populo both recruited from (and borrowed the traditions of) the contrade to form their armed neighborhood companies into a force that would have the manpower, the discipline, and the morale to take on the consorteria:
"Every company had its distinctive banner and every house in the city was administratively under the sign of a company. A dragon, a whip, a serpent, a bull, a bounding horse, a lion, a ladder: these, in different colors and on contrasting fields, were some of the leitmotifs of the twenty different banners. They were emblazoned on individual shields and helmets. Rigorous regulations required guildsmen to keep their arms near at hand, above all in troubled times. The call to arms for the twenty companies was the ringing of a special bell, posted near the main public square. A standard-bearer, flanked by four lieutenants, was in command of each company."
To knit these companies organized by neighborhood into a single cohesive force, the lawyers' guilds within the populo created a state within a state, complete with written constitutions, guild charters, legal codes, legislative and executive councils. Under these constitutions, the populo's councils would elect a capitano del popolo, a professional soldier from outside the city who would serve as a politically-neutral commander, with a direct chain of command over the gonfaloniere and lieutenants of the neighborhood companies, to lead the populo against their noble would-be overlords.
And in commune after commune, the neighborhood companies made war against the consorteria, taking the towers one by one and turning them into fortresses of the populo. The victorious guilds turned their newly-won military might into political hegemony over the commune, stripping the nobilita of their power and privilege and forcing them either into submission or exile. Then they directed their veteran neighborhood companies outward to seize control of the rural hinterland from the feudal aristocracy, until the city had become city-state.
(Ironically, in the process, the populo gave birth to the condottieri, as the nobility who had lost their landed wealth and political power took their one remaining asset - their military training and equipment - and became professional mercenaries. But that's a story for another time...)
#history#historical analysis#renaissance history#renaissance fantasy#medieval cities#city-states#urban communes#guilds#city charters#guild charters#mercenaries#nobility#artisans#burgher rights#merchants
134 notes
·
View notes
Text

she washes the clothes
#my art#forest critter things#redwall#humblewood#medieval fantasy#renaissance fantasy#weasel#sable#furry art#furry#anthro
87 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hello chums. I could use some references, inspiration, works, etc. that have a clockpunk aesthetic, or are set in fantasy worlds inspired by Renaissance-era Italy. It is very much My Thing, and I miss looking at robots with floppy hats.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sherwood Forest Faire 2024 Review
This is my first-ever Renaissance faire ! I attended the Sherwood Forest faire last weekend and had a ton of fun. This is my review, of the event. Hope you enjoy.
youtube
#gaming goddess#ren faire#renaissance faire#renaissance festival#renaissance fantasy#renaissance#mideval#historical#reinactment#review#youtube#youtube video#cosplay#costume#historical fashion#Youtube
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

What’s interesting about this to me is this is right when Renaissance festivals became a thing
I’m not sure if these were photos at Ren fests, magazine shots (bottom left just looks uniquely professional) or if this was an alt daily wear thing but I’d love to know
#Twitter#repost#renaissance festival#renaissance fantasy#60s-70s#I’ve been in the renfest scene for over half my life but I know nearly nothing about it’s own history#it’s kinda overshadowed by actual history and inaccuracies
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
will say though bing's new ai art doesn't get the difference between an arquebus and a musket...tried a few prompts and always got guns that seemed far too 'modern'
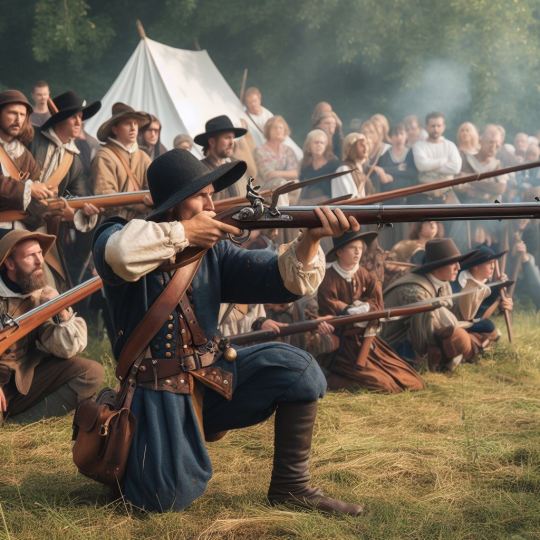
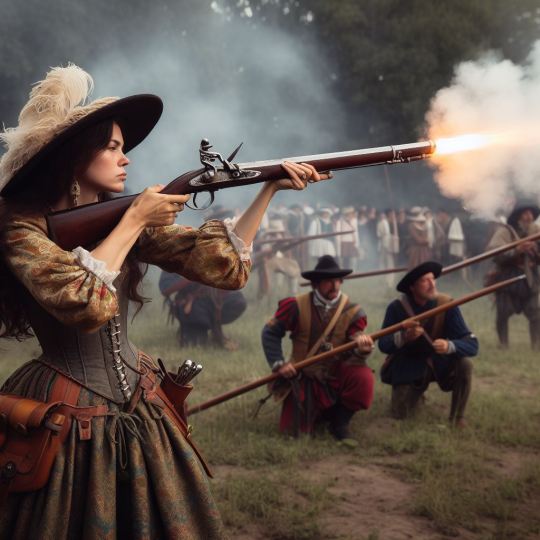




4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dundar Guild Adventure Rank Systems Explained
Rank 0: usually just staff of the guild or trainees. They do basic things such as help train people and deliver letters and packages and do shop keeping.
