#revolution army
Text





























Sabo recap -One Piece EP1089
#One Piece#One Piece anime#op anime#op#revolution army#anime#anime recap#sabo#one piece sabo#flame emperor sabo#revolutionary sabo#anime cap#dragon#dragon one piece#imu#five elders#op pic
143 notes
·
View notes
Text

Monkey D. Dragon in his twenties~
Not a teen anymore, but young enough to shock some barkeepers.
I just wanted to see if I can work out some similarities to his son when I draw him younger and some features really made it through, it seems |D
Like what you see? More fanart here:
WantedWendigo User Profile | DeviantArt
#monkey d dragon#younger version#onepiece#one piece#revolution army#luffys parents are something#everything in green#the power of YOUTH#op fanart#op
95 notes
·
View notes
Text

Otherwise I love the design, but why do the skirts always have to be so short in One Piece?
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
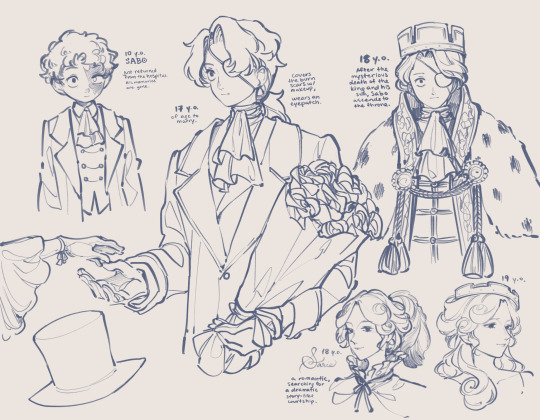
Thinking very hard about an AU idea of mine. Reluctant king Sabo AU!
In which Sabo isn’t saved by Dragon, but survives long enough to drift ashore and be saved by the doctors of Goa Kingdom, who do so only to ransom his medical bills from Sabo’s parents. Sabo’s parents take him back, thinking that his amnesia makes him a clean slate, but Sabo, young and stubborn and unsure of his entire identity, knows that everything is wrong and runs again, and again, and again.
Until at some point, he meets the Revolutionaries, and realizes that he can be useful to them, provide them information, make something good of an inescapable situation. From then on, he starts acting the noble that he was born as, in order to be a more useful informant to the Revolutionaries, until sunk cost fallacy hits and he believes that being a noble is the only way that he can be useful to the Revolutionaries. So at that point, why not take it all the way?
At 17, Sabo becomes one of Princess Sarie’s suitors, and at 17, he has doubts about using the princess for his own goals. Sarie is a romantic, and she wants a dramatic fairy tale of a romance, and she was already charmed, but the moment Sabo opens up to her about not wanting to use her to get to the throne, having lofty ambitions of helping the people (just not the people she thinks he’s talking about), Sabo becomes the one she simply must marry, because surely if she tries hard enough, she can make him love her back.
Soon after, the king and his son die. Sarie’s father and brother die. And while Sabo conveniently ascends to the throne, he also swiftly implicates his father, Outlook, in the assassination of all heirs to the throne, resulting in Outlook’s arrest and subsequent execution. And thus, at 18, Sabo becomes king, and begins to gradually institute great changes to Goa Kingdom.
Design-wise, Sabo wears an eyepatch because his damaged eye is considered a grotesque sight by nobles’ standards. Under the eyepatch, he wears heavy makeup to hide the burn scar. These are both at the behest of his birth parents, who spin a story about Sabo having been born half blind to hide the fact that Sabo had been shot by a Celestial Dragon and save face. To those who have seen his scar, they fabricate a second secret story that he was unfortunately kidnapped as a child. Sabo never does find out, until he regains his memories, where the burn scar is actually from.
#one piece#sabo#one piece au#king sabo au#I might write something for this#I have a lot of ideas for it#I love au’s where sabo helps the revolution while not being actually a member of the revolutionary army#but I very rarely see ones that I like#I am going to oc-ify sarie so much.#i think sabo would hate being king. I think he hates everything about the situation he is in#but I also think that in the wake of forgetting himself he needs some connection to cling onto#even if that connection is the extremely inspiring stranger that barely knows him but is proud of him for helping#namely dragon.#I’m still unsure where to put stelly in all of this#I think stelly gets extremely bitter when sabo starts surpassing him in everything#because he was supposed to be the successful replacement of a son#im also debating whether or not I want sabo to remember his memories before or after marineford#because the moment he regains his memories is very clear to me. I want garp to see him at the reverie and punch him.#but I don’t know if I want that to happen earlier or later
296 notes
·
View notes
Text










