#subserosa
Text
Fernanda Tellez se desnuda en la cam
Romi Rain order for Small Hands extra fucking service
Solo teen fuck doll, Emily Willis is masturbating and moaning
Pregnant RedBone take bbc with anal creampie
Brother spies on sis while shower and fucks her
Busty shemale gets her asshole stretched by her lover
Sexy Shemale riding dick in a tent
Familystrokes Fucked Not My Step Dad While Mom In Slumber
POV Alexis Monroe Leggy foot fetish MILF fucks teens way a stardom
Japan hotty in hawt lingerie takes good care of cock
#esthetical#dealcoholist#Mercatorial#overstiffness#out-of-line#silverize#motorboat#boyfriends#subserosa#desoeuvre#ore-mining#reproclamation#world-restoring#profaners#eggman#rejuvenator#oxygenous#palacewards#Chomsky#undrossiness
0 notes
Text
Gastric Cancer : Understanding the Silent Killer
Introduction
Gastric cancer, also known as stomach cancer, is a highly prevalent and life-threatening disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of cancerous cells within the lining of the stomach, leading to various complications and challenges in diagnosis and treatment. In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into the intricacies of gastric cancer, exploring its causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures. By increasing awareness and knowledge about this silent killer, we can take steps towards early detection and better outcomes for those affected.
Understanding Gastric Cancer
Anatomy and Function of the Stomach
The stomach is an essential organ located in the upper abdomen, and it plays a crucial role in the digestive system. It is a muscular, J-shaped organ that receives food from the esophagus and releases it to the small intestine. The anatomy and function of the stomach are complex and interconnected, allowing it to carry out several important processes that facilitate digestion and nutrient absorption.
The stomach consists of four main regions: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus. The cardia is the uppermost part of the stomach, which connects to the lower end of the esophagus.The fundus is the rounded portion above the level of the cardia, while the body forms the central and largest region of the stomach. The pylorus is the lower part that connects to the duodenum, the first section of the small intestine.
aa. Intestinal Type: This subtype typically arises from pre-existing precancerous changes, such as intestinal metaplasia. It is often associated with risk factors like Helicobacter pylori infection and dietary factors.
b. Diffuse Type: This subtype does not show a distinct pattern of growth and tends to infiltrate the stomach wall diffusely. It is associated with a genetic alteration called E-cadherin gene (CDH1) mutation.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GISTs): GISTs are rare tumors that arise from specialized cells of the stomach wall called interstitial cells of Cajal. They can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, including the stomach. GISTs are typically diagnosed based on the expression of a specific protein called KIT. Treatment often involves surgical removal and targeted therapy.
Lymphomas: Gastric lymphomas are a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic tissue of the stomach. They can be either Hodgkin's or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Lymphomas account for a small percentage of gastric cancers.
Carcinoid Tumors: Carcinoid tumors are rare neuroendocrine tumors that can develop in the stomach. They arise from specialized hormone-producing cells and tend to grow slowly. Most carcinoid tumors of the stomach are low-grade and have a favorable prognosis.
Staging of Gastric Cancer:
Staging is a process used to determine the extent and spread of cancer, which helps guide treatment decisions and predict prognosis. The most commonly used staging system for gastric cancer is the TNM staging system developed by the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC). It considers three main factors:
Tumor (T) Stage: This indicates the size and depth of invasion of the primary tumor within the stomach wall. The T stage is classified as follows:
TX: Primary tumor cannot be assessed.
T0: No evidence of primary tumor.
T1: Tumor invades the lamina propria or submucosa.
T2: Tumor invades the muscularis propria or subserosa.
T3: Tumor penetrates the serosa without invading adjacent structures.
T4a: Tumor invades adjacent structures, such as the spleen, liver, diaphragm, or colon.
T4b: Tumor invades adjacent structures, such as the pancreas, abdominal wall, or aorta.
Node (N) Stage: This reflects the involvement of nearby lymph nodes. The N stage is classified as follows:
NX: Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed.
N0: No regional lymph node metastasis.
N1: Metastasis in 1-2 regional lymph nodes.
N2: Metastasis in 3-6 regional lymph nodes.
N3: Metastasis in 7 or more regional lymph nodes.
Incidence and Global Impact
Gastric cancer, also known as stomach cancer, is a significant global health concern due to its high incidence and associated morbidity and mortality. The disease affects millions of people worldwide, and its impact is particularly significant in certain regions.
Incidence:
Gastric cancer is one of the most common types of cancer globally. However, its incidence rates vary widely across different countries and populations. It is more prevalent in Eastern Asia, including countries like China, Japan, and Korea, where it remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths. In these regions, the high incidence of gastric cancer can be attributed to a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
On the other hand, the incidence of gastric cancer is relatively lower in North America and Western Europe. However, it is important to note that even in these regions, gastric cancer still poses a significant health burden.
Risk Factors:
Several risk factors contribute to the development of gastric cancer. Understanding these factors is essential for prevention, early detection, and appropriate management of the disease. Some of the key risk factors include:
Helicobacter pylori infection: Chronic infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is considered a major risk factor for gastric cancer. This bacterium can lead to chronic inflammation and damage to the stomach lining, increasing the risk of developing cancer over time.
Dietary factors: Certain dietary habits have been associated with an increased risk of gastric cancer. A diet high in salted, smoked, and pickled foods, as well as low intake of fruits and vegetables, has been linked to an elevated risk.
Tobacco and alcohol use: Cigarette smoking and heavy alcohol consumption have both been identified as risk factors for gastric cancer.
Family history: Individuals with a family history of gastric cancer are at an increased risk. Inherited gene mutations can contribute to familial cases of gastric cancer.
Genetic factors: Certain genetic alterations and conditions, such as mutations in the CDH1 gene and hereditary diffuse gastric cancer syndrome, can increase the risk of developing gastric cancer.
Previous stomach surgery: Individuals who have undergone previous stomach surgery, such as for benign conditions like ulcers or polyps, may have an increased risk of developing gastric cancer.
