#men's historical fashion
Text

So I got this tag on my answer to an ask about when it became acceptable for western women to wear pants, and you know it's all I need to go on a tangent.
I think the short answer here would be men have worn skirts as long as people have worn anything, so pretty long tbh. But since I am incapable of answering anything shortly, I think we can re-frame this question:
When did skirts stop being socially acceptable for men?
So let's start with acknowledging that tunics, togas, kirtles and such men wore through history were, in fact, skirts. I think there's often a tendency to think of these as very different garments from those that women wore, but really they are not. Most of the time they were literally referred to with the same name. (I will do a very broad and simplified overview of men's clothing from ancient times to Early Middle Ages so we can get to the point which is Late Middle Ages.)
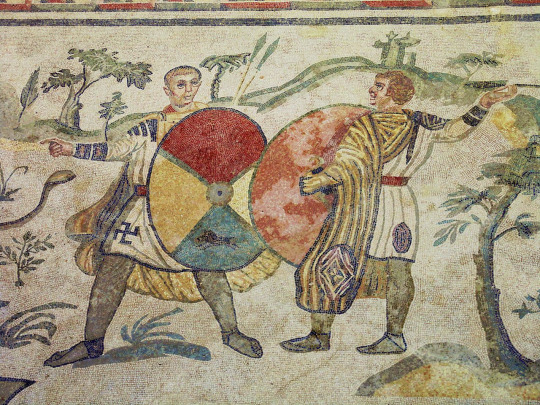
Ancient Greek men and women both wore chitons. Even it's length wasn't determined by gender, but by occupation. Athletes, soldiers and slaves wore knee-length chitons for easier movement. Roman men and women wore very similar garment, tunics. Especially in earlier ancient Rome long sleeves were associated with women, but later became more popular and unconventional for men too. Length though was still dependent on occupation and class, not gender. Toga was sure men's clothing, but worn over tunic. It was wrapped around the waist, like a dress would, and then hung over shoulder. Romans did wear leggings when they needed to. For example for leg protection when hunting as in this mosaic from 4th century. They would have been mostly used by men since men would be doing the kinds of activities that would require them. But that does not lessen the dressyness of the tunics worn here. If a woman today wears leggings under her skirt, the skirt doesn't suddenly become not a skirt.

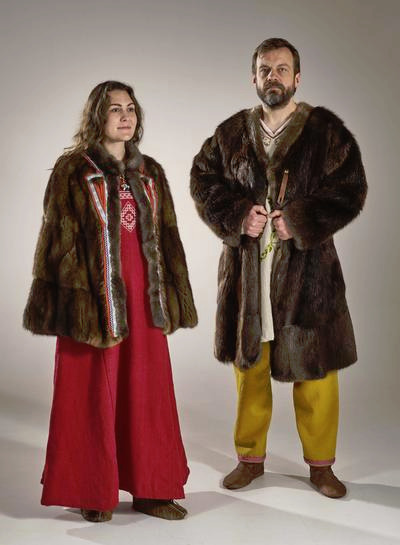
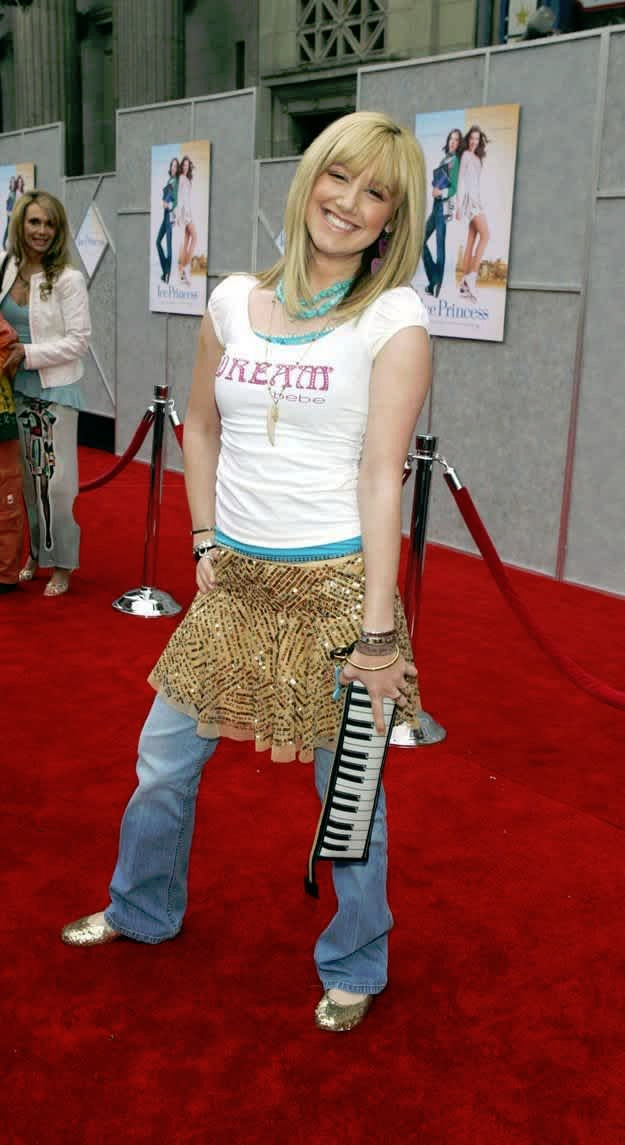
All over Europe thorough the early Middle Ages, the clothes were very similar in their basic shape and construction as in Rome and Greece. In Central and Northern Europe though people would wear pants under shorter tunics. There were exceptions to the everyone wearing a tunic trend. Celtic men wore braccae, which were pants, and short tunics and literally just shirts. Celts are the rare case, where I think we can say that men didn't wear dresses. Most other peoples in these colder areas wore at least knee-length tunics. Shorter tunics and trousers were worn again mostly by soldiers and slaves, so rarely any other woman than slave women. The trousers were though definitely trousers in Early Middle Ages. They were usually loose for easier construction and therefore not that similar to Roman leggings. However leggings style fitted pants were still used, especially by nobility. I'd say the loose trousers are a gray area. They wore both dresses and pants, but still definitely dresses. I'd say this style was very comparable to the 2000s miniskirts over jeans style. First one below is a reconstruction of Old Norse clothing by Danish history museum. The second is some celebrity from 2005. I see no difference.


When we get to the high Middle Ages tunics are still used by both men and women, and still it's length is dependent on class and activity more than gender, but there's some new developments too. Pants and skirt combo is fully out and leggings' are back in in form of hose. Hose were not in fact pants and calling them leggings is also misleading. Really they are socks. Or at least that's how they started. As it has become a trend here they were used by everyone, not just men. During early Middle Ages they were worn often with the trousers, sometimes the trousers tucked inside them making them baggy. In high Middle Ages they became very long when used with shorter tunics, fully displacing the need for trousers. They would be tied to the waist to keep them up, as they were not knitted (knitting was being invented in Egypt around this time, and some knitting was introduced to Europe during middle Ages, but it really only took off much later during Renaissance Era) and therefore not stretchy. First picture is an example of that from 1440s. Another exciting development in the High Medieval era was bliaut in France and it's sphere of influence. Bliaut was an early attempt in Europe of a fitted dress. And again used by both men and women. The second illustration below from mid 12th century shows a noble man wearing a bliaut and nicely showing off his leg covered in fitted hose. Bliaut was usually likely fitted with lacing on the sides, but it wasn't tailored (tailoring wasn't really a thing just yet) and so created a wrinkled effect around the torso.


In the 14th century things really picked up in European fashion. European kingdoms finally started to become richer and the rich started to have some extra money to put into clothing, so new trends started to pop up rapidly. Tailoring became a thing and clothes could be now cut to be very fitted, which gave birth to fitted kirtle. At the same time having extra money meant being able to spend extra money on more fabric and to create very voluminous clothing, which gave birth to the houppelande.
Kirtle was once again worn by everyone. It wasn't an undergarment, for women that would be shift and men shirt and breeches, but it was an underlayer. It could be worn in public but often had at least another layer on top of it. The bodice part, including sleeves were very fitted with lacing or buttons (though there were over-layer kirtles that had different sleeves that changed with fashions and would be usually worn over a fitted kirtle). Men's kirtles were short, earlier in 14th century knee-length but towards the end of the century even shorter styles became fashionable in some areas. First picture below shows a man with knee-length kirtle from 1450s Italy.
Houppelande was also unisex. It was a loose full-length overgown with a lot of fabric that was gathered on the neckline and could be worn belted or unbelted. The sleeves were also wide and became increasingly wider (for men and women) later in the century and into the next century. Shorter gowns similar in style and construction to the houppelande were also fashionable for men. Both of these styles are seen in the second picture below from late 14th century.


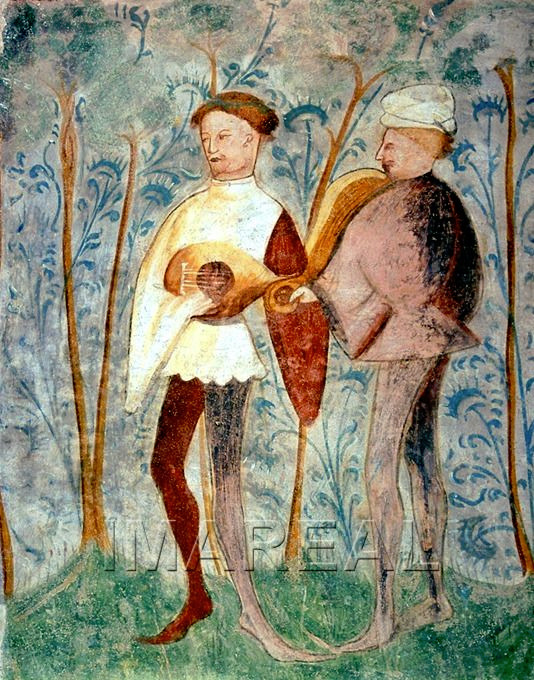
In the very end of 14th century, first signs of pantification of men can be seen. In France and it's sphere of influence the skirt part of the kirtle became so short it barely covered the breeches as seen below on these fashionable musicians from 1395-1400 France. Long houppelandes, length ranging from floor to calf, were still used by men though (the second picture, 1414 France), as were knee and thigh length gowns of similar loose style.