Rank 1: brand new, fully fledged adventurers. They're often given the safest missions. Their missions consist mostly of basic investigation, acquiring minor magic items and relics, and hunting more minor monsters.
Rank 2: This is where adventuring gets more serious. They are given increasingly more dangerous missions. Many adventurers are severely injured during expeditions and must retire at this point. Some even die before making it to higher ranks. This is the point in an adventurer's life that they'd start doing more dangerous jobs such as slaying weaker dragons and raiding hordes of more dangerous monsters.
Rank 3: Represents very seasoned adventurers. If they survive up to this point, they gain massive amounts of respect and plenty of fame. Their missions are often brutal and deadly. Most rank 3 adventurers die before making it to rank 4. Those that do survive are extremely traumatized and some decide to (or are forced to) retire due to mental health reasons. One of the leading causes of death for rank 3 adventurers is actually suicide whereas the other ranks die in combat more often.
Rank 4: Those adventurers strong enough mentally and physically to survive rank 3. They are given the most dangerous missions, often fighting alongside the very few Rank 5 adventurers. These are the people you really want to send in to save entire regions from devastating events. They do not come cheap at all, either. About 98% of Rank 4 adventurers are killed in combat before making it to the next rank. Many of those who don't die decide to retire for various reasons, such as deciding that they've amassed enough riches for themselves, completion of spiritual journeys, or mental health reasons.
Finally, Rank 5: An extremely small number of Rank 4 adventurers decide to rank up to this rank before retiring. Even the guild's current headmaster is only Rank 3. These adventurers are capable of stopping world-ending threats. There are only three known Rank 5 parties, each with 4-6 members at a time. Many Rank 5 adventurers barely go on missions due to either not feeling challenged enough anymore, or their prices being extremely high for the missions they do go on. Many also either retire entirely or decide to train new adventurers instead. Many Rank 5 adventurers barely go on missions due to either not feeling challenged enough anymore, or their prices being extremely high for the missions they do go on. Some R5 adventurers are immortalized in the writings of bards (not necessarily a magic class in this setting, some are literally just adventuring poets and writers), while others are completely forgotten by time with the exception of the Dundar Guild's massive archives.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Weiner dog wearing armor at the Michigan Renaissance Festival (2002)
#weiner dog#dog#dogs#animals#animal#cute animals#cute#renaissance#armor#aesthetic#2002#photography#cutecore#cute doggo#fairycore#princesscore#softcore#fantasy#cottagecore#puppy#miniature dachshund
24K notes
·
View notes
Text

2002 Michigan Renaissance Festival
Wiener Dog in Armor
19K notes
·
View notes
Text

After we were yelled at for being on the stage 🖤 Lady Fernese from Berserk vibes
0 notes
Text

The way Delyna's grandfather Llerar Mandas tells it, you'd think the dastardly Lord-Wizard snatched the maiden from her ancestral manor, polymorphed as cloud of netches or something. Please—the girl was caught in leather catsuit, sneaking into Divayth's tower, geared up as burglar would: lockpicks, two glass swords and a magical ring of Chameleon—mademoiselle's frivolous attempt at "slumming", no doubt. Lenient as Lord Fyr is towards petty thieves—Delyna was merely put under arrest in the tower. She spend several weeks, enjoying hospitality of Fyrs before she was released unto a representative of House Redoran. That during these weeks her addled father, Arethan rampaged through the Ashlands alongside his gang of vagabonds—supposedly as means to cope with kidnapping of his daughter—can scarcely be blamed on House Telvanni, can it not? Truly, Delyna would have been released much sooner, if not for the real fear of her accidentally perishing en-route—Tel Fyr is fairly isolated place and the surrounding waters can be dangerous.