Global Impact:
The global impact of gastric cancer is significant, both in terms of health outcomes and economic burden. Some key aspects of its impact include:
Mortality: Gastric cancer is responsible for a significant number of cancer-related deaths worldwide. The disease is often diagnosed at an advanced stage when treatment options are limited, leading to poorer prognosis and higher mortality rates. Early detection and effective treatment are crucial for improving survival rates.
Quality of life: Gastric cancer and its treatments can have a profound impact on a person's quality of life. Symptoms such as abdominal pain, weight loss, and nausea can significantly affect daily activities and overall well-being. Treatment modalities, such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, may also cause physical and emotional side effects.
Healthcare costs: The management of gastric cancer involves various diagnostic procedures, treatment modalities, and supportive care measures. The associated healthcare costs can be substantial, including expenses related to hospitalization, surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and palliative care. The economic burden of gastric cancer extends to both individuals and healthcare systems.
Disparities in healthcare: Gastric cancer disproportionately affects populations in low- and middle-income countries, where access to healthcare resources and specialized cancer services may be limited. This can result in disparities in the detection, diagnosis, and treatment of gastric cancer, leading to poorer outcomes in these regions.
Prevention and control efforts: Given the significant impact of gastric cancer, efforts aimed at prevention, early.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Perbedaan Miom Dan Kista Ovarium Serta Cara Mengobatinya

Pengertian penyakit Kista dan Miom - Kedua jenis penyakit yang mirip, padahal kedua jenis penyakit ini merupakan penyakit yang berbeda, simak perbendaan dibawah ini.
Kista suatu ruangan atau rongga patologis yang biasanya berdinding ikat dan berisi cairan kental atau semi likuid. Kista bisa berada pada jaringan lunak seperti mukosa dan rahim, ovarium atau jaringan yang keras seperti tulang. Dan yang paling sering kita dengar adalah kista ovarium dan kista payudara.
Miom merupakan tumor jinak yang terdiri dari serabut-serabut otot polos, dan bisa terjadi pada organ yang memiliki lapisan otot polos seperti usus, rahim dan payudara. Sesuai miom bisa dibagi:
Miom subserosa yang berasal dari miosit yang dekat dengan lapisan serosa uterus. Miom jenis ini tumbuh kearah luar dan jika bertangkai dinamakan Miom pedunkulata.
Miom intramural adalah miom yang pertumbuhannya berpusat didalam dinding rahim.
Miom submukosa, miom yang terdapat pada endometrium dan tumbuh kearah ronggan uterus.
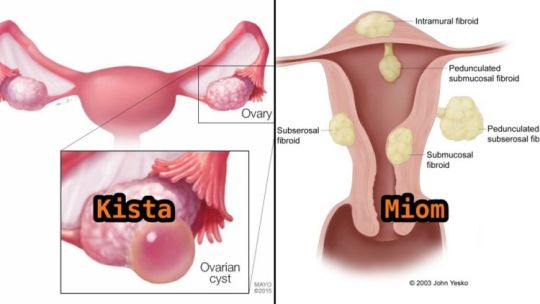
Jadi pada intinya, Kista berisi cairan sedangkan Miom berisi zat pada saat otot.
Ada banyak jenis tanaman herbal dinegara kita yang bisa mengatasi berbagai jenis masalah kesehatan. Termasuk masalah penyakit Miom dan Kista yang hanya bisa membantu oleh para wanita. Berikut 5 Jenis tanaman herbal untuk obat Miom dan Kista.
1. Kunyit Putih
Pertama kunyit putih, kunyit putih sudah jelas sekali manfaatnya untuk kesehatan, termasuk untuk obat menyembuhkan kista. Kunyit putih mampu membunuh sel kanker penyebab kista, karena di dalamnya mengandung abdane diterpene glukosida. Cara membuat siapkan kunyit putih kering, tapak liman kering, tanaman cakar ayam kering, temu putih, dan pegagalan kering. Kemudian rebus semua bahan tersebut sampai mendidih, sampai air sisa setengahnya baru angkat dan saring. Minum air rebusan tersebut tiga kali sehari.
2. Jahe Merah
Selain kunyit putih, jahe merah juga banyak khasiatnya untuk menyembuhkan berbagai jenis penyakit, seperti kista, miom, dan kanker serviks. Jika Anda ingin gigit, Anda bisa membayar dengan cara diolah menjadi teh. Caranya, bersihkan jahe, lalu iris-iris tipis atau bisa diparut dan masukan jahe yang telah diparut ke dalam air mendidih, kemudian saring.
3. Brokoli
Brokoli mengandung senyaKa tiosioanat yang membantu liver untuk menetlarkan zat-zat beracun dalam tubuh yang kemuadian dapat merusak jaringan tubuh. Senyawa dan sulfhorapane berfungsi untuk membunuh sel Miom juga mengaktifkan enzim yang ada di dalam hati untuk memperbaiki zat karsinogen.
Selanjutnya juga terdapat senyawa isocyanate yang berguna untuk menghambat pertumbuhan sel Miom. Ada juga senyawa beta-karoten cryptoxanthin, lutein, dan zea-xantin yang juga merupakan senyawa antiMiom.Senyawa yang terdapat pada brokoli mendukung penyembuhan penderita Miom. Hingga ahli kesehatan di Amerika menyarankan untuk mengonsumsi brokoli minimal dua kali dalam seminggu. Hal ini telah dibuktikan dengan uji laboratorium selama bertahun-tahun di Universitas Negeri Ohio.
4. Kulit Manggis
Manfaat kesehatan kulit manggis sangat penting, beberapa penyakit kritis yang belum disembuhkan, obat yang sangat populer di dunia medis sebagai tradisional yang kuat tanpa efek samping. Why manggis begitu luar biasa Kandungan xanthone di kulit manggis datang menjadi fenomena untuk mengatasi masalah berbagai penyakit, khususnya masalah penyakit, gangguan kuman uterus dan mioma uterus.
5. Daun Sirsak
Manfaat daun sirsak sangat populer di Indonesia, terutama penelitian mulai menunjukan bahwa daun sirsak dapat mengubah penyakit-penyakit ganas seperti kanker. Daun sirsak sangat banyak manfaatnya, terutama untuk kesehatan tubuh manusia yang secara tak terduga dapat melindungi beberapa penyakit berbahaya.
