#critical thinking and its importance in education
Text
Critical Thinking and its importance in Education
Critical thinking skills in education processes and the importance of thinking critically for a student who attends any education programme. Developing the ability to think critically is an important element for modern education approaches and models. This study intends to give a framework on the concept of thinking critically while teaching or learning. The world is getting both more technical and more complex day by day life environment, that’s why the necessity for education increases for each growing generation. The skill of thinking critically is generally accepted as a very vital stage in every field of learning, particularly in the last decades. As a study draws a general suggestion on the importance of critical thinking skills.
critical thinking not only describes the ability to think in accordance with the rules of logic and probability, but also the ability to apply these skills to real-life problems, which are not content-independent. . Critical thinking can provide you with a more insightful understanding of yourself. It will offer you an opportunity to be objective, less emotional, and more open-minded as you appreciate others' views and opinions. By thinking ahead, you will gain the confidence to present fresh perspectives and new insights into burden some concerns.
Thinking is the base of all cognitive activities or processes and is unique to human beings. It involves manipulation and analysis of information received from the environment. Such manipulation and analysis occur by means of abstracting, reasoning, imagining, problem solving, judging, and decision-making. The mind is the idea while thinking processes of the brain involved in processing information such as when we form concepts, engage in problem solving, to reason and make decisions. The history of researches on thinking depends upon the time that human beings recognized that they think. Thinking is one of the features that distinguish humans from other living beings. Thinking is the manipulation or transformation of some internal representation. In this sense thinking ability is the basic case of our life because all of us need to achieve an objective; on the other hand humans have relations in society and whereas nobody is alone. Descartes argued that thinking is reasoning, and that reason is a chain of simple ideas linked by applying strict rules of logic. Both learning and thinking are the concepts which support and complete one another. When considered from this point of view, whereas learning style and critical thinking concepts have different qualifications, it can be stated that they can be used jointly. Likewise, when literature is examined, it is seen that there are researches handling learning styles and critical thinking concepts jointly.
“Critical thinking is thinking about your thinking while you’re thinking in order to make your thinking better.”—Richard W. Paul
When the term of ‘Critical Thinking’ is searched, it is understood that there are meanings of it which are suggested in the frame of philosophy and psychology sciences but in general sense this term has not got a definite meaning. ‘Critical’, derived from the Greek word kritikos meaning to judge, arose out of the way analysis and Socratic argument comprised thinking at that time. According to Critical Thinking Cooperation (2006) critical thinking is an ability which is beyond memorization. When students think critically, they are encouraged to think for themselves, to question hypotheses, to analyze and synthesize the events, to go one step further by developing new hypotheses and test them against the facts. Questioning is the cornerstone of critical thinking which in turn is the source of knowledge formation and as such should be taught as a framework for all learning. Students are frequently conditioned in their approach to learning by experiences in teacher-cantered, textbook-driven classrooms. This situation is a disturbing case for contemporary educators, and for this reason they would rather choose the latest models and methods which are more effective in directing students to thinking. Critical thinking occurs when students are analyzing, evaluating, interpreting, or synthesizing information and applying creative thought to form an argument, solve a problem, or reach a conclusion. The aim of Critical Thinking is to promote independent thinking, personal autonomy and reasoned judgment in thought and action. This involves two related dimensions:
1. the ability to reason well and
2. The disposition to do so.
Critical thinking involves logic as well as creativity. It may involve inductive and deductive reasoning, analysis and problem-solving as well as creative, innovative and complex approaches to the resolution of issues and challenges.
#critical thinking#importance in education#critical thinking and its importance in education#blog article#daily blogs
1 note
·
View note
Text
just saw someone say that they didn't need to "get the point" of a literary novel, because they read for "entertainment" and "not to contemplate the human existence," and i think that is probably the most insane take on literature i've ever read. of course it was on tiktok.
#it's not pretentious to read for substance btw#that's just. enjoying and understanding literary works#dig below the surface a little#breaking down the barriers of academic pretension doesn't come with openly admitting a lack of understanding & interest in literature#or questioning its importance#it comes with accessible education for all#and sharing the ideas in these works with the masses#it's such a lie that you have to be some genius to read and understand literature. just think critically a little bit#literature#english literature#bookblr
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
i can't even get angry about american zoooomers falling for bullshit bc we see it all the time with boomers and x and millennials and the common denominators are 1) american education 2) the human brain
so we can and possibly should give breaks to people falling for conmen up to a point
#when you find yourself breaking into the capitol on 1/6 then you have a problem and have crossed the point#but i suspect the lack of knowledge and the tendency to wanting to believe certain things over others is going to probably kill us soon#our big brains = our downfall in the end or something#the fact i had to explain to someone i work with that is younger than me and an educated progressive#that Dobbs wouldn't have happened if hillary clinton had won in 2016#bc she would have been the one with at least 2 if not 3 or 4 supreme court nominations who would have been likely more progressive than her#is atrocious#civics - history - critical thinking - these important bits of knowledge and education and skills AREN'T being taught effectively#its why people are falling for youtube and tiktok hucksters#across the political and ideological spectrum#you are not immune to propaganda or con artists#no rb bc i refuse to break containment#i'm just tired#and i see too many bad takes#t
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
seeing mass effect 2 came out just about a year before da2 is explaining a lot to me bc 1) even tho me2 seems to be a more thought out game than da2 in just about every regard it seems like there's a lot similar stylistic impulses going on 2) bioware was REALLY into 9/11 during this timeframe apparently. i don't know what was going on over there nearly 10 years after the event that made them feel like it was finally time to start dropping their 9/11 political commentary but it was happening i guess
#i mean obviously. very important event that had and continues to have major consequences in many areas of life across the world#but in my complete lack of education in the specifics i do wonder what was going on then#kind of wonder if this is a first term obama presidency thing? (i know bioware is Canadian)#like we are far out enough from the event and there is some hope what the us will start pulling back at this point#that we start getting more critical of the initial american response?#as much as neither game is particularly inspired in this regard and da2 in particular has a lot of latent islamophobia#both games are trying to be critical of conservative islamophobia and nationalism#da2 definitely thinks its being Super Fucking Nuanced (i am not far enough into me2 to know where its whole patriot act in space plotline#goes beyond just noticing that its a thing they're doing) anyway idk if any of this is true or if I'm forgetting something major going on#at the time that these games are clearly responding to so if anyone knows more i would be very currious#ask to tag
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
keep saying i don't want 2 work another retail xmas but canNOT 4 the life of me make myself finish my goddamn fucking job applications !!!!!! death & dying & despair etc. etc.
#i dont dislike the application process for gc jobs on principle BUT#it does not mesh well w/ my difficulties re: starting & finishing tasks#but like i understand why u cant just send in a resume n hit done#NOT that there are many IT listings up atm...... and ill apply 4 clerical/admin stuff too#but an IT-1 STARTS a good $10k a year higher than a CR-5 soooooo :///#which is whatever its fine money isnt everything!! ill gladly make less if it means not hating my job!!!#but i also wanna. u know. LIVE. move out of my parents house. buy brand name snacks occasionally. maybe -gasp- go on a vacation#(not 2 say i dont make an attempt at travel now but thats with very finite savings that are def only going down not up)#also extremely frustrating 2 me the emphasis put on having a degree that completely locks me out of certain job categories#like. yes. there are for sure some where having the bg knowledge is important eg. an AU (auditor/accountant) or MA (methodologist)#and there are certain skills a degree (in theory) provides eg critical thinking research etc.#but not all of us have $40k+ to get tge fancy piece of paper saying we have those things. and u can have those skills w/o a degree#and smth like an EC which needs a degree in economics sociology or statistics is so arbitrary#and maybe not necessarily actually based in the majority of work done by the majority of positions in that category#ANYWAYS not me being bitter abt education standards YET AGAIN lol#idek if i could go to uni even if i could afford it. even tho i have 2 college diplomas id probably have 2 redo my grade 12 english 😶🌫️#also if money were no object id probably go for like. film studies or smth lol not sociology#tho. ngl. if i had the willpower and determination 4 smth so rigorous (i 100% dont) accounting does seem. interesting asdffhkkfdghh#ANYWAYS pt. 2 all this 2 say this is why i instead spent $10k+ on the only possible 2 yr diploma#that can still get u in2 the higher paying public service jobs. even tho ive discovered i Dont Particularly Care for programming. :(#thats an understatement actually i was actively in hell for like 80% of that program and the remaining 20% mostly wasnt coding
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
think its time to orphan some of my earlier works
#they're just not it.#not all of them just like a few#people enjoyed them but my writing style's very different now#i mean. ok i made a lot of decisions in my earlier (younger) writing days that#they werent problematic... just maybe uninformed and not super educated. they were not written while thinking critically abt the media#and i dont wanna delete them bc i think its important to reflect on earlier choices and its good to see how much i've progressed etc#anyway. goodbye to that one pipabeth fic i wrote in 2020 i will do you vengeance by writing some pipabeth this year
1 note
·
View note
Text
I think the 'problematic media' issue is composed of two principle parts, one superceding the other.
Firstly, and the most important to address to cut the discourse off at the head; yes, media is a vector by which social systems reinforce themselves. This is the purpose of propaganda, and this dynamic is completely intelligible to us if we consider the cases of 'person whose sole source of online interaction was 4chan, and who exclusively watched History Channel hagiography about fascist war machines', or 'person who developed inappropriate ideas about sex through watching misogynistic media'. It is plainly clear that it is both possible and common for media to influence people ideologically, as an apparatus of a given social system. Material reality dictates which social systems are given ideological hegemony in media, but media is in fact an effective tool of those systems.
Secondly, while acknowledging the first point, it is not the dominating factor, here. While media can and does influence people ideologically, often commandingly so, it is not some sort of cognitohazard. It is plainly possible to watch, even repeatedly over an extended timetrame, some given piece of fascist propaganda, or abuse apologia, or what have you, without becoming any more beholden to its ideas - if anything, becoming more opposed. The crucial thing, here, is that doing so requires some level of understanding and defence against the ideas presented. Someone with no rebuttal to fascist positions, with no even kneejerk dismissal that what they're taking in is fascist, is unlikely not to internalise something if they're surrounded by fascist media. On the other hand, someone who has been innoculated with opposing political theory, who is capable of recognising the social systems being reinforced by a given communicative work and reasonably countermand them, can watch a thousand misogynist movies, read a thousand racist books, peruse a thousand transphobic news articles, and leave with only stronger convictions to oppose these systems. Clearly, the dominating factor here is not the content of the media itself, but the content of the audience - whether the audience is able to sufficiently recognise, interrogate, and oppose the messaging in a given work.
All this is to say - yes, media can and does influence beliefs, but that that influence is completely subordinate to the question of whether the audience has any level of political theory or critical analysis. A liberal reading fascist literature, not holding any real theoretical opposition to the content of fascism, is safe so long as they can recognise and reject basic fascist signifiers. A feminist is able to recognise misogynistic logic in a given work. A communist can recognise and countermand reactionary spin in a news article or wikipedia page. While the politically-unconscious man will not recognise that his favourite sitcom is instilling him with absurdly sexist views on marriage, the issue here is not the media itself. Fundamentally - the issue of 'problematic media' is one best and principally solved by the development of political theory and political education, not by any suppression of the media itself, which is cumbersome.
880 notes
·
View notes
Text
Like, yeah, we do have a real issue with the need to elevate everything we like to a certain level of importance that it doesn't really deserve in online queer spaces and I think it mostly has to do with the fact that...nobody wants to admit they really don't know much about our history so they latch onto things that were formative for them. Which tbh is fine. If you think Riverdale is foundational queer media that takes no skin off my nose. The problem comes when, because this piece of media is important to you, you cannot stand to hear criticism of it in any capacity, which leads me to my next point.
We also have an issue with thinking critically about older queer media and the circumstances surrounding its creation in online queer spaces, which again, is a result of not knowing much about queer history.
People love Keith Harring but if you bring up his relationship with the young men he used for his art and his treatment of Latino men and boys in general, suddenly, everybody wanna get quiet. People will sensationalize Dorian Corey's story and make her a spectacle out of "love" for her but won't even bother to learn about the culture she was a part of. Y'all LOVE talking about Stonewall and Marsha P but you know NOTHING about the history of S.T.A.R.R and how she was treated by some of yall "queer elders".
These issues will continue if we don't make a genuine effort to educate ourselves about our history and allow ourselves to think critically about the media we consume, even if it's important to us.
Ain't no way in hell a discussion like this should have resulted in vicious transmisogyny and threatening to call Black people slurs over a fuckin tumblr poll, yall are all way too fucking grown to be acting like this.
#thotty speaks#thotty rants#I said I wasn't gettin down in the mud with yall but this shit is getting the fuck outta hand now#tighten the fuck up#also not everybody you don't fuck with is a part of a super secret group of bigots that don't fuck with you#sometimes people online are just fuckin bigoted on their own if you can believe it!
568 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hey, CT, I've been following you for a while and I really admire your dedication as a scholar, but I was wondering about your practice of "occult red herring traps" as you put it a few posts ago.
I understand that you're trying to get people to think critically, even skeptically, about their sources of information—which is particularly important given the subject material—but since people are treating you like an expert, don't you think you have an obligation to give them correct information? If you aren't a practicing occultist purposefully trying to be obscurantist, but are writing about the topic for the elucidation of others, what is the point of inserting falsehoods into your work?
No disrespect intended, just curious about your intentions.
Few reasons:
Im not going to claim any higher educational goals here. I do this because I think it's fun to fuck with people sometimes. That said, I have rules:
I'll never lie about anything serious. When I do spread deliberate red herrings, it's things like "Goku was present in Andalusian Spain." Or St. Christopher drove to the council of Nicea in a Dodge Charger." Things that if believed would only cause minor embarrassment.
When I do lie, I always make sure it can be easily dispelled with a simple Google search or a basic fact check. Or even just thinking about it critically for two seconds. Like hold on, I don't think Goku was in Andalusian Spain because he is a cartoon character.
I generally consider it in the spirit of Occultism. I find it fun, but its also a fun way to encourage people to not take everything I say as gospel. I don't want to be seen as "person with all the right answers and correct opinions" my opinions are often dogshit. I want to be seen as "person who can point you towards actual historical sources."