The hems continued to be short through the 15th century in France, but in other places like Italy and German sphere of influence, they were still fairly long, at least to mid thigh, through the first half of the century. In France at some point in late 13th century the very short under-kirtle started to be called doublet and they are just getting shorter in 1400s. The showing underwear problem was fixed by joined hose and the codpiece, signaling the entrance of The Sluttiest Era of men's fashion. Below is an example from 1450s Belgium of doublet and early codpiece in display. As you can see from the other figures, the overgowns of the previous century were also getting very, very short. In the next French example below from 1470s we can see the skirt shrink out of existence right before our eyes.
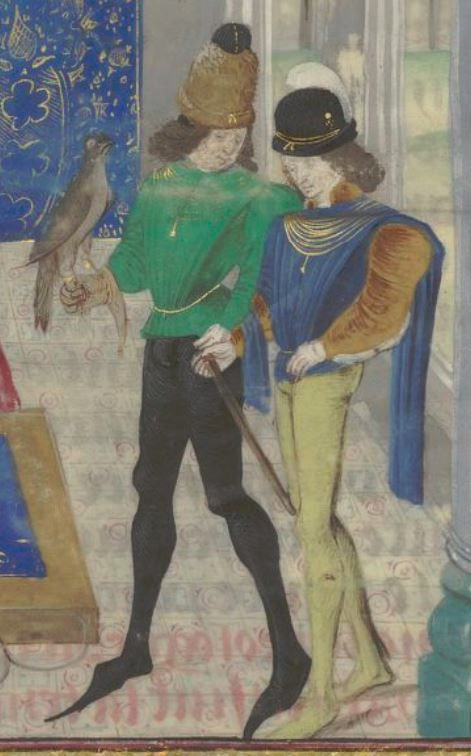


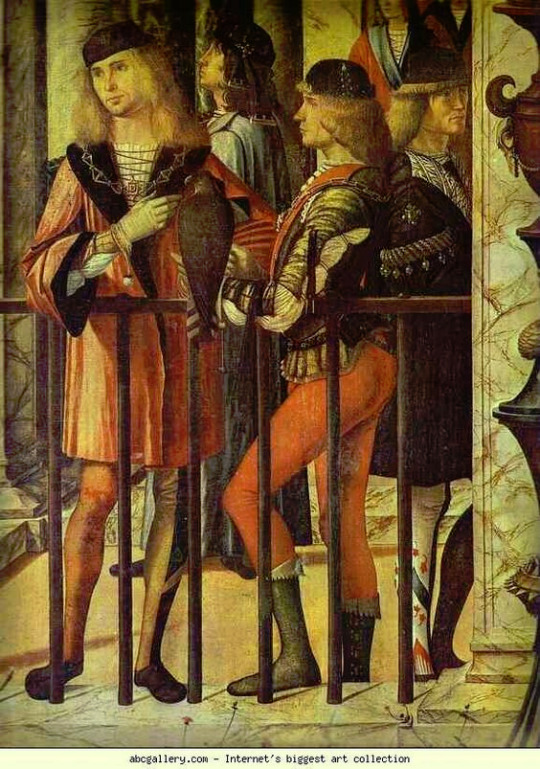
The very skimpy doublet and it's accompanying codpiece spread to the rest of the Europe in the second half of 15th century and it would only get sluttier from there. The Italians were just showing their full ass (example from 1490s). The dress was not gone yet though. The doublet and codpiece continued to be fashionable, but the overdress got longer again in the French area too. For example in the second example there's Italian soldiers in a knee length dresses from 1513.


But we have to talk about the Germans. They went absolutely mad with the whole doublet and codpiece. Just look at this 1513 painting below (first one). But they did not only do it sluttier than everyone else, they also changed the course of men's fashion.
Let's take a detour talking about the Landsknecht, the mercenary pikeman army of the Holy Roman Empire. (I'm not that knowledgeable in war history so take my war history explanation with a grain of salt.) Pikemen had recently become a formidable counter-unit against cavalry, which earlier in the Medieval Era had been the most important units. Knights were the professional highly trained cavalry, which the whole feudal system leaned against. On the other hand land units were usually not made of professional soldiers. Landsknecht were formed in late 15th century as a professional army of pikemen. They were skilled and highly organized, and quickly became a decisive force in European wars. Their military significance gave them a lot of power in the Holy Roman Empire, some were even given knighthood, which previously wasn't possible for land units, and interestingly for us they were exempt from sumptuary laws. Sumptuary laws controlled who could wear what. As the bourgeois became richer in Europe in late Middle Ages and Renaissance Era, laws were enacted to limit certain fabrics, colors and styles from those outside nobility, to uphold the hierarchy between rich bourgeois and the nobles. The Landsknecht, who were well payed mercenaries (they would mutiny, if they didn't get payed enough), went immediately absolute mad with the power to bypass sumptuary laws. Crimes against fashion (affectionate) were committed. What do you do, when you have extra money and one of your privileges is to wear every color and fabric? You wear every color and fabric. At the same time. You wear them on top of each other and so they can be seen at the same time, you slash the outer layer. In the second image you can feast your eyes on the Landsknecht.


Just to give you a little more of that good stuff, here's a selection of some of my favorite Landsknecht illustrations. This is the peak male performance. Look at those codpieces. Look at those bare legs. The tiny shorts. And savor them.
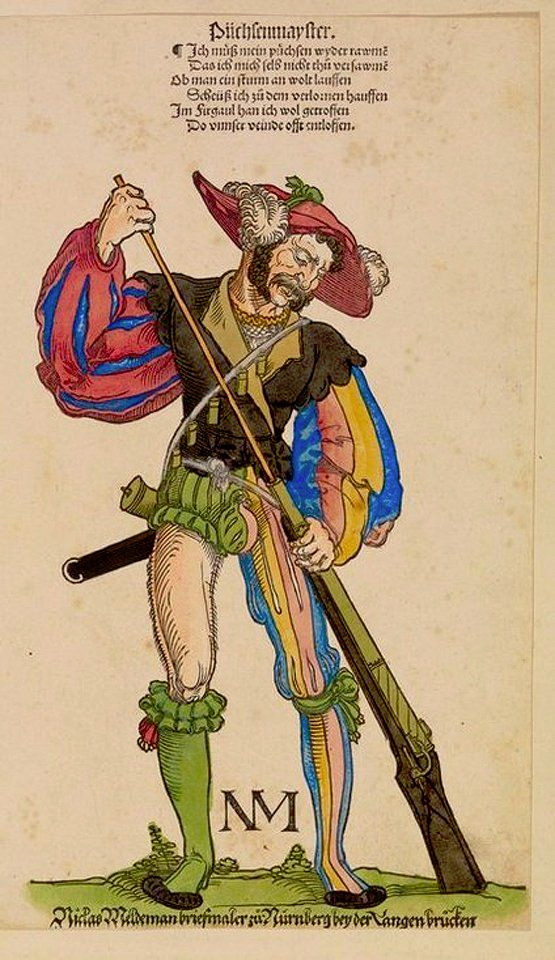




The Landsknecht were the hot shit. Their lavish and over the top influence quickly took over men's fashion in Germany in early 1500s. Slashing, the technique possibly started by them, but at least popularized by them, instantly spread all over Europe. That's how you get the typical Renaissance poof sleeves. They at first slashed the thighs of their hose, but it seems like to fit more of everything into their outfits, they started wearing the hose in two parts, upper hose and nether hose, which was a sort of return to the early Medieval trousers and knee-high hose style. The two part hose was adopted by the wider German men's fashion early in the century, but already in 1520s had spread to rest of Europe. It was first combined with the knee-length overdress that had made it's comeback in the turn of the century, like in this Italian painting from 1526 (first image). At this point knitting had become established and wide-spread craft in Europe and the stockings were born, replacing nether hose. They were basically nether hose, but from knitted fabric. The gown shortened again and turned into more of a jacket as the trunk hose became increasingly the centerpiece of the outfit, until in 1560s doublet - trunk hose combination emerged as the standard outerwear (as seen in the second example, 1569 Netherlands) putting the last nail on the coffin of the men's dress as well as the Sluttiest Era. The hose and doublet became profoundly un-slutty and un-horny, especially when the solemn Spanish influence spread all over with it's dark and muted colors.


Especially in Middle Ages, but thorough European history, trousers have been associated with soldiers. The largely accepted theory is that trousers were invented for horse riding, but in climates with cold winters, where short skirts are too cold, and long skirts are still a hazard when moving around, trousers (with or without a short skirt) are convenient for all kinds of other movement requiring activities like war. So by adopting hose as general men's clothing, men in 1500s associated masculinity with militarism. It was not a coincidence that the style came from Landsknecht. I may have been joking about them being "peak male performance", but really they were the new masculine ideals for the new age. At the time capitalism was taking form and European great powers had begun the process of violently conquering the world for money, so it's not surprising that the men, who fought for money and became rich and powerful doing so, were idealised.
Because of capitalism and increasingly centralized power, the feudal system was crumbling and with it the feudal social hierarchy. Capitalism shifted the wealth from land ownership (which feudal nobility was built upon) to capital and trade, deteriorating the hierarchy based on land. At the same time Reformation and centralized secular powers were weakening the power of the Church, wavering also the hierarchy justified by godly ordain. The ruling class was not about to give up their power, so a new social hierarchy needed to form. Through colonialism the concept of race was created and the new hierarchy was drawn from racial, gender and wealth lines. It was a long process, but it started in 1500s, and the increasing distinction between men's and women's fashions was part of drawing those lines. At the same time distinctions between white men and racialized men, as well as white women and racialized women were drawn. As in Europe up until this point, all over the world (with some exceptions) skirts were used by everyone. So when European men fully adopted the trousers, and trousers, as well as their association to military, were equated with masculinity, part of it was to emasculate racialized men, to draw distinctions.
Surprise, it was colonialism all along! Honestly if there's a societal or cultural change after Middle Ages, a good guess for the reason behind it is always colonialism. It won't be right every time, but quite a lot of times. Trousers as a concept is of course not related to colonialism, but the idea that trousers equal masculinity and especially the idea that skirts equal femininity are. So I guess decolonize masculinity by wearing skirts?
#this has been sitting in my drafts almost finished for like a year or something#historical fashion#fashion history#fashion#history#dress history#men's historical fashion#renaissance fashion#medieval fashion#western fashion#western fashion history#landsknecht
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

42nd Steet celebrated its centennial in 1925. These men are displaying what the well-dressed man would be wearing throughout those hundred years, September 29, 1925.
Photo: Bettmann Archive/Getty Images/Fine Art America
#vintage New York#1920s#42nd St.#vintage men's clothing#men's fashion#Sept. 29#historical fashion#men's historical fashion#29 Sept.#29 September#September 29
220 notes
·
View notes
Text

