#dha episode rating
Note
DHA S2 E21
Anubis der Gott " Anubis the God"
The Club has found the Secret Room. Inside they eventually find the Wall with 7 Tasks to find the Lovebomb. In the attic Mara can't sleep. She walks by at Charlotte and Luzy's door where she hears them giggling. In the kitchen she meets Magnus who also can't sleep. She offers to make him something to drink. The two stare at eachother until Kaya comes in and is pissed about it but when Mara offers him a drink he leaves. Magnus offers Mara to accompany her in the attic because she is scared alone. Up there Magnus sings Pokerface by Lady Gaga which leads them having a pillowfight on the bed. Later Magnus falls asleep on his chair. Mara strokes his cheek and watches him until she falls asleep aswell.
The next morning Kaya walks in with some flowers from Rosie's garden and sees Mara waking up Magnus.
Do I like the episode?
Yeah.
Favourite Moments:
The bits with Mara and Magnus.
Least Favourite Moment:
Don't really have one.
Favourite Character:
Magnus
What I would have done differently:
Not have Charlotte write that stuff in her diary.
" How Kaya is like when you really got to know him? Definitely alot different than everyone thinks. Much smarter. And likes to read books just like me. "
Unpopular opinion:
God I wish Mara and Kaya already broken up. Their relationship is pretty much dead.
I feel bad for Mara when she hears Luzy and Charlotte laughing inside. I've been there too. Luzy is such a horrible friend and nobody talks about it. And the way they laugh about Charlotte's crush on Kaya without even acknowleding that he is still with Mara. I don't know why they act like she doesn't even exist.
Okay this is cheesy: But the Club opens the wall with Open your heart for me
and in the kitchen Mara later meets Magnus where they really stare at eachother. And maybe that kind of connects to that their heart is open for eachother. Oh god thar sounds so cheesy. But they didn't look at eachother like that before.
Random Gifs:










Here's to the Ask Game
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
10+ Reasons Why You Should Eat Fish More Often
Fish is among the most beneficial nourishments on earth.

It's stacked with significant supplements, for example, protein and nutrient D.
Fish is likewise an extraordinary wellspring of omega-3 unsaturated fats, which are unbelievably significant for your body and cerebrum.
Here are 11 medical advantages of eating fish that are bolstered by investigate.
1. High in significant supplements
Fish is pressed with numerous supplements that a great many people are inadequate.
This incorporates excellent protein, iodine, and different nutrients and minerals.
Greasy species are now and again considered the most beneficial. That is on the grounds that greasy fish, including salmon, trout, sardines, fish, and mackerel, are higher in fat-based supplements.
This incorporates nutrient D, a fat-solvent supplement that numerous individuals are inadequate.
Greasy fish likewise brag omega-3 unsaturated fats, which are pivotal for ideal body and cerebrum work and emphatically connected to a decreased danger of numerous illnesses (1).
To meet your omega-3 prerequisites, eating greasy fish at any rate on more than one occasion per week is suggested. On the off chance that you are a veggie lover, decide on omega-3 enhancements produced using microalgae.
Outline
Fish is high in numerous significant supplements, including top notch protein, iodine, and different nutrients and minerals. Greasy assortments likewise pack omega-3 unsaturated fats and nutrient D.
2. May bring down your danger of respiratory failures and strokes
Respiratory failures and strokes are the two most normal reasons for sudden passing on the planet (2Trusted Source).
Fish is viewed as one of the most heart-sound nourishments you can eat.
Obviously, numerous enormous observational examinations show that individuals who eat fish routinely have a lower danger of cardiovascular failures, strokes, and demise from coronary illness (3Trusted Source, 4Trusted Source, 5Trusted Source, 6Trusted Source).
In one investigation in excess of 40,000 men in the United States, the individuals who routinely ate at least one servings of fish for every week had a 15% lower danger of coronary illness (7Trusted Source).
Specialists accept that greasy sorts of fish are considerably progressively helpful for heart wellbeing because of their high omega-3 unsaturated fat substance.
Rundown
Eating at any rate one serving of fish for every week has been connected to a diminished danger of coronary episodes and strokes.
3. Contain supplements that are pivotal during improvement
Omega-3 unsaturated fats are basic for development and improvement.
The omega-3 fat docosahexaenoic corrosive (DHA) is particularly significant for cerebrum and eye improvement
Consequently, it's regularly prescribed that pregnant and breastfeeding ladies eat enough omega-3 unsaturated fats
Nonetheless, some fish are high in mercury, which is connected to cerebrum formative issues.
Hence, pregnant ladies should just eat low-mercury fish, for example, salmon, sardines, and trout, and close to 12 ounces (340 grams) every week.
They ought to likewise evade crude and uncooked fish since it might contain microorganisms that can hurt the baby.
Synopsis
Fish is high in omega-3 unsaturated fats, which is fundamental for mind and eye advancement. It's suggested that pregnant and breastfeeding ladies get enough omega-3s however keep away from high-mercury fish.
4. May help cerebrum wellbeing
Your mind work regularly decays with maturing.
While mellow mental decay is ordinary, genuine neurodegenerative illnesses like Alzheimer's malady additionally exist.
Numerous observational examinations show that individuals who eat more fish have more slow paces of mental decrease
Studies additionally uncover that individuals who eat fish each week have progressively dark issue — your cerebrum's major useful tissue — in the pieces of the mind that control feeling and memory
Outline
Fish admission is connected to decreased mental decrease in more established grown-ups. Individuals who eat fish routinely additionally have increasingly dark issue in the mind communities that control memory and feeling.
5. May help forestall and treat wretchedness
Despondency is a typical state of mind.
It's described by low mind-set, misery, diminished vitality, and loss of enthusiasm forever and exercises.
In spite of the fact that it isn't examined so much as coronary illness or corpulence, despondency is at present one of the world's greatest medical issues.
Studies have discovered that individuals who eat fish consistently are significantly less prone to get discouraged
Various controlled preliminaries additionally uncover that omega-3 unsaturated fats may battle melancholy and altogether increment the adequacy of upper prescriptions
Fish and omega-3 unsaturated fats may likewise help other states of mind, for example, bipolar turmoil
Outline
Omega-3 unsaturated fats may battle sorrow both all alone and when taken with upper meds.
6. A decent dietary wellsprings of nutrient D
Nutrient D capacities like a steroid hormone in your body — and an incredible 41.6% of the U.S. populace is inadequate or low in it
Fish and fish items are among the best dietary wellsprings of nutrient D. Greasy fish like salmon and herring contain the most elevated sums
A solitary 4-ounce (113-gram) serving of cooked salmon packs around 100% of the suggested admission of nutrient D.
Some fish oils, for example, cod liver oil, are likewise exceptionally high in nutrient D, giving over 200% of the Daily Value (DV) in a solitary tablespoon (15 ml).
In the event that you don't get a lot of sun and don't eat greasy fish normally, you might need to consider taking a nutrient D supplement.
Outline
Greasy fish is a great wellspring of nutrient D, a significant supplement wherein over 40% of individuals in the United States might be inadequate.
7. May lessen your danger of immune system ailments
Immune system ailments like sort 1 diabetes happen when your insusceptible framework erroneously assaults and demolishes sound body tissues.
A few examinations interface omega-3 or fish oil admission to a decreased danger of type 1 diabetes in kids, just as a type of immune system diabetes in grown-ups
The omega-3 unsaturated fats and nutrient D in fish and fish oils might be dependable.
A few specialists accept that fish admission may likewise bring down your danger of rheumatoid joint pain and numerous sclerosis, yet the present proof is powerless, best case scenario
Synopsis
Eating fish has been connected to a decreased danger of type 1 diabetes and a few other immune system conditions.
8. May help forestall asthma in kids
Asthma is a typical illness described by constant aggravation of your aviation routes.
Paces of this condition have expanded significantly in the course of recent decades
Studies show that standard fish utilization is connected to a 24% lower danger of asthma in youngsters, yet no noteworthy impact has been found in grown-ups
Outline
A few investigations show that kids who eat more fish have a lower danger of asthma.
