#Infrastructure
Text
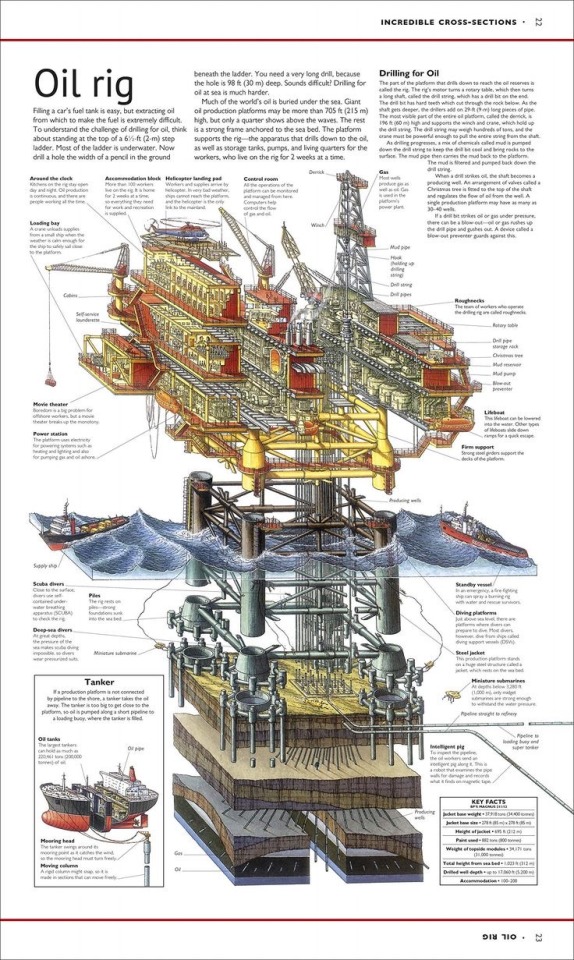
Incredible Cross Sections - Oil Rig
61 notes
·
View notes
Text