"I'm doing this for me. I can't live with what I did anymore. You're wrong. They won't win. Because one good thing came out of all of this; they showed themselves. The top one percent of the one percent, the ones in control, the ones who play God without permission, and now I'm gonna take them down. All of them."
MR. ROBOT (2015–2019)
Created by Sam Esmail
#mr robot#mr. robot#mrrobotedit#edit#tv#tvedit#tv series#tv show#rami malek#hacker#fsociety#revolution#elliot alderson#darlene alderson#angela moss#whiterose#2019#favourite tv show#dark army#cyber#ramimalekedit#evil corp
465 notes
·
View notes
Text
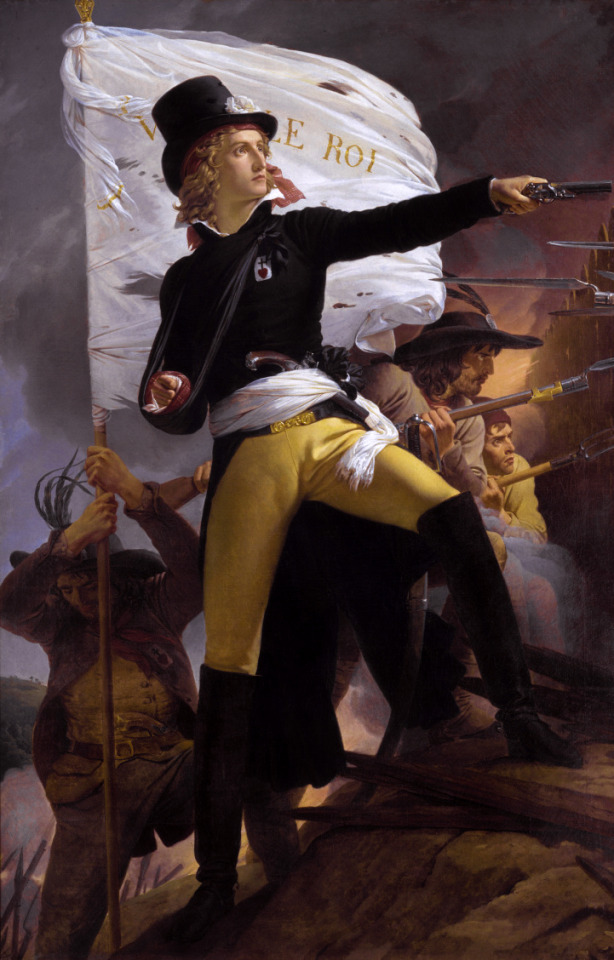

Henri de la Rochejaquelein by Pierre-Narcisse Guérin
#henri de la rochejaquelein#art#pierre narcisse guérin#portrait#war in the vendée#vendée#royalist#royalists#french revolutionary wars#french revolution#france#french#henri du vergier#vendéan#insurrection#rebellion#catholic#royal#history#europe#european#aristocratic#nobility#aristocrat#nobleman#kingdom of france#general#monarchy#army#vendéans
122 notes
·
View notes
Text
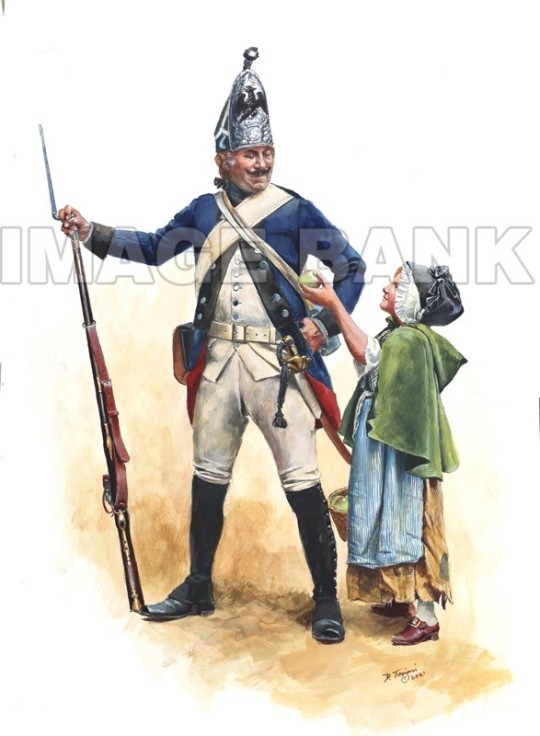
Who Wants a Non-Hessian German Troops of the American Revolution Uniform Identification Flow Chart?

Now you too can roleplay as a harried British staff officer trying to identify which troops are encamped where, or a devious rebel spy collecting intelligence.
As folks may or may not know, only roughly 50% of the German state troops who served the British Crown during the American Revolution were “Hessians” from Hesse-Cassel. There were six other states that provided “subsidy troops.” Here’s how to tell them apart at a glance.
Are their uniforms predominantly dark blue? If yes, go to the paragraph numbered 4. If no, go to the para numbered 2.
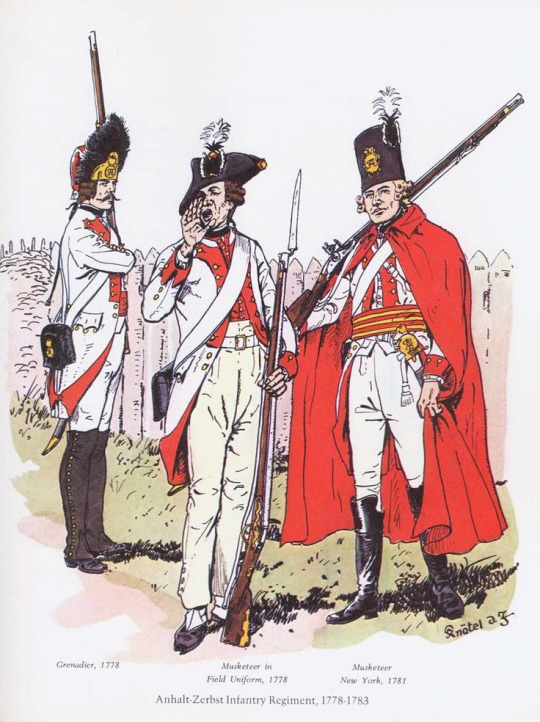
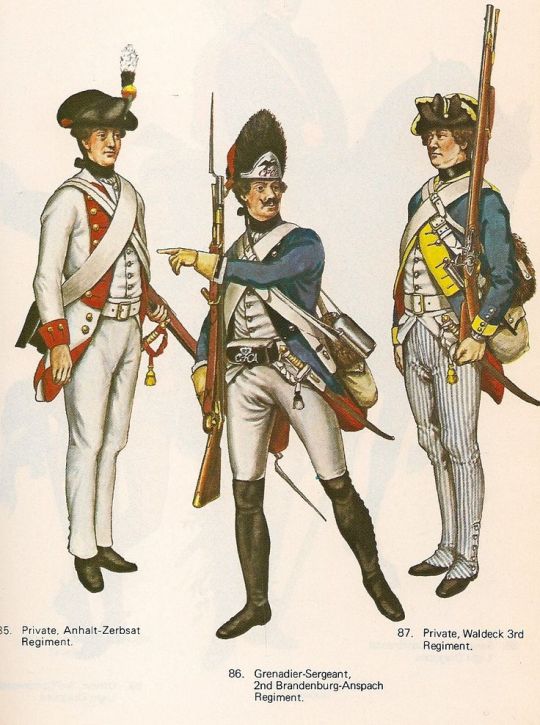
2. Are their uniforms predominantly white? If no, go to the para numbered 3. If yes, those are troops from Anhalt-Zerbst. The only German state involved in the war to take its uniform and organisational cues from Austria rather than Prussia, the single Anhalt-Zerbst line regiment deployed to America wore white regimental coats faced with red. Their grenadiers wore bearskins rather than metal-faced caps (the only other German state to do this was Waldeck). One battalion also, according to one shocked British officer, had one of the most outrageous-looking uniforms of the war, including hussar hats, red and yellow waist sashes and red cloaks - these may have been “pandour” irregulars from the edges of the Austrian empire.

