#cassini space probe
Text
voyage of the moons
#space#io#europa#jupiter#voyage of the moons#nasa#cassini space probe#great red spot#video credit: kevin m. gill
227 notes
·
View notes
Video
Cassini Space Probe
Europa & Io moons orbiting Jupiter, captured by the Cassini space probe.
Credit: NASA-JPL’s @kevinmgill.
From Paul Byrne.
33 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Asteroid Lilith Discovery & Lili Boulanger
Marc Jones wrote very little on the nodes, so last month we took a turn with several other authors and highlighted their work on the nodes. Naturally, we found some better than others like Martin Schulman, Georges Muchery and Bernice Grebner, but in all honesty we did not survey Dr. Mohan Koparkar, Haydn Paul and the Hubers, so this month, June,we are going to continue our with the nodes,…

View On WordPress
#Asteroid 1181 Lilith#Benjamin Jekhowsky#Black Moon Lilith#Bucket with a Saturn Handle#Cassini Space Probe#Dark Moon Lilith#Leo 07#Lili Boulanger#Locomotive Temperament Type#Virgo 23
0 notes
Text
Pia Tafdrup: recent poems from Bloodaxe Books

View On WordPress
#Bloodaxe Books#Cassini Space Probe#close analysis of poetry#David McDuff#Pia Tafdrup#poetry of the senses#The High Window#The Salamander Quartet
0 notes
Text
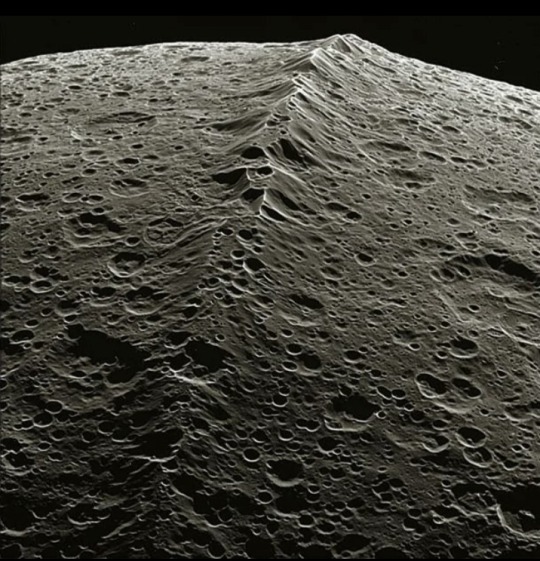
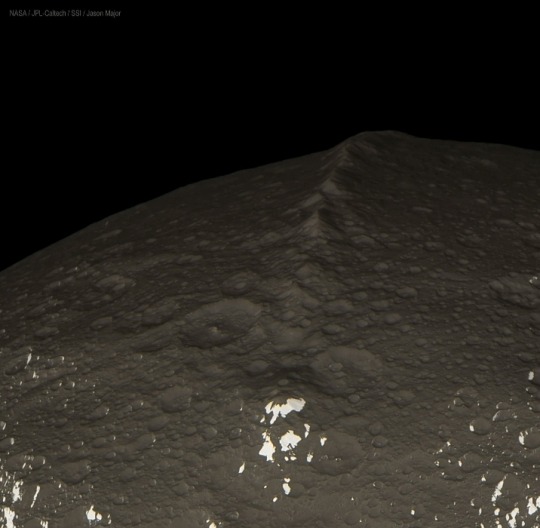

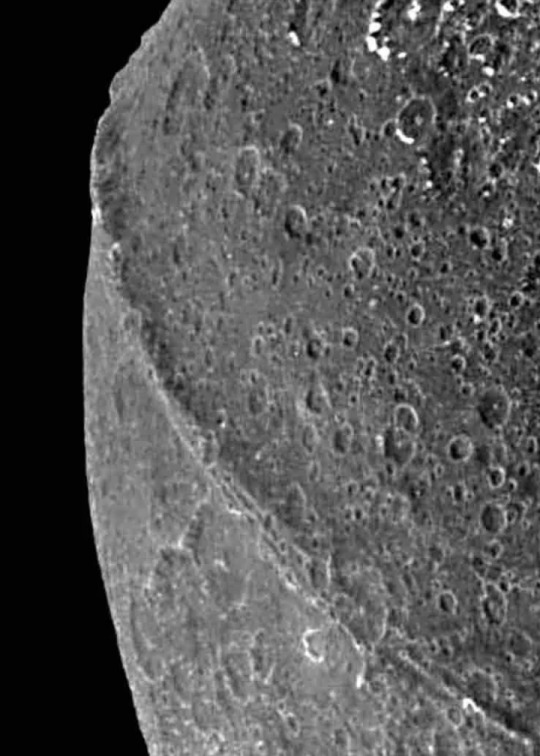

Clearest images ever taken of Equatorial Ridge on Saturn's moon Iapetus.