#morrowind#tes#art#artists on tumblr#tamriel#vvardenfell#dunmer#tesblr#house redoran#house telvanni#divayth fyr#tel fyr#nix hound#netch#elder scrolls#digital painting#baroque#renaissance fantasy#digital art#morrowind mods#the elder scrolls#morrowind art#morrowind lore#illustration#digital artist#made with krita#krita#crpg#video games#dark elf
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
A Guildsman Goes Forth to War: World-Building, Part I
(Following up from this post...)

The High Concept:
At the dawning of the 9th Century Anno Domini, a great transformation swept Europe: creatures of foklore and mythology emerged from their hidden homes in the deep forests and "Underhill" and the mountain fastnesses to once more treat with humanity. Initially, this event was believed to be prelude to an inhuman invasion or perhaps the prophecied End of Days.
Unexpectedly, it turned out that these Fair Folk were primarily interested in dynastic marriage alliances with human families. This was rejected out of hand by the Church as a threat to one's very salvation, until the leaders of the Fair Folk cheerfully agreed to baptism by their scions (since there was precedent from folklore about semi-human children being baptized) and that any children resulting from these marriages would be raised within Mother Church.
Similarly, the royalty, nobility, chivalry, and even the burghers initially moved to ban intermarriage, until the Fair Folk made it clear quite how much gold they were willing to offer as dowries and dowers. Within a few years of the first unions between humans and Fae, it became evident that these marriages were uncannily fertile (with a particular tendency to produce twins) and seemed blessed with unnatural luck when it came to infant mortality. Moreover, as the first few generations attested, the children of these marriages tended to acquire (and pass down to their own children) some portion of the beauty, long lifespans, and magical gifts of their Faerie ancestors.
