#taxonomy illustration
Text
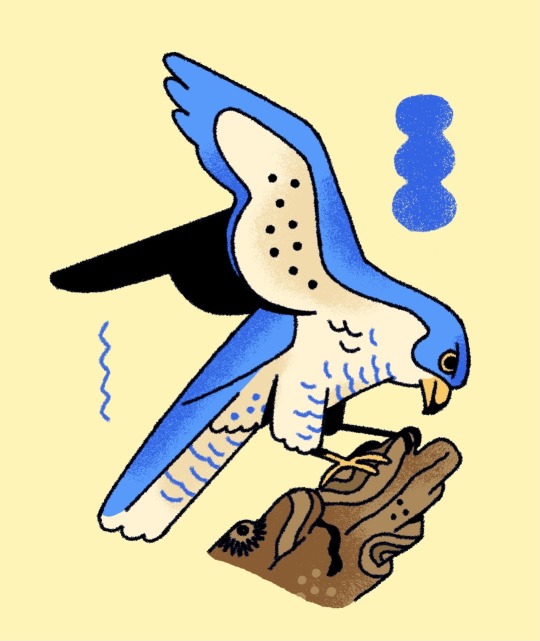

peregrine falcon 💙🫐🌊
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
It Came From The Wastebasket #05: The Trouble With Troodon
Troodontids were small bird-like theropod dinosaurs, lightly built with slender legs and sickle-shaped "raptor" claws on the second toes of their feet. They had fairly big brains proportional to their body size, rather like modern birds, and their large forward-facing eyes had good depth perception. Owl-like asymmetrical ears in some species gave them a very keen sense of hearing, suggesting they may have been nocturnal hunters using sound to pinpoint the location of small prey.
The original specimen of the namesake of the group, Troodon formosus, was a serrated tooth discovered in the 1850s, about 77 million years old and originating from the Late Cretaceous Judith River Formation fossil beds in Montana, USA. It was so little to work with that it was initially mistaken for a lizard tooth, then during the 20th century it was recognized as belonging to a dinosaur and spent time classified as a megalosaurid, then a pachycephalosaur, then finally as a small theropod similar to the Mongolian Saurornithoides.
In the late 1980s it was merged together with multiple other troodontids (including Stenonychosaurus of speculative "dinosauroid" fame), and since Troodon had been the first of all of them to be named it took priority as the genus name.
And then for a while every single Late Cretaceous troodontid specimen from North America was also lumped into Troodon, turning it into a wastebasket taxon.

The problem was that all these troodontids came from locations separated by thousands of kilometers and millions of years of time, and it's unlikely that they all actually represented just one single species. But they were only known from rare fragmentary remains, making distinguishing them from each other difficult, and the original Troodon tooth didn't really have any distinctive features either – it turns out most troodontid teeth all look exactly the same!
It was becmoning increasingly dubious whether Troodon was even a valid name at all, and during the 2010s several paleontologists began trying to sort the mess out. The old names Pectinodon and Stenonychosaurus were revived, and some 'Troodon' fossils were also split off and given completely new names, becoming Albertavenator and Latenivenatrix*.
* Although Latenivenatrix might not actually be distinct enough from Stenonychosaurus to justify having a separate name.
As of 2022, Troodon itself is now in a sort of taxonomic limbo, with some paleontologists abandoning it as a dubious name while others are still arguing in favor of continuing to use it. The name could potentially be properly rescued if the original tooth can be clearly linked to better fossil material, letting Troodon take over priority again from one of the other better-established troodontids, or by defining a new type species similar to what happened with Iguanodon.
…But with how incredibly generic that tooth is, both of those options would be very difficult.
———
Nix Illustration | Tumblr | Twitter | Patreon
#it came from the wastebasket#wastebasket taxon#taxonomy#troodon#stenonychosaurus#pectinodon#albertavenator#latenivenatrix#troodontid#maniraptora#theropod#dinosaur#paleontology#art#science illustration#paleoart#palaeoblr
629 notes
·
View notes
Text

