#chinese music
Text
Her battle vibes are too powerful 🗡️ Blindfolded little girl plays “Ascetic” 行者 on a guzheng
Musical genius 🔥
The metronome and stopwatch were put there to shut mean people up (some comments on her other videos accused her of speeding up the videos).
This video is from her channel. The same video was uploaded on her music school’s channel first. Comments there say that weapons are going to start flying soon (referring to how musical instruments can be used in combat in wuxia movies) 🤣
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
My 2023 in Mandopop/Chinese music (update & recs)

It’s been too long since I last shared some music recommendations/updates on what I’m listening to! Admittedly, I haven’t been discovering as many new artists because I’m busy listening to 薛之谦 on repeat. But we'll focus on the new.
You can check out my Spotify playlist featuring these songs (plus bonus ones). In addition, I’ve included YouTube links below.
五月天 / Mayday
五月天 is a legendary band, so of course I knew of them and had heard a few of their songs over the years. But I never proactively sought out their music until recently. I still haven’t had time to dive into their back catalog, but I’ve already found some songs I really love.
《我又初恋了》
I actually really didn’t like this song the first time I heard it, but it wormed its way into my brain. It’s just a lot of fun! Non-serious songs can be good too.
《转眼》
My favorite 五月天 song <3. I’m probably too young to fully appreciate the lyrics, but they make me feel so nostalgic and bittersweet, like transitioning to a new chapter of life and leaving the old behind.
《因为你 所以我》
This song didn’t stand out to me at first, but it grew on me! I caught myself humming it a lot. It‘s kind of corny, but it sounds so full of hope.
陈奕迅 / Eason Chan
I first started listening to 陈奕迅 a couple years ago after my Album a Day August challenge, but I’ve found that his music has grown on me over time. I believe I’ve only mentioned him once before, so I thought now was a good time to highlight my favorite of his songs.
《之外》
This is probably my favorite 陈奕迅 song. The lyrics convey a sense of hopelessness, but the overall song has a smooth, light sound.
《娱乐天空》
You know a song is good when it’s over 6 minutes long but feels like it flies by! It makes me want to get up, get moving, and be productive.
《烟味》
This song is dramatic, and I love it for that. Also has a hint of orchestral flavor.
《淘汰》
One of 陈奕迅’s most well-known songs—for a good reason. It has big Cpop ballad vibes but is definitely livelier.
白举纲 / Bai Jugang
You’re going to notice several mentions of 披荆斩棘 in this post. That’s where I “met” 白举纲. I instantly liked his voice and loved seeing him with his “brother” 高瀚宇 and “dad” 张晋! You may also see his music under his English name, Pax Congo.
《被动失控》
This is the only song on the list you could headbang to.
《Shy Boy》
I love this song because it’s cute and includes a children’s rhyme that I learned as a kid: 找啊找啊找朋友 找到一个好朋友.
苏诗丁 / Su Shiding
At some point last year I did a one-month free trial of Apple Music. It was an interesting experience because the recommendations were very different from what Spotify tends to show me. I’m glad Apple Music led me to 苏诗丁!
《LUCIFER(傲慢宗罪)》
All I can say is that this song exudes coolness and confidence. It also has a fair bit of English, but honestly I had to look up the lyrics to tell what some of it was.
《梦幻病》
This song is from the same album. It’s dreamlike but gets more frantic as it builds. Overall, it’s just a bit…unsettling.
队长 / Young Captain
I learned about 队长 from a random post on Instagram about his concert in Malaysia. I think these songs might have gone viral on 抖音 or something. I was surprised I liked them so much because they both have some rap (I’m not a rap fan), but it was love at first listen.
《11》
I love how this song builds towards the end. I spend the whole song waiting for the crescendo, and it’s great payoff.
《楼顶上的小斑鸠》
This song is like the slightly mellower sibling of the one above. But I ended up liking this one even more.
金志文 / Jin Zhiwen
金志文 was another artist who Apple Music recommended to me. I definitely need to explore his discography more but haven’t had the chance to do so yet. But he has some good stuff so far!
《自娱自乐》
Smooth and relaxing but in a fun way. Simple and no-frills but will put a smile on your face!
《远走高飞》
This one feels like enjoying the breeze on a beautiful sunny day. I also enjoy the duet with 徐佳莹 version.
163braces
163braces started out as a YouTuber posting song covers. I have watched a couple of her covers, but they didn’t leave much of an impression on me. I was pleasantly surprised by her foray into original music. I look forward to hearing what she does next!
《控制》
The song I would want as my “soundtrack” if I were a video game character. It’s energetic and loud.
《murmur》
Honestly this song is pretty similar to the first one. Sometimes I have trouble distinguishing them. But hey, if ain’t broke, don’t fix it.
小鬼 / Lil Ghost
小鬼 did what I can best describe as “pulling an MGK” by going from more rap to kinda pop-punk? That MGK album was my guilty pleasure when in came out, so I’m all for 小鬼’s new direction.
《Last Day》
This song really gave me MGK vibes. It’s about half in English, but I often don't even notice when he switches between languages.
《不良少年》
I just know I would have loved this song so much in high school. It’s an angsty teen anthem.
《为明天写封信》
I can totally imagine this song playing at the end of a 2000s teen movie! Maybe while showing a montage of the main characters graduating.
《无所求必满载而归》 by 陈粒 / Chen Li
This is technically cheating because I have recommended 陈粒 songs before, but it was at least a couple years ago. I heard this song covered on 披荆斩棘的哥哥 and immediately looked up the original. Honestly I should have known it was a 陈粒 song because you can totally tell it’s her style.
《轻红》 by 曹杨 / Young
I keep coming back to this song! It’s from a drama soundtrack. I was super surprised the first time I listened to it because I thought it was going to be a typical ballad based on the first ~45 seconds or so—it wasn’t. There is also another version by 陈雪燃 (the king of cdrama OSTs). But I actually prefer the 曹杨 version.
《时光机》 by 吴克群 / Kenji Wu
I was introduced to 吴克群 via 披荆斩棘2. He was instantly one of my favorite contestants after his team’s amazing 《新地球》 performance (check it out). This song is bouncy and a little dreamy. I kinda want to hear a remix with Harry Styles’ As It Was. I just wish it were longer than 3 minutes!
My Spotify Wrapped
I have a tradition of sharing my Spotify Wrapped, and I wanted to continue the streak in some form. So here's a quick rundown.
Top genre: 华语流行音乐
Representative city: Taipei
Minutes: 21,750
Top artists
薛之谦 / Xue Zhiqian
林宥嘉 / Yoga Lin
五月天 / Mayday
李荣浩 / Li Ronghao
陈奕迅 / Eason Chan
Top songs
《木偶人》 - 薛之谦
《狐狸》 - 薛之谦
《骆驼》 - 薛之谦
《转眼》 - 五月天
《后来的我们》 - 五月天
Also, fellow Mandopop fans should check out the Mando Gap newsletter. I stumbled upon it this year, and I know it’s going to be a great resource for discovering new artists in 2024!
#chinese music recs#cpop#c-pop#c pop#mandopop#chinese music#chinese#mandarin#mandarin chinese#chinese language#studyblr#langblr#learning languages#language learning#chinese langblr#mandarin langblr#languageblr
177 notes
·
View notes
Text





AMBER & CHENG XIAO for Hunan New Year Eve
#cheng xiao#程潇#刘逸云#liu yiyun#amber#amber liu#femaleidols#femaleidol#femaleidolsedit#chineseartistsinc#f(x)#wjsn#caps#cpop#mando pop#chinese music#c-pop#the youtube title says amber cheng xiao “open with full of se xual tension” im crying ❤️🔥❤️🔥#excuse the sht gifs bc the video was in potato quality but its okay the vibes are there bc the song they did was even worst lol#we have the 2 top idols and they made them sing a crappy chinese internet meme song i cant believe this atrocity#if you mute the video and play troublemaker over it it's 10x better 😌😌😌😌
99 notes
·
View notes
Text
Music theory notes (for science bitches) - part 2: pentatonics and friends
or, the West ain't all that.
Hello again everyone! I'm grateful for the warm reception to the first music theory notes post (aka 'what is music? from first principles'). If you haven't read it, take a look~
In that stab at a first step towards 'what is music', I tried to distinguish between what's a relatively universal mathematical structure (nearly all musical systems have the octave) and what's an arbitrary convention. But in the end I did consciously limit myself, and make a beeline for the widely used 12TET tuning system and the diatonic scales used in Western music. I wanted to avoid overwhelming myself, and... 👻 it's all around us...👻
But! But but but. This is a series on music theory. Not just one music theory. The whole damn thing. I think I'm doing a huge disservice to everyone, not least me, if that's where we stop.