As Europe approaches the dawn of the 16th century, these marriages (which have recurred every few generations according to a deeply capricious schedule by the Fair Folk) have been happening "since time out of mind," and as many as one in ten can credibly claim to be one of the so-called "Gentry."

47 notes
·
View notes
Text
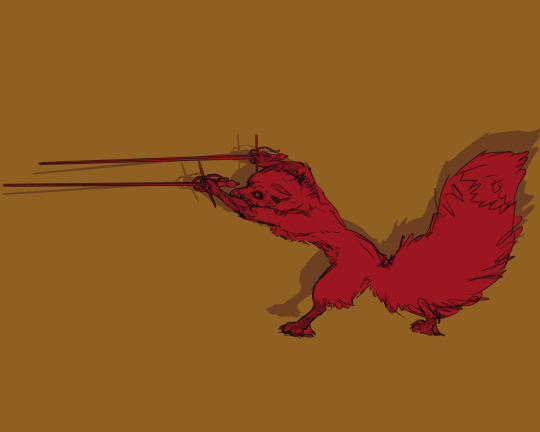

*duels you with case of rapiers* teehee :3c
(Edit: Forgot his sock markings!)
#my art#redwall#humblewood#forest critter things#medieval fantasy#renaissance fantasy#rapier#swords#digital sketch#furry art#furry#anthro
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
Synthasy Discord Hiccup
Hey, just figured out the link for the Synthasy Discord server expired. I didn't even realize it could expire lol. Should be set up with a permanent link now!
#indie ttrpg#ttrpg#ttrpg community#indie#crowdfunding#tabletop#roleplaying#game#tabletop rpg#trpg#medieval fantasy#fantasy#medieval#ttrpgs#ttrpg design#ttrpg stuff#renaissance#renaissance fantasy
0 notes
Text
Fantasy Guide to Interiors
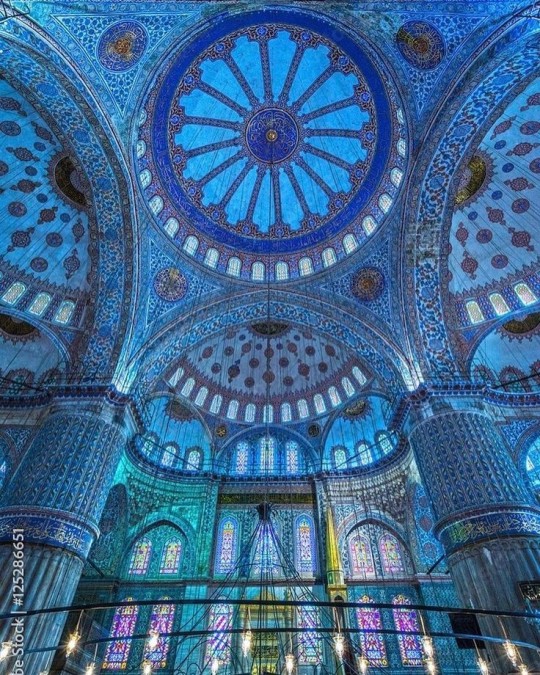
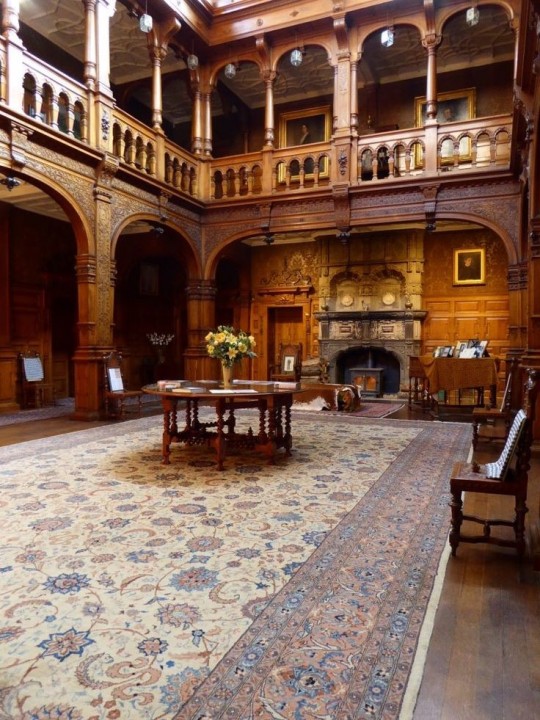
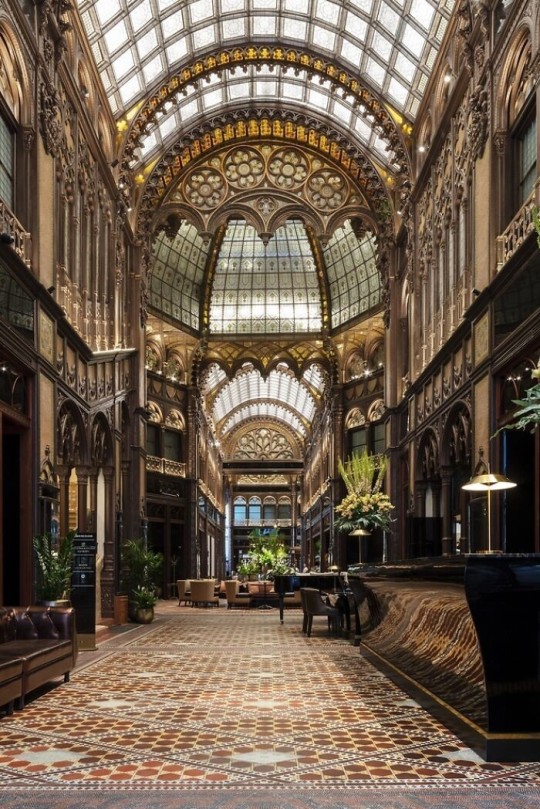





As a followup to the very popular post on architecture, I decided to add onto it by exploring the interior of each movement and the different design techniques and tastes of each era. This post at be helpful for historical fiction, fantasy or just a long read when you're bored.
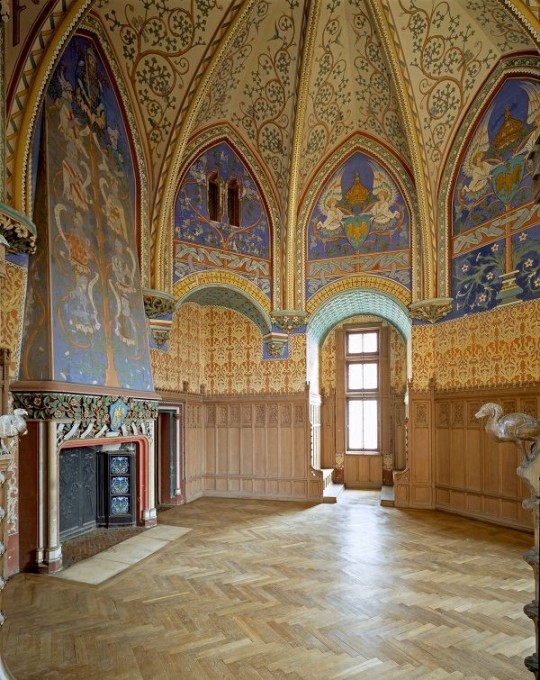
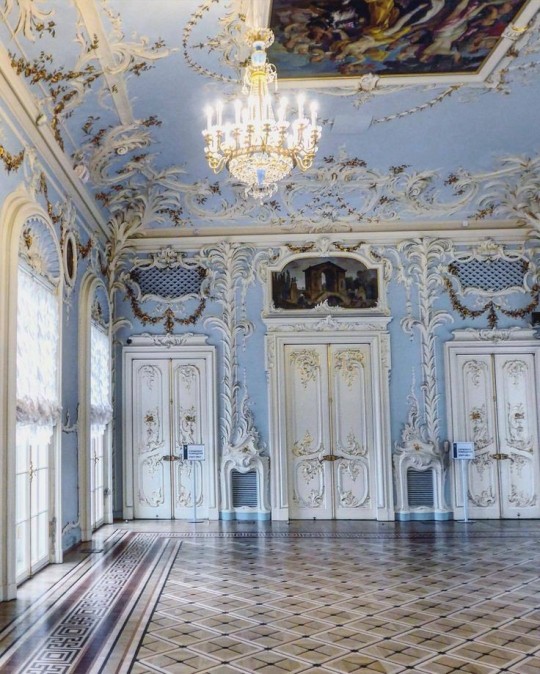



Interior Design Terms
Reeding and fluting: Fluting is a technique that consists a continuous pattern of concave grooves in a flat surface across a surface. Reeding is it's opposite.