#leftism#anti capitalism#socialism#communism#anarchy#earth day#ecosystem#eco#rewilding#environment#ecology#ecofriendly#agriculture#infrastructure#ecofashion#waste
65 notes
·
View notes
Text
As relentless rains pounded LA, the city’s “sponge” infrastructure helped gather 8.6 billion gallons of water—enough to sustain over 100,000 households for a year.
Earlier this month, the future fell on Los Angeles. A long band of moisture in the sky, known as an atmospheric river, dumped 9 inches of rain on the city over three days—over half of what the city typically gets in a year. It’s the kind of extreme rainfall that’ll get ever more extreme as the planet warms.
The city’s water managers, though, were ready and waiting. Like other urban areas around the world, in recent years LA has been transforming into a “sponge city,” replacing impermeable surfaces, like concrete, with permeable ones, like dirt and plants. It has also built out “spreading grounds,” where water accumulates and soaks into the earth.
With traditional dams and all that newfangled spongy infrastructure, between February 4 and 7 the metropolis captured 8.6 billion gallons of stormwater, enough to provide water to 106,000 households for a year. For the rainy season in total, LA has accumulated 14.7 billion gallons.
Long reliant on snowmelt and river water piped in from afar, LA is on a quest to produce as much water as it can locally. “There's going to be a lot more rain and a lot less snow, which is going to alter the way we capture snowmelt and the aqueduct water,” says Art Castro, manager of watershed management at the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power. “Dams and spreading grounds are the workhorses of local stormwater capture for either flood protection or water supply.”
Centuries of urban-planning dogma dictates using gutters, sewers, and other infrastructure to funnel rainwater out of a metropolis as quickly as possible to prevent flooding. Given the increasingly catastrophic urban flooding seen around the world, though, that clearly isn’t working anymore, so now planners are finding clever ways to capture stormwater, treating it as an asset instead of a liability. “The problem of urban hydrology is caused by a thousand small cuts,” says Michael Kiparsky, director of the Wheeler Water Institute at UC Berkeley. “No one driveway or roof in and of itself causes massive alteration of the hydrologic cycle. But combine millions of them in one area and it does. Maybe we can solve that problem with a thousand Band-Aids.”
Or in this case, sponges. The trick to making a city more absorbent is to add more gardens and other green spaces that allow water to percolate into underlying aquifers—porous subterranean materials that can hold water—which a city can then draw from in times of need. Engineers are also greening up medians and roadside areas to soak up the water that’d normally rush off streets, into sewers, and eventually out to sea...
To exploit all that free water falling from the sky, the LADWP has carved out big patches of brown in the concrete jungle. Stormwater is piped into these spreading grounds and accumulates in dirt basins. That allows it to slowly soak into the underlying aquifer, which acts as a sort of natural underground tank that can hold 28 billion gallons of water.
During a storm, the city is also gathering water in dams, some of which it diverts into the spreading grounds. “After the storm comes by, and it's a bright sunny day, you’ll still see water being released into a channel and diverted into the spreading grounds,” says Castro. That way, water moves from a reservoir where it’s exposed to sunlight and evaporation, into an aquifer where it’s banked safely underground.
On a smaller scale, LADWP has been experimenting with turning parks into mini spreading grounds, diverting stormwater there to soak into subterranean cisterns or chambers. It’s also deploying green spaces along roadways, which have the additional benefit of mitigating flooding in a neighborhood: The less concrete and the more dirt and plants, the more the built environment can soak up stormwater like the actual environment naturally does.
As an added benefit, deploying more of these green spaces, along with urban gardens, improves the mental health of residents. Plants here also “sweat,” cooling the area and beating back the urban heat island effect—the tendency for concrete to absorb solar energy and slowly release it at night. By reducing summer temperatures, you improve the physical health of residents. “The more trees, the more shade, the less heat island effect,” says Castro. “Sometimes when it’s 90 degrees in the middle of summer, it could get up to 110 underneath a bus stop.”
LA’s far from alone in going spongy. Pittsburgh is also deploying more rain gardens, and where they absolutely must have a hard surface—sidewalks, parking lots, etc.—they’re using special concrete bricks that allow water to seep through. And a growing number of municipalities are scrutinizing properties and charging owners fees if they have excessive impermeable surfaces like pavement, thus incentivizing the switch to permeable surfaces like plots of native plants or urban gardens for producing more food locally.
So the old way of stormwater management isn’t just increasingly dangerous and ineffective as the planet warms and storms get more intense—it stands in the way of a more beautiful, less sweltering, more sustainable urban landscape. LA, of all places, is showing the world there’s a better way.
-via Wired, February 19, 2024
#california#los angeles#water#rainfall#extreme weather#rain#atmospheric science#meteorology#infrastructure#green infrastructure#climate change#climate action#climate resilient#climate emergency#urban#urban landscape#flooding#flood warning#natural disasters#environmental news#climate news#good news#hope#solarpunk#hopepunk#ecopunk#sustainability#urban planning#city planning#urbanism
13K notes
·
View notes
Text

Comic by Andy Singer
16K notes
·
View notes
Text

This genocide never has been about the hostages, never will be about the hostages.
Mind you, the IDF shot and killed three hostages today. (They spoke Hebrew and held up a white flag in surrender btw).
If you still think this is about the hostages you are gravely mistaken and your ignorance is profound. 🇵🇸
#israel#israel occupation#ethnic cleansing#israeli hostages#Harei Zahav#real estate#infrastructure#genocide#from the river to the sea palestine will be free#free palestine#free gaza#gaza#palestine#pray for palestine#ceasefire#permanent ceasefire#capitalism#imperialism#colonialism#colonial violence#colonization#america#usa#israel is committing genocide#israel is a terrorist state
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
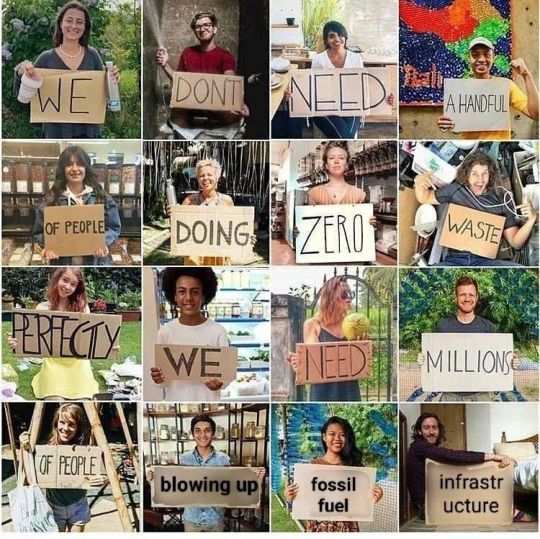