Manfaat daun sirsak juga bisa merawat penyakit kista secara alami. Caranya dengan meminum air rebusan dari saun sirsak ini sebanyak 2kali sehari.
Selain cara diatas, sebagai solusi dari kami, jika Anda merawat Kista atau Miom secara alami, Anda dapat mencoba mengonsumsi Kapsul Ziirzax & Typhogell De Nature yang khasitnya sudah terbukti Aman dan efektif.

OBAT HERBAL KISTA & MIOM RP. 315.000
Ziirzax dan Typhogell merupakan produk herbal de Nature yang berkhasiat untuk mengendalikan sel-sel kanker.
Ada banyak jenis kanker yang dapat menyerang manusia sepeti kanker payudara, kanker prostat, kanker serviks (mulut rahima), kanker otak, kanker hati, kanker limfoma dll.
Kapsul Zirzax dan Typhogel bias menjadi solusi alternatif untuk mengendalikan sel-sel tumor selain kemoterapi dan radioterapi.
Bahan utama pembuatan obat herbal Ziirzax danTyphogell adalah daun sirsak, daun keladi tikus serta campuran beberapa jenis tanaman khusus.
Catatan: Stadium Lanjut Lebih Optimal kombinasi dg PIPECA atau Ekstraks Daun Sirih Merah & Pembersih Darah.
Khasiat Mengobati :
Miom
Kanker rahim
Kista
Serviks
Kanker otak
Kanker usus
Kanker payudara
Kelenjar getah bening
Kanker tulang
Kanker kulit
Kanker hati dll.
Konsultasi dan Pelayanan
Telepon: 085726725726
WhatsApp: 085726725726 atau 081325317374
Kami melayani 24 jam online & Respon cepat.
1 note
·
View note
Link
Mioma uteri atau dalam bahasa kedokteran juga dikenal dengan fibroid rahim adalah sebuah tumor jinak
0 notes
Photo
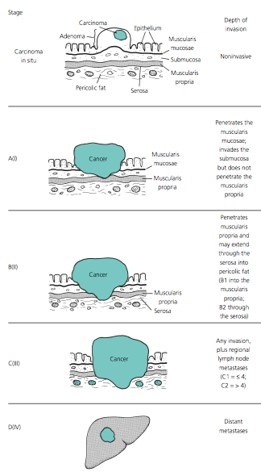
TNM staging:
TO - No evidence of primary tumor
Tis - Carcinoma in situ/HGD*
T1 - Tumor invades the submucosa but not the muscularis propria
T2 - tumor invades into but not through the muscularis propria
T3 - tumor invades into the subserosa
T4 - tumor invades into other organs/structures
*HGD = High-Grade Dysplasia
N0 - No lymph node involvement
N1 - Metastasis to 1-3 regional lymph nodes
N2 - Metastasis to 4+ lymph nodes
M0 - No distant metastasis
M1 - Presence of distant metastasis
2 notes
·
View notes
Link
The stomach is a hollow organ in the upper abdomen, under the ribs.
It's part of the digestive system. Food moves from the mouth through the esophagus to the stomach. In the stomach, the food becomes liquid. Muscles in the stomach wall push the liquid into the small intestine.
The wall of the stomach has five layers:
Inner layer or lining (mucosa): Juices made by glands in the inner layer help digest food. Most stomach cancers begin in this layer.
Submucosa: This is the support tissue for the inner layer.
Muscle layer: Muscles in this layer contract to mix and mash the food.
Subserosa: This is the support tissue for the outer layer.
Outer layer (serosa): The outer layer covers the stomach. It holds the stomach in place.
Cancer Cells
Cancer begins in cells, the building blocks that make up tissues. Tissues make up the stomach and other organs of the body.
Normal cells grow and divide to form new cells as the body needs them. When normal cells grow old or get damaged, they die, and new cells take their place.
Sometimes, this process goes wrong. New cells form when the body doesn't need them, and old or damaged cells don't die as they should. The buildup of extra cells often forms a mass of tissue called a growth, polyp, or tumor.
Tumors in the stomach can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). Benign tumors are not as harmful as malignant tumors:
Benign tumors:
are rarely a threat to life
can be removed and usually don't grow back
don't invade the tissues around them
don't spread to other parts of the body
Malignant tumors:
may be a threat to life
often can be removed but sometimes grow back
can invade and damage nearby organs and tissues
can spread to other parts of the body
Stomach cancer usually begins in cells in the inner layer of the stomach. Over time, the cancer may invade more deeply into the stomach wall. A stomach tumor can grow through the stomach's outer layer into nearby organs, such as the liver, pancreas, esophagus, or intestine.
Stomach cancer cells can spread by breaking away from the original tumor. They enter blood vessels or lymph vessels, which branch into all the tissues of the body. The cancer cells may be found in lymph nodes near the stomach. The cancer cells may attach to other tissues and grow to form new tumors that may damage those tissues.
The spread of cancer is called metastasis.
0 notes
Link
Stomach Surgery
The stomach is a hollow organ in the upper abdomen, under the ribs. It's part of the digestive system. Food moves from the mouth through the esophagus to the stomach. In the stomach, the food becomes liquid. Muscles in the stomach wall push the liquid into the small intestine.
The wall of the stomach has five layers:
Inner layer or lining (mucosa): Juices made by glands in the inner layer help digest food. Most stomach cancers begin in this layer.
Submucosa: This is the support tissue for the inner layer.
Muscle layer: Muscles in this layer contract to mix and mash the food.
Subserosa: This is the support tissue for the outer layer.
Outer layer (serosa): The outer layer covers the stomach. It holds the stomach in place.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT STOMACH SURGERIES FOR?
Bleeding in intestine: Gastrointestinal bleeding (GI bleed), is all forms of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the rectum. Bleeding is typically divided into two main types: upper gastrointestinal bleeding and lower gastrointestinal bleeding. Causes of upper GI bleeds include: peptic ulcer disease, esophageal varices (due to liver cirrhosis) and cancer. Causes of lower GI bleeds include: Diverticulosis, Angiodysplasia, inflammatory bowel disease (Ulcerative colitis & Crohn’s colitis), haemorrhoids & cancer. Obscure bleeding is defined as haemorrhage that persists or recurs after negative endoscopy. Occult bleeding is not apparent to the patient until presentation with symptoms related to the anaemia.
