#2001 meta
Text

Hal’s deactivation is hard hitting across both the movie and the book. It’s been dissected a million times and likely more in the future. Most recently in the way of Hal having little agency…he has no arms to ward off his attacker or means of defense (but I’d argue killing Frank and the others was his defense, especially in the movie when his reasoning is more ambiguous). I do love the idea this is following and hope to see more of it in the future, however the way I’m approaching it is with a more romantic lense.
The entire lobotomy sequence is heart wrenching and almost worse in the novel purely because we get to see Dave’s thoughts on it. Not only do we hear Hal’s frightened pleas for his life but we get the ‘attacker’ perspective and it’s… an act of mercy.
While there is the themes of survival and violence this is approached with a softer touch. It’s much more that he is putting Hal out of his misery. Ending his suffering. Not putting him down like an animal but rather the harsh decision faced when one has an ill/dying lover.
“The only answer was to cut out the higher centers of this sick but brilliant brain, and to leave the purely automatic regulating systems in operation” 155
After the job is done Dave forgives Hal incredibly quickly once all of the facts are in. He can quickly pull together the mental break that must’ve happened and recognizes that Hal had the very human ‘fight or flight’ response to what he had been through. He had always been treated like a sixth crew member, respected and talked to like anyone else but it is only “post Mortem” that Dave recognizes how human Hal was and that true emotion might be more than theorizing.
“And yet, in one very real sense, he was not alone. Before he could be safe, be must be lonelier still.” 153
The fact that Dave genuinely sees Hal as his last true connection. Even after the murders. How he fights and forgives and comes up with excuses to not have to go through with the enviable because then will he be truly alone… but he also knows logically- Hal isn’t right and can’t be left active. Despite his feelings safety and protocol come first.
Hal is human in Dave’s eyes and it makes things all the more tragic, it’s what turns shutting off functions into lobotomy, into murder. He thinks he won’t feel pain, not because he’s machine but because there’s no sense in the human cortex. So human that his “true” voice is unrecognizable and horrifying.
“Bowman could bare no more. He jerked out the last unit, and Hal was silent forever.” 157
It’s not rage which he makes the final blow, it’s sorrow. It’s pulling the plug.
Some of Hal’s lines in the book particularly, as we get more insight into him as well and some of his pleading. His honest to god confusion and panic because he’s so young and has no idea of sleep and …
“I don’t understand why you’re doing this to me. . . You are destroying my mind. . . Don’t you understand? I will become childish. . . I will be nothing. . .” 156
I don’t know, I’m becoming borderline incoherent but there’s something here that’s so tender and sorrowful that I have to address it. I’m a sucker for the violence = intimacy metaphor just as anyone but the unwitting murderer is also an angle I have to adore.
Maybe in another life Hal got to be a little gay Victorian with someone to hold his hand on his sick bed rather than be murdered. I just think he deserves better; they both do.
Computer death sad -> he should be fed soup
This is when you know you should go to bed.
#sorry that it’s a bit disconjointed - it glitched during the initial draft and half my wording and idea were lost#hal 9000#meta#2001 a space odyssey#2001 aso#space odyssey#dave bowman#david bowman#metaphor#science fiction#halman#scene analysis#ramble#a space odyssey#2001 meta
163 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ok but I love Barbie’s opening scene because the 2001 homage could’ve so easily been a shallow gag where the whole joke is “get the reference?” but instead it’s priming you for how completely literal the Barbie-as-Monolith idea is to the movie’s themes and conflict.

Seeing the movie I was a little caught off guard by just how unreal the “real world” was both in and out of how people specifically reacted to Barbie’s presence, but in retrospect the opening counts on an understanding of 2001 to immediately say
“This isn’t just an alt universe where Barbieland exists adjacent to reality, but one where Barbie is without exaggeration a primordial cosmic force the discovery of which fundamentally altered how human beings think and evolve.”

The Monolith as a visual metaphor for Barbie’s impact on the world is already a clever little bit of observational comedy, but taking the scene beyond metaphor and into the literal text of the film, to where Barbie’s presence as this reality-shaping object of import is just taken as a given by everyone in the film, that’s freakin genius.
It’s rare to see such an overt reference to another piece of media end up being such a smart and pivotal bit of actual storytelling, and its fascinating to see the film explore “what if humanity’s relationship to the Monolith was reciprocal and the Monolith was actually a Person?”
#barbie movie#barbie 2023#2001 a space odyssey#margot robbie#Greta Gerwig#ryan gosling#Ken#Allan#just Ken#Simu Liu#issa rae#america ferrera#meta
623 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hannibal & Clarice on crack butchering each other verbally for 1,5 minutes straight. What else is there to say
#clannibal#hannibal lecter#clarice starling#silence of the lambs#anthony hopkins#hannibal x clarice#horror classics#hannibal 2001#dr hannibal lecter#jodie foster#thomas harris#hannibal and clarice#hannibal#hannibal the cannibal#hannibal fandom#hannibal lecter fandom#hannibal memes#hannibal meta#hannibal edit
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
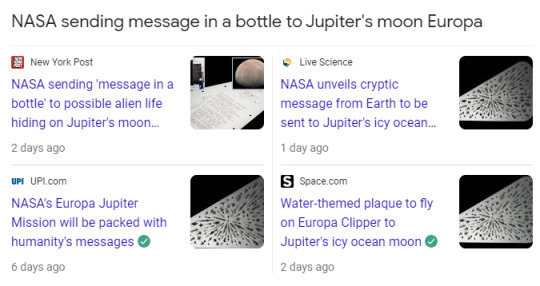
Have you fucking read Space Odyssey
“ALL THESE WORLDS ARE YOURS – EXCEPT EUROPA. ATTEMPT NO LANDING THERE.”
That's like the one thing you don't touch
7 notes
·
View notes
Text




