#German Invasion of Britain
Text
British Home Front During World War Two.
Senate House.
Senate House in Malet Street, London WC1 close to the British Museum is an Arc Deco building built between 1932 and 1937 and is now the library and administration centre for the University of London. Most days of the week many thousands of people walk past this building and the general public along with students at the University of London are seldom aware of its wartime…

View On WordPress
#Alan Malcher Historian#German Invasion of Britain#Operation Sea Lion#Senate House London WC1#University of London
0 notes
Text
In the time after the Roman legions left Britain, tradition has it that two brothers, Hengist and Horsa, led a mass Anglo-Saxon invasion, but did this really happen or is it all just a legend?
#saxon#Angle#Jute#Anglo#Anglo-Saxon#Hengist#Horsa#Britain#england#Briton#british#English#Picts#Vortigern#Germanic#invasion#pagan#christianity#ancient#history#ancient origins
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
Remember the Battle of Britain: July–October 1940.

By late 1940, Britain faced the threat of a German invasion, but the incursion would succeed only with air superiority. What followed was the first major campaign fought by opposing air forces.
For four months, the German Luftwaffe carried out attacks on British airfields, radar stations, and aircraft factories, and bombed British cities, too. But the Stukas proved too vulnerable to being intercepted, and the Germans couldn’t mass enough planes to defeat the fighter pilots of the Royal Air Force in their Hurricanes and Spitfires. Heavy casualties forced the Luftwaffe to scale down operations. Hitler’s invasion plans were put on hold indefinitely.
[Must Read: What if the Nazis Bombed Britain Earlier?]
#year 1940#German invasion#British cities#Royal Air Force#casualties#british forces#Battle of Britain#incursion
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
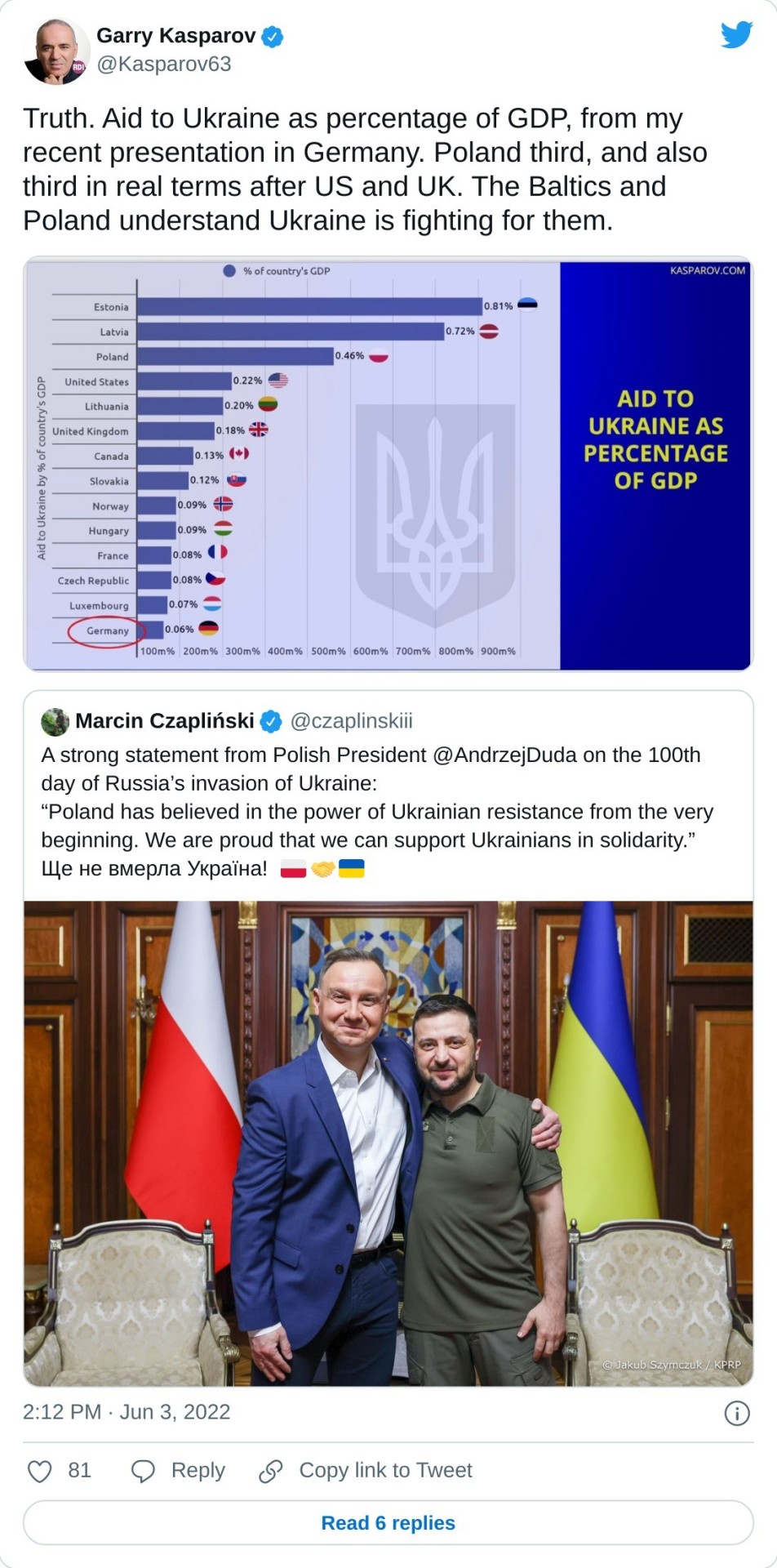
#help for ukraine#ukraine#usa#great britain#poland#estonia#lituânia#german#russian war#russia ukraine war#putin's war#criminal war#war#russian agression#criminal putin#fuck putin#putin#stop invasion#stop russia#stop war
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Clive Dunn, as he is now better known, will for many people always be Corporal Jones, Dad's Army excitable veteran of imperial wars, but in 1941 he was just twenty-one and a stretcher-bearer and orderly for Captain Eden (cousin of Anthony). He had been on the run for weeks and was frail and suffering from dysentery when he was captured. Although the Germans who caught him were friendly, even sharing their last packet of cigarettes with him, he and thousands of other British, Indian, Yugoslavian and Palestinian prisoners were then taken to barracks in Corinth, 50 miles south of Athens, where SS guards punished anyone who failed to salute them properly. During the day he sought out slit trenches to escape from the searing heat and at night he shivered in the icy dormitories. Daily rations consisted of two or three bits of water biscuit and a quarter of an inch of olive oil; his friend who had managed to hang on to his gold engagement ring exchanged it for part of a loaf of bread.
Their clothes were baked for one or more hours in huge ovens delivered to the camp. Then they were ordered to march naked several miles to the sea, past women who pulled their gawping children inside. 'For some, this was probably the most degrading moment of their lives,' Dunn wrote later. At the beach a hose fired liquid carbolic at their groins and they ran into the sea to relieve the discomfort. The only sign of defiance left to them was to sing 'Tipperary' as they marched back, still naked, to their tattered clothes. The heat had weakened the seams of Dunn's uniform and the sleeves immediately fell off, making him feel 'more ridiculous than ever'.
From Corinth they were moved back to Salonika. One day they 'staggered' thirty miles in the blazing heat and a soldier Dunn had been treating collapsed and died; three guards died from heat exhaustion. They left Greece in cattle trucks, taking it in turns to stand or sit, and relieved themselves in one petrol can; a second can contained a small quantity of water for drinking. Light and air crept in through one small, barred window near the roof bringing clues as to their whereabouts – the cool mountain air and smell of pine trees – and the time of day.
'The surrending of physical privacy became a habit – everyone suffered from diarrhoea and the petrol tin was continually full to the brim with germ-laden liquid faeces.' Emptying it out of the window was a hazardous operation that usually left the men below soaked by its noxious contents.
— The Barbed-Wire University: The Real Lives of Allied Prisoners of War in the Second World War (Midge Gillies)
#book quotes#midge gillies#history#military history#prisoners of war#ww2#german invasion of greece#britain#england#germany#nazi germany#greece#clive dunn
1 note
·
View note
Note
The disrespect toward indigenous peoples is what popped put at me today in one of your posts. I wonder how long the English have been looking down on the Welsh. We're the Saxons like that or is it the Normans who really thought they were better than everyone else. Cause it seems like it goes back a long way.
Oh, both, just in different ways. The Normals were imperialist, the Saxons were more theft and landgrab.
Something that makes me want to start hurling knives is the INCREDIBLY COMMON English myth that the Anglo-Saxons were a sweet innocent indigenous British people who were conquered and bullied by those mean nasty Normans (and Vikings), and because the Normans came over via France, that means everything was actually THEIR fault, and the true English i.e. the Anglo-Saxons, were victims too :(
When I say it's incredibly common, by the way, I really mean it. Enormous numbers of modern day English people believe this. I've seen BBC programs about the Viking invasions that claimed without a trace of irony that the Vikings would take slaves from "the native Anglo-Saxons". I've literally had English people comment this shit on posts of mine about Celtophobia and Welsh history. Like I'm there describing how the last Prince of Wales was locked in a wooden cage in Bristol Castle at the age of eight and lived out the remainder of his life there until his fifties so the Welsh would know their place, and some snivelling English cunt will straight up write a message going "Teehee really it was the Normans not the English though and they conquered the poor Anglo-Saxons too, poor England uwu"
Anyway in the dying days of the Roman empire in Britain one of the leading reasons for Rome abandoning Britannia was the constant waves of Anglo-Saxon invaders. There were so many the east coast of Britain became known as the Saxon Shore. There were so many the Romans built a line of forts that were and are literally called Saxon Shore Forts. There were so many that an official, historically documented, paid governmental position in Roman Britain was the Count of the Saxon Shore, i.e. the guy responsible for keeping the bastards out.
Rome had banned native military, of course, so when they then withdrew and took the armies with them, the people left had no defences against the incoming waves of Angles, Saxons and Jutes. England fell pretty quickly, Angles in the north, Saxons in the south, Jutes primarily in the east, I believe. What stopped their westward expansion was the Brythonic Celtic nations living in modern day Wales. And this is the origin of the Welsh dragon - those separate kingdoms needed a banner that united them, and represented Not Saxon. An anti-Saxon force. They chose a red dragon.
This is also the origin of King Arthur. An anti-Saxon king of the Brythons, who would repel these Germanic invaders. (It was several centuries later that England realised they should probably steal the term 'British', because otherwise they were marking themselves as 'not native'.)
Anyway the saving grace of the Anglo-Saxons in the end was actually that they were whiny little bitches who gave up trying to fight in Wales with its difficult mountains and fought each other instead. The whole sorry tale of the Heptarchy is the various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms fighting like cats in a bag, while Saxon king Offa built a dyke along the Welsh border and went "WELL YOU'RE NOT ALLOWED OVER HERE" and every Welsh king went "...we literally didn't want to conquer you anyway, you spectacularly sad and stupid man"
Oh, and of course, there's the name 'Wales'. Given to us specifically by the Anglo-Saxons. And translated by centuries of English scholars, mostly very smugly, as 'foreigners'. A fun bit of early propaganda, look - foreigners in our own country that they tried and failed to steal.
All of which is a circuitous way of saying - yeah, it goes way back.
2K notes
·
View notes
Photo
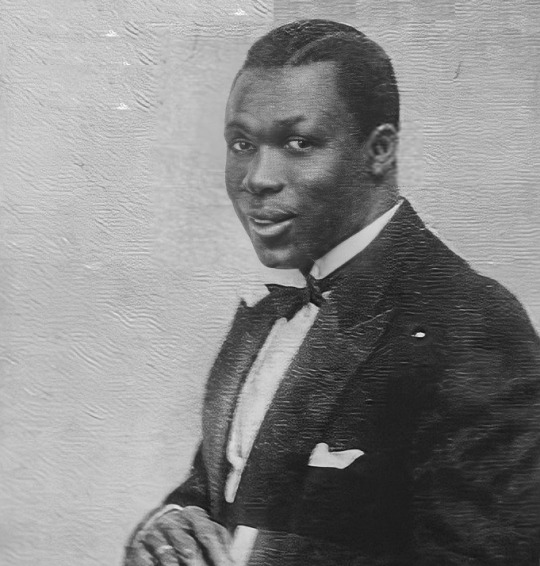