This is a family that has captivated me since I was a kid. Its strange shape and the resemblance to a kind of a little elephant, but also the fact that could be found in my country Colombia just fascinated me. I still remember the first time I saw a tapir and was able to touch it and feed it. However, a Malayan Tapir was an animal that I just could see a long time after, in the Singapore zoo.
Store Instagram
Malayan Tapir
Is the only species that live out of America and the one with the most particular color palette. Its pattern is supposed to be used as camouflage but I don't really know if works. It is curious though, that the Panda shares the same pattern but they both aren't even far related.
Another curious thing is that the babies are very similar in coloration to the ones in America. Brownish color with white spots that are actually good for camouflage.
They have very poor sigh but are compensated with a great sense of smell and hearing.
Some scientist state that there is a subspecies of the Malayan Tapir (The Tapirus indicus brevetianus, Kuiper, 1926), with the particularity of being completely black. Registered for the first time in 1924, was captured and taken to the Rotterdam zoo, where died soon after. The second one was photographed in 2000. However, taking it as a subspecies because of its coloration is inaccurate since there are no further studies that demonstrate its validity. It is actually just a case of melanism. Still, both theories are yet to be confirmed.
_____________________________________________________
Credits:
Malayan TapirMelanistic Tapir
_____________________________________________________
Thank you guys for your support. If you like the content please follow my blog. A like, reblog, or comment is very much appreciated too. Have a good one.
#tapir#malayan tapir#danta#illustration#drawing#scientific illustration#illo#wild animals#wildlife#animals#mammals#artist on tumblr#animal#illustration scientifique#inforgraphics#conservation#taxonomy#clasiffication#extinction#wild mammals#mammal
117 notes
·
View notes
Photo
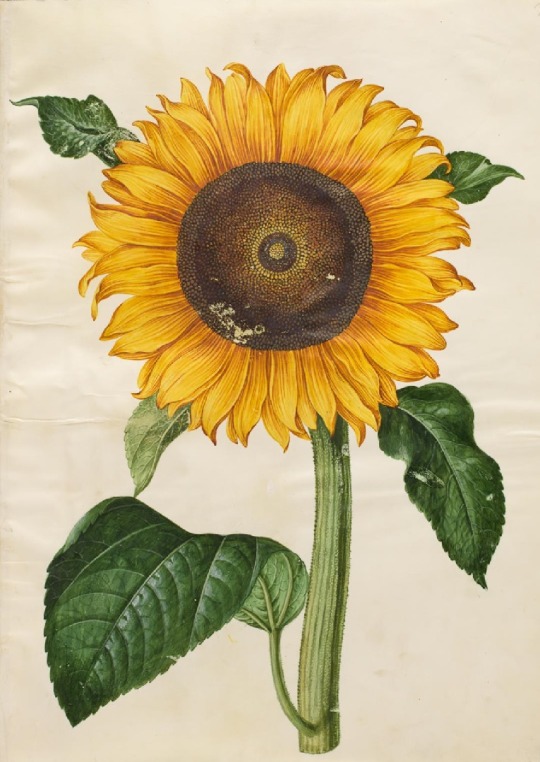
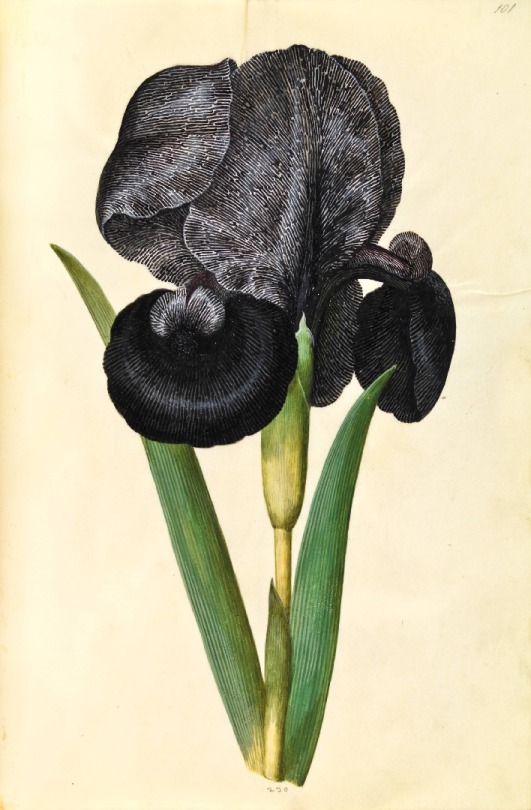
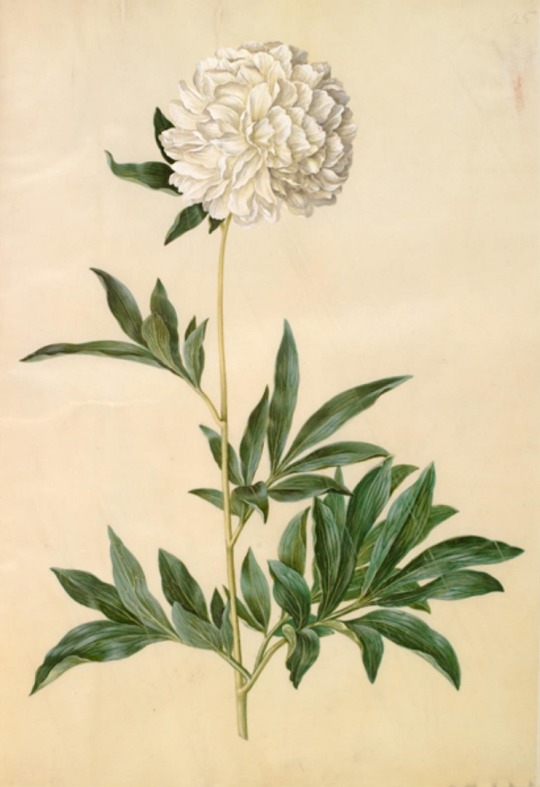
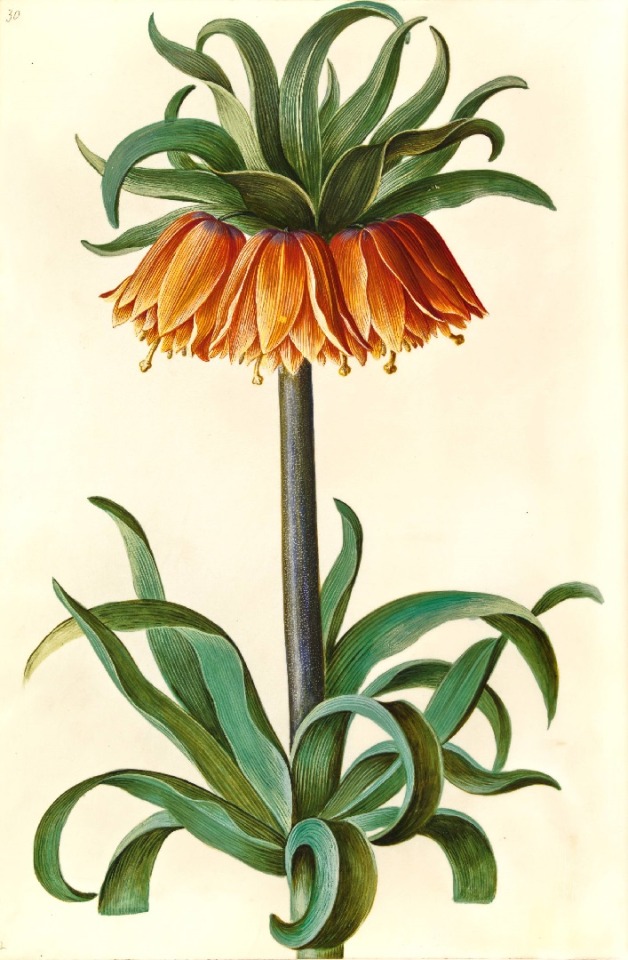
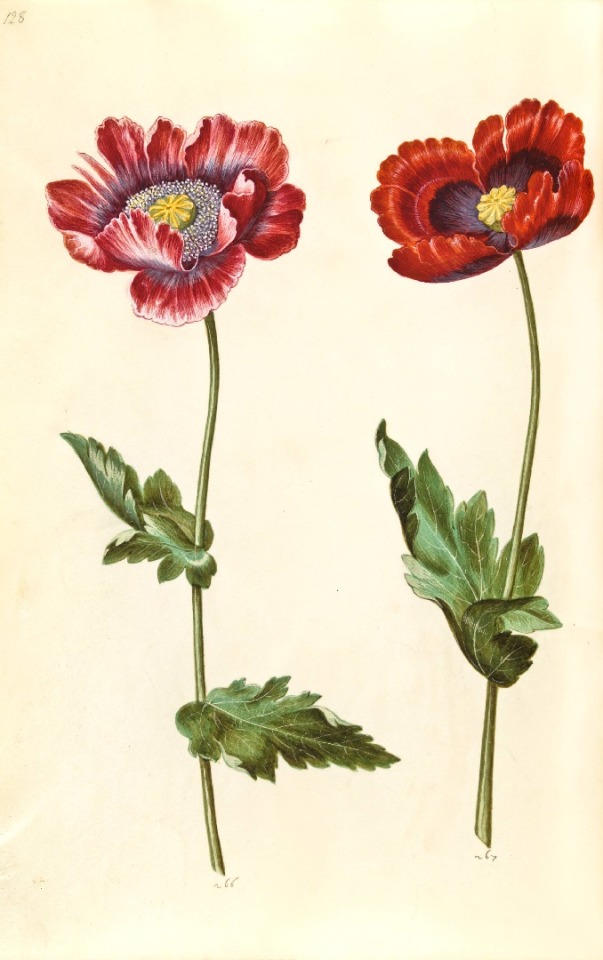
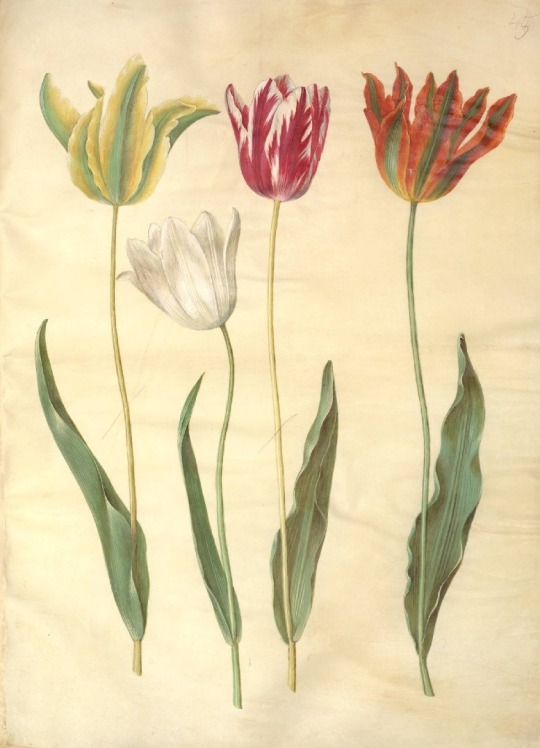
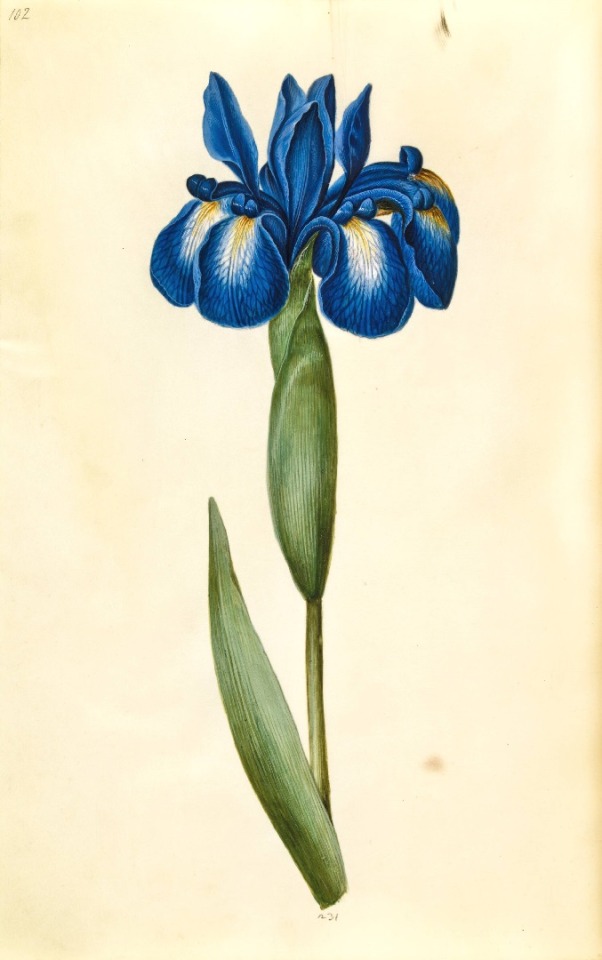
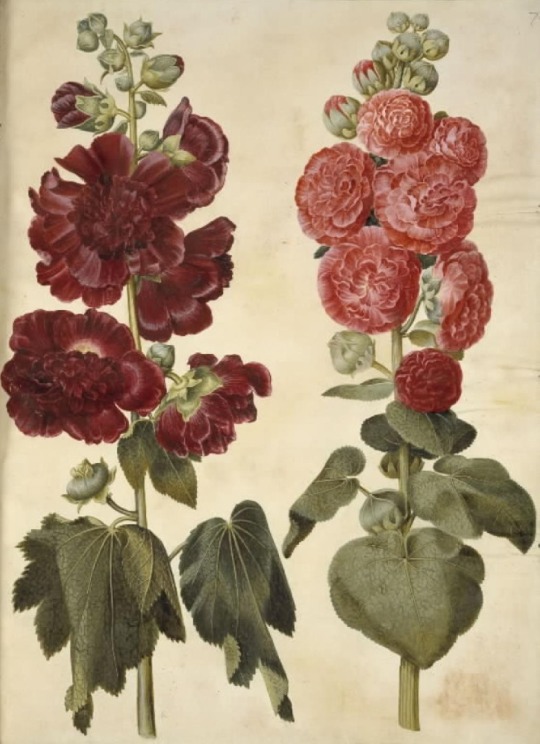
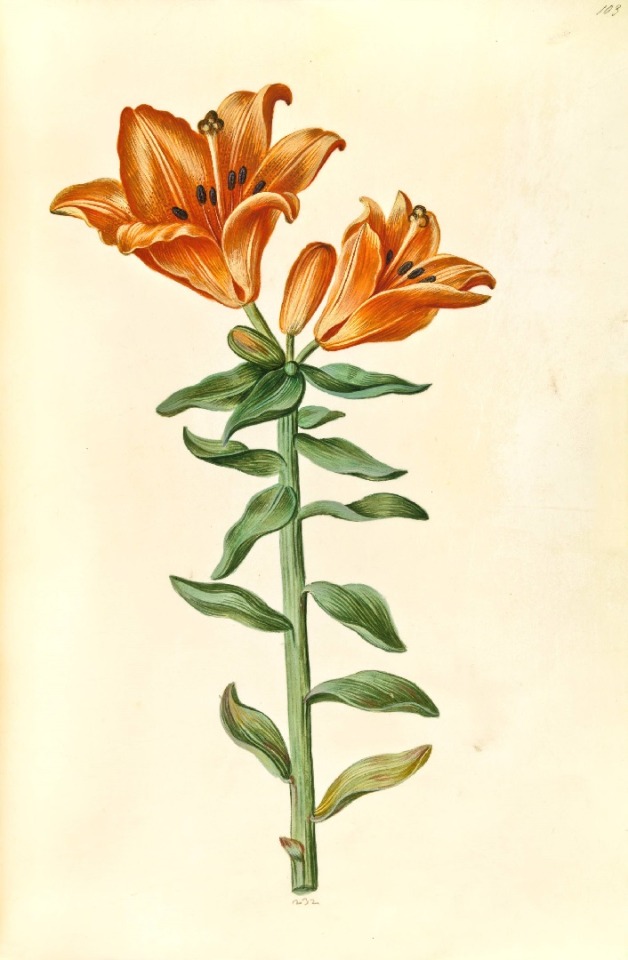










Hans Simon Holtzbecker
Common sunflower - Mourning iris - Silk peony - Crown emperor
Opium poppy - Garden tulip - Silver ragwort - English iris
Hollyhock - Fire lily
from the Gottorf Codex (Florilegium), 1649-59
#hans simon holtzbecker#book illustrations#gouache paintings#naturalist art#old art#botanic taxonomy#baroque garden#floral design#german artist#national gallery of denmark#flowers are pretty
26 notes
·
View notes
Note
as a first principles type of person. I saw the "effective for getting good fast" part and my immediate assumption was you were talking about the "trying to understand the most complex thing" being the better one, I think because I'm a math girl in an engineering world (degree) ie being put in a hostile environment (reality) where trying to find first principles is so fucking hard (we can never TRULY isolate and fix variables of the universe and it upsets me can't the electrons STAY IN PLACE while we look at them?)
thank you for this insight because truly the caveat is that it probably depends more on how available the pedagogy of one or the other is. in hexcasting specifically all of the first principles are there, you get a book with them, and if i were a patient person (i am not) i could work my way up to complex castings.
i think dismantling complexity does get you somewhat good much faster, whereas first principle derivation gets you really good somewhat slower with less gaps in knowledge and a deeper understanding since you necessarily must fully grasp the principles to build out with them. it's fun and sexy to turn yourself into a markov chain of intelligent input/output without comprehending the values of each part but boy howdy does it cause me problems. but i suppose it's not always possible to reinvent geometry just to truly work from the first (<- says a person who quit a geometry textbook last year because i refused to look up the originating proof of a problem about congruent lines and triangle orthocenters bc i couldn't reinvent geometry in a week).
i suppose ideally one would just... balance the approaches but also i may not be patient but i'm incredibly stubborn. and that's how you end up learning to write code in a language you don't even know the name of
#peter answers#incidentally this is how i became a quickbase dev but start sobbing wailing weeping etc every time someone tries to make me use pipelines#it might be SQL that i know bits of? i hope it's sql bc i really like the syntax of whatever QB formulas run in#genuinely i love this ask so much i love thinking about these things. taxonomy is my favorite sin#also your point about isolating first principles perfectly illustrates why taxonomy is inherently sinful which delights me
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Cover art: Secondary School Biology
#biology#illustration#sketch#character design#monster#scientific illustration#entomology#comic#zoology#evolution#science#taxonomy#black hole#astronomy#space#outer space#solar system#octopus#aquatic#under the sea#paleontology#dinosaur
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