Embossing: stamping, carving or moulding a symbol to make it stand out on a surface.
Paneling: Panels of carved wood or fabric a fixed to a wall in a continuous pattern.
Gilding: the use of gold to highlight features.
Glazed Tile: Ceramic or porcelain tiles coated with liquid coloured glass or enamel.
Column: A column is a pillar of stone or wood built to support a ceiling. We will see more of columns later on.
Bay Window: The Bay Window is a window projecting outward from a building.
Frescos: A design element of painting images upon wet plaster.
Mosaic: Mosaics are a design element that involves using pieces of coloured glass and fitted them together upon the floor or wall to form images.
Mouldings: ornate strips of carved wood along the top of a wall.
Wainscoting: paneling along the lower portion of a wall.
Chinoiserie: A European take on East Asian art. Usually seen in wallpaper.
Clerestory: A series of eye-level windows.
Sconces: A light fixture supported on a wall.
Niche: A sunken area within a wall.
Monochromatic: Focusing on a single colour within a scheme.
Ceiling rose: A moulding fashioned on the ceiling in the shape of a rose usually supporting a light fixture.
Baluster: the vertical bars of a railing.
Façade: front portion of a building
Lintel: Top of a door or window.
Portico: a covered structure over a door supported by columns
Eaves: the part of the roof overhanging from the building
Skirting: border around lower length of a wall
Ancient Greece
Houses were made of either sun-dried clay bricks or stone which were painted when they dried. Ground floors were decorated with coloured stones and tiles called Mosaics. Upper level floors were made from wood. Homes were furnished with tapestries and furniture, and in grand homes statues and grand altars would be found. Furniture was very skillfully crafted in Ancient Greece, much attention was paid to the carving and decoration of such things. Of course, Ancient Greece is ancient so I won't be going through all the movements but I will talk a little about columns.
Doric: Doric is the oldest of the orders and some argue it is the simplest. The columns of this style are set close together, without bases and carved with concave curves called flutes. The capitals (the top of the column) are plain often built with a curve at the base called an echinus and are topped by a square at the apex called an abacus. The entablature is marked by frieze of vertical channels/triglyphs. In between the channels would be detail of carved marble. The Parthenon in Athens is your best example of Doric architecture.
Ionic: The Ionic style was used for smaller buildings and the interiors. The columns had twin volutes, scroll-like designs on its capital. Between these scrolls, there was a carved curve known as an egg and in this style the entablature is much narrower and the frieze is thick with carvings. The example of Ionic Architecture is the Temple to Athena Nike at the Athens Acropolis.
Corinthian: The Corinthian style has some similarities with the Ionic order, the bases, entablature and columns almost the same but the capital is more ornate its base, column, and entablature, but its capital is far more ornate, commonly carved with depictions of acanthus leaves. The style was more slender than the others on this list, used less for bearing weight but more for decoration. Corinthian style can be found along the top levels of the Colosseum in Rome.
Tuscan: The Tuscan order shares much with the Doric order, but the columns are un-fluted and smooth. The entablature is far simpler, formed without triglyphs or guttae. The columns are capped with round capitals.
Composite: This style is mixed. It features the volutes of the Ionic order and the capitals of the Corinthian order. The volutes are larger in these columns and often more ornate. The column's capital is rather plain. for the capital, with no consistent differences to that above or below the capital.
Ancient Rome
Rome is well known for its outward architectural styles. However the Romans did know how to add that rizz to the interior. Ceilings were either vaulted or made from exploded beams that could be painted. The Romans were big into design. Moasics were a common interior sight, the use of little pieces of coloured glass or stone to create a larger image. Frescoes were used to add colour to the home, depicting mythical figures and beasts and also different textures such as stonework or brick. The Romans loved their furniture. Dining tables were low and the Romans ate on couches. Weaving was a popular pastime so there would be tapestries and wall hangings in the house. Rich households could even afford to import fine rugs from across the Empire. Glass was also a feature in Roman interior but windows were usually not paned as large panes were hard to make. Doors were usually treated with panels that were carved or in lain with bronze.