—
The equatorial ridge is the tallest mountain feature on Saturn's moon Iapetus.
It is 20 km (12 mi) high and is the third tallest mountain structure in the Solar System.
It runs along most of Iapetus' equator. It was discovered by the Cassini probe on 31 December 2004.
Cassini–Huygens, commonly called Cassini, was a space-research mission by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, including its rings and natural satellites.
#Saturn#Equatorial Ridge#Iapetus#moon#planet#astronomy#Cassini#Solar System#Cassini–Huygens#space probe#NASA#European Space Agency (ESA)#Italian Space Agency (ASI)
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
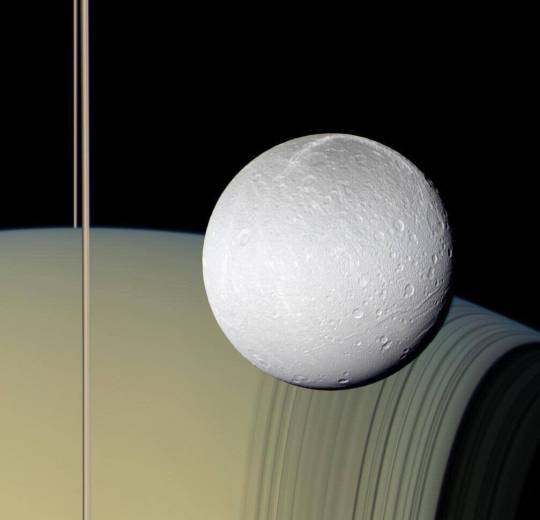

Saturn and Dione, captured by NASA Cassini.
#go for queue deploy#nasa#nasa cassini#cassini#saturn#dione#solar system#planet#moon#space#space exploration#probe#satellite#space photography#space and astronomy#astronomy#spaceflight#outer space#space program#science#technology#engineering#stem#exploration#space is cool
215 notes
·
View notes
Text
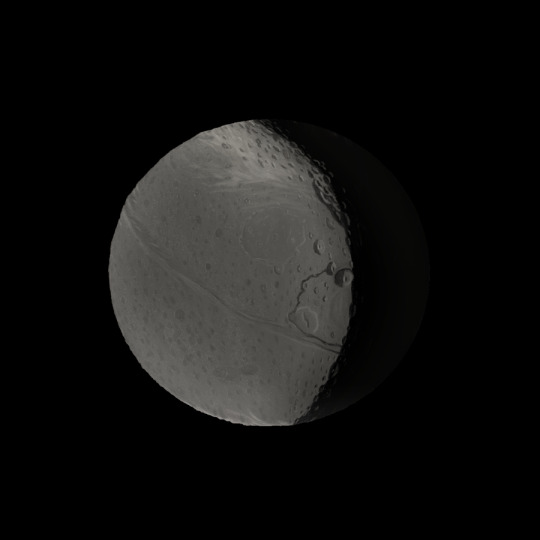

I don't know why, but I got a very strong and sudden urge to do a piece of Iapetus. I literally couldn't sleep, as all I could do was think of painting Iapetus. I kinda lost track of time, but I do know it took me just a little over an hour. It was a lot of fun, I hadn't ever really done a study like this before!
#space art#space landscape#space landscape art#iapetus#saturn#moons#moon#cassini#solar system#astronomy#planets#outer space#nasa#rings#voyager probe#voyager 1#voyager 2#2001 a space odyssey#digital art#artists on tumblr#tolbachik art#my art#space#space exploration#digital painting
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
i woke up cryinf abt cassini's intentional destruction this morning and now this blog exists so 🫶
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Last night I looked up at the night sky and couldn't stop staring at planet Mars in absolute awe
We put goddamn ROBOTS up there
That makes space feel less like a big void full of mysterious lights, and more like a playground of potential exploration and knowledge that we can actually grasp.