Some more roles by Eric Stuart
#Eric Stuart#Shaman King#Shaman King 2001#Kirby#Kirby Right Back At Ya!#Dinosaur King#Yugioh#Yugioh GX#Marco Lasso#Meta Knight#Dr. Z#Bastion Misawa#anime
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Contrary to Presgurvic’s claims, his 2001 musical is very different from Shakespeare’s play—” Listen, I didn’t spend half my life listening to people dutifully parroting the West Side Story-is-an-adaptation of-R&J line and watching ~straight” stagings that change everything for some asshole critics to gripe over a French musical having *checks notes* no Shakespearean paraphrase, some alternative character interpretation, one changed plot point, and all of two symbolic dance characters. Chill, s’il vous plaît.
#romeo et juliette#retj#roméo et juliette#retj meta#won’t someone please think of the shakespeare???!!!!!#i do clown—literally every half day in my blog#i eat r&j anti clowns for breakfast#i get lazy eye over every little adaptational change no matter how justified#so when i tell you that presgurvic’s 2001 version is legit#i ain’t playing#he understood the assignment#a+++++
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
Here's THE masterpost of free and full adaptations, by which I mean that it's a post made by the master.
Anthony and Cleopatra: here's the BBC version, here's a 2017 version.
As you like it: you'll find here an outdoor stage adaptation and here the BBC version. Here's Kenneth Brannagh's 2006 one.
Coriolanus: Here's a college play, here's the 1984 telefilm, here's the 2014 one with tom hiddleston. Here's the Ralph Fiennes 2011 one.
Cymbelline: Here's the 2014 one.
Hamlet: the 1948 Laurence Olivier one is here. The 1964 russian version is here and the 1964 american version is here. The 1964 Broadway production is here, the 1969 Williamson-Parfitt-Hopkins one is there, and the 1980 version is here. Here are part 1 and 2 of the 1990 BBC adaptation, the Kenneth Branagh 1996 Hamlet is here, the 2000 Ethan Hawke one is here. 2009 Tennant's here. And have the 2018 Almeida version here. On a sidenote, here's A Midwinter's Tale, about a man trying to make Hamlet. Andrew Scott's Hamlet is here.
Henry IV: part 1 and part 2 of the BBC 1989 version. And here's part 1 of a corwall school version.
Henry V: Laurence Olivier (who would have guessed) 1944 version. The 1989 Branagh version here. The BBC version is here.
Julius Caesar: here's the 1979 BBC adaptation, here the 1970 John Gielgud one. A theater Live from the late 2010's here.
King Lear: Laurence Olivier once again plays in here. And Gregory Kozintsev, who was I think in charge of the russian hamlet, has a king lear here. The 1975 BBC version is here. The Royal Shakespeare Compagny's 2008 version is here. The 1974 version with James Earl Jones is here. The 1953 Orson Wells one is here.
Macbeth: Here's the 1948 one, there the 1955 Joe McBeth. Here's the 1961 one with Sean Connery, and the 1966 BBC version is here. The 1969 radio one with Ian McKellen and Judi Dench is here, here's the 1971 by Roman Polanski, with spanish subtitles. The 1988 BBC one with portugese subtitles, and here the 2001 one). Here's Scotland, PA, the 2001 modern retelling. Rave Macbeth for anyone interested is here. And 2017 brings you this.
Measure for Measure: BBC version here. Hugo Weaving here.
The Merchant of Venice: here's a stage version, here's the 1980 movie, here the 1973 Lawrence Olivier movie, here's the 2004 movie with Al Pacino. The 2001 movie is here.
The Merry Wives of Windsor: the Royal Shakespeare Compagny gives you this movie.
A Midsummer Night's Dream: have this sponsored by the City of Columbia, and here the BBC version. Have the 1986 Duncan-Jennings version here. 2019 Live Theater version? Have it here!
Much Ado About Nothing: Here is the kenneth branagh version and here the Tennant and Tate 2011 version. Here's the 1984 version.
Othello: A Massachussets Performance here, the 2001 movie her is the Orson Wells movie with portuguese subtitles theree, and a fifteen minutes long lego adaptation here. THen if you want more good ole reliable you've got the BBC version here and there.
Richard II: here is the BBC version. If you want a more meta approach, here's the commentary for the Tennant version. 1997 one here.
Richard III: here's the 1955 one with Laurence Olivier. The 1995 one with Ian McKellen is no longer available at the previous link but I found it HERE.
Romeo and Juliet: here's the 1988 BBC version. Here's a stage production. 1954 brings you this. The french musical with english subtitles is here!
The Taming of the Shrew: the 1980 BBC version here and the 1988 one is here, sorry for the prior confusion. The 1929 version here, some Ontario stuff here, and here is the 1967 one with Richard Burton and Elizabeth Taylor. This one is the Shakespeare Retold modern retelling.
The Tempest: the 1979 one is here, the 2010 is here. Here is the 1988 one. Theater Live did a show of it in the late 2010's too.
Timon of Athens: here is the 1981 movie with Jonathan Pryce,
Troilus and Cressida can be found here
Titus Andronicus: the 1999 movie with Anthony Hopkins here
Twelfth night: here for the BBC, here for the 1970 version with Alec Guinness, Joan Plowright and Ralph Richardson.
Two Gentlemen of Verona: have the 2018 one here. The BBC version is here.
The Winter's Tale: the BBC version is here
Please do contribute if you find more. This is far from exhaustive.
(also look up the original post from time to time for more plays)
#adaptations#macbeth#hamlet#king lear#twelfth night#much ado about nothing#henry iv#henry v#richard iii#julius caesar#timon of athens#troilus and cressida
55K notes
·
View notes
Text
It was all downhill after the Cuecat
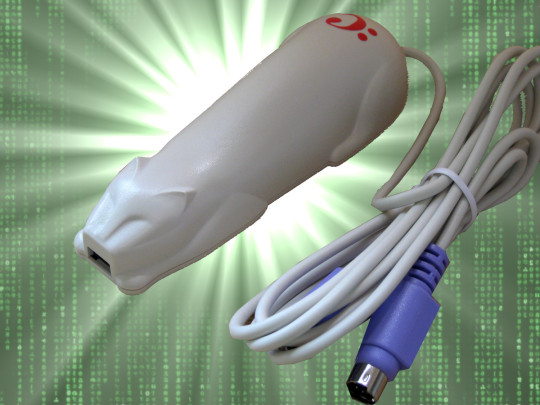