On this day, 22 July 1895, August Agbola O'Browne, the only Black person believed to have participated in the anti-Nazi Warsaw uprising of 1944 was born in Lagos, Nigeria. A professional musician and polyglot, speaking six languages, he moved to Poland in 1922, lived in Warsaw and played drums in clubs in the city. He initially took part in the defence of Warsaw during the 1939 German invasion, and later took part in the 1944 insurrection (not to be confused with the Warsaw ghetto uprising of 1943) under the codename "Ali" in the Iwo battalion. In 1958, O'Browne migrated to Britain where he died in the late 1970s. More information, sources and map: https://stories.workingclasshistory.com/article/9481/august-agbola-o'browne-born https://www.facebook.com/photo.php?fbid=665999148906637&set=a.602588028581083&type=3
267 notes
·
View notes
Text
Finished The Wages of Destruction.
Solid 9/10.
Core ideas to take away:
work creation was a minor element of Nazi economic policy, a distant secondary concern after rearmament
rearmament had widespread public support in germany
shifting to autarky took extremely hacky and likely long-run unsustainable export controls, and even *export subsidies* because imports were still an inescapably vital input to industrial production in
controlling big business was largely a "soft co-opting" project while the agriculturalists were insane morons who were much more staunchly pro-nazi
once at war, Germany was going for broke from the very beginning and there was near-zero slack they could've squeezed out more war production from
truly pitiful productivity rate from Germany's conquered continental empire - the workers were far far more productive if deported to Germany than working in home countries
German surface navy seems useless, they didn't even have the oil to run the ships, and metal would've been better used elsewhere
Speer was a shit, Tooze hates hates him
bombing campaign actually was successful! specifically taking out the Ruhr
"blitzkrieg" doctrine was developed as they went; original 1940 invasion of France battleplan was to go "right up the center" not through the Ardennes and pre-battle production focused on heavy artillery ammunition
Bigger points: German "Strategy"
Germany escalated from diplomatic crisis to war with Poland/UK/France, and to war with the Soviet Union, and then America, out of a series of perceived closing windows of opportunity. First one was seeing UK/French production overtaking them in rates and catching up on stocks. In 1940 the US fully commits to aiding Britain, creating sense of "the bombers are coming eventually" and need to gain immediate advantage by conquering the Soviet Union.
Bizarrely, German production was focused on the Luftwaffe in preparation for fighting US/UK air war as Germany was getting ready for Barbarossa!
Declaration of war on US pitched as confirming alliance with Japan, but still feels stupid. Germany could just stay quiet and force US to either engineer entry to European conflict another way or stay out. Still seems less stupid, considering this is at a time when Barbarossa is coming apart.
But overall, a sound if massively risky plan assuming you accept the insane basic assumptions. Hitler's strategic vision often gets assumed to be terrible out of disgust for the consequences of his actions and their failure.
I really do wonder what the vibe was among German economic elite from 1942 onwards, it's obvious the war is not winnable, that you're very fucked, and that everyone is coming to kill you.
Anyways, good book and worth reading/listening to. Tooze could've slimmed down on the pre-war stuff. I find him vaguely irritating with how he brings up irrelevant things just to show how smart he is but that's probably just envy.
P.S.
The original Volkswagen was just a massive scam with no actual civilian cars being produced despite taking all the payments for the vehicles. Possibly suggests two dominant strains of conservatism? Former is old aristocratic conservatism of the nobility or classic US elite; latter is the populist oppositional culture right-wingism which is about 64% scam artists.
69 notes
·
View notes
Text
‘Pimpernel of the Hellenes’, ‘Major Paddy’, ‘Enchanted maniac’: Will the real Paddy Leigh Fermor please stand up?

Paradox reconciles all contradictions.
- Patrick Leigh Fermor
So one evening I was baby sitting my nephews and nieces here in our family chalet in Verbier, high up in the Swiss Alps. It was my turn to baby sit as the rest of my family enjoyed the fantastic classical music concerts and events showcased at the two week long Verbier 30th Festival. The little scamps had gone to bed and my father and I watched an old British war movie on DVD, ‘Ill Met By Moonlight’ (1957). It was filmed by the legendary team of Michael Powell and Emeric Pressburger based on the 1950 book ‘Ill Met by Moonlight: The Abduction of General Kreipe’ by W. Stanley Moss.
I’ve seen the film a couple of times before, but until now never really paid attention to where the title came from. My father said it was from Shakespeare’s ‘A Midsummer’s Night’s Dream’ And so it was. In the play, Oberon, the king of the fairies and the Queen are having a fairly bitter drawn-out fight over custody of a changeling Indian child, and this is how the pissed off king greets the queen when they run into each other, “Ill met by moonlight, proud Titania”. Oberon is basically saying "Oh Lord, it's you..." and Titania's response is basically a flippant middle finger. One of the best modern reasons to read Shakespeare: to throw playful erudite shade at others.
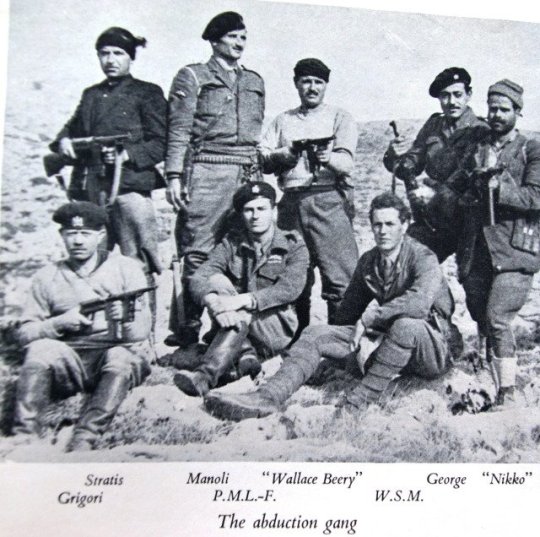

Anyway, the historical background of the film is the German invasion of Crete in May 1941. After an intense ten-day battle, Allied troops were driven back across the island, and many were evacuated from beaches along the southern coast. Some Cretans and British officers took to the mountains to organise resistance against the occupying forces. The German occupation that followed was especially brutal. Dreadful reprisals followed every act of resistance. The German commander, General Müller, insisted on taking 50 Cretan lives for every German soldier killed; he became known as ‘The Butcher of Crete’.
As a Classicist side note, there had been a close association between Britain and Crete since the early 20th century, when archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans had uncovered the sensational remains of a Minoan palace at Knossos. The headquarters of the British archaeological school in Crete was a large villa alongside the site, known as Villa Ariadne. Several archaeologists, who knew the island and its people well, went underground after the German occupation to aid the Cretan resistance. Continuing in this tradition, scholar and travel-writer Patrick Leigh Fermor, who had got to know Greece in the 1930s, joined the Special Operations Executive (SOE).
During the German occupation, Major Paddy Leigh Fermor travelled to Crete three times to help organise local resistance against the hated German occupation. On the third occasion, in February 1944, he was parachuted in with a specific mission to kidnap German commander General Müller, to boost morale on Crete along with his erstwhile SOE comrade Capt. W. Stanley Moss MC (aka Billy Moss) of the Coldstream Guards. However, just after they parachute in, General Müller was replaced by General Heinrich Kreipe, who transferred from the Russian Front. Thinking that capturing one general was as good as another, Fermor merrily go ahead with the daring kidnap operation.
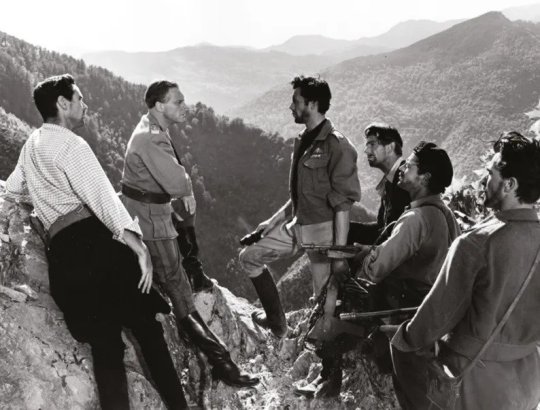

