#gaelic ireland
Text
Photos of 16th-17th century Irish clothing
Extant garments in the National Museum of Ireland
Notes: The garments in this post are all bog finds which means their current color may not be their original color. Although some of these items were found with human remains, no photos of human remains are included in this post.
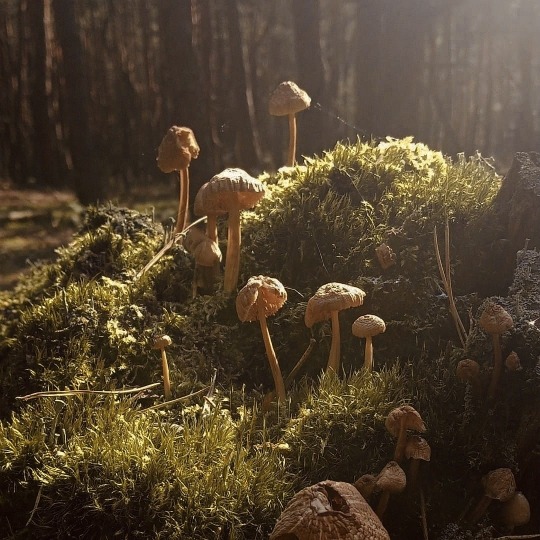
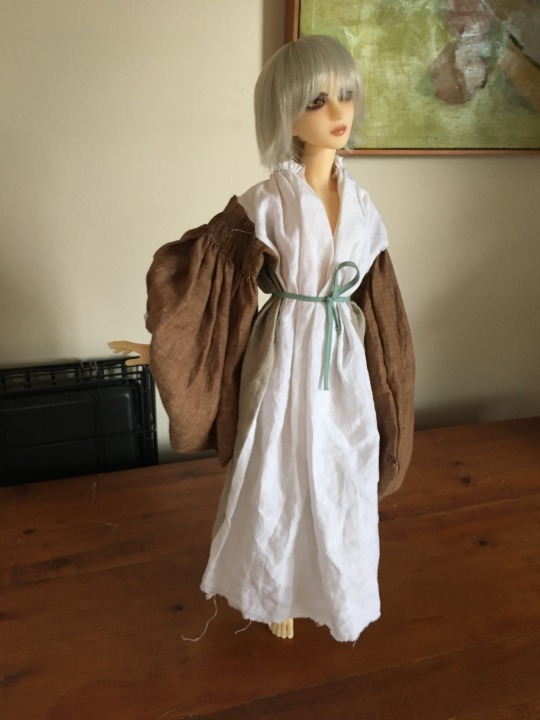
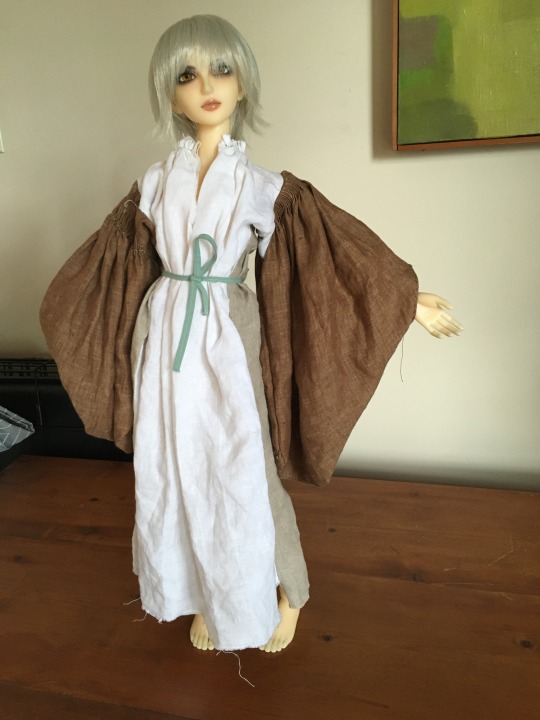
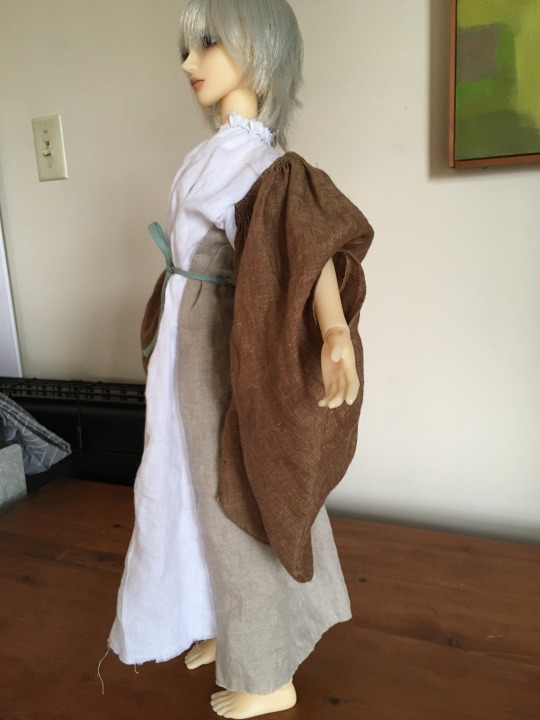
Killery Cóta Mór (great coat) and brogues:
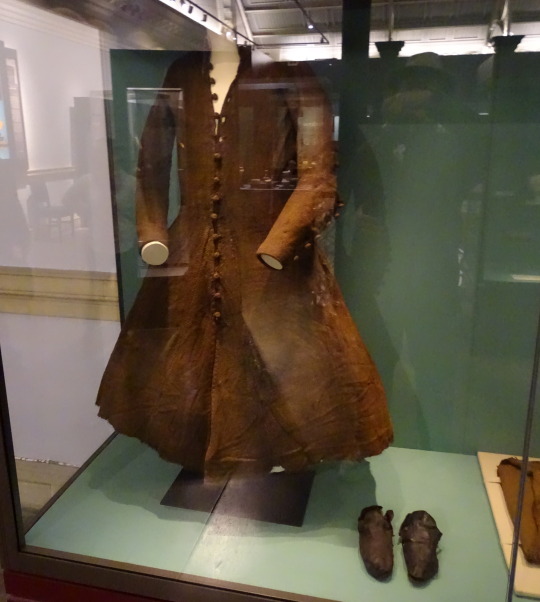

photos by hayling billy used under non-commercial, share alike license
The Killery outfit comes from an adult male bog body found in Killerry parish, Co. Sligo in 1824. It includes a cóta mór, triús, a brat, and shoes which are on display in the museum, and a sheepskin biorraid (conical hat) which fell apart shortly after it was found (Briggs and Turner 1986).
Killery triús (trews):