9. May ensure your vision in mature age
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a main source of vision hindrance and visual deficiency that generally influences more seasoned grown-ups.
Some proof proposes that fish and omega-3 unsaturated fats may ensure against this illness.
In one examination, standard fish admission was connected to a 42% lower danger of AMD in ladies.
Another examination found that eating greasy fish once every week was connected to a 53% diminished danger of neovascular ("wet") AMD.
Synopsis
Individuals who eat more fish have a much lower danger of AMD, a main source of vision weakness and visual impairment.
10. Fish may improve rest quality
Rest issue have become fantastically normal around the world.
Expanded presentation to blue light may assume a job, however a few analysts accept that nutrient D insufficiency may likewise be included
In a 6-month concentrate in 95 moderately aged men, a feast with salmon 3 times each week prompted upgrades in both rest and day by day working
The specialists guessed this was brought about by the nutrient D content.
Outline
Fundamental proof shows that eating greasy fish like salmon may improve your rest.
11. Delectable and simple to get ready
Fish is delectable and simple to get ready.
Hence, it ought to be moderately simple to join it into your eating routine. Eating fish a couple of times each week is viewed as adequate to receive its rewards.
In the event that conceivable, pick wild-got fish instead of cultivated. Wild fish will in general have more omega-3s and is more averse to be tainted with unsafe toxins.
Salmon can be readied prepared, singed, burned, or bubbled. It matches well with a huge number of vegetables and grains.
Outline
You can get ready fish in various manners, including prepared and singed. In case you're capable, select wild-got assortments over cultivated ones.
The reality
Fish is a brilliant wellspring of top notch protein. Greasy species additionally pack heart-sound omega-3 unsaturated fats.
Additionally, it has various advantages, including vision assurance and improved psychological wellness in mature age.
Also, fish is anything but difficult to get ready, so you can add it to your eating routine today.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Circadian Timeline via Jack Kruse
LINK
This is the modern warm adapted human circadian cycle:
1. Our brain wakes up with a morning surge of cortisol. That is what turns our brain on at 6 AM. VIP helps do this in long light cycles. VIP is highest at 6 AM and lowest at 6 PM. Ghrelin is also highest in the morning. Ghrelin is an incretin hormone made in the stomach that has a half-life of one hour. NPY and Agouti stimulate the production of ghrelin. Ghrelin sends a signal directly to our pituitary gland and it influences our metabolism. This is why the circadian cycle in the stomach in the morning is critical to optimal health. I laid that out here in this blog and it is an important part of the Leptin Rx reset protocol.
Circadian cycles for the obese are dramatically altered compared to non-obese individuals in the morning. In the normal person, Ghrelin is high when cortisol is highest in the early morning. In them, ghrelin drops fast when food is eaten too. In the obese, ghrelin is much lower in the morning than expected. Moreover, when food is eaten, ghrelin stays elevated for an extended amount of time. This happens because of the inflammation associated with the higher leptin levels in the morning in the obese. Melatonin is known to acutely decrease ghrelin and sometimes in tough cases, I will use supplemental melatonin to demolish the morning ghrelin spikes in people with huge appetites. This is most common in the obese, eating disorders, and in those with a severe leaky gut who crave dairy and carbohydrates. It is also very common for young paleo enthusiasts because of how they embrace blue light technology gadgets of the modern world that destroy melatonin levels in the brain. Ghrelin spikes and stimulates NPY in the hypothalamus increasing our desire and ability to eat a lot more. Leptin makes NPY decline normally, but if one is leptin resistant this does not occur and appetite is out of control at the brain level.
This is why obesity is an inflammatory brain disorder causing hormonal imbalance. Hormone imbalance implies a poor redox potential in different parts of the body. Where the potential is destroyed a certain disease will manifest. Obesity happens when it occurs at the leptin receptor or due to slow energy leak from the inner mitochondrial membrane. This means the obese person is losing energy in black box radiation. It is easy to check but few do with a thermal camera. We see this macroscopically as major alteration is sweating and down-regulation of activity due to an inability to uncouple oxidative phosphorylation at the mitochondrial level. It is not a disease of stress or emotion as medicine is trying to ram down media outlets. It is a problem of an alters the quantum biology of electron/proton tunneling across our proteins.
Moreover, this should explain why the SAD breakfast is so problematic for modern humans. It is marketed as a carbohydrate fest. It is also why the Leptin Rx recommendation for protein and fat are so high in the morning. Protein is the backbone of all life. When we are losing energy and increasing molecular chaos we need to replace our proteins to recapture our balance. It solves this problem fast. I use protein over fat in the Leptin Rx because high-fat levels with low protein in the morning cause a spike in the gastric inhibitory peptide that can induce insulin resistance by itself. I do use high fat in certain cases, like bariatric surgery, eating disorders, hypothalamic amenorrhea, or high EMF levels. Many people do not know this. This is why so many people do not buy Gary Taubes theory of “Why We Get Fat”. Gary has only part of the story correct, in my view, because obesity occurs on a spectrum just like autism does because it depends on how the environment affects epigenetic expression. When you understand circadian biology, you get a much more complete picture of how the system works on a 24-hour basis. It turns out electrons control the coupling of biochemistry in life and understanding this helps to make sense of why hormones are disrupted when electrons are not handled correctly. I became a student of circadian biology when I saw the entire view from a 30,000-foot level.
2. At 6:45 AM we will expect to see the sharpest rise in blood pressure in the entire day. This is due to many activated systems in the body getting us ready to fully supply blood to all vital areas to get us motivated to begin our day and search for food. This period of rapid BP rise is why we see so many cardiac deaths occur in early morning sleep or early wakefulness. This happens when cortisol is highest.
3. At daybreak, when the sun hits the retina, the photic stimulus begins to shut off the secretion of melatonin from the pineal gland in the brain. AM sunlight contains mostly IR light at daybreak and as we approach noon, UV light frequencies appear on the skin.
4. At 7:30 AM usually after an hour of light melatonin is completely shut off in the brain.
5. At 8:30 the gut has been awakened and peristalsis becomes more vigorous and bowel movements getting rid of yesterday’s food are very likely. This happens by protons flows to move serotonin sulfated by the light of the gut microbiome in the wall to get to the brainstem to become sulfated melatonin. This is stimulated if food is eaten around this time as well. This is called the gastrocolic reflex. Cortisol, aldosterone, and ghrelin are all raised at this time to drive activity, increase our blood pressure and stimulate feeding. This is all yoked to AM sunlight stimulus. It is blocked when we wear clothes or at work in the AM.
6. Around 9-10 AM we have the highest secretions of the sex steroid hormones in humans and these pulsatile crescendos lead to our highest alertness at around 10 AM in our day to allow us to explore our environment.
7. Our ideal muscle coordination occurs at 2:30 PM and this adapts us best to hunt for dinner at this time. An hour later we see our fastest reaction times develop from our motor systems in our CNS.
8. At 5 PM humans exhibit their greatest cardiovascular efficiency allowing for maximal exercising or hunting. This also occurs during a period of time when we have our best rates of protein synthesis in our body. This is why exercise should be optimally done in this window.
9. As the sun falls at 6 PM we begin to see a major change in the cardiovascular system about a half hour later.
10. At 6:30 PM we see our highest blood pressures due to changes in atrial natriuretic factor and antidiuretic hormone (ANF, ADH) in the renin-aldosterone axis.
11. Once this occurs over the next 30 minutes (7 PM) we begin to see a gradual rise in our body temperature as leptin (and IL-6) is released from our fat stores, with agouti’s help, slowly after dinner is eaten to signal the brain about our fat mass and inflammatory status.
12. For the next two to three hours leptin levels slowly rise as insulin levels fall. Adiponectin levels also fall during this time frame. These fat hormone signals are what activate adenosine system in our bodies. Adenosine is created over the course of the day; high levels of adenosine lead to sleepiness.
13. This peaks at 10 PM and then the circadian clock allows for melatonin secretion after 3-4 hours of total darkness. Serum leptin is rising quickly now (with agouti’s help) as it is released from the fat cells to enter the brain. Agouti is highest at this time of the day, even in a normal person.