It’s at this point that the narrative of Michael Powell and Emeric Pressburger’s ‘Ill Met by Moonlight’ (1957) picks up. Dirk Bogarde plays Paddy Leigh Fermor, David Oxley plays Moss, and Marius Goring plays the taciturn German paratroop general. Blink and you’ll miss the late great Christopher Lee making a cameo appearance as a German officer in the dentist’s room scene.
The film naturally takes some liberty with the facts but it’s a cracking yarn of high adventure and drama. Xan Fielding, a close friend of Leigh Fermor from the SOE in Cairo, was taken on as technical adviser. The fact the film was shot in in the Alpes-Maritimes in France and Italy, and on the Côte d'Azur in France, far away from the craggy valleys and mountains of Crete itself. The director Michael Powell spent some time walking in Crete to get to know the island, but decided that, with the confused and volatile state of Greek politics, it was not suitable to film there.
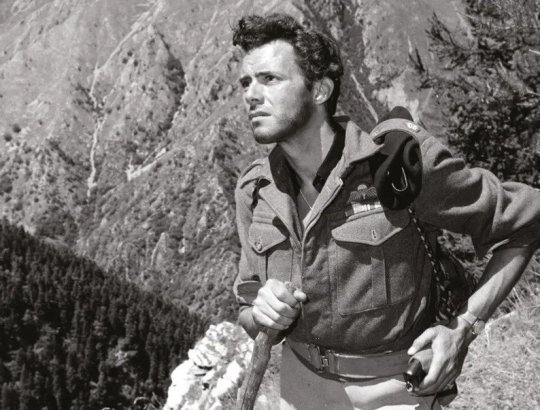

Looking back years after he had directed it Powell didn’t think much of his own film. By contrast, Paddy Leigh Fermor, who was on set throughout the film shoot, was very happy with Bogarde’s portrayal of him with Byronic glamour. Watching the movie again ‘Ill Met by Moonlight’ remains a classic and stands out from many British war films of the 1950s because of its realism. The British SOE men and the Cretan guerrillas look absolutely right for their parts. It is dramatic and full of suspense while filled with much boyish humour.
I was disappointed with one notable omission in the film that did happen in real life. According to Patrick Leigh Fermor, at dawn one day during the journey across the mountains, General Kreipe was looking at the mist rising from Mount Ida and began to recite, in Latin, the opening lines of Horace’s ninth ode:
Vides ut alta stet nive candidum
Soracte nec iam sustineant onus
silvae laborantes geluque
flumina constiterint acuto?
Behold yon Mountains hoary height,
Made higher with new Mounts of Snow;
Again behold the Winters weight
Oppress the lab’ring Woods below:
And Streams, with Icy fetters bound,
Benum’d and crampt to solid Ground
(John Dryden 1685)
Leigh Fermor picked up on the General, and recited the remaining stanzas of the Ode. ‘Ach so, Herr Major,’ said Kreipe when Leigh Fermor had finished. Both men were amazed to realise they shared a classical education and a love of ancient Latin poetry.
Leigh Fermor later wrote that it was as though the war had ceased to exist for a moment, as ‘We had both drunk from the same fountains before.’ It brought captor and captive together with a strange bond. The scene was not reproduced in the film, as Powell and Pressburger probably thought it would make the men sound too academic for a popular cinema audience.
Leigh Fermor and Kreipe met again in the early 1970s, on a Greek television show, and got on famously together. The General said Leigh Fermor had treated him chivalrously as a captive. They remained friends until Kreipe’s death.

After sharing a late night drink with my father after the film, I began to muse on the figure of Paddy Leigh Fermor, a family friend and someone I met along with his wife, Joan, as a little girl. My grandparents, and especially my grandmother, knew Paddy briefly from their days during and after the Second World War.
My father shared a few stories about him when he and my mother visited his beautiful home in Greece, where even at his advanced age he remained the most generous of hosts and the most outrageous flirt.
One of my memories was getting into his battered old Peugeot in the drive way and trying to drive it when my feet could barely touch the pedals. It wouldn’t have mattered in any case as the brakes didn’t work as he cheerfully said later as we careened around a dirt road to go around the mountains for a drive.
Many years later in April 2022, I tried to visit the home of the late Patrick and Joan Leigh Fermor - a sort of pristine shrine to their memory that one can also stay in any of the rooms as a vacation rental - in the coastal fishing village of Kadarmyli in the Peloponnese, as part of a hiking and mountaineering sojourn around Greece with ex-Army friends. We couldn’t stay there as it was already rented out to other guests, and so we stayed higher up the mountain in a villa, but we swam in front of the Fermor’s home which was on the water’s edge.
You could never put your finger on Paddy Leigh Fermor. He hid behind his gift for telling yarns, and pulling Ancient Greek verses out of the thin air, as well as boisterously singing local Greek songs with a drink in his hand.
Even after his death in 2011, the question keeps nagging as to who was Paddy Leigh Fermor?
The Dirk Bogarde film too seems to ask, who exactly is the ‘real’ Patrick Leigh Fermor - or the real anyone? Taking its title from a Shakespearian play concerned with dreams and disguises, magic and power, ‘Ill Met By Moonlight’ is all about questions of identity.
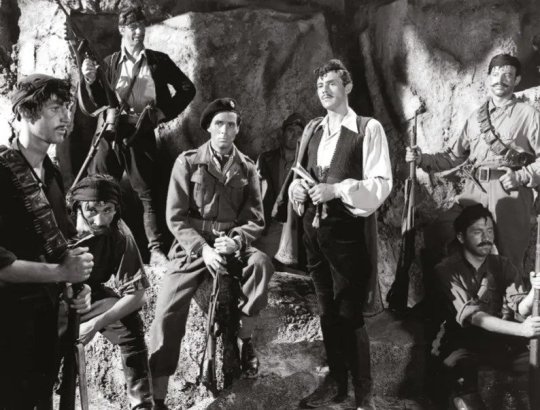

Under the film credits, we see Dirk Bogarde in uniform; then, unexpectedly, we see him in the flamboyant outfit of a Cretan hill-bandit. A title informs us that Major Leigh Fermor was also known by the Greek code-name “Philidem.” In other words, there are two of him (at least), and on one level the adventure the film is about to unfold reflects a conflict in his personality. It’s a conflict shared, unknowingly, by his Nazi opposite number, the fierce, arrogant General Kreipe (an unlikely “proud Titania,” but it’s true that he “with a monster is in love” – the monster of Nazism). Kreipe’s human side is so rigorously repressed by the demands of war and “glory” that he is genuinely unaware of it; ironically, this humanness, which constitutes the true manhood of this Teuton warrior, is revealed by a boy (equivalent to Shakespeare’s Indian Prince?) - who, in turn, is the most grown up person in the movie.
If “Philidem” appears under the credits, caped and open-shirted, a romantic dream-figure out of an operetta or a storybook, he is first seen in the film proper as a coarser, more down-to-earth version of the same thing – an ordinary Cretan peasant in a shabby suit, waiting for a bus. When he makes contact with the Resistance, his personality fragments further.

To some, he is the mystical Philidem, Pimpernel of the Hellenes and righter of wrongs. To others he is “Major Paddy,” the happy-go-lucky Englishman of popular movie myth conducting war as if it were a branch of amateur theatricals, a gentleman adventurer relying on breeding to get him through and making fun of the whole business. To Bill Moss (David Oxley), the newly arrived junior officer sent to assist him, he is the cool, fast-thinking professional soldier. And to himself? In his quietly passionate defence of Cretan life and culture, he seems someone else again: a scholar and aesthete outraged by the barbarism and folly of war, and by the moronic arrogance shown by his captive toward the Cretan people.
Whatever his persona, Leigh Fermor is a chameleon who never seems to change very radically in himself. Perhaps because he has this quality of seeming all things to all men – and being those things - he remains unfazed by the monolithic might of the German military machine. Fluent in Greek, he can also speak German like a German and is easily able to assume another disguise, that of a faceless Nazi officer. Although he and Moss make fun of themselves - “If only I had a monocle!” muses Moss when Leigh Fermor tells him he “looks like an Englishman dressed like a German, leaning against the Ritz bar” - they are able to effect the kidnapping with an ease that seems appropriately Puckish. General Kreipe is ignominiously thrust onto the floor of his own limousine, gagged, and sat upon by a couple of the peasants he so despises. Kreipe’s rage is compounded by his firm conviction that he has been snatched by “amateurs” - a belief Leigh Fermor and Moss slyly make no objection to, knowing how it will gnaw at his already shaky Master Race self-confidence.
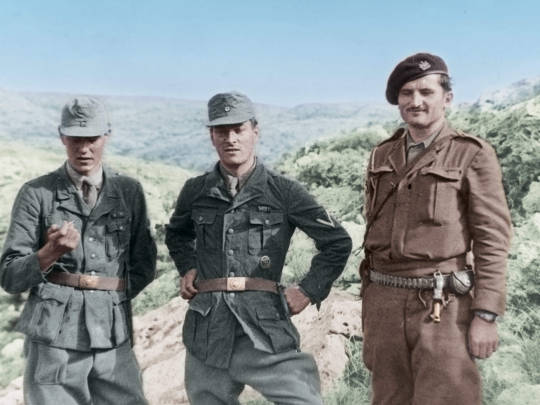

Patrick Leigh Fermor, aka Major Paddy, aka Philidem, in the film’s closing moments, is far from being self-assured intellectual or dashing amateur adventurer or legendary outlaw of the hills. He’s just a tired man who wants to go home and rest up. “How do you feel?” asks Moss. “Flat” is the reply. “You look flat!” says Moss. “I know how I’d like to look …” murmurs Leigh-Fermor wistfully. Moss knows what he’s going to say, and joins in the litany: “Like an Englishman dressed like an Englishman – and leaning against the Ritz bar!” It’s easy to imagine them ordering drinks at that renowned watering-hole with all the suavity required by this little fantasy.
Still, the film’s last images of Crete receding in the distance, until all we can see is the sea, suggests that maybe Major Paddy’s heart is really back in those hills in the “fair and fertile” land that has become as much a Powellian landscape of the mind for us as the studio-built Himalayan convent of ‘Black Narcissus’ or the monochrome Heaven of ‘A Matter of Life and Death’. And, as the film POV closing shots departs both Crete and this film, I began to think that being “dressed like an Englishman and leaning against the Ritz bar” would, for Patrick Leigh Fermor constitute yet another disguise. After all, he said he was of Irish aristocratic stock.
Traveller and writer Paddy Leigh Fermor is best known for two events. He’s known for leading the commando group in occupied Crete to kidnap General Kreipe. But he is also known for the boy who, at a mere 18 years old, set off with little money and a lot of nerve in 1933 to walk from the Hook of Holland to Constantinople.
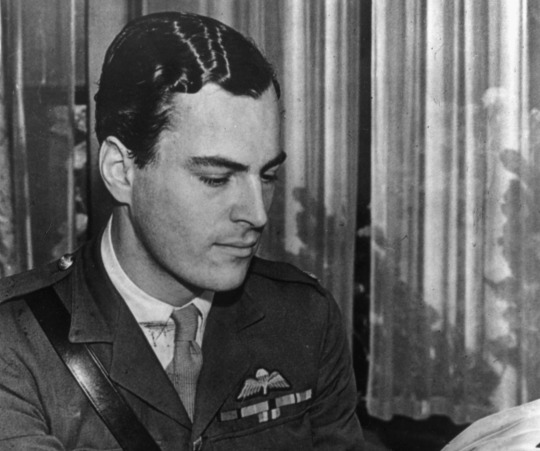