That's another planet like Earth! The stars are other Suns! Space doesn't feel so empty or scary or unreachable anymore, those are physical PLACES up there!
#space#and don't even get me STARTED on the cassini spacecraft or the ISS or the parker space probe!
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
anyway there’s a fuckass big rocket launching from cape canaveral monday and I’m trying to psych myself up for it because it’s the biggest rocket launch since the saturn v, possibly bigger, and we’re also going back to the moon
#micky speaks#it's not that I no longer find rocket launches cool as hell#I find private enterprise rocket launches annoying as fuck because fucking bezos and musk and all their bullshit#and the fact that space is so fucking commercialized now#it's hard to see past the idiocy to the real genuine progress#and the genuine emotion and curiosity that's brought to the table by the same people who wept when the cassini probe crashed#and who programmed the mars rovers to sing happy birthday#and who shouted out to the universe 'we're here'#'this is who we are'#and who showed us pluto's heart#and all the little in between#so I'm trying to find that childlike glee for space exploration again
3 notes
·
View notes
Video
Europa & Io moons orbiting Jupiter, captured by the Cassini space probe | source
9K notes
·
View notes
Link
The discovery: Saturn's vast ring system is heating the giant planet's upper atmosphere. The phenomenon has never before been seen in the solar system. It's an unexpected interaction between Saturn and its rings that potentially could provide a tool for predicting if planets around other stars have glorious Saturn-like ring systems, too.
The telltale evidence is an excess of ultraviolet radiation, seen as a spectral line of hot hydrogen in Saturn's atmosphere. The bump in radiation means that something is contaminating and heating the upper atmosphere from the outside.
The most feasible explanation is that icy ring particles raining down onto Saturn's atmosphere cause this heating. This could be due to the impact of micrometeorites, solar wind particle bombardment, solar ultraviolet radiation, or electromagnetic forces picking up electrically charged dust. All this happens under the influence of Saturn's gravitational field pulling particles into the planet. When NASA's Cassini probe plunged into Saturn's atmosphere at the end of its mission in 2017, it measured the atmospheric constituents and confirmed that many particles are falling in from the rings.
Continue Reading
193 notes
·
View notes
Text
Europa & Io moons orbiting Jupiter, captured by the Cassini space probe
72 notes
·
View notes
Text


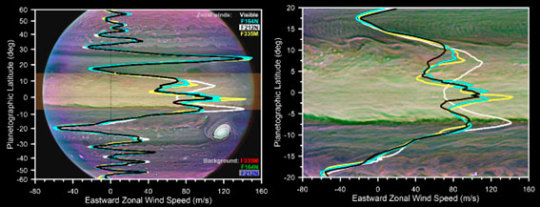
New jet stream discovered in Jupiter's upper atmosphere
The University of the Basque Country's Planetary Sciences Group is leading the discovery made by an international team and based on the analysis of observations obtained by the James Webb Space Telescope
High-speed jet streams are a common feature in the atmospheres of many planets. On the Earth, jet streams form at various latitudes and meander around the planet, changing latitude and reaching speeds approaching 400 km/h at an altitude of over 10 km above the surface. On the giant planets Jupiter and Saturn, jet streams are one of the main features of the atmosphere; they are perfectly aligned with the parallels, and are known as zonal jets. On Jupiter these jets alternate in direction at different latitudes reaching maximum speeds close to 500 km/h.High-speed jet streams are a common feature in the atmospheres of many planets. On the Earth, jet streams form at various latitudes and meander around the planet, changing latitude and reaching speeds approaching 400 km/h at an altitude of over 10 km above the surface. On the giant planets Jupiter and Saturn, jet streams are one of the main features of the atmosphere; they are perfectly aligned with the parallels, and are known as zonal jets. On Jupiter these jets alternate in direction at different latitudes reaching maximum speeds close to 500 km/h.
On 27 July 2022, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) observed the atmosphere of Jupiter as part of an international "Early Science" programme in which researchers from the Planetary Sciences Group of the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) are participating.
