#climate risk
Text
Insurance companies are making climate risk worse

Tomorrow (November 29), I'm at NYC's Strand Books with my novel The Lost Cause, a solarpunk tale of hope and danger that Rebecca Solnit called "completely delightful."

Conservatives may deride the "reality-based community" as a drag on progress and commercial expansion, but even the most noxious pump-and-dump capitalism is supposed to remain tethered to reality by two unbreakable fetters: auditing and insurance:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reality-based_community
No matter how much you value profit over ethics or human thriving, you still need honest books – even if you never show those books to the taxman or the marks. Even an outright scammer needs to know what's coming in and what's going out so they don't get caught in a liquidity trap (that is, "broke"), or overleveraged ("broke," again) exposed to market changes (you guessed it: "broke").
Unfortunately for capitalism, auditing is on its deathbed. The market is sewn up by the wildly corrupt and conflicted Big Four accounting firms that are the very definition of too big to fail/too big to jail. They keep cooking books on behalf of management to the detriment of investors. These double-entry fabrications conceal rot in giant, structurally important firms until they implode spectacularly and suddenly, leaving workers, suppliers, customers and investors in a state of utter higgeldy-piggeldy:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/29/great-andersens-ghost/#mene-mene-bezzle
In helping corporations defraud institutional investors, auditors are facilitating mass scale millionaire-on-billionaire violence, and while that may seem like the kind of fight where you're happy to see either party lose, there are inevitably a lot of noncombatants in the blast radius. Since the Enron collapse, the entire accounting sector has turned to quicksand, which is a big deal, given that it's what industrial capitalism's foundations are anchored to. There's a reason my last novel was a thriller about forensic accounting and Big Tech:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865847/red-team-blues
But accounting isn't the only bedrock that's been reduced to slurry here in capitalism's end-times. The insurance sector is meant to be an unshakably rational enterprise, imposing discipline on the rest of the economy. Sure, your company can do something stupid and reckless, but the insurance bill will be stonking, sufficient to consume the expected additional profits.
But the crash of 2008 made it clear that the largest insurance companies in the world were capable of the same wishful thinking, motivated reasoning, and short-termism that they were supposed to prevent in every other business. Without AIG – one of the largest insurers in the world – there would have been no Great Financial Crisis. The company knowingly underwrote hundreds of billions of dollars in junk bonds dressed up as AAA debt, and required a $180b bailout.
Still, many of us have nursed an ember of hope that the insurance sector would spur Big Finance and its pocket governments into taking the climate emergency seriously. When rising seas and wildfires and zoonotic plagues and famines and rolling refugee crises make cities, businesses, and homes uninsurable risks, then insurers will stop writing policies and the doom will become undeniable. Money talks, bullshit walks.
But while insurers have begun to withdraw from the most climate-endangered places (or crank up premiums), the net effect is to decrease climate resilience and increase risk, creating a "climate risk doom loop" that Advait Arun lays out brilliantly for Phenomenal World:
https://www.phenomenalworld.org/analysis/the-doom-loop/
Part of the problem is political: as people move into high-risk areas (flood-prone coastal cities, fire-threatened urban-wildlife interfaces), politicians are pulling out all the stops to keep insurers from disinvesting in these high-risk zones. They're loosening insurance regs, subsidizing policies, and imposing "disaster risk fees" on everyone in the region.
But the insurance companies themselves are simply not responding aggressively enough to the rising risk. Climate risk is correlated, after all: when everyone in a region is at flood risk, then everyone will be making a claim on the insurance company when the waters come. The insurance trick of spreading risk only works if the risks to everyone in that spread aren't correlated.
Perversely, insurance companies are heavily invested in fossil fuel companies, these being reliable money-spinners where an insurer can park and grow your premiums, on the assumption that most of the people in the risk pool won't file claims at the same time. But those same fossil-fuel assets produce the very correlated risk that could bring down the whole system.