😔 Oh Crowley..
#good omens#good omens 2#crowley#ineffable husbands#the sketch got out of hand#this series has so much stuff I love to draw like clouds fabrics historical fashion flowy hair wings religious imagery stars sad old men-#I'll get better at drawing actors at some point just bear with me for now#my art
10K notes
·
View notes
Text
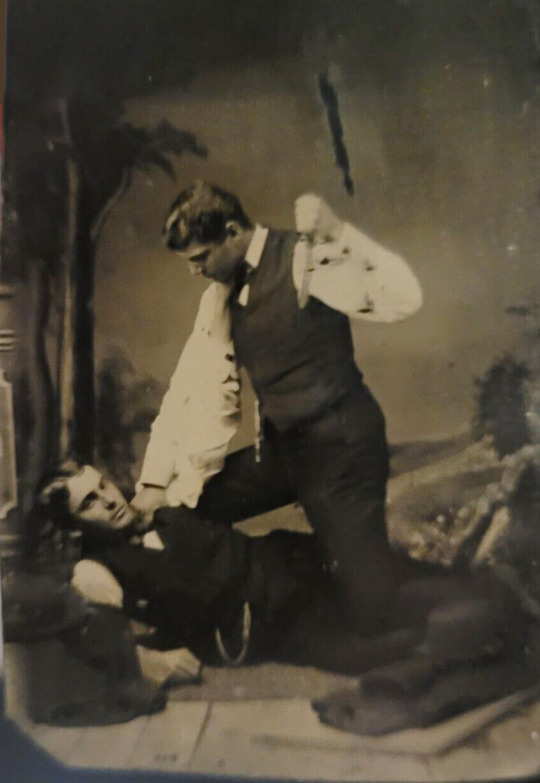

Tintype of what appears to be a light-hearted spot of stabbing between friends, circa 1880
#are they... you know... recreational homicide reenactors?#gay interest#19th century#19th century photography#tintype#ferrotype#19th century fashion#men's fashion#historical fashion#fashion history#1800s#1880s#winning hearts not acting awards
19K notes
·
View notes
Text
While I am still mad about historical men's fashion: my other pet peeve is when someone tries to do an "18th century vs. 19th century" thing, and it's literally court dress from like 1790, covered with embroidery and jewels, compared with ordinary day attire for a 19th century man.
Like. Imagine comparing the most outrageous cyber-goth club wear from the 1990s with a cheap 2010s men's business suit!
"THIS IS WHAT THE DOT COM BOOM TOOK AWAY FROM US! Men used to go to work with green plastic hair extensions and slutty fishnet tops with their tripp pants covered with bright cables and chains! Now they wear 'BUSINESS SUITS' in boring navy and black. 🙄😩💅🏻"
3K notes
·
View notes
Note
link & zelda regency era fashion please i’m on my hands and knees begging
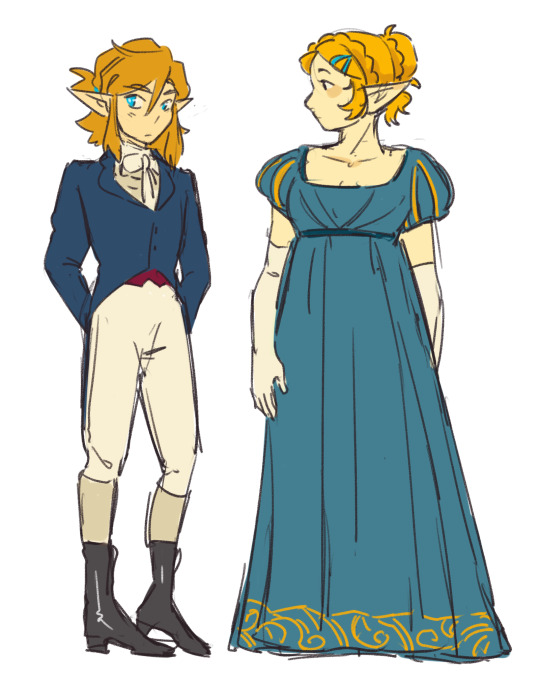

this might be the best ask ive ever recieved
#note that i did zero research beyond googling 'regency fashion' so if ur a historical fashion buff leave me alone#skribbles#asks#loz#almost also put link in a dress but i decided he can have a little suit moment for once. mens fashion in this era kind of slayed too tbh
910 notes
·
View notes
Text
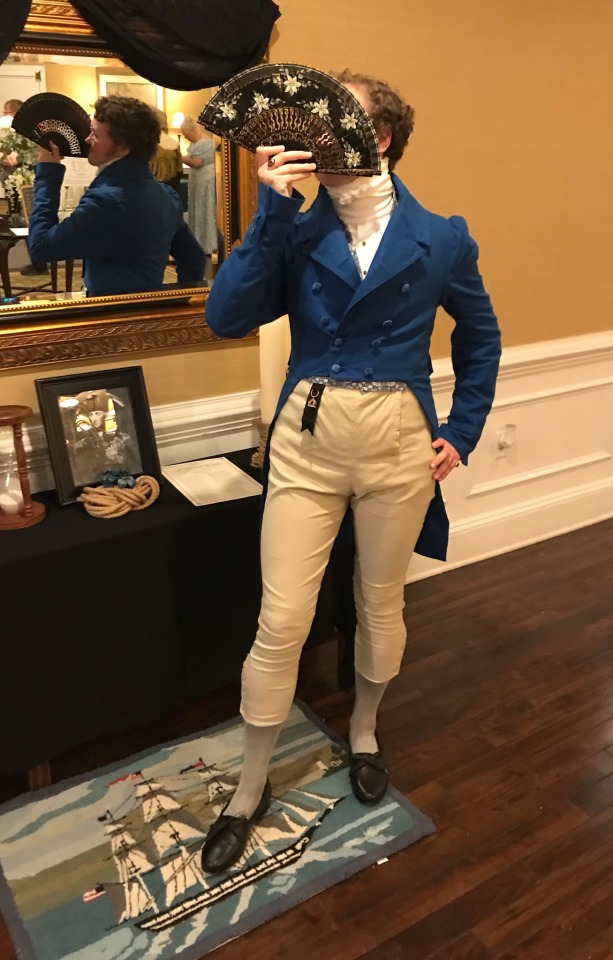
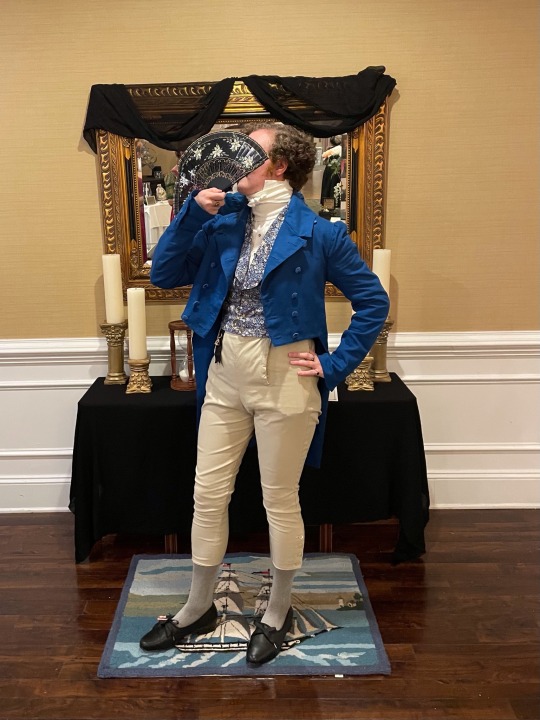
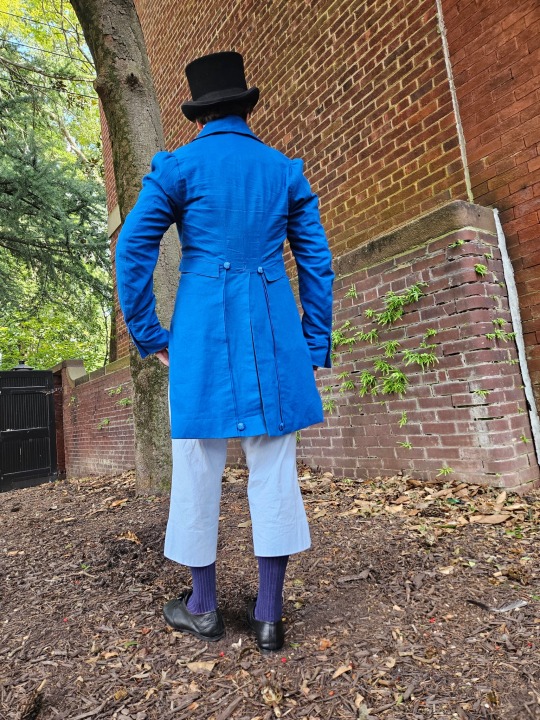




I spent quite a long time on this tailcoat and have gotten very busy without time to work on other projects, so I will dedicate a post to it.
Firstly big thank you to @vinceaddams for his deaths head button video which I used to make mine as well as links for making buckram!
Deaths head buttons weren’t really as popular any more by the regency period, but they still had Thread wrapped buttons for coats as well as one vest example I found for.
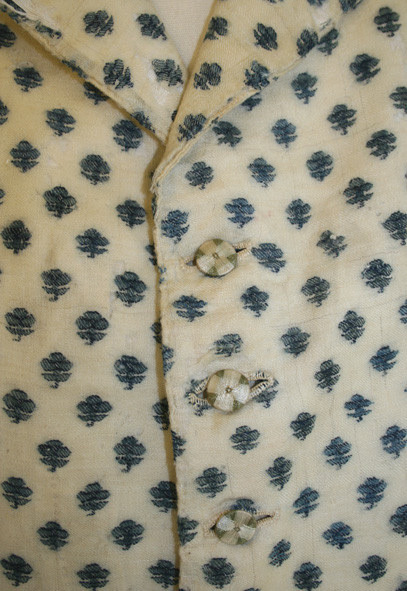
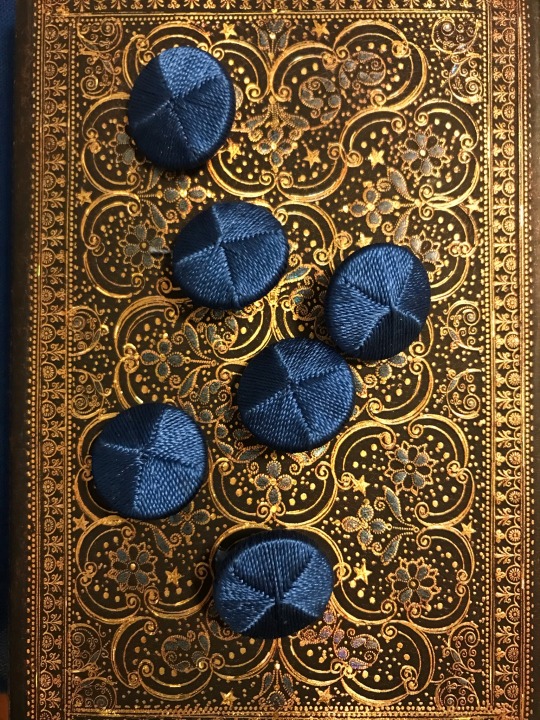



I made the buckram from scratch using linen I got at a second hand store and glue.
Decorative interior stitching was based directly off an 1830s tailcoat at the MET.