Because Jupiter is a very bright target for the JWST (whose light-collecting area is 6.3 times bigger than that of the Hubble Space Telescope), the images were acquired at wavelengths in which most of the light is absorbed by gases in the atmosphere. So the observations focused on the wavelengths in which Jupiter is darkest. This also meant that at many of these wavelengths Jupiter had never been observed with the quality needed to resolve the details of the weather systems in its atmosphere. Thanks to the JWST's features, a three-dimensional view of Jupiter's weather systems could be obtained: higher clouds appear bright in these images, and deeper clouds appear as dark regions. The JWST observations were also designed to obtain a measurement of the movements of the atmosphere by taking two sets of images separated by a full rotation of the planet, thus enabling a detailed study to be made of the cloud movements.
A new jet stream on the planet's equator
The JWST images showed that the movements that occur in the clouds covering the equator are very different from those observed in the lower clouds. These clouds are so faint that no details can be seen in them in observations obtained from the Earth or even by different space missions. However, the detailed JWST images show that at the level of these clouds, winds reach speeds of 500 km/h, while in the lower clouds, located 30 km below, they only reach 250 km/hr.
A universal phenomenon in Gas Giants
The study published in Nature Astronomy compares this new Jupiter jet with the structure of the equatorial jet stream of the gas giant Saturn, where in 2009 the UPV/EHU’s Planetary Sciences Group found a wind structure very similar to the one now revealed on Jupiter, and discovered on Saturn thanks to observations made by NASA's Cassini space probe [2-3]. On both planets, there is a fast, narrow equatorial jet at an altitude of about 200 mbar tracked by the rapid movement of equatorial clouds. On both Jupiter and Saturn, the elevated equatorial jets may be related to global temperature variations occurring in the atmospheres of these planets on a cyclical basis every few years, but which were thought to be limited in altitude at stratospheric levels to altitudes of 30-150 km above the level of the new equatorial jet stream. If the new Jupiter jet is related to these temperature oscillations in the upper atmosphere, then the equatorial jet stream should have a variable intensity on both Jupiter and Saturn, and also at much deeper levels than can be explained by existing atmospheric models. These intriguing phenomena occur near the tropopause of Jupiter and Saturn, precisely where the atmospheric dynamics change due to the fading effect of the Coriolis forces, and where the thermal properties of the atmosphere change dramatically. Future JWST observations of both Jupiter and Saturn may shed new light on these phenomena.
TOP IMAGE....Image of Jupiter obtained by the JWST and published in August last year. Acknowledgements: NASA/ESA/CSA and Jupiter Early Release Science team. Processed: Judy Schmidt (Planetary Society) and Ricardo Hueso (UPV/EHU).
CENTRE IMAGE....Images of Jupiter obtained by the JWST (Left) False colour composition. (Centre) Image obtained at a wavelength sensitive to the upper clouds. (Right) Image obtained at a wavelength sensitive to the lower clouds. Acknowledgements: NASA/ESA/CSA and Jupiter Early Release Science team. Processed: Ricardo Hueso (UPV/EHU).
LOWER IMAGE....Structure of the zonal winds on Jupiter from observations at visible wavelengths (white profile) and in different filters used in the study (coloured lines as indicated in the figure). The background image is a combination of JWST images sensitive to the upper clouds. Left-hand panel: General structure of the zonal winds. Right-hand panel: Equatorial region with the new jet stream observed in the upper clouds. Acknowledgements: NASA/ESA/CSA and Jupiter Early Release Science team.
41 notes
·
View notes
Text
Title: Then Till Now
Author: silver_penny
Artist: spiffyflypie
Rating: Teen
Pairings: Dean/Cas, Sam/Eileen, Dean & Sam, Dean & Charlie, Cas & Anna, Cas & Claire
Length: 20000
Warnings: No Archive Warnings Apply
Tags: 17776 AU, human/nonhuman relationship, alien invasion, happy ending, dialogue-heavy, rocketry
Posting Date: November 1, 2023
Summary: It's the year 17776, and Dean Winchester is used to the peace. Humanity has stabilized the climate, vanquished world hunger, and achieved equitable global co-operation. Nanobots swoop down to heal every little paper cut, and if no one is born anymore, well, no one dies either.