462 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Owl House And Restorative Justice
At the end of Season 1 of The Owl House, it is revealed that Lilith, the main overarching antagonist of that season, was the one to curse her sister Eda, one of the protagonists, to win a tournament when they were teenagers. This information causes Eda to fly into a screaming rage and attack Lilith, and understandably so.
Eda’s curse is essentially a chronic illness, one that, in Eda’s own words, has ruined her life, being the reason she’s considered a social outcast and why, before meeting King and Luz, she hadn’t gotten close to anyone in years. In season 2, it’s revealed that the curse is why she pushed away her partner Raine to the point that they broke it off with her, and that during a particularly bad flareup, she accidentally maimed her own father, leaving him half blind and with permanent nerve damage to his hands, making him unable to continue working as a Palisman carver. The curse has ruled Eda’s life for decades now, so to Eda, this is the ultimate betrayal.
In the first episode of Season 2, Lilith has defected from the Emperor’s Coven, split the curse between Eda and herself to mitigate the symptoms for her sister, and has moved in with Eda at the Owl House. While Lilith herself still feels guilty and feels she has to make it up to Eda, everyone else, Eda included, has seemingly either forgiven her or chosen to look past it. Eda even makes fun of her for feeling bad about cursing her, and Lilith’s guilt is seemingly absent for the rest of the series.
The response to this was… Less than stellar, shall we say. A lot of people were angry, saying Lilith got away with her crimes without even a slap on the wrist, and that Eda’s forgiveness of her was far too sudden.
This isn’t the first time we’ve seen this kind of critique. Amity spent years bullying Willow after her parents forced her to break off their friendship, and when she began trying to mend that relationship, the response from fans was that Willow should have been a lot more angry at Amity, and that they went back to being besties far too soon. I’ve even seen this criticism leveled at Hunter for the things he did while working for Belos, at Vee for impersonating Luz for months to trick her mother, and at Luz for hiding the fact that she helped Philip find the Collector from her friends. And it does seem strange for the show to keep tripping on this same point again and again.
Except, it’s not really. Because I think that, when viewing this show from a different angle, those supposed flaws are actually symptoms of something very important to understand – The Owl House operates on a system of crime and punishment that is very different from our world’s.
More specifically, our world mostly utilizes retributive justice. The world of The Owl House utilizes restorative justice.
So first, what do those terms mean? Broadly, they’re two different forms of handling interpersonal disputes, or dealing with crime.
Retributive justice is the one our current justice system uses, where the focus is primarily on punishing the perpetrator. Retributive justice can mean detention, suspension, expulsion, jail time, monetary fines, some kinds of community service, exile, or in more severe cases, corporal punishment or the death penalty. It’s the lens most people view the world through, where if someone hurts you, hurting them back is the correct response.
Restorative justice is a very different approach, where you instead focus on helping the victim recover from what happened, and rehabilitating the perpetrator to prevent this from happening again. Restorative justice can look like verbal or written apologies, monetary compensation for costs and trauma, therapy for both victim and perpetrator, education for the perpetrator, mediation between victim and perpetrator, a restraining order, etc.
When viewed through a retributive lens, The Owl House lets its characters get away with a lot of shit. Lilith cursing Eda, Hunter rounding up Palismen knowing they’ll be killed, Amity tormenting Willow for years, it’s all stuff that, in a retributive environment, they should be punished for, and they’re just not. Eda is only genuinely angry at Lilith for two scenes, Amity and Willow fix their relationship very quickly once Amity starts making amends, and Hunter isn’t punished at all.
However, I believe the story of The Owl House is best viewed not through a retributive lens, but through a restorative lens.
Let’s look at the Lilith-example again. Lilith’s offense was cursing Eda, which she did because she wanted to win a spot in the Emperor’s Coven. Knowing Eda was better than her, she cast a curse on her, thinking it would only last for a day. But when the time came, Eda forfeited the match, soon after which she transformed into the Owl Beast and was pelted with rocks until she ran. The curse turned out to be very permanent, and Lilith spent the next 20 years trying to fix her mistake by working for Belos to try to capture Eda, since he promised to heal her curse.
However, when she finally succeeded, Belos went back on his promise. Instead of healing Eda, he ordered her to be publicly executed. When Lilith protested, Belos essentially told her to shut up, that it was the Titan’s will, and left her there.
So, having realized her method of fixing her mistake has gone real bad, Lilith sneaks down to the Conformatorium to free Eda herself, but arrives too late and finds Luz instead. After a brief fight they end up teaming up, and Lilith leads Luz to the elevator, but they are captured by Belos and Lilith is thrown into the cage with Eda. There, she restores Eda’s partially petrified body, and after fleeing with her, Luz and King, uses a spell to split Eda’s curse evenly between their two bodies.
From a restorative justice point of view, Lilith has done pretty much everything she reasonably could do to fix things. She’s denounced the Emperor’s Coven, returned Owlbert to Luz, helped Luz find the elevator to the execution platform, saved Eda from petrification, apologized to Eda, and while there’s no way for her to cure Eda’s curse entirely, she took on half of the curse at great expense to her own health, in order to ease Eda’s symptoms.
Eda isn’t angry anymore because in her eyes, Lilith has already fixed things with her. Punishing her more at this point is pointless. What more could Lilith do, really? What other lessons could she learn? The only thing that punishment would bring at this point would be more suffering.
Let’s look at another example: Amity and Willow.
Amity’s offense was breaking off her friendship with Willow because she was a late-bloomer, bullying her for years, and allowing her friends to do so too. Willow is left with horrible self-esteem issues because of this, and combined with her failing grades, turned her into a horribly shy and withdrawn wallflower (no pun intended). After she’s moved to the plant track she starts actually getting better, but Amity and Boscha especially continue to torment her. While Amity’s bullying of Willow does peter out over time, Willow is clearly still extremely resentful of her. In an attempt to make Willow forget their friendship, Amity accidentally sets most of Willow’s memories on fire, leaving her confused, amnesiac, and unable to grasp basic concepts like that chairs are for sitting in.
Luz pushed Amity into fixing Willow’s brain by going into her mind together and piecing her memories back together. There, the Inner Willow revealed what happened to Luz and the audience.
At this point, Amity shows her that her parents were actually the ones who forced her to end the friendship because they didn’t think Willow was a suitably powerful or influential friend, threatening to make sure Willow would never get accepted into Hexside if Amity didn’t force her to leave. Amity then apologizes to Willow for going along with it, and for the bullying, and vows to make sure her friends never mess with Willow again.
Willow accepts her apology, but also makes it clear that, while it’s a start, she’s not yet ready to accept Amity in her life again. Restorative justice has not been fully attained, because to Willow, Amity hasn’t fixed everything – Boscha and her squad are still bullying her, and still consider Amity one of them. This changes two episodes later, when Amity tells Boscha to grow the fuck up when she starts bullying Willow again, and joins her and Luz’s Grudgby team despite her personal issues to get Boscha to back off. Willow doesn’t make a grand gesture of forgiveness in this episode, but it is after this point where the two become comfortable around eachother again.
Did Willow forgive Amity too quickly for years of trauma? Maybe. If she had chosen to continue keeping Amity at a distance I certainly wouldn’t have blamed her. But in the end, Amity fixed the mess she caused as best she could, and has proven herself to want to be a better person, to want to be Willow’s friend again. She worked hard to prove herself to be a person worth trusting, and Willow decided to give that trust a chance again.
And while they did become friends again, that friendship was clearly still affected by what happened, which led to bumps that the two of them had to work through. Like in Labyrinth Runners, where Amity’s overprotectiveness over Willow makes Willow feel like Amity thinks she’s incompetent, and still only sees her as the helpless person she used to be.
Willow continuing to be mad at Amity and punishing her for what she did wouldn’t be an unreasonable reaction, but it wouldn’t have fixed anything. It would certainly have an impact on Amity, seeing her former best friend rejecting her attempts to make up for what she did, but the hurt on both sides would have continued festering, because deep down, Willow missed Amity too.
In Hunter’s case, there’s the question of whether he can even be held responsible for his actions. The Palisman-kidnapping in specific was explicitly done under duress – if he failed he would face verbal and physical abuse, and be threatened with his nightmare scenario: getting thrown out of the Emperor’s Coven.
And that’s not an empty threat either. Hunter has no magic, and Belos has drilled it into him that witches without magic have no future. Without the Emperor’s Coven, his only future prospects would be starving to death on the streets or wasting away in prison. Either way, Hunter would be alone, without family or friends, without a job or job prospects, without anyone to turn to for help. Any child would be terrified of that. Hunter wasn’t always acting on direct orders – in fact he defied direct orders to stay in his room in Eclipse Lake to go look for Titan’s Blood, and then again in Hollow Mind to arrest the rebels. But he made those choices based on the idea that Belos wouldn’t want him if he was a failure, and that he needed a chance to prove that he could still be useful.
And contrary to popular belief, Hunter does know right from wrong. He has a very strong moral compass, he’s just been forced to ignore it in favor of doing whatever the Emperor wants. To shut up that little voice telling him he’s doing the wrong thing, he uses what’s called a thought-terminating cliche, a statement that feels so fundamentally true that the argument need not continue. In Hunter’s case, that statement is “It’s for the greater good.” Sure, kidnapping his new friends and abducting Palismen to feed to the Emperor and threatening someone who’s been nothing but kind to him to take the portal key from her girlfriend and justifying terrorism makes his stomach feel like he swallowed a cactus and saying it out loud makes him sound like a horrible person – but it’s for the greater good. He’s doing it to serve Belos, and Belos knows what’s best.
So by the time Hunter is out of active danger and able to rest and recover from what happened to him… what would further punishment accomplish? He already knows that he did fucked up shit while working for the EC, and he’s proven time and time again that while he’s not fighting for Belos’s approval, he’s actually a genuinely kind-hearted kid. Punishing him now would likely cause him to react very poorly, because he’s been at the wrong end of that stick so often that he’s developed severe PTSD because of it.
And if you think restorative justice is still in order – Hunter is currently hyperfixated on making sure Belos can never hurt anyone again, and for the long term, he has expressed that he wants to become a Palisman carver when he grows up. While it won’t bring back the Palismen that were killed, it will help the current Palisman population recover and reintroduce Palismen to witches who may have had to give up theirs.
When viewed through this lens, the writing of The Owl House starts to make more sense. As a show, it is extremely forgiving towards its characters – they’re still held accountable for their actions, but as long as they’re willing to grow and learn and fix the damage they caused, they are very quickly forgiven.
However, I do understand why these writing choices can be… controversial, so to say. Because it doesn’t feel very satisfying, does it? When someone hurts you on purpose, your first impulse would be to try to hurt them back, that’s just how people work.
That’s the hardest thing to come to terms with when you become an advocate for prison abolition for example – you’re not just arguing for freeing a guy who got 5 years because a cop found weed in his pockets, you’re arguing for the release, and most importantly, the humanity of some of the most vile, disgusting people this planet has ever produced. Even now, when someone commits a truly awful crime and gets sent to prison for life, my first thought is “Good, I hope they rot in there.” But that’s not justice. That’s just revenge. And revenge is not something we as a society should want to build our justice system on.
It’s not satisfying to see Lilith go from using Luz as a human shield in her fight against Eda to sleeping on the couch in Eda’s house within 2 episodes. It’s not satisfying to see Willow let Amity back into her life when Amity has hurt her so badly before, or to see Hunter become romantically involved with Willow after he literally abducted her the first time they met. But that satisfaction isn’t really the point. Revenge is satisfying in the moment, but an eye for an eye makes the whole world blind, and if someone shows a genuine willingness to change, it’s often better to give them a chance to.
However, my final point is about what happens when this approach fails. Because not everyone is willing to change. Some people, when faced with the consequences of their actions, decide to dig their heels in and refuse to admit fault, or blame the victim(s), or use those same thought-terminating cliches that Hunter used to justify their actions, “I was just following orders” being a big one.
And thus, we come to Belos.
If Belos showed a willingness to change, a genuine one, not an attempt at manipulation, should he be given the chance to? That vengeful part of me is VERY empathetically saying no. But logically, reasonably, he should be given that chance, if only because he’s a human being and no human being deserves to be mistreated. That doesn’t mean his victims are obligated to forgive him or be around him again, in fact I think that, for the sake of Hunter’s mental health, Belos should stay as far away from him as humanly possible. But he should be given the chance to start over, to truly better himself and do something good with the rest of his life.
But Belos isn’t willing to change.
Belos is a product of a bad environment and grew up with a cult-like mentality and hatred for witches that he had to adopt for his own safety. It’s hard to break out of that mentality, but not impossible. Case in point: Caleb. The tragedy of Belos’s character to me is that he had so many chances to change, so many people to help him make that leap, but all of the people who offered him that help ended up dead by his hands because he couldn’t handle the idea that he may have been wrong.
At this point, Belos is stuck. Changing would mean not only giving up on his life’s work, but acknowledging to himself that everything he’s done, mutilating his body, killing his brother, slaughtering thousands and installing himself as God-Emperor of a population he despises more than anything in order to facilitate a genocide, was completely pointless.
He can’t admit that to himself. Especially the thing about Caleb’s death. He’s sunk-cost-fallacied himself so far into a corner that all he can really do when faced with opposing viewpoints is dig his heels in even deeper and lash out in a rage at anyone who challenges him. Even now, when his body is literally falling apart at the seams, he’s still trying to commit witch-genocide, because it’s all he has.
Restorative justice doesn’t work in this case, because the perpetrator needs to be receptive to it. Logically you would assume the show would default to retributive justice, and characters like Willow and Camila do take a very vengeful glee in imagining themselves beating the snot out of Belos. But right now, the primary motivation of the Hexsquad and Hunter in particular when it comes to Belos is to end the threat he poses. As long as Belos is alive and free, he will continue to hurt and kill people, and if he can’t be talked down, he needs to be either contained or killed to prevent him from causing more harm.
The Owl House provides, in my opinion, a very nuanced take on restorative justice. It shows how it works in action, how different situations impact what it looks like, and what happens when it’s simply not an option. It’s not the most satisfying story to tell your audience, because when someone hurts our babies we want them to suffer, no matter how sorry they say they are. But in this case, I think that sacrificing that bit of audience comfort is worth it to tell the story like this.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
i'm going to keep posting my art online, train your AI on it, I don't give a shit.
People (not corporations) enjoy art because there are stories and histories and identities behind them. It's more important that people see artists making art and that they keep sharing art by real people.
Strongly believe that at the end of the day, the mission is educating and getting younger folks excited about art in *all* its facets, from fine art to commercial art and whatever lies in between, so that they have the knowledge to critically think about what they are viewing. Otherwise nothing matters.
152 notes
·
View notes
Text
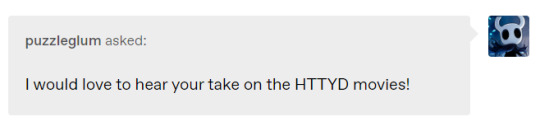
alright! we got one whole person interested, so here's my hot take:
the first "how to train your dragon" movie is WAY better than httyd 2.