Patrick Leigh Fermor was, in the words of one of his obituaries, a cross between Indiana Jones, James Bond and Graham Greene. Self-reliance and derring-do were lessons learnt from the cradle. When Fermor’s geologist father was posted to India, he and his wife left the infant with family in Northamptonshire and did not return until his fourth birthday. In retrospect, he took great delight in being sent to a school for difficult children and getting himself expelled from the King’s School, Canterbury, when he was caught holding hands with a greengrocer’s daughter eight years his senior. His school report infamously judged him ‘a dangerous mix of sophistication and recklessness’.
Sharing a flat in Shepherd’s Market, one of Mayfair’s seedier corners, Leigh Fermor schooled himself in literature, history, Latin and Greek.
He honed his character with the company of extraordinary people and the words of great writers - he had a prodigious memory for prose as well as poetry. He befriended literary lions such as Sacheverell Sitwell, Evelyn Waugh and Nancy Mitford. His travels began aged ‘eighteen-and-three-quarters’ when he rejected Sandhurst Royal Military College in order to walk the length of Europe from Hook of Holland to Constantinople. He took with him Horace’s Odes and the Oxford Book of Verse though Leigh Fermor could recite Shakespeare soliloquies, Marlowe speeches, Keats’s Odes and as he modestly put it ‘the usual pieces of Tennyson, Browning and Coleridge’ from memory.
Leigh Fermor was then a self-made man in the most literal sense.

Setting off from England in 1933, Fermor resolved to traverse Europe living like a hermit; sleeping in bars and begging for food. But his manly charms and boyish good looks found him being passed like a favourite godson from Schloss to palace by European nobility and he developed a lifelong penchant for aristocratic company. I his own words, ‘In Hungary, I borrowed a horse, then plunged into Transylvania; from Romania on into Bulgaria’. Having reached Constantinople in January 1935, Fermor continued to explore Greece where he fought on the royalist side in Macedonia quelling a republican revolution. In Athens Leigh Fermor met Balasha Cantacuzene, a Romanian countess with whom he fell in love. They were living together in a Moldovan castle when World War Two was declared.
Fluent in Greek, Leigh Fermor was posted as a liaison officer in Albania. Recruited as a Special Operations Executive (SOE), he was shipped from Cairo to German-occupied Crete where he lived disguised as a shepherd in the mountains for two years. On his third expedition to Crete in 1944, Leigh Fermor was parachuted alone onto the island and made connections in the Cretan resistance movement. While waiting for his compatriot Captain Bill Stanley Moss to land by water from Cairo, Leigh Fermor hatched a plot to kidnap German Commander General Heinrich Krieple. He liaised comfortably with Cretan partisans and bandits to pull off one of the war’s greatest coups de théâtre.

Disguised as German soldiers, Leigh Fermor and Moss stopped Krieple’s car at an improvised check point en route back to Nazi HQ in Knossos. Abandoning the General’s car after a two-hour drive, Leigh Fermor left a note indicating that the kidnappers were British so that there wouldn’t be reprisals against Cretan nationals. When the abduction of the unpopular commander was discovered, a German officer in Heraklion allegedly said ‘well, gentlemen, I think this calls for champagne’. It turns out that General Kreipe was despised by his own soldiers because, amongst other things, he objected to the stopping of his own vehicle for checking in compliance with his commands concerning approved travel orders. It’s why for instance the German troops, both in the film and in real life, dare not stop the General’s car as it drove through the check points at Heraklion.
Krieple was evacuated and taken to Cairo and Leigh Fermor entered the annals of World War Two’s most devil-may-care heroes. With characteristic panache, when he was demobbed Leigh Fermor moved into an attic room at the Ritz paying half a guinea a night. But his first travel book, ‘The Traveller’s Tree’, was not about the European odyssey or the Cretan escapades and centred on Leigh Fermor’s adventures in the Carribbean. Published in 1950, ‘The Traveller’s Tree’ was an inspiration for Ian Fleming’s second James Bond novel ‘Live and Let Die’ (1954).
As a host and house guest, Paddy Leigh Fermor was much sought-after. At one of his parties in Cairo, he counted nine crowned heads. He was a confirmed two-gin-and-tonics before lunch man and smoked eighty to 100 cigarettes a day. His party pieces included singing ‘It’s a Long Way to Tipperary’ in Hindustani and reciting ‘The Walrus and the Carpenter’ backwards. In Cyprus while staying with Laurence Durrell, Leigh Fermor apparently stunned crowds in Bella Pais into silence by singing folk songs in perfect Cretan dialect. As Durrell wrote in ‘Bitter Lemons’ (1957), ‘it is as if they want to embrace Paddy wherever he goes’.

He struck up a partiuclar friendship with the famous Mitford sisters, especially Deborah Mitford, later ‘Debo’, the Duchess of Devonshire. It was at the Devonshires’ Irish estate Lismore Castle that ‘Darling Debo’ and ‘Darling Pad’ met and began to correspond. A characteristic letter from the Duchess in 1962 reads ‘The dear old President (JFK) phoned the other day. First question was ‘Who’ve you got with you, Paddy?” He’s got you on the brain’ to which Fermor replies of a broken wrist ‘Balinese dancing’s out, for a start; so, should I ever succeed to a throne, is holding an orb. The other drawbacks will surface with time’.
After the war he travelled widely but was always drawn back to Greece. He built a house on the Mani peninsula - which had been, significantly, the only part of Magna Graecia to resist Ottoman colonisation since the fall of Constantinople in 1453. Before his death in 2011 at the age of 96, he wrote some of the most acclaimed travel books of the 20th century.
His books contain some of the finest prose writing of the past century and disprove Wilde's maxim that "it is better to have a permanent income than to be fascinating".
Charm, self-taught knowledge and enthusiasm made up for the lack of a university degree or a private income. His teenage walk across Europe and subsequent romantic sojourn in Baleni, Romania, with Princess Balasha Cantacuzene are proof enough of that. But the difficulty of capturing such an unconventional and glamorous life is made harder by the certainty that Fermor was an unreliable narrator.

He was also an infuriatingly slow writer. Driven by a life-long passion for words yet hampered by anxiety about his abilities, Leigh Fermor published eight books over 41 years.
‘The Traveller's Tree’ describes his postwar journey through the Caribbean; ‘Mani‘ and ‘Roumeli’ (1958 and 1966) draw on his experiences in Greece, where he would live for much of the latter part of his life. But it is the books that came out of his trans-Europe walk that reveal both the brilliance and the flaws. ‘A Time of Gifts’ was published in 1977, 44 years after he set out on the journey. ‘Between the Woods and the Water’ appeared nine years later. Both describe a world of privilege and poverty, communism and the rising tide of Nazism, and end with the unequivocal words, "To be continued". Yet the third volume hung like an albatross around the author's neck. As the years passed, Fermor found it impossible to shape the last part of his story in the way he wanted.
Leigh Fermor was that rarest of men: a man determined to live on his own terms, if not his own means, and who mostly - and mostly magnificently - succeeded. Always popping off on a journey when he should have been writing about the last one, always ready to party, he was forever chasing beautiful, fascinating or powerful women, even when with his wife, Joan Raynor. She was the great facilitator who funded his passion for travel and writing, as well as women, from her trust fund. His love affairs were discreet but legendary.
Leigh Fermor was happiest among the rogues. Over a lifetime on the road, he sought them, and in turn they responded to his charm, nose for adventure, and his famous wit. He was a keenly-anticipated dinner guest - once outshining Richard Burton at a London society soirée, who he cut-off midway through a recital of ‘Hamlet’. As Richard Burton stormed out, the pleading society hostess said, “But Paddy’s a war hero!” to which Burton grouchily replied, “I don’t give a damn who he is!”

His partnership with and then marriage to Joan Raynor was an open relationship, at least on Leigh Fermor’s side. Paddy saw in Joan his kindred spirit. Like him, she spent much of her youth travelling to where she pleased; largely in France, where the photographer and literary critic Cyril Connolly became besotted by her. Joan was the daughter of Sir Bolton and Lady Eyres Monsell of Dumbleton Hall, Worcestershire. She was not only stunningly pretty but also 'a beautiful ideal, with the perfect bathing dress, the most lovely face, the most elaborate evening dress', as the Eton educated Connolly described her. Joan also stood out from the upper-class beauties of her day in that she supplemented her mean rich father's allowance by earning her living as a decent photographer.
In 1946, she met Leigh Fermor in Athens, while he was deputy director of the British Institute. Joan met him at a time when he was then in a relationship with a French woman called Denise, who was pregnant with his child, which she aborted. The pair would travel to the Caribbean together under the invitation of Greek photographer Costas, falling madly in love.