When the Cassini-Huygens space probe crashes into his life – newly conscious, bluntly sarcastic, and deeply skeptical of humanity's late triumph – it's the most interesting thing to have happened to Dean in millennia.
But out in deep space, something truly interesting is stirring...
Excerpt: Bobby’s wrong about the house – it’s not too big, not for Sioux Falls and especially not for their family – but when he opens the door and the creak echoes out into a cavernous empty space, it kind of feels that way. Dean ends up in the Deancave, curling up in the best seat and summoning up something old and a little mindless to watch.
Hello.
It’s the first thing he’s heard in hours, and for a moment Dean doesn’t even recognize it as another person. But it lingers, the way real environmental sounds do. Dean mutes the TV. “Hello?”
Yes.
Dean bites his lip. “Hello, yeah. You okay?”
I’m not sure.
“Alright. What’s up? Can I help?”
I am unsure if that is something you are capable of doing.
Dean blinks. “Okay. You just soliciting or something? Sorry, man, not interested.”
I am not...soliciting.
“Okay?”
I have no interest in solicitation.
“So any reason you decided to barge into my evening, then? If you don’t need anything, you don’t want anything...”
I am talking to you on the advice of my brother.
“Who’s your brother?”
Pioneer G.
Dean blinks again and then slowly sets his remote control back down. “The – the space probe? Pioneer G?”
He likes to be called Gabriel.
Of course he does. “You’re talking to me from space?” There’s a very long pause.
Yes.
“Huh.”
I don’t know where else I would be talking from.
“Yeah,” Dean says, “of course not.”
You are also talking to me from space.
“From Earth,” Dean says absently. “Not quite the same thing.”
There had been, of course, probes on the news. How humanity built something that, millennia later, could wake up like that, for lack of a better term...that was still a mystery. The scientists were all over it, of course, but maybe a little less urgently than they might have been, once upon a time.
And now there was a spacecraft interrupting his show.
Dean clears his throat. “So, um, any reason your brother thought I would be the best person for this conversation?”
He didn’t.
Now Dean squints at the ceiling. “You know, you’re not doing a great job answering my questions.” There’s a beat. Two beats.
My apologies. Gabriel requested that I “go find one of those humans to chat with if you want to talk so much.” You were in an optimal position.
“I am, huh?”
Yes.
“You mean, like...spatially? Cosmically?”
Your position on Earth is optimal for transmission at the current moment. Also I can see your television.
Huh. “So who are you, then?” Dean asks. He kicks up his feet a bit and studies the ceiling, imagining the moon and stars that might show behind it, once the sun goes down. He racks his brains, but even back when the space program was at its height, it didn’t make top thousand on the Winchester priority list. “Hubble? Sputnik?” Sam would know more.
Cassini-Huygens.
Dean catches his breath.
DCBB 2023 Posting Schedule
38 notes
·
View notes
Text
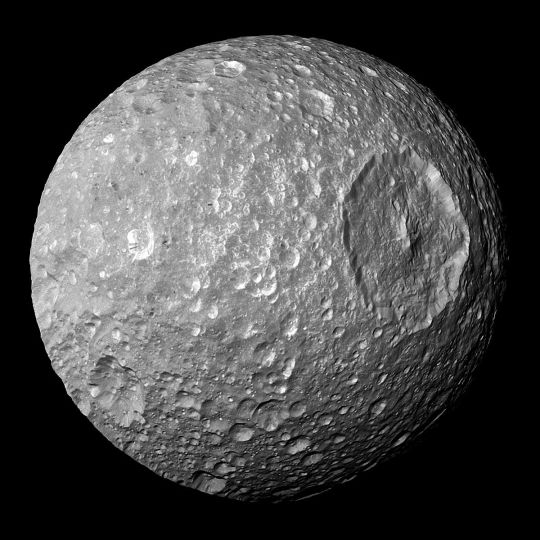

Mimas, Saturn's "Death Star" moon.
#nasa#cassini#nasa cassini#saturn#mimas#star wars#death star#moon#planet#solar system#space#spaceflight#space exploration#satellite#probe#planets#outer space#space is cool#space photography#space program#space and astronomy#science#technology#engineering#stem#exploration
96 notes
·
View notes