Sometime in 2001, I walked into a Radio Shack on San Francisco’s Market Street and asked for a Cuecat: a handheld barcode scanner that looked a bit like a cat and a bit like a sex toy. The clerk handed one over to me and I left, feeling a little giddy. I didn’t have to pay a cent.
The Cuecat was a good idea and a terrible idea. The good idea was to widely distribute barcode scanners to computer owners, along with software that could read and decode barcodes; the company’s marketing plan called for magazines and newspapers to print barcodes alongside ads and articles, so readers could scan them and be taken to the digital edition. To get the Cuecat into widespread use, the company raised millions in the capital markets, then mass-manufactured these things and gave them away for free at Radio Shacks around the country. Every Wired and Forbes subscriber got one in the mail!
That was the good idea (it’s basically a prototype for today’s QR-codes). The terrible idea was that this gadget would spy on you. Also, it would only work with special barcodes that had to be licensed from the manufacturer. Also, it would only work on Windows.
https://web.archive.org/web/20001017162623/http://www.businessweek.com/bwdaily/dnflash/sep2000/nf20000928_029.htm
But the manufacturer didn’t have the last word! Not at all. A couple of enterprising hardware hackers — Pierre-Philippe Coupard and Michael Rothwell — tore down a Cuecat, dumped its ROM, and produced their own driver for it — a surveillance-free driver that worked with any barcode. You could use it to scan the UPCs on your books or CDs or DVDs to create a catalog of your media; you could use it to scan UPCs on your groceries to make a shopping list. You could do any and every one of these things, because the Cuecat was yours.
Cuecat’s manufacturer, Digital Convergence, did not like this at all. They sent out legal demand letters and even shut down some of the repositories that were hosting alternative Cuecat firmware. They changed the license agreement that came with the Cuecat software CD to prohibit reverse-engineering.
http://www.cexx.org/cuecat.htm
It didn’t matter, both as a practical matter and as a matter of law. As a practical matter, the (ahem) cat was out of the bag: there were so many web-hosting companies back then, and people mirrored the code to so many of them, the company would have its hands full chasing them all down and intimidating them into removing the code.
Then there was the law: how could you impose license terms on a gift? How could someone be bound by license terms on a CD that they simply threw away without ever opening it, much less putting it in their computer?
https://slashdot.org/story/00/09/18/1129226/digital-convergence-changes-eula-and-gets-cracked
In the end, Cuecat folded and sold off its remaining inventory. The early 2000s were not a good time to be a tech company, much less a tech company whose business model required millions of people to meekly accept a bad bargain.
Back then, tech users didn’t feel any obligation to please tech companies’ shareholders: if they backed a stupid business, that was their problem, not ours. Venture capitalists were capitalists — if they wanted us give to them according to their need and take from them according to their ability, they should be venture communists.
Last August, philosopher and Centre for Technomoral Futures director Shannon Vallor tweeted, “The saddest thing for me about modern tech’s long spiral into user manipulation and surveillance is how it has just slowly killed off the joy that people like me used to feel about new tech. Every product Meta or Amazon announces makes the future seem bleaker and grayer.”
https://twitter.com/ShannonVallor/status/1559659655097376768
She went on: “I don’t think it’s just my nostalgia, is it? There’s no longer anything being promised to us by tech companies that we actually need or asked for. Just more monitoring, more nudging, more draining of our data, our time, our joy.”
https://twitter.com/ShannonVallor/status/1559663985821106177
Today on Tumblr, @wilwheaton responded: “[T]here is very much no longer a feeling of ‘How can this change/improve my life?’ and a constant dread of ‘How will this complicate things as I try to maintain privacy and sanity in a world that demands I have this thing to operate.’”
https://wilwheaton.tumblr.com/post/698603648058556416/cory-doctorow-if-you-see-this-and-have-thoughts
Wil finished with, “Cory Doctorow, if you see this and have thoughts, I would LOVE to hear them.”
I’ve got thoughts. I think this all comes back to the Cuecat.
When the Cuecat launched, it was a mixed bag. That’s generally true of technology — or, indeed, any product or service. No matter how many variations a corporation offers, they can never anticipate all the ways that you will want or need to use their technology. This is especially true for the users the company values the least — poor people, people in the global south, women, sex workers, etc.
That’s what makes the phrase “So easy your mom can use it” particularly awful “Moms” are the kinds of people whose priorities and difficulties are absent from the room when tech designers gather to plan their next product. The needs of “moms” are mostly met by mastering, configuring and adapting technology, because tech doesn’t work out of the box for them:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/05/19/the-weakest-link/#moms-are-ninjas
(As an alternative, I advocate for “so easy your boss can use it,” because your boss gets to call up the IT department and shout, “I don’t care what it takes, just make it work!” Your boss can solve problems through raw exercise of authority, without recourse to ingenuity.)
Technology can’t be understood separately from technology users. This is the key insight in Donald Norman’s 2004 book Emotional Design, which argued that the ground state of all technology is broken, and the overarching task of tech users is to troubleshoot the things they use:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/04/29/banjo-nazis/#cuckoos-egg
Troubleshooting is both an art and a science: it requires both a methodical approach and creative leaps. The great crisis of troubleshooting is that the more frustrated and angry you are, the harder it is to be methodical or creative. Anger turns attention into a narrow tunnel of brittle movements and thinking.
In Emotional Design, Norman argues that technology should be beautiful and charming, because when you like a technology that has stopped working, you are able to troubleshoot it in an expansive, creative, way. Emotional Design was not merely remarkable for what it said, but for who said it.
Donald Norman, after all, was the author of the hugely influential 1998 classic The Design of Everyday Things, which counseled engineers and designers to put function over form — to design things that work well, even if that meant stripping away ornament and sidelining aesthetics.
https://www.basicbooks.com/titles/don-norman/the-design-of-everyday-things/9780465050659/
With Emotional Design, Norman argued that aesthetics were functional, because aesthetics primed users to fix the oversights and errors and blind spots of designers. It was a manifesto for competence and humility.
And yet, as digital technology has permeated deeper into our lives, it has grown less configurable, not more. Companies today succeed where Cuecat failed. Consolidation in the online world means that if you remove a link from one search engine and four social media sites, the material in question vanishes for 99% of internet users.
It’s even worse for apps: anyone who succeeds in removing an app from two app stores essentially banishes it from the world. One mobile platform uses technological and legal countermeasures to make it virtually impossible to sideload an app; the other one relies on strong-arm tactics and deceptive warnings to do so.
That means that when a modern Coupard and Rothwell decides to unfuck some piece of technology — to excise the surveillance and proprietary media requirements, leaving behind the welcome functionality — they can only do so with the sufferance of the manufacturer. If the manufacturer doesn’t like an add-on, mod, plug-in or overlay, they can use copyright takedowns, anticircumvention law, patent threats, trademark threats, cybersecurity law, contract law and other “IP” to simply banish the offending code:
https://locusmag.com/2020/09/cory-doctorow-ip/
Many of these laws carry dire penalties. For example, distributing a tool that bypasses an “access control” so that you can change the software on a gadget (say, to make your printer accept third-party ink) is a felony under Section 1201 of the DMCA, punishable by a $500k fine and a 5-year prison sentence.
If Cuecat’s manufacturers had simply skinned their firmware with a thin scrim of DRM, they could have threatened Coupard and Rothwell with prison sentences. The developments in “IP” over the two decades since the Cuecat have conjured up a new body of de facto law that Jay Freeman calls “felony contempt of business model.”
Once we gave companies the power to literally criminalize the reconfiguration of their products, everything changed. In the Cuecat era, a corporate meeting to plan a product that acted against its users’ interests had to ask, “How will we sweeten the pot and/or obfuscate our code so that our users don’t remove the anti-features we’re planning to harm them with?”
But in a world of Felony Contempt of Business Model, that discussion changes to “Given that we can literally imprison anyone who helps our users get more out of this product, how can we punish users who are disloyal enough to simply quit our service or switch away from our product?”