She was the only woman that - after decades of sexual scandals - matched his own erratic behaviour. Stories of how they dined fully-clothed in the Mediterranean, dragging a table into the sea, as well as their myriad cats and olive groves, paint a restless couple, who, when not out articulating the peoples of their adopted homeland, kept themselves very busy.
The attraction between Paddy and Joan was instant. So many love affairs that Paddy indulged in seemed about as brief as the flame from a burning envelope and you expected this one with Joan to be too. But somehow, miraculously, it lasts.
The two were apart a great deal, but in their case, absence did make the heart grow fonder. While Paddy was staying in a monastery in Normandy, supposed to be thinking monk-like thoughts that he would eventually put into his masterpiece A Time To Keep Silence, he was also writing sexy letters to Joan: 'At this distance you seem about as nearly perfect a human being as can be, my darling little wretch, so it's about time I was brought to my senses.' And: 'Don't run away with anyone or I'll come and cut your bloody throat.'
She tantalised him with descriptions of Cyril Connolly making passes at her; but she, like Denise, sounded a rather desperate note when she wrote: 'I got the curse so late this month I began to hope I was having a baby and that you would have to make it a legitimate little Fermor. All hopes ruined this morning.'
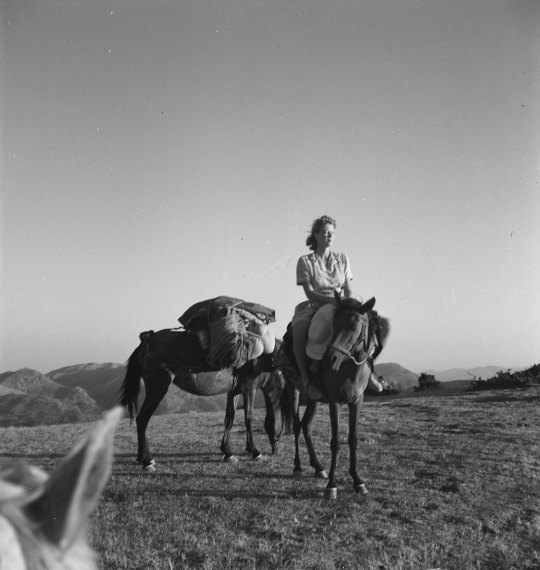

Fiercely independent - a trait that must have enamoured Paddy - they were best imagined as two pillars of a Greek temple, beside one-another but capable of holding up the roof of the world that they had built for themselves through the lens of ancient history and Hellenic culture. Indeed, it was said that they had a special ‘pact of liberty’. It is this unconquerable aura that led poet laureate John Betjeman to declare his love for her (he called her ‘Dotty’ and remarked that her eyes were as large as tennis balls). For Cyril Connolly, the photographer she shadowed, and with whom she had a scandalised affair during her first marriage, she was a “lovely boy-girl” and Laurence Durrell named her the ‘Corn Goddess’ because of her slender figure and short hair. But of all of these worthy candidates, it was the warrior-poet Patrick Leigh Fermor who finally won her heart.
To Joan, who described herself as a ‘lifelong loner’ in her diaries, her companionship with the uncomplicated Paddy was a relief. They had no children, nor did they want any - or so Paddy claimed. But those who knew Joan suspected she did want children but it never came to pass; and so she became a devoted aunt or dotted on other friends’ children. For both of them their dozens of cats gave them the next best thing to paternal satisfaction. Still, her morbid fascination with photographing cemeteries painted a much darker side.
Joan Raynor’s inheritance subsidised his peripatetic life at least until the enormous success of ‘A Time of Gifts’ in the late 1970s, which in turn created a new market for his previous volumes about Greece, ‘Mani’ and ‘Roumeli’.
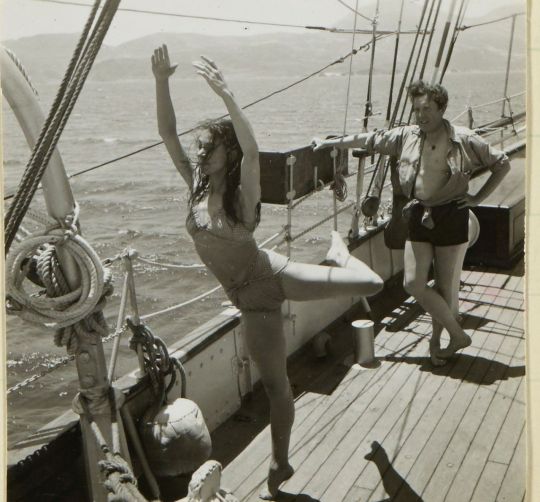

With Joan’s tacit consent, Paddy enjoyed amorous flings, discrete sexual affairs with high society women and sampled the low delights of the brothel. This activity rarely made it into his private letters, but the exceptions could be piquant. Writing in 1958 from Cameroon, where he was on the set of a John Huston movie, he told a (male) friend: “ Errol Flynn and I . . . sally forth into dark lanes of the town together on guilty excursions that remind me rather of old Greek days with you.” In a 1961 letter to the film director John Huston’s wife, Ricki, with whom Leigh Fermor had been having sex with (and would die in a car crash in 1969). “I say,” the passage begins, “what gloomy tidings about the CRABS! Could it be me?” Riffing on pubic lice and their crafty ways, he conjectures that, during a recent romp with an “old pal” in Paris, a force “must have landed” on him “and then lain up, seeing me merely as a stepping stone or a springboard to better things” - to Mrs. Huston, that is. As comic apologies for venereal infection go, the passage is surely a classic.
Like most high flying lives, it was far from blameless. Wounded women were littered in his wake. Some British visitors to Athens were less than impressed by this Englishman who posed as “more Greek than the Greeks”.
Some Greeks shared their disdain. Revisionist historians criticised his role in wartime Crete, and warned their fellow Hellenes that for all his fluency and charm, Leigh Fermor was no latter day Byron. His unoccupied car was blown up outside his Mani house, probably by members of the Greek Communist Party which he had vocally opposed. The accidental fatal shooting of a partisan in Crete led to a long blood feud which made it difficult for Leigh Fermor to re-enter the island until the 1970s, and possibly explains why he chose to settle in the Peloponnese rather than among the hills and harbours of his dreams.
His own books had already eclipsed those incidents, not only among readers of English but also in Greece, where in 2007 the government of his adopted land made him a Commander of the Order of the Phoenix for services to literature.
Travel writers such as the great Jan Morris have described Leigh Fermor as the master of their trade and its greatest exponent in the 20th century.

When ‘A Time of Gifts’ was published in 1977, Frederick Raphael wrote: “One feels he could not cross Oxford Street in less than two volumes; but then what volumes they would be!”
They are not for everyone. Leigh Fermor wrote that written English is a language whose Latinates need pegging down with simple Anglo-Saxonisms, and some feel that he personally could have made more and better use of the mallet. His exuberance is either captivating or florid. It is certainly unique among English prose styles.
Artemis Cooper, his patient and careful biographer wrote that “Paddy had found a way of writing that could deploy a lifetime’s reading and experience, while never losing sight of his ebullient, well-meaning and occasionally clumsy 18-year-old self … this was a wonderful way of disarming his readers, who would then be willing to follow him into the wildest fantasies and digressions”.
Those fantasies and digressions took decades to express. ‘A Time of Gifts’ had arguably been 40 years in the making when it was published in 1977. Its sequel, ‘Between the Woods and the Water’, did not appear until 1986. The third and final volume has been awaited ever since. Following Leigh Fermor’s death, a foot-high manuscript was apparently found on his desk.
Once he knuckled down to it, Leigh Fermor loved playing around with words. He was one of our greatest stylists and he was devoted to producing un-improvable books. But writing did not come easily to him, at least partly because it was something of a distraction from the main event, which was living an un-improvable life of unrepentant gaiety and fun.
For forty odd years, a legion of friends and admirers would beat a path to Paddy and Joan’s door. Artists, poets, royalty and writers came, all taking inspiration from their erudite hosts. A visit was an act of communion, a sharing of ideas and stories.
Leigh Fermor influenced a generation of British travel writers, including Bruce Chatwin, Colin Thubron, Philip Marsden, Nicholas Crane, Rory Stewart, and William Dalrymple. Indeed when Bruce Chatwin died, it was Paddy who scattered Chatwin’s ashes near a church in the mountains in Kardamyli.
When I was there in April 2022, I went to that same church to pay my respects.
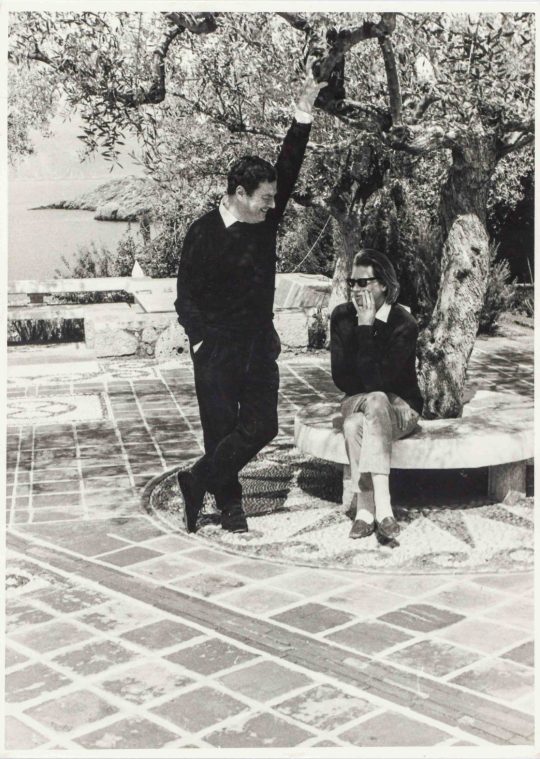

But some of Paddy’s life energy was sucked out of him when Joan died in Kardamyli in June 2003, aged 91. It was related that Joan said to her friend Olivia Stewart, who was visiting: 'I really would like to die but who'd look after Paddy?' Olivia said that she would. A few minutes later, Joan fell, hit her head - and died instantly of a brain haemorrhage. Joan had often quoted Rilke: 'The good marriage is one in which each appoints the other as guardian of his solitude.' Now Paddy Leigh Fermor was all alone.
Leigh Fermor was knighted in 2004, the day of his birthday which he delighted in like a giggling schoolboy. But he missed Joan terribly.
For the last few months of his life Leigh Fermor suffered from a cancerous tumour, and in early June 2011 he underwent a tracheotomy in Greece. As death was close, according to local Greek friends, he expressed a wish to visit England to bid goodbye to his friends, and then return to die in Kardamyli, though it is also stated that he actually wished to die in England and be buried next to his wife, Joan, in Dumbleton, Gloucestershire. He stayed on at Kardamyli until the 9th June 2011, when he left Greece for the last time. He died in England the following day, 10th June 2011, aged 96. It was reported that he had dined in full black tie on the evening of his death. Paddy had style even unto the end.