14. As these trends continue the GI tract is slowly shut down by the circadian clocks and around 11:30 PM and bowel movements are shut down for the night. This means that the vagus nerve is quiet.
15. At midnight leptin begins to enter the hypothalamus to bind to its receptor in the hypothalamus to signal energy reserves while also yoking energy metabolism to sleep via the hypocretin neurons that control all the sleep cycles. In diurnal animals, sleepiness occurs as the circadian element causes the release of the hormone melatonin and a gradual decrease in core body temperature. This drop in temperature is the stimulus to change sulfated serotonin to sulfated melatonin. This timing is affected by one’s chronotype.
16. It is the circadian rhythm that determines the ideal timing of a correctly structured and restorative sleep episode. Melatonin, the hormone from the pineal gland, called the “darkness hormone ” is of great importance in the functioning of the SCN. The most important target of melatonin in humans appears to be the SCN, as the SCN contains the highest density for melatonin receptors. A double effect of melatonin in the SCN, namely, an immediate effect and long-term effect, has encouraged its worldwide use against the ill effects of jet lag. This may not be wise to do.
As an immediate effect, melatonin is found to suppress neuronal SCN activity towards night time levels. During the daytime, the SCN neurons must run faster than normal. This is possible because the retina has more DHA in it than the brain. In terms of long-term effect, melatonin can phase shift and amplify circadian rhythmicity of the SCN. Melatonin application has been found to be useful in synchronizing the endogenous circadian rhythms not only in people who suffer from jet lag, but also in blind individuals, patients with dementia, and in shift workers. With seasonal changes in night duration, there are parallel changes in the duration of melatonin secretion, and this leads to more secretion in winter than as compared to summer. In the cold environments of fall and winter, melatonin couples to eNOS and not to light levels. In warm adapted humans in the tropics, the light remains the focus of SCN entrainment year round.
17. After the 4 hours of darkness, melatonin secretion increases and this allows plasma leptin to enter the hypothalamus if we are sensitive to its receptor. If we are leptin resistant, this process can no longer occur.
18. Once leptin enters and binds to its receptors, it affects the lateral hypothalamic tracts to immediately send a second messenger signal to the thyroid to signal it to up-regulate thyroid function and efficiency. This is how we can raise our basal metabolic rate when we are leptin sensitive. These coupled events, matched with leptin’s actions peripherally in muscles, occur at the UCP3 sites to burn fat as we sleep at a higher basal metabolic rate.
This means electron chain transport does not make ATP as usual. When leptin allows this uncoupling to occur, we make heat and not energy from normal metabolism. This means we will burn off our excess calories as pure heat. This is one reason why calories in and calories out argument makes no biologic sense once you understand how leptin works. Humans are built to burn fat at night as we sleep to lose excess weight we don’t need.
19. The timing of the leptin action is also critical. It usually occurs between 12-3 AM and is tied to when you last ate and how much darkness your retina (SCN) have seen. This generally occurs soon after our hypothalamus releases another hormone called prolactin from our pituitary gland in the brain.
20. The surge of Prolactin is normally quite large in normal darkness but is significantly diminished in artificially lit environments after sunset. This was shown in the Jessa Gamble video HERE.
This has big implications for modern humans. The reason is that prolactin release is coordinated with sleep cycles where autophagy is at its highest efficiency and where Growth Hormone is released. If this is diminished we generally see lower DHEA levels clinically and higher IL-6 levels on cytokine arrays. This is a measure of uncoupling of sleep from normal metabolism. I base every bio hack I do on this step in circadian biology because it is the most important.
21. The normal large circadian prolactin surge we should see at around midnight after leptin enters the brain, does not happen if the patient has leptin resistance, sleep apnea, or has eaten food too close (within 3-4 hours) to bedtime. This blocks leptins ability to enter the brain because of insulin spikes. As mentioned above, this step is usually impaired if you are a post-menopausal female as well. This is often why older women sleep badly and gain weight they can not seem to lose in the gym even with a good paleo template and good habits.
This is another reason I am a big advocate for bioidentical hormone optimization in women. This need is greatest in women who are warm adapted. The need is lowest in the cold-adapted females because their leptin levels are already low due to the cold. Postmenopausal women who are cold-adapted tend to do amazingly well clinically in most disease parameters in my clinical experience. The main problem they face is that their vanity and dogma keep them from using the cold pathways to become rockstars as they age.
Exercise training tends to frustrate postmenopausal women because if their hormone response is altered they have a lot of trouble as they age. Men, on the other hand, do not lose their GH levels until 50-55 years old usually. They are also protected by their testosterone levels which persist throughout life provided that they are not suffering from inflammation which directly lowers their free and total testosterone levels. GH and testosterone keep a mans heart and muscles in tip-top shape. If inflammation destroys these levels earlier in life, it can show up even in younger people. I am finding this clinical result is an epidemic in my own practice.
What happens when step 20 is broken in modern humans?
This commonly happens in diabetics, but it is now becoming a very common finding in modern humans because of the excessive use of technology after sunset. These artificial lights also tend to be quite bright and completely un-yoke the normal circadian signals from the hormone response. Light after sunset reduces the prolactin surge we normally see in humans. When we see chronic lowered prolactin surges we also see lower growth hormone secretion during the anabolic phases of sleep.
Lowered chronic GH secretion directly affects cardiac and skeletal muscle function because the process of autophagy is made less efficient as our life continues. Lowered GH and the sex steroid hormones at sleep lead to loss of cardiac function. This is why heart failure is strongly associated with low IGF-1 and sex steroid hormone levels. When growth hormone is not released in normal amounts, it also decreases our lean muscle mass and increases our fat percentage in all our organs and in our body. This leads to slowly declining organ dysfunction and poor body composition. We can measure this process clinically by looking for falling DHEA and GH/dopamine levels as we age.
What happens in normal aging in step 21?
Aging is among the most common features found in studies on modern humans when DHEA and GH craters on hormone panels. The loss of the prolactin surge is especially prominent in postmenopausal women. Most women begin to suffer from falling DHEA and GH levels around age 35-40 while they are still in peri-menopause. The higher their HS-CRP levels, the faster they enter peri-menopause and the quicker they enter menopause. They also age faster on a cellular level because their circadian chemical clocks are sped up. As a consequence, their telomeres shorten faster as well. Women have higher levels of leptin for childbearing, so they are more prone to leptin resistant issues than men. Leptin is a sexually dimorphic hormone.
This helps explain why older women struggle with cognitive haze, loss of body composition, poor sleep, and increased levels of heart disease after menopause. Many physicians think the losses they suffer are due to the loss of estrogen from ovarian failure, but the loss of growth hormone and progesterone production are far more significant in their physiology. Progesterone is the off switch to anything that is pro-growth. Modern women are usually estrogen dominant even after menopause because of mismatches in circadian biology. Cognitive loss is especially common in post-menopausal women. They also lose on average 1% of their bone mineral density per year from menopause in large part due to the loss of progesterone, not estrogen.
Loss of progesterone also corresponds to poor sleep in these women too. Replacing progesterone in women has a major effect on their sleep and bone stock. It also dramatically improves their memories and cognitive function as well.
Snacking after dinner… Effect on circadian cycles:
If you choose to eat within 4 hours of sleep you will never see the prolactin surge you need, because any spike in insulin turns off this critical sleep time release that corresponds to the cellular maximums of the autophagic process for humans. Agouti, the incretin gut hormone also rises in the blood to higher than normal levels to block leptin from entering the brain.
Diurnal cycles for agouti are coupled to NPY and have major effects on leptin. Agouti is a gene product that normally increases the release of leptin from fat cells at night to signal the brain of what the energy status is of the body. This is great when it is working well. When it is elevated due to heavy carbohydrate use in our diet it creates a massive problem. This is why late night carbohydrate snacking is a bad thing to do.
It appears 12-3 AM are the critical hours at night are where the remnants of mammalian hibernation lie for our species. These are the anabolic times for sleep when we are rebuilding our proteins and recycling our cellular contents. They are three of the most important hours in all human biology. If you miss them, you can bet you have several neolithic diseases for sure. Why do you ask? If these three hours are not reached enough during our sleep cycle, autophagy is never optimized and cellular repair does not occur in our cells. This means we are using old broken down parts in our cells as the next day arrives at 6 AM and cortisol rises again to wake us up.