i know everyone loves like, the cool warrior mom design, the romance and the "epic animation moments" in 2... but can we for a moment be honest and say the whole "hiccup becoming a leader / which dragon is the Good Alpha" plot was dumb as hell? also, the villain sucked?
the original httyd is pretty good about keeping the structural problem grounded in real societal fears. namely, fear of the unknown and of beasts. it makes sense for any ol' village dealing with such a problem. it was intelligently designed around a solid premise.
httyd 2 is like. actually, dragon taming is a big thing, even outside berk. and theres a Scary Foreign Man dragon tamer who is bad and just wants power. it's okay to other him. being a good guy is about being a protector instead of an evil, power-hungry guy... which hiccup never was anyway... so no real growth there. just be good instead of bad. wow. what a theme. very thought-provoking.
people act like httyd 3 being bad came out of nowhere, but httyd 2 was the original sin to me. it totally dropped the societal themes in favor of generic good vs evil fights and "worldbuilding" - despite having no more interesting stories to tell.
it also kind of ruined hiccup for the sake of developing him. like. his whole thing is that he can't fight, so he has to find other ways to contribute to society. he's the anti-macho hero. which ends up being important in convincing the village that dragons can be peaceful. he's empathetic to the other, because he's been othered.


meanwhile in httyd 2, hiccup's like. Cool Warrior Man, who needs to step up and be the hero king when his dad dies. he can fight just fine, because he has a cool dragon to fight with. so he's just like any warrior, but one who fights with weapons instead of brute strength. aka most fictional warriors who arent just "the heavy."
the first movie isn't beyond criticism, obviously. the animation was a little meh compared to httyd 2 - i get why visually its seen as an upgrade. plus, httyd 1 also did the thing of having like a last minute evil dragon to defeat... but that wasn't the point. the POINT was the village and its fears. the POINT was overcoming that.