3. The coats are neither white nor blue, so they must be red. In this case, the troops are Hanoverian. While still mostly following Prussian style, because they shared a ruler with Britain, Hanoverian troops wore red. Five Hanoverian regiments assisted Britain with vital Mediterranean defence during the American Revolution, before going on to fight in India. They were the only redcoat Germans fighting for the Crown outside the British Army.
4. Your Germans are wearing blue coats. Are the buttons on the coat lapels arranged 1-2-1, and do the cuffs have a “Swedish” style slit to them? If no, go to the para numbered 5. If yes, they’re from Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel. Brunswick provided the most soldiers after Hesse-Cassel, and arguably the most rounded force, with four line regiments, one dragoon regiment, one grenadier battalion and one light infantry battalion. But whether jäger, musketeers or grenadiers, they almost all had coat buttons in groups of 1-2-1 and the slit-style cuffs. Fun fact; the Brunswick crest of a racing white horse on a red field was the same as neighbouring Hanover’s.

5. Your Germans are wearing blue, but don’t have buttons in 1-2-1 and Swedish cuffs. Do they have yellow facings, and cuffs with buttons placed both horizontally and vertically? If no, go to the para numbered 6. If yes, they are from Waldeck. This German state usually provided troops for the Dutch, but raised a new unit, the 3rd English-Waldeck Regiment, for service in America. They mostly fought against the Spanish in the Deep South, where they were decimated by disease. If the unusual position of the buttons on the cuff isn’t enough, look for the belt plate bearing “FF” for “Fuerst Friedrich,” the state’s ruler.
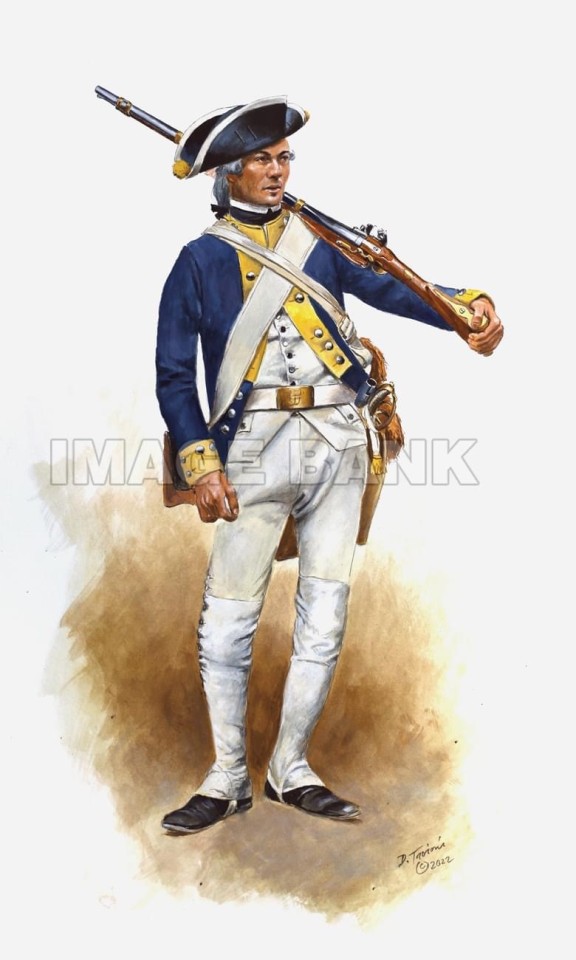

6. Do your blue Germans have red facings, cocked hats and unusual lace on their coats, shaped like a figure-of-eight? If no, go to the para numbered 7. If yes, they’re from Hesse-Hanau. This state was closely related (in the sense of its ruler, literally) to Hesse-Cassel, yet remained independent. While it provided a small amount of artillery, jägers and freikorps light infantry, its main contribution was a single line regiment, Erbprinz. Their distinctive features were scalloped lace on their cocked hats and the figure-of-eight “Brandenburg” style lace. There was also a Hesse-Cassel Regiment Erbprinz (even sharing the same colonel-in-chief), but they were fusiliers with caps rather than the Hesse-Hanau musketeers with their cocked hats. Check the mistake made by this artwork - these are Hesse-Hanau soldiers from the Infanterie Regiment Erbprinz, but they’re wearing Cassel fusilier caps. Bonus fact; Hanau and Cassel’s crest both features a rampant lion with red and white stripes, but there are subtle differences - they face opposite directions, the style of stripes are slightly different, and the Hanau lion lacks the Cassel one’s crown, but does wield a sword.

7. Do your blue-coated Germans have a black eagle on their flags and grenadier cap plates? If no, they’re probably from Hesse-Cassel. If yes, they’re from Ansbach-Bayreuth. This German state consisted of two provinces, Ansbach and Bayreuth (funny that). Besides jägers and some battalion guns, their main contribution was two infantry regiments, one from each of the two provinces. Their ruler’s crest was a black eagle, similar to the Prussian one.