🚨 A team of scientists, led by Phil Morin of NOAA, have published a new paper formally proposing two “new” species of killer whale: Bigg’s killer whales (Orcinus rectipinna) and resident killer whales (Orcinus ater).🚨
More than fifty years ago, researchers began studying the killer whales found off the west coast of North America. One keen-eyed scientist, Dr. Michael Bigg, noticed that there appeared to be two kinds of killer whales: a smaller, more gregarious form that fed on fish and a larger, stealthier type that fed on marine mammals. He and his colleagues dubbed the fish-eaters “resident” killer whales and the mammal-eaters “transient” killer whales (who were later renamed Bigg’s killer whales in his honor).
Two female Bigg’s killer whales in Washington (top) and a male and female resident killer whale in Alaska (bottom)


Many decades later, scientists have been hard at work trying to resolve whether or not these two forms are different species. It is not an easy task. This requires a thorough investigation into many factors, including evolutionary history, genetics, morphology, ecology, and behavior. In this paper, the researchers lay out all of the evidence and conclude that these two forms warrant elevation to species status.
As newly proposed species, both need new scientific names. There have been numerous killer whale species proposed and described in the past by other naturalists and researchers, including those in the North Pacific. Unfortunately, there are no type specimens— individual specimens upon which the first descriptions of a species are based—available for killer whales previously described from the North Pacific, so the researchers were left to examine drawings and illustrations of killer whales in the North Pacific in the late 1800s by Scammon and Cope.
The authors propose “Orcinus rectipinnus” for Bigg’s killer whales and “Orcinus ater” for resident killer whales. “Rectipinnus” presumably refers to tall dorsal fins, and “ater” means “black” or “dark” in Latin. Of note is the fact that a female killer whale from California originally examined and described by Scammon as “Orcinus rectipinnus” had seals in her stomach, suggesting she was a Bigg’s killer whale.
In addition, the authors note they are consulting with Indigenous tribes for a new common name for resident killer whales.
What’s next? In marine mammal biology, proposed taxonomic changes are reviewed by the Society for Marine Mammalogy’s taxonomy committee. If accepted, these species revisions become “official.” This has been an eagerly awaited paper by many in the field of killer whale biology and it is a great accomplishment, made possible by decades of research by scientists around the world.
A big thank you to lead author Phil Morin for letting me preview the manuscript and for answering my numerous questions in preparation for this post!
Read the paper here!
#killer whale#orca#science communication#marine biology#marine mammal#cetaceans#marine mammals#orcas#whales
541 notes
·
View notes
Text
My mom bought me this book for Christmas
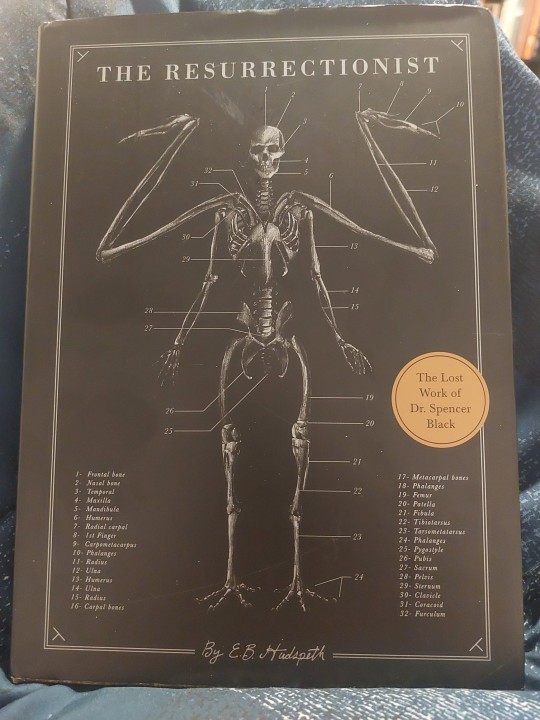
The Resurrectionist by EB Hudspeth, a fantasy field guide full of anatomical illustrations of monsters and cryptids.

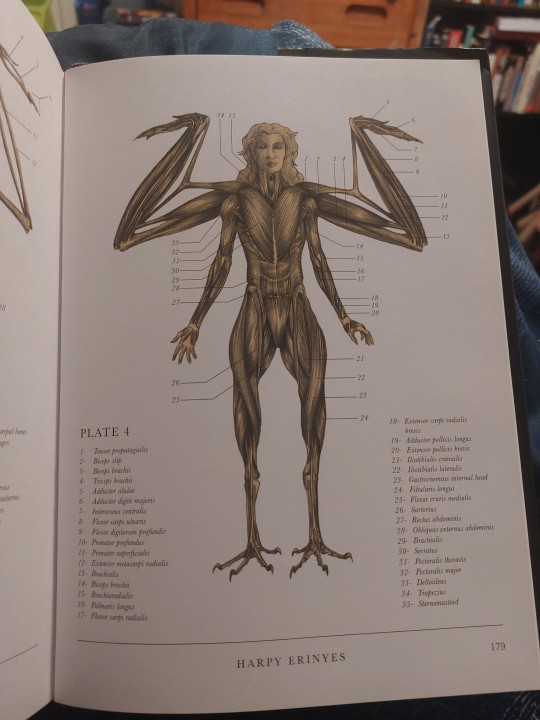


The musculoskeletal systems are fun to look at, but not nearly as in-depth as I would have liked. If you have more than a passing knowledge of taxonomy (or in my case, access to Wikipedia), a lot of the details fall apart under scrutiny
The harpy has four upper limbs connected to one shoulder girdle; it shouldn't have arms, only wings
The sphinx is not classified as a mammal, but is still somehow in the family Felidae with cats (and like the harpy is also drawn with only two girdles despite having six limbs. I will give the author credit for giving the sphinx a keel for the wing muscles to attach to)
It lists the Hindu deity Genesha as a cryptid, which is a no-no.
Cerberus is also explicitly not a mammal, but somehow still a canine (literally in the species Canis with wolves, dogs, and coyotes)
Both mermaids and dragons are listed as members of the order Caudata; the only extant members of Caudata are salamanders, which kinda makes sense for dragons, but not so much for mermaids (also, the author keeps playing it fast and loose with cladistics; both mermaids and dragons are in the same order despite being in different classes, and while dragons are explicitly said to be amphibians, mermaids are given the fictional class mammicthyes, which means mammal-fish. At that point, why not just call mermaids amphibians? Why make up a fake latin hybrid name?)
But what bugs me most of all is the classification of the Minotaur as its own order of mammal when in mythology it is explicitly described as a hybrid of two known species (made possible only by the cruel machinations of the divine, but still)

To use actual taxonomical nomenclature, the minotaur's species would be B. taurus × H. sapiens (specifically B. taurus♂ × H. sapiens♀; there are, to my knowledge, no legends of H. sapiens♂ × B. taurus♀). That's how ligers, tigons, mules, zorses, pizzly bears, narlugas, etc., are described.
If I had written this book, I would have leaned more into evolutionary biology. Most land animals have four limbs because they all evolved from boney lobe-finned fish, which split off from the boneless sharks and rays millions of years earlier, so any six-limbed vertebrates would need to be descended from a fictitious category of six-finned fish which would either be an offshoot of boney fish/tetrapods (I guess they'd be hexapods, though that term refers to insect arthropods), OR a precursor to boney and cartilaginous fish that both clades split away from much earlier (it's easier to lose structures than to gain them, so it makes more sense for a six-limbed ancestor to spawn four-limbed descendants than the other way around).
Think about how different elephants are from humans, and humans are from aligators, and aligators are from penguins, and remember that they all evolved from the same ancestor tiktaalik, an amphibious fish that existed some 375 million years ago. Imagine a precursor six-limbed species and how diverse all its descendants would look after 400 million years. Save for the occasional instance of convergent evolution causing two unrelated species to independently evolve similar body plans to fill the same niche, tetrapods and hexapods would look nothing alike. There would be very little recognizable overlap between the two. A six-limbed "pegasus" would not look like a real world horse, and a six-limbed "dragon" would not look reptilian/dinosaur-ish, for much the same reason that giraffes don't look like frogs; they're just too distantly related. Bonless sharks and boney fish and whales/dolphins all have similar looking bodyplans only because their environment requires the same hydrodynamic shape, while terrstrial vertebrates are much more physically diverse.
#biology#anatomy#monsters#cryptids#cryptozoology#book of monsters#evolution#evolutionary biology#evolutionary history#taxonomy#cladistics#science#hard fantasy#hard science fiction#hard science#tetrapod#hexapod
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo
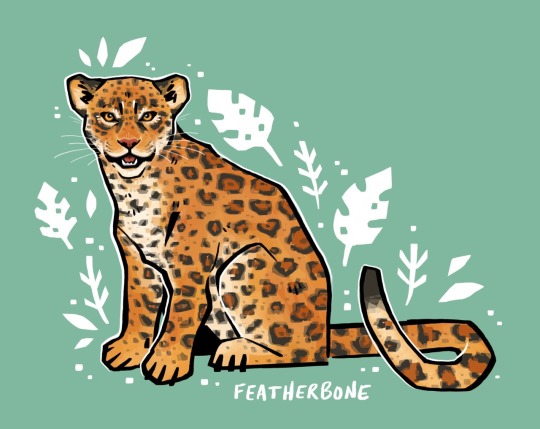
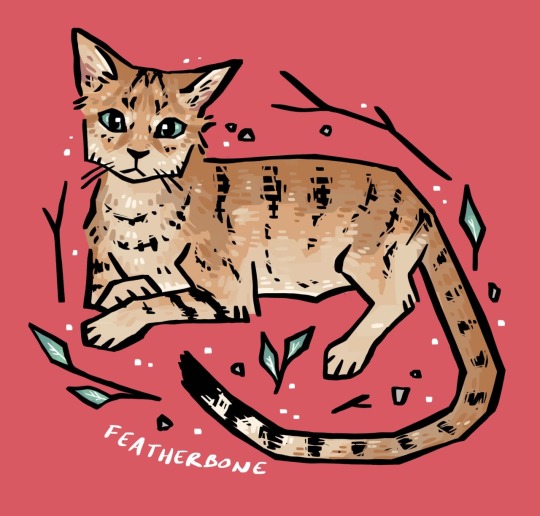
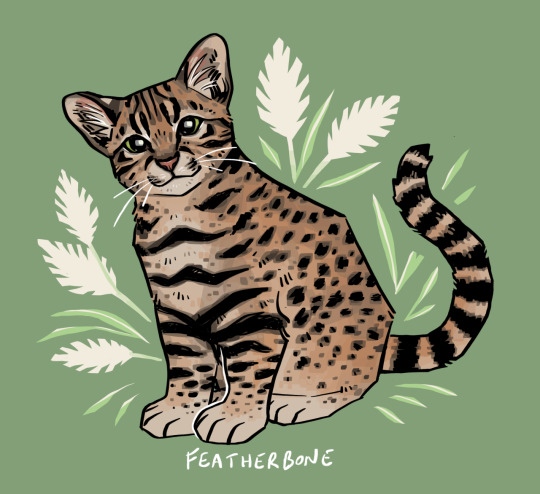










i’m coming up on a year of hosting a creature sticker club and i’ve drawn over 200 animals so far!
here are some of the felids i’ve drawn this year. big cats (pantherinae) are distinct from small cats (felinae) in that big cats car roar! except for the snow leopard. taxonomy is a weird science.
lion, bengal tiger, jagarundi, jaguar, sand cat, geoffroy’s cat, snow leopard, fishing cat, cougar, canada lynx !
[ID: illustrations of the above listed felids, - individual image descriptions in the linked individual posts. end.]
#cat#cats#big cats#small cats#wild cats#feliform#felidae#thats probably more tags than will actually functions whoops#everyone look at these cats#menagerie
714 notes
·
View notes
Text
when robots got muscles
You can blame @centrally-unplanned for this post. She(?) wrote...
The ‘chrome’ designs pioneered by illustrators like Hajime Sorayama (Sexy Robot from 1984, for example) tended to be more in vogue at this time (or just…a hot girl, who is apparently a robot, trust me bro), you don’t see designs like this too commonly until later (ask resident robo-fetishist/animator expert @canmom for details on that timeline).
After a challenge like that how can I refuse? Although the question is ‘when did robots get muscles’, this turned into something of a historical survey of robot designs from the 80s on with a throughline of biomimesis.