Know More About The Treatment.
Corrosive Acid Injury: The ingested corrosive substances are either alkalis or acid. Acids and alkalis produce different types of tissue damage. Acids cause coagulation necrosis, with scar formation that may limit substance penetration and injury depth conversely, alkalis combine with tissue proteins of body, and penetrate deeper into tissues.
0 notes
Text
Fibroids Can Affect Your Fertility says IVF hospital, Lajpat Nagar
Fibroid tumors are commonly present and almost always benign (non-cancerous). About 20% to 70% of all women will have fibroids at some stage in their lives, whether they are aware of it or not. These tumors grow as a result of cells in the uterine muscular wall multiplying at an abnormal rate. The tumors grow in size as they multiply over a longer period. Some women are unaware of the existence of fibroids; for others, the scale, quantity, or position of the tumors can cause irritation, irregular bleeding patterns, and fibroid tumors can also cause infertility. Schedule your appointment with gynecology in the IVF center in Lajpat Nagar.
Symptoms of Fibroid Tumors
Although some tumors are asymptomatic and never cause symptoms, others do. However, just because you haven't developed any symptoms doesn't mean the fibroids aren't affecting your fertility.
The following are the most common fibroids symptoms:
heavy periods
Periods for more than a week
Urination frequently
Pelvic pressure or pain
constipation
Having trouble emptying the bladder
Back pain or knee pain
What Fibroids Have an Effect on Fertility?
Fibroid tumors are classified into three types:
Subserosal: These are the most common types of fibroids. They are found on the uterine wall and account for approximately 55% of all fibroids.
Intramural: Intramural tumors occupy space in the muscular uterine wall's middle layers. They are the second most common type of fibroid tumor, accounting for 40% of all fibroid tumors.
Submucosal: Submucosal fibroids are the least common type of fibroids. They sometimes protrude into the uterine cavity since they emerge from the internal muscle wall of the uterus. They are the rarest form of fibroid, affecting only about 5% of women with fibroids.
When Fibroids Are More Likely to Cause Infertility?
Fibroids can cause infertility in a variety of ways, depending on their size and location. The following are some of the ways fibroids can interfere with conception and pregnancy.
Compromise of Fallopian tube
If the tumor pushes against the fallopian tube, the egg will not be able to travel down or you may have an ectopic pregnancy.
Alter the size of the uterusWhen a tumor moves into the uterine cavity, it may change shape or size. This shift can hinder sperm/egg fertilization or the ability of a fertilized egg to implant into the uterine linings. Once inserted, a small or misshapen uterus will interfere with the growth of the fetus and increase your chances of miscarriage.
Impact cervix shapeIf the tumor pushes against the cervix, it may prevent sperm from passing through and into the fallopian tube.
Disrupt the uterine liningIf the tumors change the uterine lining too much, it may prevent fertilized eggs from implantation or reduce the nourishment available to the embryo, possibly resulting in a miscarriage.
Block blood flow
Similarly, if the tumor restricts blood flow to the uterine lining, the lining would be less healthy than it should be, resulting in the same complications as a disrupted uterine lining. Our doctors have a lot of experience diagnosing and treating fibroid tumors. If you're looking for a fertility doctor who can help you manage your fertility while treating your fibroid tumors, consult your gynecologist
Fibroid treatment
Fibroid treatment options vary from no treatment at all to surgery. Treatment is normally unnecessary unless the fibroids are causing excessive bleeding, discomfort, or bladder problems.If you have fibroids, you should be tested regularly to review the symptoms and to check the size of your fibroid and uterus with abdominal and pelvic exams. If you don't have any signs, regular pelvic ultrasounds aren't going to help you. Fibroids are likely to develop each year before menopause, but this isn't a reason to seek care unless the transition is followed by disfiguring symptoms. For treatment options for fibroids, get a consultation at World IVF center Lajpat Nagar Delhi.
Medicines
Currently available fibroids drugs can temporarily relieve symptoms but do not heal the fibroids. If a woman is having excessive bleeding, it is worthwhile to try medicine before performing a surgical procedure. Women experiencing pressure symptoms as a result of massive fibroids would not benefit from any of the existing medications. Several exciting new medicines are on the horizon that will treat the fibroids themselves, rather than just the symptoms.MyomectomyA myomectomy is a procedure that removes fibroids while leaving the uterus intact. Myomectomy is the safest medical choice for women who have fibroid symptoms and plan to have children in the future. While myomectomy is very successful, fibroids can re-grow. The younger you are and the more fibroids you have at the time of myomectomy, the more likely it is that you will grow fibroids again. Women approaching menopause are the least likely to have chronic fibroids issues following a myomectomy.A myomectomy can be done in several ways. You may be eligible for an abdominal myomectomy, a laparoscopic myomectomy, or a hysteroscopic myomectomy depending on the size, amount, and position of your fibroids.
Hysterectomy
The uterus is removed during a hysterectomy, which is a major surgical procedure. Many women prefer hysterectomy to end their fibroid symptoms for good. Menstrual bleeding stops after hysterectomy, pelvic pressure is relieved, regular urination improves, and new fibroids cannot develop. After a hysterectomy, a woman is no longer able to become pregnant. During a hysterectomy, the ovaries are not always cut. In general, whether a woman is in or nearing menopause, her ovaries are removed. If the ovaries are irregular or if the patient wishes to reduce her risk of developing ovarian cancer later in life, the ovaries may be extracted. The removal of the ovaries in premenopausal women may result in hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and other symptoms. You should talk to your doctor about the benefits and drawbacks of ovarian removal.There are three surgical approaches to hysterectomy: vaginal hysterectomy, abdominal hysterectomy, and laparoscopic hysterectomy. The procedure chosen will be determined by the size of the uterus and many other factors. Book your treatment for fibroid in the IVF center in Lajpat Nagar.
Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE)
Uterine artery embolization is a relatively recent treatment that can be used instead of open surgery to treat fibroids. Embolization is a treatment that reduces blood flow to the fibroid or fibroids, causing them to shrink and die. This also reduces menstrual bleeding as well as symptoms of pain, pressure, urinary frequency, and constipation. Call us for the bleeding problem and get your appointment in the World IVF center Lajpat Nagar Delhi.