Of course these posts don’t account for the uniforms of the jäger corps, or musicians, or any artillery, but it can serve as a rough guide. For the proper detail, you’ll have to buy my forthcoming book on the topic!
Also would be pretty cool if someone made an actual flow chart out of this, just saying!

#hessian#hessians#german#germany#german army#german military#18th century#history#military history#american revolution#revwar#american war of independence
346 notes
·
View notes
Text
With Luffy’s and Dragon’s blood relation became public.
Dragon had a way easier time to watch and monitor over Luffy. and now that the entire revolution army knows about Dragon son they make sure any updates on Monkey D Luffy goes straight to Dragon.
#The rev army should be like aunts and uncles to Luffy#worried aunties and uncles#The revolution army#monkey d luffy#monkey D dragon#revolutionary army#emporio ivankov#Sabo#revolutionary sabo#I like to imagine he always try to keep up with his son#Good Dad Dragon#one piece
148 notes
·
View notes
Text
Paris Fire Brigade — The fire department of the city of Paris
The Paris Fire Brigade was created by Napoleon on 18 September 1811 after a devastating fire in Paris in 1810. The brigade remains the same firefighting service of Paris to this day.
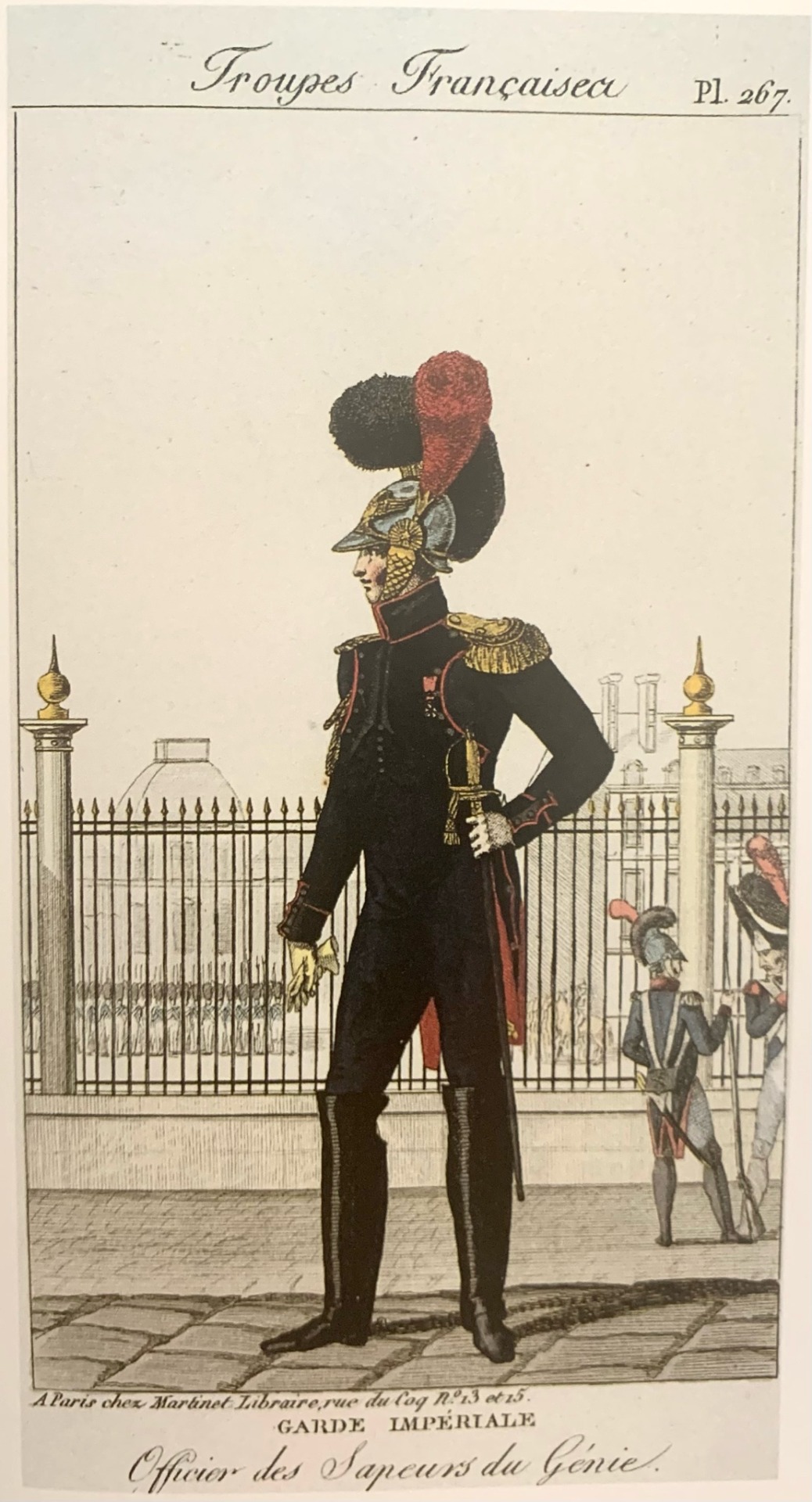