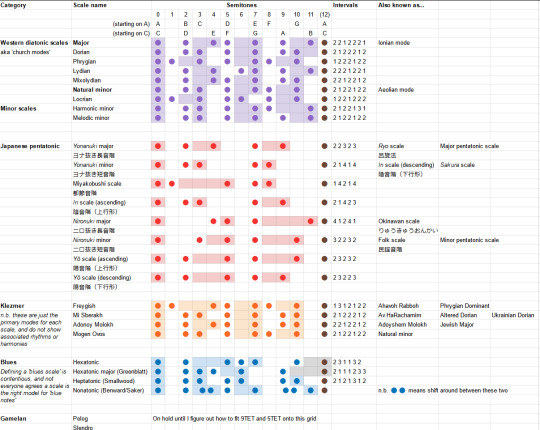
Today, then! For our second installation: 'Music theory notes (for science bitches)' will take a quick look through some examples that diverge from the diatonic scale: the erhu, Japanese pentatonic scales, gamelan, klezmer, and blues.
Also since the first part was quite abstract, we'll also having a go at using the tools we've built so far on a specific piece, the Edo-period folk song Sakura, Sakura.
Sound fun? Let's fucking gooooo
The story so far
To recap: in the first post we started by saying we're gonna be looking at tonal music, which isn't the only type of music. We introduced the idea of notes and frequencies by invoking the magic name of Fourier.
We said music can be approximated (for now) as an idealised pressure wave, which we can divide into brief windows called 'notes', and these notes are usually made of a strong sine wave at the 'fundamental frequency', plus a stack of further sine waves at integer multiples of that frequency called 'overtones'.
Then, we started constructing a culturally specific but extremely widespread system of creating structure between notes, known as '12 Tone Equal Temperament' or 12TET. The main character of this story is the interval, which is the ratio between the fundamental frequencies of two notes; we talked about how small-integer ratios of frequencies tend to be especially 'consonant' or nice-sounding.
We introduced the idea of the 'octave', which is when two notes have a frequency ratio of 2. We established the convention treating notes an octave apart as deeply related, to the point that we give them the same name. We also brought in the 'fifth', the ratio of 1.5, and talked about the idea of constructing a scale using small-integer ratios.
But we argued that if you try and build everything with those small-integer ratios you can dig yourself into a hole where moving around the musical space is rife with complications.
As a solution to this, I pulled out 'equal temperament' as an approximation with a lot of mathematical simplicity. Using a special irrational ratio called the "semitone" as a building block, we could construct the Western system of scales and modes and chords and such, where
a 'scale' is kind of like a palette for a piece of music, defined by a set of frequency ratios relative to a 'root' or 'tonic' note. this can be abstract, as in 'the major scale', or concrete, as in 'C major'.
a 'mode' is a cyclic permutation of an abstract scale. although it may contain the same notes, moving them around can change the feeling a lot!
a 'chord' is playing multiple notes at the same time. 'Triad' chords can be constructed from scales. There are other types which add or remove stuff from the triads. We'll come back to this.
I also summarised how sheet music works and the rather arbitrary choices in its construction, and at the end, I very briefly talked about chord notation.
There's a lot of ways to do this...
I recently watched a video by jazz musician and music theory youtuber Adam Neely, in which he and Philip Ewell discuss how much "music theory" is treated as synonymous with a very specific music theory which Neely glosses as "the harmonic style of 18th-century European composers". He argues, pretty convincingly imo, that 'music theory' pedagogy is seriously weakened by not taking non-white/Western models, such as Indian classical music theories, as a foil - citing Anuja Kamat's channel on Indian classical music as a great example of how to do things differently. Here's her introductory playlist on Indian classical music concepts, which I will hopefully be able to lean on in future posts:
There's two big pitfalls I wanna avoid as I teach myself music theory. I like maths a lot, and if I can fit something into a mathematical structure it's much easier for me to remember it - but I gotta be really careful not to mathwash some very arbitrary conventions and present them as more universal than they are. Music involves a lot of mathematics, but you can't reduce it to maths. It's a language for expressing emotion, not a predicate to prove.
One of the big goals of this series is to get straight in my head what has a good answer to 'why this way?', and what is just 'idk it's the convention we use'. And if something is an arbitrary convention, we gotta ask, what other conventions exist? Humans are inventive little buggers after all.
I also don't want to limit my analytical toolbox to a single 'hammer' of Western music theory, and try and force everything else into that frame. The reasons I'm learning music theory are... 1. to make my playing and singing better, and be more comfortable improvising; 2. to learn to compose stuff, which is currently a great mystery. How do they do it? I do like Western classical music, but honestly? Most of the music I enjoy is actually not Western. I want to be able to approach that music on its own terms.
For example, the erhu... for erhuample???
The instrument family I'm learning, erhu/zhonghu, is remarkably versatile - there are no frets (or even a soundboard!) to guide you, which is both a challenge and a huge freedom. You can absolutely play 12TET music on it, and it has a very beautiful sound - here is an erhu harmonising with a 12TET-tuned piano to play a song from the Princess Mononoke soundtrack, originally composed by Joe Hisaishi as an orchestral piece for the usual Western instruments...
youtube
This performance already makes heavy use of a technique called (in English) 'vibrato', where you oscillate the pitch around as you play the note (which means the whole construction that 'a note has a fixed pitch defined by a ratio' is actually an abstraction - now a note's 'frequency' represents the middle point a small range of pitches!). Vibrato is very common in Western music too, though the way you do it on an erhu and the way you do it on a violin or flute are of course a little different. (We could do an aside on Fourier analysis of vibrato here but I think that's another day's subject).
But if you listen to Chinese compositions specifically for Erhu, they take advantage of the lack of fixed pitch to zip up and down like crazy. Take the popular song Horse Racing for example, composed in the 1960s, which seems to be the closest thing to the 'iconic' erhu piece...
youtube
This can be notated in 12TET sheet music. But it's also taking full advantage of some of the unique qualities of the erhu's long string and lack of frets, like its ability to glide up and down notes, playing the full range of 'in between' frequencies on one string. The sheet music I linked there also has a notation style called 简谱 jiǎnpǔ which assigns numbers to notes. It's not so very different from Western sheet music, since it's still based on the diatonic major scale, but it's adjusted relative to the scale you're currently playing instead of always using C major. Erhu music very often includes very fast trills and a really skilled erhu/zhonghu player can jump between octaves with a level of confidence I find hard to comprehend.
I could spend this whole post putting erhu videos but let me just put one of the zhonghu specifically, which is a slightly deeper instrument; in Western terms the zhonghu (tuned to G and D) is the viola to the erhu's violin (tuned to D and A)...
youtube
To a certain degree, Chinese music is relatively easy to map across to the Western 12-tone chromatic scale. For example, the 十二律 shí'èr lǜ system uses essentially the same frequency ratios as the Pythagorean system. However, Chinese music generally makes much heavier use of pentatonic scales than Western music, and does not by default use equal temperament, instead using its own system of rational frequency ratios. correction: with the advent of Chinese orchestras in the mid-20thC, it seems that Chinese instruments now usually are tuned in equal temperament.
I would like my understanding of music theory to have a 'first class' understanding of Chinese compositions like Horse Racing (and also to have a larger reference pool lmao). I'm going to be starting formal erhu lessons next month, with a curriculum mostly focused on Chinese music. If I have interesting things to report back I'll be sure to share them!
Anyway, in a similar spirit, this post we're gonna try and do a brief survey of various musical constructs relevant to e.g. Japanese music, Klezmer, Blues, Indian classical music... I have to emphasise I am not an expert in any of these systems, so I can't promise to have the most elegant form of presentation for them, just the handles I've been able to get. I will be using Western music theory terms quite a bit still, to try and draw out the parallels and connections. But I hope it's going to be interesting all the same.
Let's start with... pentatonic scales!
Pentatonic scales
In the previous post we focused most of our attention on the diatonic scale. Confusingly, a "diatonic" scale is actually a type of heptatonic scale, meaning there are 7 notes inside an octave. As we've seen, the diatonic scale is constructed on top of the 12-semitone system.
Strictly defined, a 'diatonic' scale has five intervals of two semitones and two intervals of one semitone, and the one-semitone intervals are spread out as much as possible. So 'diatonic scales' includes the major scale and all its cyclic permutations (aka 'modes'), including the natural minor scale, but not the other two minor scales we talked about last time!
However, whoever said we should pick exactly 7 notes in the octave? That's rather arbitrary, isn't it?
After all, in illustration, a more restricted palette can often lead to a much more visually striking image. The same is perhaps even more true in music!
A pentatonic scale is, as the name suggests, a scale which has five notes in an octave. Due to all that stuff we discussed with small-number ratios, the pentatonic scales we are about to discuss can generally be mapped quite easily onto the 12-tone system. There's some reason for this - 12TET is designed to closely approximate the appealing small-number frequency ratios, so if another system uses the same frequency ratios, we can probably find a subset of 12TET that's a good match.