whenever people list why they love httyd 2 and consider it superior, its like... lists of details. like, look at the upgraded character designs, the cool flying scenes, the affection between hiccup and astrid, or the clever way hiccup's prosthetic leg is designed.
but these are film *details*, not fundamentals.
if you told me the sequel to httyd was going to have a much more generic story, ignore the themes of the original and makes its deliberately lanky and weak protagonist into Handsome Hero Warrior Boy, i'd be like. that sounds kinda bad. but the Animation Details (tm) i guessssss
i know hiccup is still "himself" in 2 to some extent, btw. he's an inventor, he's intelligent, and he initially tries to talk to the villain. but none of that ends up mattering. its arguably looked down on by the movie, which really, really wants him to step up to be the warrior king like his dad. aka a generic Hero Strongman.

i'm not totally against evolving the themes of a work to fit new conflicts, btw. sequels should generally be different from the first movie. that's fine. that's expected.
but while the new conflict in httyd 2 IS born out of the results of the previous movie, that evolution feels very literal, not thematic.
namely, the evolution is "more people have dragons now." it builds the conflict from there. its based on worldbuilding, not on theme.
i don't think a very interesting evolution.
it kinda went from, in httyd 1: "the theme is fear of the unknown. how prejudice/ignorance manifests, educating oneself through compassion, the dangers of worshipping violent masculinity, and the importance of questioning what you're taught by society."

to, in httyd 2: "the theme is dragons. who has them? what they want with them? how can the Good Guy humans protect dragons from the Bad Guys? also, being a Good Leader means being a strong Hero Man who protects his friends," without asking any deeper questions related to the themes of the first movie.

and i'm like. guys. guys.
the theme shouldn't just be "dragons."
the theme of the first movie was NOT just "dragons." the first movie could've been about people being afraid of unicorns. or large birds. or unusually intelligent bears. it was not just about literal dragons, it was about societal fears and trying to overcome our base gut instincts.
i think this is what really plagues httyd 3: it builds on the themes of the second movie, not the first.

httyd 3 asks further questions that only really revolve around the literal relationship between humans and dragons. it does not understand any broader themes of what that relationship represents.
it clearly thinks its very intelligent for asking "what do the dragons themselves want?", but that question is not respected enough to be explored in any thematically coherent way.
the only real weight its given is the argument that there will always be "bad humans" out there, and so, dragons are safer in the wild. which sure is... an argument. but its a very "othering the problem" kind of argument.
it acts like its caring about the agency of dragons, but its not really. dragons were not actually portrayed as "oppressed" in berk society after the first movie, nor lacking agency. they were only at risk of "bad individuals", to which that solution is stupid. the racialized bad guy in httyd 2 didn't steal all his dragons from berk. he caught and subjugated them, mostly from the wild.

all while looking like... this, by the way. i feel like we don't talk about that enough. all the good guys are white nordics, while the only man of color is scary, domineering and cruel. in a series of movies that was once about having empathy for the other.
MAYBE if berk had been really oppressive towards dragons in httyd 2, we could've had a theme. maybe if they treated them like a dangerous commodity that must be tightly controlled despite their nominal acceptance and inclusion, we could've had a thematically tight 3-movie arc about like fear and oppression or whatever.
but that would require, yknow... making the movies be about broad societal problems, instead of just evil individuals. and only the first movie cares about making any real societal critique.
also, the solution in httyd 3 would've still sucked. these movies, in terms of writing, really decrease in maturity from 1, down to 2, to the plummeting depths of 3.
there is no relationship of oppression that is solved by completely segregating society and going our separate ways (httyd 3). just like there is no oppression that is solved just by defeating bad individuals (httyd 2). we have to learn to coexist as equals, to educate ourselves and be compassionate to the other. even if we're afraid.
that's the dream only the first movie kept in its heart.

#httyd#how to train your dragon#httyd 2#httyd 3#how to train your dragon 2#how to train your dragon 3#long post /#media analysis#media criticism#writing#ask to tag /#racism /
277 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Black on Black Love Movement is a social movement that celebrates and promotes love, unity, and healing within the Black community. It is a response to the systemic racism and oppression that Black people have faced for centuries, which has led to trauma, self-hatred, and violence within the community.
The movement is based on the belief that Black love is the foundation of a strong and thriving Black community. It encourages Black people to love and support each other, to heal from their wounds, and to work together to create a better future for themselves and their children.
The Black on Black Love Movement is manifested in many different ways, including:
Social media campaigns: The movement has a strong presence on social media, where people use hashtags like #BlackLove and #BlackOnBlackLove to share stories, images, and videos of Black love and joy.
Art and culture: Black artists and creators are using their work to promote the Black on Black Love Movement. For example, there are many films, books, and TV shows that celebrate Black love and relationships.
Community events: Organizations and individuals across the country are hosting community events to promote Black love and unity. These events can include things like potlucks, movie nights, and workshops on Black relationships and parenting.
The Black on Black Love Movement is still in its early stages, but it is growing rapidly. It is a powerful and important movement that is helping to heal the Black community and create a better future for Black people everywhere.
Here are some specific examples of the Black on Black Love Movement:
The Black Love Campaign is a non-profit organization that is dedicated to promoting Black love and unity. The organization hosts community events, produces educational materials, and advocates for policies that support Black families and relationships.
The Black Girl Magic movement is a social media campaign that celebrates the beauty, strength, and resilience of Black women. The movement is a reminder of the importance of Black self-love and community.
The Black Boys Joy movement is a social media campaign that highlights the positivity and joy of Black boys and men. The movement is a counter-narrative to the negative stereotypes that are often associated with Black men.
These are just a few examples of the many ways that the Black on Black Love Movement is being manifested. The movement is a powerful and important force for change in the Black community.
“Racists will always call you a racist when you identify their racism. To love yourself now - is a form of racism. We are the only people who are criticized for loving ourselves. and white people think when you love yourself you hate them. No, when I love myself they become irrelevant to me.” ― John Henrik Clarke tags: racism, racists.

The Black History Channel and all of it's affiliates are proud supporters of The Black On Black Love Movement.
#black love#black history#black positivity#black africans#global black on black love#global black unity#black indigenous people#black indigenous africans
226 notes
·
View notes
Text
ALL ABOUT VIRGO ASCENDANT
Hey y'all! We've got the next installment in the ascendant series (so close to the halfway point!) with Virgo!

Ahhh Virgo, the dutiful maiden of the zodiac. I actually find Virgo to be one of the most interesting zodiac signs (mostly because Mutable Mercury in Earth is a crazy combination), and the ascendant is no less interesting!
Again, the ascendant is how the world sees us. It rules our physical body, our life path, the zodiac rulers of each house in our chart, our outlook on life, and how our energy purely manifests.
Virgo's ruler, as I said, is the observant and mischevious Mercury. But Virgo is a bit different from it's counterpart Gemini. Where Gemini is bubbly, activated, and motivated to communicate, Virgo is more about analysis. Picking things apart and reassessing it for practicality, efficiency, and economy.
The risings are much like this. They see the world as a project that can always be improved. There's always something to fix, something to readjust, something to change. They're noticing all the little details and how each detail is working in the mechanical whole.
It's why you're so put together, Virgo. These risings tend to be well-manicured. They appear neat and well-groomed, usually preferring understated clothing. They can also be a bit self-preoccupied; they always need to look or present themselves a certain way. Perhaps the eyes are bit doe-like or their features are petite and dainty. Some may wear glasses or some other accessory to highlight their intelligence and reserved nature. Regardless, their eyes always have this special intensity...like they're studying you and sizing you up. I once had a Virgo Rising friend who said whenever she goes on a date she looks first at a man's shoes, then works her way up for her analysis. Very on brand for a Virgo Rising, lol.
Virgos can range in their presentation a bit. Some are more anxious, self-aware, and self-critical. Some are more observant and analytical, quiet and reserved. Others are more warm and service-oriented. But again, there's an emphasis on efficiency and service/work.

With a 4th House Sagittarius, these risings have a very Jupiterian-like home environment. There are many opportunities to learn, grow, and these natives may be blessed in many ways regarding their homes. However, with Sagittarius we usually find there is a message and a battle between man and spirit. Being mutable fire, Sagittarius wants to both investigate it's own actions and also disseminate information. Perhaps there was scrutiny in the Virgos home regarding their actions or a specific set of beliefs were established regarding what was acceptable or permissible in the home. In an unhealed manner, Sagittarius can be very stuck in its ways and attached to its ego. The home environment could be very rigid in this way...perhaps through religion, beliefs, faith, or education! School and learning may be very important to these individuals as it is something that could've been emphasized by the parents/home environment growing up.
In their private lives, Virgo Risings can indulge themselves in a variety of exciting behaviors. These types may like to drink, smoke, and vibe out in the privacy of their own homes. Or they love to learn and read about other cultures, far-away places, and interesting people. These natives have an innate curiosity about life that's been hammered into them!
Says a lot about the Virgo's discriminatory, cerebral nature and even their penchant for condescension/criticism.
Something else I'm now thinking about...perhaps Virgos need for control comes from a chaotic home environment. Mutable signs in general can hold space for turbulence both internally and externally. These are signs who most easily adapt. The home environment could've been filled with people/parental figures coming in and out. Family staying and leaving. Parental figures who were inconsistent or irrationally angry. Avoidant parents who did not know how to deal with conflict. Again, we can keep going and going and going with these Sagittarius themes.