(Originally this was just going to be an excuse to talk about Ghost in the Shell... but I gotta be thorough.)
This was all brought on from this picture from a 1989 fanart magazine...
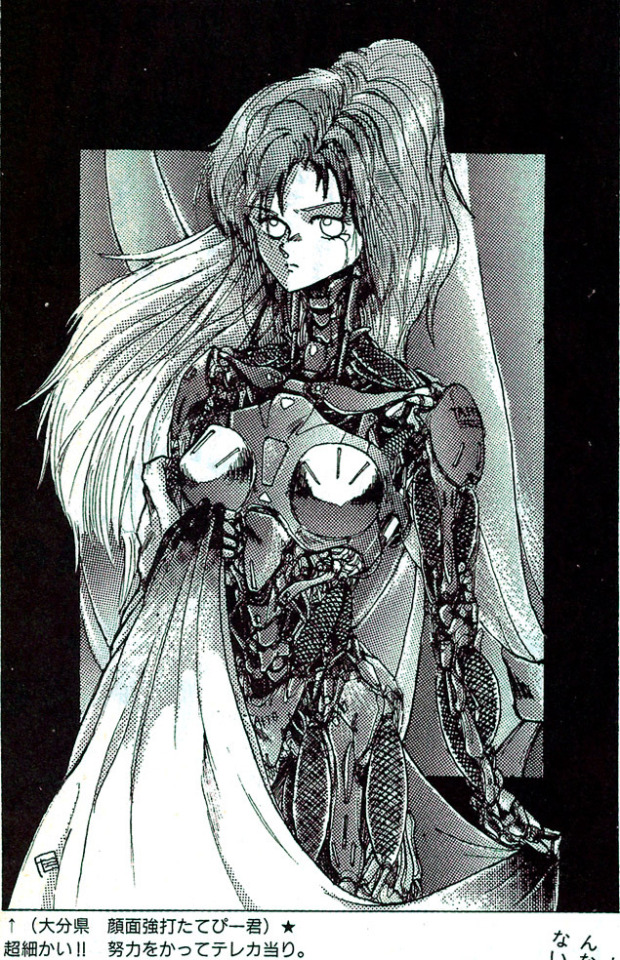
by an artist going by ‘Facepunch Tatebi-kun’ (顔面強打たてびー君, Ganmenkyouda Tatebii-kun). I remarked that it was interesting to see these kinds of ‘robot muscles’ in a picture from 1989, since I thought that kind of design became popular in the 2000s.
On some reflection, I think I gotta revise that opinion! I think ‘robot muscles’ became a thing around the mid 90s in anime; in the West I think it took a bit longer. But you can also see precursors already before that.
So. One thing artists are super into is biomimetic robots. That is, robots whose form (and perhaps function) is similar to animals, especially humans. The word ‘android’ referring to a human-like automaton dates all the way back to the late 19th century, but the modern ‘android, robot, cyborg’ taxonomy apparently became established around the 40s.
There’s two types of humanoid robot that get a lot of play, especially in anime. One is the convincingly humanlike cyborg, which is the same size and shape as a normal human; the other is a what we call in English a ‘mech’, i.e. a big robot you can sit inside.
Of course, if your androids just act like humans all the time, then there’s not much point having them be robots. To really create the frisson of contrast between human and mechanical forms you have to show the mechanism somehow. This could be because the machine isn’t perfectly human-like, and has visibly mechanical joints - take a look at the works of @sukabu89 for very inventive depiction of this theme - or, the android could be damaged or undergo maintenance.
When you attempt to translate biological forms into a more mechanical design language, the traditional way has been to use hard, rigid shapes, since these make the contrast especially clear. In more recent designs, particularly as we started to see real robots with ‘artificial muscles’ such as the ones created by Boston Dynamics, we get another sort of design language to express ‘mechanical parts’, and robots start having more biological forms with exposed plasticy muscles.
So let’s tell the story. We begin at the end of the 70s.
the dawn of mechaguro
For an early example of ‘mechaguro’ (a term I’m applying very anachronistically!), when a robot gets smashed up, we have Alien (1979). This film did a ridiculous amount to define sci-fi design language, and of course the alien itself blends mechanical and biological forms, with its glossy black surface allowing it to seem to melt into the exposed pipes of the spaceship. But let’s focus on the character Ash, a secret android who is broken apart in the second half of the film.

When Ash is torn apart by the alien, his insides consist of weird white plastic beads and a milky fluid that seems analogous to blood. It’s not clear what the function of any of this tech is - it’s intended to be vague and mysterious. The outside is biomimetic but the inside is anything but. He has a kind of artificial skin which resembles a latex mask.
The Terminator films are another major touchpoint for 80s science fiction. Late in the film, Arnie starts taking damage which reveals the Terminator skeleton underneath his fake skin.

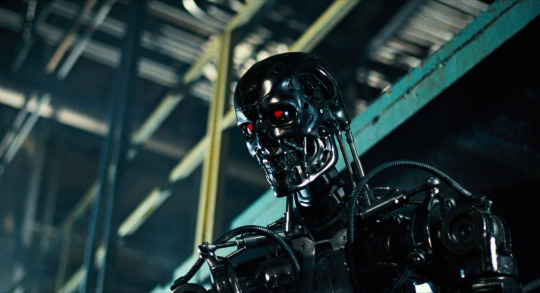
The stop-motion Terminator model is basically designed according to the principle of ‘replace human bones and muscles with hard metal bits’. So you have a metal skull, metal clavicles (which are pistons for some reason), metal shoulder blades, hydraulic pistons generally in the places where muscles are. e.g. in the above picture you can see pistons that stand in place of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and in this picture...
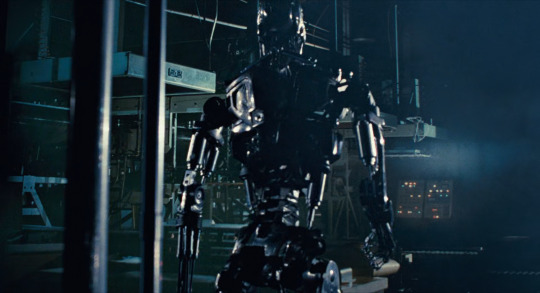
...you can see metal scapulae and piston biceps and triceps and a piston. The shoulder joint by contrast built in a very non-human-like way. Also there’s random tubes everywhere lol.
That’s generally how androids are portrayed in the 80s. The ‘droids’ in Star Wars are similar; C-3PO is an arrangement of metal plates with gaps suggestive of underlying mechanical details and rudimentary joints and pistons.
In Blade Runner, we have the Replicants, humanoid robots - but by the premise of the film, they are essentially indistinguishable from humans. So when the Replicants die, we never really get to see their robo-innards.
and now, anime
OK, that’s the big four Western 80s sci-fi movie series; what of anime? Of course, androids in anime go all the way back to Astro Boy. But most of these early designs don’t really focus on mechanical details all that much. Super robot designs are more like tokusatsu suits than anything. There were certainly instances of impressive mechanical animation in the 70s, with early experts including Kazuhide Tomonaga on Space Battleship Yamato. Then there’s Hayao Miyazaki’s episodes of Lupin III Part 2 which featured proto-Nausicaa flying a prototype of the robots from Castle in the Sky. It would be some years before anyone could come close to matching these!
The original Gundam in ‘79 famously started the ‘real robot’ movement [Animation Night, so let’s take a brief look at how a Gundam fits together.
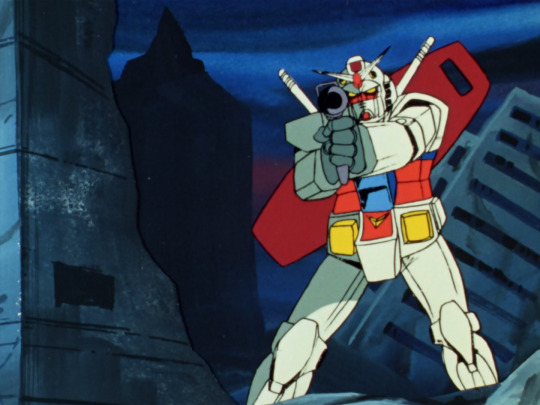

Generally speaking, the way Gundams are drawn in Gundam ‘79 is kind of rough. The methods to animate these rigid mechanical systems in super accurate perspective were just not yet established at the end of the 70s, certainly not on a TV budget. The actual joints on the Gundam are left very vague, but it broadly speaking seems to move like a human in armour.
But the OVA boom was about to begin, and while it would be a while before we saw the heights of Headgear/Production I.G./Gainax, things were going to change a lot. Mechanical design and animation was about to get much more sophisticated very very quickly.
In 1982, we have Super Dimension Fortress Macross, with robots that transformed into fighter jets. Its robots are designed by Kazutaka Miyatake, who cut his teeth doing mechanical design for Space Battleship Yamato and Daicon. The Macross TV series introduced the world to the animation of Ichirō ‘Missile Circus’ Itano. [AN64] A plane with legs... honestly looks kind of goofy, but Itano’s ambition to have a highly mobile 3D camera that could move in ways that would simply be impossible in live action marked a huge step up in how robots are animated. And this would get refined even further in the film Do You Remember Love.
In terms of design, we’re really moving our inspiration from ‘tokusatsu suit’ to ‘military hardware’ here. A Macross suit has to look like something that could transform into a plane, so its silly little arms and legs have to look kind of plane-like. In any case, we are definitely still in a world of hard and rigid robotics.
Dallos (1983-4) dir. Mamoru Oshii is known as the first OVA, if not the first successful OVA [AN115]. It features a variety of mining robots on the surface of the Moon, which are generally less humanoid, taking their design cues from JCBs...

...as well as humanoid robots with fairly clear joint patterns...