#fossil fuels#infrastructure#global warming#environmentalism#memes#meme#antifascist#co2 emissions#co2#methane#carbon dioxide#jerkmillionaires#jerkbillionaires#jerktrillionaires#eat the rich#eat the fucking rich#ausgov#politas#auspol#tasgov#taspol#australia#neoliberal capitalism#fuck neoliberals#anthony albanese#albanese government#fuck the gop#fuck the police#fuck the supreme court#fuck the patriarchy
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
Dracula Daily leading folks to read up on the historical background of its epistolary framing and discovering that same-day mail delivery used to be completely routine and not just a special perk available only to the largest corporations, and that its decline is a direct consequence of abolishing passenger rail in favour of ubiquitous car ownership isn’t the learning opportunity I expected this week, but you know what, I’ll take it.
31K notes
·
View notes
Text

646 notes
·
View notes
Text

Source
#socialism#capitalism#eat the rich#politics#us politics#health care#health#infrastructure#current events#food
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
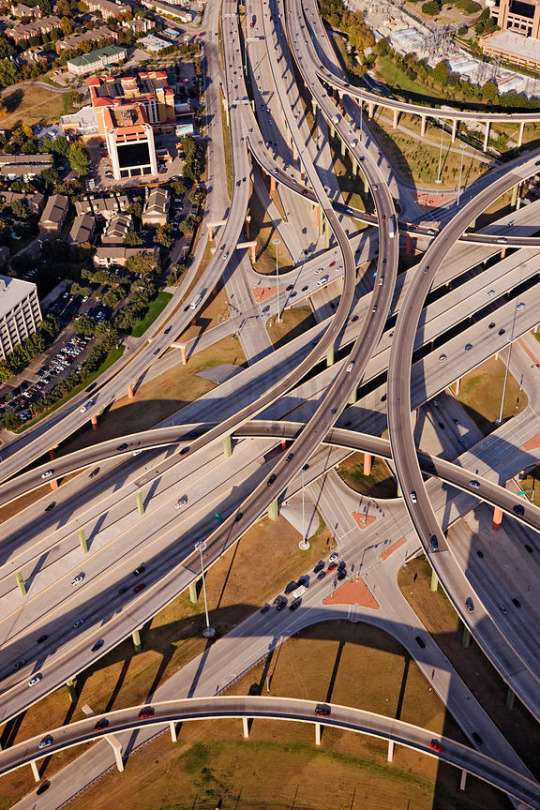
wow, apparently these shitting terrifying, tall, multilayered overpasses are mostly a texas thing. i still have nightmares about these things because i have had to traverse them in various forms throughout my whole life and theyre horrifying abberations to life especially if you have to walk under them to commute daily




