#history of race
Text
European history is not white


Someone commented this to a post I reblogged, which message is basically "we shouldn't venerate the Dead White Man HistoryTM and we should elevate other history too, but we still need to learn Dead White Man HistoryTM to understand the world today". It's basically a response to the attitude you sometimes come across in the internet that sees learning about those Dead White MenTM as not worth our time. And this person, who seems to be following this blog because they responded to my reblog, takes it as a personal attack against all white Europeans. For some reason. Well I take these comments as a personal attack against historical understanding.
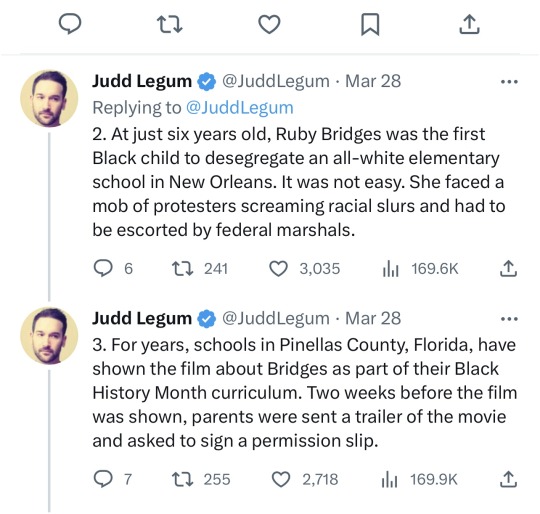
Firstly, the post clearly didn't say you shouldn't venerate any European history, because not all European history is Dead White Man HistoryTM. Obviously this person thinks European history is white, which is not true, but surely, surely, they know it's not all men? Secondly, what is "west culture"? When did it start? There is not one western culture, not one European culture. The first concept of some shared Europeanness was the Christendom in Middle Ages, but it was not exactly the same as we think of Europe today, because it did not include the pagan areas, but it included a lot of Levant and parts of Central Asia, where there were large Christian areas. And Europe was not "very white" nor was the Christendom. The more modern concept of West was cooked in tandem with race and whiteness during colonial era and Enlightenment, around 17th to 18th centuries. And Europe was certainly not very white then. The western world also includes a lot of colonized areas, so that's obviously not white history. Thirdly, implying that asking white people to apologize for European history (which no one did ask) is as ridiculous as asking black people for African history is... a choice. Black people do exist in a lot of other places than Africa, which white people should be the ones apologizing for, and really white people also have a lot to answer for about African history. Lastly, if you think the quote "anyone who thinks those dead white guys are aspirational is a white supremacist" means you as an European are demanded to apologize for your existence, maybe - as we say in Finland - that dog yelps, which the stick clanks. (I'm sorry I think I'm the funniest person in the world when I poorly translate Finnish sayings into English.)
The thing is, there is no point in European history, when Europe was white, for three reasons. 1) Whiteness was invented in 17th century and is an arbitrary concept that has changed it's meaning through time. 2) Whichever standard you use, historical or current, Europe still has never been all or overwhelmingly white, because whiteness is defined as the in-group of colonialists, and there has always been the internal Other too. In fact the racial hierarchy requires an internal Other. 3) People have always moved around a lot. The Eurasian steppe and the Mediterranean Sea have always been very important routes of migration and trade. I've been meaning to make a post proving exactly that to people like this, since as I've gathered my collection of primary images of clothing, I've also gathered quite a lot of European primary images showing non-white people, so I will use this opportunity to write that post.
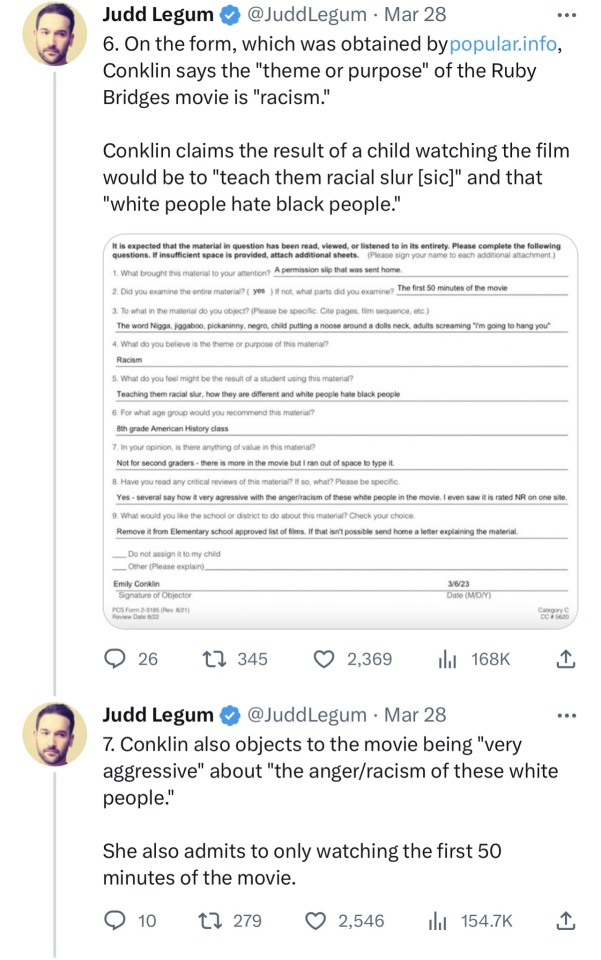
So let's start from the beginning. Were the original inhabitants of Europe white? Of course not. The original humans had dark skin so obviously first Europeans had dark skin. Whenever new DNA evidence of dark skinned early Europeans come out (like this study), the inevitable right-wing backlash that follows is so interesting to me. Like what did you think? Do you still believe the racist 17th century theories that white people and people of colour are literally different species? I'm sure these people will implode when they learn that studies (e.g. this) suggest in fact only 10 000 years ago Europeans had dark skin, and even just 5 000 years ago, when Egypt (an many others) was already doing it's civilization thing, Europeans had brown skin (another source). According to the widely accepted theory, around that time 5 000 years ago the Proto-Indo-European language developed in the Pontic-Caspian steppe, which extends from Eastern Europe to Central Asia. These Proto-Indo-Europeans first migrated to Anatolia and then to Europe and Asia. Were they white? Well, they were probably not light skinned (probably had brown skin like the other people living in Europe around that time), the Asian branch of Indo-European peoples (Persians, most Afghans, Bengalis, most Indians, etc.) are certainly not considered white today and a lot of the people today living in that area are Turkic and Mongolic people, who are also not considered white. I think this highlights how nonsensical the concept of race is, but I don't think Proto-Indo-Europeans would have been considered white with any standard.
Around Bronze Age light skin became common among the people in Europe, while in East Asia it had become wide spread earlier. This does not however mark the point when "Europe became white". During the Bronze Age there was a lot of migration back and forth in the Eurasian steppe, and the early civilizations around Mediterranean did a lot of trade between Europe, Africa and Asia, which always means also people settling in different places to establish trading posts and intermarrying. There were several imperial powers that also stretched to multiple continents, like the briefly lived Macedonian Empire that stretched from Greece to Himalayas and Phoenicians from Levant, who didn't built an empire but settled in North Africa, Sicily and Iberia. In Iron Age the Carthaginian Empire, descendants of Phoenician settlers in current Tunisia, build an Empire that spanned most of the western Mediterranean coast. Their army occupying that area included among others Italic people, Gauls, Britons, Greeks and Amazigh people.
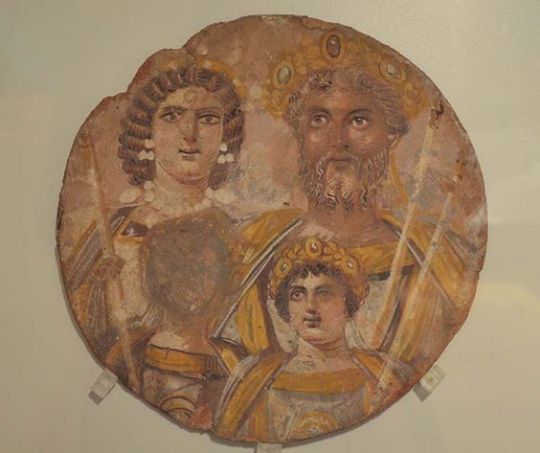
Iron Age also of course saw the rise of the Roman Republic, and later empire, but it was preceded by Etruscans, who populated Tuscan, and possibly preceded the Indo-European presence. However, weather through trade and migration with other Mediterraneans or the continuing presence of darker skin tones of the early Europeans, their art quite often depicts darker skin tones too, like seen below in first two images. Roman Empire at it's height spanned from Babylonia to the British Isles. They recruited soldiers from all provinces and intentionally used stationed them in different areas so they wouldn't be too sympathetic to possible rebels or neighboring enemies. Historical sources mention black Nubian soldiers in British Isles for example. They also built a lot of infrastructure around the empire to ensure protection and easy transportation through trade routes inside the empire. During this time Jewish groups also migrated from Levant to both North-Africa and Europe. Rome even had non-European emperors, like Septimius Severus who originated from Levant and was Punic (descendants of Phoenicians) from his father's side, and who was depicted with darker skin (third picture below). Various ethnicities with differing skin tones are represented all over Roman art, like in the fourth picture below from hunting lodge in Sicily.