I'll try not to make the other house breakdowns too wordy. For the 10th, the public image, life, and vocation of these natives is ruled by Gemini! Communication and connection is ultimately how these natives manifest service in their lives. Often Virgo Risings will become actors (Timothee Chalamet, Janelle Monae, Emma Watson). This is a good indicator for music or some other lyrical ability as well. Jay-Z himself is a Virgo Rising. Another funny way it could manifest is with the examples of Steve Jobs and Rachel Ray! One created a company that revolutionized communication forever, the other became a lively TV show personality. All very Gemini vocations. Something about the information you have to share or the way you communicate is key here, Virgo Rising. You have the potential to inspire and be seen for your articulation and your mind. Enrich the qualities of both and you shall see success. It is Mercury who awakens your authority in life.
As for the 7th house, Virgo Risings can tend to pick partners who need help or who need to be fixed or saved in some way. Or partners who are just bad for them/toxic. This is the more unhealthy side of Pisces, a sign who can be severely ungrounded and drain the energy from others. Pisces is also a bit of a helpless energy and so Virgo Risings can manifest partners who reflect this. Virgo may attract emotional people in general! People who seek to dump their worries and emotions onto the Virgo. It's a very Virgo thing unfortunately. Everyone wants you to be there mother! People may sense you can heal them in some way or emotionally fulfill them...and while that may be true...boundaries! You are not here to serve everyone, Virgo! You are here to understand yourself and to fall in love with your imperfections. A humility can be found in Virgo and Pisces can help you do this! The opposition here is that Virgo needs Piscean partners/people who inspire a dreaminess, a loftiness, and an ease in Virgo. You do not have to work all the time nor do you have to be so hard on yourself. Pisces can teach Virgo unconditional love and how to devote their energy to things that truly matter and will emotionally fulfill them. They will teach the Virgo to listen to how they feel and to truly evolve from their experiences. And Virgo, you need someone who is just as devotional as you!
Virgos have to investigate their own wounds and fears around authority and independence. There can be some guilt and wounding around leadership and being selfish (Aries 8H) that can take time to heal. There could also be wounding around being too self-focused! Virgo can be so caught up in controlling themselves and their own lives that they become vindictive and judgmental rather than open and receptive. It's about calculated risks with the 8H and acknowledging the areas of our growth so we may challenge those beliefs and unearth our power through change! Once you do, you will find a sense of peace and earthliness (Taurus 9H). Learning those Taurean themes will set you free and become your philosophy and foundation. Firm boundaries, stubbornness, holding your own. Learning to value oneself and one's abilities. Learning to hold space and be open to others as well. This is what you must learn so you may achieve your highest potential and communicate your truth! (Gemini 10th).
The esoteric ruler of Virgo is The Moon. Ultimately, Virgos learn to love without conditions, much like a mother loves their children. They focus on the immediacy of their needs rather than getting caught up in the details. Their lives become tapestries of healing and devotion rather than cold calculations. Information does not become the defense, instead it is distilled into medicinal wisdom that can benefit others. Virgo you are here to learn how to serve better.
That's all for this one folks! I had more to say here as a sidereal Pisces with a lottt of Virgo Rising friends. I tend to attract you all a LOT. Y'all bring so much rationality, care, and stability into my life and I appreciate it so deeply. I just want you Virgos to take care of yourselves and to open yourself up to new experiences! You can do it!
#virgo#astro observations#horoscope#astrology#natal chart#zodiac#astro notes#astro community#ascendant#astrology signs#astrologer#virgo rising#mercury#vulcan#the moon#natal astrology#astro placements#astro tumblr#astrology community#astrology observations#astrology notes
180 notes
·
View notes
Note
Is normalizing problematic stuff in fiction actually harmful to others in real life, or is that just something said to prevent further talk of such things?
The notion that fiction can in any way normalize "problematic stuff" is a discussionary roadblock in much the same way that the moment you try talking to certain people about certain things they whip out pedophilia as a trump card.
Its also why its actually so fucking important that from a young age we are given proper, well-rounded education and opportunities to exercise things like critical thinking, self-reflection and the ability to analyse what is in front of us to form our own conclusions instead of blindly following and believing whatever we see at first glance.
(Which applies to everything.)
Its also why its so important to separate things like creative appreciation and reality. Which we see in the whole anti vs proship debate all the time. We are supposed to observe fiction from the outside. We are not supposed to try to convert reality into fiction or exist in the real world as if we are in fiction.
Have you ever watched Hannibal and gone out to kill someone to turn them into a fancy European dish?
Have you ever watched Game of Thrones and tried to fuck your sister?
Lolita is another prime example. The amount of people who didn't understand the actual point of Lolita and still don't is fucking staggering. Lolita is supposed to make you uncomfortable because you know its not right. You know its not normal. It doesn't romanticize or normalize pedophilia and older men going after young teenage girls. It does the opposite.
There are two types of people who believe or are susceptible to believing things they see in fiction are acceptable in real life; the uneducated and the mentally unstable.
#myfandomrealitea#sephiroth speaks#reality#fandom#discourse#proshipping#proship#fanfiction#tv#movies#fiction is not reality#profic#profiction#pro fiction#proshipper
120 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Roaming into immortality”: Ten Desires and the history of Taoist immortals

As promised last month, following the freshly established tradition I have another Touhou research post to offer. This time, we’ll be looking into the literary traditions focused on Taoist immortals (or, following the Touhou convention, “hermits”, though this is a less suitable translation) and how they influenced Ten Desires. Due to space constraints and thematic coherence, note that only Seiga, Miko and Yoshika will be covered.
Before you'll begin, I need to stress that one of the sections requires a content warning. While all images are safe for viewing, there's a description of a potentially unpleasant episode involving unwanted advances, and various events leading to that; I highlighted that before the relevant paragraphs too just in case.
“Hermit”, “immortal”, “transcendent”
A post about Ten Desires must start with an introduction of the term sen, the Japanese reading of 仙, Chinese xian. Touhou specifically uses its less common derivative 仙人, sennin, though that's just a synonym. Touhou-related sources basically invariably translate this term as “hermit”. While this option can be found elsewhere too, it is not exactly optimal.
“Immortal” is actually the standard translation for both sen/xian and sennin, as far as I am aware. I did a quick survey of recent publications on Brill’s and De Gruyter’s sites and the results were fairly unambiguous, especially for books and articles published after 2000, with “hermit”, “wizard” and other alternatives being quite uncommon. The trend is not new, with sennin already translated as “immortal” in the 1960s.
When it comes to xian/sen, in a few cases arguments were made that “transcendent” or “ascendent” would be a more suitable option as it better illustrates the position of these beings, though this is a relatively recent trend, for now limited to Sinology. The idea behind it is that immortality is just one of multiple characteristics attributed to the xian, and it is ultimately the transcendence to a higher level of existence that’s the key element. I personally think the argument is sound, but not all translators have embraced it, and for now the choice is really a matter of preference. Since “immortal” is more widespread, and most of the sources in the bibliography use it, that’s what I will employ in the rest of the article, save for direct quotes from Touhou, where "hermit" will be used.
Early history of immortality in Chinese sources

Feathered immortals worshiping Xi Wangmu (from Betwixt and Between: Depictions of Immortals in Eastern Han Dynasty Tomb Reliefs by Leslie Wallace; reproduced here for educational purposes only)
The notion of pursuit of immortality, or at least longevity, is first attested in Chinese sources in the eighth century BCE, when the first bronze inscriptions revealing their authors wished to avoid death altogether appear in the archaeological record. However, the ideas which directly lead to the development of the concept of immortals as discussed here only started to develop in the fourth BCE. Initially they were associated with so-called fangshi, a class of multi-purpose esoteric specialists who often served for example as court diviners.
These ideas developed before the unification of China by Qin Shi Huang, but their importance grew after this event, as many of their proponents were warmly received in the courts of Qin and Han emperors. Some of them, like Wu of Han, even sent expeditions in search of distant lands where immortals purportedly lived, of which Penglai is the most famous.
As a curiosity it’s worth mentioning here that the reception of these pursuits was actually mixed in Chinese historiography. Some of the rationalist Eastern Han authors such as Wang Chong evaluated it critically, basically describing it as a waste of time and resources leading to poor governance.
We know relatively little about the development of beliefs focused on immortality outside of the imperial court in the Han period, though it is evident that they gained considerable prominence, and it’s even possible to speak of “immortality cults” among the general populace. That’s for example seemingly how the worship of Xi Wangmu, arguably one of the most famous Chinese deities, became widespread. Tomb paintings showing blissful immortals also appear in this period.
In art immortals were initially depicted as winged, feathered beings. The origin of this tradition remains unclear, though it has been noted that various similar bird-like beings are also listed in the Classic of Mountains and Seas, attesting to this being a widespread motif in early Chinese tradition. You might be familiar with portraying immortals as wizened sages instead. This convention only developed when the image of the immortal merged with that of the ascetic hermit in the Eastern Jin period - more on that later.
Immortals in Ge Hong’s Baopuzi

A 20th century illustration of Ge Hong (wikimedia commons)
The first formalized instructions for the pursuit of immortality were compiled during the reign of the Eastern Han. Some of them were rooted in the early Taoist tradition, which at the time was also being partially formalized under the Way of the Celestial Masters. Seemingly many Taoist works dealing with these matters were compiled, but most of them are only known from references in Ge Hong’s Baopuzi, one of the most important texts for the study of the history of ideas about immortality.
Ge Hong states that immortality can be obtained through personal virtue and specific practices, including exercise, following strict dietary restrictions and, most importantly, through engaging in alchemy, which he hails as the most effective. All the means to obtaining immortality were unified by one principle: cultivating qi, both by maintaining one’s own and by absorbing it from the right kinds of plants and minerals. Grains were held to be inappropriate food for those pursuing immortality, as it was believed they nourished the so-called “three worms”. The final goal was to be able to use morning dew or light for sustenance. The easiest way to move towards that goal was believed to be consumption of alchemical elixirs, said to possess a more potent, refined form of qi of all their carefully selected ingredients.
Needless to say, many of such magical concoctions were highly poisonous thanks to the inclusion of mercury, cinnabar and other similarly exciting substances. Ten Desires describes the consequences pretty accurately: Miko “turned to the use of various unusual materials, such as cinnabar” which “ruined her body”; as a result she “destroyed her health because of the very Taoism that was meant to grant her immortality”. Such a fate is not historically unparalleled, and there is even a strong case to be made that the notoriously erratic behavior of some of the particularly immortality-obsessed emperors was the result of alchemically induced heavy metal poisoning.
Cinnabar cocktails aside, a further important piece of information from Baopuzi is the reference to three classes of immortals, celestial (天仙), earthbound (地仙) and corpse-liberated (尸解仙). What separated these three groups was the degree to which they perfected their state before formally attaining the rank of immortal. The most refined were basically invited into heaven, with the best of the best taken there on the back of a dragon. Those who despite their efforts lacked something had to put in some additional effort themselves instead.
While the "celestial" and "earthbound" immortals are largely self-explanatory (we'll go back to them later, though), the label of “corpse-liberated” warrants a more detailed explanation. It refers to those who settled for faking own death. This act is called shijie (尸解), and involves substituting the body for an object, which is to be buried as if it was a person. Of course, immortality obtained this way was effectively second rate, though it was not impossible to become a proper celestial immortal later on. As you can probably notice, this is precisely the path to immortality ZUN has chosen for characters in Ten Desires. The term shikaisen used multiple times in the game is in fact simply the Japanese reading of 尸解仙.
Immortals in secular literature