photo by hayling billy
Killery outfit with and without brat:
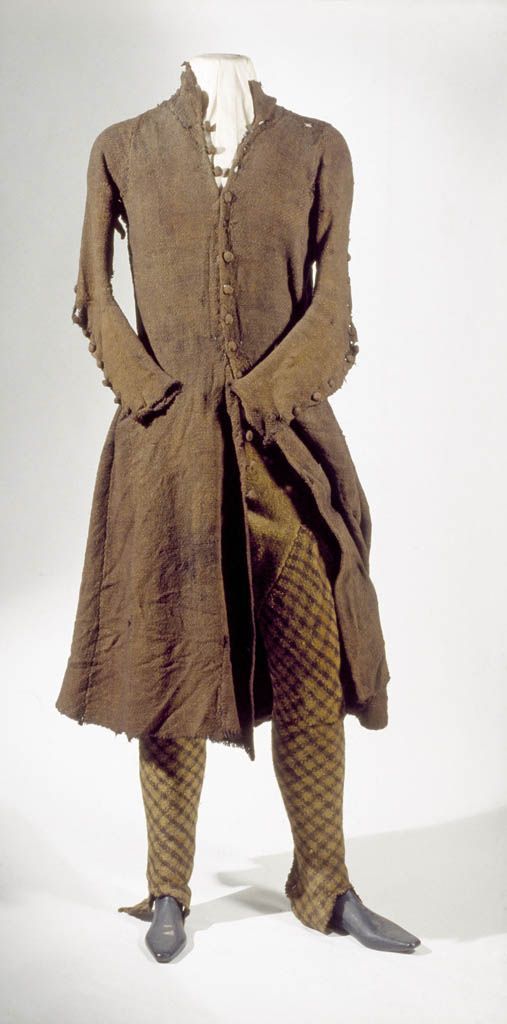
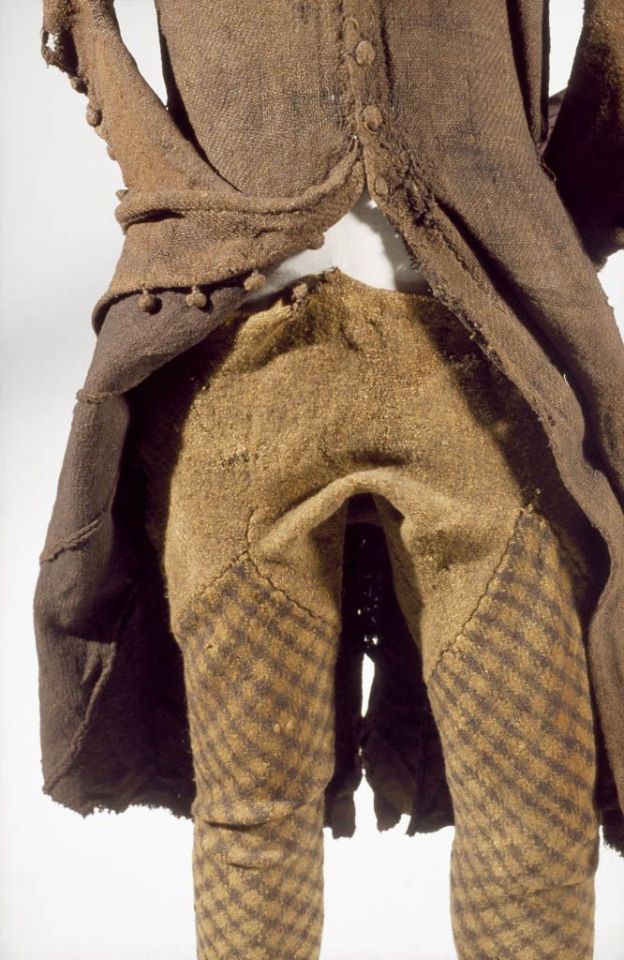
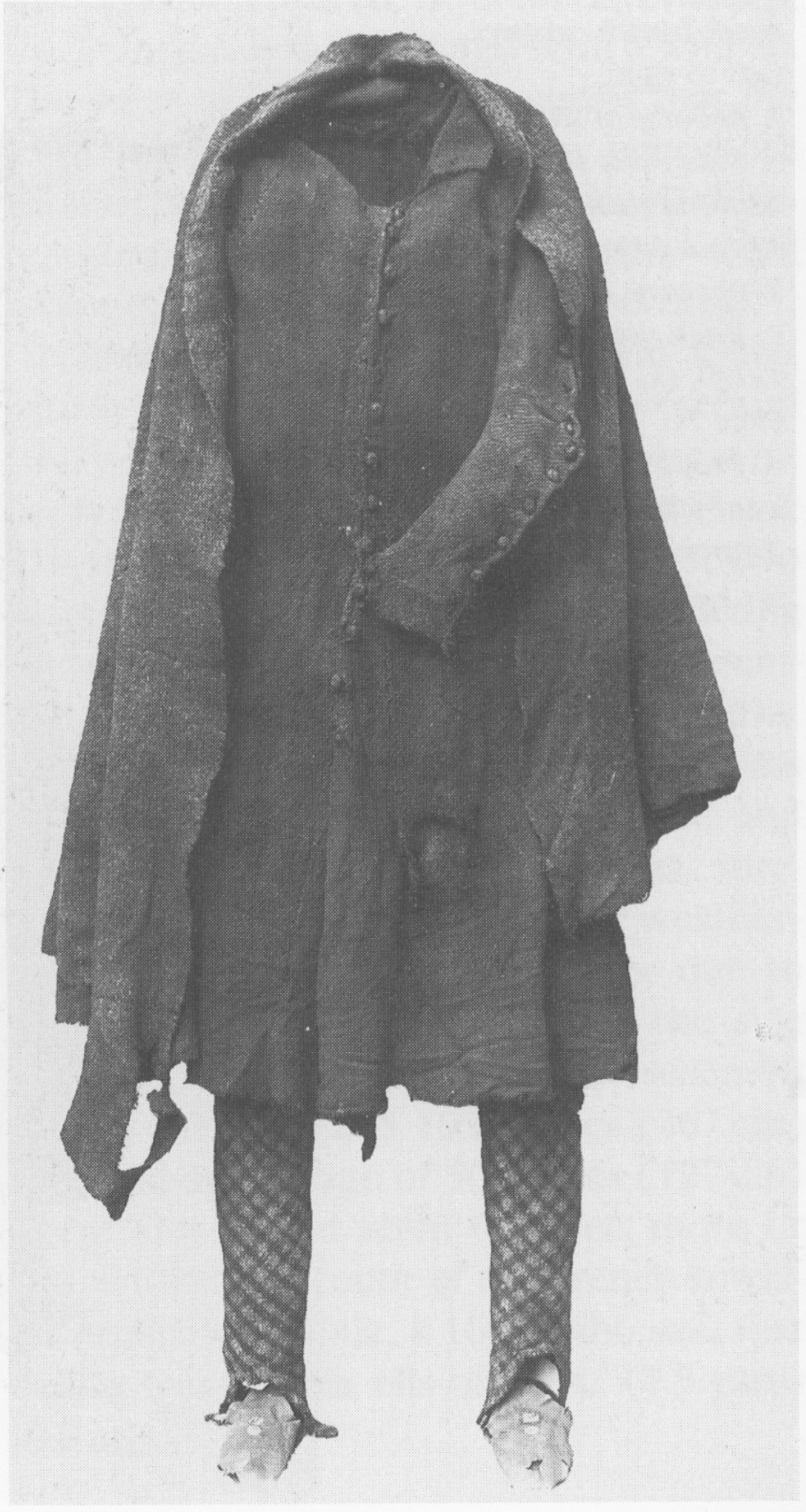