I used silk thread for all of the visible stitches, and it was like butter to hand-sew with. 100m/110 yds was more than enough for that as well.
(You can see the mutton chops I did :] )

#historical fashion#regency#1820s’ men’s fashion#menswear#regency men’s fashion#sewing#my post#fashion#regency fashion
434 notes
·
View notes
Text
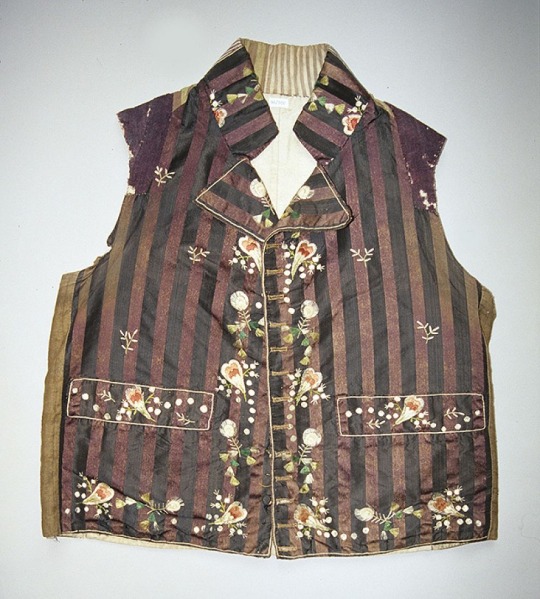
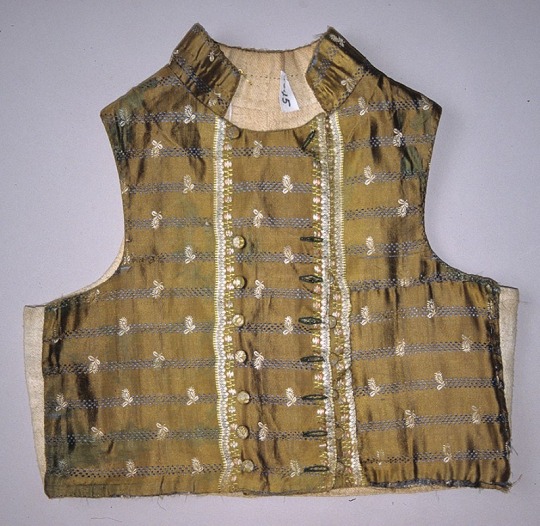
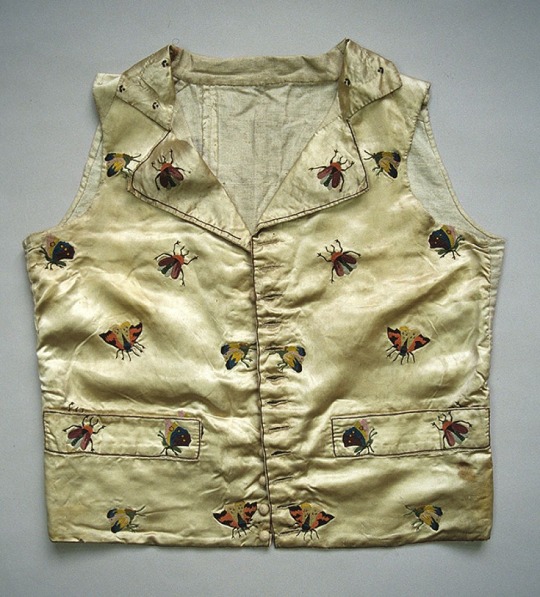
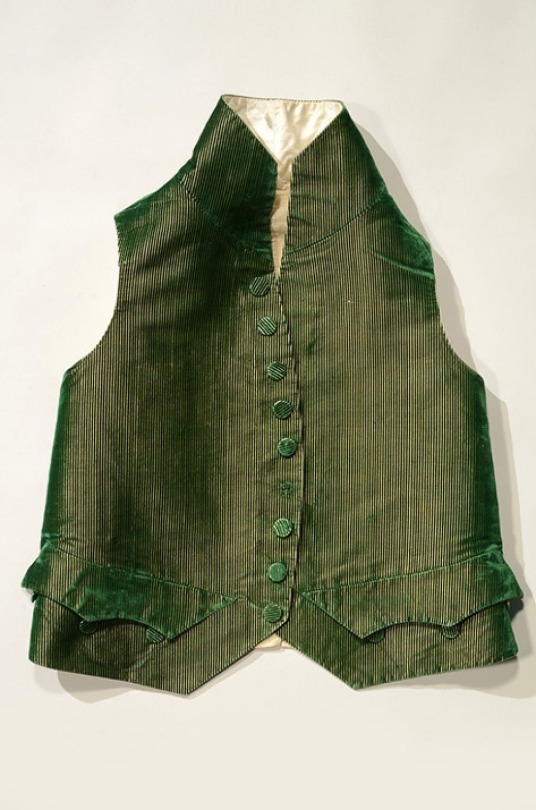
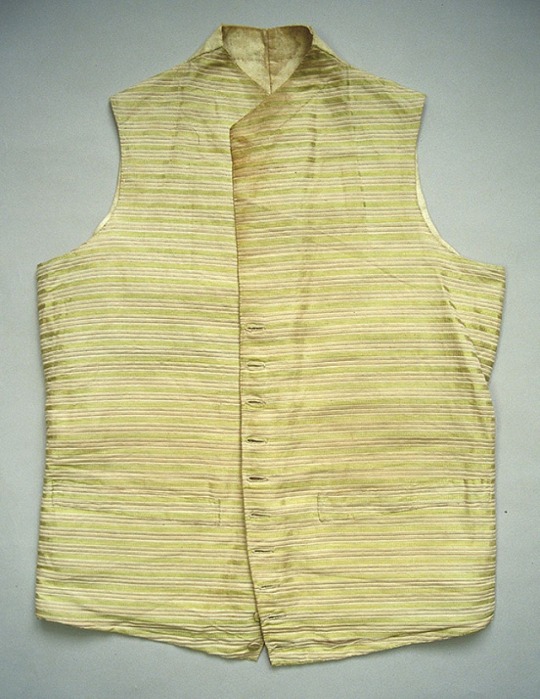









Napoleonic era men’s vests, France
Top row: 1800-1815 (1) (2) (3)
Middle Row: 1790-1810 (1), 1795-1805 (2) (3)
Bottom Row: 1805-10 (1), 1800s (2) (3)
Bayerisches Nationalmuseum
#vest#men’s vests#vests#fashion#mens fashion#napoleonic era#napoleonic#pretty#fashion history#first french empire#french empire#Bayerisches Nationalmuseum#historical fashion#history of fashion#19th century#1800s#1800s fashion#waistcoat#suit#men’s suit#suits#france#French fashion#La mode#modes#empire#empire style#textiles#fabric
551 notes
·
View notes
Text

The Farewells, James Tissot. 1872.
#aesthetic#art#art history#victorian#fashion#historical fashion#victorian aesthetic#historical art#women in art#Victorian fashion#Victorian era#women#romance#romance aesthetic#men#men in art#romantic#romance painting#romantic aesthetic#1870s#1870s aesthetic#1870s fashion#dress#gowns#grey#grey aesthetic
301 notes
·
View notes
Photo
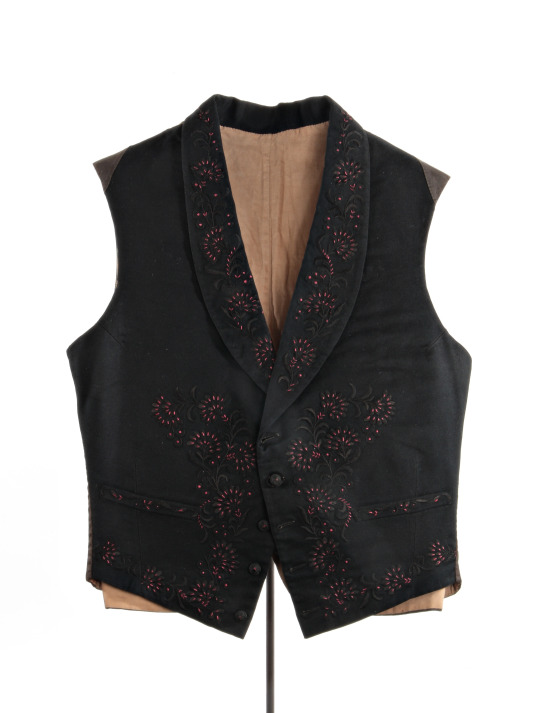
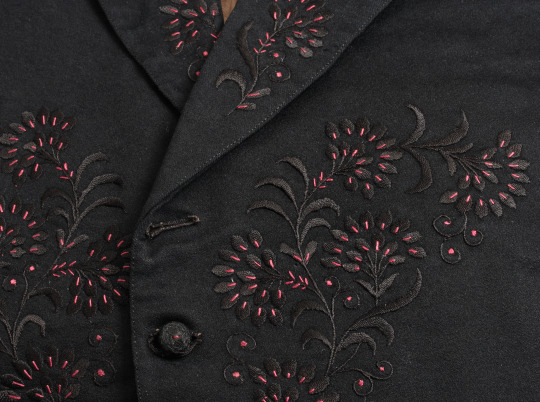


Wedding Waistcoat & Details | c.1855
4K notes
·
View notes
Note
https://www.tumblr.com/thebaconsandwichofregret/189924928150/comepraisetheinfanta-thebaconsandwichofregret
whenever i see people rbing the op without the additions i die a little inside so i thought you should have a go at debunking it 🫠
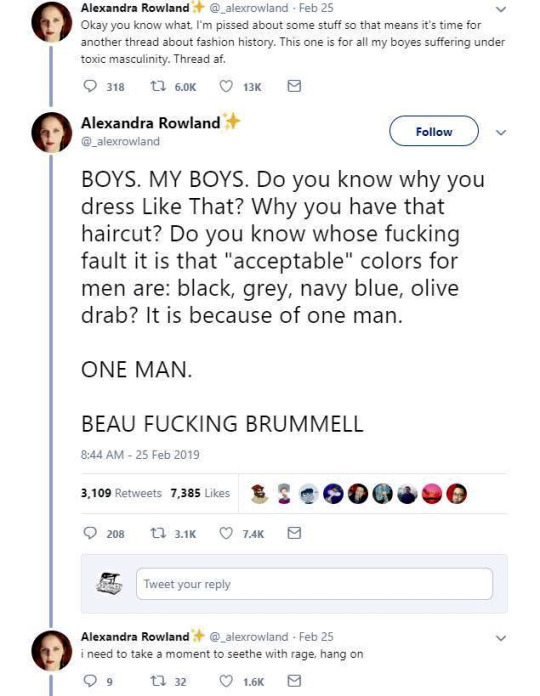