Eurasian steppe continued to be important source of migration and trade between Europe and Asia. Scythians, Iranic nomadic people, were important for facilitating the trade between East Asia and Europe through the silk road during the Iron Age. They controlled large parts of Eastern Europe ruling over Slavic people and later assimilating to the various Slavic groups after loosing their political standing. Other Iranic steppe nomads, connected to Scythian culture also populated the Eurasian steppe during and after Scythia. During the Migration Period, which happened around and after the time of Western Rome, even more different groups migrated to Europe through the steppe. Huns arrived from east to the Volga region by mid-4th century, and they likely came from the eastern parts of the steppe from Mongolian area. Their origins are unclear and they were either Mongolic, Turkic or Iranic origin, possibly some mix of them. Primary descriptions of them suggests facial features common in East Asia. They were possibly the nomadic steppe people known as Xiongnu in China, which was significant in East and Central Asia from 3rd century BCE to 2nd century CE until they moved towards west. Between 4th and 6th centuries they dominated Eastern and Central Europe and raided Roman Empire contributing to the fall of Western Rome.
After disintegration of the Hun Empire, the Huns assimilated likely to the Turkic arrivals of the second wave of the Migration Period. Turkic people originate likely in southern Siberia and in later Migration period they controlled much of the Eurasian steppe and migrated to Eastern Europe too. A Turkic Avar Khagenate (nation led by a khan) controlled much of Eastern Europe from 6th to 8th century until they were assimilated to the conquering Franks and Bulgars (another Turkic people). The Bulgars established the Bulgarian Empire, which lasted from 7th to 11th in the Balkans. The Bulgars eventually adopted the language and culture of the local Southern Slavic people. The second wave of Migration Period also saw the Moor conquest of Iberia and Sicily. Moors were not a single ethnic group but Arab and various Amazigh Muslims. Their presence in the Iberian peninsula lasted from 8th to 15th century and they controlled Sicily from 9th to 11th century until the Norman conquest. During the Norman rule though, the various religious and ethnic groups (which also included Greeks and Italic people) continued to live in relative harmony and the North-African Muslim presence continued till 13th century. Let's be clear that the Northern Europe was also not white. Vikings also got their hands into the second wave migration action and traveled widely to east and west. Viking crews were not exclusively Scandinavians, but recruited along their travels various other people, as DNA evidence proves. They also traded with Byzantium (when they weren't raiding it) and Turkic people, intermarried and bought slaves, some of which were not white or European. A Muslim traveler even wrote one of the most important accounts of Vikings when encountering them in Volga.
By this point it should already be clear that Medieval Europe was neither white, but there's more. Romani people, who originate from India and speak Indo-Aryan language, arrived around 12th century to Balkans. They continued to migrate through Europe, by 14th century they were in Italy, by 15th century in Germany and by 16h century in Britain and Sweden. Another wave of Romani migration from Persia through North-Africa, arrived in Europe around 15th century. Then there's the Mongol Empire. In 13th century they ruled very briefly a massive portion of the whole Eurasian continent, including the Eastern Europe. After reaching it's largest extent, it quickly disintegrated. The Eurasian Steppe became the Golden Horde, but lost most of the Eastern-Europe, except Pontic-Caspian Steppe. They ruled over Slavs, Circissians, Turkic groups and Finno-Ugric groups till early 15th century. The Mongolian rulers assimilated to the Turkic people, who had been the previous rulers in most of the steppe. These Turkic people of the Golden Horde came to be known as Tatars. Golden Horde eventually split into several Tatar khagenates in 15th century, when the khagenates, except the Crimean Khagenate, were conquered by the Tsardom of Moscovy. Crimean Khagenate was annexed by the Russian Empire in 1783. Crusades were a movement from Europe to Levant, but they also meant intermarriage in the the Crusader kingdoms especially between the European and Levant Christians, and some movement back and froth between these kingdoms and Europe, trade and a lot of movement back after the Crusader kingdoms were defeated in 13th century. Generally too trade across the Mediterranean sea was extensive and led to migration and intermarriage.
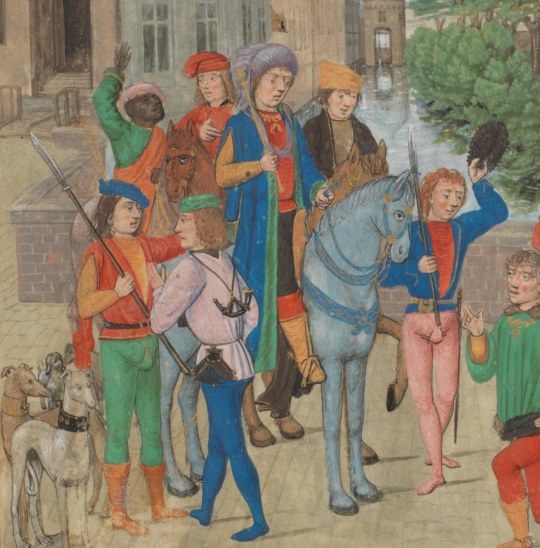
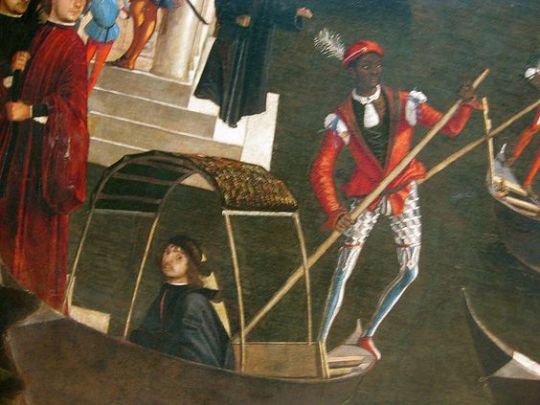
And here's some example of people of colour in Medieval European art, shown as part of the majority white European societies. First is from a 15th century French manuscript depicting Burgundy court with dark skin courtier and lady in waiting. Second one is from a Flemish manuscript from 15th century of courtiers, including a black courtier, going for a hunt. Third is a 15th century Venetian gondolier with dark skin.