Ancient Egypt
Egypt was one of the first great civilisations, known for its immense and grand structures. Wealthy Egyptians had grand homes. The walls were painted or plastered usually with bright colours and hues. The Egyptians are cool because they mapped out their buildings in such a way to adhere to astrological movements meaning on special days if the calendar the temple or monuments were in the right place always. The columns of Egyptian where thicker, more bulbous and often had capitals shaped like bundles of papyrus reeds. Woven mats and tapestries were popular decor. Motifs from the river such as palms, papyrus and reeds were popular symbols used.
Ancient Africa
African Architecture is a very mixed bag and more structurally different and impressive than Hollywood would have you believe. Far beyond the common depictions of primitive buildings, the African nations were among the giants of their time in architecture, no style quite the same as the last but just as breathtaking.
Rwandan Architecture: The Rwandans commonly built of hardened clay with thatched roofs of dried grass or reeds. Mats of woven reeds carpeted the floors of royal abodes. These residences folded about a large public area known as a karubanda and were often so large that they became almost like a maze, connecting different chambers/huts of all kinds of uses be they residential or for other purposes.
Ashanti Architecture: The Ashanti style can be found in present day Ghana. The style incorporates walls of plaster formed of mud and designed with bright paint and buildings with a courtyard at the heart, not unlike another examples on this post. The Ashanti also formed their buildings of the favourite method of wattle and daub.
Nubian Architecture: Nubia, in modern day Ethiopia, was home to the Nubians who were one of the world's most impressive architects at the beginning of the architecture world and probably would be more talked about if it weren't for the Egyptians building monuments only up the road. The Nubians were famous for building the speos, tall tower-like spires carved of stone. The Nubians used a variety of materials and skills to build, for example wattle and daub and mudbrick. The Kingdom of Kush, the people who took over the Nubian Empire was a fan of Egyptian works even if they didn't like them very much. The Kushites began building pyramid-like structures such at the sight of Gebel Barkal
Japanese Interiors
Japenese interior design rests upon 7 principles. Kanso (簡素)- Simplicity, Fukinsei (不均整)- Asymmetry, Shizen (自然)- Natural, Shibumi (渋味) – Simple beauty, Yugen (幽玄)- subtle grace, Datsuzoku (脱俗) – freedom from habitual behaviour, Seijaku (静寂)- tranquillity.
Common features of Japanese Interior Design:
Shoji walls: these are the screens you think of when you think of the traditional Japanese homes. They are made of wooden frames, rice paper and used to partition
Tatami: Tatami mats are used within Japanese households to blanket the floors. They were made of rice straw and rush straw, laid down to cushion the floor.
Genkan: The Genkan was a sunken space between the front door and the rest of the house. This area is meant to separate the home from the outside and is where shoes are discarded before entering.
Japanese furniture: often lowest, close to the ground. These include tables and chairs but often tanked are replaced by zabuton, large cushions. Furniture is usually carved of wood in a minimalist design.
Nature: As both the Shinto and Buddhist beliefs are great influences upon architecture, there is a strong presence of nature with the architecture. Wood is used for this reason and natural light is prevalent with in the home. The orientation is meant to reflect the best view of the world.
Islamic World Interior
The Islamic world has one of the most beautiful and impressive interior design styles across the world. Colour and detail are absolute staples in the movement. Windows are usually not paned with glass but covered in ornate lattices known as jali. The jali give ventilation, light and privacy to the home. Islamic Interiors are ornate and colourful, using coloured ceramic tiles. The upper parts of walls and ceilings are usually flat decorated with arabesques (foliate ornamentation), while the lower wall areas were usually tiled. Features such as honeycombed ceilings, horseshoe arches, stalactite-fringed arches and stalactite vaults (Muqarnas) are prevalent among many famous Islamic buildings such as the Alhambra and the Blue Mosque.
Byzantine (330/395–1453 A. D)
The Byzantine Empire or Eastern Roman Empire was where eat met west, leading to a melting pot of different interior designs based on early Christian styles and Persian influences. Mosaics are probably what you think of when you think of the Byzantine Empire. Ivory was also a popular feature in the Interiors, with carved ivory or the use of it in inlay. The use of gold as a decorative feature usually by way of repoussé (decorating metals by hammering in the design from the backside of the metal). Fabrics from Persia, heavily embroidered and intricately woven along with silks from afar a field as China, would also be used to upholster furniture or be used as wall hangings. The Byzantines favoured natural light, usually from the use of copolas.