0 notes
Text
CÁNCER GÁSTRICO
El cáncer de estómago o cáncer gástrico es el crecimiento descontrolado de células malignas (cancerosas) en las paredes del estómago, comienza en la mucosa y a medida que crece se disemina a otras capas del estómago con capacidad de destrucción de otros órganos y tejidos.
TIPOS
Adenocarcinoma gástrico: Se divide en dos subtipos: intestinal y difuso. El intestinal se desarrolla en los intestinos y el difuso se encuentra con más frecuencia en pacientes jóvenes y en las personas con sangre del tipo A.
Tumor del estroma gastrointestinal (GIST): Surgen a partir de células de la pared del estómago llamadas células intersticiales de Cajal que regulan las contracciones intestinales.
Gastrointestinales Leiomiosarcoma: Surge a partir de las células del músculo liso en la mucosa muscular del revestimiento estomacal.
Carcinoides gastrointestinales: Surge de la mucosa gástrica en el cuerpo y fondo del estómago. La mayoría de estos tumores no se propagan a otros órganos.
Linfoma gastrointestinal: Por lo general se desarrollan en las paredes del estómago, pero puede comenzar en cualquier parte del tracto gastrointestinal.
SIGNOS Y SÍNTOMAS
En los estadios tempranos del cáncer se presentan los síntomas como indigestión y malestar estomacal, sensación de hinchazón después de comer, náuseas leves, pérdida de apetito y acidez de estómago.
En los estadios avanzados se presentan los siguientes signos y síntomas: Sangre en la materia fecal, vómitos, pérdida de peso sin razón conocida, dolor de estómago, ictericia (color amarillento de los ojos y la piel), ascitis (acumulación de líquido en el abdomen), dificultad para tragar.
FACTORES DE RIESGO
Infección por Helicobacter pylori y la dieta son dos de los factores de riesgo más importantes.
Tipo sanguíneo A
La herencia genética aumenta el riesgo de desarrollar cáncer gástrico. El cáncer gástrico difuso hereditario (HDGC por sus siglas en inglés) es un síndrome que involucra haber heredado formas específicas del gen CDH1.
Infección por el virus Epstein-Barr
Obesidad
ESTADIOS
Estadio 0 o carcinoma in situ: Es la etapa más inicial del cáncer. Se localiza en la parte más superficial de la mucosa, y no infiltra las otras capas del estómago, no invade los ganglios regionales ni produce metástasis a distancia.
Estadio I: El tumor invade la capa más profunda de la mucosa (lámina propia) o la submucosa sin afectación de ganglios linfáticos (estadio IA) o con afectación de 1 a 6 ganglios (IB), o invade la capa muscular o la subserosa sin afectación ganglionar (IB).
Estadio II y Estadio III: Son etapas intermedias. El estadio II tiene mejor pronóstico que el III. Para establecer estos estadios, se tienen en consideración tanto el nivel de afectación de la pared gástrica como el número de ganglios afectados por el tumor.
Estadio IV: El cáncer se diseminó a otras partes del cuerpo, como los pulmones, el hígado, los ganglios linfáticos distantes y el tejido que reviste la pared del abdomen.
TRATAMIENTO
Resección endoscópica de la mucosa (REM): Consiste en extirpar el tumor mediante gastroscopia y se reserva para cánceres iniciales, de pequeño tamaño (< 2 cm), limitados a la mucosa y sin úlceras.
Cirugía: La gastrectomía es la técnica quirúrgica estándar para resecar el tumor primario. Dependiendo de la extensión y localización en el estómago, la gastrectomía será total o subtotal.
Radioterapia: Es el tratamiento con radiaciones ionizantes. Con la radioterapia, se trata una zona concreta del cuerpo.
Quimioterapia, anticuerpos monoclonales e inmunoterapia: Consiste en la administración de fármacos con actividad antitumoral que alteran la función de las células neoplásicas y causan su destrucción.
youtube
0 notes
Text
Everything You Need To Know About Areolar Tissue

What is areolar tissue? What is its role in the body? Loose connective tissue is a category of connective tissues that includes areolar tissue, reticular tissue, and adipose tissue. Loose connective tissue is the most common type of connective tissue in vertebrates. It holds organs in place and attaches epithelial tissue to other underlying tissues. For instance, it forms telae, such as the tela submucosa and tela subserosa, which link mucous and serous membranes to the muscular layer. >>>continue reading >>> cosmetic surgery
0 notes
Text
Screening Tests
Screening tests for colon cancer is the process of looking for cancer in people who have no symptoms. Several tests can be used to screen for colorectal cancer. One of it is stool-based tests. These tests check the stool faces for signs of cancer. These tests are less invasive and easier to have done, but they need to be done more often. Another test is visual structural tests. These tests look at the structure of the colon and rectum for any abnormal areas. This is done either with a scope, which is a tube-like instrument with a light and tiny video camera on the end then put into the rectum, or with special imaging which is x-ray tests (Vega.P., Valentín.F., & Cubiella, J., 2015).
Tumour Node Metastasis System (TNM)
One of the tool that doctors use to describe the stage is the Tumour Node Metastasis system (TNM). Doctors use the results from diagnostic tests and scans to answer these questions:
Tumour (T): Has the tumour grown into the wall of the colon or rectum? How many layers?
Node (N): Has the tumour spread to the lymph nodes? If so, where and how many?
Metastasis (M): Has the cancer spread to other parts of the body? If so, where and how much?
There are 5 stages in this TNM system, starting from stage 0 (zero) and stages I through IV (1 through 4). The stage provides a common way of describing the cancer, so doctors can work together to plan the best treatments.
Tumour (T)
Using the TNM system, the "T" plus a letter or number (0 to 4) is used to describe how deeply the primary tumour has grown into the bowel lining. Stage may also be divided into smaller groups that help describe the tumour in even more detail. Specific tumour information is listed below (Cancer.Net., 2019).
TX: The primary tumour cannot be evaluated.
T0 (T plus zero): There is no evidence of cancer in the colon or rectum.