The system is in trouble. US claims from "natural disasters" are topping $100b/year – up from $4.6b in 2000. Home insurance premiums are up (21%!), but it's not enough, especially in drowning Florida and Texas (which is also both roasting and freezing):
https://grist.org/economics/as-climate-risks-mount-the-insurance-safety-net-is-collapsing/
Insurers who put premiums up to cover this new risk run into a paradox: the higher premiums get, the more risk-tolerant customers get. When flood insurance is cheap, lots of homeowners will stump up for it and create a big, uncorrelated risk-pool. When premiums skyrocket, the only people who buy flood policies are homeowners who are dead certain their house is gonna get flooded out and soon. Now you have a risk pool consisting solely of highly correlated, high risk homes. The technical term for this in the insurance trade is: "bad."
But it gets worse: people who decide not to buy policies as prices go up may be doing their own "motivated reasoning" and "mispricing their risk." That is, they may decide, "If I can't afford to move, and I can't afford to sell my house because it's in a flood-zone, and I can't afford insurance, I guess that means I'm going to live here and be uninsured and hope for the best."
This is also bad. The amount of uninsured losses from US climate disaster "dwarfs" insured losses:
https://www.reuters.com/business/environment/hurricanes-floods-bring-120-billion-insurance-losses-2022-2023-01-09/
Here's the doom-loop in a nutshell:
As carbon emissions continue to accumulate, more people are put at risk of climate disaster, while the damages from those disasters intensifies. Vulnerability will drive disinvestment, which in turn exacerbates vulnerability.
Also: the browner and poorer you are, the worse you have it: you are impacted "first and worst":
https://www.climaterealityproject.org/frontline-fenceline-communities
As Arun writes, "Tinkering with insurance markets will not solve their real issues—we must patch the gaping holes in the financial system itself." We have to end the loop that sees the poorest places least insured, and the loss of insurance leading to abandonment by people with money and agency, which zeroes out the budget for climate remediation and resiliency where it is most needed.
The insurance sector is part of the finance industry, and it is disinvesting in climate-endagered places and instead doubling down on its bets on fossil fuels. We can't rely on the insurance sector to discipline other industries by generating "price signals" about the true underlying climate risk. And insurance doesn't just invest in fossil fuels – they're also a major buyer of municipal and state bonds, which means they're part of the "bond vigilante" investors whose decisions constrain the ability of cities to raise and spend money for climate remediation.
When American cities, territories and regions can't float bonds, they historically get taken over and handed to an unelected "control board" who represents distant creditors, not citizens. This is especially true when the people who live in those places are Black or brown – think Puerto Rico or Detroit or Flint. These control board administrators make creditors whole by tearing the people apart.
This is the real doom loop: insurers pull out of poor places threatened by climate disasters. They invest in the fossil fuels that worsen those disasters. They join with bond vigilantes to force disinvestment from infrastructure maintenance and resiliency in those places. Then, the next climate disaster creates more uninsured losses. Lather, rinse, repeat.
Finance and insurance are betting heavily on climate risk modeling – not to avert this crisis, but to ensure that their finances remain intact though it. What's more, it won't work. As climate effects get bigger, they get less predictable – and harder to avoid. The point of insurance is spreading risk, not reducing it. We shouldn't and can't rely on insurance creating price-signals to reduce our climate risk.
But the climate doom-loop can be put in reverse – not by market spending, but by public spending. As Arun writes, we need to create "a global investment architecture that is safe for spending":
https://tanjasail.wordpress.com/2023/10/06/a-world-safe-for-spending/
Public investment in emissions reduction and resiliency can offset climate risk, by reducing future global warming and by making places better prepared to endure the weather and other events that are locked in by past emissions. A just transition will "loosen liquidity constraints on investment in communities made vulnerable by the financial system."
Austerity is a bad investment strategy. Failure to maintain and improve infrastructure doesn't just shift costs into the future, it increases those costs far in excess of any rational discount based on the time value of money. Public institutions should discipline markets, not the other way around. Don't give Wall Street a veto over our climate spending. A National Investment Authority could subordinate markets to human thriving:
https://democracyjournal.org/arguments/industrial-policy-requires-public-not-just-private-equity/
Insurance need not be pitted against human survival. Saving the cities and regions whose bonds are held by insurance companies is good for those companies: "Breaking the climate risk doom loop is the best disaster insurance policy money can buy."