Illustrations created by Aaron Martinet between 1807 and 1814. Top: Imperial Guard, Engineer Sapper. Bottom: Imperial Guard, Officer of Engineer Sappers. These were the military positions which were transitioned into the fire department.
The deadly fire at the Austrian embassy ball in July 1810, during the festivities for his marriage to Marie Louise, reminded the Emperor of the importance of a well-functioning fire service in the capital.
Despite the courage and dedication of the gardes pompes [firefighters of the old organization], who are sometimes falsely accused of numerous shortcomings, the firefighting service revealed its weaknesses: delays, insufficient and unreliable equipment, poorly trained personnel and incompetent managers. The staff present at the embassy on the day of the tragedy were cleared of all suspicion by an investigation led by the Count of Montalivet. On the other hand, the leaders of the old organization were dismissed, and the corps des gardes pompes was abolished.
After this catastrophe, the Emperor reorganized this public service by creating the first military corps of firefighters, made up of the engineers from the Imperial Guard who were dedicated to defending the imperial chateaux against fire.
At the behest of Emperor Napoleon I, the creation of the Paris fire department [bataillon de sapeurs pompiers de Paris] by imperial decree on 18 September 1811 was an original and innovative step, marking the transition from a civil and municipal organization to a military body. The choice of such an atypical status for a public service echoes the creation, eleven years earlier, of the Paris Police Prefecture, an equally singular legal administrative body.
From its creation, this military corps was placed under the authority of the Paris Police Prefecture, who was responsible for the security of the capital. After a long process, this military status and subordination to a prefect became the logical consequence of the spirit of the decree of 12 messidor year 8.
When the battalion was formed in 1811, the Paris fire department took on a new mission: fighting fires, the importance and development of which they were still unaware of.
Four companies were then created to respond to fires. Relying on a typically military functional triptych (extensive training of men, systematic technological research and implementation of efficient operational procedures), the battalion quickly made its new environment its own, and by the end of the second half of the 19th century, had become a model for the organization of public fire-fighting services and a national, even international reference.
Several fire chiefs succeeded one another until 1814. At that date, command was entrusted to battalion commander Plazanet. He provided the battalion with an instruction manual, made it compulsory for sappers to be stationed in barracks, and introduced gymnastics to train efficient and daring rescuers.
Source: Brigade de sapeurs-pompiers de Paris — Le Bataillon
Picture source: Napoleon's Army: 1807-1814 as Depicted in the Prints of Aaron Martinet, By Guy C. Dempsey, Jr., (Section: Support Troops)
#firefighters#Napoleon#napoleon bonaparte#napoleonic era#napoleonic#first french empire#french empire#19th century#history#Paris#french revolution#Aaron martinet#france#french history#fire department#Napoleon’s reforms#napoleonic reforms#reforms#art#Napoleon's Army: 1807-1814 as Depicted in the Prints of Aaron Martinet#prints#Paris Fire Brigade#fire brigade#bataillon de sapeurs pompiers de Paris#Brigade de sapeurs-pompiers de Paris
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
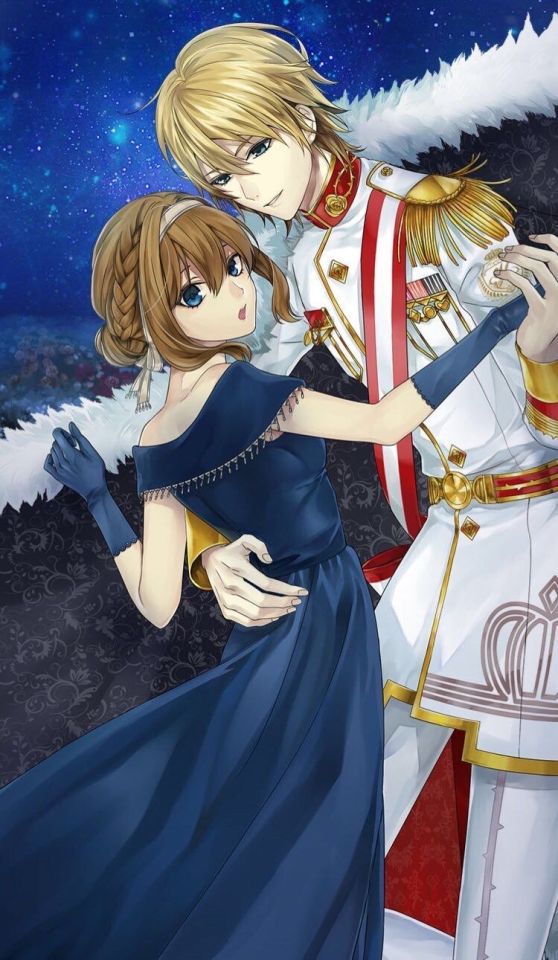


cg redraw :>
#ikemen revolution#ikerev#im sweating#i wanna do more lance stuff too#idk what it is that bit me in the ass#but the red army has me in a chokehold rn
124 notes
·
View notes
Text
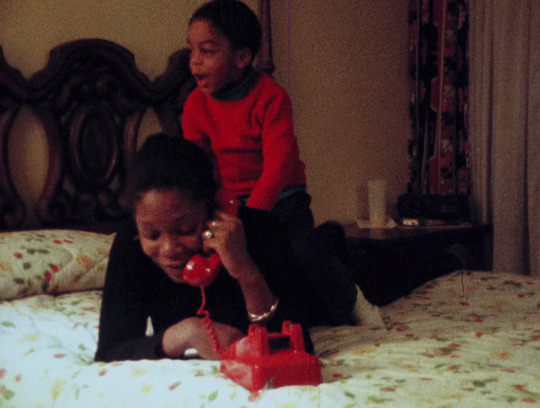
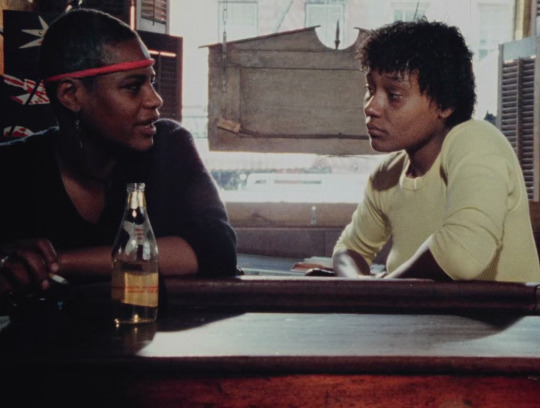