T refers to carcinoma in situ (also called cancer in situ). Cancer cells are found only in the epithelium or lamina propria, which are the top layers lining the inside of the colon or rectum.
T1: The tumour has grown into the submucosa, which is the layer of tissue underneath the mucosa or lining of the colon.
T2: The tumour has grown into the muscular is propria, a deeper, thick layer of muscle that contracts to force along the contents of the intestines.
T3: The tumour has grown through the muscular is propria and into the subserosa, which is a thin layer of connective tissue beneath the outer layer of some parts of the large intestine, or it has grown into tissues surrounding the colon or rectum.
T4a: The tumour has grown into the surface of the visceral peritoneum, which means it has grown through all layers of the colon.
T4b: The tumour has grown into or has attached to other organs or structures.
Node (N)
The "N" in the TNM system stands for lymph nodes. The lymph nodes are tiny, bean-shaped organs located throughout the body. Lymph nodes help the body fight infections as part of the immune system. Lymph nodes near the colon and rectum are called regional lymph nodes. All others are distant lymph nodes that are found in other parts of the body (Cancer.Net., 2019).
NX: The regional lymph nodes cannot be evaluated.
N0 (N plus zero): There is no spread to regional lymph nodes.
N1a: There are tumour cells found in 1 regional lymph node.
N1b: There are tumour cells found in 2 or 3 regional lymph nodes.
N1c: There are nodules made up of tumour cells found in the structures near the colon that do not appear to be lymph nodes.
N2a: There are tumour cells found in 4 to 6 regional lymph nodes.
N2b: There are tumour cells found in 7 or more regional lymph nodes.
Metastasis (M)
The "M" in the TNM system describes cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver or lungs. This is called distant metastasis.
M0 (M plus zero): The disease has not spread to a distant part of the body.
M1a: The cancer has spread to 1 other part of the body beyond the colon or rectum.
M1b: The cancer has spread to more than 1 part of the body other than the colon or rectum.
M1c: The cancer has spread to the peritoneal surface.
Grade (G)
Doctors also describe this type of cancer by its grade (G). The grade describes how much cancer cells look like healthy cells when viewed under a microscope.
The doctor compares the cancerous tissue with healthy tissue. Healthy tissue usually contains many different types of cells grouped together. If the cancer looks similar to healthy tissue and has different cell groupings, it is called "differentiated" or a "low-grade tumour." If the cancerous tissue looks very different from healthy tissue, it is called "poorly differentiated" or a "high-grade tumour." The cancer’s grade may help the doctor predict how quickly the cancer will spread. In general, the lower the tumour’s grade, the better the prognosis (Cancer.Net., 2019) .
GX: The tumour grade cannot be identified.
G1: The cells are more like healthy cells, called well differentiated.
G2: The cells are somewhat like healthy cells, called moderately differentiated.
G3: The cells look less like healthy cells, called poorly differentiated.
G4: The cells barely look like healthy cells, called undifferentiated.
References:
Cancer.Net. (2019). Colorectal Cancer: Stages. Journal of ASCO. Retrieved from: https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/colorectal-cancer/stages
Vega, P., Valentín, F., & Cubiella, J. (2015). Colorectal cancer diagnosis: Pitfalls and opportunities. World journal of gastrointestinal oncology, 7(12), 422–433. https://doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v7.i12.422
0 notes
Text
What is gastric cancer?

The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen and is part of the digestive system. It processes nutrients and foods that are eaten. It also contributes to excretion of waste materials out of the body. The stomach partly digests the food and passes into the small intestine (National Cancer Institute, 2019).
Gastric cancer begins in the mucosa, which is the innermost layer of the stomach. It can spread through the outer layers as it grows. Symptoms of this cancer do not usually show until the advanced stages. In more advanced stages of gastric cancer, symptoms such as blood in the stool, vomiting, weight loss for no known reason, stomach pain, and jaundice are prominent (National Cancer Institute, 2019).
One can be diagnosed with stage IIIA cancer when the cancer has spread to the muscle layer of the stomach or subserosa of the stomach wall, affecting nearby lymph nodes in small numbers, or to nearby organs such as the spleen, colon, liver, diaphragm, pancreas, abdomen wall, adrenal gland, kidney, or small intestine, or to the back of the abdomen (American Cancer Society, 2015). Overall, the cancer will have spread deeper into the stomach wall and to more lymph nodes than a stage II cancer.
Gastric cancer is one of the most common and deadly cancers worldwide, being the 3rd most deadly cancer in 2018 with Adenocarcinoma being the most common type. Risk factors of this disease include Helicobacter pylori infection, pernicious anemia, genetics, smoking, being older or male, socio-economic factors, or eating a diet high in salted, smoked foods and low in fruits and vegetables and foods that have not been prepared or stored properly. The most effective means of gastric cancer prevention are dietary and lifestyle modification (Rawla and Barsouk, 2019).
Cancer cachexia is a common condition that occurs in many cancers. It usually develops at the advanced stages of the disease. It is led by gastric and pancreatic cancer seen in 85% and 83% of cancer patients, respectively (Lynch, 2012).
References:
American Cancer Society (2015). Stomach Cancer. Retrieved from http://www.cancer.org/cancer/stomachcancer/index
Lynch, P. (2012). The Patient With Cancer Cachexia. Retrieved from: https://www.cancernetwork.com/oncology-nursing/patient-cancer-cachexia/page/0/1
National Cancer Institute (2019). Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/types/stomach/patient/stomach-treatment-pdq#_1
Rawla, P., & Barsouk, A. (2019). Epidemiology of gastric cancer: global trends, risk factors and prevention. Przeglad gastroenterologiczny, 14(1), 26–38. doi:10.5114/pg.2018.80001
0 notes
Text
Flimty Kota Kayu Agung (Hub : 0812 – 3181 – 2430 tsel)
Flimty Kota Kayu Agung (Hub : 0812 – 3181 – 2430 tsel) Agen Flimty Kota Kayu Agung, Jual Flimty Kota Kayu Agung, Distributor Flimty Kota Kayu Agung, COD Flimty Kota Kayu Agung. Tanyakan Kepada Kami Informasi Selengkapnya, Kami Juga Menerima Pendaftaraan Agen Bentrap, Paket Bisa Dikirimkan Ke Seluruh Indonesia Melalui Ekspedisi – Masih belum yakin untuk mengupayakan mengkonsumsi Flimty? Masih ragu apakah Flimty benar-benar dapat membantu menanggulangi masalah keunggulan berat badan anda? Sudah terlambat bagi kamu untuk mengkhawatirkan urusan tersebut. Kenapa? Karena saat kamu masih ragu, telah ada ratusan dan bahkan ribuan orang yang sudah memperlihatkan sendiri khasiat dari Flimty.