Of course, fitting 12TET doesn't mean it matches the diatonic scale, necessarily. Still, once you're on the 12 tone system, there's enough diatonic scales out there that you can often define a pentatonic scale in terms of a delta relative to one of the diatonic scale modes. Like, 'shift this degree down, delete that degree'.
Final caveat: I'm not sure if it's strictly correct to use equal temperament in all these examples, but all the sources I find define these scales using Western music notation, so we'll have to go with that.
Sakura, sakura and the yonanuki scale
Let's start with Japanese music. Here's the Edo-period folk song Sakura, Sakura, which is one of the most iconic pieces of Japanese music¸ especially abroad:
youtube
This uses the in scale, also known as the sakura pentatonic scale, one of a few widely used pentatonic scales in Japanese folk music, along with the yo scale, insen scale and iwato scale... according to English-language sources.
Finding the actual Japanese was a bit difficult - so far as I can tell the Japanese wiki page for Sakura, Sakura never mentions the scale named after it! - but eventually I found a page for pentatonic scales, or 五音音階 goon onkai. So we can finally determine the kanji for this scale is 陰音階 in onkai or 陰旋法 in senpou. [Amusingly, the JP wiki article on pentatonic scales actually leads with... Scottish folk songs and gamelan before it goes into Japanese music.]
However, perhaps more pertinent is this page: ヨナ抜き音階 which introduces the terms yonanuki onkai and ニロ抜き音階 nironuki onkai. This can be glossed as 'leave out the fourth (yo) and seventh (na) scale' and 'leave out the second (ni) and sixth (ro) scale', describing two procedures to construct pentatonic scales from a diatonic scale.
Let's recap major and minor. Last time we defined them using semitone intervals from a root note (the one in brackets is the next octave):
position: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, (8)
major: 0, 2, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11, (12)
minor: 0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, (12)
From here we can construct some pentatonic scales. Firstly, here are your yonanuki scales - the ones that delete the fourth and seventh:
major: 0, 2, 4, 7, 9, (12)
minor: 0, 2, 3, 7, 8, (12)
Starting on C for the major and A for the minor (the ones with the blank key signature), this is how you notate that in Western sheet music. As you can see, we have just deleted a couple of steps.


The first one is the 'standard' major pentatonic scale in Western music theory; it's also called the ryo scale in traditional Japanese music (呂旋法 ryosenpou). The second one is a mode (cyclic permutation) of a scale called 都節音階 miyakobushi, which is apparently equivalent to the in scale.
In terms of gaps between successive notes, these go:
major: 2, 2, 3, 2, 3 - very even
minor: 2, 1, 4, 1, 4 - whoah, huge intervals!
The miyakobushi scale, for comparison, goes...
miyakobushi (absolute): 0, 1, 5, 7, 8, (12)
miyakobushi (deltas): 1, 4, 2, 1, 4
JP wikipedia lists two different versions of the 陰旋法 (in scale), for ascending and descending. Starting on C, one goes C, D, Eb, G, A; the other goes C, D, Eb, G, Ab. Let's convert that into my preferred semitone interval notation:
in scale (absolute, asc): 0, 2, 3, 7, 9, (12)
in scale (relative, asc): 2, 1, 4, 2, 3
in scale (absolute, desc): 0, 2, 3, 7, 8, (12)
in scale (relative, desc): 2, 1, 4, 1, 4
So we see that the 'descending form' of the in scale matches the minor yonanuki scale, and it's a mode (cyclic permutation) of the miyakobushi scale.
We've talked a great deal about the names and construction of the different type of scales, but beyond the vague gesture to the standard associations of 'major upbeat, minor sad/mysterious' I don't think we've really looked at how a scale actually affects a piece of music.
So let's have a look at the semitone intervals in Sakura, Sakura in absolute terms from to the first note...
sakura, sakura, ya yoi no so ra-a wa
0, 0, 2; 0, 0, 2; 0, 2, 3, 2, 0, 2-0, -4
and in relative terms between successive notes:
sa ku ra, sa ku ra, ya yo i no so ra-a wa
0, 0, +2; -2, 0, +2; -2, +2, +1, -1, -2, +2, -2, -4
If you listen to Sakura, Sakura, pay attention to the end of the first line - that wa suddenly drops down a huge distance (a major second - for some reason I miscalculated this and thought it was a tritone) and that's where it feels like damn, OK, this song is really cooking! It catches you by surprise. We can identify these intervals as belonging to the in/yoyanuki minor scale, and even starting on its root note.
Although its subject matter is actually pretty positive (hey, check it out guys, the cherry blossoms are falling!), Sakura, Sakura sounds mournful and mysterious. What makes it sound 'minor'? The first phrase doesn't actually tell you what key we're in, that jump of 2 semitones could happen in major or minor. But the second phrase, introduces the pattern of going up 2, then up 1, from the root note - that's the minor scale pattern. What takes it beyond just 'we're in minor'? That surprise tritone move down. According to the rough working model that 'dissonant notes create tension, consonant notes resolve it', this creates a ton of tension. This analysis is bunk, there isn't a tritone. It's a big jump but it's not that big a jump.
How does it eventually wrap up? The final phrase of Sakura, Sakura goes...
i za ya, i za ya, mi ni yu - u ka nn
0, 0, 2; 0, 0, 2; -5, -4, 2, 0, -4, -5
0, 0, +2; -2, 0, +2; -5, +1, +4, -2, -4, -1
Here's my attempt to try and do a very basic tonal/interval analysis. We start out this phrase with the same notes as the opening bars, but abruptly diverge in bar 3, slowing down at the same time, which provides a hint that things are about to come to a close. The move of -5 down is a perfect fourth; in contrast to the tritone major second we had before, this is considered a very consonant interval. (A perfect fourth down is also equivalent to going up a fifth and then down an octave. So we're 'ending on the fifth'.) We move up a little and down insteps of 4, 2, and 1, which are less dramatic. Then we come back down and end on the fifth. We still have those 4-steps next to 1 steps which is the big flag that says 'whoah we're in the sakura pentatonic scale', but we're bleeding off some of the tension here.
Linguistically, the song also ends on the mora ん, the only mora that is only a consonant (rather than a vowel or consonant-vowel), and that long drawn-out voiced consonant gives a feeling of gradually trailing away. So you could call it a very 'soft' ending.
Is this 'tension + resolution' model how a Japanese music theorist would analyse this song? It seems to be a reasonably effective model when applied to Japanese music by... various music theorist youtubers, but I don't really know! That's something I want to find out more about.
Something raised on the English wiki is the idea that the miyakobushi scale is divided into two groups, spanning a fourth each, which is apparently summarised by someone called Koizumi Fumio in a book written in 1974:

Each group goes up 1 (a semitone or minor second), then 4 (major third), for a total of 5 (perfect fourth). The edges of these little blocks are considered 'nucleus' notes, and they're of special importance.
Can we see this in action if we look at Sakura, Sakura? ...ehhhh. I admit, the way I think of the song is shaped by the way I play it on the zhonghu; I think of the first two two-bar phrases as the 'upper part' and the third phrase as the 'lower part', and neither lines up neatly with these little groups. Still. I suspect Koizumi Fumio, author of Nihon no ongaku, knows a little more about this than I do, so I figure it's worth a mention.
Aside: on absorbing a song
Sakura, Sakura is kinda special to me because it's like the second piece I learned to play on zhonghu (after Twinkle, Twinkle Little Star lmao). I can't play it well, but I am proud that I have learned to play it at least recognisably.
The process of learning to play it involved writing out tabs and trying out different ways of moving my hand. I transcribed Sakura Sakura down to start on F, since that way the open G string of the zhonghu could be the lowest note of the piece, and worked out a tab for it using a tab system I cooked up with my friend. Here's what it looks like. The system counts semitones up from the open string, and it uses an underline to mark the lower string.
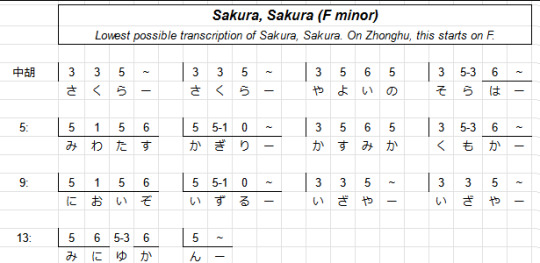
(Also, credit where it's due - I would never have made any progress learning about music if not for my friend Maki Yamazaki, a prodigiously multitalented self-taught musician who can play dozens of instruments, and also the person who sold me her old zhonghu for dirt cheap, if you're wondering why a white British girl might be learning such an unusual instrument. You can and should check our her music here! Maki has done more than absolutely anyone to make music comprehensible to me, and a lot of this post is inspired by discussing the previous post with her.)