The outfit is generally dated to the 17th c. (Dunlevy 1989). It matches Luke Gernon's 1620 description of Irish men's winter apparel:
"in winter he weares a frise cote. The trowse is along stocke of frise, close to his thighes, and drawne on almost to his waste, but very scant, and the pryde of it is, to weare it so in suspence, that the beholder may still suspecte it to be falling from his arse. It is cutt with a pouche before, which is drawne together with a string."
Additional photos of the outfit: cóta front, hem, buttons, and brat.
Shinrone gown:
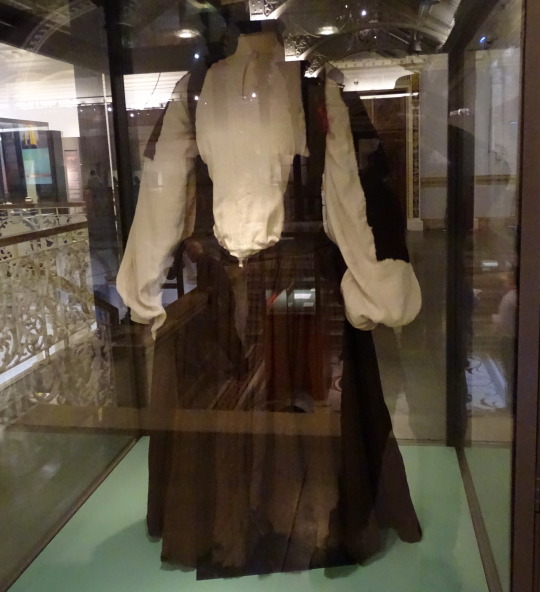

photo by hayling billy
The Shinrone gown was found in a bog in 1843 in Co. Tipperary near Shinrone, Co. Offaly. Unlike the Killery outfit, there were no human remains or other items found with it (Briggs and Turner 1986). The ends of the sleeves and possibly also the bottom of the skirt are missing. The sleeves would have had wrist cuffs or ties that allowed them to be fastened around the wearer's wrists. It probably also had loops or rings along the U-shaped center-front opening for lacing. It is typically dated late 16th-early 17th c, based on its similarity to a circa 1575 illustration by Lucas DeHeere and to the dresses described by Luke Gernon in 1620 (Dunlevy 1989, McGann 2000). It could be older however, because Laurent Vital described dresses with this type of sleeve in 1518.
Copyrighted, better quality photos: left front, right front, back Additional details: side-front, front waistline
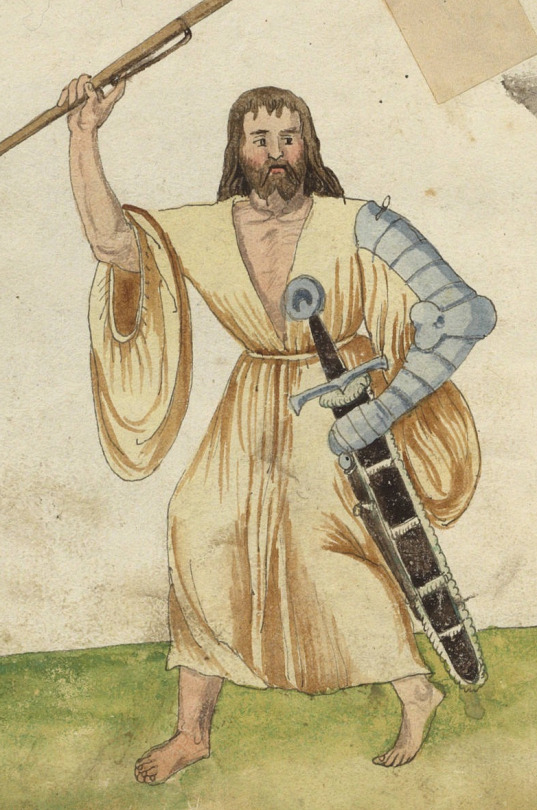
Tipperary Cóta Mór:
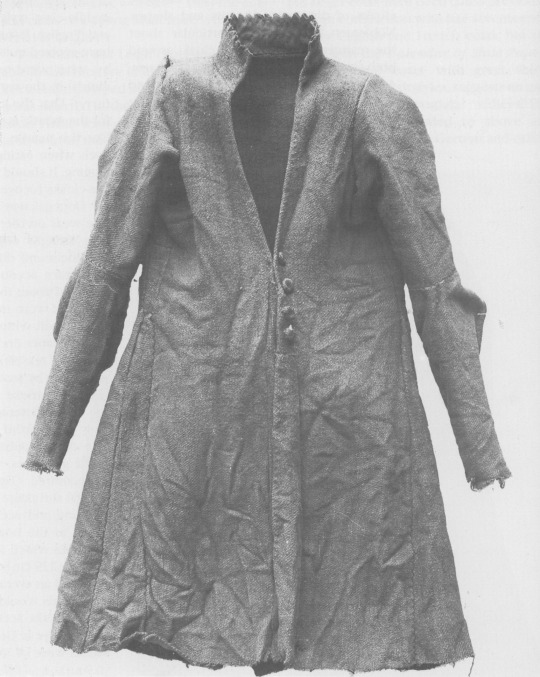