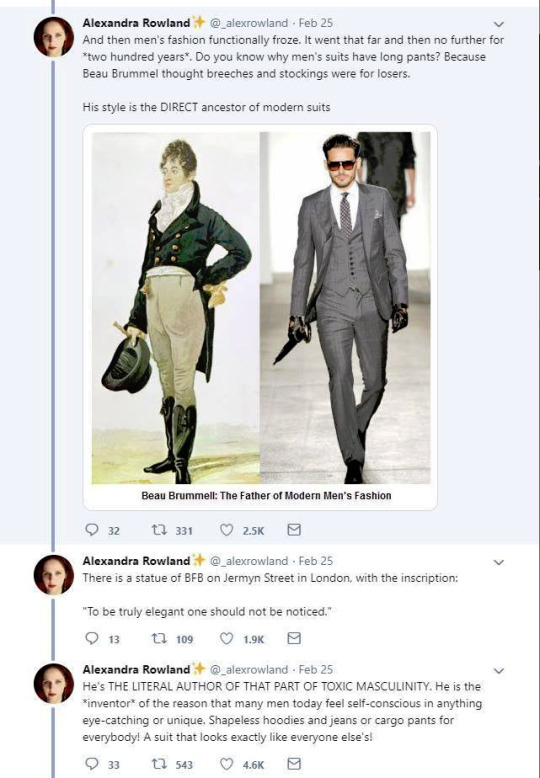
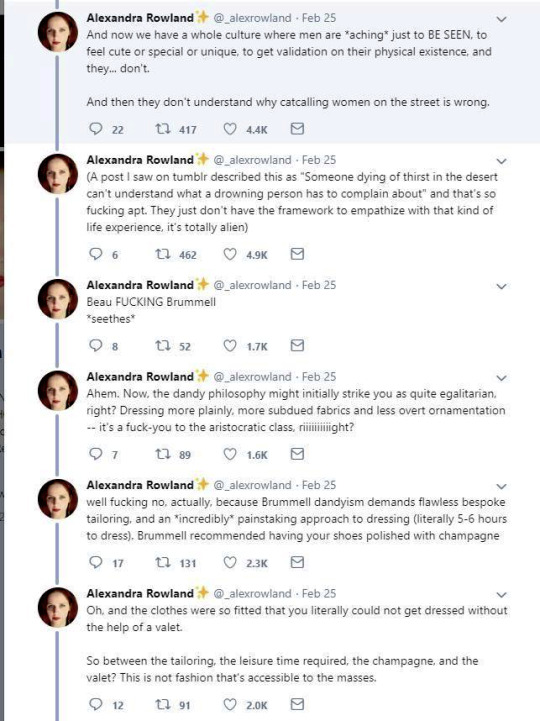
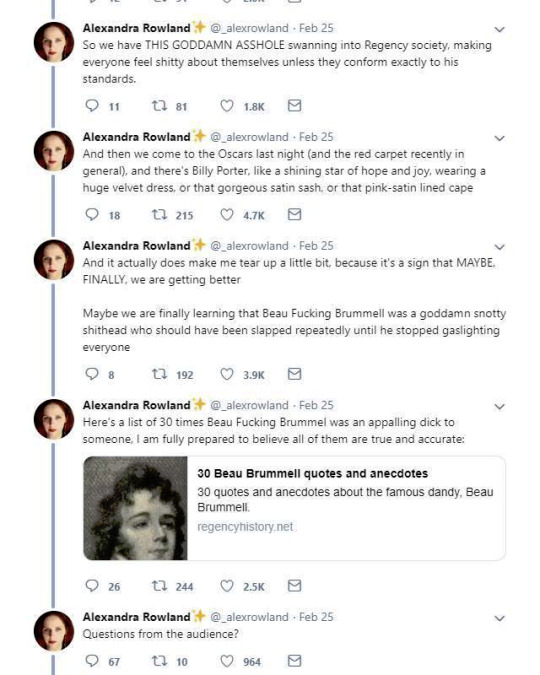
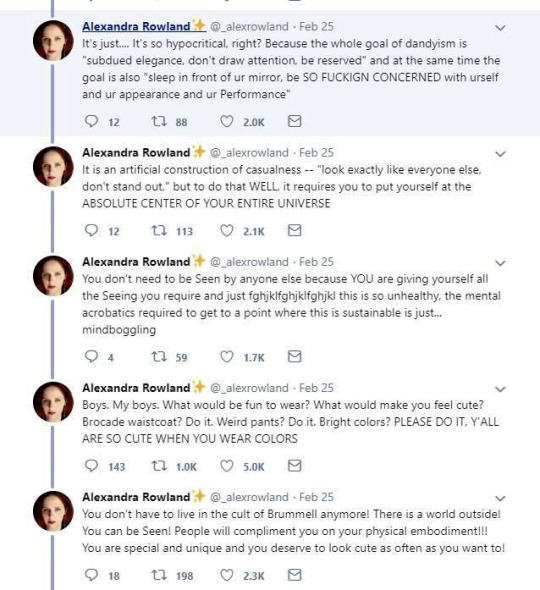
So these are the tweets from the post. I had blissfully not come across it before. This is one of the weirdest takes I have ever seen. It's amazing to see these fashion history takes that are so boldly and confidently wrong and inaccurate.
It's honestly hilariously ignorant to think that a massive cultural and societal shift that took couple of centuries, was all because one guy. It's so reductive and even goes to the great man territory to pick one person to blame for something like this that really had much more broad and complex reasons than "a guy did it". It's stressed in this tread that Beau Brummell was not noble or a gentile and "just some guy", so how would he singlehandedly change the fashions and concept of masculinity of the whole western world? He was a London socialite, it's not like most of his contemporaries in continential Europe knew about him. Like maybe the French, but does anyone really believe people in Eastern-Europe or Nordic countries or in the Mediterranean knew about? Not to mention places like US. Yet everyone dressed like that in his lifetime, so how could his influence reach so far so quickly? Not even kings and queens could so directly and massively shift the fashions. So in the face of it the whole claim is ridiculous, but it's also full of inaccuracies.
The shift from Rococo fashion to regency fashion was extremely stark and quick in both men and women's fashion, but it happened during 1780s and 1790s, before Beau Brummell became a well known figure in the London society (he was born in 1778 and became well-known in the society after his military career, during which he befriended the Prince of Wales, around the end of 1790s). Here's first an example from 1780s and then from 1793-94 and 1797.



The one from 1780s still has some rococo elements like the wig, but it's already much more toned down and the coat is already turning from frock coat to a tail coat. It's an example of the more casual men's countryside dress from the period. The court dress was still quite elaborate, though also toned down from the 1770s. But there's a big shift when it comes to the examples from 1790s. They are unmistakably Regency fashion. All of these example are French too. I'm sure these people had no idea and gained no influence from an unknown middle class English officer. So what did actually happen? Well, I'm pretty sure the French Revolution in 1789 had a little bigger impact on the European society and fashion than Beau Brummell.
I'm not going to go too deep into this, since I'm working on an in depth post about the masculinity and fashion in the modern era and I go into detail about how the French Revolution had a massive part in shaping them. But the short version is that the French revolutionaries rejected the elaborate fashions of the Rococo French nobility (in both men and women's fashion) as those over the top fashions stood as symbols of the excess wealth of the nobility and the extreme wealth gap between then and the rest of the people. This is also why the high fashion was getting toned down thorough the 1780s before the Revolution. The anger towards the ruling class was mounting at the time and it encouraged the nobility to down down and try to act a little more palatable in their aesthetics to maybe appease the angry people without doing any actual change to address the wealth gap and the centralized power.
The revolutionaries looked for ideal masculinity and femininity elsewhere then. To contrast themselves against the ruling class, they looked to the antiquity and it's simplicity as well as the peasantry and the country gentleman fashion. Romanticism was the driving force behind the artistic expression of the Revolution. It weaved nationalism to the class struggle that was at the core of the revolutionary movement. So the Revolution was not just the working class and peasantry against the ruling class, but the French People against the nobility. This is when physical labour, militarism, dominance and leadership, really became intrinsically attached to masculinity, as the ideal man of the revolutionaries was a working peasant, who with military power took the the power back to the people from the nobility. The democracy would not last long, but it's not a mistake that only men could vote under the new democracy after the Revolution was won. It's also not a mistake that even when the post-Revolution France eventually abolished slavery (but not without some push-back first and a couple of slave revolts to force their hands) they did not give most people of color rights to vote. Since colonialism whiteness had become intrinsic part of masculinity and femininity, which was part of the dehumanization of everyone else, and the new form of masculinity and femininity born out of the Revolution did not contest that. In fact the Enlightenment philosophy that had laid the ground work for the Revolution and the Romantic movement and it's nationalism that were driving force in it, in no way contested colonialism or it's white supremacy. Which is why the power in the new democracy went to the (mostly) white men.
These elements were in the new men's fashion too. Nationalism, the idealization of militarism and antiquity seen as the origins of democracy made it and especially Antique Rome perfect inspiration for the Revolutionary France. The short hairstyle was inspired from the Roman fashion seen in statues. The fashionable tail coat was influenced by military uniforms and the short jackets of the working class. The long trousers also came from working class dress. Here's examples of the revolutionary fashion from first 1792 and then around 1790.
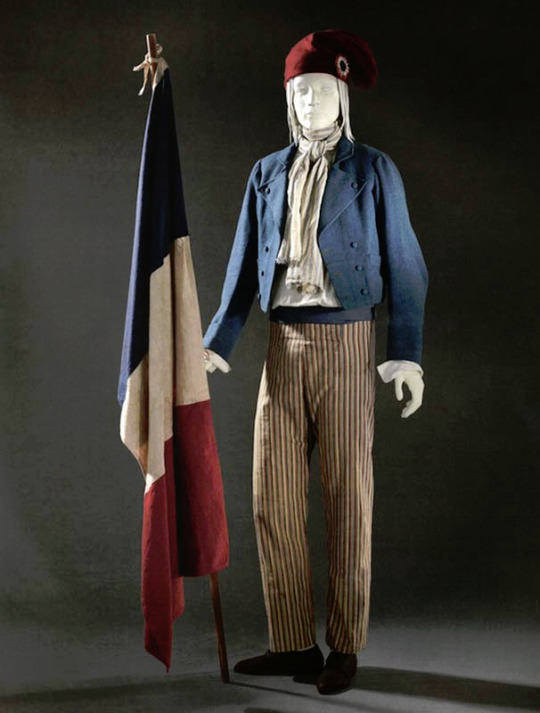