I found Arun's work to be especially bracing because of the book I'm touring now, The Lost Cause, a solarpunk novel set in a world in which vast public investment is being made to address the climate emergency that is everywhere and all at once:
https://us.macmillan.com/books/9781250865939/the-lost-cause
There is something profoundly hopeful about the belief that we can do something about these foreseeable disasters – rather than remaining frozen in place until the disaster is upon us and it's too late. As Rebecca Solnit says, inhabiting this place in your imagination is "Completely delightful. Neither utopian nor dystopian, it portrays life in SoCal in a future woven from our successes (Green New Deal!), failures (climate chaos anyway), and unresolved conflicts (old MAGA dudes). I loved it."

If you'd like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here's a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/11/28/re-re-reinsurance/#useless-price-signals
#pluralistic#doom loop#insurance#insuretech#climate#climate risk#climate emergency#the lost cause#market forces#risk management#price signals#control boards#decarbonization#bond vigilantes#climate resilience
262 notes
·
View notes
Text
Europe unprepared for climate risks, scientists warn
Europe is the world’s fastest growing continent and climate risks threaten its energy and food security, ecosystems, infrastructure, water resources, financial stability and human health.
According to an assessment published today by the European Environment Agency (EEA), many of these risks have already reached critical levels and could become catastrophic without urgent and decisive action.
The extreme heat, drought, wildfires and floods that have been occurring on the planet in recent years will worsen in Europe even under an optimistic global warming scenario and will affect living conditions across the continent. The EEA has published the first ever European Climate Risk Assessment (EUCRA) to help prioritise climate change adaptation policies and climate-sensitive sectors.
European adaptation policies and measures are not keeping pace with rapidly increasing risks. In many cases, gradual adaptation will not be enough, and as many climate resilience measures take a long time, urgent action may be required even for risks that are not yet critical.
Read more HERE

#world news#world politics#news#europe#european news#european union#eu politics#eu news#green politics#climate risk#climate change#climate crisis#climate action#climate catastrophe#climate emergency#environment
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
"'Smoking gun proof': fossil fuel industry knew of climate danger as early as 1954"
"There is overwhelming evidence the oil and gas industry has been misleading the public and regulators around the climate risks of their product for 70 years. Trusting them to be part of the solutions is foolhardy."


#fossil fuels#fossil fools#fossil fuel industry#climate danger#history#1954#oil#gas#industry#misleading#public#regulators#climate change#climate crisis#climate action#climate catastrophe#climate emergency#climate risk#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#fuck neoliberals#neoliberal capitalism#anthony albanese#albanese government#ecology#pollution
6 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
What is the RISKIEST Region in the US as the Climate Changes?
#youtube#pbs#climate change#data#climate risk#pbs terra#environment#nature#propublica#noaa#psa#advice#economics#hannah hess#rhodium group#maiya may#future#predictions
10 notes
·
View notes
Text
EY: Αύξηση εσόδων, κερδών και συμφωνιών το 2024 προβλέπουν οι CEOs,
Οι Διευθύνοντες Σύμβουλοι είναι αισιόδοξοι για αύξηση των εσόδων και της κερδοφορίας το 2024, παρά τις δύσκολες οικονομικές συνθήκες παγκοσμίως, σύμφωνα με την πιο πρόσφατη έκδοση της τακτικής έρευνας, EY CEO Outlook Pulse.
Continue reading EY: Αύξηση εσόδων, κερδών και συμφωνιών το 2024 προβλέπουν οι CEOs,

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Happy New Year with a View on Climate Change and AI
Happy New Year to all our readers.
We hope 2024 will become a great year in all ways.
Lucubrate Magazine: January 1st 2024
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been proven to be an essential engine of green economic development, yet how it will affect the internal structure of the green economy is unknown. Recent AI advancements have unveiled transformative prospects and opportunities to enhance and optimize environmental performance and efficiency. These strides have, in turn,…

View On WordPress
#AI#AI technologies#Arteficial intelligence#Climate#Climate change#Climate risk#Costs of climate change#Development#Environment#environmental protection#Future#Global environmental changes#Simulation in virtual environments#Skills#technology#World
0 notes
Text
En Californie, avec le réchauffement climatique, le risque d’une méga-inondation dévastatrice a doublé
J'ai pensé que cet article de Courrier international pourrait t'intéresser :
Le réchauffement climatique a fait doubler la probabilité d’une méga-inondation aux conséquences catastrophiques en Californie, selon une étude publiée dans la revue Science Advances, relayée samedi 13 août par le Los Angeles Times
Selon les travaux de chercheurs de l’université UCLA, le déluge qui [...]