Born in Flames (Lizzie Borden, 1983)
#films watched in 2023#Born in Flames#Lizzie Borden#1983#quote#feminism#army#violence#eighties#science fiction#independent cinema#fantastic#dystopia#fashion#smoke#guns#sunglasses#revolution#ocho
179 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Basics Of American Revolutionary War Uniforms:
Basic descriptions I wrote of each layer of a Continental Army soldier's uniform in order of what you'd put on first to what you'd put on last, starting with:
Shirts:
In the 18th century, a man with a shirt was considered naked, so the shirt was a part of every outfit (although it was often covered in other layers of clothing). The shirts worn by the soldiers in the revolution were designed to be as comfortable as humanly possible, so they were very long, often stopping mid-thigh or just below the knee, loose and flowy, and had lots of ruffles at the top. Shirts also had long, puffy sleeves. The shirts were so comfortable that they would function as nightgowns too. All a man had to do to get ready for bed was take off all of the other layers of his uniform. The shirts were plain white or a yellowish colour, depending on how many times they'd been worn. Collars were high but not as high as collars in the 1790s, and sleeve cuffs were either closed by cuff links (little button things) or they'd just have cute lace at the end. Contrary to some ridiculous but funny assumptions I've heard from people who don't study historical fashion, shirts were not hard to put on, and they were simply pulled over the wearer's head like you would put on any other shirt. Shirts were closed together using buttons (a favourite of mine), linen, thread ties, or different combinations of the forementioned. Buttons tended to be small and made out of either thread, horn, leather, or even leather. Because the shirts were made out of soft, thin materials such as linen, cotton, and light flannel and were worn all the time, they were usually the first clothing items to wear out and break. Due to supply problems, there were periods of time during the revolution where men had to wear their breaking shirts and couldn't replace them. Another thing about shirts that I read somewhere (can not find the source for the life of me) is that Washington told his soldiers to wear hunting shirts because he felt that they were practical in every kind of weather. However, the site did say that they only wore them towards the start of the war and in certain regiments.
Neck accessories (for lack of a better term):
Like I briefly mentioned with the shirts, people in the 18th century had a really weird idea of what counts as naked, and they believed that a man without any kind of neck covering over his shirt was still naked. Cravats and neck stocks were two commonly worn neck garments during the revolution. Cravats were made out of silk, linen, or cotton and could be put on in a range of different ways. When they were untied, they were simply long strips of fabric. There are many ways to tie a cravat. I'm not very good at explaining things, so if you need to figure out how to tie an 18th-century cravat, I recommend looking up a YouTube tutorial. Cravats could also be accessorised with cute brooches and such. There were two different, commonly worn in the continental army, types of neckstock in the 18th century. Number 1 was made of the same materials and had the same colour as a cravat, but number 2 was dark in colour and made of leather. The biggest difference between neckstocks and cravats is how you put them on. Neckstocks aren't meant to be tied like cravats; they have a buckle on one end, so they're meant to be put on more like a belt. Oh, and in case you're wondering, the buckle always goes at the back.
Stockings:
Oh my god, I could talk about revolutionary war stockings forever. They're actually so adorable and cutesy, and I just love them. So the stockings are the pretty little white tights that the 18th century seems to be known for, and they were mainly made via knitting and were made out of either wool, cotton, linen, silk, or a fabric blend of any of the aforementioned. Stockings were usually made using knitting machines, but there were still plenty of people who made them by hand. Stockings in the 18th century were not at all short either; they went above the knee (so basically thigh highs). One of my favourite parts about 18th-century stockings is the garters that secure them into place. The garters were belt things that would wrap around their legs to make sure the stockings wouldn't fall down, and they were usually made out of leather, cloth, lace, or a ribbon tied into a bow. I physically cannot speak of these things without saying aww in my mind.
Culottes:
Also known as knee-breeches, but lets be honest, culottes sound cooler. The culottes worn by 18th-century soldiers were a bit different; instead of having a line of visible buttons at the crotch area to put the culottes on like jeans, they had fewer buttons—usually about 1 or 2—at the top of the culottes, and those buttons would be hidden by the waistcoat. Culottes in the Revolutionary War had a much higher waistband; most culottes in the 18th century had a low waistband, but culottes of the Continental Army had a waistband that went just above the soldiers actual waist. And culottes never stopped lower than the shinbone (to show off the stockings). Culottes were white or off white and were made of either buckskin, elk, sheepskin, wool, linen, velvet, silk, or fabric blends of any of the aforementioned. Culottes were very tight because they were worn so that when the soldiers were riding their horses, which they did a lot, the horse needed to feel every movement of the leg so that it could understand what the rider wanted it to do, and that was much harder if the rider was wearing super loose, flowy pants. Culottes were closed at the side of the knee with more small buttons or ties. Buttons on culottes were usually made of either metal, leather, or horn and covered in cloth or wrapped in thread.
Waistcoats:
Although waistcoats with sleeves did exist in the 18th century, they weren't as popular as waistcoats without sleeves. Going back to the weird 18th century undestanding of what is nude, a man wearing breeches, a shirt, a cravat or neckstock, and an unsleeved waistcoat would still be counted as naked. This is one of the things I see a lot of period dramas get wrong. I understand the overcoat-less look looks cool and attractive, but in the 18th century, that would be like a man going outside wearing no clothes. Oh, and another thing that a lot of period dramas mess up on is that men did not show their shirt sleeves in public; that was considered crude and abnormal; it wasn't illegal, just something you'd get judged for. There were two sub-types of waistcoats: double-breasted and single-breasted. These sub-types actually have nothing to do with breasts at all. In fact, the sub-types are about buttons. Double-breasted means a waistcoat with two rows of buttons, and single-breasted means a waistcoat with one row of buttons. Back to the uniform of the continental army, at the start of the revolution, soldiers wore single-breasted waistcoats in the most popular style of the 1750s and 1760s, but by the end of the revolution, they'd switched to wearing the 1770s style waistcoat, just going by a general pattern I've seen in changes to parts of the uniform. I'm assuming that the switch would have happened in 1779. In case you're wondering, the difference between the 1750s–1760s style and the 1770s style is their length; the former stopped mid-thigh, the latter stopped just below the hip. Waistcoats were usually made of linen, wool, velvet, silk, or a fabric blend of any of the aforementioned. They were made with all different colours and patterns, but in the continental army, they wore beige and off-white waistcoats. The waistcoat buttons were made of horn, metal, or leather and were sometimes wrapped in thread or fabric to make them the same colour as the waistcoat.
Sashes:
Sashes are a detail of the continental army uniform that I see a lot of people (and sites explaining the layers of the uniform) skip over. Continental army sashes were very important because they showed the wearer's position in the army. Green means the wearer is an aide-de-camp or brigade major; pink means the wearer is a brigadier general or a major general; and finally, blue means the wearer is a commander-in-chief. This system was made by Washington in 1775 and was used by the army throughout the war. The sashes were likely made using silk or wool. There was another, separate system with sashes; colonels, lieutenant colonels, majors, captains, sub-alterns, serjeants, and corporals could wear a red sash around their waist. However, this system was likely an optional thing because I've seen many portraits of men in those ranks from 1775–1779—they ditched the system in 1779—and I've seen only one of them where the person is wearing one of the red waist sashes.
Overcoats:
At this point, you are no longer considered naked; congratulations. So there were two kinds of overcoats in the 18th century: frock coats and dress coats. Dress coats were for super-rich people, and frock coats were for everyone else. Dress coats didn't have functional pockets, and the only reason why people thought that they were better than a frock coat was that they were expensive and sometimes prettier. Frock coats had a double-breasted front (same definition as with the waistcoats), functional pockets, and a high, round neckline. You can probably guess what kind of coat the soldiers of the Continental Army wore. They wore blue wool and linen frock coats with large gold or silver metal buttons on the cuffs and facings. George Washington and his officers wore buff-coloured facings with thick buff-coloured cuffs, and most other officers wore red facings with red cuffs. The coats had coattails and stopped midthigh, but the whole button and facing thing stopped just below the hip. The overcoats had this interesting triangle coat tail design thing at the back that I tried to figure out how to describe, but I couldn't. Here's a picture of what I mean by the two different kinds of frock coats worn by the soldiers that I mentioned in this paragraph: the one on the left is the one worn by Washington and his officers, and the one on the right is the other one:


[image credit, Samson Historical and Common Threads: Army]
I have just been told the name of the triangle things, they're called vents and they're to make sure the soldiers could ride horses without messing up their uniform. :)
Epaulettes:
The epaulettes serve the same purpose as the sashes: to declare the wearers rank; however, epaulettes are much more confusing because the epaulette system changed halfway through the war. So, the epaulette system for 1776–1779 goes like this: commanders, major-generals, brigadier generals, colonels, lieutenant-colonels, and majors wore a gold epaulette on each shoulder; captains wore a single gold epaulette on their right shoulder; sub-alterns wore a single gold epaulette on their left shoulder; serjeants wore a red epaulette made of cloth on their right shoulder; and corporals wore a green epaulette made of cloth on their left shoulder. The system from 1779-1784 goes like this, commanders wore a gold epaulette on each shoulder with 3 silver stars, major-generals wore a gold epaulette on each shoulder with 2 silver stars, brigadier-generals wore a gold epaulette on each shoulder with 1 silver star, colonels, lieutenant colonels and majors wore a gold epaulette with no stars on each shoulder, captains wore a gold epaulette on their right shoulder, sub-alterns wore an epaulette on their left shoulder, senior non-commisioned officers wore a red epaulette made of cloth and adorned with a crescent moon shape made of brass on each shoulder, sergeants wore a red epaulette made of cloth on the right shoulder, corporals wore a green epaulette made of cloth on their right shoulder and lastly, privates wore no epaulettes.
Hats:
Tricorn, bicorn and round were a must. Round hats were hats that were cocked on one side, bicorn hats were hats that were cocked on two sides and tricorn hats were hats that were cocked on three sides. Most of the time Continental army soldiers pinned them and folded them on the sides. Soldiers carrying muskets wore the hat in a different way to normal civillians, civillians would have the hat the normal way, center point forward but when carrying a musket over their shoulder, soldiers would turn their hat so that the left part was facing forward. In this position, the two sides of the hat would be almost flat so they could sling their muskets over their shoulders without having to worry about knocking their hat off. The hats white edges were made using worsted wool braid and the hat itself if expensive was made of beaver felt or camel's down painted black and if it was cheap it was just made of black wool felt. Hats were not always worn, I'd say they were more of a formality because I have seen very few portraits of soldiers wearing them.
Hat Cockades:
Hat cockades were made of ribbon or wool and were a sort of decoration to be pinned to the wearer's hat. They were like sashes and epaulettes; they indicated the wearer's rank in the continental army. And the system changed in 1779. So the system before 1779 worked like this: subalterns wore a green hat cockade, captains wore a yellow hat cockade, majors and brigade majors wore a red hat cockade, colonels wore a pink hat cockade, and lieutenant colonels wore a green hat cockade. In 1779, they changed it to honour and celebrate America's military alliance with France, so the colourful insignia were removed, and instead every soldier, regardless of rank, wore a plain black and white hat cockade. French soldiers had a cockade with black in the middle, surrounded by white, and American soldiers had a cockade with white in the middle, surrounded by black. Later on, in 1783, the black and white cockades were named the union cockades and were to be worn on the left breast, close to the heart.
Shoes:
There were actually a few periods of time during the war where some of the soldiers didn't have shoes, such as during the Christmas Day crossing and the winter of 1777–1778. But when they were supplied with shoes (most of the time they were), they wore one of two styles. The classic 'little lad' shoes, as I call them, and riding boots 'Little lad' shoes were shoes made with black leather and secured with a buckle. Little lad shoes had a small heel bit at the bottom, likely meant to make the wearer look taller because, despite tall people being considered the most attractive, most people in the 18th century were very short. Riding boots had an even higher heel and a part at the top of the boots that could be rolled down to fit the wearer. When rolled down, they just look like normal riding boots but with brown cuffs at the top. Interesting shoe-related fact that I thought would be cool to put here: in the 18th century, they didn't make right or left shoes; they made what they called straights, and you were meant to switch which foot you wore them on every day to 'wear them off evenly'. Riding boots were made with leather and were black on the outside and brown on the inside. Riding boots were very tall (they went under soldiers' kneecaps) and worn for the same reason as culottes, to make horse riding easier. It's meant to prevent saddle pinching, have a sturdy toe to protect feet while on the ground, and have a big heel to prevent slipping through stirrups.