We can measure this efficiency of this process by checking DHEA and IL-6 levels. I also like to measure hormone panels to see if the inflammation has destroyed any other hormone cascades in aging men or women. This is vital in taking care of older people and treating their longevity. IL-6 levels correspond to Leptin resistant states as well. This makes sleep and metabolic coupling tightly controlled by circadian biology at all times of our life. It is magnified because sleep gets worse as we age and our DHEA, HDL, and HS CRP rise. This is where, during a bio-hack, we can see why circadian mismatches can cause neolithic diseases in humans. Often times we can find the same issues develop much earlier in a young paleo person who has a lot of mismatches in their circadian biology. I test them the same way I would an older person.
Prolactin, Doc?
You must be asking, why is this prolactin hormone so important in a warm adapted human? Prolactin is not just a hormone that secretes human milk. That is the best-known action of prolactin, but not the most important. Immediately after prolactin is released during sleep, another signal is sent to the anterior pituitary to release the largest amount of Growth Hormone as we sleep (GH). GH is stimulated only during autophagic sleep cycles in stage 3 and 4 to increase protein synthesis for muscle growth while you’re dissipating heat via the uncoupling proteins. This is where the major release of GH occurs in humans post-puberty when they are warm adapted. 99.9% reading this blog are warm adapted. If you chose to become cold adapted the GH story radically changes, as laid out in CT-6. GH and dopamine are analog proteins.
The implications here are huge for the warm adapted human if this prolactin surge is not adequate to allow us to enter the anabolic stages of sleep. Prolactin surge is diminished by both artificial lights at night and by foods that stimulate NPY, (namely carbs and protein) when they are eaten in fall and winter when biology says they should not be available.
If you are leptin resistant for any reason, have sleep apnea, you will always have an altered body composition because of a low GH level and an altered sex steroid profiles on testing. The reason is that DHEA is the immediate precursor for those hormones and is always low in people with bad sleep efficiency. Most VLCers who are warm adapted face this very problem today. VLC diet is best used in the cold-adapted mammal and not the modern warm adapted lifestyle. In essence, this diet is a mismatch for our modern lifestyle. This is why so many bloggers think ketosis is a dirty word for performance and body composition.
This all implies that as you age you will have higher body fat %, lower muscle mass %, if autophagy is not optimized by great sleep. This is precisely what we see today in most modern humans as they age. Invariably, their sleep cycles and sleep durations are poor and decreased from their childhood levels. As they age, there is a chronic insidious erosion of circadian biology by decisions made by modern humans over and over again.
What about temperature variations in warm adapted humans?
Where does temperature enter the picture? In warm-blooded animals, homeotherms, such as humans, can change their metabolism in order to keep their heat production equal to the heat loss. Such animals have a temperature control system and thereby maintain a rather constant core temperature. Warm-blooded animals live with the advantage of an unchanged cell activity and temperature in their core. However, the human core temperature falls during the estrogen phase of the menstrual cycle (pro-growth) and during sleep (circadian rhythm by melatonin).
The lowest temperature of the day for modern humans is usually between 2 AM and 6 AM. The temperature cycle is part of the normal circadian periodicity. Our biological clock seems to be synchronized with the rotation of the globe daily. Meal composition and timing, light cycles and temperature play a role in altering normal cycles and autophagic optimization.
Ovulation releases a sharp rise in morning temperature with its estrogen surge. Progesterone effects seem to explain the higher temperature in the last phase of the menstrual cycle where it calms the pro growth effects of estrogen. In post-menopausal women, this balance is usually not ideal, and it leads to many menopausal complaints these women face today.
The reduced temperature induced by melatonin in sleep is needed for Central Nervous System autophagic repair, for another, less well-known reason. The lowered temperature sets the stage for the biologic quantum effects to be optimal on our neurons microtubules that facilitate learning and neuronal spouting that occurs brain-wide.
This is why if you don’t sleep well you feel bad the next morning and your mental performance suffers the next few days on cognitive tasks. Research also shows your learning is severely impaired because of lowered BDNF and changes in diurnal cortisol due to the sleep deficit. This is why we monitor truck drivers’ and airline pilots’ sleep and wake cycles by law!
Moreover, in hospitalized ICU patients or the elderly when this occurs, it sets the stage for the appearance of acute onset delirium. This is exacerbated when they also have a simultaneous cytokine storm from sepsis or obesity. We see this often in hospitalized patients who cannot sleep well in ICUs. Acute delirium states very much look the same as chronic sleep deprivation patients we see clinically as well. Inducing cold, using progesterone and using hypnotics helps manage these conditions. I mentioned this in my hour-long PaleoFX talk last week.
Okay, nonscientists take a breather. Geeks are up: So today we are going to look more closely at how circadian biology sculpts our species. We will assume the sun rises for us today at 6 AM. About two hours before the sunrise we are at our lowest body temperature and this signal is sent to our hypothalamus to the hypocretin neurons that link metabolism (leptin receptor) to the sleep cycle clocks. This temperature dip signals that sleep is coming to an end and that the brain needs to raise its cortisol levels to wake up the cerebral cortex not connected to the autonomic portions of the brain in the brainstem.
This is called the reticular activating system. When the reticular activating system is damaged, humans remain in a sleep-like state called coma. Neurosurgeons call this a chronic vegetative state. The release of cortisol is a neurochemical signal from the hypothalamus that allows the reticular activating system to wake up the cerebral cortex in the AM by increasing water flows from the CSF, Matrix, and cytosol.
Now we have to think about what season we are in? Is a long light cycle (summer) or is a short one that is cold (winter)?
VIP regulates the circadian rhythm in humans and most mammals. VIP is a gut hormone and is found in our taste receptors too! So if we taste the sweetness from carbs in our diet when it’s warm and they are growing in the environment, our brain is expecting us to be in a warm season rather than a cold one. So sweet means warm to the brain, not cold. If you mismatch that and eat carbs at the wrong seasonal time, you create inflammation in the brain and it throws off our chemical clocks in our cells and ages us faster. That means our telomeres get shorter. This is not good.
Even geekier: Taste perception and its relationship to glucose homeostasis begin with stimulation of taste cells located in tongue taste buds. There are five basic taste modalities: bitter, sweet, umami, salty, and sour. Taste cells are clustered into taste buds in the tongue epithelium. Mammals have four different types of taste cells (types I, II, III, and IV), exhibiting different molecular phenotypes and functional roles.
Type I cells are glial-like cells that maintain taste bud structure. Type II taste cells transduce sweet, bitter, or umami stimuli and communicate information through G-protein coupled transduction cascades. Type III cells synapse directly with afferent nerve fibers from three cranial nerves and most release serotonin upon depolarization. Type IV basal cells are rapidly dividing progenitor cells that differentiate into type I, II, and III cells. Along with biogenic amine neurotransmitters, it is becoming evident that multiple peptide hormones including glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), cholecystokinin (CCK), and neuropeptide Y (NPY) as well as VIP are located in taste cells, potentially acting as signaling modulators of multiple gustatory stimuli.
The circadian clock not only can generate its own rhythms but can also be entrained by the environmental light-dark (LD) cycle. Multiple single-cell circadian oscillators that are present in the clock can, when synchronized, generate coordinated circadian outputs which ultimately regulate the overt rhythms.
VIP is a gut polypeptide, has been identified as one of the main neurotransmitters of SCN neurons, and participates in SCN function. These SCN neurons are retino-recipient and are found in the core of the SCN. They are activated by light, and exogenous application of VIP can reset the circadian clock in a manner similar to that of light application, both in vitro and in vivo. It is estimated that 9%-24 % of SCN neurons express VIP.
Leptin was originally described as an adipocyte-derived cytokine that signals to the hypothalamus to regulate food intake and energy expenditure. Leptin signals through its receptor, which is closely related to the gp130 cytokine receptor. Leptin can induce expression of the neuropeptide gene vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) through the VIP cytokine response element, the same element that mediates the response to the gp130 cytokines. Leptin acts synergistically with TGF-beta to activate transcription through this element.