Four Immortals Saluting Longevity by Shang Xi (wikimedia commons)
The importance of the search for immortality grew during the Six Dynasties period. Seemingly in all strata of society a common reaction to frequent political turmoil was to seek solutions in Taoism and still relatively new Buddhism. This in turn left a huge impact on Chinese culture of this era as a whole.
What is of particular relevance for this article is less the straightforward religious dimension of immortality, and more its reflection in literature. Works about immortals were already being written in the Western Han period, with the oldest surviving example being Liexian Zhuan (列仙傳) attributed to Liu Xiang, who lived in the first century BCE. Their importance only grew with time due to the aforementioned process, and they became a well established part of both poetry and prose. For example, a sixth century treatise on literary genres, Xiao Tong’s Selections of Refined Literature (文選; Wenxuan), pretty much the main source to fall back on in the study of pre-Tang literature, recognizes youxian (遊仙), literally “roaming into immortality”, as a distinct type of lyrical poetry. There’s a considerably degree of nuance to this term, since 遊 has the implications of leisurely, playful activity, but these lexical considerations are beyond the scope of this article.
While in some cases the tales of immortals focused on figures primarily known for other reasons, like the Yellow Emperor, Chang'e or Laozi, many document the lives of historical pursuers of immortality instead. Well attested fangshi and Taoist masters appear in such a context, for instance Anqi Sheng or Liu An (according to a legend he ascended to heaven with his entire household, including dogs and other animals).
The literary biographies, or rather hagiographies, of immortals often highlighted their personal eccentricities, tied to their detachment from society. The archetypal eccentric immortals are obviously the members of the group popularly known as the Eight Immortals, though this is a much later development, and the genre conventions formed centuries earlier.
Literature about immortals is interesting from a modern perspective because at least in part it was arguably a secular pursuit. As secular as something could be prior to the rise of the modern notion of secularism, that is (see Mark Teeuwen’s article on Edo period secularism for some arguments against seeing secularism as an entirely modern phenomenon). This is not merely the modern perception, for clarity - the earliest statements to that effect can be found in works of literary criticism from the second century or so. The writers were chiefly scholars, courtiers and officials, not clergy, and naturally their works are not recognized as “canonical” Taoist literature.
Some of these authors took the topic of immortals into rather peculiar directions. According to Xiaofei Kang, during the Six Dynasties period amorous encounters with female immortals (仙女, xiannü) were a “fashionable topic among literati”, while in the subsequent Tang period some authors compared courtesans they sometimes were actually involved with to immortals metaphorically. She notes that they effectively created a genre of works focused on immortals which was no longer really describing the pursuit of immortality, but rather “encounters with enchanting beauties, both real and imagined”.
Needless to say, the literature about immortals remained relevant in later periods, and new stories continued to be written under the reign of subsequent dynasties. Many can be found in Pu Songling’s famous Liaozhai (Strange Tales from a Chinese Studio). This collection was written in the Qing period and remains in wide circulation today as a literary classic.
Pu Songling’s tale of Qing’e: the origin of Seiga

Pu Songling (wikimedia commons)
It is beyond the scope of this article to discuss all of Pu Songling’s tales about immortals, but there is one which necessitates further discussion, namely Qing’e, which is very obviously the basis for Seiga’s character. This makes her somewhat unusual among Touhou characters - while the story she is based on deals with religious themes, and fiction can shape religious views at times (as evidenced by the popularity of Sun Wukong or the image of hell in Divine Comedy), I found no indication Qing’e was ever views as anything but a literary character.
Like the rest of Liaozhai, the Qing’e tale has been translated into English in the 2000s. Songling’s works have an older and more famous translation too, but it’s just a selection, and it has many issues, which you can read about here. You can read parts of the more modern translation on Google Books. Obviously it can also be found easily in other places. I will also summarize the story of Qing’e below for convenience.
This is where the content warning I mentioned applies: the story is not very explicit, but there are is a scene of what I think counts as attempted sexual assault and other generally unsavory moments of that sort, so if that bothers you, skip ahead to the next section.
The beginning of the story introduces a certain Huo Huan (霍桓) from Shanxi, a sheltered young man of unspecified age (he’s older than 13 but “ignorant of adult desire”, which is pretty vague). He lives in the same neighborhood as the eponymous Qing’e (青娥), a teenage daughter of a certain mr. Wu (武), who was apparently a devout Taoist. Qing’e secretly read through her father’s personal collection, developing an admiration for He Xiangu in the process. When mr. Wu left for the mountains to become an immortal, his daughter declared she will never marry. Her decision is presumably meant to mirror one of the versions of the tale of He Xiangnu, who reportedly attained immortality by remaining celibate and consuming mineral powders (granted, you can also find versions where her immortal career started when she was seduced by Lü Dongbin, but that does not match the story here).
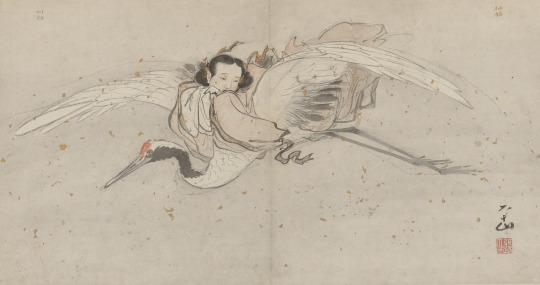
He Xiangnu by Zhang Lu (wikimedia commons)
Huan sees Qing’e outside at some point and, without really talking to her, decides she has to marry her and asks his mother to send someone to arrange that. she doesn’t think it’s a good idea, but eventually caves in. Lo and behold, it doesn’t work and the Wu family is not interested in the proposal. Huan then meets an unrelated Taoist, who offers him a magical tiny spade (one chi long) used to dig up Taoist-preferred herbs (a key component of the immortality keto diet), which can quite literally hack through stone. This convenient deus ex machina gives Huo the idea to hack through the walls of the Wu residence to see Qing’e. Note that the narrator does not approve of this plan, and calls it an “illegal act”. Alas, it comes to pass anyway,
With this newfound power Huan watches Qing’e undress before she goes to bed and then listens to her breathing while she is asleep, as one does with women they saw exactly once before. Eventually he falls asleep himself on her bed. Needless to say, when Qing’e wakes up she is less than thrilled and summons her servants. They assume Huan is a thief, but he tries to explain himself. He’s set free, but the magical tool is confiscated.
Since Huan does not know when to quit, he arranges for a second round of matchmaking afterwards. While apparently Qing’e is cautiously optimistic about it this time, her mother is less than thrilled after learning there are now holes in their residence’s walls. She insults the matchmakers, Huan and Huan’s mother. This in turn makes Huan’s mother angry. She apparently concludes that Huan and Qing’e had sex, and declares that instead of damaging her good name someone should’ve just killed them both on the spot. Qing’e is genuinely sad about this and sends a messenger to smooth things over. However, ultimately nothing really comes out of it.
Some time later, Huan starts a career as a helper of his town’s magistrate, Ou. The latter is surprised to learn he is not married yet, and after hearing about his unsuccessful endeavors intervenes himself. With the help of other local officials he secures the permission of Qing’e’s mother, and the marriage is officially arranged.
A year later, Qing’e arrived at Huan's home. She brings the magical tool with her, and declares that it is no longer needed. However, Huan decides to carry it with him as a good luck charm, pointing out acquiring it was what led to their marriage. Some time later newlyweds have a son, Mengxian, but Qing’e is not interested in raising him and entrusts that entirely to a nurse. After some more time, in the eighth year of their marriage, she announces to Huan that their time together is coming to a close, and there is nothing to be done about this. Shortly after that, she seemingly dies, and Huan and his mother bury her - or so they think, at least.
In the aftermath of this event Huan’s mother falls sick, and inexplicably develops a craving for fish soup, which is hard to obtain in the area the story takes place according to the narrator. Huan, as a staunch believer in filial piety, decides to embark on a journey to procure some. He is initially unsuccessful, but he manages to get some from Wang, an old man he encountered in the mountains. The latter also offers to introduce him to a beautiful woman, but Huan is focused on the quest for fish soup and declines.

Contemporary Chinese fish soup (wikimedia commons)
With the power of fish soup Huan’s mother’s health is restored, and when it becomes clear she’s going to be fine he decides to seek Wang again. He does not find him, but after a long trek in the mountains he instead stumbles upon an unusual cave. Unusual because there’s a house inside it. a house which, as it turns out, is inhabited by Qing’e.
Qing’e is surprised to see Huan. She explains that she faked her death and in reality a bamboo cane was buried in her place. She concludes that if Huan found her, they are presumably fated to be together as immortals. He is then taken to her father, who as established earlier also became an immortal. The initial reception is positive, but Huan makes a scene demanding that Qing’e have sex with him and keeps clutching her arm when she declines. Qinge’s father intervenes, and kicks him out for attempted sacrilege in his hermitage.
Alas, Huan can’t get a clue as already established. He cannot see the house anymore because due to a trick there’s only a cliff in front of him after the doors close, but that’s not really enough to stop him, as he suddenly remembers he has the magical tool with him. He starts digging, and despite insults hurled at him from behind the rocks eventually makes a sizable hole in the cliff. At this point someone, presumably Qing’e’s father, gets fed up, and throws Qing’e out through the hole to get him to leave.
Qing’e, to put it lightly, is not very keen on this turn of events. She nonetheless returns with Huan to his house. Shortly after that they moved elsewhere, to Yidu, where they lived for eighteen years. Qing’e at some point gave birth to a second child, a nameless daughter, who doesn’t really factor into the story. All we hear about her is that she married into a local family.
Eventually Hano’s mother dies. Qing’e picks an auspicious location for her resting place, and tasks Huan and Mengxian with preparing the burial. A month later, she and Huan disappear, leaving the new adult Mengxian alone.
In the final scene of the story, Megxian, who apparently spent the first twenty or so years of his adult life unsuccessfully attempting to pass the imperial examination, meets a certain Zhongxian, and is amazed to learn they bear the same surname. The two quickly realize they’re brothers, and decide to meet with their parents, but they fail to accomplish that since they left Zhongxian’s house in the meanwhile.
The narrator comments that while Huan’s actions were “foolish” and “crazy”, everything he had striven for was granted to him as a reward for his filial piety, and then marvels why nobody stopped him and Qing’e from having more inevitably abandoned children. “That’s really strange,” he remarks.
Seiga’s character between ZUN’s innovations and Taoist tradition

