#chinese nationals 2020
Text
was watching a video on wendigoon going over all the controversies and shit and i'm not here to talk about it i'm just here to say that im so glad someone fucking cleared up the whole "he's white" thing because for as race blind as i fucking am i was pretty sure that man Was Not white 😭 but hey how could i be sure when ppl like charlie white exist... 😞
#luly talks#i took until like 2020 or past to find out he wasn't asian i was like so fucking convinced of it#but yeah no like wendigoon isn't even that fair skinned#btw today i was literally thinking about my race blindness bc like that's literally how i was raised when i was a kid i didnt know race lik#a thing. yknow.#i understood nationalities for sure i understood China existed becuase well there's a lot of chinese immigration over here esp when i was#a child (now its rarer isnt it? i mean i cant fucking blame them lmao but i really feel like you dont see as many chinese ppl anymore)#but the whole idea about skintone meaning something or fucking. facial features was just. something i didnt think about#i did apparently get very surprising when i saw a african man for the first time according to my grandma#i was a fucking toddler i was like 4 or 5 btw i didnt know any better 😭#i did also call a horse a big dog like i was just a easily confused child#anyway when it came to my peers like. i even learnt about our country's native ppl and the diff tribes and their culture#(to an extent. which is super cool btw) in primary school BUT EVEN THEN i just.#like i just grew up in blissful unawareness i didnt think there was any difference between ppl like#we live in the same country and we speak the same language that's all i need to know you're like me 👍#being a child truly is of the silliest it gets
0 notes
Photo

Trump Republicans will continue to make excuses for their boss not doing anything about three surveillance balloon incursions form China during the previous administration.
Chinese Balloons Were Spotted Near US Bases During Trump’s Era
Alleged Chinese spy balloons were spotted on several occasions during President Donald Trump’s administration, including three instances where they traveled near sensitive US military facilities and training areas, according to people familiar with the matter.
The balloons were spotted near Texas, Florida and Hawaii, as well as the Pacific Ocean island of Guam, where the US has naval and Air Force bases – according to the people who requested anonymity to discuss intelligence matters. The balloons also flew near Norfolk, Virginia, and Coronado, California - two ports where the US stations its prized aircraft carriers.
The balloons that overflew Guam and Norfolk were thought to have radar-jamming capabilities, while the flights near Norfolk, where the US stations aircraft carriers, came around the time China was launching its own such vessel.
The balloons near Norfolk and Coronado both flew at a lower altitude over the ocean, but within US air space, according to the officials who served during the Trump administration.
Perhaps Trump was too busy sending classified materials to Vladimir Putin to take notice. Biden is giving Putin hell in Ukraine and still had time to safely shoot the Chinese balloon down last weekend. Biden is 1 for 1 with Chinese balloons while Trump was 0 for 3.
Trump loves kissing up to dictators. Maybe he thinks it makes him look strong if he acts like the butt boy for thugs. Before the pandemic, Trump couldn’t heap enough praise on Xi.
Trump on China’s Xi: ‘We love each other’

^^^ source
Of course Trump abruptly turned on Xi when he needed a scapegoat for his administration’s abysmal pandemic response in 2020 and had to pump up his racist base. Before January of 2020 Trump gave Xi a free ride.
Currently, in light of the Trump balloon scandal, Republicans are hoping Americans still have short memories.
#donald trump#surveillance aircraft#trump missed three chinese balloons#trump balloon scandal#national security#china#xi jinping#trump republicans#the gop#republicans make excuses for trump failures#election 2020
1 note
·
View note
Text
BEIJING — China’s struggling real estate developers won’t be getting a major bailout, Chinese authorities have indicated, warning that those who “harm the interests of the masses” will be punished.
“For real estate companies that are seriously insolvent and have lost the ability to operate, those that must go bankrupt should go bankrupt, or be restructured, in accordance with the law and market principles,” Ni Hong, Minister of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, said at a press conference Saturday.
“Those who commit acts that harm the interests of the masses will be resolutely investigated and punished in accordance with the law,” he said. “They will be made to pay the due price.”
That’s according to a CNBC translation of his Mandarin-language remarks published in an official transcript of the press conference, held alongside China’s annual parliamentary meetings.
Ni’s comments come as major real estate developers from Evergrande to Country Garden have defaulted on their debt, while plunging new home sales have put future business into question.
In 2020, Beijing cracked down on developers’ high reliance on debt for growth in an attempt to clamp down on property market speculation. But many developers soon ran out of money to finish building apartments, which are typically sold to homebuyers in China ahead of completion. Some buyers stopped paying their mortgages in a boycott.
Authorities have since announced measures to provide some developers with financing. But the national stance on reducing the role of real estate in the economy hasn’t changed.
This year’s annual government gathering has emphasized the country’s focus on investing in and building up high-end manufacturing capabilities. In contrast, the leadership has not mentioned the massive real estate sector as much.
Real estate barely came up during a press conference focused on the economy last week, while Ni was speaking during a meeting that focused on “people’s livelihoods.”
Ni said authorities would promote housing sales and the development of affordable housing, while emphasizing the need to consider the longer term.
Near-term changes in the property sector have a significant impact on China’s overall economy.
Real estate was once about 25% of China’s GDP, when including related sectors such as construction. UBS analysts estimated late last year that property now accounts for about 22% of the economy.
Last week, Premier Li Qiang said in his government work report that in the year ahead, China would “move faster to foster a new development model for real estate.”
“We will scale up the building and supply of government-subsidized housing and improve the basic systems for commodity housing to meet people’s essential need for a home to live in and their different demands for better housing,” an English-language version of the report said.
next time you complain about how things are in America, consider that if you lived in some kind of scary communist country like China, you wouldn't even get to fund a bailout for the real estate company owners who ruined the economy like you can (whether you like it or not) in the good old US of A! 🇺🇲
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Suriya, Ajay Devgan Best Actor: Winners at 68th National Awards [see complete list] | KKG INFO
Suriya, Ajay Devgan Best Actor: Winners at 68th National Awards [see complete list] | KKG INFO
Shah Rukh Khan, Katrina Kaif test positive for Covid-19, Bollywood on alert
The 68th National Film Awards on Friday honored the best films in Indian cinema for the year 2020. The Tamil film Surarai Potru directed by Sudha Kongara won five awards including Best Film. Malayalam film Ayyapanum Kosyum also made a strong appearance at the prestigious event.
Ranbir Kapoor wants to have a ‘different…

View On WordPress
#68th#actor#Aiyapanum Koshium#Ajay#Ajay Devgn#Aparna Balamurali#Awards#Biju Menon#chinese hot actors#complete#Devgan#hot actors and singers#hot actors of the 90s#INFO#KKG#list#movies with hot actors on netflix#National#National Awards#National Awards 2020#Surarai alliance#Suriya#the sun#Winners
0 notes
Text
"Around the world, mangrove forests have undergone a decades-long decline that is just now slowing to a halt.
In Pakistan, by contrast, mangroves expanded nearly threefold between 1986 and 2020, according to a 2022 analysis of satellite data.
Experts attribute this success to massive mangrove planting and conservation, as well as concerted community engagement.
Many in Pakistan are looking to mangroves to bolster precious fish stocks and defend against the mounting effects of climate change — even as threats to mangroves, such as wood harvesting and camel grazing, continue with no end in sight."
"His sandaled feet drenched in black mud, Rashid Rasheed points to one of the mangrove nurseries he’s been looking after for the past few years. With wooden walls topped by green netting, a dozen nurseries shelter thousands of saplings.
Rasheed, a researcher and nursery expert with the government of Balochistan province in Pakistan, has been leading a drive to establish nurseries in the coastal town of Dam. The goal is to expand and enhance the town’s scattered patches of natural mangrove forest, which have shriveled due to human activities.
“These nurseries have 50,000 saplings that are ready to be transported to the creeks for planting” Rasheed tells Mongabay.
Rasheed’s work is part of a five-year project initiated in 2019 by the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ South China Sea Institute of Oceanography that has planted mangroves on 16 hectares (40 acres) at Dam, and at other sites in Balochistan and neighboring Sindh province.
It’s one of many projects aiming to restore Pakistan’s mangroves. These semiaquatic trees offer a host of benefits, such as protecting coasts against storms and rising sea levels, providing habitat for fish, birds, and other wildlife, sequestering carbon better than most other ecosystems on Earth, and sustaining the livelihoods of some 120 million people globally, according to the IUCN.
Around the world, mangrove forests have undergone a decades-long decline that’s just now slowing to a halt. But Pakistan bucks this trend. The country’s mangroves expanded from 48,331 hectares in 1986 to 143,930 hectares in 2020 (119,430 to 355,659 acres), a nearly threefold increase, according to a 2022 analysis of satellite data. “It is because of the constant endeavor by government and NGOs,” the analysis states, citing restoration, research, and awareness-raising campaigns “now being religiously carried out to conserve and regrow mangroves” by local, national and foreign bodies. Fishing communities, who depend on mangroves for fuel, shelter and as fish nurseries, are often key to the success of Pakistan’s mangrove restoration, providing the labor for planting and protection."
-via Mongabay, February 5, 2024
#pakistan#mangrove#forest#ecosystem#reforestation#carbon emissions#climate change#climate crisis#climate action#fishing#community engagement#good news#hope
359 notes
·
View notes
Text
By Julia Conley
Common Dreams
April 25, 2023
Scientists are so alarmed by a new study on ocean warming that some declined to speak about it on the record, the BBC reported Tuesday.