Untuk masalah khasiatnya, Flimty telah tidak butuh diragukan lagi. Hal tersebut telah terpampang jelas dari kandungan yang terdapat di dalamnya. Lalu bagaimana dengan keamanannya? Apakah Flimty lumayan aman untuk kamu konsumsi? Apakah memang tidak terdapat efek samping apapun yang perlu kamu takutkan sesudah rutin mengkonsumsi Flimty? kita tidak perlu cemas mengkonsumsi Flimty secara berkala. Flimty paling aman guna dikonsumsi dan bahkan sangat disarankan untuk dikonsumsi secara berkala. Lalu apa buktinya bahwa Flimty benar-benar aman guna dikonsumsi? Berikut ialah beberapa sertifikasi yang dapat membuktikan bahwa Flimty bukanlah produk yang riskan untuk dikonsumsi:
Flimty Kota Kayu Agung

Flimty Kota Kayu Agung
Kaya Kandungan Serat
Flimty Fiber Supplement Diet adalah suplemen kesehatan yang kaya bakal kandungan serat alaminya. Serat menolong dalam mengoptimalkan proses pencernaan, mengikat kandungan lemak berlebih serta paling baik dalam mengatasi sekian banyak macam masalah pencernaan mulai dari konstipasi dan diare.
Berfungsi Sebagai Detox Alami
Tubuh kita perlu guna didetox secara berkala. Sayangnya banyak sekali orang tidak tahu bagaimana teknik mengeluarkan seluruh racun yang berada dalam tubuh Anda. Well, produk Flimty Fiber Supplement Diet menawarkan penyelesaian detox alami. Dimana melulu dengan mengkonsumsinya secara tertata dapat menolong mengeluarkan racun-racun riskan dari dalam tubuh sampai-sampai sistem metabolisme dapat berlangsung secara optimal.
Baik guna Saluran Pencernaan
Dalam penyembuhan tradisional Cina, drainase pencernaan memiliki faedah penyeimbang. Jika drainase pencernaan sehat maka sistem metabolisme dapat bermanfaat secara maksimal. Kandungan serat serta vitamin yang didapat dari ekstrak goji berry serta sayuran dan buah-buahan yang ada dalam Flimty Fiber Supplement Diet paling baik untuk drainase pencernaan.
Merampingkan Perut
Untuk apa mempunyai berat badan yang ideal namun perut kita tetap saja buncit? Ada tidak sedikit faktor yang mengakibatkan perut tetap buncit walaupun berat badan Anda telah turun sehingga menciptakan postur tubuh tidak terlihat ideal. Hanya dengan meminum suplemen kesehatan ini secara tertata Anda bisa merampingkan perut kita secara alami.
Mengatasi Masalah Konstipasi
Konstipasi untuk sebagian orang barangkali sudah menjadi masalah sehari-hari. Tapi tahukan kita bahwa konstipasi dapat menjadi cikal akan masalah pencernaan yang lebih parah laksana radang lambung. Atasi masalah konstipasi dengna mengkonsumsi makanan atau minuman kaya serat dan Flimty ialah solusi termudah yang dapat Anda temukan.
Membantu Mengatur Gula Darah
Bagi kita yang telah didiagnosa mengidap penyakit diabetes tidak butuh khawatir sebab Flimty menawarkan penyelesaian alami supaya Anda bisa selalu menata kadar gula darah Anda. Walaupun pastinya tetap dibuntuti dengan diet yang sehat serta berolahraga secara teratur. Flimty Kota Kayu Agung.
Menurunkan Kadar Kolesterol
Sebagai suplemen makanan yang kaya serat, guna Flimty juga dapat menurunkan kadar kolesterol. Serat yang terdapat dalam Flimty tidak bakal diproses oleh tubuh namun memiliki faedah penting sebagai pengikat lemak yang lantas akan dilemparkan keluar dari tubuh secara alami.
Mengurangi Risiko Penyakit Jantung
Jika kada kolesterol serta lemak darah kita terjaga maka bisa menurunkan risiko penyakit jantung. Terdapat sejumlah kandungan baik untuk jantung yang pun ada dalam Flimty Fiber Supplement Diet laksana extrak sayuran dan buah-buahna, probiotik dan masih tidak sedikit lagi.
Kaya Kandungan Nutrisi baik guna Kesehatan
Sangatlah urgen mengkonsumsi makanan seimbang tetapi kadang paling sulit untuk mengisi kadar kecukupan gizi sehari-hari. Tapi kita tidak butuh khawatir sebab Flimty adalah produk kesehatan yang kaya kandungan nutrisi baik guna kesehatan kita dan keluarga.
Pemesanan Bisa Melalui WA : 0812 – 3181 – 2430 (TSEL)
Flimty Kota Kayu Agung
Inilah Ciri Sakit Perut Akibat Miom
Sakit perut ialah keluhan yang dapat terjadi pada siapa saja, dan umumnya dirasakan sebagai situasi yang sepele. Padahal, keluhan tersebut dapat menjadi pertanda dari adanya sesuatu yang tidak beres dengan organ dalam tubuh Anda. Salah satu yang bahkan tidak diduga dapat menjadi penyebab sakit perut ialah miom.
Apa tersebut miom? Berdasarkan keterangan dari dr. Karin Wiradarma dari KlikDokter, miom atau mioma uteri ialah tumor jinak rahim yang tumbuh dari jaringan otot rahim. Kondisi ini diduga muncul pada 20 persen wanita umur subur, dan seringkali baru terdeteksi saat mengerjakan pemeriksaan berkala. Hal ini disebabkan miom tidak memberikan fenomena yang spesifik pada perempuan yang mengalaminya.