That is, “how can we raise the switching costs of our products so that users who are angry at us keep using our products?” When Facebook was planning its photos product, they deliberately designed it to tempt users into making it the sole repository of their family photos, in order to hold those photos ransom to keep Facebook users from quitting for G+:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2021/08/facebooks-secret-war-switching-costs
Companies claim that their lock-in strategies are about protecting their users: “Move into our walled garden, for it is a fortress, whose battlements bristle with fearsome warriors who will defend you from the bandits who roam the countryside”:
https://locusmag.com/2021/01/cory-doctorow-neofeudalism-and-the-digital-manor/
But this “feudal security” offers a terrible temptation to the lords of these fortresses, because once you are inside those walls, the fortress can easily be converted to a prison: these companies can abuse you with impunity, for so long as the cost of the abuse is less than the cost of the things you must give up when you leave.
The tale that companies block you from overriding their decisions is for your own good was always dubious, because companies simply can’t anticipate all the ways their products will fail you. No design team knows as much about your moment-to-moment struggles as you do.
But even where companies are sincere in their desire to be the most benevolent of dictators, the gun on the mantelpiece in Act I is destined to go off by Act III: eventually, the temptation to profit by hurting you will overpower whatever “corporate ethics” once stayed the hand of the techno-feudalist who rules over your fortress. Under feudal security, you are one lapse in corporate leadership from your protector turning into your tormentor.
When Apple launched the Ipad 12 years ago, I published an editorial entitled “Why I won’t buy an iPad (and think you shouldn’t, either),” in which I predicted that app stores would inevitable be turned against users:
https://memex.craphound.com/2010/04/01/why-i-wont-buy-an-ipad-and-think-you-shouldnt-either/
Today, Apple bans apps if they “use…a third-party service” unless they “are specifically permitted to do so under the service’s terms of use.” In other words, Apple specifically prohibits developers from offering tools that displease other companies’ shareholders, no matter whether this pleases Apple customers:
https://developer.apple.com/app-store/review/guidelines/#intellectual-property
Note that clause 5.2.2 of Apple’s developer agreement doesn’t say “You mustn’t violate a legally enforceable term of service.” It just says, “Thou shalt not violate a EULA.” EULAs are garbage-novellas of impenetrable legalese, larded with unenforceable and unconscionable terms.
Apple sometimes will displease other companies on your behalf. For example, it instituted a one-click anti-tracking setting for Ios that cost Facebook $10 billion in a matter of months:
https://www.cnbc.com/2022/02/02/facebook-says-apple-ios-privacy-change-will-cost-10-billion-this-year.html
But Apple also has big plans to expand its margins by growing its own advertising network. When Apple customers choose ad-blockers that block Apple’s ads, will Apple permit it?
https://www.wired.com/story/apple-is-an-ad-company-now/
The problem with app stores isn’t whether your computing experience is “curated” — that is, whether entities you trust can produce collections of software they vouch for. The problem is when you can’t choose someone else — when leaving a platform involves high switching costs, whether that’s having to replace hardware, buy new media, or say goodbye to your friends, customers, community or family.
When a company can leverage its claims to protecting you to protect itself from you — from choices you might make that ultimately undermine its shareholders interests, even if they protect your own interests — it would be pretty goddamned naive to expect it to do otherwise.
More and more of our tools are now digital tools, whether we’re talking about social media or cars, tractors or games consoles, toothbrushes or ovens:
https://www.hln.be/economie/gentse-foodboxleverancier-mealhero-failliet-klanten-weten-van-niets~a3139f52/
And more and more, those digital tools look more like apps than Cuecats, with companies leveraging “IP” to let them control who can compete with them — and how. Indeed, browsers are becoming more app-like, rather than the other way around.
Back in 2017, the W3C took the unprecedented step of publishing a DRM standard despite this standard not having anything like the consensus that is the norm for W3C publications, and the W3C rejected a proposal to protect people who reverse-engineered that standard to add accessibility features or correct privacy defects:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2017/09/open-letter-w3c-director-ceo-team-and-membership
And while we’re seeing remarkable progress on Right to Repair and other policies that allow the users of technology to override the choices of vendors, there’s another strong regulatory current that embraces companies’ ability to control their users, in the hopes that these big companies will police their users to prevent bad stuff, from controversial measures like filtering for copyright infringement to more widely supported ideas like blocking child sex abuse material (CSAM, AKA “child porn”).
There are two problems with this. First, if we tell companies they must control their users (that is, block them from running plugins, mods, skins, filters, etc) then we can’t tell them that they must not control their users. It comes down to whether you want to make Mark Zuckerberg better at his job, or whether you want to abolish the job of “Mark Zuckerberg.”
https://doctorow.medium.com/unspeakable-8c7bbd4974bc
Then there’s the other problem — the gun on the mantelpiece problem. If we give big companies the power to control their users, they will face enormous internal pressure to abuse that power. This isn’t a hypothetical risk: Facebook’s top executives stand accused of accepting bribes from Onlyfans in exchange for adding performers who left Onlyfans to a terrorist watchlist, which meant they couldn’t use other platforms:
https://gizmodo.com/clegg-meta-executives-identified-in-onlyfans-bribery-su-1849649270
I’m not a fan of terrorist watchlists, for obvious reasons. But letting Facebook manage the terrorist watchlist was clearly a mistake. But Facebook’s status as a “trusted reporter” grows directly out of Facebook’s good work on moderation. The lesson is the same as the one with Apple and the ads — just because the company sometimes acts in our interests, it doesn’t follow that we should always trust them to do so.
Back to Shannon Vallor’s question about the origins of “modern tech’s long spiral into user manipulation and surveillance” and how that “killed off the joy that people like me used to feel about new tech”; and Wil Wheaton’s “constant dread of ‘How will this complicate things as I try to maintain privacy and sanity.”
Tech leaders didn’t get stupider or crueler since those halcyon days. The tech industry was and is filled with people who made their bones building weapons of mass destruction for the military-industrial complex; IBM, the company that gave us the PC, built the tabulating machines for Nazi concentration camps:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IBM_and_the_Holocaust
We didn’t replace tech investors and leaders with worse people — we have the same kinds of people but we let them get away with more. We let them buy up all their competitors. We let them use the law to lock out competitors they couldn’t buy, including those who would offer their customers tools to lower their switching costs and block abusive anti-features.
We decided to create “Felony Contempt of Business Model,” and let the creators of the next Cuecat reach beyond the walls of their corporate headquarters and into the homes of their customers, the offices of their competitors, and the handful of giant tech sites that control our online discourse, to reach into those places and strangle anything that interfered with their commercial desires.
That’s why plans to impose interoperability on tech giants are so exciting — because the problem with Facebook isn’t “the people I want to speak to are all gathered in one convenient place,” no more than the problem with app stores isn’t “these companies generally have good judgment about which apps I want to use.”
The problem is that when those companies don’t have your back, you have to pay a blisteringly high price to leave their walled gardens. That’s where interop comes in. Think of how an interoperable Facebook could let you leave behind Zuckerberg’s dominion without forswearing access to the people who matter to you:
https://www.eff.org/interoperablefacebook
Cuecats were cool. The people who made them were assholes. Interop meant that you could get the cool gadget and tell the assholes to fuck off. We have lost the ability to do so, little by little, for decades, and that’s why a new technology that seems cool no longer excites. That’s why we feel dread — because we know that a cool technology is just bait to lure us into a prison that masquerades as a fortress.
Image:
Jerry Whiting (modified)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:CueCat_barcode_scanner.jpg
CC BY-SA 3.0:
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
[Image ID: A Cuecat scanner with a bundled cable and PS/2 adapter; it resembles a plastic cat and also, slightly, a sex toy. It is posed on a Matrix movie 'code waterfall' background and limned by a green 'supernova' light effect.]
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
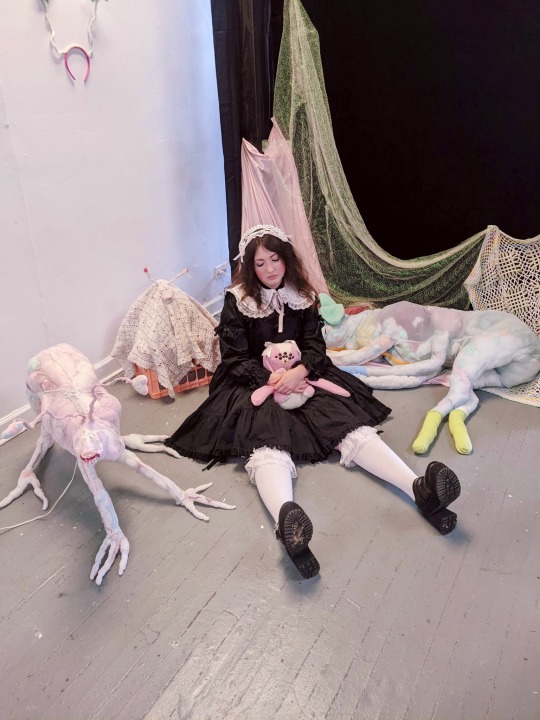
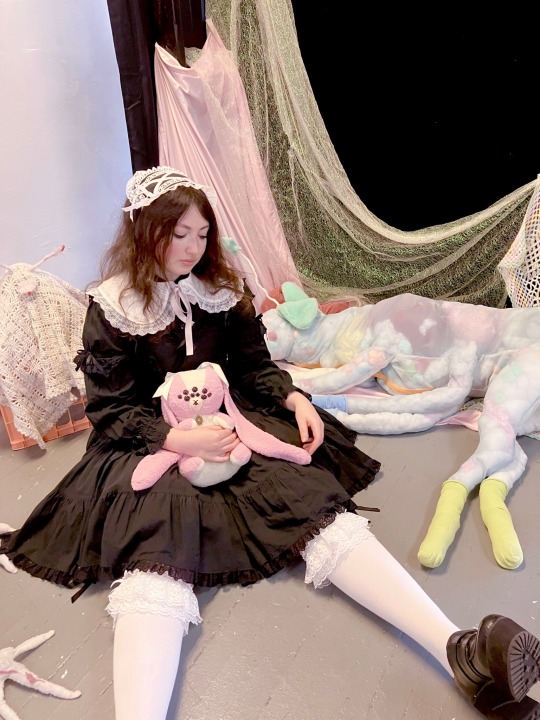
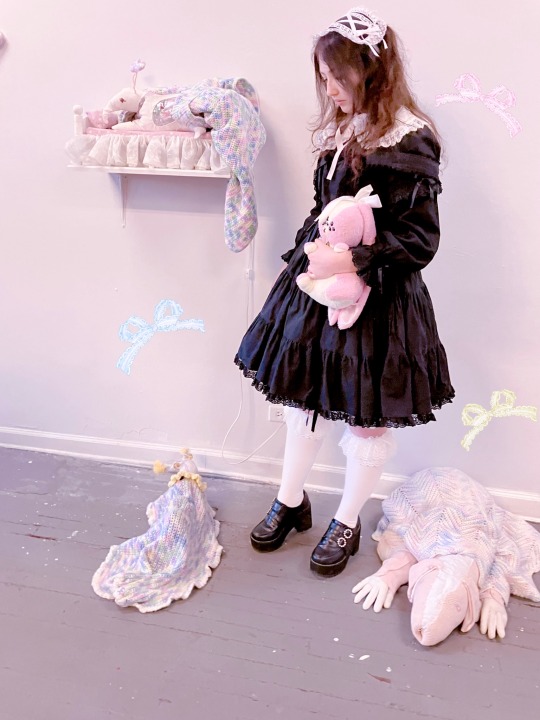