"One spoke of being 'extremely worried and completely stressed,'" the outlet reported regarding a scientist who was approached about research published in the journal Earth System Science Data on April 17, as the study warned that the ocean is heating up more rapidly than experts previously realized—posing a greater risk for sea-level rise, extreme weather, and the loss of marine ecosystems.
Scientists from institutions including Mercator Ocean International in France, Scripps Institution of Oceanography in the United States, and Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research collaborated to discover that as the planet has accumulated as much heat in the past 15 years as it did in the previous 45 years, the majority of the excess heat has been absorbed by the oceans.
In March, researchers examining the ocean off the east coast of North America found that the water's surface was 13.8°C, or 14.8°F, hotter than the average temperature between 1981 and 2011.
The study notes that a rapid drop in shipping-related pollution could be behind some of the most recent warming, since fuel regulations introduced in 2020 by the International Maritime Organization reduced the heat-reflecting aerosol particles in the atmosphere and caused the ocean to absorb more energy.
But that doesn't account for the average global ocean surface temperature rising by 0.9°C from preindustrial levels, with 0.6°C taking place in the last four decades.
The study represents "one of those 'sit up and read very carefully' moments," said former BBC science editor David Shukman.
Lead study author Karina Von Schuckmann of Mercator Ocean International told the BBC that "it's not yet well established, why such a rapid change, and such a huge change is happening."
"We have doubled the heat in the climate system the last 15 years, I don't want to say this is climate change, or natural variability or a mixture of both, we don't know yet," she said. "But we do see this change."
Scientists have consistently warned that the continued burning of fossil fuels by humans is heating the planet, including the oceans. Hotter oceans could lead to further glacial melting—in turn weakening ocean currents that carry warm water across the globe and support the global food chain—as well as intensified hurricanes and tropical storms, ocean acidification, and rising sea levels due to thermal expansion.
A study published earlier this year also found that rising ocean temperatures combined with high levels of salinity lead to the "stratification" of the oceans, and in turn, a loss of oxygen in the water.
"Deoxygenation itself is a nightmare for not only marine life and ecosystems but also for humans and our terrestrial ecosystems," researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Center for Atmospheric Research, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration said in January. "Reducing oceanic diversity and displacing important species can wreak havoc on fishing-dependent communities and their economies, and this can have a ripple effect on the way most people are able to interact with their environment."
The unusual warming trend over recent years has been detected as a strong El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is expected to form in the coming months—a naturally occurring phenomenon that warms oceans and will reverse the cooling impact of La Niña, which has been in effect for the past three years.
"If a new El Niño comes on top of it, we will probably have additional global warming of 0.2-0.25°C," Dr. Josef Ludescher of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Research told the BBC.
The world's oceans are a crucial tool in moderating the climate, as they absorb heat trapped in the atmosphere by greenhouse gases.
Too much warming has led to concerns among scientists that "as more heat goes into the ocean, the waters may be less able to store excess energy," the BBC reported.
The anxiety of climate experts regarding the new findings, said the global climate action movement Extinction Rebellion, drives home the point that "scientists are just people with lives and families who've learnt to understand the implications of data better."
Read more.
#climate change#global warming#ocean warming#ocean acidification#deep ocean currents#degradation of ecosystems#ocean deoxygenation
966 notes
·
View notes
Text
China revealed this week it aims to spend more than a billion dollars to bolster manufacturing and domestic tech in a bid to remain globally competitive, while divulging little new support for the struggling real estate market.
Industrial support clearly ranked first on Beijing’s priority list for the year ahead, according to three major plans released this week as part of China’s annual parliamentary meetings.
One of those reports, from the Ministry of Finance, said the central government would allocate 10.4 billion yuan ($1.45 billion) “to rebuild industrial foundations and promote high-quality development of the manufacturing sector.”
While that’s down from the 13.3 billion yuan earmarked for the same category last year, the sector overall gained greater prominence. In 2023, plans to spend on industrial development came second to support for consumption.
“Unlike other economies that went through a wrenching adjustment in their housing market, China’s investment rate isn’t falling,” HSBC’s chief Asia economist Frederic Neumann and a team said in a report Friday. “Instead, [capital expenditure] is shifting towards infrastructure and, importantly, manufacturing.”[...]
Chinese authorities in 2020 intensified a crackdown on real estate developers’ high reliance on debt for growth. Property sales have since plunged while developers have run out of money to finish many projects, cutting into what was once about 25% of China’s GDP when including related sectors such as construction.[...]
Despite widespread attention on whether Beijing would bail out the property sector, real estate got no mention in the finance ministry’s spending plans, and limited attention in a ministry-level press conference about the economy during the parliamentary meetings. Instead, the housing minister was included in the lineup for a press conference about people’s livelihoods.
“Supporting the modernization of the industrial system” came first in the finance ministry’s report, followed by “supporting the implementation of the strategy of invigorating China through science and education.”
Within that second priority, the finance ministry said it would allocate 31.3 billion yuan for improving vocational education. Amid high youth unemployment, especially for university graduates, electric car company BYD and battery maker CATL are among those working with vocational schools to train staff for their expanding workforce.[...]
The report from the National Development and Reform Commission, the top economic planner, reiterated government plans to support some developers’ financing needs — under the eighth item on the priority list that called for preventing financial risks. The government work report presented by Premier Li Qiang gave real estate a similar level of prominence.
8 Mar 24
China will improve home sales in a "forceful" and "orderly" way, Minister of Housing and Urban-Rural Development Ni Hong said on Saturday (Mar 9), as weak demand in the country's beleaguered residential property market persists.[...]
Some developers should be allowed to go bankrupt or restructured according to legal and market-based rules, Ni said told a press conference on the sidelines of the annual meeting of parliament in Beijing.
Premier Li Qiang said this week that China will quicken the development of "a new model" for the troubled sector, focussing on building more affordable housing and meeting demand for homes.
But China will insist that "housing is for living in, not for speculation" when formulating a new development model for the sector, Ni said, reiterating an official line against property speculation.
9 Mar 24
184 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why I hate the '89 天安门广场 protests
In 1991, the Soviet Union was illegally dissolved. A few years later, the piece-meal destruction of Yugoslavia ended in war and genocide. The western, liberal/neoliberal world celebrated their destruction of state socialism. What had they accomplished?
CW: child prostitution, drug use, violence, death
Child prostitution in post-USSR Russia during the 1990s
The Children of Leningradskiy
Homeless children drug use
1993 constitutional crisis protests
These videos are about Russia only. There were 15 republics in the USSR. The dissolution of the USSR was an unmitigated humanitarian and economic disaster. All standards of life metrics from income to lifespan dropped to the floor. The GDP of Russia plummeted. Billionaires, bureaucrats, and especially foreign capital snatched up formerly Soviet state assets for pennies and reduced millions to poverty and destitution. At least 12 million people died as a DIRECT result of the dissolution of the USSR. Look at the former USSR: 15-20 countries (depending on who you ask) fighting each other in perpetual regional warfare. The concrete and cement plants in Turkmenistan sit empty and decaying. The Ukrainian shipyards on the Black sea, too.
So why bring up the USSR or Yugoslavia at all? Because they are a case and point in why you cannot let attempted color revolutions and liberalization protests take hold. The imperialists found that by employing this trick, of 'peaceful protests' they can destabilize then split apart nations then rob them blind. When a color revolution succeeds, people suffer on an unbelievable scale. The protestors in the USSR during glasnost wanted liberalization of the economy, freedom, democracy, so on and so forth, the usual western imperialist dog whistles. What they got was Yeltsin (and later Putin), poverty, and death.
Thankfully, the color revolution in China failed. It was crushed. so now we have a compare-and-contrast game (how fun!!!) between the handling of color revolutions in the USSR and in China. The MATERIAL EFFECT of the color revolutions in the former Soviet-bloc was the destruction of state socialism, the robbing of state assets, the destitution of the whole population, the penetration of foreign capital, the splitting of a once unified country into warlord states. On the other hand, the Chinese state remained and by 2020, eliminated absolute poverty.
IF the protestors had gotten what they wanted, IF the Chinese state was destroyed, we would see the EXACT same thing that happened to Yugoslavia, the USSR, East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Albania, and so on and so on repeat here. Except on an UNIMAGINABLE scale. 1.1 BILLION people were living in China in 1990. 1.1 BILLION reduced to poverty like you see in those videos, if not worse. Hundreds of billions of dollars of state assets in banks, factories, military, science, would have been stolen. Every bit of progress that Mao had accomplished would be rolled back to line the pockets of western imperialists. The country would most definitely be split up into warring regions, Xinjiang, TIbet, the Northeast, the Southwest, as much carnage as can be wrought to a people. THIS is the material reality that would greet the Chinese people if the '89 protestors got what they wanted.
They were chanting for child prostitution. For mass slavery. For mass poverty. For mass starvation. They stood on the side of the most evil entity to ever grace this planet. I will never forgive them.
Some reading on the '89 protests
189 notes
·
View notes
Text



SORA of ENHYPEN 𓊆ྀི❤︎𓊇ྀི
STAGE NAME sora (소라)
BIRTH NAME jung sora (정소라)
POSITION - *
BIRTHDAY october 31st, 2003
ZODIAC SIGN scorpio
CHINESE ZODIAC goat
HEIGHT 162cm (5’3”)
WEIGHT 44kg (99lbs)
BLOOD TYPE a
MBTI ENTP
NATIONALITY korean
REPRESENTATIVE EMOJI 🐯
MIC. COLOR pink
SORA FACTS
She is from Ilsan, South Korea.
She is the oldest child of four, and has three younger brothers. (2009, 2014, 2018)
Training Period: 3 years, 2 months/2015–2018 (Cre.Ker Ent) 1 year, 3 months/2019–2020 (BigHit Ent.)