...and more humanoid robots too.
The eponymous Dallos, however, is a huge humanoid robot that looks like this...
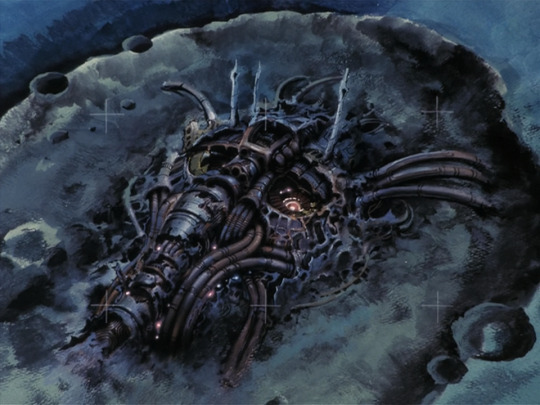

Here we have a pile of mechanical shapes that vaguely calls to mind a human face. It’s suggestive of motifs we’d see later in works like Akira.
A year later in 1985, Megazone 23 really kicks off the OVA boom in earnest [AN 103]. It also has a robot, in the form of a transforming bike that can become a humanoid piloted mech...
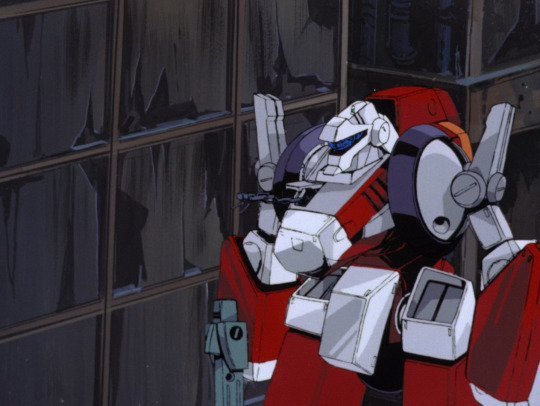

You can see mechanical designs and shading have become considerably more detailed; its motion is a lot more complex as well with a ton of indulgent background animation shots. The actual details of the bike -> robot transformation are rather brushed over. But to sort of sum up the design language: we have organic but hard-edged shapes contrasted by inorganic but round shapes. (These terms ‘organic’ and ‘inorganic’ refer mostly to symmetry and a sense of ‘flow’ in the shape.) There are few right angles as such, but a lot of broadly boxy topology. The shapes are broken up by elaborate specular highlights in complex shapes, a motif of the later Kanada school.
OK, but that’s all variants on ‘rigid robot’ so far - what about the androids? What about the more directly biological designs?
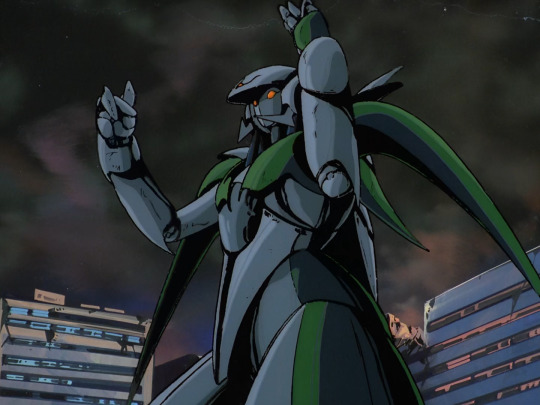
Following the enormous success of Megazone 23 Part I, Toshiki Hirano got the chance to adapt his favourite lesbian cosmic horror hentai manga Fight! Iczer One into a rather more tame OVA which released from 1985-87. In terms of mechanical design, this starts to do some interesting moves towards blending biological and mechanical forms...

Of course it has a robot in addition to the requisite bishōjo and lightsabers. In contrast to the boxy shapes we’ve seen so far, the robots in Iczer-One have a much more curvy organic sort of design language. Still, there is not a lot of emphasis on the precise details of mechanical articulation outside of select shots. (It is however notable for the first ever Obari punch!)

Despite the change in shape language, these are still very clearly animated as metal plates and not yet muscles.
In 1984 we have a very important film (for this narrative, and in general), Nausicaa of the Valley of the Wind, the film that created Studio Ghibli. Here we have the ‘God Warriors’, giant humanoid weapons with the ability to shoot a massive laser out of their mouth. Rather than robots, these are very much biological in nature, having to be grown in a kind of cocoon. In the film version of Nausicaa, an incomplete God Warrior is released, leading to an iconic scene animated by Hideaki Anno in which the God Warrior attempts to blow up the oncoming wave of Ohmu.

The God Warrior’s melting flesh is gorgeously animated, bubbling and sloughing off in great big lumps as the skeleton pokes out from underneath. Throughout, Nausicaa is full of beautiful and impressive animation of both machines (mainly planes) and biological (the giant insects), but the God Warriors, as human-made lifeforms, bring the two together. However, this strand wouldn’t be especially followed up on for a long long time.
Right, but what about Bubblebum Crisis (1987-91)? That is, after all, the iconic 80s robot girl OVA. It’s inspired heavily by Western robot-related films like Terminator and Blade Runner; here we have ‘Boomers’ (never stops being funny) as androids that can appear convincingly human. Like the Terminator, the underlying metal parts can burst out. Here we have a metal frame designed to resemble muscles, and also metal tentacles.
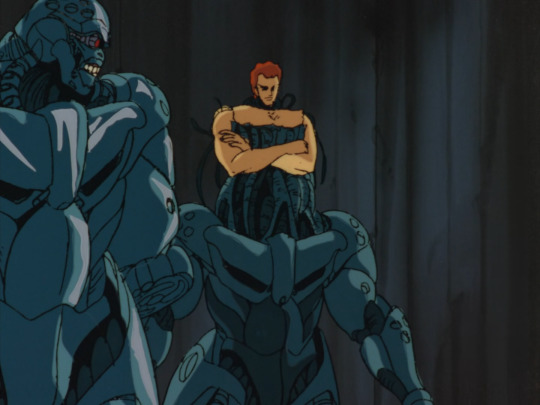
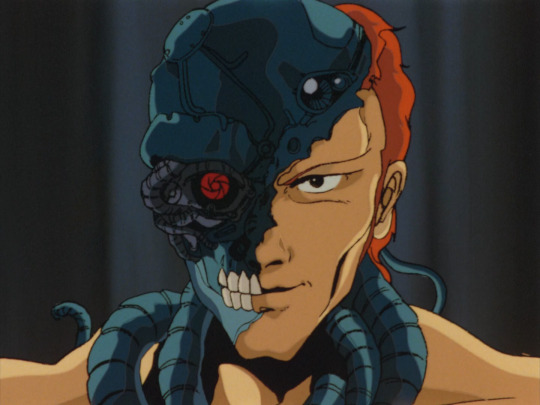


The shapes of these robots are a lot more organic. The robot neck has tubes that sort of resemble the neck muscles, metal plates that resemble pectorals and abs and deltoids and biceps and so on. You’ve even got a direct riff on the Terminator ‘fleshy face falling away to reveal metal skull with glowing red eye’! Under the plates there are clusters of tubes which also heavily resemble muscles. Also you’ve got the classic ‘three small circles’ motif there.
Contrasted against them are the Knight Sabers, who aren’t cyborgs as such but fight in powered exoskeletons which fit the design motifs of robot girls.
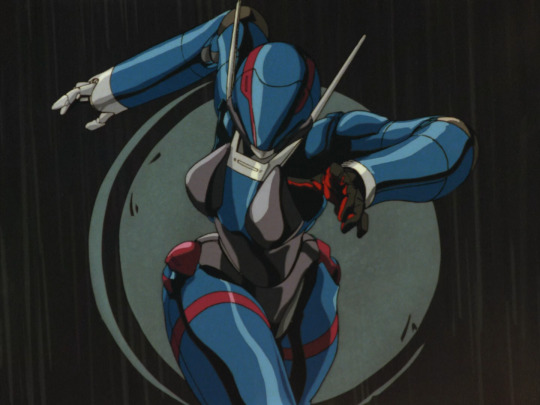

These suits are quite form-fitting, with a rubber under-layer and metal shells on top. There is definitely some attention paid to how they’ll articulate around the joints. One very recognisable 80s motif is the sort of extending spike thingies you can see on her hat there; there’s also the jets that extend out behind the suit. And, you have that multi-layer shiny highlighting of course!
Still, the way the characters move in Bubblegum Crisis is still very squarely Kanada School poses; big movements, lots of held poses accentuated by flashing and line boil, not a lot of concern for conservation of momentum or anything like that.
For a contrasting strand we can look at the rise of the ‘Otomo school’ (if you will) of realism. Around the end of the 80s, a pool of talented animators were gathering around Katsuhiro Otomo. Their most famous work is Akira, but I’m actually going to begin with Robot Carnival (1987), a wonderful anthology of short films from 1987. This features a huge variety of interpretations of the concept of robots.

For example, for Kōji Morimoto, later co-founder of Studio 4°C, the robot is a kind of cobbled-together steampunk Frankenstein’s monster. It’s a very cool design with all sorts of asymmetries and exposed parts suggesting its cobbled-together nature. And although all the robot does in this short is stand up and then fall over, a great deal of attention is paid to the little details of its articulation and its movement through space.

Presence, directed by Yasuomi Umetsu, is notable for its steps in the direction of realism - Umetsu’s characters are hyperdetailed and in some ways over-drawn. The opening shots establish this is a world where lifelike androids are common, when an android gets his head kicked off and stolen by children. Here the robot-as-doll metaphor comes in, something that will be increasingly central in the next decade. The robot girl is essentially a human-sized doll in a room full of other toys. Her creator smashes her to pieces with a wrench; later her ghost visits him as an old man. We see the girl attached to a bunch of wires, but she bleeds like a human.
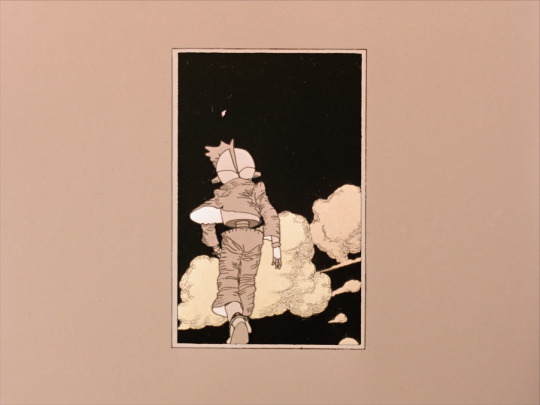

Cloud by Manabu Ōhashi features another humanoid robot, an Astro Boy-like child recognisable as a robot based on his segmented torso and legs and robotic ear... cones. Here the robot is a standin for human emotions, the boy’s struggles projected onto the constantly changing sky as he walks against the wind.
Strange Tales of Meiji Machine Culture: Westerner’s Invasion by Hiroyuki Kitakubo (later to direct Golden Boy, Roujin Z and Blood: The Last Vampire) is a sendup of mecha shows in which two very goofy looking steampunk robots operated respectively by Japanese and Western crews duke it out, laying waste to the city around them. The Japanese robot is basically a big wooden samurai...
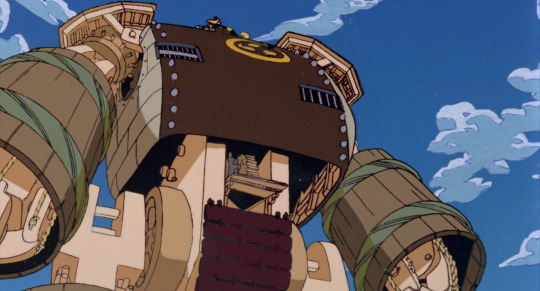
and the Western (more specifically American) robot is, uh

sorta big barrel with little eyes on top? I’m not entirely sure what the deal is with this design!
That’s really not relevant to our story tbh I just think it’s a neat short.
Chicken Man and Red Neck, by Takashi Nakamura, features especially distinctive robot designs. The film is kind of a dream sequence in which a terrified drunk man witnesses the revels of the machines of Tokyo, transformed into robots; the robots are extremely shaped, moving through a world that is pretty much just pistons...
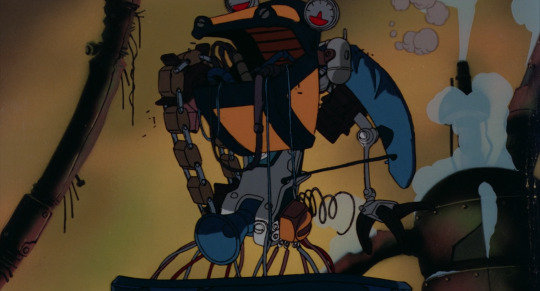
These robots call to mind the dancing demons in Fantasia’s Night On Bald Mountain sequence, or even Bosch.