A Guard of Honour was formed by the Intelligence Corps and a bugler from his former regiment, the Irish Guards, delivered the ‘Last Post’ at Paddy’s funeral. As had been his wish, he was buried beside Joan. On his gravestone in Dumbleton cemetery is an inscription in Greek, a quote from Constantine Cavafy: “In addition, he was that best of all things, Hellenic.”
Although Joan had passed away at the age of ninety-one, after suffering a fall in the Mani. Her body was repatriated to Dumbleton, the place of her birth - ironic that her dream was to be as far as she could possibly go from the rolling humdrum Worcestershire hills. But perhaps she intended to return all along. When Paddy was buried beside her it seemed that the ‘pact of liberty’ that these two lonely souls had forged themselves could be tested in the great elsewhere. Joan was more than his muse (as many of her obituaries were at pains to declare) but his greatest adventure.
To come around full circle from the movie ‘Ill Met By Moonlight’ (1957) that I saw that night in Verbier, my father told me that rather poignantly, General Kreipe, the German commander Leigh Fermor had captured - once an enemy, and later a friend - left behind notes and photographs from across his life. On one of those notes, it was discovered, the following was scribbled from a brief visit to Greece: “Somewhere, amidst all the disarray, was the story of Joan and Paddy, and” it concluded, “…of their lives together.”

His life with Joan and all that she meant to him was one part of the mosaic of who Paddy Leigh Fermor was. But it’s incomplete.
Paddy didn’t like the idea of a biography, and neither did Joan when she was alive. But friends had persuaded them that unless Paddy appointed someone to write his life, he might find himself the subject of a book whether he liked it or not. In Artemis Cooper they couldn’t have chosen a better writer to chronicle Paddy’s life as a man of action and letters. Cooper, was the daughter of another accomplished diplomat and historian, John Julius Norwich, and grand-daughter of Duff and Diana Cooper. As the wife of the historian Antony Beevor, she became a trusted friend of the Leigh Fermors. Cooper was too good of a historian to let her friendship lead her astray from being a faithful but serious biographer. Knowing this, she was told she could go ahead, but she had to promise not to publish anything until after they were both dead.
Paddy did not like being interviewed, and would keep her questions at bay with a torrent of dazzling conversation. He was the master at deflecting discussions away from himself.
He was also very unwilling to let Cooper see many of his papers, though the refusal always couched in excuses. ‘Oh dear, the Diary…’ It was the only surviving one from his great walk across Europe, and I was aching to read it. ‘Well it’s in constant use, you see, as I plug away at Vol III,’ he would say. Or, ‘My mother’s letters? Ah yes, why not. But it’s too awful, I simply cannot remember where they’ve got to…’ It was quite obvious that he and Joan, while being unfailingly generous, welcoming and hospitable, were determined to reveal as little as possible of their private lives.
While they were more than happy to talk about books, travels, friends, Crete, Greece, the war, anything - they would not tell her any more than they would have told the average journalist. But she persisted and got closer than most. He showed particularly gallantry in not talking about his romantic entanglements. But she soon twigged that anytime he described a woman as ‘an old pal’ it was a sure bet that he had an affair with her.

Intriguingly, Paddy liked to claim he was descended from Counts of the Holy Roman Empire, who came to Austria from Sligo. Paddy could recite ‘The Dead at Clomacnoise’ (in translation) and perhaps did so during a handful of flying visits to Ireland in the 1950s and 1960s, partying hard at Luggala House or Lismore Castle, or making friends with Patrick Kavanagh and Sean O’Faolain in Dublin pubs. He once provoked a massive brawl at the Kildare Hunt Ball, and was rescued from a true pounding by Ricki Huston, a beautiful Italian-American dancer, John Huston’s fourth wife and Paddy’s lover not long afterwards.
And yet, a note of caution about Paddy’s Irish roots is sounded by his biographer, Artemis Cooper, who also co-edited ‘The Broken Road’, the final, posthumously published instalment of the trilogy. “I’m not a great believer in his Irish roots,” she said of Leigh Fermor in an interview, “His mother, who was a compulsive fantasist, liked to think that her family was related to the Viscount Taaffes, of Ballymote. Her father was apparently born in County Cork. But she was never what you might call a reliable witness. She was an extraordinary person, though. Imaginative, impulsive, impossible - just the way the Irish are supposed to be, come to think of it. She was also one of those sad women, who grew up at the turn of the last century, who never found an outlet for their talents and energies, nor the right man, come to that. All she had was Paddy, and she didn’t get much of him.”
And I think that’s the point, no one really got much of Paddy Leigh Fermor even as he only gave a crumb of himself to others but still most felt grateful that it was enough to fill one’s belly and still feel overfed by him.
Paddy never tried to get to the bottom of his Irish ancestry, afraid, no doubt, of disturbing the bloom that had grown on history and his past, a recurring trait. “His memory was extraordinary,” Artemis Cooper noted, “but it lay dangerously close to his imagination and it was a very porous border.”

Within the Greek imagination many Greeks saw in Paddy Leigh Fermor as the second coming of Lord Byron. It’s not a bad comparison.
Lord Byron claimed that swimming the Hellespont was his greatest achievement. 174 years or so later, another English writer, Patrick Leigh Fermor - also, like Byron, revered by many Greeks for his part in a war of liberation - repeated the feat. Leigh Fermor, however, was 69 when he did it and continued to do it into his 80s. Byron was a mere 22 years old lad. The Hellespont swim, with its mix of literature, adventure, travel, bravery, eccentricity and romance, is an apt metaphor for Leigh Fermor’s life. Paddy Leigh Fermor was the Byron of his time. Both men had an idealised vision of Greece, were scholars and men of action, could endure harsh conditions, fought for Greek freedom, were recklessly courageous, liked to dress up and displayed a panache that impressed their Greek comrades. Like a good magician it was also a way to misdirect and conceal one’s true self.

What or who was the true Paddy Leigh Fermor?
Like Byron, Leigh Fermor appeared as a charismatic and assured figure. He was a sightseer, consuming travel, culture, and history for pleasure. He was an aristocrat moving in the social circles of his time. He was a gifted amateur scholar, speculating on literary and historical sources. Leigh Fermor, Byron’s own identity, is subject to textual distortion; it emerges from a piece of occasional prose in his books and is shaped by the claims of correspondence on a peculiarly fluid consciousness.
There is no hard and fast distinction to be drawn here between real and imagined, only a continuity of relative fictions that lie between memory and imagination as his biographer asserted. If there is a will to assert identity here, to disentangle fact and fiction, to give things as they really are and nail down the real Leigh Fermor then it is somewhere between the two. This is where we will find Paddy.
For many his death marked the passing of an extraordinary man: soldier, writer, adventurer, a charmer, a gallant romantic. As a writer he discovered a knack for drawing people out and for stringing history, language, and observation into narrative, and his timing was perfect. Paddy often indulged in florid displays of classical erudition. His learned digressions and serpentine style, his mannered mandarin gestures, even baroque prose, which Lawrence Durrell called truffled and dense with plumage, were influenced by the work of Charles Doughty and T.E. Lawrence. But one can’t compare him. I agree with the acclaimed writer Colin Thurbon who said, “There is, in the end, nobody like him. A famous raconteur and polymath. Generous, life-loving and good-hearted to a fault. Enormously good company, but touched by well-camouflaged insecurities. I would rank him very highly. ‘The finest travel writer of his generation’ is a fair assessment.”
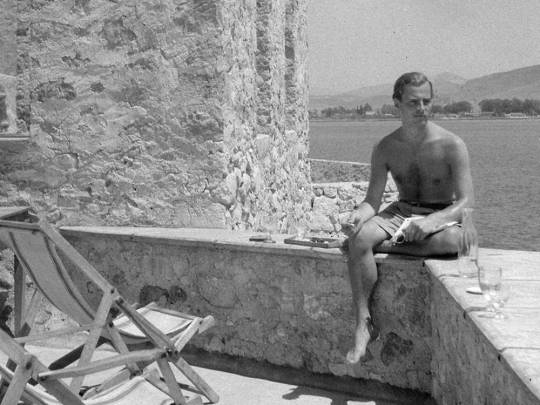