She was in I.O.I previously and placed 2nd in Produce 101 Season 1 with 782,883 votes.
She ranked 2nd in the final episode of I-LAND with 1,362,913 votes.
She is the current MC for Inkigayo with Yeonjun and Woonhak. (July 2023)
She is a former Cre.Ker and BigHit Entertainments trainee and knows The Boyz well from training with them.
She played Jungkook’s partner in ‘Love Yourself’ highlight reel.
Byeolies is Sora’s fandom name created by fans.
Education: Chadwick International School
Sora speaks Korean and English fluently. She understands Japanese but isn’t confident in speaking it.
Her English name is Lucy. She chose it because she liked the song Lucy In the Sky With Diamonds.
Her favorite colors are lavender and coral.
She was on a swim team when she was younger.
She auditioned as a joke in 2015.
She has her own room in ENHYPEN’s dorm.
She has a Chihuahua named Miso.
She played Jung Somi in The Man From Nowhere in 2010, the daughter of Won Bin’s character in the movie who was kidnapped. She won Best New Actress at the 2010 Korean Film Awards for her role.
She also played Do Kyunghee, Cha Eunwoo’s character’s sister, in My Gangnam Beauty in 2018.
She is childhood friends with RIIZE’s Seunghan. (WeVerse 2023.09.8)
Specialty: Vocal and dance
Hobbies: Making friends, drawing, taking care of others
Charming Point: Her eyes, lips and cheeks
Her nickname(s) are Korea’s Golden Girl, Doll, ‘Malgeumi’ (bright), Da Vinci, Mermaid, ‘Nation’s Girl Next Door’, ‘Nation’s Little Sister’, Star.
Likes: Jay, Sunoo, swimming, her dog, makeup
Dislikes: Waking up, being taken care of, pineapple pizza, Mint Choco
Motto: Expect nothing.
* Position is currently being inferred.
inspired by @enmi-land & @laladellakang <3
poly ot7 enhypen fic with female 8th member, don’t like don’t read !!!
#˖ ࣪ . ࿐ ♡ ˚ . sora ⌗ profile#enhypen#enhypen 8th member#enhypen female addition#enhypen addition#kpop female oc#kpop female addition#enhypen imagines#enhypen scenarios#enhypen fluff#enhypen reactions#kpop imagines#kpop scenarios#bts female addition#txt female addition#txt 6th member#le sserafim 6th member#stray kids 9th member#ateez 9th member
147 notes
·
View notes
Text
What's Happening in China? The November 2022 Protests
Hello! I know that there's so much going on in the world right now, so not everyone may be aware of what is happening in China right now. I thought that I would try to write a brief explainer, because the current wave of protests is truly unprecedented in the past 30+ years, and there is a lot of fear over what may happen next. For context, I'm doing this as someone who has a PhD in Asian Studies specialising in contemporary Chinese politics, so I don't know everything but I have researched China for many years.
I'll post some decent links at the end along with some China specialists & journalists I follow on Twitter (yeah I know, but it's still the place for the stuff at the moment). Here are the bullet points for those who just want a brief update:
Xi Jinping's government is still enacting a strict Zero Covid policy enforced by state surveillance and strict lockdowns.
On 24 November a fire in an apartment in Urumqi, Xinjiang province, killed 10. Many blamed strict quarantine policies on preventing evacuation.
Protests followed and have since spread nationwide.
Protesters are taking steps not seen since Tiananmen in 1989, including public chants for Xi and the CCP to step down.
Everyone is currently unsure how the government will respond.
More in-depth discussion and links under the cut:
First a caveat: this is my own analysis/explanation as a Chinese politics specialist. I will include links to read further from other experts and journalists. Also, this will be quite long, so sorry about that!
China's (aka Xi Jinping's) Covid Policy:
The first and most important context: Xi has committed to a strict Zero Covid policy in China, and has refused to change course. Now, other countries have had similar approaches and they undoubtedly saved lives - I was fortunate to live in New Zealand until this year, and Prime Minister Ardern's Zero Covid approach in 2020-2021 helped protect many. The difference is in the style/scope of enforcement, the use of vaccines, and the variant at play. China has stepped up its control on public life over the past 10 years, and has used this to enforce strict quarantine measures without full regard to the impact on people's lives - stories of people not getting food were common. Quarantine has also become a feared situation, as China moves people to facilities often little better than prisons and allegedly without much protection from catching Covid within. A personal friend in Zhengzhou went through national, then provincial, then local quarantines when moving back from NZ, and she has since done her best to avoid going back for her own mental and physical health. Xi has also committed China to its two home-grown vaccines, Sinovac and Sinopharm, both of which have low/dubious efficacy and are considered ineffective against new variants. Finally, with delta and then omicron most of the Zero-Covid countries have modified their approach due to the inability to maintain zero cases. China remains the only country still enacting whole-city eradication lockdowns, and they have become more frequent to the point that several are happening at any given time. The result is a population that is incredibly frustrated and losing hope amidst endless lockdowns and perceived ineffectiveness to address the pandemic.
Other Issues at Play:
Beyond the Covid situation, China is also wrestling with the continued slowdown in its economic growth. While its economic rise and annual GDP growth was nigh meteoric from the 80s to the 00s, it has been slowing over the past ten years, and the government is attempting to manage the transition away from an export-oriented economy to a more fully developed one. However, things are still uncertain, and Covid has taken its toll as it has elsewhere the past couple of years. Youth unemployment in particular is reaching new highs at around 20%, and Xi largely ignored this in his speech at the Party Congress in October (where he entered an unprecedented third term). As a result of the perceived uselessness of China's harsh work culture and its failure to result in a better life, many young Chinese have been promoting 躺平 tǎng píng or "lying flat", aka doing the bare minimum just to get by (similar to the English "quiet quitting"). The combination of economic issues and a botched Covid approach is important, as these directly affect the lives of ordinary middle-class Chinese, and historical it has only been when this occurred that mass movements really took off. The most famous, Tiananmen in 1989, followed China's opening up economic reforms and the dismantling of many economic safety nets allowing for growing inequality. While movements in China often grow to include other topics, having a foundation in something negatively impacting the average Han Chinese person's livelihood is important.
The Spark - 24 Nov 2022 Urumqi Apartment Fire:
The current protests were sparked by a recent fire that broke out in a flat in Urumqi, capital of the Xinjiang province. (This is the same Xinjiang that is home to the Uighur people, against whom China has enacted a campaign of genocide and cultural destruction.) The fire occurred in the evening and resulted in 10 deaths, which many online blamed on the strict lockdown measures imposed by officials, who prevented people from leaving their homes. It even resulted in a rare public apology by city officials. However, with anger being so high nationwide, in addition to many smaller protests that have occurred over the past two years, this incident has ignited a nationwide movement.
The Protests and Their Significance:
The protests that have broken out over the past couple of days representing the largest and most significant challenge to the leadership since the 1989 Tiananmen movement. Similar to that movement, these protests have occurred at universities and cities across the country, with many students taking part openly. This scale is almost unseen in China, particularly for an anti-government protest. Other than Tiananmen in 1989, the most widespread movements that have occurred have been incidents such as the protest of the 1999 Belgrade bombings or the 2005 and then 2012 anti-Japanese protests, all of which were about anger toward a foreign country.
Beyond the scale the protests are hugely significant in their message as well. Protesters are publicly shouting the phrases "习近平下台 Xí Jìnpíng xiàtái!" and "共产党 下台 Gòngchǎndǎng xiàtái!", which mean "Xi Jinping, step down/resign!" and "CCP, step down/resign!" respectively. To shout a direct slogan for the government to resign is unheard of in China, particularly as Xi has tightened control of civil society. And people are doing this across the country in the thousands, openly and in front of police. This is a major challenge for a leader and party who have prioritised regime stability as a core interest for the majority of their history.
Looking Ahead:
Right now, as of 15:00 Australian Eastern time on Monday, 28 November 2022, the protests are only in their first couple of days and we are unsure as to how the government will respond. Police have already been seen beating protesters and journalists and dragging them away in vehicles. However, in many cases the protests have largely been monitored by police but still permitted to occur. There seems to be uncertainty as to how they want to respond just yet, and as such no unified approach.
Many potential outcomes exist, and I would warn everyone to be careful in overplaying what can be achieved. Most experts I have read are not really expecting this to result in Xi's resignation or regime change - these things are possible, surely, but it is a major task to achieve and the unity & scale of the protest movement remains to be fully seen. The government may retaliate with a hard crackdown as it has done with Tiananmen and other protests throughout the years. It may also quietly revamp some policies without publicly admitting a change in order to both pacify protesters and save face. The CCP often uses mixed tactics, both coopting and suppressing protest movements over the years depending on the situation. Changing from Zero Covid may prove more challenging though, given how much Xi has staked his political reputation on enforcing it.
What is important for everyone online, especially those of us abroad, is to watch out for the misinformation campaign the government will launch to counter these protests. Already twitter is reportedly seeing hundreds of Chinese bot accounts mass post escort advertisements using various city names in order to drown out protest results in the site's search engine. Chinese officials will also likely invoke the standard narrative of Western influence and CIA tactics as the reason behind the protests, as they did during the Hong Kong protests.
Finally, there will be a new surge of misinformation and bad takes from tankies, or leftists who uncritically support authoritarian regimes so long as they are anti-US. An infamous one, the Qiao Collective, has already worked to shift the narrative away from the protests and onto debating the merits of Zero Covid. This is largely similar to pro-Putin leftists attempting the justify his invasion of Ukraine. Always remember that the same values that you use to criticise Western countries should be used to criticise authoritarian regimes as well - opposing US militarism and racism, for example, is not incompatible with opposing China's acts of genocide and state suppression. If you want further info (and some good sardonic humour) on the absurd takes and misinfo from pro-China tankies, I would recommend checking out Brian Hioe in the links below.