Seiga explaining the powers of a hermit; if only there was a term which makes this explanation even more straightforward... (WaHH chapter 12.1)
As you’ve probably noticed, Seiga’s bio in the Ten Desires omake is remarkably faithful to the adapted source. Even her name is just a Japanese reading of the combination of Qing’e’s given name with the family name of her husband. It does not seem that everything unfolded identically in Touhou, though. There is no indication in the bio, or anywhere else for that matter, that Seiga went back after faking her death, and we instead learn that she decided to travel to Japan, since Taoist “hermits” were uncommon there. Additionally, Seiga presumably kept the confiscated chisel, since her ability, which she eagerly demonstrates in Wild and Horned Hermit, is rather obviously a direct reference to the tale of Qing’e. I will admit that while I do not question Pu Songling’s talent and enjoyed many of his tales, I think ZUN’s version is more satisfying than the original, perhaps because from a modern perspective Qing’e is arguably a more compelling protagonist than her husband, and Touhou effectively treats her as the main character in this story.
Something that I believe is relatively well known is that Seiga’s entire character is a bit of an anachronism: to encounter Miko, she would need to be alive through the end of the Six Dynasties period already. However, since ZUN adapted much of the tale of Qing’e directly, like her forerunner she idolizes He Xiangnu, who according to legends about her was only born in the Tang period, and attained the status of an immortal in the early eighth century, during the reign of emperor Zhongzong - nearly a century after Miko’s semi-historical counterpart passed away. I do not think this mistake is meaningful. Save for the references to He Xiangnu and imperial examinations, the tale of Qing’e is set in a largely timeless world. I would presume it’s just a small mistake on ZUN’s part, and he didn’t check the chronology while summarizing the part of the story he wanted to use in Seiga’s bio. There is no need to ponder if Seiga’s power lets her travel in time, as the wiki (which, as we all know, prides itself in maintaining “neutrality” and enforcing correct exegesis of the source material, especially Hisami’s bio) does.
There is a further aspect of Seiga’s character which might evoke works about immortals, though I am not sure if this was intentional. As we learn from her entry in Symposium of Post-Mysticism, she “cannot become a celestial due to her personality, but that does not seem to bother her”. The term dixian which I already brought up before designated immortals who were not interested in ascension to heaven. According to Ge Hong, there were actually many benefits to such a fate, and while nominally a dixian ranked below a tianxian (in Touhou terms, a celestial), they had much more freedom. He states that the archetypal immortal Peng Zu, who spent over 800 years on earth, did so because the upper echelons of the heavenly hierarchy are occupied by well established deities, and any immortal joining their ranks would be burdened with tiresome tasks and obliged to act as servants, making their life less enjoyable than it would be on earth.

Peng Zu (wikimedia commons)
Poetry describing the earthbound immortals originally developed in the third and fourth centuries. Parallels can be drawn between their protagonists who reject the celestial bureaucracy with a different class of literary characters popular at the same period - non-conformist recluses who did not care about the mundane, earthly administration. The dixian is essentially a merge between the classical supernatural immortal and the archetypal hermit. This sort of immortality was a metaphor for unrestrained freedom first and foremost.
I will stress again that I have doubts about whether ZUN was aware of this when he came up with Seiga, but it certainly does fit her well. Also, more recently, in Who’s Who of Humans and Yokai in Gensokyo he actually says that “she may be the most hermit-ish character here”. I’d hazard that even if he was not aware of this idea before, he probably is now, in some capacity at least. It’s not like Seiga’s status as a “wicked hermit” was ever tied to lack of interest in heaven, as opposed to necromancy, so this does not contradict anything established.
Reception of Chinese tales about immortals in Japan
Obviously, ZUN is not the first person in Japan to adapt literature about immortals.Something that needs to be stressed before delving deeper into the topic is that transfer of beliefs, and especially tales, pertaining to immortals to Japan did not constitute the spread of Taoism as an organized religion. It is instead simply an aspect of the widespread adoption of elements of Chinese culture. While Taoist ideas were an aspect of this phenomenon, we know relatively little about how they were transmitted to Japan, though there was clearly no effort to introduce the religion itself in a formal manner the way Buddhism was. This topic ultimately can’t be explored here in detail due to space constraints. but most likely what occurred was gradual introduction of certain elements in informal contexts: through art, Buddhist borrowings or poorly documented individual ventures.
The earliest recorded example of reception of motifs related to immortals in Japan is likely the tale of Tajimamori from the Nihon Shoki, which involves a quest for items granting immortality. The much better known tale of Urashima Taro, also preserved in this source, is another candidate, and as a matter of fact was recognized as an example of literature about immortals in the Heian period already.

Ōe no Masafusa (wikimedia commons)
However, our main source of the early Japanese perception of immortals are not the early “national chronicles”, but rather Honchō Shinsenden (本朝神仙伝). Its author was Ōe no Masafusa (1041-1111), an official and scholar from the Heian period. His career culminated when he was appointed to the prestigious position of the governor of Kyushu, though he eventually abdicated to dedicate himself to writing. His work is classified as an example of setsuwa. At the same time it is also firmly tied to the already discussed tradition of Chinese secular immortal literature, and can effectively be considered an attempt at creating a Japanese equivalent of collections of biographies of immortals. Obviously it has its own unique peculiarities to offer too.
Masafusa’s work presents an interesting case of fusion of the Taoist-influenced Chinese notion of immortality with Buddhist ideas: the immortals are compared to hijiri (Buddhist “holy men”) and “living Buddhas” (ikibotoke). This is not entirely a novelty, as while Buddhists are absent from Chinese compilations of biographies of immortals, Laozi’s ascent to immortality was nonetheless at times described in similar terms as Buddhist Nirvana, at least in sources from the fifth century. There was also a preexisting Buddhist tradition of legendary long-lived patriarchs awaiting the coming of Maitreya or simply extending their lifespans to save more beings. Therefore, while innovative, this combination of Taoist and Buddhist elements was hardly something unparalleled or contradictory.
The selection of figures described as immortals in Honchō Shinsenden is also a bit different than in its Chinese forerunners. Legendary heroes and historical statesmen do show up, as expected. However, alchemists and members of Taoist clergy are missing, since they were not exactly common in Japan. Buddhist monks effectively replace them as the main social group among immortals, though it does not seem religious devotion is the deciding factor. Ultimately there is no clear pattern, not even that of virtuous life: Masafusa’s immortals as a group are not meant to be moral examples, even though some of them are portrayed as paragons of virtue.
It seems ultimately what Masafusa wanted to do is present stories he personally found interesting or awe-inspiring, and there was no religious aim behind his work. Some of his choices were actually criticized as inappropriate by his contemporaries, in particular the inclusions of Zenchū and Zensan, who according to polemics were not immortals, but merely devout Buddhists taken into a Pure Land (a heavenly realm created by and inhabited by a Buddha) in their current forms, without reincarnation. This argument follows the well established aspect of esoteric Buddhist doctrine, which enabled the possibility of achieving enlightenment in one’s current incarnation.
A total of thirty seven tales formed the original manuscript, though not all of them survive. They range from long, grandiose narratives about figures like Yamato Takeru and En no Gyoja to brief, almost comedic accounts of the tribulations of anonymous figures such as the “stick-beaten immortal” (who learned how to levitate, but only up to the height of one shaku, which meant that he could not even escape children hitting him with sticks) or the “old seller of white chopsticks” (whose title tells you a lot about his economic situation). Only two are ultimately important here, though: those of the semi-historical prince Shotoku, and the firmly historical poet, historian and eccentric Miyako no Yoshika.
Simply put, I believe Honchō Shinsenden is responsible both for the portrayal of Shotoku as a Taoist immortal and for the inclusion of a character (vaguely) based on Miyako no Yoshika in Ten Desires.
Honchō Shinsenden’s Shotoku and Toyosatomimi no Miko

The image of prince Shotoku through the ages
Prince Shotoku (聖徳太子) is one of the highest profile figures to ever be portrayed in Touhou, and as such arguably requires no lengthy introduction. He purportedly lived from February 7, 574 to April 8, 622, and served as a regent on behalf of his aunt, empress Suiko. He is traditionally credited with spreading Buddhism in Japan, ordaining numerous monks, writing commentaries on sutras, vanquishing rivals such as Mononobe no Moriya with the help of the Soga clan, and so on. He might have not existed at all, or perhaps he did, but played nowhere near as major of a role in Japanese history as traditionally assumed. The academic debate started a few decades ago, and remains ongoing. Its outcome isn’t really important here, since regardless of Shotoku’s disputed historicity, he came to be well established both as a religious figure and as a literary character. At various points in time and for various people, Shotoku was, in no particular order, the ideal statesman, a manifestation of Kannon, a peerless military commander, a yaoi protagonist and, most importantly, an immortal.
In Honchō Shinsenden, Shotoku is referred to as “prince Jōgu” (上宮), though we do get the mandatory Shotoku namedrop indirectly when his virtue (聖徳) is highlighted.. He is actually one of the two only of the listed immortals who can be classified at least vaguely as “statesmen”, the other being Yamato Takeru. For unknown reasons, Masafusa got some details wrong: according to him Shotoku’s father was Bidatsu. This view is unparalleled, and there is no real reason to doubt the conventional genealogy, which firmly positions him as a son of Yomei and his half-sister Anahobe no Hashihito. We learn that his birth was foretold by a dream in which his mother saw a golden figure who entrusted her with a child who will spread the dharma. This is in itself a combination of Taoist and Buddhist elements, seemingly an attempt at imitating a legend about the birth of Laozi, which in turn depended on a legend about the birth of the historical Buddha.
Naturally, Shotoku already displayed supernatural abilities as a child. Masafusa reports that whoever touched him was imbued with a “lasting fragrance”. A variant of the well known tale which his Touhou counterpart’s name and ability reference is presented here too, though a key detail differs - Shotoku can listen to eight, rather than ten, people according to Masafusa. This is not unparalleled, and therefore probably isn’t a mistake unlike the unexpected genealogical change mentioned before.
A major event from Shotoku’s life relayed by Honchō Shinsenden is an alleged meeting between him and Illa (Nichira), a Korean monk living in Japan. The historicity of this episode is debatable, as Illa died when Shotoku (if he was real in the first place, of course) was only eleven years old. He identifies the prince as the bodhisattva Kannon, and pays respect to him as such. In response Shotoku emitted a beam of light from between his eyebrows, which reflects both Taoist and Buddhist traditions about manifesting supernatural powers.
Illa's alter ego Atago Gongen (wikimedia commons)
Interestingly, Illa responds by doing the same, thus revealing his own supernatural character. We know from other sources that Illa could be identified as the true identity of Atago Gongen, the tengu-like deity of Mount Atago. Bernard Faure notes parallels can be drawn between his portrayals as a foreign supernatural ally of Shotoku and as the human alter ego of a deity with the traditions pertaining to Hata no Kawakatsu. There is also an “immortal of Mount Atago” in Honchō Shinsenden, but his identity is left unspecified. It's worth noting that in Symposium of Post-Mysticism Byakuren and Marisa at one point discuss the existence of “hermit-like tengu”. Illa truthers… we can make it happen if we believe strong enough… Jokes aside, I’m actually cautiously optimistic that Illa might some day end up being the first Korean character in Touhou, at least implicitly. Given the inclusion of references to Hata no Kawakatsu, odds are decent ZUN knows about him too.
In another anecdote, we are introduced to another member of Shotoku’s supernatural supporting cast, the black steed of Kai. This horse is credited with being able to travel the distance of a thousand ri in a single move. This is seemingly an adaptation of a Taoist motif too, as immortals were believed to favor traveling on supernaturally fast steeds, or in cloud chariots drawn by such animals, or to move instantaneously through other means. The fabulous distance of 1000 (or even 10000) ri is conventional, too.