As a child I didn’t really know who Paddy Leigh Fermor was other than this very cheerful and charismatic old man was kind, attentive, and took a boyish delight in everything you were doing. Only later on in adulthood was it clear to that Paddy was not only among the outstanding writers of his time but one of its most remarkable characters, a perfect hybrid of the man of action and the man of letters. Equally comfortable with princes and peasants, in caves or châteaux, he had amassed an enviable rich experience of places and people. “Quite the most enchanting maniac I’ve ever met,” pronounced Lawrence Durrell, and nearly everyone who’d crossed paths with him had, it seemed, come away similarly dazzled.
I am equally dazzled - more smitten in retrospect - for alas they don’t make men like Paddy any more. But every time I dip back into his books I think I discover a little bit more of who Paddy Leigh Fermor was because I find him some where between my memory and my imagination.
#essay#paddy leigh fermor#leigh fermor#joan raynor#joan leigh fermor#greece#crete#second world war#SOE#war#british army#history#general kreipe#stanley moss#literature#author#writer#travel#explorer#wanderlust#travel writing#europe#mani#peloponnese#kardamlyi#lord byron#ill met by moonmight#film#movie#personal
110 notes
·
View notes
Photo
Allied Bombing of Germany
The Allied strategic bombing of Germany during World War II (1939-45) had multiple aims, which included destroying Germany's capacity to produce weapons; disrupting transport networks and supplies of oil, steel, and coal; destroying the German air force; and breaking civilian morale. To these ends, industrial cities, factories, railways, airfields, and dams were struck throughout the conflict.
Secondary goals of the strategic bombing campaign by the British Royal Air Force (RAF) and United States Army Air Force (USAAF) included boosting home morale that Germany was paying a price for its invasion of Europe and bombing of Britain. Another aim was to demonstrate to the USSR that the Western allies were assisting the Soviet campaign on the Eastern Front. Some Allied commanders believed that the war could be won using air power alone, avoiding a land invasion. As it turned out, despite the bombers causing tremendous physical damage and the deaths of hundreds of thousands of civilians, Germany fought on, and only a land operation from the east and west would finally win the war.
Why Did the Allies Bomb Germany?
The official military objectives of the strategic bombing of Germany are indicated in several directives formulated by the Allied Joint Chiefs of Staff. The Casablanca conference in January 1943 noted that the objective of the bombing offensive was:
The progressive destruction and dislocation of the German military, industrial and economic system, and the undermining of the morale of the German people to a point where their capacity for armed resistance is fatally weakened.
(Dear, 196)
The Casablanca objective was amended by the Pointblank Directive of June 1943. This emphasised the importance of destroying German fighter plane production in readiness for the D-Day Normandy landings (Operation Overlord) planned for the summer of 1944. Before the Allies could contemplate a land invasion of Continental Europe they had to achieve air superiority or their armada would be destroyed. The Quebec conference of August 1943 reaffirmed the objectives of Casablanca and Pointblank but removed the objective regarding civilian morale.
Other aims of the bombings, perhaps not officially expressed but there, nonetheless, were to show the British and American public and Russia that something was being done to take the war to Germany. In the absence of a land attack on Germany, bombing was the next best thing. As the German Armaments Minister Albert Speer (1905-1981) noted, the air war became "a second front", one that absorbed men and machines which otherwise could have been used on the Eastern Front against Russia and in coastal defences in northern France.
Continue reading...
26 notes
·
View notes
Text
His Last Bow
Originally titled in full "His Last Bow. The War Service of Sherlock Holmes" and later "His Last Bow: An Epilogue of Sherlock Holmes", this was originally published in 1917.
It is the final story in His Last Bow, the final short story in the canon covered by Letters from Watson and agreed by all the key chronologists to be the final canon appearance of Holmes and Watson.
Sir Arthur Conan Doyle had openly supported British entry into the First World War in 1914.
The story came about after a visit to the Western Front in 1916; asked by a French general what Holmes was doing, Doyle had responded that he was too old to serve. He then decided to write this story as a means of boosting morale.
To put it mildly, the British public had gone a bit spy-crazy in the lead up to the war; fearing "Teutons serving them croutons" i.e. Germans living in the UK acting as intelligence agents for the Kaiser.
The Riddle of the Sands is one such work of popular literature on this theme, which is the subject of Letters from Carruthers coming in September.
There was also the fantastical works of William Le Queux, who started off with the French and Russians as his enemies before switching to the Germans; he also had his works serialised in the Daily Mail, a British middle-market tabloid that was founded in 1896 and has been happily engaging in right-wing sensationalism since to the point Wikipedia has banned them as a source. Le Queux for his part believed the Germans were out to get him for exposing their spy networks - he hadn't, they weren't and the Metropolitan Police refused him protection.
The Benz company had produced the first practical motor car in 1885; they of course later merged with Daimler to become Mercedez-Benz. I cannot find a 100hp example of their vehicles.
The German Chancellor in 1914, Theobald von Bethmann Hollweg, was a moderate, who reluctantly went along with many German policies like unrestricted submarine warfare and tried to initiate peace proposals on a number of occasions in the war before being ousted in 1917.
Flushing is the historical English name for the Dutch port of Vlissingen; it had a ferry connection to Sheerness until 1994.
At the outbreak of war, diplomats on both sides were allowed to return home unmolested, after locking down their embassies and burning anything sensitive they could not take with them.
Britain, France and Prussia had signed a treaty in 1839 guaranteeing the neutrality and independence of Belgium. The German invasion of the country on 3 August gave the UK justification for war and moved a Cabinet divided over the matter to firm unity.
There was a fear of Irish civil war at this point; the Liberal government, reliant on Irish and Labour support for a Commons majority after the two elections of 1910, had passed legislation creating a devolved government for the island, called Home Rule. This was vehemently opposed by Ulster Protestants and both sides were receiving weapons - from Germany in fact - in preparation for a fight as Whitehall tried to arrange a compromise. The Germans in fact believed the British would be distracted by a civil war, but in fact the Home Rule legislation was suspended for the duration and both militias decided to support the war effort. That stopped things... until the more radicial Irish Republic Brotherhood launched the Easter Rising of 1916.
"Window-breaking Furies" refers to the suffragette movement that sort votes for women, some of who engaged in direct action like breaking windows and also planting bombs or arson, although they made sure the latter was done when the buildings were empty to avoid killing anyone. These tactics were as controversial at the time as the tactics of modern-day groups like Just Stop Oil. When the war broke out, the suffragettes stopped their militant actions and supported the war effort; their imprisoned members being released as part of an amnesty.
John Bull is a national personification of the UK, typically a stout middle-aged man in a Union Jack waistcoast, frequently seen in cartoons at this time. He rather fell out of popular use post-war and is rarely seen today, unlike Britannia, who remains a widely used figure.
The Rosyth Dockyard was built from 1909 for refitting Royal Navy ships and submarines; although now privatised, it retains that role and is currently building the five Type 31 frigates.
Carlton Terrace was the home of the German Embassy until 1945; after the war, the property and its contents were sold off at auction. The Federal Republic of Germany set up at Belgrave Square in 1951 and remains there to this day.
Junkers were the land-owning aristocracy of Prussia, who exercised considerable political power up until 1945, at which point most of their holdings ended up in the USSR, Poland or what became East Germany. The land was broken up, usually ending up in collective farms; accused of war crimes, those Junkers who ended up in Soviet hands frequently ended up in NKVD camps or even executed. Their descendants did not get them back after reunification.
The King's English is another name for Received Pronunciation, the "standard" dialect and accent of British English.
Tokay or Tokaji is a sweet wine from the Tokaj regions of Hungary and Slovakia, the designation being protected under EU law in a similar way to Champagne. Imperial Tokay, which was the highest quality Tokaji Essencia, was reserved for the Austrian imperial cellars, often being passed to other European monarchs as gifts. This stuff is still drinkable after over 200 years and even the relatively new stuff isn't cheap.
A naval flotilla would be based at Harwich in both World Wars.
The reference to Holmes being sixty here is where the common estimate of 1854 being his birth year comes from.
Portland is a prison and young offenders' institution in Dorset. Notable past inmates include George Edalji (whose miscarriage of justice was exposed by Doyle), John Babbacombe Lee ("The Man They Couldn't Hang") and the controversial comedian Roy "Chubby" Brown.
Fratton is an area of Portsmouth.
In reality, the Home Section of the Secret Service Bureau, later MI5, had managed to identify the key German agents by monitoring their postal correspondence. The police then rounded them up in August 1914 and once the cross-sea cables were cut, contact with any agents in the UK became close to impossible. Little intelligence of any use came from them in any event; the Germans seem to have not even been aware of the British Expeditionary Force being sent to France, which was hardly a small event. Gustav Steinhauer, head of German naval intelligence's British section, got subjected to a rant about his agency's incompetence from the Kaiser that lasted the better part of two hours.
Twelve German spies would be executed during the war, eleven by firing squad at the Tower of London, which hosted its final execution (also of a spy) in 1941.
Skibbareen is a town in County Cork, now in Ireland.
The final speech by Holmes at the end also featured in the 1942 Basil Rathbone film Sherlock Holmes and the Voice of Terror, based on this story.
So Holmes and Watson drive off into the sunset. What happened to them after that? All we know is that both survived the war and at some point Dr Watson stopped writing about his dear friend. They deserve to have had a long retirement.
I will be doing these for the individual chapters of the novels next year; I have already done ones for the first two chapters of A Study in Scarlet that I will repost.
44 notes
·
View notes
Note
So, Zimmerman and the German Empire had hoped to entice Mexico to join the Central powers of the US entered the war on the side of Britain and France. My question is why? Mexico was already fighting its own bloody civil war and didn’t really seem in a position to help Germany. So why didn’t the Germans reach out to the ABC states; Argentina, Brazil, and Columbia?
Mexico had a land border. Argentina, Brazil, and Colombia would have needed to launch a naval invasion which was *highly* dubious (not to say that Mexico starting a land war against the USA wasn't also dubious). In fact, the Mexican commission that investigated the feasibility of the German plan came to the following conclusions:
Mexico was currently engaging in a civil war and lacked the military capacity to wage war against the United States
Even if they weren't, Mexico did not have the capability to effectively fight the United States, given their easy occupation of Veracruz in 1914.
Even if they somehow won, administering the promised new territories (Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona) was beyond Mexican civilian government capabilities.
It would void their treaties with Argentina, Brazil, and Colombia which would be positively devastating to their foreign standing and trade relationships.
Germany couldn't finance their war like they said they could.
So yeah, Carranza was very smart to reject Zimmerman's plan.
Thanks for the question, Anon.
SomethingLikeALawyer, Hand of the King
16 notes
·
View notes
Text