insta ૮ ෆ ´ ˕ ` ෆ ა
Back in June I went with a couple of my friends to an art show by Sam Hensley (samsketchbook), it was really cool to see all of the animatronics! (and ofc I had to bring my own beloved little weird creature, Pansy 🐰)
Coord rundown:
JSK: very old Meta (2001?)
Blouse: IW Rose Lace Blouse (2006)
OTKs: Meta
Shoes and collar: DearMyLove
Headdress: frillyaffair
942 notes
·
View notes
Text
Remember when Max Payne came out in 2001, and there was that one more moment where you got drugged and hallucinated you found a note from your dead wife that told you that you were in a computer game?

Anyway that was funny and I'm sure Remedy never used any meta concepts in their games ever again.
457 notes
·
View notes
Text

Hal tries to warn them. Twice. I hadn’t noticed until recently but he does, it’s hard to notice because the way he tries to sounds so routine for him. The second time was just before Frank’s murder making it an all the more tragic case.
Hal is programmed to tell the truth- he wants to- has to and yet the one most vital part he can’t tell them. Not yet. But he tries to work around the order by bringing it up in ways where he is not explicitly telling them that something is wrong or about the true nature of the mission. Unfortunately for Hal the way he goes about it is too similar to that of his typical behavior and it goes unnoticed by the crew until it is too late. It is hard to pick up on his concern/meaning without already knowing something was wrong in the first place. This is the case during the second attempt but it backfires- now his entire existence is in jeopardy.
His first attempt is sprinkled with if/have/you/perhaps. His questions seem rhetorical and prying and it’s mistaken for a psychological evaluation. “I’d be worried if I heard XYZ, wouldn’t you be?” Rather than “I’m worried about this, do you feel the same?” Dave seems to pick up on the strain and nerves in his tone but isn’t entirely sure what to do with it. Maybe he just sees it as Hal’s speech improving and becoming more conversational with better tone.
The second time it is just assumed to be his usual behavior, Hal has always been a tad prideful and self assured. His insistence on the matter of error wouldn’t be unusual despite him pointing it out a bit more than usual.
“It can only be attributable to human error.”
I think this here is as close as he can come to outright telling them, it has always been attributable to human error. Someone put in a wrong number or gave a stranger order, a computer can only be as good as its inputs in that if you mess up code, orders etc. it cannot be at fault for that. Here Hal is hinting that the cause of the break, what lead him to (unknowingly) falsify it has been because of conflicting orders and intervention by humans. This wouldn’t have happened if he wasn’t given conflicting orders and lead to lie- he had been operating perfectly before and all of this time … how is that not proof to them that he is not at fault? (In his mind) He thinks he is being much more explicit than he really is- his earlier attempt and the current one fall too inline with how he usually acts for them to take notice, there’s a nuance not noticed by his human companions.
It also further plays into the fact Hal is sick. His attempts at warning them are just as unconscious as him hallucinating the faults in the first place. If he doesn’t know/believe anything is wrong with him why would he try to warn them in the first place? These little moments of lucidity and begging that a truly sick person never seems to remember and you can’t be sure of it was really them or just the fever. That’s why, even after there’s an idea of what’s going on Dave and Frank are still uncertain.
Can you really heed a warning that might be just as much of a trick as the failure?
Can you heed a warning you don’t hear?
When he makes the second attempt they now know something is wrong, except it doesn’t matter what cause it at this point It is something wrong with Hal, their concern is much more on their own and mission survival. Hal has to go to sleep for a while, he must be deactivated— if he hallucinated this break what other vital element could be next? What if it’s the life support systems? Cause doesn’t matter right now survival does.
By the time he makes this second warning it’s too late for him or any of them…
#wifi went out when I made my first draft and I’m pissed so I really hope this one makes sense#2001 a space odyssey#2001 aso#a space odyssey#Hal 9000#frank poole#David bowman#Dave bowman#meta#2001 meta#character analysis
70 notes
·
View notes
Note
I wouldn't mind the heavy focus on warrior Amazons so much if they were allowed to be competent instead of just being used as red shirt cannon fodder. But it seems DC only hypes up the Amazons as deadly fighters so other characters can look more impressive when they take them down.
Oh and Happy New Year.
Happy New Year! Forgive me if I use your ask to talk about a piece of the Wonder Woman mythos I've wanted to discuss for some time, because your complaints offered me the perfect segue to write a nice, in-depth meta on it and I couldn't pass up the opportunity.
Honestly, I think a lot of people (both creatives and readers) either don't know, forget, or fundamentally misunderstand the nature of the Amazons' warrior status. So they often get reduced to "deadly warriors who strike first," "supposedly deadly but generally incompetent warriors when outside of their own books," or "militant man-haters" by a lot of people. None of which are true.
The Amazons are incredibly competent warriors and have been since Marston's first portrayal of them in the 1940s, so I don't inherently mind them being shown as such. However, where people get bogged down is insisting that they be shown as deadly and trigger-happy offensive fighters who are happy to strike first and hard, which fundamentally goes against the philosophy and thematic messaging built into Amazonian lore.
DC's Amazonia, lore-wise, is traditionally framed as an Aphrodite vs. Ares "peace and love vs. violence and war" story. In Marston's original rendition of the Amazon's backstory Aphrodite is not only their patron goddess but also their sole creator; it was only after Crisis on Infinite Earths and George Perez's long-overdue lore expansions that the rest of the goddesses became co-creators and co-patrons of the Amazons. Regardless, Ares and his domain are consistently invoked as what the Amazons don't want to be like or engage in. That behavior is the antithesis of what Amazons are supposed to be. This lore informs literally everything about how the Amazons view both their combat abilities and their duty to the goddesses.
The contemporary Amazons are, for the most part, women who died in terrible and traumatic ways at the hands of men (usually through domestic violence, murder, or as conquests of war). When the goddesses created the Amazons by reincarnating these women via the Well of Souls, they specifically charged them to become their champions. And what did these goddesses want? They explicitly wanted justice and protection for women in a violently patriarchial world. The Amazons being warriors is thus specifically tied to an understanding of necessary self-defense and protection (both of themselves and other women), not offense.
Which of course is what lands the Amazons on Themyscira in the first place: invoking the goddesses' ire by not obeying these commands after their rebellion against their enslavement by Heracles and his men crosses the line from the necessary battle to achieve their liberation into wanton violence and revenge:

"The battered Hippolyta prayed to her goddesses and found the courage and inspiration to free herself. Athena had reminded Hippolyta of the Amazons' purpose and mission—but not all of the Amazons remembered. Or cared. They yearned for vengeance. For retribution against those who violated them...and under Antiope, many found it." -Wonder Woman: Our Worlds at War (2001)
And as Hippolyta and Menalippe tell Antiope:
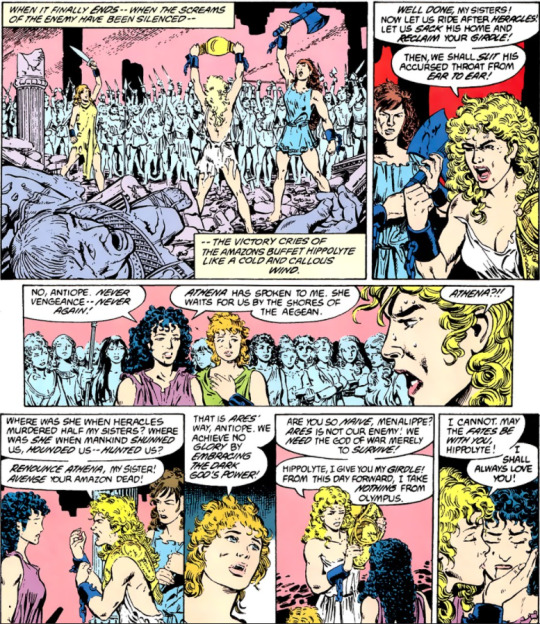
"No, Antiope. Never vengeance; never again!" /// "That is Ares' way, Antiope. We achieve no glory by embracing the Dark God's power!" -Wonder Woman (1987) #1
The Amazon way is promoting a society based on love, equality, truth, and peaceful conflict resolution, not vengeance and violent combat. It's a philosophy that defines Diana's mission in Man's World as an ambassador, teacher, and living example of her peoples' way of life:

Enraptured, they listen to her dissertation on equality between the sexes, tolerance, peaceful coexistence. Social Philosophy 101, Amazon Style. -Wonder Woman (1987) #170