Finally, keep in mind that this is a grass-roots protest made by people in China, who are putting their own lives at risk to demonstrate openly like this. There have already been so many acts of bravery by those who just want a better future for themselves and their country, and it is belittling and disingenuous to wave away everything they are doing as being just a "Western front" or a few "fringe extremists".
Links:
BBC live coverage page with links to analysis and articles
ABC (Australia) analysis
South China Morning Post analysis
Experts & Journalists to Check Out:
Brian Hioe - Journalist & China writer, New Bloom Magazine
Bonnie Glaser - China scholar, German Marshall Fund
Vicky Xu - Journalist & researcher, Australian Strategic Policy Institute
Stephen McDonnell - Journalist, BBC
M Taylor Fravel - China scholar, MIT
New Zealand Contemporary China Research Centre - NZ's hub of China scholarship (I was fortunate to attend their conferences during my PhD there, they do great work!)
If you've reached the end I hope this helps with understanding what's going on right now! A lot of us who know friends and whanau in China are worried for their safety, so please spread the word and let's hope that there is something of a positive outcome ahead.
#孟珏’s china corner#中国#上海#习近平#习近平下台#共产党下台#China#Shanghai#China protests#China protests 2022#Xi Jinping#Xi Jinping step down#CCP step down#Xi Jinping resign#CCP resign#乌鲁木齐#Urumqi#Urumqi fire#Urumqi apartment fire
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
stop asian hate
long before the chinese exclusion act in 1882, there has always been hate towards asians in the U.S. since covid, the amount of hatred asians have had to face had surged and asian hate crimes have risen in the past years. According to NBC News, the hate crimes have risen 339% compared to 2020. i hope those who feel superior and racist towards asians wake up and realize that they have no right to hate someone and harass, commit crimes against, and bully people purely based off their race. the world is an ugly place, but it doesn’t have to be. i hope they realize that no good will come from hating on asians, and the racism in the U.S. needs to end. i pray for those who have been victims of the hate crimes and that there will be a time in the future when we can all be accepting and loving of one another while not ignoring the fact that we are different, but embracing it and living in peace.
#stop asian hate#stop asian violence#lawblr#high school#discover#usa#history#explore#equal rights#equality#lawyer#studyblr#study space#law#passion project#university#study tips#us#united states#nyc#new york city#new york#los angeles#california#us history#culture#world history
324 notes
·
View notes
Note
I've been talking with a few people irl about the TikTok ban and I was wondering if I could get your take on it? (iirc you work in election security). Mainly I'd like to know why TikTok/China is *uniquely* bad wrt dating mining/potential election interference when we've seen other companies/governments do the same thing (thinking of the Russian psyops here on Tumblr in 2016). It feels like the scope is so narrow that it doesn't come close to targeting the root problem (user privacy and data mining as a whole), leading me to think it's only point is "ooh China Scary". Thoughts? (No worries if you'd rather not get into it, I just thought of you as someone who might have more insight/informed opinions on the matter).
So I'm not really familiar with all the details of the case and certainly not all the details of the bill. But I will give my perspective:
TikTok as a particular threat to users' data and privacy has been known for some time in the cybersecurity world. US government employees and contractors have been straight-up forbidden to have it on their phones for some time now. I, for example, have never had it on my phone because of these security concerns. (Worth noting, I'm not a government employee or contractor, it was just a known-to-be dangerous app in the cybersecurity world so I avoided it.)
This is because the parent company, as I understand, has known connections to the Chinese government that have been exploited in the past. For example, to target journalists.
Worth noting, another app that would potentially be on the chopping block is WeChat, which also has close ties to (or is outright owned by?) the Chinese government. This is just speculation on my part but it's based on the fact that all the concerns around TikTok are there for WeChat too and it has also been banned on government devices in some states, so I imagine it would be next if the bill passes.
I think this is important to note because I've seen some hot takes here on Tumblr have said that the entire case against TikTok is made up and there is no security threat. That is simply not true. The concerns have been there for a while.
However, the question of what to do about it is a thorny one.
The determination seems to be that so long as TikTok is still owned by its parent company with its direct ties to the Chinese government, there really is no way to guarantee that it's safe to use. From that angle, demanding that the company sever ties and set up some form of local ownership makes sense.
I am not a lawyer, but, that being said, forcing them to sell their local operations to a locally-based buyer is a pretty invasive and unusual step for legislators to take against a private company, even in a clear case of spying. I'm sure TikTok's widespread popularity is a big part of the threat it poses, which lends to the argument used to justify such an extreme step. (Because it is on so many phones, it really could be a danger to national security.)
That said, at one point young activists on TikTok embarrassed Trump (lots of good context in this article) while he was campaigning in 2020, and there was some talk then about shutting it down which seemed pretty clearly linked to how it was used as a platform to organize against him. I'm sure there's at least some right wing antipathy towards the app that has a political basis going back to this event. Trump signed an executive order banning it, the ban going into effect got bogged down in the courts, and then Biden rescinded that executive order when he got into office, pending an investigation into the threat it posed.
Those investigations seem to have further confirmed that the Chinese government is getting access to US user data through the app, and further confirmed it as a security threat.
Now, to muddy the waters further, there's several dodgy investment funds including one owned by former Secretary of the Treasury to Trump Steven Mnuchin that are circling with an interest to buy TikTok if it does sell. That's very concerning.
Funds like Mnuchin's interest in purchasing TikTok (even though they do invest in other technologies too, so it is in their portfolio) definitely makes the motivations behind the sale look pretty damning as momentum builds, that it could be some sort of money grab here in the US.
China has also pointed out that forcing the sale of a company because of spying concerns like this opens a whole can of worms. If China thinks that, say, Microsoft is spying on their citizens, could they force the US company to sell its operations in China to a Chinese investor? Could they force Google? Could they even further polarize the internet in general between "free" and "not free" (as in, behind the great Chinese or Russian firewall, as examples) if this precedent is set, so that no Western companies can operate in authoritarian states without selling their local operations there to a government-controlled organization, and thus be unable protect their users there? Or, if you don't have so rosy a view of Western companies, could it effectively deal a blow to international trade in general by saying you have to have to sell any overseas arms of a company to someone who is from there? Again, I'm not a lawyer, but this is a hell of a can of worms to open.
But again, this is muddy because China absolutely is spying on TikTok users. The security reason for all of this is real. What to do about it is the really muddled part that has a ton of consequences, and from that angle I agree with people who are against this bill. Tons of bad faith consequences could come out of it. But the concerns kicking off the bill are real.
73 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The Two Mongolias
The native Mongolian peoples have historically lived in the Mongolian People’s Republic and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in the People’s Republic of China, which together once comprised Greater Mongolia. While Inner Mongolia is an autonomous subnational division of China, the nation of Mongolia (sometimes known as Outer Mongolia) is a free and open state with a democratic government.
Political and historical reasons led to the split of Mongolia into these two regions. One important contributing aspect is that, in the 19th century, Han Chinese farmers were drawn to the Mongolian region in search of land to cultivate due to population pressure in China’s south. Conflicts with herders resulted from this, and Outer Mongolia gained independence in 1912 and Inner Mongolia gained administrative autonomy in 1932.
Is a reunion between the two Mongolias possible?
Sources:
Beal, Rich. "A tale of two Mongolias." Koryo Group. 14 October 2020.
Salisbury, Harrison E. "The two Mongolias are bitter enemies." The New York Times. 17 October 1977.
by anthro.atlas
116 notes
·
View notes
Text
Exploring Chinese names of Taiwan

A while ago, I stumbled across this press release for Taiwan's National Names Statistical Analysis report. Then I clicked on the full report and spent days glued to my screen reading it!
So, courtesy of Taiwan's Ministry of the Interior, let's look at some of the data. We will look at: top given names, top full names, and top unisex names.
Format:
陈淑芬 | 陳淑芬 Chén Shūfēn | Chén Shúfēn / 3747人
简体 | 繁體 读音 | 台湾读音 / 人数
(Simp.) | (trad.) (pronunciation) | (Taiwan pronunciation) / (# people)
I put simplified first for consistency with the rest of my blog. 简体 | 繁體 is the convention I use in many other posts.
Top 10 given names (by decade)
The report shows the top names by decade, which is really fascinating because you can see how tastes and trends changed over time. I'm just going to show the overall top 10 and last three full decades (1990s, 2000s, and 2010s) but you can see the rest on pg. 280 of the report (pg. 281 of the PDF).