One of the main chemical constituents of SCN neurons is the vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP). Such neurons are retino-recipient and activated by light. Exogenous application of VIP resets the SCN circadian clock in a light-like manner both in vivo and in vitro. These resetting actions appear to be mediated through the VPAC2 receptor (a type of receptor for VIP). Unexpectedly, genetically ablating expression of the VPAC2 receptor renders the circadian clock arrhythmic at the molecular, neurophysiological and behavioral levels. These findings indicate that this intrinsic neuropeptide acting through the VPAC2 receptor participates in both resettings to light and maintenance of ongoing rhythmicity of the SCN.
Neurosurgery geeks only: In mammals, the part of the nervous system responsible for most circadian behavior can be localized to the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN). Although previous studies suggest that each SCN neuron may be an independent oscillator, these pacemaker cells must be synchronized to each other as well as to the environment to function adaptively. Therefore, answers to questions about cell-to-cell communication within the SCN lie at the core of understanding how his timing system operates. The daily cycle of light and dark is the dominant environmental cue responsible for synchronizing this biological timing system to the environment. The SCN neurons receive photic information directly from the retinal-hypothalamic tract (RHT). My Vermont 2017 video gets deep into the physics of the retina.
Many of the SCN neurons that receive retinal input from these cells are located in the ventrolateral (or core) region of the SCN and express GABA and, in many cases, vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and the Peptide Histidine Isoleucine. These retino-recipient cells then convey this environmental information to the rest of the SCN. In brain slice preparations, application of VIP alters the firing rate of SCN neurons through a VPAC2 receptor-dependent mechanism and induces expression of mPer1 and mPer2 genes. These two genes are how the circadian cycles yoke directly to the cell cycle and are related to tumor suppressor genes and oncogenesis when mismatches occur chronically in modern man.
Functionally, the administration of VIP, and to a lesser extent PHI, can cause phase shifts of the circadian rhythms in vivo and in vitro in man.
The role of AVP (arginine/vasopressin) in circadian timekeeping has also been well established in the neurosurgery literature. Its role in the control of the circadian rhythm of food and water intake has been reported and well documented. Another intrinsic neuropeptide, VIP, acting through a VPAC2 receptor (a type of receptor for VIP), participates in both resetting to light and maintenance of ongoing rhythmicity of the SCN. NPY and GABA seem to be the neurotransmitters in the projection from the intergeniculate leaflet to the SCN adjacent to CN II. Raphe nuclei projections to the SCN contain serotonin as an NT. AVP and prokineticin 2 are seen in the outputs from the SCN as efferents.
NPY, which is an established neurotransmitter of the geniculohypothalamic tract (GHT), was found to regulate SCN neuronal activity and to produce long-lasting suppression of firing rate of SCN neurons. When co-applied with NPY, NT (neurotensin) was found to dampen the profound inhibitory effect of NPY. So when NPY is high, which would be in equatorial or high light conditions, NPY basically makes the SCN less efficient and allows animals to perform outside their normal circadian boundaries. They stay awake longer for eating and for reproduction in high light times during summer.
All geeks reunite: VIP (along with GRP and AVP) show circadian variations in the level of mRNA in constant contact with environmental conditions from our tongue and our gut. When light becomes long-lasting in summer, NPY dominates the SCN in mammals when light becomes low and the temperature falls to 50-55 degrees constantly at our surface cold receptors, and eNOS rises and blocks all photic input to SCN and circadian rhythms are maintained by a new program. Alpha MSH induces and potentiates that seasonal change within the hypothalamus as laid out in CT-6 blog.
The moral: So the brain is wired for foods when they grow naturally, not when we feel or think we can/should eat them regardless of their availability in modern times.
Leptin sensitivity directly regulates VIP production. VIP regulates the circadian rhythm and entrains the SCN to light. When it is cold, leptin is released from fat cells in large amounts, and we begin to use eNOS to entrain our SCN to cold cycles and we should avoid carbs like the plague then. Remember from CT-6, cold empties fat cells like screaming fire would empty a crowded cinema. In cold, the pituitary-hypothalamic portal is involved in the production of lots of alpha MSH and ACTH. When MSH rises, you are allowing the brain to control everything to get you to optimal. This should make it abundantly clear that cold and warm adapted mammals are not sharing the same circadian biology. Cold selects for supreme LS and superior hormone optimization as laid out in the CT 6 blog.
In long-light summer cycles, when VIP is controlling the SCN again, androgens normalize if the mammal is leptin sensitive. VIP usually fixes our Vitamin D level to optimal too. VIP is a master controller of all inflammation for circadian cycles, but leptin is the hormone that produces VIP in the correct amounts even in light cycles. So if we are leptin resistant for any reason in long-light cycles, we have no control over our circadian cycles and this leads to neolithic diseases.
Normally, VIP lowers our cytokines as the light cycle lessens as the day progresses. At night time the cell is more reduced and not as oxidized. Reduced means better cellular health and oxidized means more cellular inflammation. The act of cellular reduction happens in autophagy during sleep with repair processes. Remember VIP is highest in the morning and this helps it elevate cortisol to wake us up. This is also why cortisol levels are highest when we start our days and lowest in the night when we sleep.
#jack kruse#circadian#fix circadian things first#mito mojo#more better mitochondria#all the circadian things
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fish Oils Save Young Accident Victims from Permanent Brain Damage

Every when in a fantastic while, mainstream physicians avert from their "criterion of care" clinical bags as well as attempt to utilize uncommon methods with non-pharmaceutical substances that supply surprisingly reliable outcomes.
In March 2010, high college pupil Bobby Ghassemi was gotten of his crashed automobile as well as airlifted to a nearby Virginia hospital extra dead compared to life with severe brain trauma. But you 'd soon figure out exactly how fish oil assisted him to recovery.
Dr. Michael Lew observed, " For all intents and also purposes, he was dead on the scene. I'm considering the records, and also they report a Glasgow Coma Rating of three. A brick or piece of wood has a Glascow Coma Rating of 3. It's dead."
Bobby was placed in extensive care in a coma with all the device possible to maintain him a breath from fatality. The health center's doctors commented that his brain injury was so poor, it was a wonder that he was to life adequate to be in a coma.
They told Bobby's dad as well as mother it was uncertain he would certainly be greater than a veggie if he appeared of the coma. He 'd be not able to talk or recognize his family.
Time to Wager with an Unusual Intervention
After 10 days, Bobby was still comatose, but stable. His daddy, Peter Ghassemi, felt extra ought to be done than preserving stability in a coma. So he began asking around to old Military pals and was resulted in Military colonel Dr. Micheal Lewis.
Dr. Lewis suggested fish oil based upon a very early episode of a West Virginia coal miner that hardly survived a mining mishap with severe brain damage.
Except for severe myelin sheath damage (anxious system's fatty safety coats) from breathing poisonous fumes, Randall's problem had actually looked like Bobby's.
The 26-year-old miner, Randall McCloy, was "on death's front door," inning accordance with Randall's healthcare facility neurosurgeon, Dr. Julian Bailes.
He and also the various other physicians after that decided to pass up the regular delay and also see after Randall was supported in intensive treatment. Also as some recuperation is seen after a brain injury, the brain cells remain to die from dynamic inflammation.
Dr. Bailes recognized that the mind needs to eat omega-3 fatty acids to recover swelling as well as boost mind and also anxious system cell growth.
Unlike plant based omega-3s, fish oils do not call for the body to convert ALA into the extra effective facets of omega-3 fat, DHA as well as EPA. Much more concerning that here.
After talking about Randall's condition with fish oil omega-3 professionals, Dr. Bailes identified that 20 grams, nearly 15 times the typical supplement dose, fed through Randall's feeding tube everyday might bring him around.
This successful event was clarified to Bobby's daddy. In order to conquer authoritative medical "criterion of treatment" resistance, Peter constantly urged the healthcare facility staff to try the fish oil. Ultimately the healthcare facility yielded.