When you want to make a song playable on an instrument, you have to perform some interpretation. Which fingers should play which notes? When should you move your hand? How do you make sure you hit the right notes? At some point this kind of movement becomes second nature, but I'm at the stage, just like a player encountering a new genre of videogame, where I still don't have the muscle memory or habituation to how things work, and each of these little details has to be worked out one by one. But this is great, because this process makes me way more intimately familiar with the contours of the song. Trying to analyse the moves it makes like the above even more so.
More Japanese scales
So, to sum up what we've observed, the beautiful minor sounds of Sakura Sakura come from a pentatonic scale which can be constructed by taking the diatonic scale and blasting certain notes into the sea, namely the fourth and the seventh of the scale. But what about the nironuki scale? Well, this time we delete the second and the sixth. So we get, in absolute terms:
major nironuki (abs): 0, 4, 5, 7, 11, (12)
major nironuki (rel): 4, 1, 2, 4, 1
minor nironuki (abs): 0, 3, 5, 7, 10, (12)
minor nironuki (rel): 3, 2, 2, 3, 2
Hold on a minute, doesn't that look rather familiar? The major nironuki scale is a permutation, though not a cyclic permutation, of the minor yonanuki scale. And the minor nironuki scale is a cyclic permutation (mode) of the major one.
Nevertheless, these scales have names and significance of their own. The major one is known as the 琉球音階 ryūkyū onkai or Okinawan scale. The minor one is what Western music would call a 'minor pentatonic scale'. It also mentions a couple of other names for it, like the 民謡音階 minyou onkai (folk scale).
We also have the yō scale, which like the in scale, comes in ascending and descending forms. You want these too? Yeah? Ok, here we go.
yō scale (asc, abs): 0, 2, 5, 7, 10, (12)
yō scale (asc, rel): 2, 3, 2, 3, 2
yō scale (desc, abs): 0, 2, 5, 7, 9, (12)
yō scale (desc, rel): 2, 3, 2, 2, 3
The yō scale is what's called an anhemitonic pentatonic scale, which is just a fancy way of saying it doesn't have semitones. (The in scale in turn is hemitonic). The ascending form is also called the 律戦法 ritsusenpou. Here's the complete table of all the variants I've found so far.
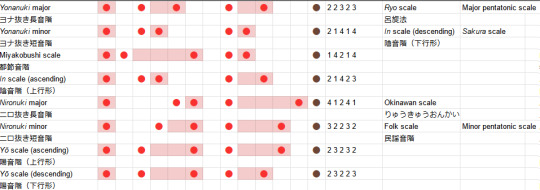
So, in summary: Japanese music uses a lot of pentatonic scales. (In a future post we can hopefully see how that applies in modern Japanese music). These pentatonic scales can be constructed by deleting two notes from the diatonic scales. In general, you land in one of two zones: the anhemitonic side, where all the intervals between successive notes, are 2 and 3, and the hemitonic side, where the intervals are spicier 1s and 4s and a lone 2. From there, you can move between other pentatonic scales by cyclic permutations and reversal.
If you analyse Japanese music from a Western lens, you might well end up interpreting it according to one of the modes of the major scale. In fact, the 8-bit music theory video I posted last time takes this approach. This isn't wrong per se, it's a viable way to getting insight into how the tune works if you want to ask the question 'how does this conjure emotions and how do I get the same effects', but it's worthwhile to know what analytical frame the composers are likely to be using.
Gamelan - when 12TET won't cut it
Gamelan is a form of Indonesian ensemble music. I do not at this time know a ton about it, but here's a performance:
youtube
However, if you're reading my blog then it's likely that if know gamelan from anywhere, it's most likely the soundtrack to Akira composed by Shōji Yamashiro.
youtube
This blends traditional gamelan instrumentation and voices with modern synths to create an incredibly bold and (for most viewers outside Indonesia!) unfamiliar sound to accompany the film's themes of psychic awakening and evolution. It was an inspired choice, adding a lot to an already great film.
'A gamelan' is the ensemble; 'gamelan' is also the style of music. There are many different types of gamelan associated with different occasions - some gamelans are only allowed to form for special ceremonies. Gamelan is also used as a soundtrack in accompaniment to other art forms, such as wayang kulit and wayang wong (respectively, shadow puppetry and dance).
Since gamelan music evidently uses quite a bit of percussion, and so far we've been focused on the type of music played on strings and wind instruments - a brief comment on the limitations of our abstractions. Many types of drums don't fit the 'tonal music' frame we've outlined so far, creating a broad frequency spectrum that's close to an enveloped burst of white noise rather than a sharply peaked fundamental + overtones. There's a ton to study in drumming, and if this series continues you bet I'll try to understand it.
But there are tonal percussion instruments, and a lot of them are to be found in gamelan, particularly in the metalophone family (e.g. the ugal or jegogan). The Western 'xylophone' and 'glockenspiel' also belong to this family. Besides metalophones, you've got bells, steel drums, tuning forks etc. Tuning a percussion instrument is a matter of adjusting the shape of the metal to adjust the resonant frequency of its normal modes. I imagine it's really fiddly.
In any case, the profile of a percussion note is quite different from the continual impulse provided by e.g. a violin bow. You get a big burst across all frequencies and then everything but the resonant mode dies out, leaving the ringing with a much simpler spectrum.
Anyway, let's get on to scales and shit. While I have the Japanese wikipedia page on pentatonic scales open, that it mentions a gamelan scale called pelog (written ᮕᮦᮜᮧᮌ᮪, ꦥꦺꦭꦺꦴꦒ꧀ or ᬧᬾᬮᭀᬕ᭄ in different languages) meaning 'beautiful'. Pelog is not strictly one scale, but a family of tunings which vary across Indonesia. Depending on who you ask, it might in some cases be reasonably close to a 9-tone equal temperament (9TET), which means a number of notes can't be represented in 12TET - you have that 4 12TET semitones would be equivalent to 3 9TET semitones. From this is drawn a heptatonic scale, but not one that can be mapped exactly to any 12TET heptatonic scale. Isn't that fun!
To represent scales that don't exactly fit the tuning of 12TET, there's a logarithmic unit of measure called the 'cent'. Each 12TET semitone contains 100 cents, so in terms of ratios, a cent is the the 1200th root of 2. In this system, a 9TET semitone is 133 cents. Some steps in the pelog heptatonic scale would then be two 9TET semitones, and others one 9TET semitone. However, this system of 'semitones' does not seem to be how gamelan music is actually notated - it's assumed you already have an established pelog tuning and can play within that. So it's a little difficult for me to give you a decent representation of a gamelan scale that isn't approximated by 12TET.
From the 7-tone pelog scale, whatever it happens to be where you live, you can further derive pentatonic scales. These have various names, like the pelog selisir used in the gamelan gong kebyar. I'm not going to itemise them here both because I haven't actually been able to find the basic pelog tunings (at least by their 9TET approximation).
Another scale used in gamelan is called slendro, a five tone scale of 'very roughly' equal intervals. Five is coprime with 12, so there's no straightforward mapping of any part of this scale to the 12-tone system. But more than that, fully even scales are quite rare in the places we've looked so far. (Though apparently within slendro, you can play a note that's deliberately 'out of place', called 'miring'. This transforms the mood from 'light, cheerful and busy' to one appropriate to scenes of 'homesickness, love missing, sadness, death, languishing'.)
The Western musical notation system is plainly unsuited for gamelan, and naturally it has its own system - or rather several systems. In one method, the seven tones of the pelog are numbered 1 through 7, and a subset of those numbers are used to enumerate slendro tuning. You can write it on a grid similar to a musical staff.
But we could wonder with this research - is the attempt to map pélog to 'equal temperament' an external imposition? Presented with a tuning system with seven intervals that are not consistently equal temperament, averaging them to construct an equal temperament hypothesis on that basis, and finally attempting to prove that gamelan players 'prefer' equal temperament... well, they do at least bother to ask, but I'm not entirely convinced that 9TET or 5TET is the right model. Unfortunately, most of the literature I'm able to find on gamelan music theory with a cursory search is by Western researchers.