#nature#history#economy#tourism#california#united states#megafloods#climatic changes#los angeles#climate risk
0 notes
Text
AYESHA RASCOE, HOST:
With Spain and Portugal saying that hundreds of people have died from the heat waves sweeping through Europe this month, the longer-term view might come as a surprise. Over the past 50 years, the number of deaths attributed to weather-related disasters has actually fallen. Yes, you heard that right. The World Meteorological Organization says that the number of disasters has increased five times over the past 50 years, but the number of fatalities has fallen by two-thirds. Vox climate writer Umair Irfan has delved into this paradox and joins us now. Welcome to the program, Umair.
UMAIR IRFAN: Thanks for having me, Ayesha.
RASCOE: So how can this be? Like, how can the number of deaths be falling even though we hear the news, we see the disasters? You know, seas are rising, summers are hotter, hurricanes seem to be getting stronger. So how is it possible that deaths can be down?
IRFAN: Well, there are two main factors here. One is better forecasting - basically being able to get ahead of these disasters and then hopefully being able to get people out of harm's way. So that's really prominent with things like hurricanes and heat waves. We can actually see those things days in advance. The other side of the equation is how well we can cope with things like storms, fires and heat waves when they do occur. So we have better tools - things like sea walls. We have better building codes. We have firefighting teams that can get people out of fire zones. And so between those two aspects - you know, the better forecasting and the better tools - we've been able to avert a lot of deaths, even though the global population has grown about fourfold since the start of the 20th century.
RASCOE: Are the technological advances that you're talking about available even in less-developed areas?
IRFAN: It's not, unfortunately. And you're hitting on a very important point. You know, the WMO pointed out that about 90% of disaster-related fatalities that occur today are occurring in developing countries. And there's a huge gap in terms of being able to anticipate these disasters before they occur and being able to respond to them and being able to rebuild in their aftermath. And that really is a big shortfall that a lot of world leaders are starting to get concerned about...
You know, the World Meteorological Organization, they launched this initiative to basically say that they want the whole world covered by disaster early warning systems over the next five years. And they think that this is something that's going to be taking a big bite out of the fatalities and the casualties caused by these disasters. So I think it's worth highlighting the progress that's made, but also the progress that we still need to make.
-via NPR, July 17, 2022
Thanks so much to @gardening-tea-lesbian for the link!
#weather#extreme weather#extreme heat#natural disasters#climate anxiety#climate crisis#climate change#flood warning#disaster response#disaster relief#disaster risk reduction#hurricanes#tsunami#earthquake#wildfire#tornado#good news#hope#hope posting#climate optimism
430 notes
·
View notes
Photo
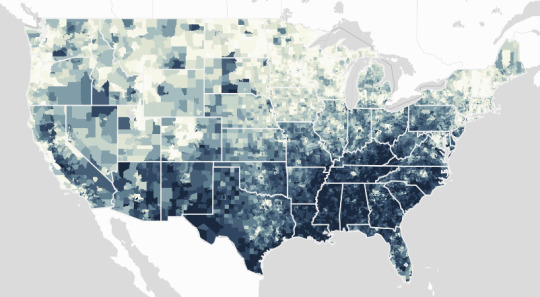
Overall Climate Vulnerability
123 notes
·
View notes
Text

"Unexpected" my ass. We've been screaming for over a decade now about how we're approaching an existential risk to humankind. When are people, including scientists, going to acknowledge how little we actually know? Why are we leaving this to chance instead of demanding better?