photos from Dunlevy 1989 and hayling billy
Another Cóta Mór. This one is from Co. Tipperary, exact find spot and date unknown. Like the Shinrone gown, it was not found with human remains or other items (Ó Floinn 1995). It is probably also from the 17th century (Dunlevy 1989).
Additional photos: front, side, front buttons, front detail, side
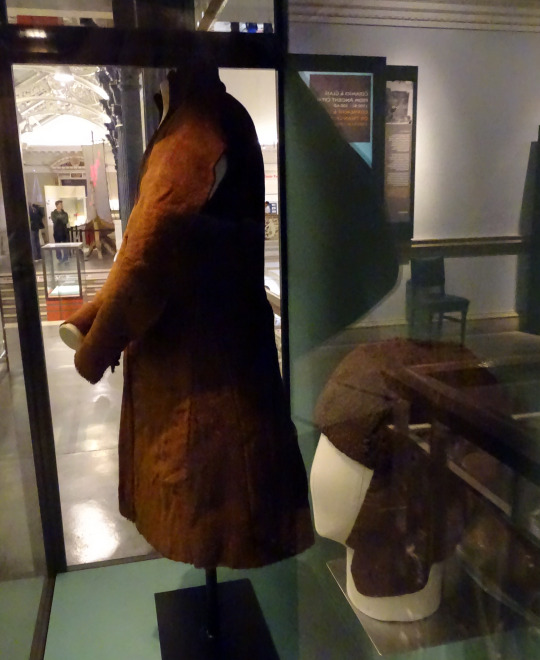
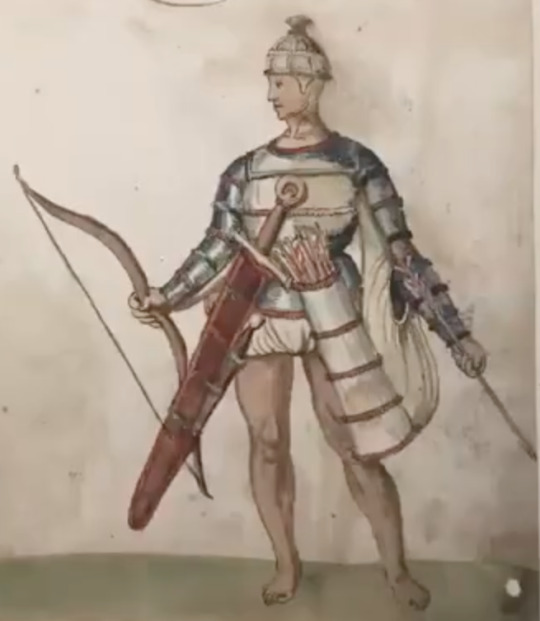
Brat and hats:
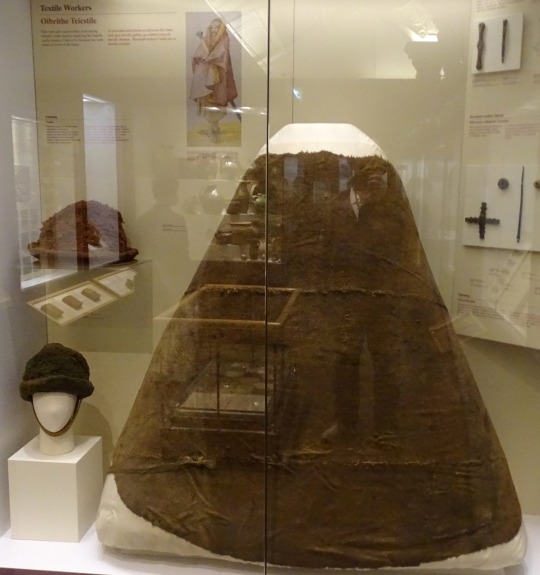

photo by hayling billy
I haven't been able to find any clear photos of the label on this display, but based on the excellent condition and the presence of the leather tie, I think this is the Meenybradden woman's brat.
Closeup of the tie:

The Meenybradden woman is a bog body found in Meenybradden bog, Co. Donegal in 1978. The brat was wrapped around her as a shroud and secured with the leather tie (Delaney and Ó Floinn 1995). No other garments or artifacts were found with her, although she may have been wearing a linen garment such as a léine when she was buried. Linen tends to not survive in bogs. The Meenybradden woman has a calibrated radiocarbon date of AD 1130-1310, but some archaeologist have suggested humic contamination from the peat may be throwing off the dating. Her brat is identical in cut to others from the 16th-17th centuries (Delaney and Ó Floinn 1995).

Meenybradden brat laid flat. (photo from Delaney and Ó Floinn 1995)
Wool hats:
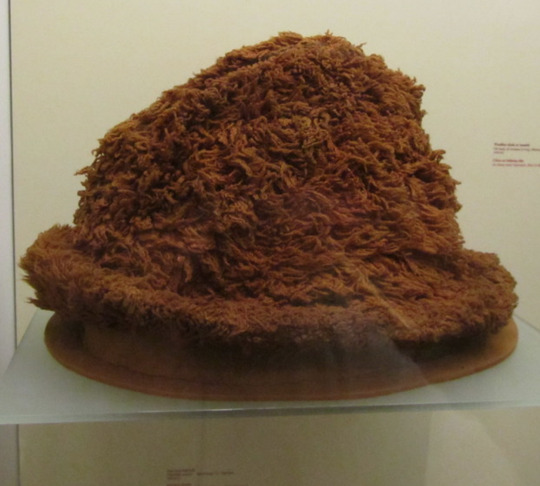
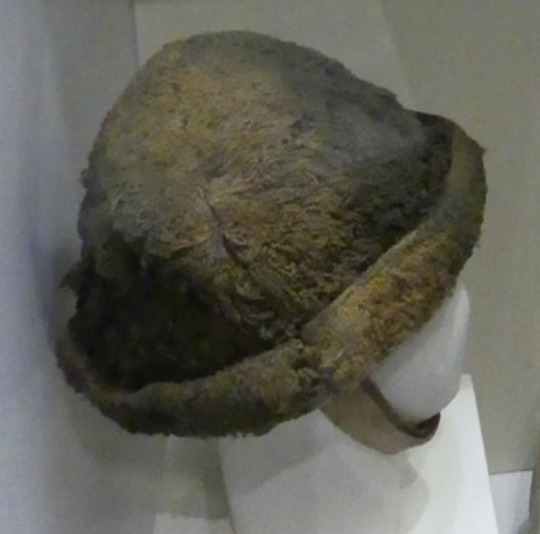