5K notes
·
View notes
Text
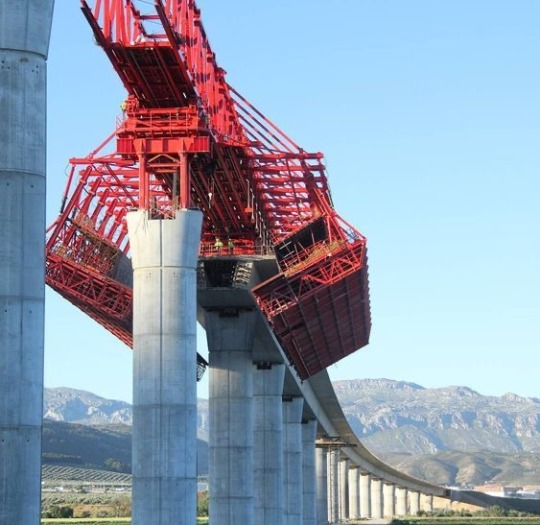

high speed rail construction, China
27 notes
·
View notes
Text


Republicans prove that every time they are in the White House, they never pass infrastructure spending.
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
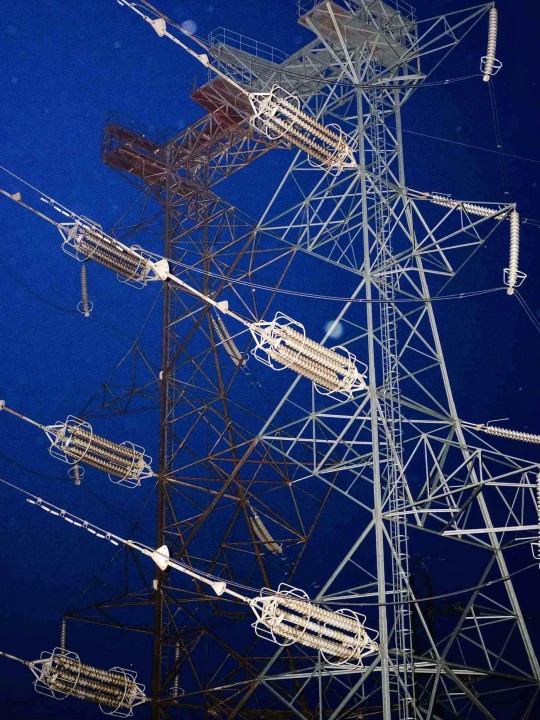

#photography#dimitri djuric#art#2020s#energy#power#culture#electric#infrastructure#photos#aesthetic#night#electrical grid#engineering#technology#light#science#electricity#power grid#communication#⚡ ⚡ ⚡
2K notes
·
View notes
Text



I love transformations like this. It used to be a canal, then they turned it into a freeway, and now the canal has been restored 😍.
#The Netherlands#Holland#Utrecht#Nederland#Dutch#Infrastructure#Nature#removing canals and replacing them with a freeway is always a mistake#glad they fixed it now
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Cars vs Accessible Worlds
Alright, let me talk about one thing in terms of accessibility in science fiction settings - and Solarpunk specifically - that also has more than one side to it: Cars and accessibility. Because it is more complicated than you'd thing.
See: The fact that our world is so car centric really, really hinders accessibility. Wide streets are a hindrance for even normal pedastrians, cyclists and so on. If I want to get from A to B, and the route crosses a street, and there is only a traffic light every like 500 meters, it means tat I usually need either to risk my life or take the long way around to get there. And that is a fucking bother even when you are healthy and can easily take that long way around. And the more car centric a society is, the worse the issue becomes. Here in Germany it is a lot easier still to cross a street than in many places in the US.
And of course this gets a lot worse if you are disabled. Be it that you just cannot walk that far. Or if you are blind and cannot even see in what direction you could go for the next traffic light. Or if you are hard of hearing or deaf, you might be more in danger of being surprised by a car. (And that is without going into how electric cars being so fucking quiet makes stuff even more dangerous.) And, you know, neurodivergent people might also just struggle with the fucking noise that is created by roads and is often inescapable in big cities.
And of course even outside of the environmental issues, the constant presence of cars is also a health risk. Not just because of the risk of accidents, but also due to the pollution and how it interacts. Even if we all were driving electric cars, there would still be all those microplastics created by tires and streets and stuff.
So, really. We do need to move away from car centric infrastructure to make our lives healthier and to make the world more accessible for disabled people too.
BUT...
But there is the issue that some disabled people still might be in need to use some sort of personal transportation device that can cover both short and large distances, because for one reason or another public transport just does not work and cannot work for them.
For example someone with severe anxiety issues, or someone who will be easily suffering from sensory overwhelm. There might be other issues, too. Just some folks will always need something like cars.
And of course there is also the fact that stuff like emergency services will still need streets accessible to cars. Because the emergency services will just not get around using something like cars to get to all the places they might be needed.
And this... makes things complicated. Because infrastructure should not be car centric, no. But it needs to be accessible by cars - and be it just for emergency services.
This is just something that I would love to see more talked about especially within the Solarpunk sphere.
#solarpunk#lunarpunk#infrastructure#car centric infrastructure#anti cars#mobility#public transport#accessibility#disability rights#disability#15 minute city#trains
149 notes
·
View notes