In Renaissance Era Europe was only increasing it's trade and therefore had even more connections outside Europe. The first picture below is Lisbon, which had strong trade relationship with Africa, depicted in late 16th century. People with darker skin tones were part all classes. Second image is an Italian portrait of probably a seamstress from 16th century. Third one is a portrait of one of the personal guards of the Holy Roman Emperor. Fourth image is a portrait of Alessandro de' Medici, duke of Florence, who was noted for his brown complexion, and the modern scholarly theory is that his mother was a (likely brown) Italian peasant woman.
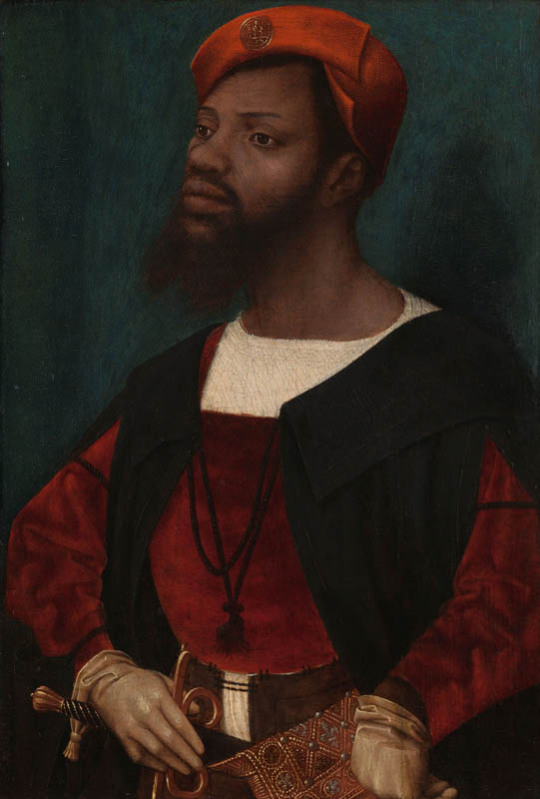




Colonialism begun in the Renaissance Era, but the wide spread colonial extraction and slavery really got going in the 17th century. Racial hierarchy was developed initially to justify the trans-Atlantic slave trade specifically. That's why the early racial essentialism was mostly focused on establishing differences between white Europeans and black Africans. Whiteness was the default, many theories believed humans were originally white and non-whites "degenerated" either through their lives (some believed dark skin was basically a tan or a desease and that everyone was born white) or through history. Originally white people included West-Asians, some Central-Asians, some North-Africans and even sometimes Indigenous Americans in addition to Europeans. The category of white inevitably shrank as more justifications for atrocities of the ever expanding colonial exploitation were required. The colonial exploitation facilitated development of capitalism and the industrial revolution, which led to extreme class inequality and worsening poverty in the European colonial powers. This eventually became an issue for the beneficiaries of colonialism as worker movements and socialism were suddenly very appealing to the working class.
So what did the ruling classes do? Shrink whiteness and give white working classes and middle classes justifications to oppress others. Jews and Roma people had long been common scapegoats and targets of oppression. Their oppression was updated to the modern era and racial categories were built for that purpose. The colonial powers had practiced in their own neighborhoods before starting their colonial projects in earnest and many of those European proto-colonies were developed to the modern colonial model and justified the same way. In 19th century, when racial pseudoscience was reaching it's peak, Slavs, others in Balkan, the Irish (more broadly Celts), Sámi (who had lost their white card very early), Finns, Southern Italians, the Spanish, the Southern French and Greeks all were considered at least not fully white. The Southern Europeans and many Slavs were not even colonized (at least in the modern sense, though with some cases like Greeks it's more complicated than that), but they looked too much and were culturally too similar to other non-white Mediterraneans, and they were generally quite poor. In many of these cases, like Italians, the French and Slavs, it was primarily others belonging in the same group, who were making them into second class citizens. All this is to highlight how very malleable the concept of race is and that it's not at all easy to define the race of historical people.
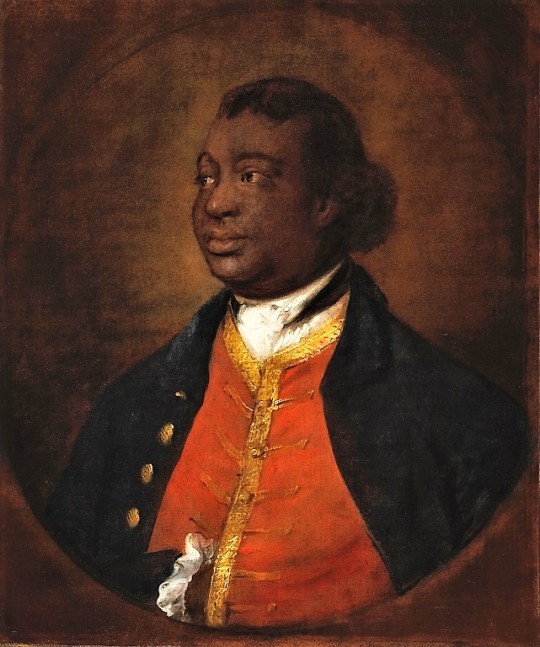
However, even if we would go with the racial categories of today, Europe was still far from being all white in this period. You had Roma, who certainly are not included in whiteness today, and European Jews, whose whiteness is very conditional, descendants of Moors in Southern Europe and Tatars and Turks in Eastern Europe and Turkey, which today is often not thought of as part of Europe, but historically certainly was. And then colonialism brought even more people into Europe forcibly, in search of work because their home was destroyed or for diplomatic and business reasons. There were then even more people of colour, but they were more segregated from the white society. Black slaves and servants are very much represented in European art from 17th century onward, but these were not the only roles non-white people in Europe were in, which I will use these examples to show. First is a Flemish portrait of Congo's Emissary, Dom Miguel de Castro, 1643. Second is a 1650 portrait of a Moorish Spanish man Juan de Pareja, who was enslaved by the artist as artisanal assistant, but was freed and became a successful artist himself. Third is a 1768 portrait of Ignatius Sancho, a British-African writer and abolitionist, who had escaped slavery as a 20-year-old. Fourth painting is from 1778 of Dido Elizabeth Belle, a British gentlewoman born to a slave mother who was recognized as a legitimate daughter by her father, and her cousin. The fifth portrait is of an unknown woman by (probably) a Swiss painter from late 18th century. Sixth is a 1760s Italian portrait of a young black man.