There's a fairly long history of Western composers taking inspiration from gamelan, notably Debussy and Saty. And of course, modern Indonesian composers such as I Nyoman Windha have also been finding ways to combine gamelan with Western styles. Here's a piece composed by him (unfortunately not a splendid recording):
youtube
Klezmer - layer 'em up
If you've known me for long enough you might remember the time I had a huge Daniel Kahn and the Painted Bird phase. (I still think he's great, I just did that thing where I obsessively listen to one small set of things for a period). And I'd also listen to old revolutionary songs in Yiddish all the time. Because of course I did lmao. Anyway, here's a song that combines both: Kahn's modern arrangement of Arbetlose Marsch in English and Yiddish:
youtube
That's a style of music called klezmer, developed by Ashkenazi Jews in Central/Eastern Europe starting in the late 1500s and 1600s. It's a blend of a whole bunch of different traditions, combining elements from Jewish religious music with other neighbouring folk music traditions and European music at large. When things really kicked off at the end of the 19th century, klezmer musicians were often a part of the Jewish socialist movement (and came up with some real bangers - the Tsar may have been shot by the Bolsheviks but tbh, Daloy Politsey already killed him). But equally there's a reason it sounds insanely danceable: it was very often used for dances.
The rest of the 20th century happened, but klezmer survived all the genocides and there are lots of different modern klezmer bands.
The defining characteristics of klezmer per Wikipedia are... ok, this is quite long...
Klezmer musicians apply the overall style to available specific techniques on each melodic instrument. They incorporate and elaborate the vocal melodies of Jewish religious practice, including khazones, davenen, and paraliturgical song, extending the range of human voice into the musical expression possible on instruments.[21] Among those stylistic elements that are considered typically "Jewish" in Klezmer music are those which are shared with cantorial or Hasidic vocal ornaments, including dreydlekh ("tear in the voice"; plural of dreidel)[22][23] and imitations of sighing or laughing ("laughter through tears").[24] Various Yiddish terms were used for these vocal-like ornaments such as קרעכץ (Krekhts, "groan" or "moan"), קנײטש (kneytsh, "wrinkle" or "fold"), and קװעטש (kvetsh, "pressure" or "stress").[10] Other ornaments such as trills, grace notes, appoggiaturas, glitshn (glissandos), tshoks (a kind of bent notes of cackle-like sound), flageolets (string harmonics),[22][25]pedal notes, mordents, slides and typical Klezmer cadences are also important to the style.[18]
So evidently klezmer will be relevant throughout this series, but for now, since we're trying to flesh out the picture of 'how is tuning formed', let's take a look at the notes.
So it's absolutely possible to fit klezmer into the 12TET system. But we're going to need to crack open a few new scales. Though the Wikipedia editors enumerating this list caution us: "Another problem in listing these terms as simple eight-note (octatonic) scales is that it makes it harder to see how Klezmer melodic structures can work as five-note pentachords, how parts of different modes typically interact, and what the cultural significance of a given mode might be in a traditional Klezmer context."
With that caution in mind, let's at least see what we're given. First of all we have the Freygish or Ahavoh Rabboh scale, one of the most common pieces, good friend of the Western phrygian but with an extra semitone. Then there's Mi Sbererakh or Av HaRachamim which is a mode of it, that's popular around Ukraine. Adonoy Molokh or Adoyshem Molokh is the major scale but you drop the seventh a semitone. Mogen Ovos is the same as the natural minor at least on the interval level.
Which means, without the jargon, here are the semitones (wow wouldn't it be nice if you had tables on here?):

position: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, (8)
freygish: 0, 1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, (12)
deltas: 1, 3, 1, 2, 1, 2, 2
mi sberakh: 0, 2, 3, 6, 7, 9, 10, (12)
deltas: 2, 1, 3, 2, 2, 1, 2
adonoy m.: 0, 2, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, (12)
deltas: 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2
mogen o.: 0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, (12)
deltas: 2, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2
...that's a big block of numbers to make your eyes glaze over huh. Maybe this 'convert everything to semitone deltas' thing isn't all it's cracked up to be... or maybe what I need to do is actually visualise it somehow? Some kinda big old graph showing all the different scales we've worked out so far and how they relate to each other? ...hold your horses...
[It seems like what I've done is reinvent something called 'musical set theory', incidentally.]
OK, having enumerated these, let's return to the Wikipedian's caution. What is a pentachord? Pretty simple, it's a chord of five notes. Mind you, some people define it as five successive notes of a diatonic scale.
In klezmer, you've got a bunch of different instruments playing at once creating a really dense sound texture. Presumably one of the things you do when you play klezmer is try and get the different instruments in your ensemble to hit the different levels of that pentachord. How does that work? Well, if we consult the sources, we find this scan of a half-handwritten PDF presenting considerably more detail on the modes and how they're played. The scales above are combined with a 'motivic scheme' presenting different patterns that notes tend to follow, and a 'typical cadence'. Moreover, these modes can have 'sub-modes' which tend to follow when the main mode gets established.
To me reading this, I can kind of imagine the process of composing/improvisation within this system almost like a state machine. It's not just that you have a scale, you have a certain state you're in in the music (e.g. main mode or sub-mode), and a set of transitional moves you can potentially make for the next segment. That's probably too rigid a model though. There's also a more specific aspect discussed in the book that a klezmer musician needs to know how to move between their repertoire of klezmer pieces - what pieces can sensibly follow from what.
Ultimately, I don't want to give you a long list of stuff to memorise. (Sure, if you want to play klezmer, you probably need to get familiar with how to use these modes, but that's between you and your klezmer group). Rather I want to make sure we don't have any illusion that the Western church modes are the only correct way to compose music.
Blues - can anyone agree?
Blues is a style of music developed by Black musicians in the American south in the late 1800s, directly or indirectly massively influential on just about every genre to follow, but especially jazz. It's got a very characteristic style defined by among other elements use of 'blue notes' that don't fit the standard diatonic scale. According to various theorists, you can add the blue notes to a scale to construct something called the 'blues scale'. According to certain other theorists, this exercise is futile, and Blues techniques can't be reduced to a scale.
So for the last part of today's whirlwind tour of scales, let's take a brief look at the blues...
There are a few different blues scales. The most popular definition seems to be a hexatonic scale. We'll start with the minor pentatonic scale, or in Japanese, the minor nironuki scale - which is to say we take the minor diatonic scale and delete positions 2 and 6. That gives:
minor nironuki (abs): 0, 3, 5, 7, 10, (12)
minor nironuki (rel): 3, 2, 2, 3, 2
Now we need to add a new note, the 'flat fifth degree' of the original scale. In other words, 6 semitones above the root - the dreaded tritone!
hexatonic blues (abs): 0, 3, 5, 6, 7, 10, (12)
hexatonic blues (rel): 3, 2, 1, 1, 3, 2
Easy enough right? Listen to that, it does sound kinda blues-y. But hold your horses! Moments after defining this scale, we read...
A major feature of the blues scale is the use of blue notes—notes that are played or sung microtonally, at a slightly higher or lower pitch than standard.[5] However, since blue notes are considered alternative inflections, a blues scale may be considered to not fit the traditional definition of a scale.
So, if you want to play blues, it's not enough to mechanically play a specific scale in 12TET. You also gotta break the palette a little bit.
There's also a 'major blues' heptatonic scale which goes 0, 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, according to one guy called Dan Greenblatt.
But that's not the only attempt to enumerate the 'blues scale'. Other authors will give you slightly longer scales. For example, if you ask Smallwood:
heptatonic blues (abs): 0, 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, (12)
heptatonic blues (rel): 2, 1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 2
which isn't quite a mode of any of those klezmer scales we saw previously, but nearly!
If you ask Benward and Saker, meanwhile, a Blues scale could actually be nonatonic scale, where you add flattened versions of a couple of notes to the major scale.
nonatonic blues (abs): 0, 2, 3/4, 5, 7, 9, 10/11, (12)
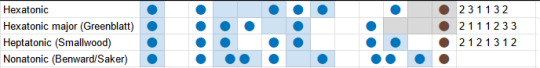
There's also an idea that you should play notes in between the semitones, i.e. quarter tones, which would be a freq ratio of the 24th root of 2 if you're keeping score at home.
The upshot of all this is probably that going too far formalise the blues is probably not in the spirit of the blues, but if you want to go in a blues-y direction it will probably mean insert an extra, flattened version of a note to one of your scales. Muck around and see what works, I guess!
Of course, there's a lot more to Blues than just tweaking a scale. For example, 'twelve bar blues' is a specific formalised chord progression that is especially universal in Jazz. What it means for chords to 'progress' is a whole subject, and I think that's the next thing I'll try to understand for post 3. Hopefully we'll be furnished with a slightly broader model of how music works as we go there though.
To wrap up, here's the spreadsheet showing all the 12TET scales encountered so far in this series in a visual way. There's obviously plenty more out there, but this is not ultimately a series about scales. It's all well and good to have a list of what exists, but it's pointless if we don't know how to use it.
Phew
Mind you even with all this, we haven't covered at all some of the most complex systems of tonal music - I've only made the vaguest gesture towards Indian classical music, Chinese music, Jazz... That's way beyond me at the moment. But maybe not forever.