Hats from Boolabaun, Co. Tipperary made of wool felt which has been cut and sewn to form the shape. They have togs of unspun wool worked into them giving them the appearance of faux fur. Dunlevy suggests a 15th-16th c date for them (Dunlevy 1989, McClintock 1943).
Wool cloak:
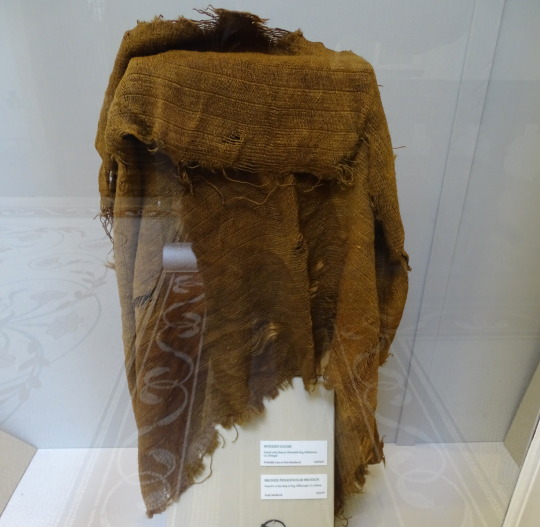

photo by hayling billy
The museum label says it's from Glenmalin bog, Malinmore, Co. Donegal, but I think this may be a mistake. According to Ó Floinn (1995), the artifact with accession number 1946:416 from Malinmore, Co. Donegal is a bale of linen. Ó Floinn's table also gives accession number 1946:416* for a group of clothing from Owenduff, Co. Mayo which includes a gown, a jacket, and a cloak. If the cloak in the photo is actually the one from Owenduff, it is probably from the 17th c (Dunlevy 1989). Alternatively, someone might have misidentified a wool cloak as a bale of linen. The museum label dates this as late Medieval to post-Medieval.
*Either Ó Floinn made a typo or this is a mistake in the museum records. Museums are not supposed to give the same accession number to 2 different artifacts. In the NMI's defense, 1946 was probably a messy year for everyone.
Bibliography:
Briggs, C. S. and Turner, R. C. (1986). Appendix: a gazetteer of bog burials from Britain and Ireland. In I. Stead, J. B. Bourke and D. Brothwell (eds) Lindow Man: the Body in the Bog (p. 181–95). British Museum Publications Ltd.
Delaney, M. and Ó Floinn, R. (1995). A Bog Body from Meenybradden Bog, County Donegal, Ireland. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 123–32). British Museum Press.
Dunlevy, Mairead (1989). Dress in Ireland. B. T. Batsford LTD, London.
Gernon, Luke (1620). A Discourse of Ireland. https://celt.ucc.ie/published/E620001/
McClintock, H. F. (1943). Old Irish and Highland Dress. Dundalgan Press, Dundalk.
McGann, K. (2000). What the Irish Wore/The Shinrone Gown — An Irish Dress from the Elizabethan Age. Reconstructing History. http://web.archive.org/web/20080217032749/http:/www.reconstructinghistory.com/irish/shinrone.html
O’Floinn, R. (1995). Recent research into Irish bog bodies. In R. C. Turner and R. G. Scaife (eds) Bog Bodies: New Discoveries and New Perspectives (p. 137–45). British Museum Press.
Vital, Laurent (1518). Archduke Ferdinand's visit to Kinsale in Ireland, an extract from Le Premier Voyage de Charles-Quint en Espagne, de 1517 à 1518. translated by Dorothy Convery and edited by me. https://irish-dress-history.tumblr.com/post/721163132699131904/laurent-vitals-1518-description-of-ireland
#16th century#17th century#irish dress#dress history#gaelic ireland#historical men's fashion#historical women's fashion#bog finds#irish history#historical dress#brog#bratanna#irish mantle#headwear#triús#cóta mór
62 notes
·
View notes
Text




The Psalter of St Columba is a 6th century manuscript thought to be the first book written in Ireland.
The story goes that the manuscript was secretly copied by St Columba (Colum Cille) from a book he was lent, and St Finnian of Movilla, the lender of the original, claimed the copy should be returned to him as well. The Irish King Diamait judged that Finnian was in the right, which has been cited as the first instance of copyright law. The decision was so controversial it sparked a battle, and Columba was exiled to the island of Iona.
While the story may be apocryphal, the book became a holy relic in the keeping of Clan O'Donnell, who in the 11th century constructed an elaborate silver cumdach (book reliquary) to house it, and a tradition arose of carrying it three times around the O'Donnell warriors before a battle, gaining it the name "Cathach" or "Battler". It remained the property of the O'Donnells until 1843, when Sir Richard O'Donel entrusted it to the Royal Irish Academy.
#happy st patrick's day here's a story about two unrelated saints#gaelic script is so clear compared to gothic#manuscript#ireland#shiny objects
107 notes
·
View notes
Text
Irish, Welsh and Scottish Gaelic speakers, I need your help! 🇮🇪🏴🏴
For a piece of academic writing I am working on right now, I was wondering if in the context of those three languages, you have positive or negative examples of:
1) The presence of non-standard dialects digitally or in the media (any content creator you know, any regular speakers on the radio that actively uses a non-standard dialect, or on the contrary, you only encounter standard Irish/Welsh/Gaelic. If you have any example of non-standard writing too, for example in the printed press, I am all ears)
2) Do you speak and/or write a non-standard dialect and have been looked down upon for it by other speakers? If yes what dialect and in what context
3) What do you think about purification practices in which loan-words from English are replaced by new words? Which words do you use? If you study the language formally, which are taught to you?
Thank you, and please reblog!
- A grateful Celtic student
#Irish#Gaelic#Scottish Gaelic#Welsh#gaeilge#cymraeg#Gàidhlig#Ireland#Scotland#Wales#Celtic languages#Minroty languages#Linguistics#Standardisation#Celtic#Celtic studies#Languages#Alba#Mostly for native speakers but also non-native fluent speakers that regularly interact with the language
61 notes
·
View notes
Text