#climate change#climate crisis#current events#science#Given the number of natalists in the world you'd think existential risk would be the most important moral argument you can make#Not to mention their current and or future children won't have a world in which to grow old#But what would I know#fucking hate it here
43 notes
·
View notes
Text
Did you guys know coughing nearly nonstop for ~36 hours Hurts. My throat hurts my chest hurts my abdominal muscles hurt. Coughing is Exercise
#The weather just will not stop being Xtreme Asthma Risk so my body can't calm down#I hate it here I need to live in a climate-controlled greenhouse or on the moon
12 notes
·
View notes
Note
Misty deserves to go ape shit. Let her do murder.
I’m a fan of Misty drowning Leopardstar when they get to the lake. After all the shit Leopardstar did and let happen even after Tigerclan disbanded, Misty won’t let it blow a second time, or with a stone for the symbolism (can you tell Bonefall has infected me?)
I refuse to believe she didn’t take at least one of Blackstar’s lives and there’s no quotes in canon saying otherwise so I’m right by default :)
Dueling him wasn’t a request, it was her right in her mind and she dared anyone to deny her rights again.
you 🤝 me
pro misty going murder mode
Also BIG yeah on that last point. He executed her brother, he wouldn’t be able to show his face if he denied her right to retribution. You have nine lives and yet you deserve none of them, nine lives but I’ll take one and may you never forget it.
#deer rambles#giggling and kicking my feet thinking about cat fuels#i mentioned it in my tags but i do love bonefall’s post tpb rc political climate#how the ideology of Tigerstar still lingers and Leopardstar only allows it to fester#and it posits the solution when this happen: rip out the weed#leopardstar wasn’t going to risk losing her community for her attitude#she was the one who was going to make it spread
24 notes
·
View notes
Quote
According to First Street Foundation, the top 10 counties in the nation with the most climate abandonment areas despite having above-average population growth include Harris County. Three Texas counties rank worse than Harris: Bexar (with 17.1% of blocks in climate abandonment areas), El Paso (12.7%) and Tarrant (9.8%).
Residents leave Houston neighborhoods thanks in part to climate change | Kinder Institute for Urban Research | Rice University
0 notes
Text
Ρωσία: 60 οι νεκροί και πάνω από 100 τραυματίες από την τρομοκρατική επίθεση
Στους 60 ανέρχονται οι νεκροί και πάνω από 100 οι τραυματίες από την τρομοκρατική επίθεση σε συναυλιακό χώρο στη Ρωσία, για την οποία ανέλαβε την ευθύνη το Ισλαμικό Κράτος.
Continue reading Ρωσία: 60 οι νεκροί και πάνω από 100 τραυματίες από την τρομοκρατική επίθεση

View On WordPress
0 notes
Link
Long before Roe was overturned, providers’ desire to avoid risk—from professional ostracization to picketing to shootings—shadowed abortion care. This is why medical schools often refrained from offering training in terminating pregnancies, and why abortion procedures were not regularly performed in the vast majority of public hospitals. Since Dobbs, some medical institutions have gone further, hesitating to provide care to women such as Christina Zielke, who was rushed to a hospital in Painesville, Ohio, last September after experiencing heavy bleeding from a miscarriage. Instead of performing a dilation-and-curettage procedure to remove the pregnancy tissue from her uterus, the hospital staff discharged Zielke, apparently in response to a six-week abortion ban that had been passed by the Ohio state legislature. Zielke was soon lying in a bathtub in a pool of blood, wondering if she would die. After she lost consciousness, her family called 911, and paramedics eventually took her back to the hospital, where a doctor performed the procedure.
Such horror stories are a predictable consequence of the fear that criminalizing abortion has spread through the medical community. For fifty years, Roe protected providers from legal risks like the ones taken on by the Jane Collective, an underground network of women in Chicago. Collective members arranged more than eleven thousand illegal abortions in the late nineteen-sixties and early seventies, until a team of detectives raided their makeshift clinic and charged them with multiple counts of “conspiracy to commit abortion.” (Just before their cases went to trial, the Supreme Court legalized abortion.) Arguably, providers face greater legal dangers now than they did before Roe. Carole Joffe, a sociologist who has written about the history of abortion, told me that doctors who performed illegal procedures in the past “typically received sentences of a few years,” whereas physicians today face “an aggressive anti-abortion movement that, in some states, is calling for life imprisonment.” Abortion opponents have also targeted organizations such as Planned Parenthood with spurious lawsuits and violent attacks, in an effort to shut them down.