Next up: I'm going to try and finally wrap my head around chords and make sense of what it means for them to 'progress', have 'movement' etc. And maybe render a bit more concrete the vague stuff I said about 'tension' and 'resolution'.
(Also: I definitely know I have friends on here who are very widely knowledgeable about music theory. If I've made any major mistakes, please let me know! At some point I hope to republish this series with nicer formatting on canmom.art, and it would be great to fix the bugs by then!)
#Youtube#music theory#music notes#music#notes#japanese music#gamelan#chinese music#klezmer#blues#i took my new adhd meds and hyperfocused on this all day instead of working ><
120 notes
·
View notes
Text
FF by Hualun (Chinese: 花伦) from the wʌndərlænd EP
#somethingneweveryday#music#chinese music#hualun#花伦#zooo#zoo (hualun)#zhu ming kang#朱明康#ding mao#dingmao#丁茂#mao ding#ambient#electronica#Bandcamp
20 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
Found this song I like called "Scent of Haitang" (海棠香) and translated the lyrics given people's interest in the haitang flower(* , *). It's not a song about 2ha but fits the mood and plot of 2ha pretty well, also the singer did sing a 2ha fan song (I translated it here).
Lyrics translation of "Scent of Haitang" below cut:
那一年未曾說出心上人模樣
That year I failed to put into words the looks of my beloved
卻只敢在你身旁眺望著月亮
And only had the courage to gaze at the moon by your side
當月光向下流淌讓影子成雙
When moonlight flowed down to cast shadows of the pair of us
閉上眼只聽見風在唱
I closed my eyes and only heard the wind singing
風唱著一聲一聲 添記憶惆悵
One tune after another, the wind adds another wistful memory
又唱著一句一句 心事要隱藏
One line after another, saying that matters of the heart need to be hidden
你聽啊一段一段 織成天羅地網
Listen, one strand after another, it weaves an inescapable web
我情願一步一步 在其間探訪
I'd rather explore its snare one step at a time
可命數要我拱手相讓 如何讓
But fate demands that I give it up meekly - how should I?
我不讓 偏不讓
I won't give it up, stubbornly I simply won't give it up
繡一朵無香海棠在我心上 當想念綻放
Embroider a scentless haitang on my heart when my longing blooms
那是我最溫柔的謊在輪迴流浪
That's my gentlest lie wandering through the cycles of reincarnations
這一朵無香海棠是你目光 接住我憂傷
This scentless haitang is your gaze that holds my sorrow
有愛恨才不枉走人間一趟
Journey through life is worthwhile only when you're acquainted with love and hate
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
an (incomplete) list of traditional chinese instruments
I recently had the chance to attend a few lectures by members of the National Chinese Orchestra - Taiwan, and I thought I'd share some of the information they gave (this is by no means a complete list and is based mostly on the notes I took during lecture)
Chinese instruments are divided into four families of instruments: woodwind, bow string, plucked string, and percussion. They are also divided into eight categories based on the material they are made of (or, in some cases, used to be made of). These categories are stone, earth, bamboo, metal, skin, silk, wood, and gourd.
笛子 (dízi)
There are five main types of 笛子: 曲笛 (qūdí),梆笛 (bāngdí),大笛 (dàdí),小笛 (xiǎodí),and 口笛 (kǒudí)。 They are traditionally made of bamboo and vary in length, resulting in different note ranges and timbres. 曲笛 and 梆笛 are the most common. 梆笛 is higher pitched and brighter due to its shorter length, and it is often used in music from northern China. 曲笛 has a much warmer, rounder sound due to its longer length and is often used in southern music. 口笛 is the shortest of them all and is very shrill; it is often used to imitate bird calls. 笛子 are similar to Western flutes in that the musician controls the pitch through covering or uncovering the finger holes, but the way the instruments produce sound is different. Western flutes create sound through the vibration of the air in the instrument, and while this is part of how the 笛子 produces sound, it also has a membrane that vibrates to produce sound. 笛子 are included in the woodwind family and the bamboo category.


笛子 (左边),笙 (右边)
笙 (shēng)
The 笙 is the oldest reed instrument in the world. It is a woodwind instrument consisting of many vertical pipes with reeds at the base that the musician controls through various keys in order to play specific notes. It produces sound through a reed at the mouthpiece of the instrument that the musician vibrates with their breath. It is the only reed instrument in the world that can be played both by blowing out and by breathing in. This is due to a door-like cut-out in the reed. The 笙 can play 38 notes across three octaves. Not only can it play single notes, but it can also play chords made of multiple notes played at the same time. It has been used in a wide range of music from traditional accompaniment (to 唢呐 or 笛子) to modern jazz pieces to solo pieces. In the modern day, it is often used in Chinese orchestras as melody and/or accompaniment. 笙 is included in the woodwind family and the gourd category.
二胡 (èrhú)
The 二胡 is one of the most well-known traditional Chinese instruments. It has only two strings that the musician plays with an animal-hair bow. At the base of the 二胡 there is a small drum that has a snake skin membrane on one side. This membrane vibrates in addition to the strings' vibration, creating a distinct sound. The 二胡 is often used to imitate animal noises, such as a galloping horse, in addition to its musical notes. The musician holds the 二胡 upright as they play it, keeping pressure on the strings with one hand and using the bow with the other. Unlike many Western string instruments, the 二胡 does not have a finger board. This allows the musician to play a wide range of notes and utilize many different techniques. 二胡 is included in the bowed string family and the silk category.
革胡 (géhú)
This is one of the newest Chinese instruments. The 革胡 was created in the 1950s. Many Chinese orchestras were using cello as a bass instrument, and the 革胡 was created in order to fill the gap in the bass register in Chinese orchestras. Even still, it is a very rare instrument, and the NCO - Taiwan is one of the only orchestras who uses it in its ensemble. It was made as a combination of the cello and the 二胡。This was done in order to get the full bass sound of cello while being able to blend more easily with the 二胡 and other Chinese instruments. The strings on the 革胡 correspond to the same notes as they do on the cello, but the 革胡 also has a drum at its base similar to the 二胡。This drum was originally covered with a snake skin membrane like the 二胡, but since it is a significantly larger area to cover, it is now covered with a man-made polymer. The 革胡 is included in the bowed string family and, though it was created after silk strings fell out of use, it is included in the silk category.
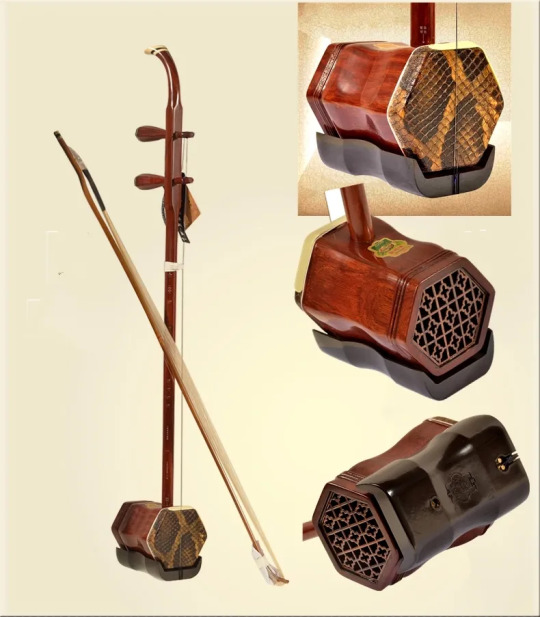



二胡 (左边),革胡 (中间),扬琴 (右边)
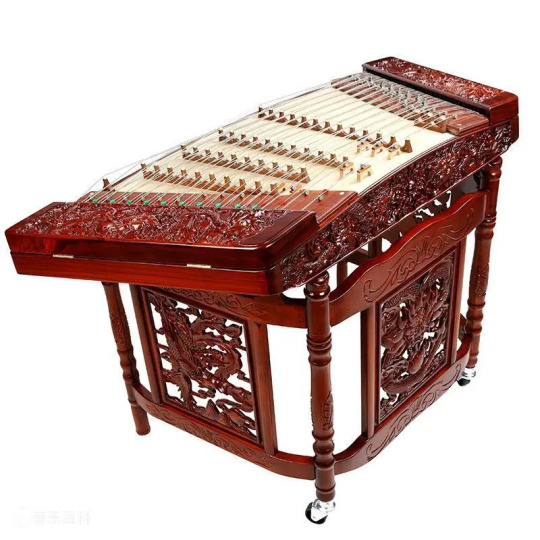
扬琴 (yángqín)
The 扬琴, also sometimes written 洋琴, is a percussion instrument. It was originally from Persia before it was brought to China through trade. Many countries have their own versions of this instrument, originally called the santūr, and like others' variations, the Chinese version has become unique to China. The 扬琴 has 144 strings that the musician hits with thin bamboo mallets. The strings vibrate, producing various musical notes. What is unique about the 扬琴 as compared to other variations is that it uses bamboo mallets. These are a lot more flexible than wooden mallets, and so the musician is able to play very quick notes using the vibrations of the mallet. This also allows the musician to use techniques that are unique to the 扬琴。扬琴 is included in percussion family and the silk category (the strings used to be made of silk, but they are now often made of steel).