Indian Interiors
India is of course, the font of all intricate designs. India's history is sectioned into many eras but we will focus on a few to give you an idea of prevalent techniques and tastes.
The Gupta Empire (320 – 650 CE): The Gupta era was a time of stone carving. As impressive as the outside of these buildings are, the Interiors are just as amazing. Gupta era buildings featured many details such as ogee (circular or horseshoe arch), gavaksha/chandrashala (the motif centred these arches), ashlar masonry (built of squared stone blocks) with ceilings of plain, flat slabs of stone.
Delhi Sultanate (1206–1526): Another period of beautifully carved stone. The Delhi sultanate had influence from the Islamic world, with heavy uses of mosaics, brackets, intricate mouldings, columns and and hypostyle halls.
Mughal Empire (1526–1857): Stonework was also important on the Mughal Empire. Intricately carved stonework was seen in the pillars, low relief panels depicting nature images and jalis (marble screens). Stonework was also decorated in a stye known as pietra dura/parchin kari with inscriptions and geometric designs using colored stones to create images. Tilework was also popular during this period. Moasic tiles were cut and fitted together to create larger patters while cuerda seca tiles were coloured tiles outlined with black.
Chinese Interiors
Common features of Chinese Interiors
Use of Colours: Colour in Chinese Interior is usually vibrant and bold. Red and Black are are traditional colours, meant to bring luck, happiness, power, knowledge and stability to the household.
Latticework: Lattices are a staple in Chinese interiors most often seen on shutters, screens, doors of cabinets snf even traditional beds.
Lacquer: Multiple coats of lacquer are applied to furniture or cabinets (now walls) and then carved. The skill is called Diaoqi (雕漆).
Decorative Screens: Screens are used to partition off part of a room. They are usually of carved wood, pained with very intricate murals.
Shrines: Spaces were reserved on the home to honour ancestors, usually consisting of an altar where offerings could be made.
Of course, Chinese Interiors are not all the same through the different eras. While some details and techniques were interchangeable through different dynasties, usually a dynasty had a notable style or deviation. These aren't all the dynasties of course but a few interesting examples.
Song Dynasty (960–1279): The Song Dynasty is known for its stonework. Sculpture was an important part of Song Dynasty interior. It was in this period than brick and stone work became the most used material. The Song Dynasty was also known for its very intricate attention to detail, paintings, and used tiles.
Ming Dynasty(1368–1644): Ceilings were adorned with cloisons usually featuring yellow reed work. The floors would be of flagstones usually of deep tones, mostly black. The Ming Dynasty favoured richly coloured silk hangings, tapestries and furnishings. Furniture was usually carved of darker woods, arrayed in a certain way to bring peace to the dwelling.
Han Dynasty (206 BC-220 AD): Interior walls were plastered and painted to show important figures and scenes. Lacquer, though it was discovered earlier, came into greater prominence with better skill in this era.
Tang Dynasty (618–907) : The colour palette is restrained, reserved. But the Tang dynasty is not without it's beauty. Earthenware reached it's peak in this era, many homes would display fine examples as well. The Tang dynasty is famous for its upturned eaves, the ceilings supported by timber columns mounted with metal or stone bases. Glazed tiles were popular in this era, either a fixed to the roof or decorating a screen wall.
Romanesque (6th -11th century/12th)
Romanesque Architecture is a span between the end of Roman Empire to the Gothic style. Taking inspiration from the Roman and Byzantine Empires, the Romanesque period incorporates many of the styles. The most common details are carved floral and foliage symbols with the stonework of the Romanesque buildings. Cable mouldings or twisted rope-like carvings would have framed doorways. As per the name, Romansque Interiors relied heavily on its love and admiration for Rome. The Romanesque style uses geometric shapes as statements using curves, circles snf arches. The colours would be clean and warm, focusing on minimal ornamentation.
Gothic Architecture (12th Century - 16th Century)
The Gothic style is what you think of when you think of old European cathedrals and probably one of the beautiful of the styles on this list and one of most recognisable. The Gothic style is a dramatic, opposing sight and one of the easiest to describe. Decoration in this era became more ornate, stonework began to sport carving and modelling in a way it did not before. The ceilings moved away from barreled vaults to quadripartite and sexpartite vaulting. Columns slimmed as other supportive structures were invented. Intricate stained glass windows began their popularity here. In Gothic structures, everything is very symmetrical and even.
Mediaeval (500 AD to 1500)
Interiors of mediaeval homes are not quite as drab as Hollywood likes to make out. Building materials may be hidden by plaster in rich homes, sometimes even painted. Floors were either dirt strewn with rushes or flagstones in larger homes. Stonework was popular, especially around fireplaces. Grand homes would be decorated with intricate woodwork, carved heraldic beasts and wall hangings of fine fabrics.