Planned Parenthood’s motto is “Care. No matter what.” These words suggest an uncompromising commitment to serving patients. Yet some pro-choice advocates feel that the group, along with other large organizations that have shaped the modern abortion-rights movement, has lately seemed more focussed on self-preservation than on taking bold risks. Tracy Weitz, a reproductive-rights scholar who directs the Center on Health, Risk, and Society, at American University, told me she is worried that these groups are being guided too strongly by attorneys whose priority is to shield them from lawsuits. The mission of Planned Parenthood is not “institutional survival,” Weitz said. “Their entire goal, their mission, is to serve patients.” If caution supersedes this goal, she warns, not only will patients suffer but the pro-choice movement will fall into a familiar trap. “One of the critiques of the abortion-rights movement is that we put too much faith in the law, believing that it would protect the right to abortion,” she said. “I think it’s ironic that all of a sudden we have turned over this movement to a whole new group of lawyers—not constitutional lawyers but risk managers.”
In the fall of 2021, a preview of how these dynamics could play out in a post-Roe era unfolded in Texas, after Governor Greg Abbott signed the Texas “heartbeat” bill. Better known as S.B. 8, the law banned abortion after six weeks of pregnancy, and it offered a ten-thousand-dollar bounty to any private citizen who successfully sued someone involved in such a procedure. In the view of some analysts, S.B. 8 was plainly unconstitutional—Roe v. Wade was then still federal law—and designed to intimidate both patients and providers. (Indeed, Planned Parenthood joined the A.C.L.U. and other groups in a lawsuit to block S.B. 8.) One might imagine that Planned Parenthood and other large pro-choice organizations, including the National Abortion Federation, which funds and supports many independent clinics, would have responded to this threat by urging providers to continue offering care and by pledging to defend anyone named in a lawsuit. Vicki Saporta, who served as the N.A.F.’s president until 2018, believes that such a strategy would have been both feasible and effective. “There could have been a legal-defense fund set up to pay out various ten-thousand-dollar suits while S.B. 8 was being challenged, and, in the meantime, care could have continued to be provided,” she said. Planned Parenthood and its affiliates, whose net assets exceed two billion dollars, have “the wherewithal to raise the legal-defense money,” she added.
Instead, Planned Parenthood’s South Texas affiliate instructed its providers to stop performing all abortions, even before six weeks. The affiliate’s apparent anxiety about lawsuits was shared by Planned Parenthood’s leaders and by its attorneys in Washington, who warned that Republicans in Texas could weaponize S.B. 8 to try to bankrupt the organization. Meanwhile, the N.A.F. announced that it would stop funding any providers and patients who didn’t comply with S.B. 8—and even pressed clinics to perform a second ultrasound after patients had endured Texas’s mandatory twenty-four-hour waiting period, in case a heartbeat could be detected then. Many Texas doctors refused to adhere to the N.A.F. directive. In fact, some physicians had the impulse to publicly flout S.B. 8. Shortly after the law took effect, Alan Braid, a provider in San Antonio, published an op-ed in the Washington Post in which he acknowledged having performed an abortion after the six-week limit. He explained that in the early seventies, while completing his ob-gyn residency, he had seen several women die from illegal abortions. “I understand that by providing an abortion beyond the new legal limit, I am taking a personal risk, but it’s something I believe in strongly,” he wrote. Braid told me recently that, at the time, he’d talked to several physicians who shared his feelings and who, like him, were willing to defy S.B. 8. If doctors were willing to fight, he wondered, why were institutions designed to protect women’s rights capitulating?
#what I'm reading#abortion#planned parenthood#reproductive justice#this was an absolutely maddening article but reified a lot of things I have been frustrated about over the past year/years#and intersects a lot with some stuff I've been thinking about wrt how disastrous the ngo-ification of feminism has been for women#and how the medical field (for many reasons understandably) and large organizations writ large and inherently risk averse#which means they are terribly positions to fight back against the anti abortion movement in this political climate#it's super frustrating...the way pp markets itself (and raises millions of $$) as the vanguard of the resistence vs what they actually do#feels super disingenuous and gross#*are inherently
37 notes
·
View notes