Otomo’s own segments feature the Robot Carnival itself, a vast mechanical structure built as... well some kind of entertaining spectacle, but which now drives around the post-apocalyptic wasteland dropping robots which explode as bombs. It’s cute.
OK, to wrap up the 80s, we gotta cover Akira (1988) [AN34]! Akira has plenty of impressive mechanical animation of helicopters, hovercraft thingies, satellite lasers and of course the famous bike, but it doesn’t really feature robots as such - but what it does have is a blending of mechanical and biological forms in its climactic sequence where Tetsuo’s psychic powers go out of control. First, wires start to spread like the roots of a plant from his robot arm - less an actual machine and more something he assembled with his psychic powers...

He takes a bullet, and the mechanical wires and muscles start to blend together and spread out like a slime mold...
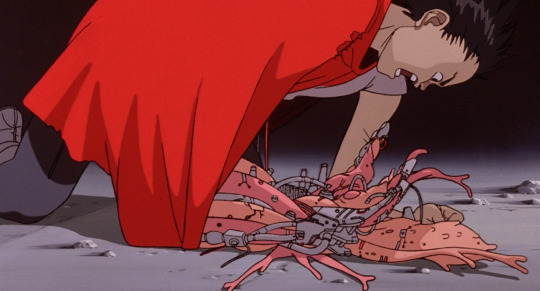
...which he can extend as essentially a giant tentacle.
When his powers fully go off the rails, he bulges out into big blobs of flesh which have both veins and wires running over them. These burst out of the metallic parts as well.

He turns into essentially a giant biomechanical baby.

Did Akira invent these images of blending biology and machinery? Probably not, but I’m not really familiar enough with manga of the time to say. What can at least be said is that Otomo’s absurdly meticulous style could really sell it. Otomo was truly a god of perspective and detail; Akira the film was an enormous, prestigious production that threw ludicrous effort and resources towards realising his vision (which doesn’t mean it paid its inbetweeners much more...). A lot of the animators who worked on Akira would go on to be prominent in...
the 1990s
So, the 1990s. If the 80s was dominated by the later Kanada School, the new movement of the 90s, at least as far as film animation goes, was ‘realism’.
But before we get onto that, let’s take a brief look at Gunnm (1990). Known as Battle Angel Alita in the West, this manga by Yukito Kishiro depicts a world in which most people are cyborgs; it was adapted to an OVA by Madhouse in 1993 and became wildly popular overseas. Its protagonist Gally, aka Alita, starts out the story as a wrecked cyborg body like this...
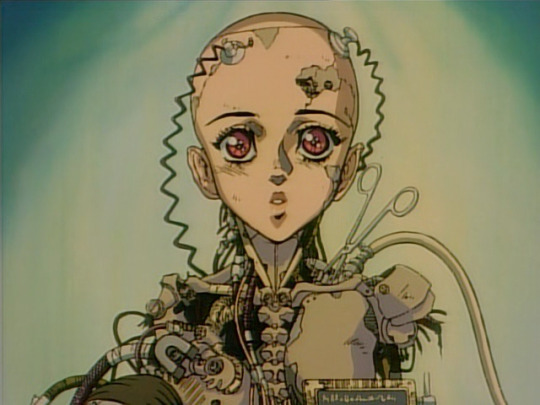
Looking at this design, you can see similar patterns as we have so far. We have metal clavicles, metal sternocleidomastoid muscle, metal pectorals, metal spine. There aren’t robot muscles, per se, but there’s a lot of attention to detail on mimicking biological shapes.
Before long she is rebuilt (twice in the manga, once in the anime). Her new body is like this...
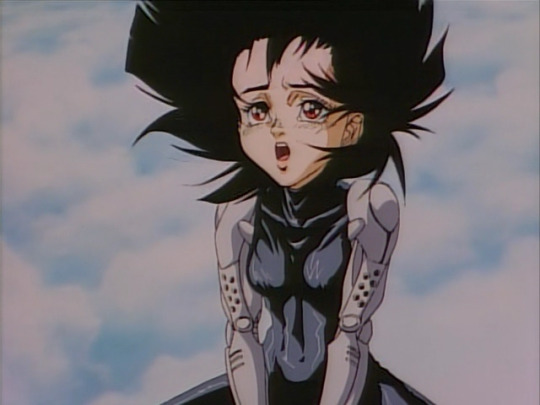

...which is to say a skintight bodysuit in the middle, and metal arms. These arms, although designed in a way that indicates hard surface and with a hinge joint at the elbow, are designed in a way that mimics the flow of muscles in a human arm. By contrast, her sorta-love interest Yugo has a body like this:
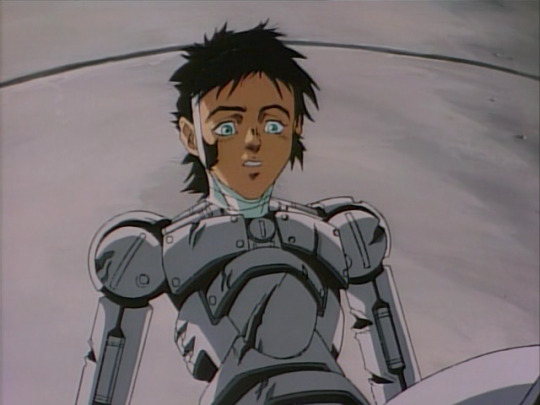
which gets mashed to pieces in the finale of the OVA. There’s a striking mechaguro scene in which Gally catches Yugo, but leaves him hanging by a fraying arm, which snaps, leaving him to fall to his death. Compared to later iterations of the ‘robot arm torn apart’ device, this one’s relatively light on detail...
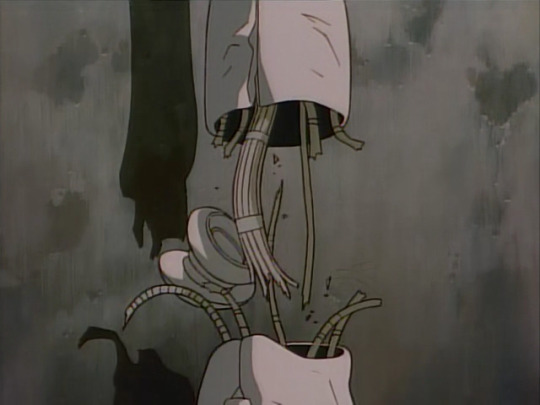
Cyborg bodies in Gunnm are used as a visual indication of character type. Gally has curves but also sleek robo muscles: she’s a Beautiful Fighting Girl, sweet but also extremely powerful. A huge ‘muscular’ cyborg with wide shoulders is likely to be a brute. Yugo here has much more plain, simple shapes with visible bolts, not precision pieces like Gally.
I don’t know how much of this originates with Gunnm. I’m sure the idea of cyborg girls was in the air long before, but this became an influential example on the tail end of the time of the 80s bishōjo. One device that is notable here is the idea of a ‘full body cyborg’, which is only human down to the brain (or perhaps not even that). Body swapping is a major theme in Gunnm, something that would be expanded on before long...
And if that was going out, what was coming in? Let’s look at Patlabor, which traces the evolution of the Headgear artistic collective and IG Tatsunoko into Production I.G.. This is about as down to earth as giant robot stories can get, with robots as just everyday machines used for work and by the cops. But where things really go nuts in animation terms is the opening to Patlabor 2 (1993).
youtube
Here you can see some of the most impressive sequences of mechanical animation ever drawn. We see pilot Noa testing out the robot, and especially notable are the scenes of the hand flexing and of walking. Enormous attention is paid to the articulation of joints. The robot’s hand can swivel 360 degrees, unlike a human; however, like a human, the articulation of the fingers seems to be controlled by hydraulics in the forearm (whereas in humans, the muscles and tendons in the forearm control our fingers). When the robot’s foot steps, it flexes like a real human foot, with believable joints, and a sensible arrangement of pistons to absorb force.
It’s not imitating a human’s muscles, but the attention to the details of the robot’s mechanical design serves precisely to draw our attention to the ways it’s like/unlike a human - the robot’s hand impossible motion immediately contrasted with its pilot shot from the same angle. And the perspective drawing is absolutely impeccable. The robot is made of purely rigid structures, and the way rigid structures articulate is not at all how a human’s joints articulate.
The sequence above was animated by Atsushi Takeuchi. But across the board, the bar was getting pushed for mechanical animation. For example, observe this cut from Mobile Suit Gundam: The 08th MS Team (1996-1999), in which the robot tears off its own arm and beats up another robot. The precision of the way the joints are animated and the way the robots move in space is just completely on another level compared to what Gundam had been doing a couple of decades prior.
Anyway, we’re here to talk about robot muscles, and we’re just a few years out from that now!
The year that robots got muscles, at least as far as anime is concerned, is 1995.
You can probably guess the next part. In 1995, we get Eva and GitS. Let’s start with GitS, to continue the Production I.G./Mamoru Oshii thread. The opening sequence of GitS, animated by - who else could it be? - Hiroyuki Okiura - has to be one of the most iconic segments of video ever drawn. Here’s a merely 720p youtube upload but go and find the place you have GitS stored on your hard drive and watch it in proper quality eh.
youtube
OK, yes, a lot of it is a naked lady floating around, sue me or whatever. But the sense of form. We see early on an appearance of ‘robot muscles’, here closely resembling real muscles...
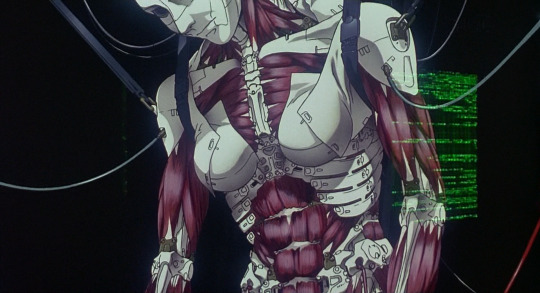
We can see from the way this is drawn that it’s made of a combination of artificial muscles, solid segments, and flexible, fabric-like panels. One of my favourite shots at the beginning shows the solid segments of the skull clicking into place. Here we have a very clear contrast between the angular, hard edges of the mechanical pieces against the organic forms of a human body.
Elsewhere in the film, we see various incredibly cool bits of ‘wouldn’t be fucked up if a body did this‘, like the fingers...
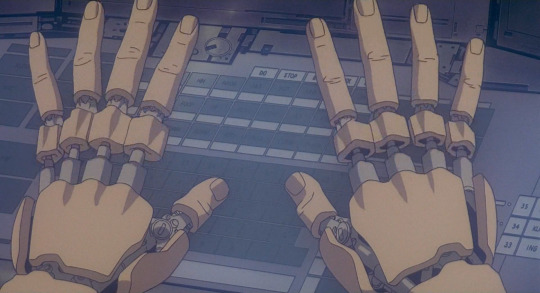
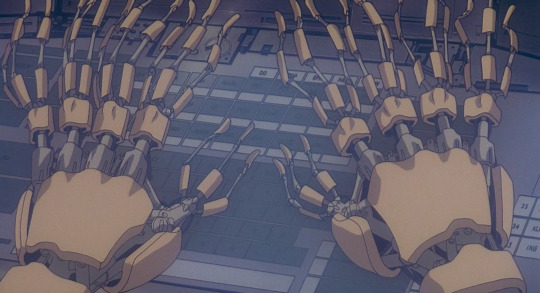
Here, what we expect to be soft biological fingers is contrasted with unexpected rigidity, mechanical joints under a shell.
Also in this scene we encounter a robot body that has been stripped of her arms, legs and hips but is nevertheless still alive...


most extraordinary hacker in the history of cybercrime and you have your titties out and yet you still can’t get them to stop misgendering you, smh
For the Terminator, having its body smashed up and continuing to walk was a demonstration of its strength. Here, as would become perhaps an increasing motif, having a robot body is a source of vulnerability: people can do things to you that would kill an ordinary human but you keep going through it. Not surprisingly, ‘robot body maintenance’ is a recurring porn device. (One that GitS deploys in SAC s2).
But of course this all builds up to the all time classics of mechaguro scene at the ending where the Major attempts to tear off the hatch of a spider tank. Muscles ripple individually under the surface of her skin, her arms bulge in exaggerated contraction, and then her arms fully tear apart under the force.