Renaissance (late 1300s-1600s)
The Renaissance was a period of great artistry and splendor. The revival of old styles injected symmetry and colour into the homes. Frescoes were back. Painted mouldings adorned the ceilings and walls. Furniture became more ornate, fixed with luxurious upholstery and fine carvings. Caryatids (pillars in the shape of women), grotesques, Roman and Greek images were used to spruce up the place. Floors began to become more intricate, with coloured stone and marble. Modelled stucco, sgraffiti arabesques (made by cutting lines through a layer of plaster or stucco to reveal an underlayer), and fine wall painting were used in brilliant combinations in the early part of the 16th century.
Tudor Interior (1485-1603)
The Tudor period is a starkly unique style within England and very recognisable. Windows were fixed with lattice work, usually casement. Stained glass was also in in this period, usually depicting figures and heraldic beasts. Rooms would be panelled with wood or plastered. Walls would be adorned with tapestries or embroidered hangings. Windows and furniture would be furnished with fine fabrics such as brocade. Floors would typically be of wood, sometimes strewn with rush matting mixed with fresh herbs and flowers to freshen the room.
Baroque (1600 to 1750)
The Baroque period was a time for splendor and for splashing the cash. The interior of a baroque room was usually intricate, usually of a light palette, featuring a very high ceiling heavy with detail. Furniture would choke the room, ornately carved and stitched with very high quality fabrics. The rooms would be full of art not limited to just paintings but also sculptures of marble or bronze, large intricate mirrors, moldings along the walls which may be heavily gilded, chandeliers and detailed paneling.
Victorian (1837-1901)
We think of the interiors of Victorian homes as dowdy and dark but that isn't true. The Victorians favoured tapestries, intricate rugs, decorated wallpaper, exquisitely furniture, and surprisingly, bright colour. Dyes were more widely available to people of all stations and the Victorians did not want for colour. Patterns and details were usually nature inspired, usually floral or vines. Walls could also be painted to mimic a building material such as wood or marble and most likely painted in rich tones. The Victorians were suckers for furniture, preferring them grandly carved with fine fabric usually embroidered or buttoned. And they did not believe in minimalism. If you could fit another piece of furniture in a room, it was going in there. Floors were almost eclusively wood laid with the previously mentioned rugs. But the Victorians did enjoy tiled floors but restricted them to entrances. The Victorians were quite in touch with their green thumbs so expect a lot of flowers and greenery inside. with various elaborately decorated patterned rugs. And remember, the Victorians loved to display as much wealth as they could. Every shelf, cabinet, case and ledge would be chocked full of ornaments and antiques.
Edwardian/The Gilded Age/Belle Epoque (1880s-1914)
This period (I've lumped them together for simplicity) began to move away from the deep tones and ornate patterns of the Victorian period. Colour became more neutral. Nature still had a place in design. Stained glass began to become popular, especially on lampshades and light fixtures. Embossing started to gain popularity and tile work began to expand from the entrance halls to other parts of the house. Furniture began to move away from dark wood, some families favouring breathable woods like wicker. The rooms would be less cluttered.
Art Deco (1920s-1930s)
The 1920s was a time of buzz and change. Gone were the refined tastes of the pre-war era and now the wow factor was in. Walls were smoother, buildings were sharper and more jagged, doorways and windows were decorated with reeding and fluting. Pastels were in, as was the heavy use of black and white, along with gold. Mirrors and glass were in, injecting light into rooms. Gold, silver, steel and chrome were used in furnishings and decor. Geometric shapes were a favourite design choice. Again, high quality and bold fabrics were used such as animal skins or colourful velvet. It was all a rejection of the Art Noveau movement, away from nature focusing on the man made.
Modernism (1930 - 1965)
Modernism came after the Art Deco movement. Fuss and feathers were out the door and now, practicality was in. Materials used are shown as they are, wood is not painted, metal is not coated. Bright colours were acceptable but neutral palettes were favoured. Interiors were open and favoured large windows. Furniture was practical, for use rather than the ornamentation, featuring plain details of any and geometric shapes. Away from Art Deco, everything is straight, linear and streamlined.
#This took forever#I'm very tired#But enjoy#I covered as much as I could find#Fantasy Guide to interiors#interior design#Architecture#writings#writing resources#Writing reference#Writing advice#Writer's research#writing research#Writer's rescources#Writing help#Mediaeval#Renaissance#Chinese Interiors#Japanese Interiors#Indian interiors#writing#writeblr#writing reference#writing advice#writer#spilled words#writers
3K notes
·
View notes