At his high school graduation, Bobby took off his cap and also swung it to the supporting trainees. His significant three month healing had left him with some weakness on his left side and also strolling problem, for which he had just begun treatment. He was back.
0 notes
Text
What are some natural ways to stop asthma attacks?

These are some natural ways to stop asthma attacks-
(However, we recommend you to find better asthma treatment in case of emergency)
Adopt a healthy diet

Start by eating more fresh, organic fruits and vegetables.
It is also recommended to avoid the regular consumption of food facilitating the maintenance of the inflammatory ground (meat, poultry, dairy products) and to privilege a food rich or supplemented in omega-3 with a long chain.
If you don’t have a fish allergy, eating it every other day is enough. Otherwise, use DHA-phospholipid, derived from chicken eggs (DHA2: 1 sachet per day, obviously in the absence of allergy associated with eggs) or complete perilla oil (1 teaspoon per day).
We talk about the whole oil because it combines edible oil with a small percentage of its essential oil. Perilla oil, thanks to its richness in omega-3 (alpha-linolenic acid) and the anti-inflammatory properties of its essential oil, helps reduce allergic symptoms.
Correct deficiencies in essential nutrients
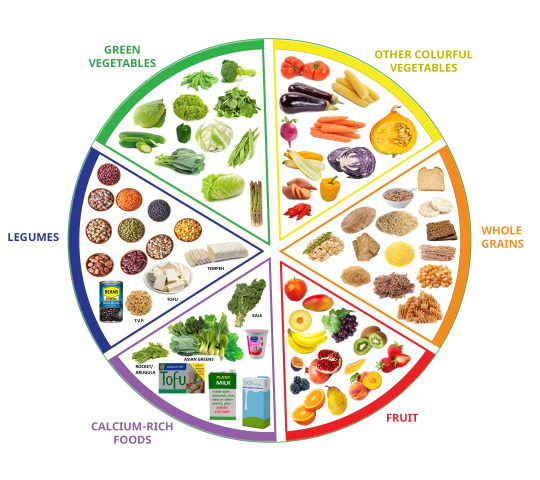
It must start at an early age: at 8 years old, children who have received a mineral vitamin supplement before 4 years have a 40% lower rate of allergic manifestations.
The most concerned nutrients are vitamins A, C, and D, magnesium, zinc, and flavonoids including quercetin which, in addition to antioxidant and antiviral powers, has the most powerful natural antiallergic power, because it inhibits the release of l histamine. But it is difficult to absorb, so it is recommended to always consume it in combination with bromelain.
This rebalancing can hardly be done alone because it requires sufficient knowledge that only a doctor trained in nutritherapy today has.
Above all, don’t stop the sport!

The practice of sport, under certain conditions, decreases the level of stress, strengthens the thoracic musculature and improves the respiratory and cardiac functions.
Treat depressive background

Regularity in learning new habits is not easy. This need is particularly badly accepted by asthmatic adolescents who have presented a major episode of asthma, often in connection with an underlying depressive field.
In these cases, consideration should be given to implementing supportive psychotherapy. This therapeutic practice will be effectively complemented by the concomitant intake of omega-3 and supplements aimed at restoring the normal secretion of neurotransmitters. This will restore brain neuroplasticity as well as a balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic autonomic nervous systems.
Herbal medicine

Boswellia serrata resin (the central remedy in Ayurvedic medicine) inhibits the production of several mediators of inflammation, particularly leukotrienes. A universal action within the organism: it restores the intestinal mucosa in its integrity and its function, does the same at the respiratory level and improves arthritis rheumatism. In general, manufacturers recommend 4 to 6 capsules per day at the start, in adults.
The climbing ivy extract (Hedera helix) reduces bronchial constriction and promotes the elimination of mucus. It is available as Activox in pharmacies (its dosage varies according to age), but it can also be found in health food stores.
Complex formulas are also interesting for improving the allergic terrain such as Ribum (Ribes nigrum and Fraxinus excelsior), anti-infective, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and analgesia: 1 tsp. coffee at mealtimes.
Aromatherapy

At least six essential oils have the power to decrease the expression of cyclooxygenase (COX-2), the enzyme that promotes the release of powerful inflammatory mediators (prostaglandins of series 2) at the same leveled as effective as resveratrol. The substance believed to be responsible for this potent anti-inflammatory effect is carvacrol.
The essential oils for which this effect has been demonstrated are those of bergamot (Citrus bergamia), clove (Eugenia caryophyllata), eucalyptus, fennel (Foeniculum vulgare), rose and thyme (Thymus vulgaris à carvacrol). Taking these EOs under medical supervision is a precious help to improve in a lasting and well-tolerated way the chronic inflammatory field of the asthmatic.
Complexes are also interesting, such as Respir’aroma, although this is intended for use against winter aggressions (inhalation, pectoral massage, spray on the pillow).
(However, we recommend you to find better asthma treatment in case of emergency)
Thanks
#asthma#asthma treatment#asthma symptoms#asthmaspecialist#asthma treatment drugs#asthma doctors#asthma attack#natural therapy#ayurvedic
0 notes
Text
10 Things that Will Change Your Life Immediately

I'm going to go through really quickly to ten different things
But what I want you to do is be able to memorize these ten things
And so what we're gonna do is we're gonna go through and I'm gonna teach you this very quickly
A way of putting it onto your body and we're gonna put it onto your body just for ease So I'm gonna give you the ten keys
To having an ageless mind. Every single one of them, you've either heard me say or you intuitively know that these are important
That's not the reason I'm saying it
The reason I'm saying it is to take knowledge and turn it into power and I want you to take those ideas and have them
Have real impact and what I want you to do is when I'm going through it I want you to cycle through and on a piece of paper
Rate yourself on a scale of zero to ten how well am I doing in that category? One third of your memory is
Predetermined by genetics and biology. Let's say two-thirds is in your control. These are the ten things I would focus on
So the first one is a good brain diet
Good brain diet. So on a scale of zero to ten
What's an honest assessment if you're honest and true to yourself? Where are you on your diet?
So we talked about the the most important foods for your brain that are neurological like protecting, they're
Neuroprotective. So we're talking about avocados. We're talking about blueberries or what I call brain berries, right? We're talking about broccoli
We're talking about eggs. If this is allowed by your diet. We're talking about coconut oil or olive oil
We're talking about green leafy dark vegetables wild salmon if you're allowed to if that's part of your your your diet also as well
Turmeric I do every morning. I do like an almond turmeric like tea right all these things are neuro protective number two killing ANTs
automatic negative thoughts how well are you controlling your self-talk On a scale of zero to ten honestly even have you done this with me
How strong are you zero to ten do your thoughts make a difference? Yes, or yes
If I say constantly I'm getting too old. Is that gonna be self-fulfilling? Yes for you? Yes, if I say I'm forgetful
I have a bad memory if you fight for your limitations you get to keep them
So your mind is always eavesdropping on your self-talk. That's number two number three Exercise
and really what we're talking about here is movement
You're the number one function of your brain is to control your movement All right
That's why we know there's not just a brain body connection but a body brain connection that using your body in different ways
stimulates neurogenesis, it stimulates neuroplasticity
It stimulates brain derived nootropic factors, which is the fertilizer for making new connections
So you have to move but we live in a very sedentary life, right?
I was reading this book talking about barefoot kids and how we're taking away seesaws and Sprint's, you know swings and all these things
We're over protecting them and then we're putting them in a very sterile environment They're not moving as much right they're always on their devices and they're not getting the brain growth
Right, and it's leaning to learning challenges so on but how much you're moving every single day?
They say they say sitting is the new smoking
Right, you do not want to sit eight hours a day and just and just study
I'm gonna go through the rest fast number four brain nutrients brain vitamins Because we're at a...you know, we're traveling when I may even eat the best foods ever
Are you supplementing with there are certain nutrients and I would just have I would make this a no-brainer
I would just go to your functional medicine doctor and get like hormonal tests full-spectrum tests food
Sensitivity and just see what your baseline is because I really do believe people are bio individual
Like and I've seen all the research talk to so many
Individuals find out what works for you because if you're the most important supplement is DHA for the brain
All right, that's number four number five positive peer group so rate yourself zero to ten How inspired encouraged
challenged
Energized are you by your peer group and again peer is choice
I'm not talking about your family, but although they may be or your peer but the people that you choose, right?