Here, we’re showing her as mechanical not by contrasting rigid forms with biological ones, but by exaggerating the biological ones to the point of doing something extremely unnatural. Human muscles do not generally flex in such an individual way, nor are they strong enough to tear the arm apart, but robot muscles? Yeah, they could do that. This sets up the next scene where the Major lies unnaturally still, but can still exert control through hacking through her union with the Puppet Master.
Robots holding onto something so hard their arms explode has become... if not a recurring image, then at least one that was called back decades later in Violet Evergarden.
The final scene of GitS brings back the image of robot-as-doll, with the Major’s consciousness now uploaded into a black-market robot body that resembles a child in a dress.

This is further expounded on in Oshii’s second GitS movie Innocence (2004), with its Ballade of the Puppets in the soundtrack as Batou and Togusa (and eventually, the Major) are attacked by essentially an army of ball-jointed doll gynoids. The puppets’ movements are extremely unnatural and erratic acrobatics, constantly flipping all over the place; when hit by bullets, panels pop open to reveal the underlying brass skeleton. It’s a very cool image. (The thing that lets the sequence down is the extremely dated CGI and aggressive digital compositing.)
It also has Donna Harraway as a literal cyborg!
Now, the GitS movies didn’t drop fully formed out of nowhere, but draw on the work of Masamune Shirow. The manga has a somewhat different design sensibility than the movie, distinctive and shiny as all Shirow’s art. It is more rounded and organic, less cold.
So, the basic design of a cyberbody originates with Shirow. You can see it on this page (unfortunately from a flipped version, translation Dark Horse):

You might be able to determine from how the nurses are dressed that, yeah, the GitS manga is in significant part fetish porn. But really nerdy fetish porn, which is the best kind. This chapter is almost entirely dedicated to explaining how cyborg bodies are constructed in great detail, from the ‘sensory film’ (that’s what’s being applied in the opening to the 1995 film) to the hair implantation.

It’s interesting seeing how some of the more out-there designs of the manga, like Chief Aramaki, are transformed into the realist style of Hiroyuki Okiura. It’s Okiura, so it works great of course.
I don’t know if there are manga examples of such detail about cyborg bodies that predate Shirow.
Anyway, that’s just one of the two punches dropped in 1995. The other is Neon Genesis Evangelion. To the pedants: sure, the Evas are not actually robots, but they’re giant cyborgs that play the role of ‘robot’ in the story and they look like robots so I’m counting them.

Anyway, the thing about the Evas is they are incredibly lithe. They run, rip and tear and swing heavy objects around in a way that’s both weighty and distinctly biological. Their bodies are extremely flexible compared to prior mechs (look at how much the spines bend in that Iso cut from EoE!), but not without hard, rigid components such as the shoulder towers. Their jaws are bestial but feature mechanical-like components like interlocking hexagonal teeth and jet-like vents. They are in short a fantastic design that blends biological and mechanical features.
The impact of Eva on just about everything can’t be overstated, but as far as robot design, well. There certainly were works that leaned on the precedent set by Eva, as for example RahXephon, which also treats robots as something spiritual, prone to popping into a blob of weird little bubbles just like in Eva.
There’s a great deal missing from this account. I am very focused on anime because I’ve watched a lot more anime than I’ve read manga or played games from this period. So I’m sure there’s major foundational works I’m missing here!
the 2000s
When did the West start to catch up? eh that’s subjective - David Cronenberg was way ahead of the game! - but specifically in the sense of robots with mechanical muscles, I think the major points in the timeline go a bit like this.
In 1999, there’s the Matrix, which leans heavily on anime. This features a similar ‘robot takeover’ premise to Terminator, but here it’s biomimetic robots modelled after squids, with clouds of constantly moving tentacles that sweep behind them. After making a cool half a billion dollars, the Wachowskis decided to pay all their favourite anime directors to make short films. I’m not going to comment on every part of the Animatrix, since most of it isn’t really relevant, but I will point to this horrifying cut by Takeshi Honda in The Second Renaissance in which a robot woman has her clothes torn and then skin bashed off by a mob. The framing, motion, her expression of abject terror, and the ‘reveal’ of her ‘true’ nature, all viscerally call to mind a trans bashing.
On the manga side, a big one to mention is Gantz, a gory nihilistic seinen manga which ran from 2000-2013. The characters in Gantz fight in special latex-like suits which take on the appearance of muscles while engaging superstrength, but can also sustain damage that causes them to drip fluids from ports located at the neck and become fatal to their wearer. Gantz was adapted to anime by Ichirō Itano in 2004, but I haven’t seen it so I can’t comment on any notable animation.
Cyborgs are a favourite subject of games, but in the 2000s, games are really pushing art direction and biopunk stuff is in. Half Life 2 (2004) has its spider-crab like Striders and dropships and so on. Oddworld: Abe’s Oddysee (1997) bases its whole concept around the sheer variety of weird creatures that would inhabit its dystopian factory. And I gotta give a shoutout to Septerra Core (1999) - in case one other person has played that lmao
At some point after 2005, Boston Dynamics became a viral sensation thanks to their robot BigDog. BigDog is just welded steel and hydraulics, but its lifelike hopping movement style definitely brought to mind the idea that the future of robots is going to be in biomimesis.
So, 2007, here comes Crysis to melt your PC! This is an FPS with the not-uncommon premise of being a supersoldier fighting (country America hates) and also aliens, but its gimmick was that you have a special exosuit that wraps around your body with artificial muscles, making you much stronger and manlier or whatever.
youtube
This is indicated by a visualisation that could be right out of a toothpaste ad, where tiny little balls drop into the character’s pores and somehow go straight into the bloodstream which is of course a void full of flying red blood cells. And so on. It sold the game, though! The ad there focuses almost entirely on the suit and not the character wearing it, who is basically an irrelevant soldier man. What it entailed in gameplay terms is that you have a mode switcher so you can have strength or armour or invisibility or whatever. But it’s cool military superscience, you see!
Anyway. Not like my preferred flavour of cyborg is any less stupid I guess x3
In the same year, Bayformers started. These films’ robots are honestly just visual noise, there’s so many moving metal shards going every which way that it’s next to impossible to discern any sort of underlying mechanical principle. A similar ‘overwhelming business’ visual effect would be applied the next year in Iron Man, kicking off the MCU. So mechanical muscles definitely weren’t the only expression of ‘hyper-advanced robot’ in Western visual media in the late 2000s.
I’m going to end my story with two more games: Horizon Zero Dawn and NieR Automata.
Horizon features a world inhabited by a large variety of robot animals, using the peak of AAA rendering techniques. The robots are designed to be biomimetic after both modern animals and prehistoric ones, and feature a combination of hard surfaces and softer biological muscles. For example, a robot horse:
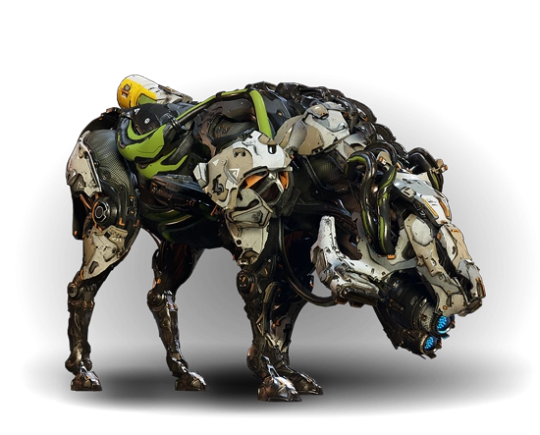

The discipline of making designs like these now has a name: it’s called ‘hard surface modelling’ and it involves boolean operations and bevels and other techniques designed to create a balance of hard edges on a surface against the smoother parts. The design language of Horizon says that the hard plates are white, the soft parts are very dark and may be patterned like a cloth texture, and there can be small colour accents here and there.
I think you can definitely see the influence of Boston Dynamics’s robots (and recent military tech in general) in these designs, iterated on through a decade and a half of increasingly intra-referential concept art. They are visually very busy designs, but there are a couple of recognisable features that draw attention by being inorganic, such as the cylindrical fuel tank at the back. Vitally, the silhouette is very readable.

This robot T. rex for comparison serves as a world boss monster, and you can see it’s got a bunch of military looking attachments that look like radars and missile launchers and so on. As real tech evolved, so too did our idea of what a scary robot ought to look like.
So, that’s where this kind of design pattern has gone in mainstream games.
Now to finish, a brief comment on NieR Automata. Its designs draw hard on those of Ghost in the Shell. Visually it draws a strong contrast between the Machine Lifeforms, who have inorganic shapes (spheres and cylinders) and very visible and plausible mechanical joints, and the doll-like androids, who might as well be human (although A2 provides some contrast in an android who is damaged enough for the underlying materials to show through). The mechanical nature of the androids is communicated by the acrobatic way they move and the interface elements, and dead androids you find in the field - and later when they start losing arms and stuff, it’s a whole thing. But just like humans in Yoko Taro Games, they’re capable of dying in a puddle of blood.
(I guess if you take one thing from this post it’s that if you’re a robot, don’t expect to keep your arms.)
Robot muscles gives you a chance to give both the ‘anatomy porn’ of drawing something very precisely right, with the added bonus of giving you a reason to draw the muscles écorché, and the chance to make it weird and defamiliarised by splitting it with mechanical elements. In short... they look cool!
In this whole post I’ve basically not touched at all on illustration. I can point to a variety of illustrations of robot girls, but in terms of periodising them, I just don’t think I know enough. Though it’s safe to say that cyborg bodies in various states of construction or disrepair are now a mainstream of concept art - and that Ghost in the Shell is usually cited as an influence. I don’t know if robot muscles ever truly became the mainstream way to depict a robot, but it does feel like they’re increasingly common.
One artist I will briefly mention (besides sukabu), mostly bc I think they’re neat, is Haruyo Megurimu, who draws these very intricate designs of ‘necrotech’ which is sort of very biological robots extending out of human bodies - limbs extended on long spindly insectoid strands, jaws splitting open, that kinda thing. Can’t say who influenced them or anything but it’s a compelling extension of the idea into a particular corner of aesthetic space.
And that’s all I’ve got I think. There’s definitely big gaps like. More recent sci-movies. Western comics. Nevertheless, that’s an arc.
If you’ve read this far: thank you for indulging my autism.
787 notes
·
View notes
Text

Mustelids of the British Isles
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
It Came From The Trash Heap (We Don't Talk About Kholumolumo)
A wastebasket taxon is what happens when species can't be easily classified and instead get hurled into a "catch-all" category.
…But that's not the only kind of taxonomic tangle that can befall a new discovery.
When a scientific name is assigned to a new species, but it isn't given a corresponding formal description and type specimen, it becomes a nomen nudum – a "naked name". Without a proper description and assigned holotype the name isn't valid, and the new species isn't technically accepted by the wider scientific community.
This has even happened to some surprisingly famous names. In the 1920s Velociraptor mongoliensis was briefly given the nomen nudum "Ovoraptor djadochtari" before getting its much more familiar name when it was officially described. Meanwhile the giant pterosaur Quetzalcoatlus northropi was stuck as a nomen nudum for decades, only finally getting a proper published description in 2021.
And there's another particular long-standing nomen nudum that became mildly infamous – "Thotobolosaurus", the "trash heap lizard".