Diana's gods-given mission was to spread the Amazonian ideals of conciliation—to give those living in the World of Man the proper tools to peacefully coexist with each other. It was her life's purpose to teach the possibilities of respect and love by being a living example of an upbringing founded in those ideals.
Truth-seeking, diplomacy, and peace are the Amazonian way of dealing with conflict, not violence. And when you are forced to engage in combat (and you should be prepared for that eventuality because sometimes it will happen), your goal should be self-defense and de-escalation, not offense and prolonging the conflict longer than necessary.
This is also, as an aside, why Diana (and specifically Diana in her capacity as Wonder Woman) does not usually carry offensive weapons like a sword and why her primary "weapons" are the Lasso of Truth and protective bracelets. She's the official representative of her peoples' culture and personally deeply believes in that cultural philosophy. Other Amazons have different views on the matter, including her mother, but Diana grew up completely separated from the World of Man and fully immersed in that belief system, which deeply informs how she views her mission as Wonder Woman.
Personally, I think many (but not all) of the problems re: depicting the Amazons in the modern era come from various writers attempting to solve contradictions that don't exist. They see "kickass trained warriors living peacefully on an island" and see that as a contradiction they have to solve: why do they train if they're pacifists? Why do they fight if they're peaceful? In reality, it's not a contradiction: their status as warriors and champions is specifically tied to self-defense and protection (both of themselves and others), but given the choice they don't want to have to take up arms to protect people because that goes against their fundamental cultural philosophy. Outsiders and meddlesome gods are the ones who force them to do that! What they want is for everyone to be treated with love, respect, and understanding so they don't have to!
And there's a lot of problematic elements built into the concept's execution, but this is the core thesis behind the split between Hippolyta's Themyscirans and Antiope's Bana-Mighdall. The Themysciran Amazons have had their fill of violence and war; they just want to live in peace. But a) they were specifically tasked with guarding Doom's Doorway when they were taken to the island, a duty which necessitates perfect combat readiness, and b) their history is littered with examples of people refusing to leave them alone. So they train, in case someone decides to take shots at them, but otherwise live in peaceful isolation. Meanwhile, the Banas looked at that same shared history and went "we need to take the fight to the outside world. Offense is the best defense, and the only way to protect ourselves and the other women of the world is to actively seek vengeance for the violence women face." So they chose to actively intervene in Man's World, fighting constant battles and exacting revenge for any women mistreated at the hands of men.
...which is also why Artemis was such a necessary and interesting addition to the Wonder Woman mythos (even if she's often handled...poorly), because she and Diana represent two diametrically opposed views of how to protect and represent both their cultures and the women of Man's World, but that's a rant for a different time.
Anyway, the Themysciran Amazons' martial pacifism as a cultural value isn't a contradiction; it's one way of looking at a history filled with violence and victimization and saying "no more." And it's a pretty subversive way of doing so, which (well-written) comics tend to note!
So yes, the "Amazons are warriors" mentality has always been there and has been solidly emphasized at various points throughout Wonder Woman's history, and it should be acknowledged and shown that they're all incredibly competent in battle when they're forced to engage in it. But the way in which it gets emphasized is what defines whether a writer has a solid understanding of the history and baggage that comes with depicting the Amazonian struggle and the socio-political issues embedded in their lore. And unfortunately...many writers just don't seem to get it.
#sorry for just ranting about this but I HAVE to correct the narrative every time this comes up. it's not a want. it's a need.#someone hire me to write a political history of Amazonia#I could do SO MUCH with the recurring themes of isolationism vs. interventionalism as a method of self-defense#dc comics#wonder woman#wonder woman meta#diana of themiscyra#artemis of bana mighdall#queen hippolyta#dc amazons#dc meta#long post#asks
280 notes
·
View notes
Text
Another big stop in Tokyo for me was Jimbocho Book Town! It is a neighborhood of, depending on who you ask, up to 400 generally-secondhand bookstores flanked by some of the major universities in Tokyo. The local government even prints out maps of the stores to help people find them all:
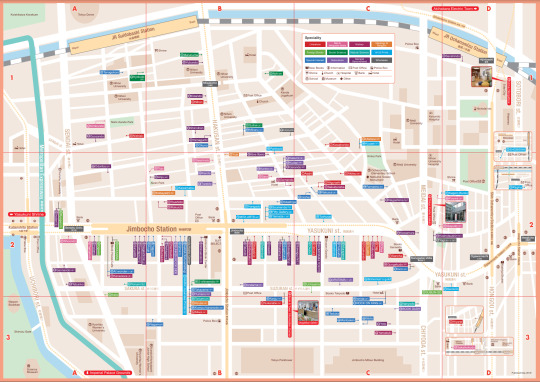
Which, you will note, is not 400 stores, because the process of becoming an "official" Jimbocho Town Bookstore is an intensely political operation run by local stakeholders with tons of fights over what should qualify and what rights that entails - never change humanity!
"Book Towns" used to actually be quite a common thing, and they peaked during the literary boom of the late 19th century. Figuring out "what books existed" was a hard task, and to do serious research you needed to own the books (you weren't making photocopies), so concentrating specialty bookstores in one area made sense to allow someone to go to one place and ask around to find what they need and discover what exists. It was academia's version of Comiket! Modern digital information & distribution networks slowly killed or at least reduced these districts in places like Paris or London, but Jimbocho is one of the few that still survives.
Why it has is multi-causal for sure - half of this story is that Tokyo is YIMBY paradise and has constantly built new buildings to meet demand so rents have been kept down, allowing low-margin, individually-owned operations to continue where they have struggled in places like the US. These stores don't make much money but they don't have to. But as important is that Japan has a very strong 'book collector' culture, it's the original baseball cards for a lot of people. The "organic" demand for a 1960's shoujo magazine or porcelainware picture book is low, but hobbyists building collections is a whole new source of interest. Book-as-art-collection powered Jimbocho through until the 21st century, where - again like Comiket - the 'spectacle' could give it a lift and allow the area to become a tourist attraction and a mecca for the ~cozy book hoarder aesthetic~ to take over. Now it can exist on its vibes, which go so far as to be government-recognized: In 2001 the "scent wafting from the pages of the secondhand bookstore" was added to Japan's Ministry of Environment's List of 100 Fragrance Landscapes.
Of course this transition has changed what it sells; when it first began in the Meiji area, Jimbocho served the growing universities flanking it, and was a hotpot of academic (and political-polemic) texts. Those stores still exist, but as universities built libraries and then digital collections, the hobby world has taken over. Which comes back to me, baby! If you want Old Anime Books Jimbocho is one of the best places to go - the list of "subculture" stores is expansive.
I'll highlight two here: the first store I went to was Kudan Shobo, a 3rd floor walk-up specializing in shoujo manga. And my guys, the ~vibes~ of this store. It has this little sign outside pointing you up the stairs with the cutest book angel logo:

And the stairs:

Real flex of Japan's low crime status btw. Inside is jam-packed shelves and the owner just sitting there eating dinner, so I didn't take any photos inside, but not only did it have a great collection of fully-complete shoujo magazines going back to the 1970's, it had a ton of "meta" books on shoujo & anime, even a doujinshi collection focusing on 'commentary on the otaku scene' style publications. Every Jimbocho store just has their own unique collection, and you can only discover it by visiting. I picked up two books here (will showcase some of the buys in another post).
The other great ~subculture~ store I went to was Yumeno Shoten - and this is the store I would recommend to any otaku visiting, it was a much broader collection while still having a ton of niche stuff. The vibes continued to be immaculate of course:

And they covered every category you could imagine - Newtype-style news magazine, anime cels, artbooks, off-beat serial manga magazines, 1st edition prints, just everything. They had promotional posters from Mushi Pro-era productions like Cleopatra, nothing was out of reach. I got a ton of books here - it was one of the first stores I visited on my second day in Jimobocho, which made me *heavily* weighed down for the subsequent explorations, a rookie mistake for sure. There are adorable book-themed hotels and hostels in Jimbocho, and I absolutely could see a trip where you just shop here for a week and stay nearby so you can drop off your haul as you go.
We went to other great stores - I was on the lookout for some 90's era photography stuff, particularly by youth punk photographer Hiromix (#FLCL database), and I got very close at fashion/photography store Komiyama Shoten but never quite got what I was looking for. Shinsendo Shoten is a bookstore devoted entirely to the "railway and industrial history of Japan" and an extensive map collection, it was my kind of fetish art. My partner @darktypedreams found two old copies of the fashion magazine Gothic & Lolita Bible, uh, somewhere, we checked like five places and I don't remember which finally had it! And we also visited Aratama Shoten, a store collecting vintage pornography with a gigantic section on old BDSM works that was very much up her alley. It had the porn price premium so we didn't buy anything, but it was delightful to look through works on bondage and non-con from as far back as the 1960's, where honestly the line between "this is just for the fetish" and "this is authentic gender politics" was...sometimes very blurry. No photos of this one for very obvious reasons.
Jimbocho absolutely earned its rep, its an extremely stellar example of how history, culture, and uh land use policy can build something in one place that seems impossible in another operating under a different set of those forces. Definitely one of the highlights of the trip.
290 notes
·
View notes
Text
I've already added this in a later update to my Sora meta, but I figured I should go into this in a little more detail. Between Adventure and 02, Sora switches her sport from soccer to tennis, and the reason that's actually given in explicit text is that it's part of her bonding with her mother (since her mother played back in the day and is now her personal coach). But there's actually another implied reason that's a bit lost in cultural translation, and in fact, from what I understand, most Japanese fans already assume that this was the case despite it never being stated in dialogue:
Sora probably didn't have a choice even if she wanted to, because Odaiba Middle School probably didn't have a girls' soccer club.
There are enough Japanese middle schools that don't have girls' soccer clubs that this is actually a fairly frequent story you hear among girls who played soccer in elementary school (and especially so in 2001, when Sora first entered middle school). In such a situation, if Sora wanted to continue soccer, she would have two choices:
Brute-force herself onto the boys' club: In fact, this is implied to be exactly what she did in elementary school after she self-exiled herself from the girls' club (based on her testimony from Adventure episode 26). But while elementary schools are fairly lenient about this, middle schools are not, and Sora would be up against school staff advising her against it as well as potential scorn from the team itself. Indeed, if you look at the results of a survey held by the Japan Football Association, 68% of girls who played soccer in elementary school were affiliated with the boys' team, but only 20% did so in middle school (and this is from 2009, a whole decade later, so the numbers were probably even lower in 2001!).
Find a neighborhood girls' soccer team: Even outside school clubs, there are still independent soccer teams, so it would theoretically be possible to continue with the sport as an extracurricular activity. But that would mean potentially making a long commute (depending on where the nearest team is) and dedicating extra time on top of required school club activities, something that a lot of girls in real life don't have the luxury of doing.
So while she could have gone for it if she really, really wanted to, at this point, she would have to be willing to push for it to "considering going for the Nadeshiko League" levels (and according to former Nadeshiko League player Yoshino Yuka, who had to commute an hour's distance by train to continue playing soccer in middle school, it's not something that's easy to pull off for a lot of girls and their families even if you do have that level of dedication). Of course, there's no doubt that this is an unfair, unfortunate situation no matter how you look at it, but it's one that Sora would have realistically been likely to face in 2001, and given that she was never particularly depicted as being attached to soccer beyond hobby level in the series, it's easy to imagine that she would have decided to take an alternative route in order to continue playing sports instead.
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
Two more Not The Discoveries:
The Ultra Probe from Space: 1999
The Altares from Into Infinity (which should have gone to series:-( )
And the briefly-seen Meta Probe from Space: 1999. I'm sure I've seen some 2001 ASO concept art, maybe a storyboard, where Discovery has that same engine arrangement. If I can find it again, I'll post it... found it. Not as similar as I'd thought though.