To be very clear, the revolutionaries were not a single entity with single ideology. They were collection of movements, who were united in their shared desire to overthrow the ruling class and establish some sort of democracy. But inside the movement were much more radical movements than what eventually ended in power after the French nobility. Socialists, abolitionists, feminists, slaves and others also fought for the Revolution and there was a lot of internal struggle too. Romantic movement was also very varied and contained extremely nationalistic elements as well as outright socialist elements.
Beyond the direct and stark effect the French Revolution had in especially France, but everywhere in the western world, the 18th century fashion was never as extreme as in France. If you put the most elaborate French court fashions of mid 1700s and Beau Brummell's style next to each other the difference is certainly massive, but fashion for men as well as women was always much more restrained and somber in England. Here's an English example from 1755-65 and for comparison a French example from 1755.
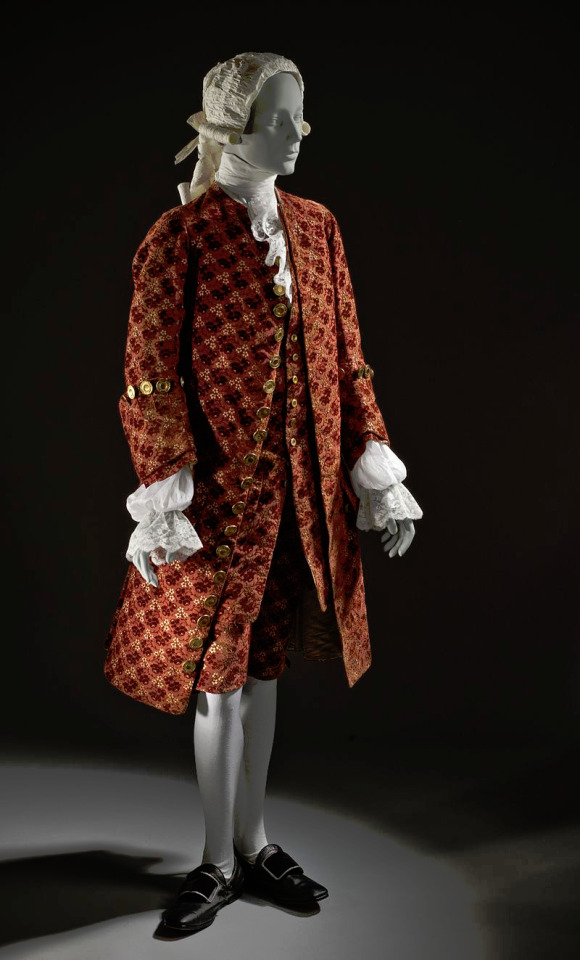


In fact as the tensions were rising in France the upper class begun to adopt the more toned down English styles. After the Revolution the new Republican styles would spread to Britain too. In Britain though Romanticism had a more pronounced effect as it stayed firmly monarchist. Therefore the English fashion was especially influenced by the styles worn by country side gentlemen.
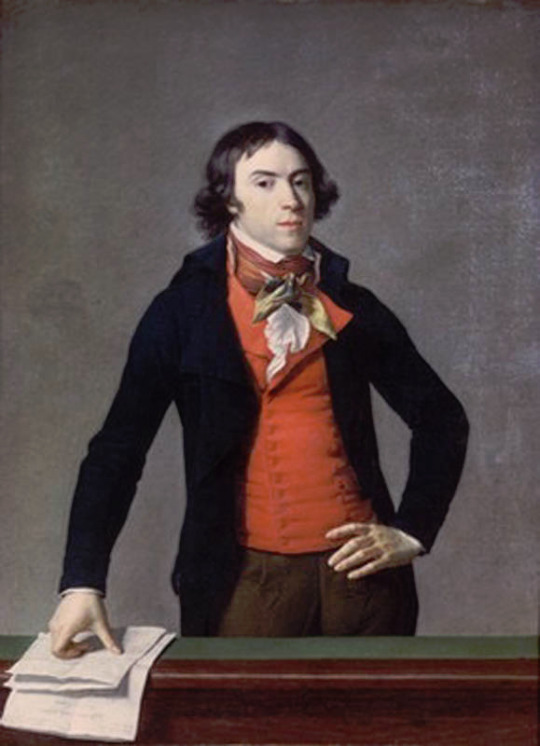
There's another claim in the thread that fully fails to understand the broad implications of fashion and societal gender and how these things change and evolve. It's the claim that Beau Brummell created the modern men's suit and he's the reason the suit has long trousers. We already went through how long trousers got into men's fashion and it was not him. But the writer is not wrong in saying that Beau Brummell's outfit in this picture is a direct ancestor of modern men's suit. It is.

But you know what else is a direct ancestor of men's suit? This.
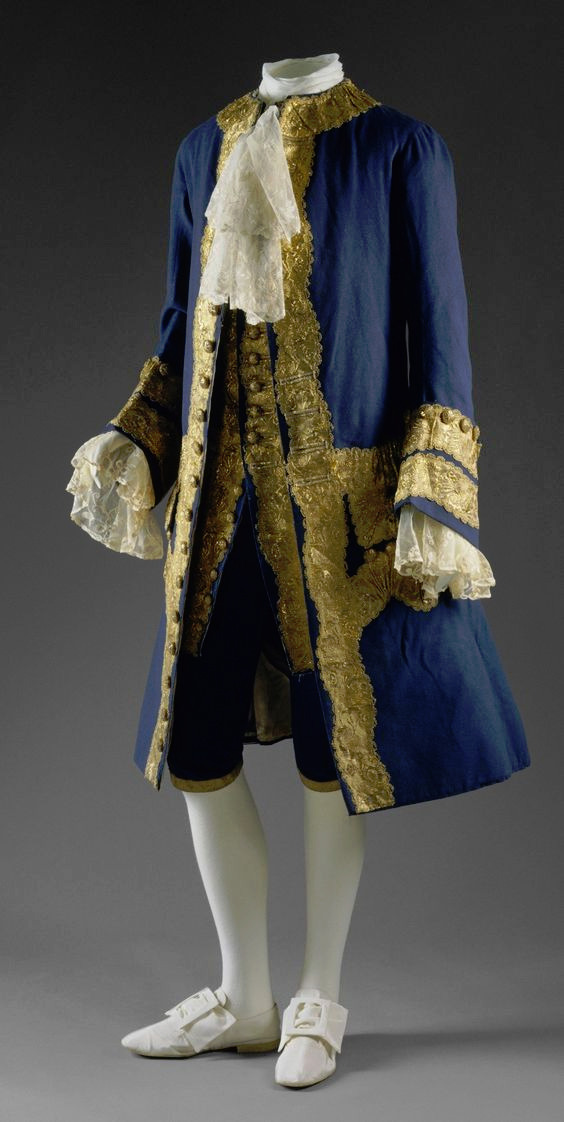

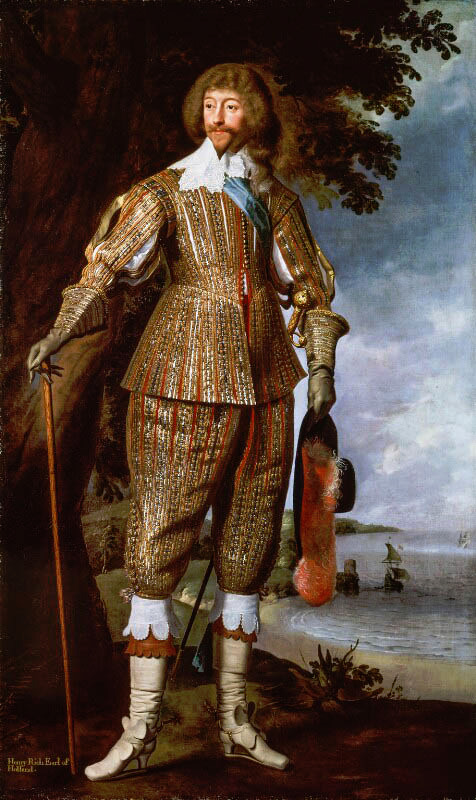
The modern three piece suit has it roots as far as in late 17th century. Before suit men wore doublets, which style resembled women's fashion much closer than the suits would after it (as seen in these examples from 1630s). However the distinction between men and women's fashion had started to grow much earlier. A big shift that happened during the 16th century was that men stopped wearing skirts. Men and women wore the same garments for centuries before that. The styles and silhouettes for men and women had some differences (the skirts were often shorter for men for example) but they were parallel to each other. I wrote a whole very long post about how skirts stopped being acceptable for men. In it I write about how the shift in men's fashion was part of the large shift from feudalism to colonialism and capitalism, that needed a new hierarchy to justify the new system after the previous divinely justified feudal hierarchy was no longer an option. The new hierarchy was white supremacist patriarchy and therefore needed a clearer distinction between white men and white woman, that would also help distinct white people from the racialised people.


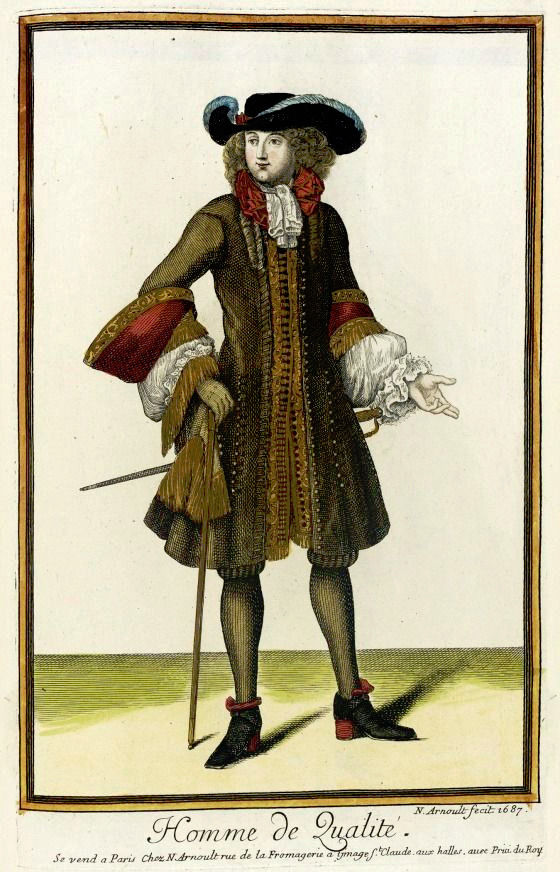
But such fundamental changes in the societal structure and culture are long processes. The process was continuing in the latter half of the 17th century, when Orientalism first became very popular. Orientalism is the dehumanization and fetishization of Asia and North-Africa, and it was born as the European colonial project was properly getting going in Asia. Colonialism in Asia and North-Africa took a little different form. I suspect it was because it was not that long ago, when Europeans had felt inferior to many of the peoples and empires in Asia and North-Africa, which they had always had much closer relationships with than the rest of Africa and certainly the Americas. I think that's why Orientalism is such a mix of coveting Asian and North-African cultures and bodies in a very fetishistic ways, while also demeaning and diminishing them. Nevertheless, Orientalism had a huge impact on European fashion in late 17th century. Both the way men and women's clothing was made after that to this day was strongly impacted by Orientalism. The coat and waistcoat combination was an adaptation of Turkish fashion. The three piece suit became popular in 1670s and fully took over men's fashion in 1680s (an example from 1687). The cravat was also adopted around the same time to men's wear from a light cavalry mercenary army in the Habsburgian Empire known as the Croats or Cravats. They were mainly Croatian, which to Western European was almost "Oriental" due to their proximity to Asia and Turkey in particular, and therefore the popularization of cravats as a fashion item was also influenced by Orientalism.