feeling real normal about this song 👍
#local scot struggling to learn scottish gaelic is wrecked by song about dying languages; more at ten#im sure this applies outwith ireland/scotland/wales too but i dont know enough about that#hozier#unreal unearth
299 notes
·
View notes
Text
Something that gets left out in some eclectic discussions of the celtic fire festivals is that they are the end of one season and the start of another
Imbolg- Start of Spring
Bealtaine- Start of Summer
Lúnasa- Start of Autumn
Samhain- Start of Winter
Which makes sense because in Ireland the seasons are generally defined as:
Spring – February, March, April
Summer – May, June, July
Autumn – August, September, October
Winter – November, December, January
Like if you went up to a random person in Ireland today and asked them what season February is in they’d say Spring.
Seasons are obviously different across the world, in fact many places don’t have 4 seasons so the misunderstanding makes sense but seeing people frame Imbolc as “Oh its not a spring festival its the just bringing back of light” is just factually wrong.
#féile#irish paganism#gaelic paganism#celtic paganism#Irish polytheism#gaelic polytheism#celtic polytheism#gaelpol#iripol#witch#I think other places use the solstaces/equinoxes?#this is a weirdly common thing tho#magic#ireland#mine#witchblr
212 notes
·
View notes
Text
Speakers of non-English languages of the UK and Ireland wanted!!
Since it’s World Mother Language Day today (February the 21st), I’m thinking of doing a series of posts on the native non-English languages of the United Kingdom and Ireland, with some information and short interviews.
For this, I am looking for both native speakers/signers and learners (with or without parentage/heritage of the language in question) of the following languages:
- Scottish Gaelic
- Irish
- Welsh
- Any sign language of the United Kingdom or Ireland (e.g. BSL)
- Any other minority language indigenous to the United Kingdom or Ireland. By this I mean primarily spoken only within the UK or Ireland as a minority, or spoken very little elsewhere. For example: Cornish, Manx, Shelta, or Anglo-Romani, not languages like Polish or Bengali that are minority within the UK but have a significant speaker base elsewhere. (I am aware that I am fishing for some of these *cough* Cornish *cough*...but you never know!)
- Any language or variety that you speak that you feel is linguistically / culturally distinct from Standard English that you would like to inform more people about. For example: Shetlandic, Scots, Ulster Scots.
I don’t have anything finalised yet, but if you would be wiling to speak to me about some text-based interviews for the sake of qualitative and informative tumblr posts, please send me a message!
(NB: if I have used any names of languages that are not preferred, tell me and I will change them. I don’t know a lot about the non-Celtic and non-Germanic languages here, which is part of my reason for wanting to make this series of posts in the first place.)
Please reblog so more people see this!
- meichenxi
#irish#welsh#scottish gaelic#gaelic#bsl#world mother language day#please reblog <3#every single time I tell anyone (brits included) about the variety of languages that exist natively in the UK and Ireland I die a little#<< that is a joke and I enjoy informing others but also. there's more than english please#cornish and breton and manx....look. if ANYONE on the internet is learning those languages as a second language learner#they are on Tumblr. this I know to be true#*manifesting*#cornish is on my list of celtic languages to learn in the future. but first gaelic. and then welsh since my family is moving there#and THEN perhaps cornish. *meme voice* I just think it's neat!#I also like the challenge of being at the forefront of a revival moment that is almost entirely made up of nerds (affectionate)
455 notes
·
View notes
Text
non-irish people reading 'gailege' and 'gaelic', the names of two completely distinct celtic languages

#languages#irish#gailege#gaelic#celtic languages#sorry to the person who posted that poll but c'mon#it's been 12 years since tfa came out#there is no excuse#'google isn't helpful' did you actually google it or did you take fics written by non-irish americans at face value#'what language do they speak in ireland' will get you irish and english at the very top of the screen
150 notes
·
View notes
Text









Irish Language (Gaeilge)
Níl aon tinteán mar do thinteán féin. There's no fireside like your own.
– Irish proverb
#and fock the english#i love you ireland#big up cork big up derry big up dublin#shout out barry keoghan and oscar wilde and fiona gallagher and ayo edebiri#ireland#irish#irish language#irish literature#gaelic#gaelige#languages#foreign languages#langblr#studyblr#langspo#studyspo#celtic#irish aesthetic#celtic aesthetic#moodboard#nature#nature moodboard#countryside#irish countryside#indigenous languages
66 notes
·
View notes
Text
Just to let everyone know, Ireland has its own language, and so does Scotland.
SCOTLAND'S is called Gaelic and is pronounced Gah-lic
IRELAND'S is called Irish, or Gaeilge/Gaeilinn/Gaeilic depending on dialect when being said in the language.
Gaelic, pronounced Gay-lic, is an Irish sport (gaelic football) and a term used when talking about Irish culture.
STOP CALLING "IRISH" GAELIC AND STOP CONFUSING IT WITH SCOTTISH GAELIC!!!! Please do actual research before writing either into your fantasy books too.
#irish#ireland#scottish#scotland#gaelic#gaeilge#its not hard#writing#writers#fantasy#fantasy writing#writers on tumblr#language
45 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Map of Ireland in Gaelic, 1948.
230 notes
·
View notes
Text
Patterning a 16th c. Irish léine sleeve


Mid-16th c. images of the léine from "Drawn after the Quick" and Codice de Trajes
The léine of 16th century Ireland had huge, iconic sleeves. Sadly, we have neither surviving examples of this garment, nor detailed period documentation, so we don't know how these sleeves were made. I have seen a couple different sewing patterns purposed, but none of these match the voluminous, gathered sleeves shown in the Codice de Trajes and the costume album of Christoph von Sternsee. This is my attempt to create a sleeve pattern that better matches the surviving evidence.
The cut of léine sleeves probably varied across 16th c. Ireland, potentially impacted by factors like a person's wealth or where in Ireland they lived. It almost certainly changed over time as more of Ireland fell to English colonial conquest. The wearing of the large-sleeved léine was banned by King Henry VIII (McClintock 1943). Lucas de Heere’s circa 1575 illustrations show women with much smaller sleeves than earlier images. However, at least during the early part of the century, sleeves did not vary by gender. According to Laurent Vital, the only difference between a man's léine and a woman's léine was that the woman's had gores in the bottom it make it fuller (Vital 1518).
My goal with this project is to create a léine sleeve pattern for an early to mid-16th c. Irish person living outside of the Pale. Since none of the period images or texts are very detailed, I am combining information from several sources.
Englishman Edmund Campion who visited Ireland in 1569 gave the following derisive description of the léine: “Linnen shirts the rich doe weare for wantonnes and bravery, with wide hanging sleeves playted, thirtie yards are little enough for one of them” (Campion 1571).
Campion’s claim that the sleeves were pleated initially struck me as strange. English and continental European shirts from this period frequently had gathered sleeves (Mikhaila and Malcolm-Davies 2006, Arnold, Tiramani and Levey 2008), but pleating isn’t the same thing as gathering. However, other period writers made similar claims. Writing in 1596, Edmund Spenser mentioned "thicke foulded lynnen shirtes” as a garment worn by the Irish (Spencer 1633).
Similarly, Fynes Moryson described the léine as being made of “thirty or forty ells [of linen] in a shirt all gathered and wrinkled,” elsewhere he described it as “folded in wrinckles” (Moryson 1617).
In The Image of Irelande, John Derricke gave the following description of the léine:
Their shirtes be verie straunge,/ not reachyng paste the thie:/ With pleates on pleates thei pleated are,/ as thicke as pleates maie lye./ Whose sleves hang trailing doune/ almoste unto the Shoe (Derricke 1581)
Assuming that Derricke’s description is not just poetic license, I know of one 16th century construction method that matches the description “pleats on pleats [. . .] as thick as pleats may lie,” and that is cartridge pleating. Cartridge pleating is a technique that is more commonly used on thick fabrics like woolens, because a lot of fabric bulk is needed to keep the pleats standing properly, but extant 16th and early 17th c. neck ruffs use cartridge pleating to join massive lengths of fine linen to a neck band (Arnold, Tiramani and Levey 2008).