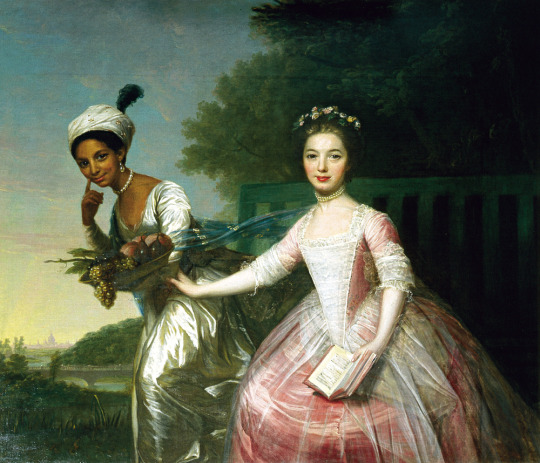
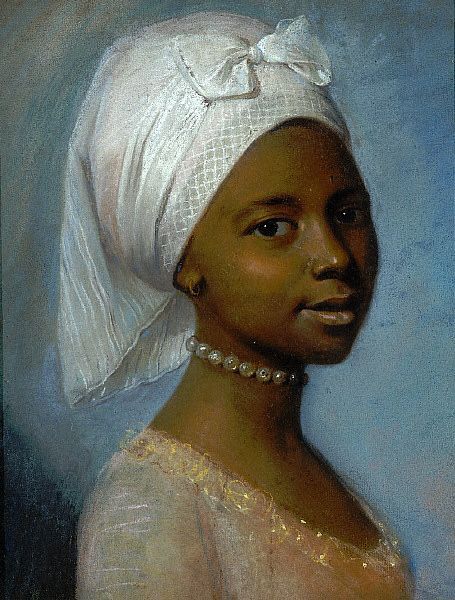

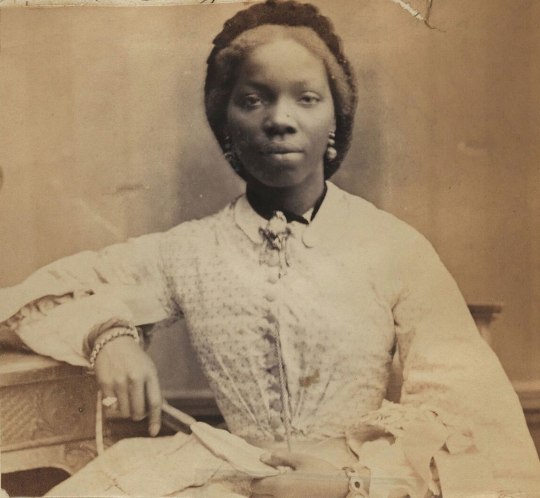
In late 18th century England abolished slavery in British Isles first, then in early 19th century in the whole British Empire, thanks to the continuous campaign of free Black people and some white allies, notably Quakers. Around the same time slavery was abolished in France (briefly till Napoleon got to power) after the French revolution. This meant there were a lot more free black people in Europe after that. In 18th century the Europeans, British especially, were colonizing Asia as much they could, which meant that in 19th century there started to also be a lot more Asian, especially Indian people in Europe. First picture below is of Thomas Alexander Dumas, who was son of a black slave woman and a white noble French man and became a general in the French revolutionary army. His son was one of the most well-known French authors, Alexander Dumas, who wrote The Count of Monte Cristo and The Three Musketeers. Second portrait is of Jean-Baptiste Belley, a Senegalese former slave, who became French revolutionary politician. Third portrait is from 1810 of Dean Mahomed, an Indian-British entrepreneur, who established the first Indian restaurant in London. Forth is Arab-Javanese Romantic painter Saleh Syarif Bustaman, who spend years in Europe. Fifth is a 1862 photo of Sara Forbes Bonnetta, originally named Aina, princess of Edbago clan of Yoruba, who was captured into slavery as a child, but later freed and made Queen Victoria's ward and goddaughter. She married a Nigerian businessman, naval officer and statesman, James Pinson Labulo Davies (sixth picture).
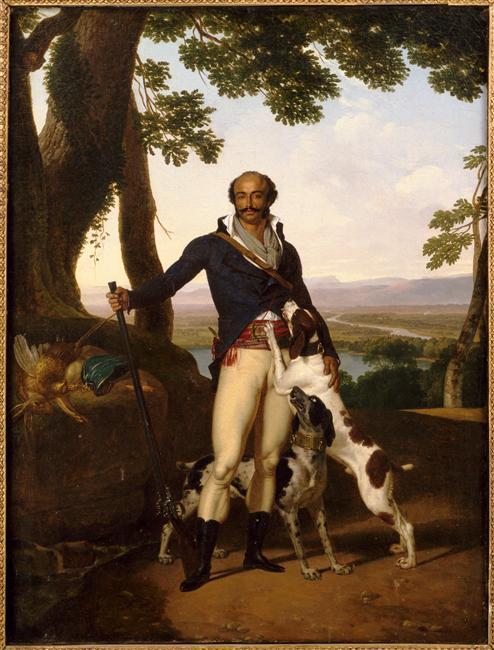
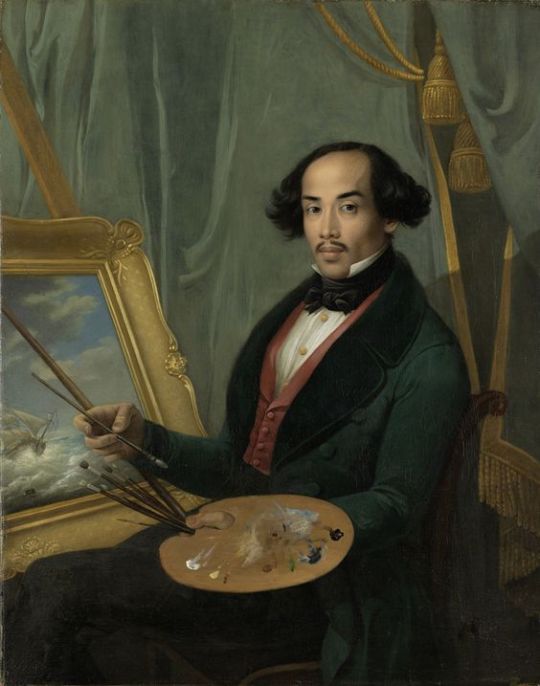






So any guesses on at what point was that "very white Europe" when the "west culture" begun? It kinda seems to me that it never actually existed.
#history#poc history#black history#historical art#european history#history of race#colonialism#racism#slavery#painting#photograph
174 notes
·
View notes
Note
did african americans ever gain the benefits of the new deal or were they deliberately excluded by fdr or his administration?
The short version is "yes, but."