Male

Overall
家豪 Jiāháo / 14,038人
志明 Zhìmíng / 12,719人
建宏 Jiànhóng / 12,196人
俊杰 | 俊傑 Jùnjié / 12,187人
俊宏 Jùnhóng / 11,189人
志豪 Zhìháo / 10,676人
志伟 | 志偉 Zhìwěi / 10,563人
承翰 Chénghàn / 9726人
冠宇 Guànyǔ / 9655人
志强 | 志強 Zhìqiáng / 9101人
1991-2000
家豪 Jiāháo / 4039人
冠宇 Guànyǔ / 3603人
冠廷 Guàntíng / 3399人
承翰 Chénghàn / 3008人
宗翰 Zōnghàn / 2831人
柏翰 Bóhàn / 2594人
彦廷 | 彥廷 Yàntíng / 2502人
冠霖 Guànlín / 2114人
俊杰 | 俊傑 Jùnjié / 2084人
承恩 Chéng’ēn / 1918人
2001-2010
承恩 Chéng’ēn / 2997人
承翰 Chénghàn / 2636人
冠廷 Guàntíng / 2452人
冠宇 Guànyǔ / 2206人
宇翔 Yǔxiáng / 1938人
柏翰 Bóhàn / 1885人
彦廷 | 彥廷 Yàntíng / 1610人
冠霖 Guànlín / 1509人
柏宇 Bóyǔ / 1471人
柏谚 | 柏諺 Bóyàn / 1409人
2011-2020
承恩 Chéng’ēn / 2215人
宥廷 Yòutíng / 2036人
品睿 Pǐnruì / 2021人
宸睿 Chénruì / 1904人
宇恩 Yǔ’ēn / 1860人
宇翔 Yǔxiáng / 1713人
承翰 Chénghàn / 1556人
宥辰 Yòuchén / 1532人
柏睿 Bóruì / 1511人
睿恩 Ruì’ēn / 1503人
Female
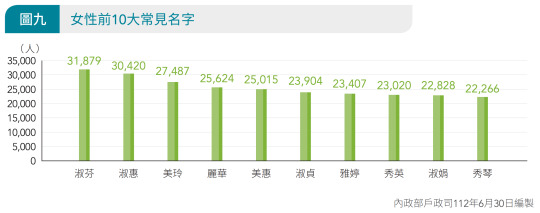
Overall
淑芬 Shūfēn | Shúfēn / 31,879人
淑惠 Shūhuì | Shúhuì / 30,420人
美玲 Měilíng / 27,487人
丽华 | 麗華 Lìhuá / 25,624人
美惠 Měihuì / 25,015人
淑贞 | 淑貞 Shūzhēn | Shúzhēn / 23,904人
雅婷 Yǎtíng / 23,407人
秀英 Xiùyīng / 23,020人
淑娟 Shūjuān | Shújuān / 22,828人
秀琴 Xiùqín / 22,266人
1991-2000
雅婷 Yǎtíng / 5797人
怡君 Yíjūn / 3575人
怡婷 Yítíng / 3183人
雅雯 Yǎwén / 3084人
诗涵 | 詩涵 Shīhán / 3006人
钰婷 | 鈺婷 Yùtíng / 2775人
怡萱 Yíxuān / 2729人
雅筑 Yǎzhù | Yǎzhú / 2700人
郁婷 Yùtíng / 2600人
宜庭 Yítíng / 2555人
2001-2010
宜蓁 Yízhēn / 2629人
欣妤 Xīnyú / 1643人
诗涵 | 詩涵 Shīhán / 1610人
思妤 Sīyú / 1561人
雅婷 Yǎtíng / 1439人
宜庭 Yítíng / 1394人
佳颖 | 佳穎 Jiāyǐng / 1375人
品妤 Pǐnyú / 1336人
子涵 Zǐhán / 1271人
怡萱 Yíxuān / 1258人
2011-2020
品妍 Pǐnyán/ 2421人
子晴 Zǐqíng / 2087人
咏晴 | 詠晴 Yǒngqíng / 2001人
品妤 Pǐnyú / 1697人
禹彤 Yǔtóng / 1578人
羽彤 Yǔtóng / 1434人
芯语 | 芯語 Xīnyǔ / 1342人
宥蓁 Yòuzhēn / 1226人
语彤 | 語彤 Yǔtóng / 1221人
苡晴 Yǐqíng / 1164人
Top 10 full names
In Mainland China the most common full names are usually something like 张伟 and 李娜. In Taiwan, 单名 (single-character given names) are much rarer, so the results are very different. We can also really see the dominance of the surname 陈 here. The rest of the top 100 are on pg. 268 of the report (pg. 269 of the PDF).
Male

陈冠宇 | 陳冠宇 Chén Guànyǔ / 4021人
陈建宏 | 陳建宏 Chén Jiànhóng / 3524人
张家豪 | 張家豪 Zhāng Jiāháo / 2890人
陈俊宏 | 陳俊宏 Chén Jùnhóng / 2801人
陈冠廷 | 陳冠廷 Chén Guàntíng / 2469人
陈柏宇 | 陳柏宇 Chén Bóyǔ / 2383人
林建宏 Lín Jiànhóng / 2375人
陈柏翰 | 陳柏翰 Chén Bóhàn / 2353人
陈彦廷 | 陳彥廷 Chén Yàntíng / 2249人
陈信宏 | 陳信宏 Chén Xìnhóng / 2120人
Female

陈怡君 | 陳怡君 Chén Yíjūn / 5744人
林怡君 Lín Yíjūn / 4401人
陈淑芬 | 陳淑芬 Chén Shūfēn | Chén Shúfēn / 3747人
张雅婷 | 張雅婷 Zhāng Yǎtíng / 3491人
陈美玲 | 陳美玲 Chén Měilíng / 3235人
陈怡如 | 陳怡如 Chén Yírú / 3121人
陈美惠 | 陳美惠 Chén Měihuì / 3103人
陈淑惠 | 陳淑惠 Chén Shūhuì | Chén Shúhuì / 2921人
林淑惠 Lín Shūhuì | Lín Shúhuì / 2903人
陈淑贞 | 陳淑貞 Chén Shūzhēn | Chén Shúzhēn / 2751人
Unisex/gender-neutral names

Do you want a name that doesn't strongly lean towards masculine or feminine? The report also highlight the common names across genders. It seems their criteria for this was names falling between 40% male-60% female and 60% male-40% female.
To clarify, they actually looked at the top 100 full names, not given names. For instance, 宥均 Yòujūn was on the list three times with three different surnames. But I re-sorted the list by given name since I was curious to see that. You can find the original data on pg. 270 of the report (pg. 271 of the PDF).
宥均 Yòujūn
Total: 1804人
Male: 54.77%
Female: 45.23%
佳霖 Jiālín
Total: 1111人
Male: 51.67%
Female: 48.33%
家华 | 家華 Jiāhuá
Total: 923人
Male: 53.41%
Female: 46.59%
郁文 Yùwén
Total: 847人
Male: 43.68%
Female: 56.32%
禹安 Yǔ’ān
Total: 789人
Male: 51.71%
Female: 48.29%
以恩 Yǐ’ēn
Total: 730人
Male: 49.32%
Female: 50.68%
孟儒 Mèngrú
Total: 643人
Male: 55.05%
Female: 44.95%
冠桦 | 冠樺 Guànhuà
Total: 643人
Male: 52.26%
Female: 47.74%
靖恩 Jìng’ēn
Total: 621人
Male: 44.93%
Female: 55.07%
品辰 Pǐnchén
Total: 600人
Male: 58.83%
Female: 41.17%
Notes
The report is INCREDIBLY detailed. I'm not kidding. The body of the report is not that long, but it has a very long appendix with about 200 pages of tables. Here are some examples of data included that I didn't mention:
Most popular given names people changed their names to
Most common 单名 and 叠字名字
Most common last names by city/county
Indigenous peoples' use of the Latin alphabet for names
Prevalence of multi-character surnames
And so, so much more!
And FYI, the report uses the ROC calendar, which starts with the founding of the Republic of China. To convert from the ROC calendar to the Gregorian calendar, add 111.
Ex:
1年=1912
112年=2023
Pronunciation & tones
冠 is a 多音字 that is pronounced guān or guàn. I went with guàn because that seems to be more common in names from what I've observed.
柏 is also a 多音字 that can be pronounced bǎi or bó. MDBG says Taiwan doesn't have the bǎi pronunciation. I usually hear it read as bó in names, so that's what I'm going with.
MDBG also says 淑 is pronounced shú (not shū) in Taiwan. Likewise, it says 筑 is zhú (not zhù). I'll take their word for it.
I tried to put apostrophes in the right places (like for 承恩 Chéng’ēn), but I'm really bad at knowing when and where to use it. Please pardon any mistakes!
See similar posts:
Chinese surnames that are more common in Taiwan
A closer look at Chinese names
Analyzing Chinese names: Syllables & tones
The evolution of Chinese names (Kontinentalist)
#chinese names#taiwan#chinese name#taiwanese names#taiwanese name#chinese#mandarin#mandarin chinese#chinese language#studyblr#langblr#learning languages#language learning#chinese langblr#mandarin langblr#languageblr
75 notes
·
View notes
Text
This is asymmetrical warfare which is finding alternative ways to defeat a rival like the U.S. that has a far superior military.
Republican apocalyptic terrorists and our foreign adversaries hope that infrastructure attacks will destabilize the U.S. and lead to its collapse as a nation. This has been a common theme among far-right groups and evangelical assholes. There’s been a series of domestic terrorist attacks on power stations and other infrastructure soft targets since Trump lost in 2020. They believe after two weeks without electricity the US will collapse. Then the various MAGA groups will start their civil/race war and try to “purge” the rest of us. The Obama’s recently produced a movie for Netflix based on this premise (Leave the World Behind). Towards the end of the film the central character explains how it works; shut off the power, spread confusion through targeted misleading propaganda, and stir up division through internal attacks.
China, Russia, North Korea, and Middle Eastern states have been working this angle for years but now it is accelerating with far right domestic terrorists onboard. This goes way beyond just election interference which the oligarchs support.