https://web.northeastern.edu/music-chinese/
https://www.britannica.com/art/Chinese-music/Classification-of-instruments
https://www.britannica.com/art/yangqin
#i had some extra time today so thought i'd finally get to this#as always if there is something incorrect please let me know#langblr#mandarin#chinese#learn chinese#learn mandarin#chinese music#chinese culture
50 notes
·
View notes
Text










容祖兒-說真的 / Joey Yung- Honesty, CD booklet (2001)
#joey yung#容祖兒#mandarin pop#mandopop#chinese#chinese pop#chinese music#graphic design#y2k aesthetic#y2k#2001#2001 music#y2k vibes
23 notes
·
View notes
Text




#tanjianci #jct #檀健次
Watch this video on Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/shorts/oWqMmjQ48nw
#Tan Jian Ci#檀健次#2023#Chinese singer#Chinese actor#JC-T#Jianci Tan#多多#阿酸#阿次次#舞林萌主#chinese dancer#youtube#short#short video#chinese music#chinese pop#cpop#Xiang Liu#Fangfeng Bei
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Wang Chuan Feng Hua Lu (忘川风华录) Masterpost

Wang Chuan Feng Hua Lu (忘川风华录) is a Vocal synth (Vocaloid and SynthV) music project. It consists of songs themed around different figures throughout Chinese history. The project is a collaboration between different artists and creatives, with music and videos featuring prominent traditional Chinese elements. The project's title translates to "The Records of Magnificence of the Wangchuan" - In Chinese mythology, "Wangchuan" (or River of Forgetting) is a river in the Underworld that can rid one of their past life's memories, similar to the river Lethe.
A mobile game adaptation has also been developed by NetEast. Unfortunately, I haven't played it so I can't give much insight on it. However, I assume that its premise is similar to that of the idea behind the project as a whole: all these historical figures meeting each other in the Underworld after they died. Maybe.
You can find all the songs on Bilibili. The official Weibo can be found here. The game's website, which includes all characters appearing so far in the game, can be found here, and its Weibo can be found here.
(If you prefer YouTube, I've also put together a handy playlist. Please know that most of these videos are reposts though, so please watch the original Bilibili MVs if you can!)
This blog is where I will be posting everything I feel like I need to say about the songs in this project. A lot of it is lifted from my Twitter account but will be in much more detail. Note that I probably won't touch collab songs, or songs that don't focus solely on the project's own characters.
Disclaimer: I do not speak Chinese, nor am I an expert on Chinese history. Therefore, I cannot reliably translate the lyrics to these songs, nor my words should be taken as gospel. I am merely a nerd gushing about my hyperfixation.
Playlist
多情岸 【Duo Qing An】 ➼ B link
洛阳怀 【Luo Yang Huai】 ➼ B link
易水诀 【Yi Shui Jue】 ➼ B link
山河令 【Shan He Ling】 ➼ B link
簪花人间 【Zhan Hua Ren Jian】 ➼ B link
栖凰 【Qi Huang】 ➼ B link
心上秋 【Xin Shang Qiu】 ➼ B link
祖龙吟 【Zu Long Yin】 ➼ B link
如见青山 【Ru Jian Qing Shan】 ➼ B link
竹林间 【Zhu Lin Jian】 ➼ B link
天下局 【Tian Xia Ju】 ➼ B link
青鸟衔风 【Qing Niao Xian Feng】 ➼ B link
木兰行 【Mu Lan Xing】 ➼ B link
好字唯之 【Hao Zi Wei Zhi】 ➼ B link
不可道 【Bu Ke Dao】 ➼ B link
水叙湖风 【Shui Xu Hu Feng】 (collab) ➼ B link
是非 【Shi Fei】 ➼ B link
风起甘露 【Feng Qi Gan Lu】 (collab) ➼ B link
谓剑 【Wei Jian】 ➼ B link
万象霜天 【Wan Xiang Shuang Tian】 (New Year event song) ➼ B link
千秋梦 【Qian Qiu Meng】 ➼ B link
易安难安 【Yi An Nan An】 ➼ B link
惊鹊 【Jing Que】 ➼ B link
高歌破阵 【Gao Ge Po Zhen】 (collab) ➼ B link
不赴 【Bu Fu】 ➼ B link
西行 【Xi Xing】 ➼ B link
大航海家 【Da Hang Hai Jia】 ➼ B link
牡丹乱 【Mu Dan Luan】 (collab) ➼ B link
倾国 【Qing Guo】 (collab) ➼ B link
相虎 【Xiang Hu】 ➼ B link
补天裂 【Bu Tian Lie】 ➼ B link
此期盈期 【Ci Qi Ying Qi】 (1st anniversary song) ➼ B link
破云来 【Po Yun Lai】 ➼ B link
归钓吟 【Gui Diao Yin】 ➼ B link
始见千秋 【Shi Jian Qian Qiu】 ➼ B link
临川浮梦 【Lin Chuan Fu Meng】 ➼ B link
将军行 【Jiang Jun Xing】 ➼ B link
妄语人间 【Wang Yu Ren Jian】 ➼ B link
数风流 【Shu Feng Liu】 (2nd anniversary song) ➼ B link
问剑春秋 【Wen Jian Chun Qiu】 ➼ B link
起战令 【Qi Zhan Ling】 ➼ B link
人间应又雪 【Ren Jian Ying You Xue】 ➼ B link
旷古回响 【Kuang Gu Hui Xiang】 ➼ B link
墨隐侠声 【Mo Yin Xia Sheng】 ➼ B link
桃源故人 【Tao Yuan Gu Ren】 (3rd anniversary song) ➼ B link
*Note: The anniversary songs are probably for the game's anniversaries, as the project itself is more than 5 years old.
Albums
Vol 1: 溯洄 【Su Hui】
Includes character songs from Duo Qing An to Zhu Lin Jian. Features human vocals.
Vol 2: 踏浪 【Ta Lang】
Includes character songs from Tian Xia Ju to Jing Que.
Vol 3: 数风流 【Shu Feng Liu】
Includes character songs from Bu Fu to Wang Yu Ren Jian, an unreleased song titled 燕双归 【Yan Shuang Gui】, and the two anniversary songs.
Visual character guide:
PRE-QIN | QIN | WESTERN CHU | HAN | THREE KINGDOMS | JIN | NORTH & SOUTHERN DYNASTIES | TANG | FIVE DYNASTIES & TEN KINGDOMS | SONG | YUAN | MING | QING | DREAM
#忘川风华录#wang chuan feng hua lu#wcfhl#chinese music#vocasynth#vocaloid#synthv#vocaloid project#synth v project#synthesizer v#vocal synths#long post#this is the culmination of a 3 year brainrot#i will try my best
7 notes
·
View notes
Audio
Listen to: Amitabha Buddha's Pure Land Meditation by John Martini Music

16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Chinese Music I Listened to This Spring/Summer

I think it’s been a few months since I posted about Chinese music/cpop, so I thought I’d provide an update on what I’ve been listening to this past spring/part of summer.
And of course, I made a Spotify playlist to go along with this post. And each song name is linked to YouTube for those of you who don’t use Spotify. The Spotify playlist includes a few “bonus” songs.
薛之谦 / Joker Xue
In my last music post, I called 薛之谦 “my latest Mandopop obsession.” I’ve still been listening to his music a lot, but I’ve had different songs on repeat lately. His slower and quieter songs have been speaking to me a lot more.
《像风一样》 is the musical version of a deep breath. But a sorrowful, long deep breath. The lyrics are quite sad really, but this song also makes me feel at peace.
《哑巴》 is that song that I never skip when it comes on shuffle. It starts out very quietly, so sometimes in the car I can’t even hear that it’s begun, But it picks up towards the middle/end.
《那是你离开了北京的生活》 was a song I used to overlook. But luckily I gave it a second chance! It’s once again a sad yet beautiful song. The lyrics are making me tear up a bit, not gonna lie.
《变废为宝》 kinda goes over my head lyrically, but the vibe isn’t as sad as the previous 3 songs. It gives me a slightly hopeful feeling.
《动物世界》 is the darkest and gloomiest out of these 5 songs. It sounds a bit on-edge and unsettled.
韦礼安 / WeiBird
Similarly, I’ve also continued listening to 韦礼安 this spring.