In 1941 a secret British radio station called on Germans to rise up against Hitler. Run by German exiles, it was explicitly left wing. The station’s target audience was “the Good German”. Its broadcasts were serious and idealistic: a ray of light amid totalitarian darkness. They were also a complete flop. With Nazi propaganda rampant, and Hitler’s armies seemingly invincible and on the march across Europe, few bothered to listen in.
It was at this point that Britain’s wartime intelligence services tried a more radical approach. That summer, a talented journalist called Sefton Delmer was given the job of beating the Nazis at their own information game. Delmer spent his childhood in Berlin and spoke fluent German. In the early 1930s he chronicled Hitler’s rise to power – flying in the Führer’s plane and attending his mass rallies – as a correspondent for the Daily Express.
Working from an English country house, Delmer launched an experimental radio station. He called it Gustaf Siegfried Eins, or GS1. Instead of invoking lofty precepts, or Marxism, Delmer targeted what he called the “inner pig-dog”. The answer to Goebbels, Delmer concluded, was more Goebbels. His radio show became a grotesque cabaret aimed at the worst and most Schwein-like aspects of human nature.
As Peter Pomerantsev writes in his compelling new study How to Win an Information War, Delmer was a “nearly forgotten genius of propaganda”. GS1 backed Hitler and was staunchly anti-Bolshevik. Its mysterious leader, dubbed der Chef, ridiculed Churchill using foul Berlin slang. At the same time the station lambasted the Nazi elite as a group of decadent crooks. They stole and whored, it said, as British planes bombed and decent Germans suffered.
Delmer’s goal was to undermine nazism from within, by turning ordinary citizens against their aloof party bosses. A cast of Jewish refugees and former cabaret artists played the role of Nazis. Recordings took place in a billiards room, located inside the Woburn Abbey estate in Bedfordshire, a centre of wartime operations. Some of the content was real. Other elements were made up, including titillating accounts of SS orgies at a Bavarian monastery.
The station was a sensation. Large numbers of Germans tuned in. The US embassy in Berlin – America had yet to enter the war – thought it to be the work of German nationalists or disgruntled army officers. The Nazis fretted about its influence. One unimpressed person was Stafford Cripps, the future chancellor of the exchequer, who complained to Anthony Eden, the then minister for foreign affairs, about the station’s use of “filthy pornography”.
By 1943, Delmer’s counter-propaganda operation had grown. He and his now expanded team ran a live news bulletin aimed at German soldiers, the Soldatensender Calais, as well as a series of clandestine radio programmes in a variety of languages. Delmer’s artist wife Isabel joined in. She drew explicit pictures showing a blonde woman having sex with a dark-skinned foreigner. Partisans sent the pamphlets to homesick German troops stationed in Crete.
Others who made a contribution to Delmer’s productions included Ian Fleming, the creator of James Bond, and the 26-year-old future novelist Muriel Spark. Fleming worked for naval intelligence. He brought titbits of information that made the show feel genuine, including the latest results from U-boat football leagues. Many Germans guessed the station was British. But they listened anyway, feeling it represented “them”.
Pomerantsev is an expert on propaganda and the author of two previous books on the subject, Nothing Is True and Everything Is Possible and This Is Not Propaganda. The son of political dissidents in Kyiv, he was born in Ukraine and grew up in London. During the 00s he lived in Moscow and worked there as a TV producer. Since Vladimir Putin’s 2022 invasion he has been part of a project that documents Russian war crimes in Ukraine.
Like Delmer, Pomeranstev has personal experience of two rival cultures: one authoritarian, the other liberal and democratic. He draws parallels between the fascist 1930s and our own populist age. The same “underlying mindset” can be seen in dictators such as Putin and Xi Jinping, and wannabe strongmen and bullies such as Donald Trump. “Propagandists across the world and across the ages play on the same emotional notes like well-worn scales,” he observes.
In Pomerantsev’s view, propaganda works not because it convinces, or even confuses. Its real power lies in its ability to convey a sense of belonging, he argues. Those left behind feel themselves emboldened and part of a special community. It is a world of grievance, victimhood and enemies, where facts are meaningless. What matters are feelings and the illusion propaganda lends of “individual agency”. Its practitioners bend reality. And – as with Putin’s fictions about Ukraine – make murder possible.
The book offers a few ideas as to how we might fight back. When horrors were uncovered in Bucha, the town near Kyiv where Russian soldiers executed civilians, Ukraine’s president, Volodymyr Zelenskiy, appealed to the Russian people. This didn’t cut through. Most preferred to believe the version shown on state TV: that Moscow was waging a defensive fight against “neo-Nazis”. It was a comforting lie that absolved Russians of personal responsibility.
Ukrainian activists hit a similar wall when they cold-called Russians and told them about the destruction caused by Kremlin bombing. Many called relatives in St Petersburg and other Russian cities to explain they were under attack. Typically, their family members did not believe them. “They really brainwashed you over there,” one said.
The activists had more success when they mentioned taxes or travel restrictions – issues that spoke to the self-interested “pig-dog”. Pomerantsev suggests that Delmer’s approach worked because he allowed people to care about the truth again, nudging them towards independent thought, while avoiding the pitfall of obvious disloyalty. He brought wit and creativity to his anti-propaganda efforts as well, turning his radio shows into bravura transmissions.
Pomerantsev makes an intriguing comparison between der Chef and Yevgeny Prigozhin, the Russian oligarch who in summer 2023 staged a short-lived rebellion against Putin. Two months later, Prigozhin died in a plane crash. The oligarch was a charismatic figure who roasted Russia’s generals for their incompetent handling of the war. He used earthy prison slang. It was this ability to communicate in plain language that made him popular – and a rival.
The book muses on whether Delmer was ultimately good or bad. Are tricks and subterfuge justified in pursuit of noble goals? It concludes that the journalist’s greatest insight was his understanding of his own ordinariness, and how this might be exploited by unscrupulous governments and rabble-rousing individuals. “He was vulnerable to propaganda for the same reasons we all are – through the need to fit in and conform,” Pomerantsev notes.
Daily inspiration. Discover more photos at Just for Books…?
16 notes
·
View notes
Text
Heinrich Prinz zu Sayyn-Wittgenstein

This is Heinrich Wittgenstein, a German Night Fighters ace, timeline:
1916: He was born in Copenhagen
1932: He joined the Hitler Youth
1933: He became a Kameradschaftsführer (group leader).
1933: Adolf Hitler was appointed Reich Chancellor
1933: From Easter until fall of 1933 he led the group's military-sports activities as a Wehrsportleiter
1934: He led the work unit 2/1/113 (Gefolgschaft) and received further pre-military sports training at the different camps of the unit 113 (Bann) and at the Regional Leaders' School (Gebietsführerschule)
1935: He received his Abitur from the Realgymnasium, a higher education facility, in Freiburg in Breisgau.
1937: Wittgenstein decided on a military career and joined the 17. Kavallerie-Regiment (17th Cavalry Regiment) in Bamberg.
1937: He transferred to the Luftwaffe in the summer and, in October, he was accepted at the flight training school in Braunschweig.
1938: He received his officer's commission and was promoted to Leutnant (second lieutenant)
1939: The Second World War began.
1940: Wittgenstein experienced his first combat action on the Western Front in the Battle of France and, later, during the Battle of Britain.
1940: He received the Iron Cross second class.
1940: He received the Iron Cross first class.
1940-41: Wittgenstein returned to pilot school and took his Luftwaffe Advanced Pilot's Certificate 2
1941: In preparation for Operation Barbarossa, the German invasion of the Soviet Union, his unit moved to Eichwalde in East Prussia.
1941: Wittgenstein transferred to the night fighter force. By this time, he had flown 150 combat missions.
1941:
1942: Wittgenstein had left KG 51 by January, after he had volunteered for the night fighter force and been appointed Staffelkapitän (squadron leader).
1942: He claimed his first nocturnal victory.
1942: Wittgenstein received the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (Ritterkreuz des Eisernen Kreuzes) on 7 October 1942, after 22 aerial victories.
1943: Wittgenstein was moved to the Eastern Front in February 1943 after he had been appointed Gruppenkommandeur (group commander) of the IV./Nachtjagdgeschwader 5 (IV./NJG 5—4th Squadron of the 5th Night Fighter Wing) on 1 December 1942.
1943: He was appointed Gruppenkommandeur of the II./NJG 3.
1943: Wittgenstein became the 290th recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves after 54 aerial victories .
1943: Wittgenstein was ordered to take over command of the II./Nachtjagdgeschwader 2 (II./NJG 2—2nd Groupe of the 2nd Night Fighter Wing).
1944: He was appointed Geschwaderkommodore (wing commander) of NJG 2 ; he had already reached 68 aerial victories.
1944: He died on January 21st.
1944: He was posthumously awarded the 44th Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves and Swords.
Sources:
Wikipedia: Heinrich Wittgenstein
Military Wiki: Heinrich Wittgenstein
❗❗I DON'T SUPPORT NAZISM,FASCISM OR ZIONISM IN ANY WAY, THIS IS JUST AN EDUCATIONAL POST❗❗
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
00QAD Night in: “World on Fire” episode 1 (2019)

Join us for episode 1 of the series World on Fire (featuring Sean Bean) hosted by @kmk1701d!
Synopsis via IMDB:
“A story of the effects of World War II on the lives of ordinary people from all sides of the conflict. The first of seven episodes tells the story of the first year of the war, starting with the German invasion of Poland in September 1939 and ending with the Battle of Britain.”
Watch party details:
Date: Sunday, December 31, 2023
Time: 2pm New York / 7pm London / 2am Hong Kong (Monday)
Location: 00QAD Discord server in the #event_chatroom. Please send us a non-anon ask to receive an invite. All invites are subject to expire within a day unless you wish to be an active part of the fandom.
14 notes
·
View notes
Note
Raises hand. Hi. I like history. Here's my theory for the ultrakill timeline. I get rambly so. Im sorry
If Ultrakill takes place in the future of a worse ww1, you have to consider the political climate of the time, which was more of a bar fight that started because someone hit your friend while trying to hit someone else. Main points though:
- The central powers were all having tensions already due to the rise in nationalist ideals, while the Allies had a few members who only joined the war for more political influence around the globe (mainly Japan and Russia, both of which planned to invade other countries anyway and now had a pretty good excuse).
- Russia still invades Germany, causing tensions to rise even further and for escalations in technological warfare to be taken. [Particularly in guns, tanks and bombs]
- Japan still takes Chinese and pacific territory, which causes its own individual problem in eastern territories.
The entry of the United States in 1917 [The war irl ends in 1918]
I think it's safe to assume that instead of backing down like it happened in real life, The Central Powers went in even deeper, creating machines to fight in the place of humans, which made them too dangerous even for the US to handle, and so causes the creation of nuclear bombs, which will eventually be what causes the total annihilation of humanity [Most likely because they were all activated at once]. But let's put a pin on that.
- Everything was made very hastily in WW1 for invasion purposes, so that would explain why a lot of them seem to be human operated (or at least partially influenced/controlled?) like the Guttermen, so those were likely the first few machines invented. Big, robust and durable for as long as German defences held.
- If we are to believe that the Earthmover was japanese-made, then there's a great possibility that there was more involvement from Japan in the combat, and that it switched sides at some point for some kind of benefit in European soil. Given the size and structure of the machine, my main theory is that it wasn't housing civilians, but rather soldiers (maybe even machines? My bet is on SwordsMachines) which would get carried to battle and ensure a higher chance of survival since they'd be getting dropped off a higher advantage point.
- Since the United States joined much later on and was overseas [making it harder for invasions], they had the technological upperhand, which lends credibility to your theory that the V1 machines were manufactured over there. V1 was made to destroy Earthmovers, so it happened at least a good few decades before the end.
- Streetcleaners might've been built by the Allies from what I gather, especially given the destruction France and Britain endured during the war, and given their general aesthetic I don't doubt it. Also a very hasty design, probably because things were building up and there was high demand to get rid of all the corpses.
So recap: Guttermen are German, Earthmovers/Swordsmachines are Japanese (who changed sides at some point, giving the US ground to attack them), Streetcleaners are probably Ally-sided but I'm unsure, and V1/V2 are american, built to counter all their ancestors. And all of this isn't considering the hell expeditions yet, which is where Drones would come in as less of a combat-focused machine and more of a tool.
Sorry for rambling in your inbox, I think I'm insane after trying to rationalize Ultrakill (<- in a good way)
!!! No don't be sorry this is awesome and makes a lot of sense!!! :DD tysm!!! I'm not going to lie my knowledge on WW1 is severely lacking so it's nice to see someone with more knowledge than me give their opinion!!
13 notes
·
View notes