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the first half century of his career, Robert Jay Lifton published five books based on long-term studies of seemingly vastly different topics. For his first book, “Thought Reform and the Psychology of Totalism,” Lifton interviewed former inmates of Chinese reëducation camps. Trained as both a psychiatrist and a psychoanalyst, Lifton used the interviews to understand the psychological—rather than the political or ideological—structure of totalitarianism. His next topic was Hiroshima; his 1968 book “Death in Life,” based on extended associative interviews with survivors of the atomic bomb, earned Lifton the National Book Award. He then turned to the psychology of Vietnam War veterans and, soon after, Nazis. In both of the resulting books—“Home from the War” and “The Nazi Doctors”—Lifton strove to understand the capacity of ordinary people to commit atrocities. In his final interview-based book, “Destroying the World to Save It: Aum Shinrikyo, Apocalyptic Violence, and the New Global Terrorism,” which was published in 1999, Lifton examined the psychology and ideology of a cult.
Lifton is fascinated by the range and plasticity of the human mind, its ability to contort to the demands of totalitarian control, to find justification for the unimaginable—the Holocaust, war crimes, the atomic bomb—and yet recover, and reconjure hope. In a century when humanity discovered its capacity for mass destruction, Lifton studied the psychology of both the victims and the perpetrators of horror. “We are all survivors of Hiroshima, and, in our imaginations, of future nuclear holocaust,” he wrote at the end of “Death in Life.” How do we live with such knowledge? When does it lead to more atrocities and when does it result in what Lifton called, in a later book, “species-wide agreement”?
Lifton’s big books, though based on rigorous research, were written for popular audiences. He writes, essentially, by lecturing into a Dictaphone, giving even his most ambitious works a distinctive spoken quality. In between his five large studies, Lifton published academic books, papers and essays, and two books of cartoons, “Birds” and “PsychoBirds.” (Every cartoon features two bird heads with dialogue bubbles, such as, “ ‘All of a sudden I had this wonderful feeling: I am me!’ ” “You were wrong.”) Lifton’s impact on the study and treatment of trauma is unparalleled. In a 2020 tribute to Lifton in the Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, his former colleague Charles Strozier wrote that a chapter in “Death in Life” on the psychology of survivors “has never been surpassed, only repeated many times and frequently diluted in its power. All those working with survivors of trauma, personal or sociohistorical, must immerse themselves in his work.”
Lifton was also a prolific political activist. He opposed the war in Vietnam and spent years working in the anti-nuclear movement. In the past twenty-five years, Lifton wrote a memoir—“Witness to an Extreme Century”—and several books that synthesize his ideas. His most recent book, “Surviving Our Catastrophes,” combines reminiscences with the argument that survivors—whether of wars, nuclear explosions, the ongoing climate emergency, COVID, or other catastrophic events—can lead others on a path to reinvention. If human life is unsustainable as we have become accustomed to living it, it is likely up to survivors—people who have stared into the abyss of catastrophe—to imagine and enact new ways of living.
Lifton grew up in Brooklyn and spent most of his adult life between New York City and Massachusetts. He and his wife, Betty Jean Kirschner, an author of children’s books and an advocate for open adoption, had a house in Wellfleet, on Cape Cod, that hosted annual meetings of the Wellfleet Group, which brought together psychoanalysts and other intellectuals to exchange ideas. Kirschner died in 2010. A couple of years later, at a dinner party, Lifton met the political theorist Nancy Rosenblum, who became a Wellfleet Group participant and his partner. In March, 2020, Lifton and Rosenblum left his apartment on the Upper West Side for her house in Truro, Massachusetts, near the very tip of Cape Cod, where Lifton, who is ninety-seven, continues to work every day. In September, days after “Surviving Our Catastrophes” was published, I visited him there. The transcript of our conversations has been edited for length and clarity.
I would like to go through some terms that seem key to your work. I thought I’d start with “totalism.”
O.K. Totalism is an all-or-none commitment to an ideology. It involves an impulse toward action. And it’s a closed state, because a totalist sees the world through his or her ideology. A totalist seeks to own reality.
And when you say “totalist,” do you mean a leader or aspiring leader, or anyone else committed to the ideology?
Can be either. It can be a guru of a cult, or a cult-like arrangement. The Trumpist movement, for instance, is cult-like in many ways. And it is overt in its efforts to own reality, overt in its solipsism.
How is it cult-like?
He forms a certain kind of relationship with followers. Especially his base, as they call it, his most fervent followers, who, in a way, experience high states at his rallies and in relation to what he says or does.
Your definition of totalism seems very similar to Hannah Arendt’s definition of totalitarian ideology. Is the difference that it’s applicable not just to states but also to smaller groups?
It’s like a psychological version of totalitarianism, yes, applicable to various groups. As we see now, there’s a kind of hunger for totalism. It stems mainly from dislocation. There’s something in us as human beings which seeks fixity and definiteness and absoluteness. We’re vulnerable to totalism. But it’s most pronounced during times of stress and dislocation. Certainly Trump and his allies are calling for a totalism. Trump himself doesn’t have the capacity to sustain an actual continuous ideology. But by simply declaring his falsehoods to be true and embracing that version of totalism, he can mesmerize his followers and they can depend upon him for every truth in the world.
You have another great term: “thought-terminating cliché.”
Thought-terminating cliché is being stuck in the language of totalism. So that any idea that one has that is separate from totalism is wrong and has to be terminated.
What would be an example from Trumpism?
The Big Lie. Trump’s promulgation of the Big Lie has surprised everyone with the extent to which it can be accepted and believed if constantly reiterated.
Did it surprise you?
It did. Like others, I was fooled in the sense of expecting him to be so absurd that, for instance, that he wouldn’t be nominated for the Presidency in the first place.
Next on my list is “atrocity-producing situation.”
That’s very important to me. When I looked at the Vietnam War, especially antiwar veterans, I felt they had been placed in an atrocity-producing situation. What I meant by that was a combination of military policies and individual psychology. There was a kind of angry grief. Really all of the My Lai massacre could be seen as a combination of military policy and angry grief. The men had just lost their beloved older sergeant, George Cox, who had been a kind of father figure. He had stepped on a booby trap. The company commander had a ceremony. He said, “There are no innocent civilians in this area.” He gave them carte blanche to kill everyone. The eulogy for Sergeant Cox combined with military policy to unleash the slaughter of My Lai, in which almost five hundred people were killed in one morning.
You’ve written that people who commit atrocities in an atrocity-producing situation would never do it under different circumstances.
People go into an atrocity-producing situation no more violent, or no more moral or immoral, than you or me. Ordinary people commit atrocities.
That brings us to “malignant normality.”
It describes a situation that is harmful and destructive but becomes routinized, becomes the norm, becomes accepted behavior. I came to that by looking at malignant nuclear normality. After the Second World War, the assumption was that we might have to use the weapon again. At Harvard’s Kennedy School of Government, a group of faculty members wrote a book called “Living with Nuclear Weapons.” There was a book by Joseph Nye called “Nuclear Ethics.” His “nuclear ethics” included using the weapon. Later there was Star Wars, the anti-missile missiles which really encouraged first-strike use. These were examples of malignant nuclear normality. Other examples were the scenarios by people like [the physicists] Edward Teller and Herman Kahn in which we could use the weapons and recover readily from nuclear war. We could win nuclear wars.
And now, according to the Doomsday Clock, we’re closer to possible nuclear disaster than ever before. Yet there doesn’t seem to be the same sense of pervasive dread that there was in the seventies and eighties.
I think in our minds apocalyptic events merge. I see parallels between nuclear and climate threats. Charles Strozier and I did a study of nuclear fear. People spoke of nuclear fear and climate fear in the same sentence. It’s as if the mind has a certain area for apocalyptic events. I speak of “climate swerve,” of growing awareness of climate danger. And nuclear awareness was diminishing. But that doesn’t mean that nuclear fear was gone. It was still there in the Zeitgeist and it’s still very much with us, the combination of nuclear and climate change, and now COVID, of course.
How about “psychic numbing”?
Psychic numbing is a diminished capacity or inclination to feel. One point about psychic numbing, which could otherwise resemble other defense mechanisms, like de-realization or repression: it only is concerned with feeling and nonfeeling. Of course, psychic numbing can also be protective. People in Hiroshima had to numb themselves. People in Auschwitz had to numb themselves quite severely in order to get through that experience. People would say, “I was a different person in Auschwitz.” They would say, “I simply stopped feeling.” Much of life involves keeping the balance between numbing and feeling, given the catastrophes that confront us.
A related concept that you use, which comes from Martin Buber, is “imagining the real.”
It’s attributed to Martin Buber, but as far as I can tell, nobody knows exactly where he used it. It really means the difficulty in taking in what is actual. Imagining the real becomes necessary for imagining our catastrophes and confronting them and for that turn by which the helpless victim becomes the active survivor who promotes renewal and resilience.
How does that relate to another one of your concepts, nuclearism?
Nuclearism is the embrace of nuclear weapons to solve various human problems and the commitment to their use. I speak of a strange early expression of nuclearism between Oppenheimer and Niels Bohr, who was a great mentor of Oppenheimer. Bohr came to Los Alamos. And they would have abstract conversations. They had this idea that nuclear weapons could be both a source of destruction and havoc and a source of good because their use would prevent any wars in the future. And that view has never left us. Oppenheimer never quite renounced it, though, at other times, he said he had blood on his hands—in his famous meeting with Truman.
Have you seen the movie “Oppenheimer”?
Yes. I thought it was a well-made film by a gifted filmmaker. But it missed this issue of nuclearism. It missed the Bohr-Oppenheimer interaction. And worst of all, it said nothing about what happened in Hiroshima. It had just a fleeting image of his thinking about Hiroshima. My view is that his success in making the weapon was the source of his personal catastrophe. He was deeply ambivalent about his legacy. I’m very sensitive to that because that was how I got to my preoccupation with Oppenheimer: through having studied Hiroshima, having lived there for six months, and then asking myself, What happened on the other side of the bomb—the people who made it, the people who used it? They underwent a kind of numbing. It’s also true that Oppenheimer, in relationship to the larger hydrogen bombs, became the most vociferous critic of nuclearism. That’s part of his story. The moral of Oppenheimer’s story is that we need abolition. That’s the only human solution.