Cartridge pleating on a thick woolen fabric
A person unfamiliar with sewing methods and terms might well describe cartridge pleating as looking like folds, gathers, or wrinkles.
The léine sleeve patterns commonly used in modern reconstructions are completely flat, like a Japanese kimono sleeve with rounded corners. (There’s also a version which has a drawstring or gathering running along the top of the sleeve. This is a 20th c. Ren Fair invention which has no historical basis.)
The end-on views of the sleeve openings in the recently-discovered images from Codice de Trajes and the costume album of Christoph von Sternsee clearly show that this is not correct. The rounded shape they show for the sleeve end can only be achieved through gathering.


Archer from the von Sternsee costume album and the O’Brien messenger from The Image of Irelande
The best illustration of a léine in The Image of Irelande, the messenger on plate 7, also provides evidence for a gathered sleeve. The way the fabric drapes in the middle of the sleeve suggests that the sleeve is gathered at both ends. Furthermore, the way the mass of a léine sleeve centers under the wearer’s arm when the wearer holds their arm out straight, like the O’Brien messenger, but hangs down like a trumpet when the wearer lowers their arm, like on von Sternsee’s archer also suggests that the sleeve is a symmetrical shape that is gathered at both ends and not a trumpet shape that is only gathered at the wrist end.
With these elements in mind, I went looking for a pattern which would create the correct shape. I used Jean Hunnisett's 15th c. bagpipe sleeve pattern from Period Costume for Stage and Screen and the sleeve pattern from this 1630s English waistcoat (published in Seventeenth-Century Women’s Dress Patterns) as a starting point.

1630s waistcoat sleeve pattern
I replaced the curved sleeve heads in these patterns with the straight sleeve end and square underarm gusset typical of mid-16th-18th c. shirts, since the léine, like the shirt, is an unfitted linen garment, and because the straight edge is much easier to gather all the way around. I don't have any actual evidence for square gussets in 16th c. Ireland, but this pattern definitely needs an ungathered piece at the underarm. Anyone who is bothered by the lack of evidence can use a triangular gusset like the one on the 15th c. Moy gown instead.
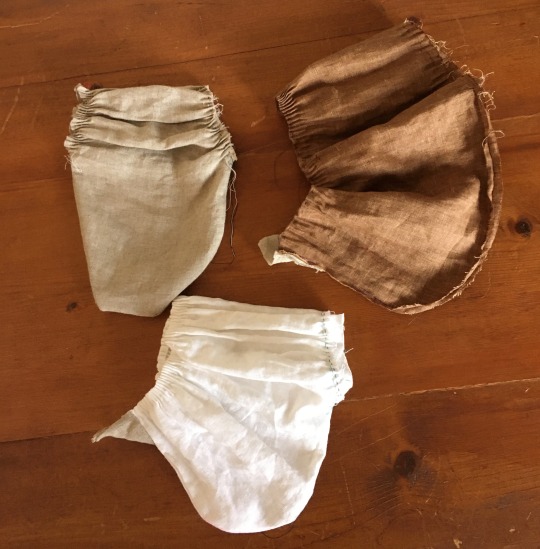
After that, I experimented with mock-ups until I figured out how to get the correct proportions. I don't have any training in patterning or draping, so this took several tries. I used my 1/3 scale ball-jointed doll (24 inches tall) as model, because he required a lot less fabric and sewing. Since this was just a mock-up, I used random linen remnants from my stash, and I didn't bother to finish most of the edges.
Here is the final sleeve with the seams sewn together, but before doing the gathering:

This sleeve, on his right arm, is based on the gathered-wrist cuff version of the léine from Codice de Trajes, the von Sternsee album, and The Image of Irelande.
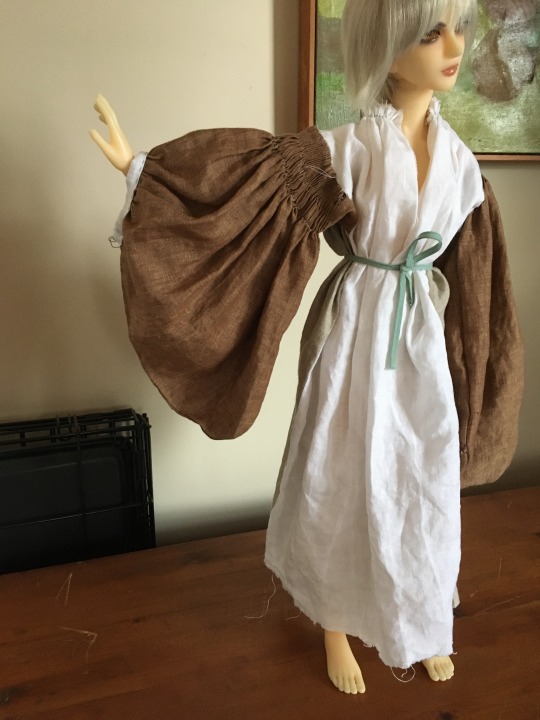



This sleeve ended up with me having to gather 31 inches of fabric into a 5-inch armscye. So yeah, cartridge pleating became necessary, because there is no way to make that kind of reduction work with regular gathering. I also had to do some smocking to get the giant mass of fabric better controlled before I could attach it to the body of the léine.
While this pattern might seem absurd, (it does call for a sleeve end wider than the wear is tall to be pleated into the armscye,) a close examination of John Michael Wright's 1680 portrait of Sir Neil O'Neill shows remarkably similar sleeves.

While this painting is from a century later than my target time period and the clothing clearly shows changes like the addition of English-style shirt sleeve ruffles, the shirt still has elements which I have seen no where else in late 17th c. fashion that are probably derived from earlier Irish dress.

The doublet worn over top prevents it from hanging down properly, but this shirt sleeve has the same bagpipe shape as the 16th c. léine. I have highlighted it in magenta to make this easier to see. The fine, regular folds near the top of the sleeve (highlighted in yellow) are probably the result of smocking or cartridge pleating, indicating that this sleeve, like my purposed pattern, has a large amount of fabric gathered or pleated to the armscye. The wrist end of the sleeve has 3 rows of smocking stitches sewn with silk thread, which shows that the sleeve cuff has a huge amount of fabric gathered into it.
Historically, silk was the thread of choice for smocking, because it is smoother and has greater tensile strength than wool, linen, or cotton. Several 16th c. sources note that the Irish used silk thread when making their léinte (Gresh 2021). Laurent Vital described Irish women as wearing, "chemises with wide sleeves, worked around the collar and in the seams with silk needlework of different colours" (1518). The presence of smocking on O'Neill's shirt combined with my experience trying to recreate this sleeve makes me think that at least some of that 16th c. silk needlework was smocking.
For the left sleeve of my mock-up, I tried to recreate the flatter sleeves from "Drawn After the Quicke". These sleeves do not have a gathered wristband.