So either get a new group or choose who you're gonna let effect you positive peer group Because it really affects your your brain zero to ten
Really fast number six clean environment how clean is your environment?
How organized is it? Zero to ten. And you know this right is your external world? Reflected by your internal world and vice versa because it's a feedback loop
Have you ever cleaned your room clean your desktop clean your work area and all of a sudden you have clarity of thought?
the reason why I brought up the
Boxing match is this is because I go over there
We watch this fight and afterwards I was like, you know, I was me sitting here Sylvester Stallone on the couch here and then to his left was Arnold Schwarzenegger
And I swear if you took a picture that like they'd be like who photoshopped that Asian dude in had that photo?
But I was like
What does it take to be a champion like those guys?
And then Arnold said Jim the difference between the amateur and a champion
Is a champion's willing to push past the pain period just like for those who did the exercise over the past few days?
It's that intensity and getting in is there a pain period in a relationship?
Is there a pain period sometimes in the health crisis is there pain period also in your business? multiple pain periods
Right the ability to push past that's where the period is now because you've just in days and days here you feel like your attention
Is wandering and going different places. This is the time when it counts just like with your workout, right?
So if Lorenzo and his team's here, that would be that would be the goal. So that's number That's number six number seven sleep on
On a scale of zero to ten. How good is your sleep? It's important for your brain three really simple reasons
It's where you consolidate short to long-term memory. That's where you actually remember.
You
do not even when you're doing these workouts build your muscles when you're working out you build it when you rest
Same thing with your mental muscles same thing with your memory
So that's where you can solid a short to long-term memory the other reason why you sleep is it cleans plaque out that could lead
to dementia and potentially brain aging challenges
The last reason why is how you dream? Right your REM sleep your REM, your REM stages of your sleep
That's very important because that's where your creativity that's where I'm telling you like We did a whole thing on super brain on how to remember your dreams
But specifically why do you want to member your dreams because you learn all day your brain doesn't shut off at night
It's it's more active at night. And so Elias Howe created a sewing machine in his dream You know Paul McCartney came out with the song "Yesterday" in his dream. Mary Shelley came up with Frankenstein in his dream
periodic table came to a chemist in his dream
What are you dreaming about at night that could solve a lot of the problems in your business in your life?
But you forget it the next morning
That's why the first thing I do in my morning routine is remember my dreams and six steps on how to do that
We we talked about in Super brain. After that sleep eight brain protection. Are you protecting your brain?
And I'm not just talking about about wearing a helmet in extreme sports. Yes, that's obvious I've had series of you know, traumatic brain injuries and concussions and all those challenges Yes, but I mean like things like EMFs like we did a podcast episode specifically talking about Electromagnetic fields and how it's affecting the brain. Is that affecting the brain you think do you think it's norm?
Do you think we evolved or born to be able to be able to handle all the electricity that's coming out of these smart devices?
You know, I read recently that over 90% of kids sleep with their phones underneath their pillows right? Not on airplane mode, right?
So it's big big big challenge
We just did two videos on that have four million views in just a matter of weeks. You should watch watch those videos
EMFs protect your brain number nine new learnings new learnings Meaning that you might have seen the longevity
This is a longevity conference on the cover of Time magazine where there was this study on nuns
Who were living 80 90 and above. What was the secret to their longevity?
First part part of it was their emotional faith gratitude the other half lifelong learners
These group of women were just learning everyday reading every day having deep conversations doing the work every single day
It added years to their life and
Life to their years. So always learning and I'm preaching the choir here But I know for a fact most of you could actually push it even more
Alright, that's how you create neurogenesis and neuroplasticity. If you want to know the secret to having an ageless mine
Neurogenesis says you could create new brain cells to the day you die Neuroplasticity is saying if you create new connections to the day you die
The two most important factors outside of sleep that's going to promote neurogenesis neuroplasticity
novelty and nutrition
just like your body you have to give it novelty or
Stimulus and you have to give it nutrition and feed that muscle. Does that make sense? Same thing with your mental muscles, so novelty of movement novelty of ideas
But most people as we grow older and I mean chronological age we shut down because we feel like we know everything right?
So there's no novelty that's there. There's a Rumi quote that says "Sell your cleverness for bewilderment"
Like when's the last time you felt bewildered? remember
You don't have creativity or have focus or have a memory or have bewilderment Or have love or have motivation or have energy you do those things
You do energy you do creativity do focus you do bewilderment
so we're taking nouns turning into verbs and we're taking a structure a
process a strategy and now you can replicate that at will and finally the last thing number 10 stress management
And this is the invisible one, right? nobody wants to talk about
But you're under a how many people didn't realize how much stress they were under until they were like hanging out here on the beach
Because because it's like fish they don't see the water because it's there all the time
But we are under so much environmental stress pollutants, environment stress, emotional stress, work stress cognitive stress financial stress
And we don't realize that but you don't get the best of the best out of that right? It's good for fight-or-flight
sympathetic mode
But when you in a code when you want to be about it's not good if you need to think if you're in stress
It doesn't help you study, when you're stressed, it doesn't help you give a presentation, when you're stressed, it doesn't help you perform
Cognitively because it shuts down cortisol. Adrenaline big parts of your brain. So stress management. So, how are you managing your stress?
0 notes
Text
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Benefits, Foods, & Supplements
Source: Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Benefits, Foods, & Supplements
by Dr. Edward Group DC, NP, DACBN, DCBCN, DABFM
Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their role in brain and heart health but are they all they’re cracked up to be? Should you take fish oil to get your daily dose of omega-3s, or should you opt for plant-based options instead? So many questions! If DHA, EPA, and ALA sound like alphabet soup to you, read on — we’ll provide clarity.
What Are Fatty Acids?
To begin, let’s look at fatty acids in general. Fatty acids are the building blocks of all fats (lipids). Every fatty acid contains an acid connected to a long chain of carbon and hydrogen molecules.
Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated. In other words, the long carbon chain is either saturated or “full of” hydrogens, or not. If all carbons are single-bonded to hydrogens, the chain stretches out straight. These straight chains stack up and stick together, forming a solid material — as happens with animal fat or coconut oil — at room temperature. In contrast, an unsaturated fatty acid has double bonds that cause the chain to “kink” or bend. These kinked up chains do not stack up or stick together like saturated fats do, so they stay in liquid form.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
That brings us to omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s play a critical role in your body, forming part of every cell’s structural membranes. They also help brain cells send messages through neurotransmitters and provide energy within the cardiovascular, immune, and endocrine systems, among other functions.
The “omega” represents the tail end of the fatty acid molecule, and the “3” indicates that the last double bond is three carbons from the chain’s end. Omega-3 fatty acids are considered polyunsaturated fats.
EPA, ALA, & DHA, Oh My!
Eleven types of omega-3 fatty acids exist, but just three play an important role in human physiology and health: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA).[1] Of the three, only ALA is considered an essential fatty acid. This means that your body does not make it and you must get it from food or supplements. Your body can convert ALA to EPA and DHA, making these latter two not “essential” fatty acids, but the conversion process occurs at such a low rate (between 2 and 10 percent) that, for all practical purposes, you need to get EPA and DHA from your diet.[1, 2]
Also, don’t confuse alpha-linoleic acid with the other “ALA” which is alpha-lipoic acid, which is not an omega-3 at all. For the purpose of this article, ALA refers to the omega-3.
Omega-3 Health Benefits
As the building blocks of fats in the human body, fatty acids play an integral role in energy storage, brain activity and mental health, heart health, and more. Below are the top health benefits that omega-3 fatty acids provide to your body and mind.