《女孩》 was love at first listen when I heard it covered on Chuang 2021 (which I just watched this spring). I instantly went to look up who it was by and was pleasant surprised to see it was a 韦礼安 song! This song is just so cute—but in a good way!
《不用告诉我》 was not very memorable to me at first, but then I found that I had the line 让我卑微地享受 片刻的永久 stuck in my head. Oddly, this song really feels like an album intro song to me, but it’s #6 in the tracklist.
《记得回来》 has pretty simple lyrics that I think many of us can understand, which is a huge plus. It’s the perfect song to belt along to (even as someone who sucks at singing).
《忽然》 is basically the definition of a song that starts slow and then builds up to an explosion. It even has a nifty guitar solo. 10/10 recommend.
《如果可以》 is a huge hit for a reason. It does give off major “movie theme song” vibes, which can be a turn-off, but I still like it. Also, there are official Japanese and Korean versions, so if you’re learning those languages, check them out!
徐佳莹 / LaLa Hsu
《言不由衷》 is a song I’ve heard many times before because I’ve listened to the album it’s from a lot. Oddly, it never stood out to me before, but I somehow “rediscovered” it this spring and really fell in love.
邱锋泽 / Feng Ze
《冰山》 is just super catchy! Part of me registers that the lyrics are actually a bit sad, but I end up singing along with a smile on my face. Whoops.
《年青有为》is one of two songs to the same melody. The other song is sung in Cantonese, and it’s called 《一表人才》. They both also include singer 吕爵安. Honestly this song isn’t that special. I just like it.
《潜台词》 is actually a duet with 黄伟晋. This song really drilled its way into my head. I seriously cannot stop humming it! It has a somewhat slow and mellow but also hard-hitting. Surprisingly, I don’t mind the rap (I’m not a big rap fan).
《日环食》 was the first Feng Ze song that clicked with me. It’s a relatively simple song, but that’s not necessarily a bad thing. It feels quite earnest.
九泽CP / Nine Chen & Feng Ze
九泽CP is a duo comprised of Nine Chen (陈零九) and Feng Ze (邱锋泽). I have to learn how to distinguish their voices (something I am not good at in general). This feels like cheating somehow because it means I have way too many Feng Ze songs here.
《偷走你的心》 is bubblegum pop, but I love it. It’s so infectious and makes me feel bubbly. I love the little opening sax(?) moment too. It reminds me a bit of a kpop song with the short rap sections. Only thing I don’t like is that it’s too short!
《绝对发言》 has a lot in common with the previous song, but it’s a little more funky and spirited in my opinion. If you like one, I’m sure you’ll like the other.
《最后一秒钟》 is quite different from the two right above. It’s more somber and serious, but I think the duo pulled off this style very well as well. It does not feel nearly like a 5 minute song!
井胧 / Jing Long
I was introduce to Jing Long while watching Chuang 2021, and *SPOILER* I was very upset that he did not make it to the final because I love his unique voice! Fortunately, he seems to be doing pretty well for himself from what I’ve seen.
《不删》 is another song that I can understand very easily. Sometimes I feel a bit silly listening to a song about WeChat, but obviously this song is about much more than just that. Jing Long’s voice conveys the emotions so well.
《丢了你》 - In the time between when I started drafting this post and today, this song was removed from US Spotify and then added back. Get your act together, Spotify and music labels! I was distressed to see it greyed out—then it suddenly reappeared! But anyway the song is really good.
华晨宇&杨宗纬 / Hua Chenyu & Aska Yang
《国王与乞丐》 is not at all a recent discovering, but for some reason I’ve been drawn back to it lately. It’s a lovely duet. But something wacky has been going on with the 《异类》 album on US Spotify too. I kept having to remove and then readd this song to my playlist. You’ve been warned!
#chinese music recs#cpop#c-pop#c pop#mandopop#chinese music#chinese language#mandarin chinese#langblr#language#languages#language blog#language learning#learning languages#language study#language lover#learn chinese#learn mandarin#learning chinese#learning mandarin#language studyblr#薛之谦#薛之謙#Xue Zhiqian#韦礼安#韋禮安#weibird#邱锋泽#邱鋒澤#feng ze
189 notes
·
View notes
Text




SONG QIAN for Hunan New Year Eve
#song qian#宋茜#Victoria#f(x)#femaleidolsedit#femaleidol#femaleidols#chineseartistsinc#cdramasource#*4#cpop#mando pop#chinese music#c-pop#cactor#after the performance finishes it cuts to amber cheering 🥺😭😭💕💕💕💕
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
Learning a language so I can understand music lyrics is so much more motivating than just being like “I should learn this to better myself and because languages are useful.”
It’s so cool to go from understanding nothing to suddenly pronouns start standing out, then other words - I know I’ve really internalized a word when I start noticing it in songs, that’s happened with things like 现在 (xianzai, now), 告诉 (gaosu, tell), and 不必 (bu bi, no need/don’t need to).
And now I’m at the point where I’ll listen to songs and they sound like: “you don’t need to… something something… say you love me…” “when I can’t forget you, will you something something…” “either you’re there or where are you, I can’t tell because I can’t hear the tone on na when it’s music…” “quick, tell me you’re… on your way to come? Except there’s one word in there I don’t know?”
It’s so motivating in multiple ways - immediate confirmation that I’m making progress, and when I can only understand half a sentence it definitely makes me want to learn the rest!
But this is why I cannot get into k-pop - my brain can only handle one entirely new language at a time, and I would not be able to just listen to it and not want to understand.
44 notes
·
View notes
Text

張露 (chang loo), 扇舞 (fan dancing), 1970
archive.org / discogs
#chang loo#chinese classical#chinese music#classical music#1970s#70s#graphic design#album art#album cover#cultreslut
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
extraterrestrial love | a chinese indie/pop playlist
"i'll find you again in every universe. let us be a little more honest, let us have a little more time." — ruporas / [youtube link]
01. 天外來物 / Extraterrestrial Object
✦ 你降落的 太突然了, 我刚好呢 又路过了
✦ Your arrival was so sudden, I had just happened to pass by
02. 我睡不著 / I Can't Sleep
✦ 你 心臟秘密 等待某個人開啟
✦ The secret of your heart is waiting to be opened
03. 烟火星辰 / Fireworks & Stars
✦ 你越過星海 攜著光而來
✦ You crossed the sea of stars and came to me, bringing light
04. 火星記 / Mercury Records
✦ 穿过时间的缝隙 它依然真实地 吸引我轨迹
✦ From beyond a rift in time, [your eyes] pull me into orbit
05. 我會等 / I Will Wait
✦ 在於你一起去看 外面世界 到底有多大
✦ I will go with you, to see how big the world really is
06. 黑月光 / Black Moonlight
✦ 無論走多久星塵風沙 那月光於我是鎧甲
✦ No matter how long I walk through the stardust, wind, and sand, the moonlight shining upon me is my armor
07. 行星戀 / Parallel
✦ 我等待恆星划過天空的那一天 實現著約定的時間點
✦ I'm waiting for the day when stars streak across the sky, signaling the reunion we promised
08. 睡 / Sleep
✦ 菸兒的火光是代表存在的連結
✦ The cigarette's flame represents the connection of our existence
09. 行星 / Planet
✦ 清醒卻發現 你仍然遠方
✦ When I wake, I find that you're still far away
10. 披星戴月的想你 / Miss You Day and Night
✦ 我會披星戴月的想你 我會奮不顧身的前進
✦ I'll miss you day and night, but I'll keep going forward fearlessly
11. 夜空中最亮的星 / The Brightest Star in the Night Sky
✦ 夜空中最亮的星,能否记起 ,曾与我同行,消失在风里的身影
✦ The brightest star in the sky, can it remember, the shadow who once walked beside me?
12. 星月花火 / Star, Moon, Sparkle
✦ 静 静静地听 月亮说什么
✦ Listen quietly to what the moon says
13. 藍夜 / Blue Night
✦ 藍色的夜 擁抱著我們
✦ The blue night embraces us
14. 月落 / Moonset
✦ 每首歌 想你是否醒著
✦ Every song wonders whether you're awake
15. 月旁月光 / Besides the Light of the Moon
✦ 好大的月亮 妳有看到嗎
✦ What a big moon, did you see it?
16. 愛到宇宙爆開 / Love Bomb
✦ Oh 親愛 請你填滿愛到宇宙爆開
✦ Oh dear, I hope you're filled with love until the universe explodes
#music#playlist#spotify playlist#youtube playlist#cpop#chinese music#despite the quote source this is not a vashwood fanmix...unless? idk vashwood enjoyers let me know#中文歌曲#jay rambles#works best on a 5 sec crossfade i think :-)!#tried to make a coherent plot with the lyric selections haha#hope everyone has a good new years eve!!!
5 notes
·
View notes