Hair:
Originally I planned on not mentioning it on this list because it's not something that you can wear but there were uniform rules about hair in the continental army so I guess it is technically part of the uniform. In the 18th century they viewed men with facial hair was considered wrong and unusual in normal day-to-day life so if course it wasn't acceptable in a military setting. In the continental army they had a rule that men needed to shave every three days. They went against this rule a few times but only when they were desperate. Now on the topic of hair as in, not facial hair, the hair on their head was usually tied into a low ponytail with a blue ribbon or - for some men - cut short. 18th century men LOVED their long hair and did not want to cut their hair short even though they were told it should prevent lice. Wigs and hair powder were fashionable in the 18th century but not many men could afford wigs and it's not like they had a ridiculous supply of hair powder so most of the time they had their natural hair colour showing.
It's important to note that this is just the standard uniform that most men wore; each regiment had its own unique uniform, so if your project has anything to do with a specific regiment, either do your own research or ask me about it in the comments or my asks. This is also post-1775 because 1775 had no uniform. If I have gotten anything wrong, please do not feel afraid to correct me in the comments, and I'll edit the post.
Sources:
https://historyofmassachusetts.org/uniforms-revolutionary-war-soldiers/
https://www.srcalifornia.com/flags/revuniforms1.htm
https://www.bostonteapartyship.com/uniforms-of-the-american-revolution
https://ufpro.com/blog/american-revolutionary-war-study-military-uniforms-across-battlefield
https://www.washingtoncrossingpark.org/continental-army-clothing/#:~:text=Over%20their%20shirts%2C%20soldiers%20would,unit%20a%20soldier%20belonged%20to.
https://www.crazycrow.com/site/tricorn-hat-history/
https://www.si.edu/object/george-washingtons-uniform%3Anmah_434863#:~:text=This%20blue%20wool%20coat%20is,buff%20wool%2C%20with%20gilt%20buttons.
http://www.colonialuniforms.com/revolutionary-war-coats.html
https://www.berkleyhistorical.org/revolutionary-war-uniform
https://www.samsonhistorical.com/en-ca/products/mens-riding-boots
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Riding_boot
#american revolution#american revolutionary war#amrev#american history#revolutionary war#history#historical fashion#fashion history#18th century#18th century fashion#continental army#military history#military uniforms#war history#war of independence#On-partiality's rambles
126 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's ten at night and I can't stop thinking about Dragon, Kuma and Iva founding the revolutionary army together and how close they were and a lot of fandom only speculated they were close by inference but it's basically canon that they were CLOSE, like those three are FRIENDS and that is just... that makes me so happy. I love that Iva has Dragon and Kuma, I love that Kuma has Dragon and Iva, I love that Dragon has Iva and Kuma. And I love that they all had a hand in training Sabo. He is their legacy 🥺 he is the revolutions legacy. He carries pieces from all of them. I am so emotional over the revs. They mean everything to me.
#revolutionary army#one piece#found family#i cannot wait for oda to give us the full story#i cannot wait to see fandom finally giving the revs the love they deserve#i will never understand why theyre not more popular#'prodi they just dont show up a lot'#know who else doesnt show up a lot?#shanks#roger#and yet!#POPULAR AF#the fucking MARINES have more of a fan base#the fucking COPS yo!#the COPS!!!!!#irl people are excited about saying fuck cops and lets start a revolution#but in op the revolutionaries are side eyed and the marines get fangirls#I AM SO#LOOK AT DRAGON AND TELL ME HE ISNT A DILF#prodi he isnt#PEOPLE SIMP OVER FU KING BUGGY THE CLOWN AND THINK DRAGON IS UGLY?!?!?!#naturally people can like what they want of course#but theyre W R O N G
91 notes
·
View notes
Text

This kid will either:
a) Die a very, very horrifying death
b) Survive and be important as hell in the future
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
(amrev) Book pile got a new addition today AYYY
(thx Hannah :33)


#nerd stuff#amrev#american revolution#baron von steuben#von steuben#queer history#lgbtq history#ofc im using that tag for him teehee#books#booktok#history#history nerd#americanrevolution#american revolutionary war#continental army#friedrich wilhem von steuben#mount vernon#18th century#freiherr von steuben#pls tell me thats a tag smh#yeah uh#idk how tags work#and#idk what else to tag#bc#idk what ik doing#TEEHEE
34 notes
·
View notes
Text

Victory or Death, Advance on Trenton by Don Troiani
#don troiani#art#american revolution#american revolutionary war#alexander hamilton#george washington#artillery#cannons#history#american#america#north america#continental army#trenton#virginia regiment#flag
55 notes
·
View notes