If you read the work of Ira Katznelson, Martha Biondi, Tom Sugrue, and others, the picture of the New Deal as it related to African-Americans is not one of comprehensive exclusion, but rather partial access on a discriminatory basis, depending on where you lived and where you worked.
The Faustian bargain that FDR made with the Dixiecrats was based on an either/or proposition that Dixiecrat legislators would vote for New Deal programs, but on the condition that they would either be jointly operated by state/local and the Federal government, or they would have occupational exclusions (chiefly agricultural and domestic workers). The objective was that either all-white Southern governments would be able to racially discriminate (as long as they could come up with a facially-neutral justification) or that the New Deal's national programs would exclude a supermajority of black people in the South, where sharecropping was the dominant occupation for black men and domestic service was the dominant occupation for black women, respectively. (IIRC, it was about 70% for both men and women.)
However, the intent wasn't to completely cut off black people from the New Deal - Southern governments desperately wanted Federal money to boost incomes and thus consumer spending without undermining their low-wage, low tax, low benefits political economy - but rather to ensure that black people's access to public benefits was under white control. So, for example, Southern governments did not want black workers to get access to Unemployment Insurance or Old Age Insurance, because those were entitlement programs where national eligibility and benefit standards would give people a due process right to social insurance. Instead, they wanted to funnel black workers into Aid to Dependent Children or Old Age Assistance (what we think of as "welfare"), where they could use the threat of arbitrary denial to keep black people compliant and achieve other policy objectives.
In addition to cutting people off benefits as punishment for violating the color line by trying to register to vote or hiring a lawyer or trying to buy land etc., Southern governments would routinely engage in a seasonal practice whereby ADC and OAA recipients would be kicked off the rolls when the cotton-planting and cotton-picking season came around in order to ensure a large and desperate workforce, and then re-added to the rolls to provide them with income during the winter months so that farmers didn't have to pay them a living wage.

You'll note that everything I've talked about above had to do with black people living in the South. The story was very different in the North, where black people could vote and largely worked in manufacturing and other occupations that were not excluded from New Deal programs (although black women did face a double burden, in that many of them still worked in domestic service). As a result, black workers were able to benefit from Unemployment Insurance, Old Age Insurance, the Fair Labor Standards Act, the Wagner Act, et al. and dealt with governments that were less interested in systematically discriminating against them. Not uninterested - there's a long history of Welfare Departments using dehumanizing regulations to exert social control on black people - but it tended to be a subtler and more patchwork form of discrimination than under Jim Crow.

The one major exception to this was in the area of housing. One of the peculiar manifestations of American racism is that the South was largely uninterested in residential segregation and focused instead on political, economic, and social control, and that the North was the reverse. Whether it was through the red-lining of the Federal Housing Administration and HOLC or straightforward racial segregation in public housing constructed by the Federal Housing Authority, Northern governments and communities went to great (and oftentimes violent) lengths to ensure that white neighborhoods and black neighborhoods were kept separate.
But here again, the pattern was one of partial access on a discriminatory basis. Black residents of Northern cities could get apartments in public housing, but only in buildings designated as black-only that were located in poor black neighorhoods. Some black residents might be able to get a mortgage from a black-owned bank to buy a house in a segregated neighborhood, but because they were cut off from the FHA and thus from the GI Bill, most black workers couldn't afford the option of overpaying for lower quality houses and the ones who could generally did not generate much long-term equity because their property was considered less valuable.
So there you have it.
#new deal#history#u.s history#policy history#social policy#economic policy#historiography#historical analysis#history of race
43 notes
·
View notes
Quote
What is Africa to me? Once I should have answered the question simply: I should have said 'fatherland' or perhaps better 'motherland' because I was born in the century when walls of race were clear and straight; when the world consisted of mutually exclusive races; and even though the edges might be blurred, there was no question of exact definition and understanding of the meaning of the word. […]
Since then the concept of race has so changed and presented so much of contradiction that as I face Africa I ask myself: what is it between us that constitutes a tie which I can feel better than I can explain? Africa is, of course, my fatherland. Yet neither my father nor my father's father ever saw Africa or knew its meaning or cared overmuch for it. My mother's folk were closer and yet their direct connection, in culture and race, became tenuous; still, my tie to Africa is strong. On this vast continent were born and lived a large portion of my direct ancestors going back a thousand years or more. The mark of their heritage is upon me in color and hair. These are obvious things, but of little meaning in themselves; only important as they stand for real and more subtle differences from other men. Whether they do or not, I do not know nor does science know today.
But one thing is sure and that is the fact that since the fifteenth century these ancestors of mine and their other descendants have had a common history; have suffered a common disaster and have one long memory. The actual ties of heritage between the individuals of this group, vary with the ancestors that they have in common and many others: Europeans and Semites, perhaps Mongolians, certainly American Indians. But the physical bond is least and the badge of color relatively unimportant save as a badge; the real essence of this kinship is its social heritage of slavery; the discrimination and insult; and this heritage binds together not simply the children of Africa, but extends through yellow Asia and into the South Seas. It is this unity that draws me to Africa.
W. E. B. Du Bois, Dusk of Dawn: An Essay Toward an Autobiography of a Race Concept (1940)
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

"Out of the many possible identities anyone could claim at the entangled borders of empire, those who claimed to be ‘English’ made race their linchpin, while ‘Spaniards’ deliberately did not. In this eye-opening and groundbreaking study, April Lee Hatfield illuminates how the construction of ‘Anglo’ and ‘Latin’ narratives of exclusion and belonging in the body politic began as early as the mid-seventeenth century in and around Jamaica. Boundaries of Belonging is sure to become a classic on the comparative history of race in the continent."
#uwlibraries#history books#caribbean history#colonial history#british history#spanish history#history of race
4 notes
·
View notes
Text

15K notes
·
View notes
Text

#slavery#ron desantis#jason aldean#education#politics#florida#racism deniers#whitewashing history#crt#critical race theory#dei
4K notes
·
View notes
Photo




Untucked: RuPaul's Drag Race | S7E6
↳ bonus:

#rpdredit#rupauls drag race#kennedy davenport#katya zamolodchikova#katya zamo#katya#ginger minj#s7#rpdr#and i was watching untucked moments and i had to gif this beautiful piece of drag race history#s7 untucked is my favorite idc what yall think#s7 is my favorite SEASON#imagine being a s7 hater in the good year of 2023 some people need to grow up#~~~
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
#tulsa oklahoma#black tumblr#race riots#tulsa#black history#black literature#black community#civil rights#black history is american history#american history#black wallstreet#black history matters#black history month
541 notes
·
View notes
Text
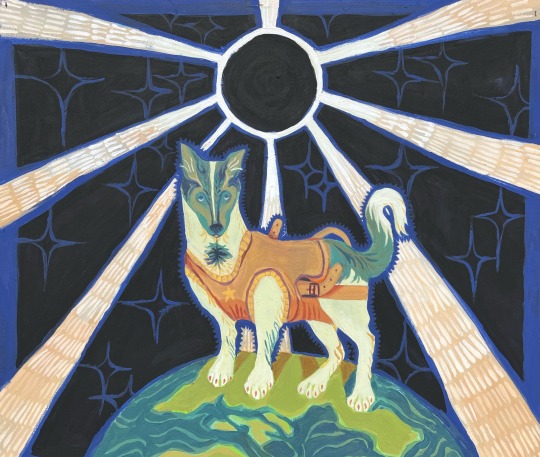