Shotoku traveling through the sky on his supernatural horse (Smithsonian Institution; reproduced here for educational purposes only)
Of course, the black steed (kurokoma) is also the very same horse that served as the basis for Saki. While allusions to this connection is probably the second most common genre of fanart of her, it surprisingly took ZUN four whole years to acknowledge it outside of a track title, specifically through two lines in the vs mode of Unlimited Dream of All Living Ghost. Time will tell if anything will come out of it, I’m personally skeptical seeing as we have yet to see a canon work do anything with the connection between Okina and Hata no Kawakatsu even though it was acknowledged in an interview. I hope I am wrong, though.
Shotoku’s various accomplishments are not described in detail, though Masafusa does bring up his famous seventeen articles constitution and the establishment of Shitenno-ji, and additionally states that teachings linked to the Yuezhi people from Central Asia were associated with it (unique opportunity to justify bringing Central Asian deities like Nana and Weshparkar into Touhou).
The final and most important part of Shotoku’s biography, the circumstances of his death - or rather his acquisition of immortality - is only partially preserved. According to Masafusa, one day he simply informed his wife (presumably Kawashide no Iratsume, as opposed to one of the other three wives) that he cannot exist anymore in a “defiled” world and “transformed” himself. It is actually not explained how he even mastered the techniques allowing that, presumably because we are meant to attribute this miraculous feat to his status as a saintly Buddhist. The authors behind the most recent English translation, Christoph Kleine and Livia Kohn, suggest that in the lost final sentence(s) Masafusa might have combined the Taoist take on immortality with Amida’s pure land, but this is ultimately speculative.
ZUN actually went for something closer to the Chinese model with Miko - she was explicitly taught by Seiga. The notion of immortals mentoring those they deem worthy to pursue the same path is a widespread motif, and even some of the Eight Immortals gained their status this way. This idea is absent altogether from Honchō Shinsenden, perhaps since it was tied to formal transfer of Taoist teachings. While this is an innovation, I would argue it’s still true to Shotoku legends, considering they are already filled with miracle-working visitors from distant lands, from Illa and Hata no Kawakatsu to considerably more famous Bodhidharma.
From eccentric to immortal: the literary afterlife of Miyako no Yoshika

Miyako no Yoshika (wikimedia commons)
As I already said, the second tale from Honchō Shinsenden relevant to Ten Desires is that focused on Miyako no Yoshika. He obviously shares no direct connection with prince Shotoku. Or with Qing’e, for that matter. Unlike prince Shotoku, he left a solid paper trail behind, and there’s no doubt that despite having quite a career as a legendary figure, he was originally a historical person. He lived from 834 to 879, in the Heian period. He was a calligrapher, a poet, an imperial official and for a brief time even an assistant to the envoy to Bohai (Balhae). The inclusion of a character based on him in Ten Desires might seem puzzling at first glance, since none of this seems particularly relevant to the game, and Yoshika’s omake bio doesn’t say much that helps here, beyond calling her a “corpse from ancient Japan”. However, I believe Honchō Shinsenden sheds some light on this mystery.
In Honchō Shinsenden, Miyako no Yoshika belongs to the small category of literati pursuing immortality, a status he only shares with Tachibana no Masamichi. There are a number of other immortals listed who are neither monks nor statesmen, and can be broadly classified as laypeople, though none of them seem to have much to do with those two. In contrast with figures like prince Shotoku, described as pious sages, the fictionalized take on Yoshika is meant to highlight extreme eccentricity instead. This is an element common in accounts of Chinese immortals’ lives too, as I highlighted before. You might also remember this topic from the Zanmu article from last month.
As we learn, Yoshika, who was originally known as Kuwahara (misread by Masafusa as Haraaka, an actually unattested surname) no Kotomichi but changed first his family name (for unknown reasons) and then also his given name because of a poem he liked, decided to become an immortal under rather unusual circumstances. In the very beginning of his career, after spending a night with the concubine of an official from the Bureau of Examination who was meant to examine him the next day, Yoshika decided that his goal in life should be to become an “eccentric immortal”. He passed his official exam without any trouble, with an unparalleled score. Graffiti in the academy he attended proclaimed him the “world’s greatest maniac” (so he comes prepackaged with a Touhou-appropriate title). He attained widespread acclaim for his wit and poetic skill. In his free time, he engages in celebrated literati pastimes such as drinking and sleeping with courtesans (Masafusa does not specify if he wrote about that, like his Tang counterparts did).

Sugawara no Michizane, Yoshika's apparent nemesis (wikimedia commons)
Alas, Yoshika’s career ultimately did not go entirely according to his whims. The beginning of the end was the day when he acted as the examiner of a new rising star, Sugawa no Michizane. The latter has proven himself to be even more skilled than him, and eventually rose to a higher rank than Yoshika. The latter could not bear this perceived offense against him and one day left his life behind to return to the pursuit of immortality. He aimed at the mountains, hoping to find immortals there to learn their techniques. Masafusa does not provide much detail about his further life, but states that after many journeys he evidently accomplished his goal, as he was purportedly seen alive and well a century after his alleged death.
It’s worth pointing out here that this course of events follows a Taoist motif: becoming disillusioned with one's own career, or with earthly affairs in general, is a common catalyst for search of the Taoist way in literature. A point can actually be made that of all the immortals in the Honchō Shinsenden is the most quintessentially Taoist one (despite not actually being a Taoist), the most direct example of the Chinese model being adapted for a Japanese historical figure, with no addition of the Buddhist components. He even resembles the typical image of a Tang scholar-bureaucrat invested in search for immortality just as much as in amorous adventures. This arguably makes him the perfect basis for a character in a game centered on Taoist immortals in Japan, though truth to be told I feel that in contrast with Seiga and Miko, ZUN’s Yoshika does not live up to her forerunner.
Legends about Miyako no Yoshika in other sources, or the remarkable poetic career of Ibaraki-doji

The oni of Rashomon and Miyako no Yoshika, as depicted by Ginko Adachi (Yokohama Art Museum; reproduced here for educational purposes only)
Some of you might wonder where Ibaraki-doji fits into this, considering the pretty direct reference to Yoshika's poetry in Wild and Horned Hermit. Masafusa, as a matter of fact, does allude to one more legend while highlighting Yoshika’s poetic talent, though he doesn’t go into detail. There’s no direct supernatural encounter - a nameless demonic inhabitant of Kyoto’s gate only hears a poem from passersby marveling at it and becomes “deeply moved”, but that’s it. The name Ibaraki-doji doesn’t show up at all, and there’s no mention of the oni finishing the poem, which is a mainstay of later versions.
Another of Masafusa’s works, Gōdansho (江談抄), also doesn’t use the name Ibaraki-dōji, or mention an actual encounter between Yoshika and the oni - he merely hears an unnamed passerby hum the poem and comments on it, calling it touching. However, the Kamakura period collection Jikkinshō already presents the version which gained the most traction in the long run, with the poem being a collaboration between Miyako no Yoshika and an oni. He later recites the full composition to Sugawara no Michizane, who is correctly able to point out only some of it is Yoshika’s own work, while the rest was added by an oni. However, once again, the name Ibaraki-doji is nowhere to be found.
On the other hand, while the story of Ibaraki-doji can be found in Taiheiki and other similar sources, it takes place far away from the capital in these early versions. The location was changed in noh adaptations of the legend to Rashomon, presumably due to its preexisting associations with supernatural creatures. By the time Toriyama Sekien published one if his famous bestiaries, Konjaku Hyakki Shūi, it seems the idea that the oni inhabiting this gate who was encountered by Yoshika and Watanabe no Tsuna’s nemesis Ibaraki-doji, who fought him there, were one and the same was already well established. Note that Sekien’s description of the oni of Rashomon actually doesn’t use the name Ibaraki-doji, though we do know he was aware of it.
It’s worth noting that the oni of Rashomon seemingly had a broader interest in fine arts, since there is also a legend in which he meets the famous biwa player Minamoto no Hiromasa and shows him his own skills with this instrument. However, this is ultimately not directly relevant to Yoshika, so you will have to wait until the next article, which will cover Shuten-doji and Ibaraki-doji in detail, to learn more.

The oni of Rashomon, as depicted by Toriyama Sekien (wikimedia commons)
Bibliography
Bernard Faure, From Bodhidharma to Daruma : The Hidden Life of a Zen Patriarch
Xiaofei Kang, The Cult of the Fox: Power, Gender, and Popular Religion in Late Imperial and Modern China
Zornica Kirkova, Roaming into the Beyond: Representations of Xian Immortality in Early Medieval Chinese Verse
Christoph Kleine & Livia Kohn, Daoist Immortality and Buddhist Holiness: A Study and Translation of the Honchō shinsen-den
Michelle Osterfeld Li, Ambiguous Bodies. Reading the Grotesque in Japanese Setsuwa Tales
Masato Mori, "Konjaku Monogatari-shū": Supernatural Creatures and Order
Masuo Shin'ichirō, Daoism in Japan (published in Brill’s Daoism Handbook)
Leslie Wallace, Betwixt and Between: Depictions of Immortals in Eastern Han Dynasty Tomb Reliefs
288 notes
·
View notes