The Regency three piece suit also has all the same elements as the suit 150 years earlier, the individual pieces had just evolved into different different cuts. The three piece suit in fact still has the same elements to this day, they have just kept evolving.
My point is not to in any way deny Beau Brummell's influence on Regency fashion. He was the most influential fashion icon for men in his era after all. I hope this just made it very clear that these bigger changes are not about individual people but much larger shifts and movements in society and culture. His actual influence was popularizing some of the English countryside styles mentioned before in the fashionable London society, making extremely elaborate cravats into the fashionable items of the day and becoming the image of the English dandy.
The picture of him above shows him the typical English countryside suit with dark blue tail coat, white cravat and light pantaloons with polished hessian boots. He helped to make the outfit and pantaloons in general fashionable. Breeches would stay as the formal leg wear for some a decade still, till young fashionable men would start to use black or gray pantaloons in formal events too. Pantaloons were very fitted, but the trousers, that were fashionably quite narrow at the time, but looser, really came into the casual fashion in 1810s. As seen before their roots come from the working class fashion that was first popularized in the French Revolution, but they had been very informal and while they were still not quite as formal to be able to use in a formal event, they became acceptable in more casual events. Beau Brummell is credited for inventing or at least popularizing pants that have strap to go under the foot in order to keep them straight. Here's first a painting from of a gentleman in a very country style emphasized by the setting. Then a illustration from 1810 of a full formal dress with breeches and a fashion plate from 1817 of day wear with trousers.
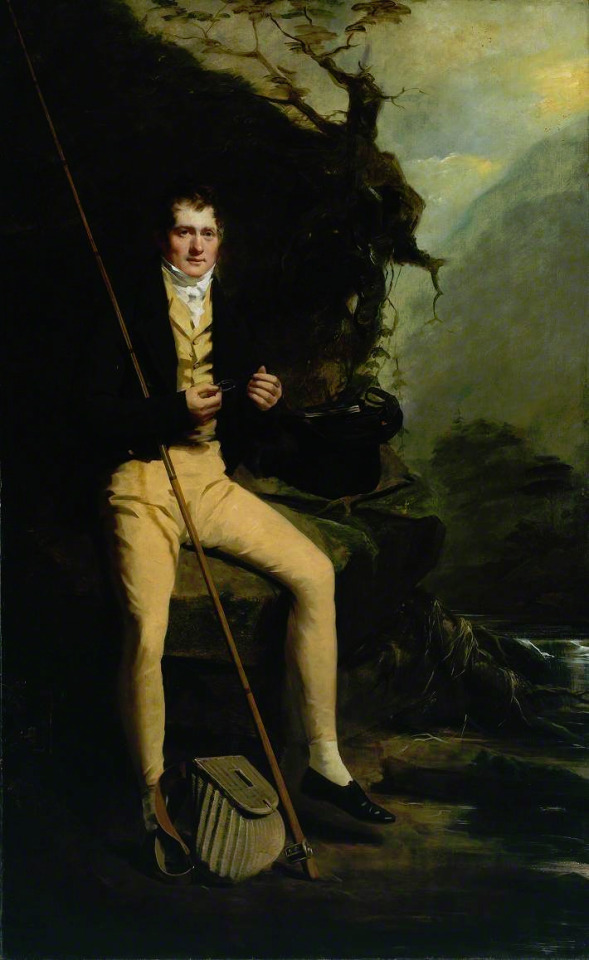
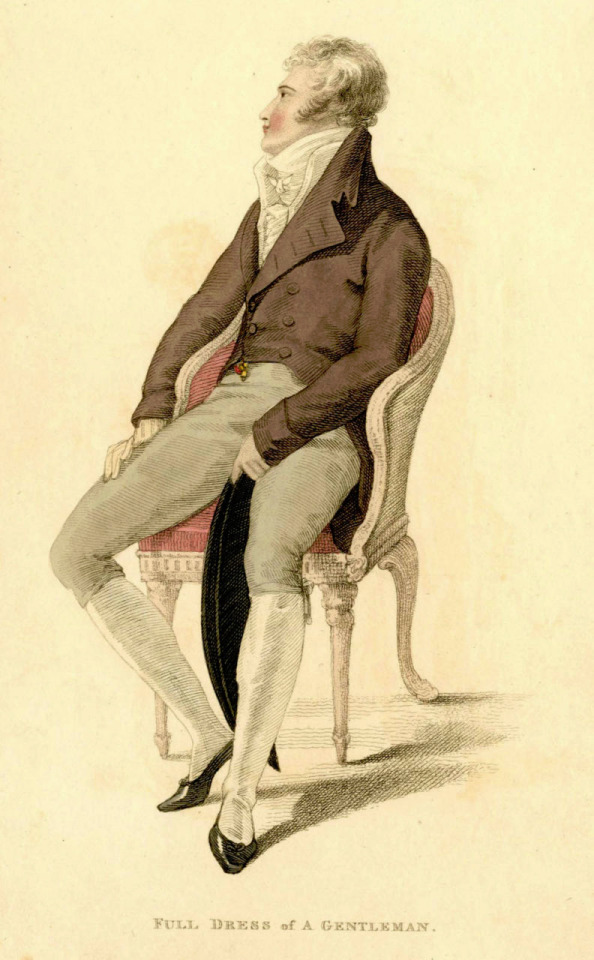



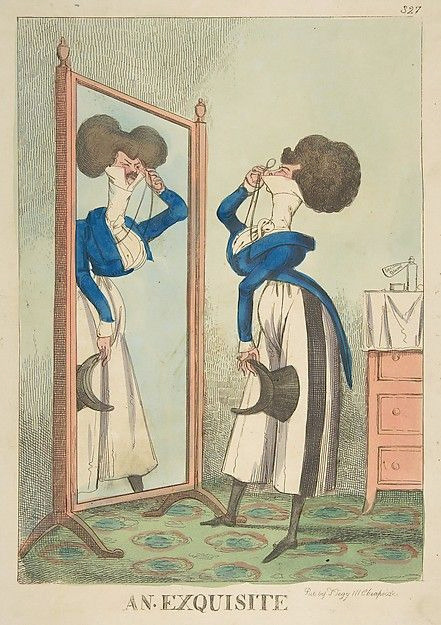
The thread also misses what dandy really was. Dandy was the embodiment of the middle class social mobility of the modern era. He was the "self-made man", the fashionable middle class and the new celebrity of a post-feudal era. He dressed in refined fashionable countryside middle class clothing and was celebrated for his style and refinement, not for his birth. Ironically though, there was a distinct reactionary quality to the Regency dandy. After all dandy did not embody social equality, but mobility. He was the ideal man of the capitalist hierarchy. A bit of dilemma for the dandy was that being extremely fashionable was central to the dandy, but after the French revolution being too fashionable and too concerned about looks had been associated with the aristocracy and was now therefore unmanly. Which is why dandy quickly came to be seen as effeminate. There is a lot of satiric cartoons from the time period that make fun of dandies and their preoccupation with fashion and looks. Here's couple from around 1810s.