Patron Saint of One Way Trips (2024)
24x36
Acrylic on Wood
#my art#illustration#painting#Laika#russia#Russian history#space race#laika art#1960s#My sweet girl#eclipse
439 notes
·
View notes
Text
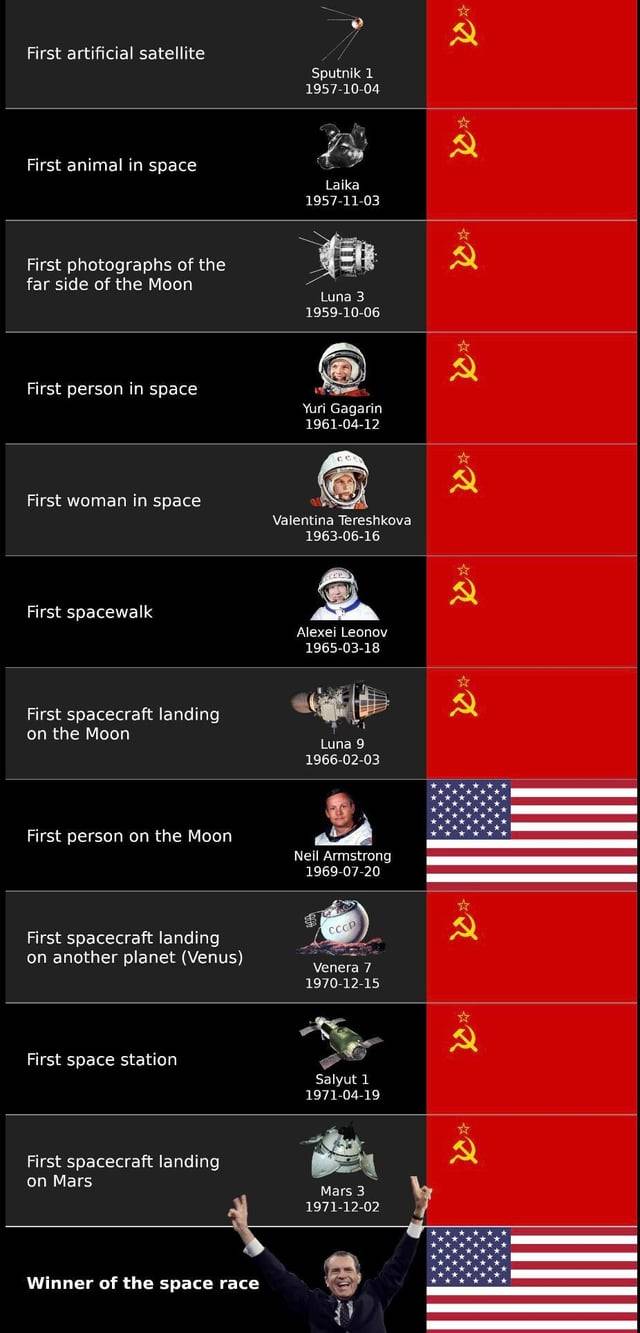
Since people wanna celebrate the moon landing so bad, lemme remind you which country actually hit most milestones in the space race first (image source in alt)
2K notes
·
View notes
Text