By abolition, you mean destruction of all existing weapons?
Yes, and not building any new ones.
Have you been following the war in Ukraine? Do you see Putin as engaging in nuclearism?
I do. He has a constant threat of using nuclear weapons. Some feel that his very threat is all that he can do. But we can’t always be certain. I think he is aware of the danger of nuclear weapons to the human race. He has shown that awareness, and it has been expressed at times by his spokesman. But we can’t ever fully know. His emotions are so otherwise extreme.
There’s a messianic ideology in Russia. And the line used on Russian television is, “If we blow up the world, at least we will go straight to Heaven. And they will just croak.”
There’s always been that idea with nuclearism. One somehow feels that one’s own group will survive and others will die. It’s an illusion, of course, but it’s one of the many that we call forth in relation to nuclear danger.
Are you in touch with any of your former Russian counterparts in the anti-nuclear movement?
I’ve never entirely left the anti-nuclear movements. I’ve been particularly active in Physicians for Social Responsibility. We had meetings—or bombings, as we used to call it—in different cities in the country, describing what would happen if a nuclear war occurred. We had a very simple message: we’re physicians and we’d like to be able to patch you up after this war, but it won’t really be possible because all medical facilities will be destroyed, and probably you’ll be dead, and we’ll be dead. We did the same internationally with the International Physicians for the Prevention of Nuclear War, which won the Nobel Peace Prize. There’s a part of the movement that’s not appreciated sufficiently. [Yevgeny] Chazov, who was the main Soviet representative, was a friend of Gorbachev’s, and he was feeding Gorbachev this view of common security. And Gorbachev quickly took on the view of nuclear weapons that we had. There used to be a toast: either an American or a Soviet would get up and say, “I toast you and your leaders and your people. And your survival, because if you survive, we survive. And if you die, we die.”
Let’s talk about proteanism.
Proteanism is, of course, named after the notorious shape-shifter Proteus. It suggests a self that is in motion, that is multiple rather than made up of fixed ideas, and changeable and can be transformed. There is an ongoing struggle between proteanism and fixity. Proteanism is no guarantee of achievement or of ridding ourselves of danger. But proteanism has more possibility of taking us toward a species mentality. A species mentality means that we are concerned with the fate of the human species. Whenever we take action for opposing climate change, or COVID, or even the threat to our democratic procedure, we’re expressing ourselves on behalf of the human species. And that species-self and species commitment is crucial to our emergence from these dilemmas.
Next term: “witnessing professional.”
I went to Hiroshima because I was already anti-nuclear. When I got there, I discovered that, seventeen years after the bomb was dropped, there had been no over-all, inclusive study of what happened to that city and to groups of people in it. I wanted to conduct a scientific study, having a protocol and asking everyone similar questions—although I altered my method by encouraging them to associate. But I also realized that I wanted to bear witness to what happened to that city. I wanted to tell the world. I wanted to give a retelling, from my standpoint, as a psychological professional, of what happened to that city. That was how I came to see myself as a witnessing professional. It was to be a form of active witness. There were people in Hiroshima who embodied the struggle to bear witness. One of them was a historian who was at the edge of the city who said, “I looked down and saw that Hiroshima had disappeared.” That image of the city disappearing took hold in my head and became central to my life afterward. And the image that kept reverberating in my mind was, one plane, one bomb, one city. I was making clear—at least to myself at first and then, perhaps, to others,—that bearing witness and taking action was something that we needed from professionals and others.
I have two terms left on my list. One is “survivor.”
There is a distinction I make between the helpless victim and the survivor as agent of change. At the end of my Hiroshima book, I had a very long section describing the survivor. Survivors of large catastrophes are quite special. Because they have doubts about the continuation of the human race. Survivors of painful family loss or the loss of people close to them share the need to give meaning to that survival. People can claim to be survivors if they’re not; survivors themselves may sometimes take out their frustration on people immediately around them. There are all kinds of problems about survivors. Still, survivors have a certain knowledge through what they have experienced that no one else has. Survivors have surprised me by saying such things as “Auschwitz was terrible, but I’m glad that I could have such an experience.” I was amazed to hear such things. Of course, they didn’t really mean that they enjoyed it. But they were trying to say that they realized they had some value and some importance through what they had been through. And that’s what I came to think of as survivor power or survivor wisdom.
Do you have views on contemporary American usage of the words “survivor” and “victim”?
We still struggle with those two terms. The Trumpists come to see themselves as victims rather than survivors. They are victims of what they call “the steal.” In seeing themselves as victims, they take on a kind of righteousness. They can even develop a false survivor mission, of sustaining the Big Lie.
The last term I have on my list is “continuity of life.”
When I finished my first study, I wanted a theory for what I had done, so to speak. [The psychoanalyst] Erik Erikson spoke of identity. I could speak of Chinese Communism as turning the identity of the Chinese filial son into the filial Communist. But when it came to Hiroshima, Erikson didn’t have much to say in his work about the issue of death. I realized I had to come to a different idea set, and it was death and the continuity of life. In Hiroshima, I really was confronted with large-scale death—but also the question of the continuity of life, as victims could transform themselves into survivors.
Like some of your other ideas, this makes me think of Arendt’s writing. Something that was important to her was the idea that every birth is a new beginning, a new political possibility. And, relatedly, what stands between us and the triumph of totalitarianism is “the supreme capacity of man” to invent something new.
I think she’s saying there that it’s the human mind that does all this. The human mind is so many-sided and so surprising. And at times contradictory. It can be open to the wildest claims that it itself can create. That has been a staggering recognition. The human self can take us anywhere and everywhere.
Let me ask you one more Arendt question. Is there a parallel between your concept of “malignant normality” and her “banality of evil”?
There is. When Arendt speaks of the “banality of evil,” I agree—in the sense that evil can be a response to an atrocity-producing situation, it can be performed by ordinary people. But I would modify it a little bit and say that after one has been involved in committing evil, one changes. The person is no longer so banal. Nor is the evil, of course.
Your late wife, B.J., was a member of the Wellfleet Group. Your new partner, Nancy Rosenblum, makes appearances in your new book. Can I ask you to talk about combining your romantic, domestic, and intellectual relationships?
In the case of B.J., she was a kind of co-host with me to the meetings for all those fifty years and she had lots of intellectual ideas of her own, as a reformer in adoption and an authority on the psychology of adoption. And in the case of Nancy Rosenblum, as you know, she’s a very accomplished political theorist. She came to speak at Wellfleet. She gave a very humorous talk called “Activist Envy.” She had always been a very progressive theorist and has taken stands but never considered herself an activist, whereas just about everybody at the Wellfleet meeting combined scholarship and activism.
People have been talking more about love in later life. It’s very real, and it’s a different form of love, because, you know, one is quite formed at that stage of life. And perhaps has a better knowledge of who one is. And what a relationship is and what it can be. But there’s still something called love that has an intensity and a special quality that is beyond the everyday, and it actually has been crucial to me and my work in the last decade or so. And actually, I’ve been helpful to Nancy, too, because we have similar interests, although we come to them from different intellectual perspectives. We talk a lot about things. That’s been a really special part of my life for the last decade. On the other hand, she’s also quite aware of my age and situation. The threat of death—or at least the loss of capacity to function well—hovers over me. You asked me whether I have a fear of death. I’m sure I do. I’m not a religious figure who has transcended all this. For me, part of the longevity is a will to live and a desire to live. To continue working and continue what is a happy situation for me.
You’re about twenty years older than Nancy, right?
Twenty-one years older.
So you are at different stages in your lives.
Very much. It means that she does a lot of things, with me and for me, that enable me to function. It has to do with a lot of details and personal help. I sometimes get concerned about that because it becomes very demanding for her. She’s now working on a book on ungoverning. She needs time and space for that work.
What is your work routine? Are you still seeing patients?
I don’t. Very early on, I found that even having one patient, one has to be interested in that patient and available for that patient. It somehow interrupted my sense of being an intense researcher. So I stopped seeing patients quite a long time ago. I get up in the morning and have breakfast. Not necessarily all that early. I do a lot of good sleeping. Check my e-mails after breakfast. And then pretty much go to work at my desk at nine-thirty or ten. And stay there for a couple of hours or more. Have a late lunch. Nap, at some point. A little bit before lunch and then late in the day as well. I can close my eyes for five minutes and feel restored. I learned that trick from my father, from whom I learned many things. I’m likely to go back to my desk after lunch and to work with an assistant. My method is sort of laborious, but it works for me. I dictate the first few drafts. And then look at it on the computer and correct it, and finally turn it into written work.
I can’t drink anymore, unfortunately. I never drank much, but I used to love a Scotch before dinner or sometimes a vodka tonic. Now I drink mostly water or Pellegrino. We will have that kind of drink at maybe six o’clock and maybe listen to some news. These days, we get tired of the news. But a big part of my routine is to find an alternate universe. And that’s sports. I’m a lover of baseball. I’m still an avid fan of the Los Angeles Dodgers, even though they moved from Brooklyn to Los Angeles in 1957. You’d think that my protean self would let them go. Norman Mailer, who also is from Brooklyn, said, “They moved away. I say, ‘Fuck them.’ ” But there’s a deep sense of loyalty in me. I also like to watch football, which is interesting, because I disapprove of much football. It’s so harmful to its participants. So, it’s a clear-cut, conscious contradiction. It’s also a very interesting game, which has almost a military-like arrangement and shows very special skills and sudden intensity.