Discovered next to a literal trash pile in the village of Maphutseng in Lesotho, a few scattered and broken bones of this "prosauropod" sauropodomorph dinosaur were first found in 1930. But it wasn't until the mid-1950s that a more extensive bonebed began to be unearthed at the site, and over the next decade over 1000 fossil fragments were collected.
In the mid-1960s the remains were initially classified as belonging to Euskelosaurus browni (which is now considered to be a wastebasket taxon), but just a few years later in 1970 the "Maphutseng Beast" was re-evaluated as a species new to science. It was referred to as "Thotobolosaurus mabeatae" – based on the local name of the discovery site, "Thotobolo ea ‘Ma-Beata" (trash heap of Beata’s mother) – but this name was never actually formally published.
Despite "Thotobolosaurus" being an undescribed nomen nudum it nonetheless went on to be repeatedly referenced in scientific literature over the next few decades, and appeared in several popular dinosaur books (even as recently as 2020!).
In the mid-1990s it was alternatively named "Kholumolumosaurus ellenbergerorum" in a Ph.D. dissertation, with this name derived from the kholumolumo, a reptilian creature in Sotho mythology, and the Ellenberger brothers who worked on the site. But this also didn't count as a formal publication and instead became a second nomen nudum for the species.
Eventually, 90 years after the first bones were found and 50 years after the debut of the name "Thotobolosaurus", this long-neglected sauropodomorph was finally given a proper published full anatomical description in 2020.
And it also got a third name, this time officially valid, based on the second one from the 1990s: Kholumolumo ellenbergerorum.
For something associated with trash for so long, Kholumolumo is actually now one of the most completely-known prosauropods. At least five different individuals were present in the collected fossil material, possibly as many as ten, and between them most of the full skeleton is represented – with the exception of the skulls, which are only known from a couple of small fragments.
We now know Kholumolumo was rather heavily-built, with chunky limb bones and unusually short shinbones. It would have been one of the biggest animals around in the Late Triassic (~210 million years ago), measuring at least 9m long (~30') and weighing around 1.7 tonnes (1.9 US tons), but despite its size it seems to have still been bipedal.
Due to the highly disarticulated nature of the bones the fossil site may have been a "bone accumulation area", a place where dismembered bits and pieces of different carcasses were regularly carried to be eaten by a predator or scavenger – essentially a trash heap, fittingly enough. A couple of "rauisuchian" teeth have actually been found among the remains, which might indicate what was chomping on these particular Kholumolumo.
———
Nix Illustration | Tumblr | Twitter | Patreon
#it came from the wastebasket#nomen nudum#taxonomy#kholumolumo#thotobolosaurus#prosauropod#massopoda#sauropodomorpha#dinosaur#paleontology#art#science illustration#paleoart#palaeoblr
290 notes
·
View notes
Text
hmm okay to round up some current disparate tmagp thoughts into one place:
-> the fear taxonomy: I'm not quite sure where I sit on the desires theory currently, but I think it's worth noting that while both of our case subjects from the first episode were explicitly afraid of the spooky things happening to them, none of the rest have been, and I think it's really interesting that tom the horror blogger's whole problem was that he was so desensitized to fear it made him foolhardy (the exact thing our lovely ms georgina barker overcompensated so hard to avoid). yes, you could pick probably any archives statement and try to frame it around a desire instead of a fear because that's how character motivations work, but I don't think it's wrong to point out that since episode two all of our subjects have been remarkably chill about the Horrors happening to them. I'm not totally onboard with the desires at time of writing, I think there a few details that don't quite line up with that idea, but I'm still keeping a pin in the theory.
I also don't think it's wrong to point out that things like "music so hauntingly beautiful it makes a crowd tear itself to bloody pieces" and "paranoia and eye-related gore popping up in conjunction to the magnus institute" are familiar scenarios and seem to match up to the entities as we know them. those are very specific motifs connected to very specific types of Horrors and I think saying it's random coincidence that we're seeing them again is a bit of a weird take.
-> norris, chester, and augustus. in-universe, these voices appeared out of nowhere about a year ago, and one of the central mysteries set up so far is "what the hell is up with all this weird tech?", I think it is a perfectly reasonable assumption to think these voices are part of the mystery and not just an excuse to get jonny and alex's voices in the show. if that were the case, why would there be a third voice? yes, this podcast is meant to be comprehensible to new listeners, but I don't think that rules out any direct ties to archives, I think part of the function of having fresh protagonists who don't know anything about the events of archives is that, if the audience needs to learn anything about the first show, they can learn it along with a viewer-surrogate character.
personally, I think it very unlikely that the voices are literally jon, martin, and jonah's actual consciousnesses trapped in computers, I think those characters' stories are done and there's something funkier happening here (neither them nor not them but a secret third thing, yknow), but dismissing any idea that the voices are related to the characters, again, feels like a weird take.
-> gwen bouchard. honestly I feel like the way the production team have treated gwen's connection to elias vs the way some fans have come at is kind of illustrative. I've seen a couple of groups of fans get weirdly smug about the idea that we don't know gwen is related to elias, her name could just be a red herring, meanwhile on the tmagp post-launch stream everyone there took it as obvious that gwen is a bouchard and thus related to elias. not everything is red herrings, guys. it would be an extremely weird writing move to set up a bunch of stuff with clear links and parallels to archives and have it all be meaningless.
118 notes
·
View notes
Text

I'm just going to start talking about my celestials each month to give you all some low effort and fun(for me) content. Also doing full illustrations of them as well, with some design notes at the end.
My interpretation of loodvigg, named Fhobia Denta Latrostratous (they're one of the three celstials with a full name at the moment) is a fair bit different from other's interpretations of it for extremely personal reasons. They're a tad bit strange, and creepy looking, but overall they are a compassionate (in their own strange way, like almost everything about them) and creative individual that's held as a role model for all shadowkind. They also have a lavender colored ring around their pupils so their eyes aren't fully pink, which is the main difference from the cannon loodvigg, along with the subtly different feathers, lower body, markings on the abdomen, and scales on the arms.
They are generally unexpressive (tonealy, the main way monsters express their emotions) yet VERY emotional. Over the years they gradually became more in control of their emotions due to sheer life experience, but they are still a little more irrational and driven by emotion than most of the other celestials.
They hate being touched, loud sudden/repetitive noises, math, people or things that get too into the meaning of art and other stuff like that, and the texture of a few things like fish meat or coarse fabrics. There are very few things they have a neutral opinion on, one of which is the taste of blood by itself.
They love keeping up their appearance in most situations, for example, their hair isn't naturally like that, they use their saliva like hair jell and specifically style it to look like that, also they would be absolutely rancid smelling and filthy with their diet of fresh meat and preferred locals of wet warm caves. They spend a lot of time cleaning themselves, which is extremely rare for monsters. They also like eating more than your average monster, they eat like a toddler because of how preoccupied with eating they get, collecting/making taxidermy and other oddities, and all critters, especially invertebrates though.
They are majorly interested in biological sciences, specifically preservation and taxonomy. They gave the celestials and dof era monsters/critters their scientific names(no I don't have scientific names for the celestials yet, I've kinda ran out of ideas for scientific names tbh). They happen to spend a lot of their time in a very large cave network with a lot of different types of caves that make good enclosures for keeping critters to study.
They care a lot about the other celestials as they are siblings and gets very angry if something bad happens to them, only if they feel it's undeserved, their empathy is a bit wacky and inconsistent.
Also most shadow monsters tend to share in its odd mannerisms, sometimes the behaviors show up in completely non shadow affiliated monsters and no one knows why.
Disclaimer (I think that's the right word), yes you guessed right, Fhobia and the large majority of the shadow monsters are autistic, the term isn't used in universe as the monsters don't have a word for autism as they aren't that into psychology and "the way that monster is" has worked in place of a proper word historically, monsters aren't into categorizing others.
as for design notes and process here it is! all the stuff in red boxes are final.

183 notes
·
View notes
Text
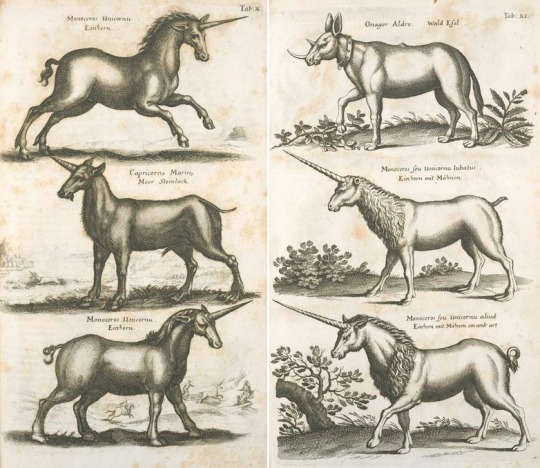



So in writing the history of identification/taxonomy chapter for The Everyday Naturalist, I spent a lot of time poring over scans and reprints of very old western European natural history books. This included a lot of medieval bestiaries, which were usually illuminated manuscripts with the colorful, stylized artwork so common from that era. It wasn't until the European Renaissance that you started seeing more of an emphasis on realistic artwork, and by the time you get to the transitional period between the late Renaissance and the Enlightenment engravings based on original drawings were very common for illustrating books on animals and plants.
A lot of the images passed around as "antique scientific illustrations" stem from the mid-17th century Historiae Naturalis written by John Jonston and illustrated by Matthäus Merian the Elder. By this point in history numerous European nations were sending ships around the globe to bring back resources, which included a significant number of natural history specimens. The sheer variety and biodiversity represented by these gave naturalists in these countries an overwhelming amount of fodder for study, classification, and publication.
However, there was still the perennial problem that not everyone writing or illustrating these seemingly exotic species could access them in person. Medieval bestiaries, and their predecessor the Physiologus, tended to mix natural history with religious allegory, and often the writers had never actually seen the species they were describing. Since they had to go on secondhand (or thirdhand, or fifteenthhand) information, things sometimes got lost in translation like a big game of Telephone. And the situation was still the same by the time Jonston and Merian were working on the Historiae Naturalis.
Which is why that venerable attempt to catalog as many of the animals in the known world as possible includes, amid pages of real animals like molluscs, deer, and bats (categorized with the birds!), you also had descriptions and engravings of six different unicorn species. Jonston did remark that he was going entirely on the word of others and cited his sources wherever he could, but it seems as though most of them were treating the unicorn as a separate beast from the rhinoceros or antelopes. (You can find a scan of the entire Historiae Naturalis de Quadrupedibus here, if you want to read for yourself.)
This is probably the last major natural history work in which unicorns and other mythical animals would be presented as equally real as flesh-and-blood animals; once the Enlightenment got into full swing, the sciences sought empirical evidence, and hearsay was generally no longer considered good enough for publication. So there's something a little charming about this text that bridges the gap between the ancient bestiaries with their blurring of fact and fiction, and the modern emphasis on chasing down the truth behind the myths.
#natural history#Historiae Naturalis#scientific illustration#antique illustration#vintage illustration#bestiaries#science#unicorns#animals#wildlife#nature#Renaissance#medieval art#medieval history#bestiary#history#art history#antique animals
74 notes
·
View notes