This is recent history. Ruby Bridges is 68yrs old and she is still alive.
Emily Conklin is thee definition of a racist Karen, and she is trying to whitewash the history white children learn by erasing a rated PG Disney movie that has already been shown for years in Pinellas County schools, usually as a part of Black History Month.
Two immediate thoughts that come to mind are:
“The people who threw rocks at Ruby Bridges for trying to go to school in 1960 now are upset their grandchildren might learn about them throwing rocks at Ruby Bridges for trying to go to school.”
and
“IF BLACK CHILDREN ARE OLD ENOUGH TO EXPERIENCE RACISM, WHITE CHILDREN ARE OLD ENOUGH TO LEARN ABOUT IT”
Look, Ruby Bridges was six years old when racist white parents (men and women) threw rocks and hissy fits because she was trying to get an education. A full year younger than most of the white children who are now being “protected” from learning the truth about what their grandparents did.
I guess these delicate snowflakes are so triggered by the racism of their elders that they need to get the Republican governor to whitewash away the truth.
I’m almost 40yrs old and I used to wonder how it was that in college, white kids my age genuinely believed that Martin Luther King, Jr. died of old age. But somehow, every single Black person my age knew the truth. How does that happen?? This is how it happens. This is a prime example of precisely how that happened and still happens—because to “protect” them from the truth, white kids weren’t taught that he was assassinated. It’s literally no different than raising generations of white kids to believe that 2+2=5. There’s going to be serious problems when they hit the real world. But what can I say? Conservatives like ‘em dumb and ignorant.
Anyway, this is how you get generations of fully grown white adults who truly honestly believe foolishness like “racism is over,” or “Martin Luther King basically ended racism,” or, “we don’t need affirmative action because there is no more racism; if anything it’s white people who are more discriminated against now.” (The majority of white people polled said the same thing in the 1960s too, btw).
Keeping as many white people as possible ignorant of the truth does not happen by accident. It’s very intentional. And that’s not to say that ALL white people are ignorant of the truth. Some of them, like Emily Conklin, know the truth, but just do not care.
And make no mistake: The same white people who want to keep their white children “pure” and “innocent” have ZERO problems criminalizing and sending young Black children directly to jail for even the slightest misbehavior in a classroom.
Evil, racist cowards (redundant, I know).
#politics#emily conklin#republicans#ruby bridges#whitewashing history#erasure#north shore elementary school#black history#crt#critical race theory#book banning#florida#floriduh#ron desantis
2K notes
·
View notes
Note
I'm not as upset as some by inaccuracies in entertainment based on historical events, but in real life Queen Charlotte wasn't Black, right?
There is a theory out there about Charlotte having African ancestry and/or "African features," but it's mostly held by this one particular guy who's a historian of the African diaspora, it's not widely accepted, and even then de Valdes' argument is that Charlotte's African heritage came from a Portuguese royal marriage some 300 years previously - whether a 21st century observer would consider her black is pretty unlikely and really depends on how much credence you're willing to put into a few hostile observers' comments that were (in my opinion) just using racist sterotypes to insult Queen Charlotte rather than accurately describing what she looked like.
If you're asking about Bridgerton and it's spinoff, I think this is a case where the showrunners know that they're building off this theory to create essentially an alternate history where Queen Charlotte and a number of other aristocrats are black, and those characters frequently discuss what it means to be black and trying to rise in British society, and so on.
This creative decision raises some tricky questions. On the one hand, there are real issues when it comes to representation on TV and ensuring that BAME actors in the UK have equal opportunity in their careers given the prominence of period pieces in British film and television. And ultimately, color-blind casting is completely harmless - the 2021 Green Knight movie was some of the best Arthuriana ever made, and no one cared or should care that Dev Patel isn't a white Welsh guy.
On the other hand, as various black critics and commentators have noted, Bridgerton et al. isn't a case of color-blind casting, but rather of color-conscious casting, where the actors' race is a significant element of the plot. And this raises some potentially troubling issues about whether making a TV show about elite black aspiration and upward mobility in 18th century Britain can be squared with Britain's history of slavery and the slave trade and the very real discrimination faced by black Britons in this period. For example, the real Queen Charlotte notably ignored abolitionist petitions directed at her, and was pretty harshly (and ironically, through some rather racist political cartoons) criticized for not partaking in the anti-slavery boycott of sugar. There was even a slave ship called the Queen Charlotte. Is this history sympatico with a portrayal of Charlotte as a racial trailblazer in British society?
How one weighs the relative importance of these issues to TV shows that are ultimately adaptations of romance novels more focused on Regency handjobs than the nuances of 18th century social history is a question that's ultimately above my pay grade, and I feel it's more appropriate for me to listen to what said black critics have to say (incidentally, let me recommend the YouTuber Princess_Weeks, who has some very good video essays on the subject).
#history#british history#queen charlotte#bridgerton#cultural history#history of race#social history#slavery#boycotts
68 notes
·
View notes
Text
I thought some of my Tumblr mutuals would be interested to see this article.
Viola Ford Fletcher, aged 109, just published a memoir 'Don't Let Them Bury My Story' about her experience during the Greenwood/Tulsa Massacre. It will be available for purchase August 15th.
"Her memoir, “Don’t Let Them Bury My Story,” is a call to action for readers to pursue truth, justice and reconciliation no matter how long it takes. Written with graphic details of the 1921 Tulsa Race Massacre that she witnessed at age seven, Fletcher said she hoped to preserve a narrative of events that was nearly lost to a lack of acknowledgement from mainstream historians and political leaders.
The questions I had then remain to this day,” Fletcher writes in the book. “How could you just give a mob of violent, crazed, racist people a bunch of deadly weapons and allow them — no, encourage them — to go out and kill innocent Black folks and demolish a whole community?”
“As it turns out, we were victims of a lie,” she writes.
Fletcher notes in her memoir just how much history she has lived through — from several virus outbreaks preceding the coronavirus pandemic, to the Great Depression of 1929 and the Great Recession of 2008 to every war and international conflict of the last seven decades. She has watched the Rev. Martin Luther King, Jr. lead the national Civil Rights Movement, seen the historic election of former President Barack Obama and witnessed the rise of the Black Lives Matter movement."
#Tulsa Race Massacre#Tulsa Race Riot#Greenwood#Black Wall Street#1921#Oklahoma#Viola Ford Fletcher#Don't Let Them Bury My Story#Book#Memoir#Novel#Library#History#Black Lives Matter#BLM
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
to me the whole point of f1, and why i got into it, is that the cars are these meticulously engineered machines that - under the right circumstances - are fucking magical to watch. like for example, a wide angle shot of a car absolutely glued to the ground while going through a sleek S chicane?? 😮💨🤤
street tracks are just bumpy, with awkward super slow 90-degree corners, vision is obscured too, and it’s such a waste imo to have these incredible cars race in spaces where they don’t reach their full potential.
#the character and history of real race tracks create such a special atmosphere too!!#i want elevation changes and huge grand stands#i want to see more of the track and the cars than whatever view we can have between city buildings#i don’t want drivers tiptoeing around apartment blocks and wine bars like wtf are we doinggggggg#f1
367 notes
·
View notes
Text
Characters reconnecting with their ancestral cultures in an interplanetary setting
@pixiedustandpetrichor asked:
Hi! I am writing a novel with three main female characters in an interplanetary setting. They grow up as orphans in an Irish-coded country and as children are mostly exposed to solely that culture, but they leave after becoming adults.
Character A is Tuareg-coded, B Mongolian-coded, and C is Germanic-coded. It isn’t central to the story, but I would like them to get in touch with/learn more about their ancestral cultures, especially in terms of religion. A does this by actually visiting the planet her parents came from, but B and C do not.
What can I do to depict their relationships with said cultures and their journey to reconnect with them? Would it be realistic for each of them to have different mixed feelings about participating in these cultures and for them to retain some sense of belonging to the culture they grew up in as well? Thank you for your time.
Hello, asker! WWC doesn’t have Tuareg or Mongol mods at the moment, so we're not able to speak to the specifics of cultural and religious reconnection for these particular groups. Still, I want to take this opportunity to provide some general context and elements to consider when writing Tuareg-coded characters, or other characters from groups that have experienced colonization in the real world. My fellow mods will then share thoughts about cultural reconnection in general and with respect to Germanic heritage in particular.
Drawing inspiration from groups that have experienced colonization
As you’re probably aware, the Tuareg are an ethnic group indigenous to North Africa. As with many indigenous groups, they have experienced colonization multiple times over the course of their history. Colonization often leads to the loss or erasure of certain aspects of culture as the colonized people are pressured to conform to the culture of the dominant group. In many cases, it’s near impossible to say what the ancestral culture of a colonized group was prior to colonization.
When coding a fictional culture based on a group that was colonized in the real world, it's important to ask questions about:
Which aspects of culture you're portraying
Where these aspects come from
Whether you're ready to tackle their implications for the world you're building