Is religion important to you?
I don’t have any formal religion. And I really dislike most religious groups. When I tried to arrange a bar mitzvah for my son, all my progressive friends, rabbis or not, somehow insisted you had to join a temple and participate. I didn’t. I couldn’t do any of those things. He never was bar mitzvah. But in any case, I see religion as a great force in human experience. Like many people, I make a distinction between a certain amount of spirituality and formal religion. One rabbi friend once said to me, “You’re more religious than I am.” That had to do with intense commitments to others. I have a certain respect for what religion can do. We once had a distinguished religious figure come to our study to organize a conference on why religion can be so contradictory. It can serve humankind and their spirit and freedom and it can suppress their freedom. Every religion has both of those possibilities. So, when there is an atheist movement, I don’t join it because it seems to be as intensely anti-religious as the religious people are committed to religion. I’ve been friendly with [the theologian] Harvey Cox, who was brought up as a fundamentalist and always tried to be a progressive fundamentalist, which is a hard thing to do. He would promise me every year that the evangelicals are becoming more progressive, but they never have.
Can you tell me about the Wellfleet Group? How did it function?
The Wellfleet Group has been very central to my life. It lasted for fifty years. It began as an arena for disseminating Erik Erikson’s ideas. When the building of my Wellfleet home was completed, in the mid-sixties, it included a little shack. We put two very large oak tables at the center of it. Erik and I had talked about having meetings, and that was immediately a place to do it. So the next year, in ’66, we began the meetings. I was always the organizer, but Erik always had a kind of veto power. You didn’t want anybody who criticized him in any case. And then it became increasingly an expression of my interests. I presented my Hiroshima work there and my work with veterans and all kinds of studies. Over time, the meetings became more activist. For instance, in 1968, right after the terrible uprising [at the Democratic National Convention] that was so suppressed, Richard Goodwin came and described what happened.
Under my control, the meeting increasingly took up issues of war and peace. And nuclear weapons. I never believed that people with active antipathies should get together until they recognize what they have in common. I don’t think that’s necessarily productive or indicative. I think one does better to surround oneself with people of a general similarity in world view who sustain one another in their originality. The Wellfleet meetings became a mixture of the academic and non-academic in the usual sense of that word. But also a sort of soirée, where all kinds of interesting minds could exchange thoughts. We would meet once a year, at first for a week or so and then for a few days, and they were very intense. And then there was a Wellfleet meeting underground, where, when everybody left the meeting, whatever it was—nine or ten at night—they would drink at local motels, where they stayed, and have further thoughts, though I wasn’t privy to that.
How many people participated?
This shack could hold as many as forty people. We ended them after the fiftieth year. We were all getting older, especially me. But then, even after the meetings ended, we had luncheons in New York, which we called Wellfleet in New York, or luncheons in Wellfleet, which we called Wellfleet in Wellfleet. You asked whether I miss them. I do, in a way. But it’s one of what I call renunciations, not because I want to get rid of them but because a moment in life comes when you must get rid of them, just as I had to stop playing tennis eventually. I played tennis from my twenties through my sixties. Certainly, the memories of them are very important to me. I remember moments from different meetings, but also just the meetings themselves, because, perhaps, the communal idea was as important as any.
Do you find it easy to adjust to your physical environment? This was Nancy’s place?
Yes, this is Nancy’s place. Much more equipped for the Cape winters and just a more solid house. For us to do all the things, including medical things she helps me with, this house was much more suitable. Even the walk between the main house and my study [in Wellfleet] required effort. So we’ve been living here now for about four years. And we’ve enjoyed it. Of course, the view helps. I wake up every morning and look out to kind of take stock. What’s happening? Is it sunny or cloudy? What boats are visible? And then we go on with the day.
In the new book, you praise President Biden and Vice-President Harris for their early efforts to commemorate people who had died of COVID. Do you feel that is an example of the sort of sustained narrative that you say is necessary?
It’s hard to create the collective mourning that COVID requires. Certainly, the Biden Administration, right at its beginning, made a worthwhile attempt to do that, when they lit those lights around the pool near the Lincoln Memorial, four hundred of them, for the four hundred thousand Americans who had died. And then there was another ceremony. And they encouraged people to put candles in their windows or ring bells, to make it participatory. But it’s hard to sustain that. There are proposals for a memorial for COVID. It’s hard to do and yet worth trying.
You observe that the 1918 pandemic is virtually gone from memory.
That’s an amazing thing. Fifty million people. The biggest pandemic anywhere ever. And almost no public commemoration of it. When COVID came along, there wasn’t a model which could have perhaps served as some way of understanding. They used similar forms of masks and distancing. But there was no public remembrance of it.
Some scholars have suggested that it’s because there are no heroes and no villains, no military-style imagery to rely on to create a commemoration.
Well, that’s true. It’s also in a way true of climate. And yet there are survivors of it. And they have been speaking out. They form groups. Groups called Long COVID SOS or Widows of COVID-19 or COVID Survivors for Change. They have names that suggest that they are committed to telling the society about it and improving the society’s treatment of it.
Your book “The Climate Swerve,” published in 2017, seemed very hopeful. You wrote about the beginning of a species-wide agreement. Has this hope been tempered?
I don’t think I’m any less hopeful than I was when I wrote “The Climate Swerve.” In my new book [“Surviving Our Catastrophes”], the hope is still there, but the focus is much more on survivor wisdom and survivor power. In either case, I was never completely optimistic—but hopeful that there are these possibilities.
There’s something else I’d like to mention that’s happened in my old age. I’ve had a long interaction with psychoanalysis. Erik Erikson taught me how to be ambivalent about psychoanalysis. It was a bigger problem for him, in a way, because he came from it completely and yet turned against its fixity when it was overly traditionalized. In my case, I knew it was important, but I also knew it could be harmful because it was so traditionalized. I feared that my eccentric way of life might be seen as neurotic. But now, in my older age, the analysts want me. A couple of them approached me a few years ago to give the keynote talk at a meeting on my work. I was surprised but very happy to do it. They were extremely warm as though they were itching to, in need of, bringing psychoanalysis into society, and recognizing more of the issues that I was concerned with, having to do with totalism and fixity. Since then, they’ve invited me to publish in their journal. It’s satisfying, because psychoanalysis has been so important for my formation.
What was it about your life style that you thought your analyst would be critical of?
I feared that they would see that somebody who went out into the world and interviewed Chinese students and intellectuals or Western European teachers and diplomats and scholars was a little bit eccentric, or even neurotic.
The fact that you were interviewing people instead of doing pure academic research?
Yes, that’s right. A more “normal” life might have been to open up an office on the Upper West Side to see psychoanalytical, psychotherapeutic patients. And to work regularly with the psychoanalytic movement. I found myself seeking a different kind of life.
Tell me about the moment when you decided to seek a different kind of life.
In 1954, my wife and I had been living in Hong Kong for just three months, and I’d been interviewing Chinese students and intellectuals, and Western scholars and diplomats, and China-watchers and Westerners who had been in China and imprisoned. I was fascinated by thought reform because it was a coercive effort at change based on self-criticism and confession. I wanted to stay there, but at that time, I had done nothing. I hadn’t had my psychiatric residency and I hadn’t entered psychoanalytic training. Also, my money was running out. My wife, B.J., was O.K. either way. I walked through the streets thinking about it and wondering, and I came back after a long walk through Hong Kong and said, “Look, we just can’t stay. I don’t see any way we can.” But the next day, I was asking her to help type up an application for a local research grant that would enable me to stay. It was a crucial decision because it was the beginning of my identity as a psychiatrist in the world.
You have been professionally active for seventy-five years. This allows you to do something almost no one else on the planet can do: connect and compare events such as the Second World War, the Korean War, the nuclear race, the climate crisis, and the COVID pandemic. It’s a particularly remarkable feat during this ahistorical moment.
Absolutely. But in a certain sense, there’s no such thing as an ahistorical time. Americans can seem ahistorical, but history is always in us. It helps create us. That’s what the psychohistorical approach is all about. For me to have that long flow of history, yes, I felt, gave me a perspective.
You called the twentieth century “an extreme century.” What are your thoughts on the twenty-first?
The twentieth century brought us Auschwitz and Hiroshima. The twenty-first, I guess, brought us Trump. And a whole newly intensified right wing. Some call it populism. But it’s right-wing fanaticism and violence. We still have the catastrophic threats. And they are now sustained threats. There have been some writers who speak of all that we achieved over the course of the twentieth century and the first decades of the twenty-first century. And that’s true. There are achievements in the way of having overcome slavery and torture—for the most part, by no means entirely, but seeing it as bad. Having created institutions that serve individuals. But our so-called better angels are in many ways defeated by right-wing fanaticism.
If you could still go out and conduct interviews, what would you want to study?
I might want to study people who are combating fanaticism and their role in institutions. And I might also want to study people who are attracted to potential violence—not with the hope of winning them over but of further grasping their views. That was the kind of perspective from which I studied Nazi doctors. I’ve interviewed people both of a kind I was deeply sympathetic to and of a kind I was deeply antagonistic toward.
Is there anything I haven’t asked you about?
I would say something on this idea of hope and possibility. My temperament is in the direction of hopefulness. Sometimes, when Nancy and I have discussions, she’s more pessimistic and I more hopeful with the same material at hand. I have a temperament toward hopefulness. But for me to sustain that hopefulness, I require evidence. And I seek that evidence in my work.
107 notes
·
View notes