In conclusion it's pretty ridiculous to say modern men's fashion was all created by one guy. The real reason why men's formal suit (and to be clear more colorful and elaborate styles have come and gone from men's informal fashion during that time) has been what it is for more than hundred years is because much bigger changes, like capitalism, colonialism, Orientalism and white supremacist patriarchy.
#fashion history#dress history#history#regency fashion#historical fashion#men's historical fashion#18th century fashion#answers#anon
362 notes
·
View notes
Photo
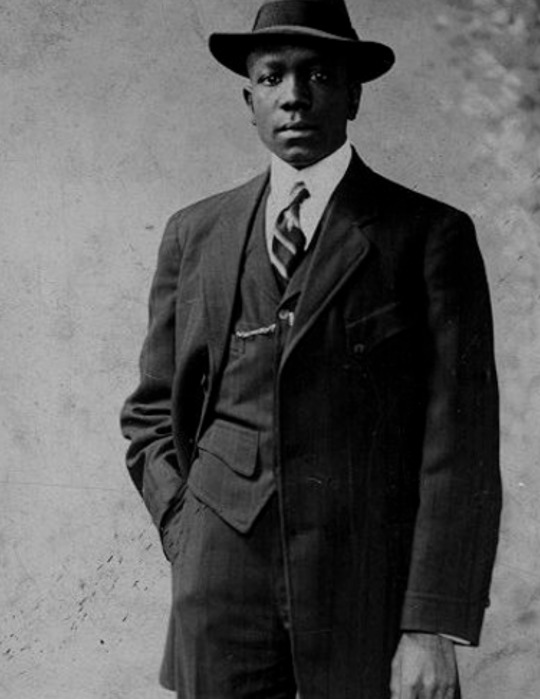
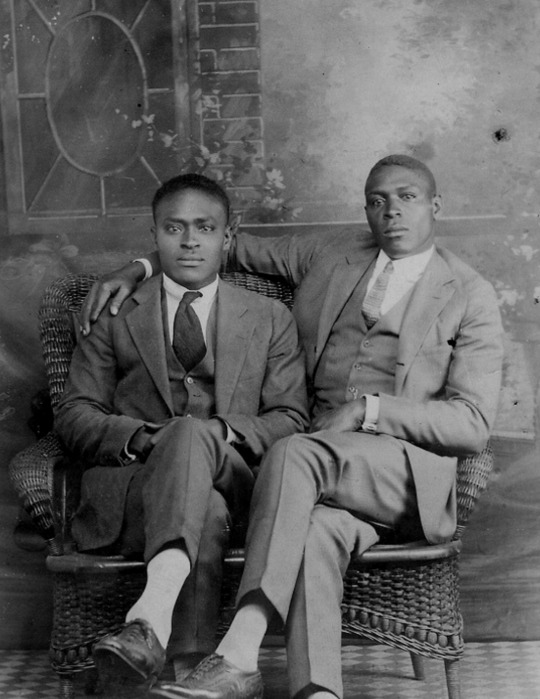
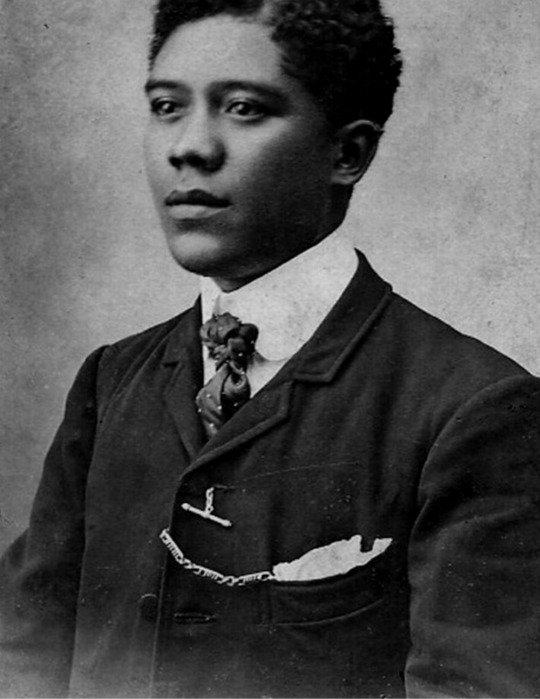
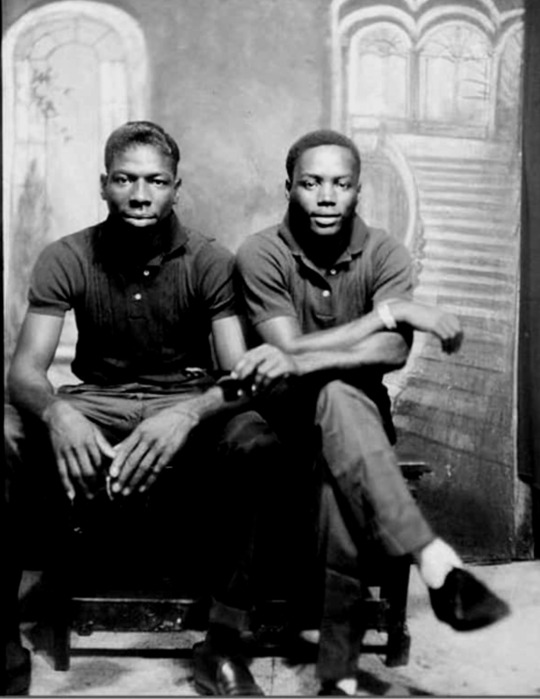
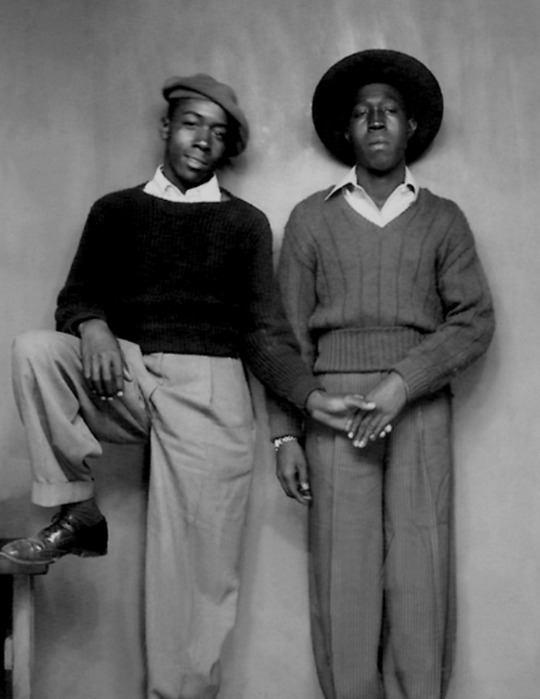
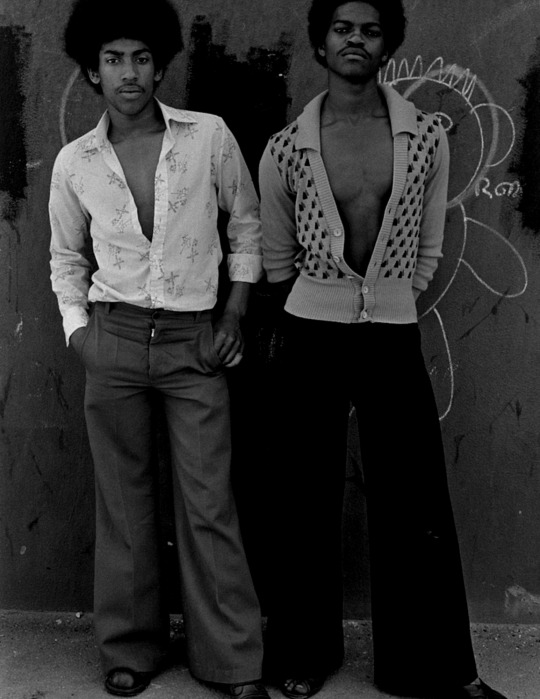
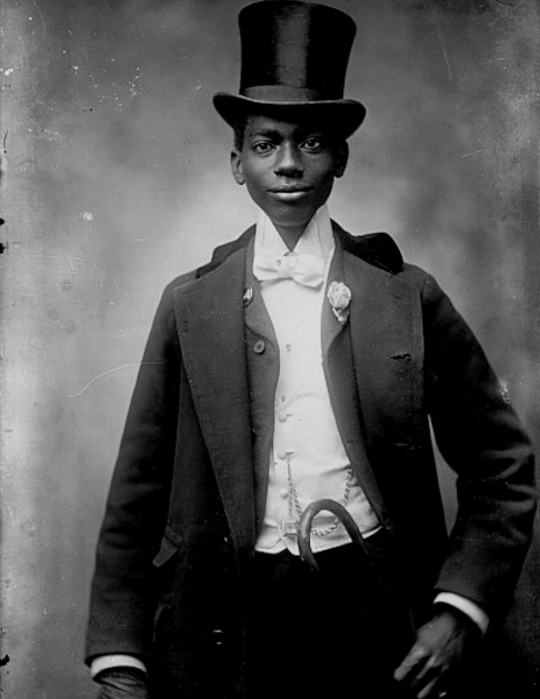



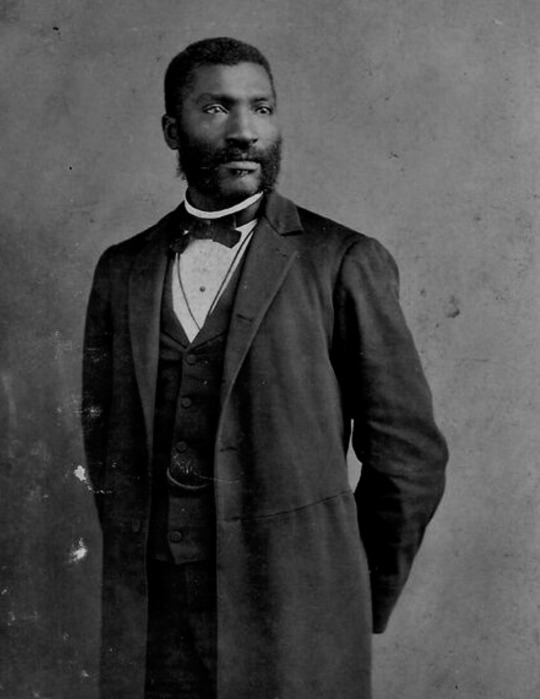






vintage men’s fashion in black history
#i did a women edition so here's the mens one#history#vintage photography#photography#beauty#vintage#fashion#vintage fashion#historical clothing#historical#black history
3K notes
·
View notes
Photo
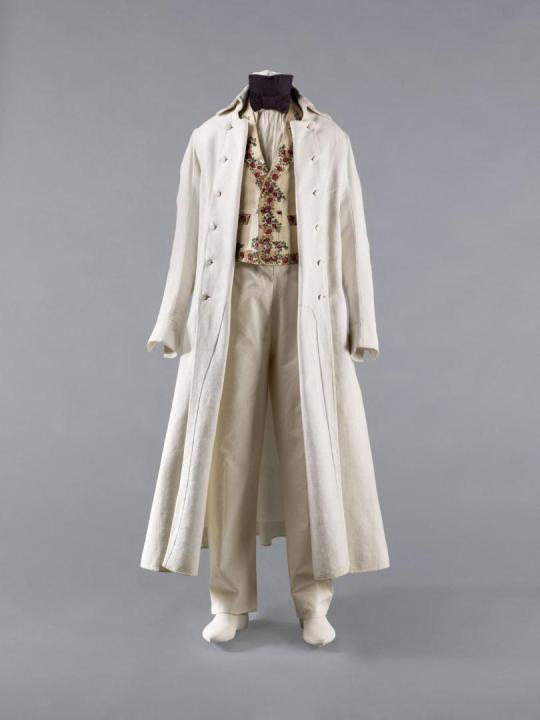

Ensemble
c.1815-1825
Palais Galliera
#ensemble#fashion history#historical fashion#menswear#1810s#1820s#mens fashion#frock coat#trousers#vest#1815#1820#1825#linen#cotton#palais galliera#popular
995 notes
·
View notes
Text

Tintype of two seasoned sea dogs sitting calmly before the storm, c. 1860s
#in love with this man for choosing THIS backdrop for his portrait with his little dog#his brooding eyes; his clenched fists; the roiling sea about to devour its latest victims—and a fluffy lil pupper in his lap 🐶#19th century#1800s#1860s#1860s fashion#19th century fashion#fashion history#historical fashion#men's fashion#menswear#nautical#19th century photography#ferrotype#tintype#19th century men#vintage men#full fathom five thy chewtoy lies
822 notes
·
View notes
Text
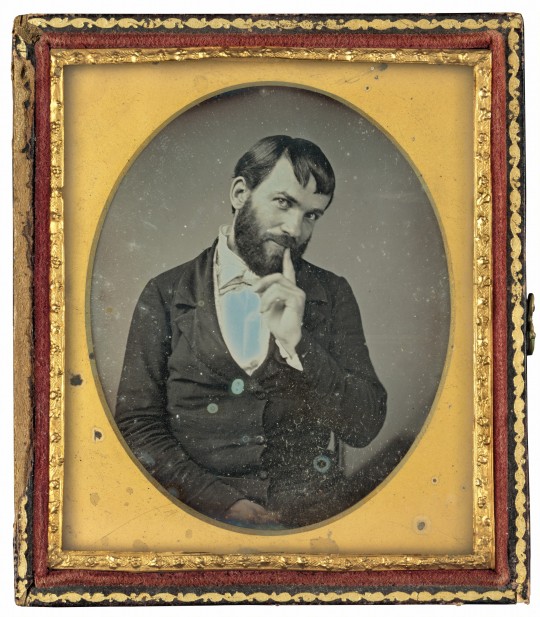
Eighteen-fifties man being silly in the photography studio, what will he do!

538 notes
·
View notes