It’s not necessarily wrong to use elements of coding that draw from cultural aspects influenced by colonization. As I said, it can be very difficult, even impossible, to portray a “pure” culture as it would have been had colonization not occurred–because we simply can’t know what that alternate history would look like, and because so much has been lost or intentionally suppressed that the gaps in our knowledge are too wide to breach. But it’s important to be aware of where these cultural elements are coming from.
Where is your coding coming from and what are the implications?
For example, while the Tuareg today are majoritarily Muslim, this was not the case prior to the Arab conquest of North Africa. Some elements of Tuareg culture today, such as tea ceremonies, are derived from the influence of Arab and Muslim culture and likely did not exist prior to the 20th century. As you’re developing the culture of the Tuareg-coded group in your fictional setting, you have to decide whether to include these elements. There is no right answer–it will depend on what you’re trying to do and why.
Is your setting in our far future, in which case we can assume your Tuareg-coded group is distantly related to today’s Tuareg?
In that case, they will probably have kept many cultural aspects their ancestors acquired through their interactions with other cultures around them–including cultural groups that colonized them. They may–let’s build hopeful worlds!–have reclaimed aspects of their ancestral culture they’d been forced to abandon due to colonization. They may also have acquired new aspects of culture over time. This can be very fun to explore if you have the time and space to do so.
I would recommend speaking with Tuareg people to get a better grasp of how they see their culture evolving over the next however many centuries or millennia, what they wish to see and what seems realistic to them.
Alternatively, maybe your setting is a secondary world unrelated to ours and you only want to draw inspiration from the real-world Tuareg, not represent them exactly. In that case, you need to decide which period of history you’re drawing from, as Tuareg culture is different today from what it was 50 years ago, and different still from 200 years ago or 1000 years ago. You’ll need to research the historical period you’re choosing in order to figure out what was happening at that time and what the cultural influences were. If it’s pre-colonial, you’ll probably want to avoid including cultural elements influenced by colonization from groups that arrived later on.
Finally, if the time period you’re drawing from is post-colonial:
Are you planning to account for the effects of colonization on Tuareg culture?
Will you have an in-world equivalent for the colonization that occurred in real life?
For example, will the Tuareg-coded characters in your world be from a nomadic culture that was forced to become sedentary over the years and lost much of their traditions due to colonial pressure to conform?
Where did this pressure come from in your world–is it different from what happened in ours? If so, how different? And what are the consequences?
Writing about colonization can be quite the baggage to bring into a fictional setting. I’m not saying it can’t be done, but it will certainly require sensitivity and care in portraying it.
In summary: think it through
I’m not saying all this to discourage you, but to point out some of the considerations at play when drawing inspiration from a real-life culture that has experienced colonization. Similar challenges arise for coding based on any other indigenous group in the world.
My advice to you, then, is to first sit down and decide where and when in history your coding is coming from, and what you’re trying to achieve with it. This will help you figure out:
which elements of contemporary Tuareg culture are pertinent to include
How much your coding will be influenced by the Tuareg’s real-life history
To what extent that will inform the rest of the world you’re creating
This, in turn, may help in deciding how to portray your character’s reconnection journey.
Again, I am not Tuareg and this is by no means meant to be an exhaustive list of considerations for writing Tuareg-coded characters, only a few places to start.
If any Tuareg or Amazigh readers would like to chime in with suggestions of their own, please do. As always, please make sure your comments adhere to the WWC code of conduct.
- Niki
Pulling from diaspora and TRA narratives of cultural reconnection
Marika here: This ask plotline could also pull directly from diaspora and TRA narratives of cultural reconnection. Many diaspora and TRA cultural reconnection stories are, in effect, about navigating the difficult process of resuscitating, or renewing ties to culture using limited resources in environments that often lack necessary cultural infrastructure or scaffolding.
See this question here to the Japanese team for suggestions of how to handle such a storyline in a similar sci-fi setting.
More reading: Japanese-coded girl from future
-Marika
Reconnecting with German heritage
Hi, it’s Shira. I’m not sure whether German-Jewish counts as Germanic for the purposes of your post but since German Jews were more assimilated than other Ashkies, Germanness does feel real and relevant to my life (especially because my father worked there for approximately the last decade of his life.) NOTE: when I see “Germanic” vs German I think of cultures from 1500 years ago, not 100-200 years ago, so I can’t help you there, but I’d be surprised as a reader if a character focused on that for reconnection to the exclusion of the 19th century etc.
People in the United States specifically, reconnecting with German heritage, often lean into Bayerischer/Bavarian kitsch, I’ve noticed. Personally, though, what I find most relevant is:
1. The food (although I’ve come to learn that what I grew up eating was closer to veal/chicken scallopini than actual schnitzel because it was drenched in lemon, but I do like the other foods like the potato salad and sweet and sour red cabbage etc.) Your character could try making one of these “ancestral” foods as a way to reconnect?
2. The classical music, because I’m a second generation professional musician – if character C plays an instrument, leaning into that might be meaningful (Beethoven, Bach, Brahms, Mendelssohn, Clara Schumann and her husband Robert, etc.)
3. The nature, especially specifics that I enjoyed during my time there – personally, I loved the bright pink flowers all over the chestnut trees, but there are a lot of choices especially because of the Alps. If C is an artist maybe they can sketch something Germany-related from old photographs they found on the Space Internet?
I think it is VERY realistic for the characters to remain connected to the culture in which they were raised, by the way, whether or not they have positive feelings about it. Culture isn’t an inherited trait. Sure, if they want to completely walk away, they can, but I bet there are still ways it will creep back in without them realizing it simply because it’s really hard to have universal knowledge of the origins of all our quirks. Plus, not everyone feels alienated from their raised-culture just because they’re genetically something else.
P.S. There is also Oktoberfest, which I don’t really get into but is a thing, and beer, which is another point of German cultural pride.
German gentiles, weigh in – y’all have your own stuff, I know! OH YEAH so for German Christians, Christmas “markets” are a whole thing. That’s worth looking up.
–S
What do you mean by Germanic?
Hello it’s Sci! I had to study German history for my historical fantasy novel set in the late 18th century Holy Roman Empire. I am not sure what is meant by Germanic as that can encompass a variety of things.
Germanic people: from the Classical Period of Roman Empire and early Middle Ages. Similar to Mod Shira, I unfortunately can’t help very much here.
The Germanosphere: regions that spoke German, which includes modern day Germany, Austria/Hungary, Switzerland, Lichtenstein, Belgium, and Luxembourg. I generally define this as the regions captured in the Hapsburg Empire along with Switzerland usually encompassing “Central Europe.”
Modern German national identity (i.e. German): post Napoleon and the Congress of Vienna (> 1815) only including the territory of modern day Germany.*
I ask this because modern German national identity is surprisingly recent since Germany only popped up in 1871 under Otto von Bismarck. Previously, Germany was divided into smaller states and city states as a very decentralized region under the German Confederation and before that, the Holy Roman Empire. Depending on the era, you can see different conflicts and divides. During the early days of the Protestant Reformation started by Martin Luther, the northern and southern German territories generally split along Protestant-Catholic lines. The 18th century saw Austria and Prussia as the foci of global power who warred against each other even though both were part of the Holy Roman Empire.
Other states and city-states like Baden-Wurttemberg or Saxony sometimes had power but it was typically more localized compared to Austria. Post-WW2, you saw the split of Germany into West Germany run under capitalism and East Germany run under communism as a satellite Soviet state leading to more modern cultural divides. Due to heavy decentralization historically, each region had its own character with religious and cultural divides.
Assuming that the Germanic character is not from the classical period or early Middle Ages but not from the 19th century either, you can include your character reconnecting to classical folklore like that of Krampus (if they’re Christian), German literature and music like the works of Johann Wolfgang von Goethe or Mozart, or German philosophy like Immanuel Kant.
*A major wrinkle: German royals and nobility married into other states and nations frequently with Britain and Russia being notable examples. In Britain, the House of Hanover took over after the Stuart House died without clear direct heirs. When Queen Victoria married the German prince Albert, they celebrated Christmas with a tree and brought the German tradition of a Christmas tree to Britain and the British Empire. Only during World War I did the royal family’s house of Hanover name change from House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha to the more “English-sounding” Windsor. As a result, the German cultural influence may be even more widespread than we think.
However, without more specific descriptors of what Germanic means in the context of your story, it can be difficult to determine which aspects of German culture your character could reconnect to.
-Mod Sci
#culture#cultural disconnect#cultural reconnect#race coding#ethnic coding#German#Mongol#Tuareg#setting#science fiction#Jewish#Colonialism#History#North Africa#Arab#Muslim#history
337 notes
·
View notes