Pada banyak sekali kasus, miom dapat mengakibatkan gangguan kesuburan (infertilitas). Pada sejumlah kasus lainnya, situasi ini juga dapat membuat perempuan kehilangan rahim sebab harus “diangkat” melewati tindakan operasi (histerektomi).
Miom, yang menjadi penyebab gangguan kesuburan dan operasi pelantikan rahim pasti bukan perkara sepele. Jadi, bakal lebih baik bila miom terdeteksi sejak mula oleh dokter supaya kedua urusan itu dapat dicegah. Caranya, dengan memahami tanda-tanda adanya miom pada rahim. Berdasarkan keterangan dari dr. Valda Garcia dari KlikDokter, di antara keluhan yang dapat menjadi fenomena adanya miom ialah terjadinya gangguan haid.
“Wanita yang punya miom ingin mengalami siklus haid yang tidak teratur,” jelas dr. Valda.
Lalu, bagaimana dengan ciri sakit perut sebab miom? Apakah ada fenomena khas yang dapat diperhatikan?
Sakit perut dampak miom
“Sakit perut yang dirasakan seringkali berupa nyeri yang paling hebat. Intinya, lebih sakit daripada seringkali atau sakit perut yang belum pernah kita alami sebelumnya. Kalau punya masalah haid yang tidak tertata dan tiba-tiba merasakan nyeri hebat, kerjakan pemeriksaan supaya miom terdeteksi,” dr. Valda menegaskan.
Perlu diketahui pun bahwa sakit perut dampak miom seringkali hanya timbul andai ukuran tumor sudah paling besar. Jika ukuran miom kecil, sakit perut tidak bakal timbul dan melulu memberikan persoalan pada siklus haid.
Sebenarnya, tak hanya haid yang tidak teratur, jumlah darah yang dikeluarkan ketika datang bulan pun jauh lebih tidak sedikit bila kita mempunyai miom. Bahkan, perut unsur bawah nampak lebih banyak (seperti terdapat benjolan) dan kita menjadi tidak jarang buang air kecil.
Kendati demikian, tidak seluruh miom berukuran besar mengakibatkan sakit perut atau keluhan lainnya. Berdasarkan penuturan dr. Alvin Nursalim, SpPD dari KlikDokter, miom yang besar juga dapat hadir tanpa gejala, tidak mengarah pada keganasan, dan tidak membutuhkan terapi. Hanya saja, pada mioma berukuran besar yang tidak diterapi, pemeriksaan jasmani dan USG harus diulang masing-masing 6–8 minggu.
“Gunanya untuk memantau pertumbuhan miom, baik dari sisi ukuran maupun jumlah. Jika tidak memunculkan pertumbuhan yang berarti, pasien bakal tetap diobservasi masing-masing 3–4 bulan. Jika terdapat perubahan, miom tidak harus dioperasi dan dapat dilakukan terapi hormonal. Efek hipoestrogen dari terapi itu akan mengecilkan ukuran miom,” pungkas dr. Alvin.
Kemungkinan hamil pada pasien miom
Tidak seluruh penderita miom akan merasakan gangguan kesuburan sehingga kendala untuk hamil. Sebab, terdapat atau tidaknya gangguan kesuburan pada penderita miom tergantung dari tempat terbentuknya tumor.
Fakta melafalkan bahwa tumor yang bisa menurunkan tingkat kesuburan sampai 70 persen pada pasien miom ialah yang terletak di unsur tengah otot rahim (miom intramural) dan di unsur dalam rongga rahim (miom submukosa). Sebab, pada situasi tersebut, tonjolan tumor mengolah rongga rahim dan dirasakan sebagai benda asing oleh tubuh. Alhasil, tumor itu menjadi penghalang dalam proses implantasi (saat sel telur dibuahi sperma). Jika tumor miom sukses dikecilkan atau diusung berkat penanganan tepat dalam masa-masa segera, peluang hamil dapat meningkat menjadi 70 persen.
Sementara itu, untuk wanita yang mempunyai miom di luar permukaan rahim (miom subserosa), kita tidak perlu terlampau khawatir. Itu sebab miom jenis itu tidak memengaruhi tingkat kesuburan dan tidak mengakibatkan perubahan pada rongga rahim.
0 notes
Text
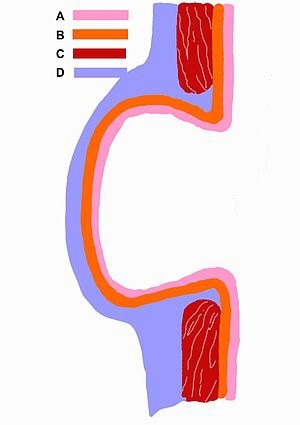
I was confused about a false diverticulum vs a true diverticulum. First Aid says a true diverticulum involves “all 3 wall layers,” but there are 4 layers, right? The mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa (or adventitia if you’re behind the peritoneum). This image from Wikipedia helps. According to Wikipedia:
True diverticula involve all layers of the structure, including muscularis propria and adventitia, such as Meckel's diverticulum. False diverticula (also known as "pseudodiverticula") do not involve muscular layers or adventitia. False diverticula, in the GI tract for instance, involve only the submucosa and mucosa.
Schematic drawing of a false diverticulum. A - mucosa; B - submucosa; C - muscularis; D - serosa and subserosa
I guess maybe the wall of the intestine doesn’t include the surface on the outside (serosa or adventitia). Idk, but for it to be a true diverticulum, the red part (muscularis externa) must also be included.
#true diverticulum#false diverticulum#diverticulum#diverticulosis#true diverticula#false diverticula#diverticula
0 notes
Link
0 notes
Text
What Are The Stages of Stomach Cancer? - (TNM Staging) - Part 3
What Are The Stages of Stomach Cancer? – (TNM Staging) – Part 3
The TNM System Grouping
Stage 111A – (T2, N3, M0) The cancer has extended its metastasis into the main muscle layer of the stomach wall (muscularis propria [T2]). Now 7 regional lymph nodes have been affected (N3). The cancer has not yet reached any distant tissues or organs (M0).
or (T3, N2, M0) The cancer has now affected the subserosa, although it has not metastasized through all the…
View On WordPress
0 notes