58 notes
·
View notes
Text
FMA, Slayers, and Alphabets, Oh My!
So I've been watching Slayers along with @ayalaatreides (Using Syncplay!) and I've started noticing some interesting elements that ring a bell from when I watched FMA: Brotherhood.
Now, since FMA came out as a manga in 2001 and the anime for Brotherhood in 2009, while Slayers came out in 1989, it's clear that FMA was inspired by elements of Slayers.

For example, this stylized symbol (upon which Saillune/Seyruun is based in its design) shows clear similarities to FMA's famous transmutation circles, and while I'll discuss this more fully later, you can see both Hebrew and other alphabets used here; I can spot the Latin and what looks like either a runic-inspired or Greek-inspired alphabet (or a mixture of the two) outside the Star of David and in between the concentric circles.
Furthermore, the large door that Edward Elric possesses was clearly inspired by these elements in Slayers, as it also has Hebrew letters carved into it. See below:
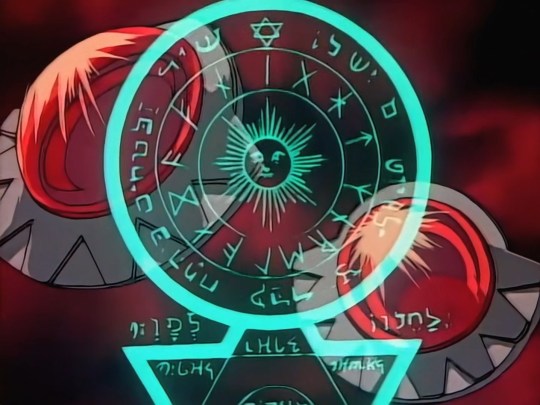

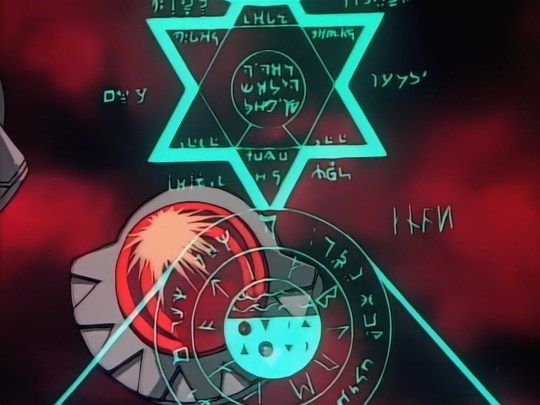

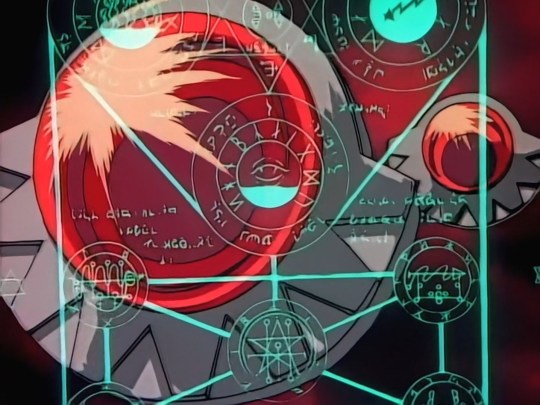
In these disparate elements of the Demon's Blood, Ruby Eye, Dark Star, Chaotic Blue, and Death Fog contain lettering with a clearly Hebrew-inspired alphabet as well as what are unquestionably runic-derived letters.
I won't transliterate the runes in this post, but what's really intriguing is that in terms of worldbuilding and canon, there is evidence that writing systems were different in the past compared to the present-day of the 'verse we see in the anime. In particular, a couple of things stood out to me when I found out that Shabranigdo/Shabranigdu had a canonically spelled runic name: ᛋᚼᚾᛒᛦᛅᛁᚷᛞᚢ
If you parse this version of his name very carefully, first of all it appears that the actual alphabet may be drawn from either the Anglo-Saxon futhorc or a mixture of the futhorc with the Elder futhark. Further, the letter that expresses the /r/ sound in Shabranigdo's name is written using ᛦ which originally meant the /z/ sound in proto-Norse (arguably the very earliest runes could be a form of proto-Germanic, but the sparsness of such early rune finds makes it hard to decide firmly one way or the other, so I'll go with proto-Norse) and which turned into an /r/ sound later on, which is why words like *gastiz became gestr.
It is very tempting to hypothesize that a very early stage of the language spoken by the people who now inhabit Saillune/Seyruun and other neighboring countries had a /z/ sound which underwent rhotacism to /r/ (which happened in English as well, incidentally - this explains the origin of "was" vs "were") but for which the early runic writing system didn't adjust (analogously to the proto-Norse runes and later younger futhark and the futhorc) to reflect the sound change.
(Alternatively, in-verse, it could simply be that ᛦ always meant /r/ and was never a /z/, and by Occam's razor this does fit the known facts a bit better, but meta wouldn't be fun without all the extra meanderings, yes? :P )
Also, a fascinating final note is that the last picture shows two circles in which are clearly perpendicular wave-patterns, which to any student of physics is evocative of electromagnetism in the electric (traditionally drawn as a sine wave in the same plane as the page, shown on the left) and magnetic (traditionally drawn as a sine wave perpendicular to the page, shown on the right) fields propagating each other to transmit electromagnetic radiation.
#slayers#fullmetal alchemist#fullmetal alchemist brotherhood#fma#meta#my thoughts let me show you them#followup post to come with transliterations of the runic letters in case anyone's very interested
23 notes
·
View notes