This sleeve used basically the same pattern, but the lack of gathering at the wrist opening meant that the whole sleeve was slightly smaller, so I only had to pleat 26 in of fabric into the armscye instead of 31 in. This was just enough of a difference that I could set the sleeve without smocking it first, unlike the right sleeve. I guess this is the more budget-friendly option for your less wealthy kern.



I also made the curve at the bottom of the sleeve wider to give this one a more square shape.
Some of my failed experiments:

I would like to thank my friend Nikki for loaning me her smocking machine. This project would have been a much bigger pain if I had to do all those gathering stitches by hand.
Since this post has gotten rather long, I am putting the actual drafting instruction for this sleeve pattern in a separate post.
If anyone would like to support my work financially, I now have a ko-fi page.
Bibliography:
Arnold, Janet, Tiramani, J., & Levey, S. (2008). Patterns of Fashion 4. Macmillan, London.
Campion, Edmund. (1571). A Historie of Ireland, Written in the Yeare 1571. Dublin. https://archive.org/details/historieofirelan00campuoft/historieofirelan00campuoft/page/n5/mode/2up
Derricke, John. (1581). The Image of Irelande, with the discoverie of a Woodkarne. John Daie, London. https://archive.org/details/imageofirelandew00derr/page/n29/mode/2up?view=theater
Hunnisett, Jean. (1996). Period Costume for Stage & Screen: Patterns for Women's Dress, Medieval-1500. Players Press, Inc, Studio City.
Gresh, Robert. (2021). The Saffron Shirt, Part 1: Saffron and Silk, Urine and Grease. Wilde Irish. https://www.wildeirishe.com/post/the-saffron-shirt-part-1-saffron-and-silk-urine-and-grease
McClintock, H. F. (1943). Old Irish and Highland Dress. Dundalgan Press, Dundalk.
McGann, K. (2008). The Invention of Drawstrings and Pleated Sleeves. Reconstructing History. https://reconstructinghistory.com/blogs/irish/the-invention-of-drawstrings-and-pleated-sleeves-1
Mikhaila, Ninya, & Malcolm-Davies, Jane (2006). The Tudor Tailor. Quite Specific Media Group, Ltd, London.
Moryson, Fynes. (1617). An Itinerary Containing His Ten Yeeres Travell through the Twelve Dominions of Germany, Bohmerland, Sweitzerland, Netherland, Denmarke, Poland, Italy, Turky, France, England, Scotland & Ireland. volume 4. https://ia801307.us.archive.org/16/items/fynesmorysons04moryuoft/fynesmorysons04moryuoft.pdf
North, Susan and Jenny Tiramani, eds. (2011). Seventeenth-Century Women’s Dress Patterns, vol.1, V&A Publishing, London.
Spencer, Edmund. (1633). A View of the present State of Ireland. https://celt.ucc.ie/published/E500000-001/index.html
Vital, Laurent (1518). Archduke Ferdinand's visit to Kinsale in Ireland, an extract from Le Premier Voyage de Charles-Quint en Espagne, de 1517 à 1518. translated by Dorothy Convery. https://irish-dress-history.tumblr.com/post/721163132699131904/laurent-vitals-1518-description-of-ireland
#16th century#irish dress#dress history#leine#art#gaelic ireland#irish history#historical men's fashion#historical dress#historical women's fashion#sewing
24 notes
·
View notes
Text
Irish people in the UK, can any of us speak irish…
So many people in my school and my area are irish or half irish and so few of us even have one word of irish. My friend, A, is half irish half jewish and although her mum is nearly fluent she only has some duolingo irish. N, fully irish and not a word of it. E, half irish half chinese is fluent in chinese but only knows one word of irish. M, half ghanain half irish and again- no irish. Even myself, half irish half romani i only have duolingo knowledge and it upsets me that i cant find anyone who speaks it and i have no native speaker influence due to me not seeing my irish family anymore.
I implore anyone- connection or no connection to the language- to give gaeilge or any celtic/dying language a go.
#gaeilge#irish#languages#celtic#gaelic#scottish#ireland#scotland#welsh#wales#cornwall#cornish#celtic solidarity#celtic languages
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
#OTD in 1876 – The Society for the Preservation of the Irish Language is formed in Dublin.
“In order to de-Anglicize ourselves, we must at once arrest the decay of the language. We must bring pressure upon our politicians not to snuff it out by their racist discouragement merely because they do not themselves understand it. We must arouse some spark of patriotic inspiration among the peasantry who still use the language, and put an end to that shameful state of feeling — a…

View On WordPress
#British Rule#Douglas Hyde#Gaelic League#Gaelic Union#Horace Plunkett#Ireland#Irish language#SPIL#The Society for the Preservation of the Irish Language
34 notes
·
View notes
Text
Yo I need someone who's fluent in Gaeilge what would be a word that's close to clairvoyance? Like with this meaning:

I'm tryna do a thing here but Google translate won't give me shit and I'm not that good at my Gaeilge.
18 notes
·
View notes
Text
It'd be cool to come up with Pagan alternatives to the days of the week in the Gaelic languages, since the current ones have such Christian meanings
DiLuain can stay since moon worship is a thing, but perhaps we might change the Latin to "Latha na Gealaich"?
DiMairt could be "Latha na Mhór-ribhinne" (The Morrigan's Day) in keeping with the "M" sound of "Mairt"
DiCiadain needs to go since it refers to a Christian fast, so why not make it Latha an Daghdha? (A sort of oblique reference to Wednesday being "Wodan's Day" in English perhaps?
DiarDaoin again refers to fasts, so maybe "Latha Lùgha"?
DihAoine, another fast, so how about "Latha Aoidh" since it sounds kinda similar to "aoin"?
DiSathairne isn't Christian so much as the wrong kind of pagan, so I'm not against leaving it as is, but as long as we're going with new names, why not "Latha Manannain"?
DiDòmhnaich is perhaps the most explicitly Christian, but since we have "Latha na Gealaich" already, I propose substituting "Latha na Gréine"
I was obviously a bit inspired by the Germanic names here, but I'm curious to see what everyone else's thoughts are! I came up with these off the top of my head, so I make no guarantees about their appropriateness or linguistic accuracy (I'm a Gaelic learner, not a fluent speaker).
#gaelpol#gaelic polytheism#gaelic paganism#scottish gaelic#gàidhlig#gaidhlig#paganism#pagan#an dagda#the morrigan#lugh#aed#manannan mac lir#ireland#irish mythology#gaelic mythology
49 notes
·
View notes
Text

While individual letters are straight forward to pronounce in irish, I find that two vowels together can still sometimes trip me up. I've made a non exhaustive list of the vowel combos. Please note that pronunciation is dependent on dialect.
They are each listed as (irish letters)-(english pronunciation)-(example word)
If there's any mistakes please let me know too.
294 notes
·
View notes