Promotes Restful Sleep
Restful sleep is important for memory, focus, and energy levels. Getting adequate DHA, in particular, helps you get better quality sleep — and more of it. One study linked lower blood levels of DHA to poor sleep quality in children. Algae oil DHA supplementation led children to have seven fewer wake episodes and 58 minutes more rest per night.[3] While scientists aren’t entirely sure why DHA is so critical to slumber, they hypothesize that lower levels in the brain may interfere with melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.[3]
Boosts Brain Health
Omega-3 fatty acids play an important role in brain function, including memory and cognition — the process of thinking. The substance that insulates brain cells and helps them communicate with one another, myelin, is made up of omega-3 fatty acids and proteins. When the body lacks omega-3s, myelin sheaths erode, causing memory to decline.
People with Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, multiple sclerosis, and other neurological disorders are often deficient in omega-3 fatty acids.[1, 4] Yet getting enough boosts memory and cognition.[1] While omega-3s are especially helpful in aging individuals, studies show they also improve nonverbal reasoning, logical memory, and working memory in healthy middle-aged adults.[4] Getting enough omega-3s during pregnancy and when breastfeeding — as well as for young children — is essential for proper brain development.
Lifts Your Mood
Omega-3 fatty acids help regulate and even improve your mood. Some studies suggest that omega-3s may help certain mood disorders.[5] Omega-3 supplementation can also help reduce the chance that women going through menopause will become depressed,[6] and can reduce symptoms of pre-menstrual syndrome.[7] Some studies suggest omega-3 supplementation reduces oppositional behavior, restlessness, aggression, and inattention in children with ADHD.[1]
Omega-3 fatty acids, along with the hormone vitamin D, play a role in the synthesis or creation of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a critical role in having a happy mood.[8] Scientists also theorize that omega-3s promote a positive mood by promoting normal levels of homocysteine and inflammatory cytokines circulating in the blood — the same way they improve heart health.[5]
Supports Cardiovascular Health
As mentioned, omega-3s normalize levels of cytokines in the blood, substances that inflame and irritate the body’s organs and tissues, leading to poor heart health, among other things.[5] One way that omega-3s help the cardiovascular system is by discouraging too many omega-6 fatty acids, which promote inflammation, from forming.[9, 10]
Omega-3 supplements also reduce triglyceride build-up in the blood, which is linked to an increased risk of heart attack and stroke; this is true even though omega-3 dietary supplements actually contain triglycerides![11] Supplementing with omega-3s can help promote normal cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood pressure.[1]
Ensures Eyes Are Healthy
Both your brain and eyes contain high levels of omega-3 fatty acids. But can taking omega-3s improve eye health and vision? The retina — the part at the back of the eye that allows you to see color and light — has high levels of DHA, and studies suggest that taking DHA can discourage retinal degeneration (also called macular degeneration).[12] Studies on human development also show that taking omega-3s — especially DHA — during pregnancy helps ensure an infant’s eyes develop properly.[12]
Soothes Joint Tenderness
Because of their anti-inflammatory properties, omega-3 fatty acids may reduce joint tenderness and discomfort, particularly in cases of rheumatoid arthritis.[1] Omega-3s help so much that they have reduced some patients’ need for additional medications.[1] Some studies have looked at how taking omega-3s affects bones, particularly bone density and osteoporosis, but so far the evidence is inconclusive.[1]
Supports Weight Loss Efforts
How can taking a fat supplement help you lose weight? It turns out omega-3 consumption may help reduce appetite and feelings of hunger. In one study, eating a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids left people feeling fuller up to two hours after a meal.[13] These effects may not apply universally though. Studies have found that omega-3 increased levels of the “fullness hormone” leptin in obese individuals while decreasing it in non-obese people.[14]
Helps You Breathe Easier
An asthma attack occurs when the lungs, trachea, and airways become inflamed, bringing on a hacking, wheezing cough. Asthma attacks may be triggered by allergens, smoke, stress, or even inhaling cold air. By reducing swelling in the body — particularly in the airways and lungs — omega-3 fatty acids may reduce the risk of asthmatic attack.[15, 16]
Normalizes Blood Sugar
Regularly elevated blood sugar is one of the main indicators of diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and other health conditions. When people get metabolic syndrome, they often have high blood sugar, insulin resistance, obesity, high triglycerides, and low good (HDL) cholesterol. Studies show that taking omega-3s improves these symptoms and reduces insulin resistance. In other words, it helps cells take up glucose, preventing too much from circulating in the blood.[17] For other tips, check out our article on natural ways to reduce blood sugar.
Omega-3 Foods
Omega-3 fatty acids are present in a variety of natural foods including leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and beans. Many plant sources contain ALA, while you can get DHA from fish oil as well as algae oil. See the table below for a variety of plant-based sources of omega-3s.
Selected Plant-Based Food Sources of ALA
Food Grams of ALA Per Serving Flaxseed oil, 1 tbsp 7.26 Chia seeds, 1 ounce 5.06 English walnuts, 1 ounce 2.57 Flaxseed, whole, 1 tbsp 2.35 Black walnuts, 1 ounce 0.76 Refried beans, canned, vegetarian, ½ cup 0.21 Kidney beans, canned ½ cup 0.10 Baked beans, canned, vegetarian, ½ cup 0.07
Omega-3 Supplements
Adding omega-3 fatty acid supplement to your daily regimen of vitamins and minerals is a great idea. While the most popular and common omega-3 supplements are fish oil, krill oil, and cod liver oil, many healthcare providers suggest that you avoid fish sources altogether given the rising levels of mercury and other toxic metals now found in many types of cold water fish.[18] Instead, choose vegan, plant-sourced supplements such as algae, micro-algae oil, or flaxseed oil. Most plant sources contain ALA, only algae or micro-algae oil contain EPA, DHA, and ALA.
How Much Omega-3 Should I Take?
Recommended intake levels of omega-3, established by the Institute of Medicine’s Food and Nutrition Board vary by age.[1] For children and adults above one-year-old, the intake level is for ALA only since it’s the only “essential” omega-3 that you must get from your diet. For non-breastfed infants, the board established values for total omega-3 consumption equivalent to the amount they would receive if breastfed. Breastfed babies do not need omega-3 supplementation.
The suggested intake for an adult man is 1.6 grams (1,600 milligrams or mg), and for an adult woman 1.1 grams (1,100 mg), increasing to 1.4 grams (1,400 mg) during pregnancy. Consult the chart below for appropriate amounts for all ages.
Age Male Female Pregnancy Lactation Birth to 6 months* 0.5 g 0.5 g 7 to 12 months* 0.5 g 0.5 g 1 to 3 years** 0.7 g 0.7 g 4 to 8 years** 0.9 g 0.9 g 9 to 13 years** 1.2 g 1.0 g 14 to 18 years** 1.6 g 1.1 g 1.4 g 1.3 g 19 to 50 years** 1.6 g 1.1 g 1.4 g 1.3 g 51+ years** 1.6 g 1.1 g
*As total omega-3s
**As ALA
Optimal Ratios of Omega-6 to Omega-3
Omega-6 fatty acids (which have their final double bond six carbons from the end of the chain) are found in plant sources like walnuts, sunflower seeds, and corn. Omega-6 fatty acids tend to be associated with inflammation. While inflammation is a normal and necessary reaction to infection, when it persists and creates systemic inflammation, health problems result. Omega-3 fatty acids can counteract the effects of omega-6s by keeping them in balance.
Experts recommend that we get omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids in a 2:1 ratio, which speeds the body’s conversion of ALA to EPA and DHA. However, many people — especially vegetarians — tend to get more omega-6s (in a ratio up to 10:1).[19] Seaweed and algae are the only plant-based sources of EPA and DHA, but you can also eat more plant-based ALA-containing foods or take supplements to optimize this ratio and get it closer to 2:1.
Signs of Omega-3 Deficiency
Dry, itchy, scaly skin
Brain fog
Weak immune system
Low energy levels
An omega-3 fatty acid deficiency usually appears initially as dermatitis — dry, itchy, scaly skin.[1] An omega-3 deficiency may also cause brain fog, affect cognitive function and the immune system, and reduce energy levels. If you are experiencing memory issues, excessive fatigue, or you keep getting colds and other bugs, you may want to consider supplementing with omega-3s.
Omega-3 Side Effects
For the most part, side effects of omega-3 supplementation are mild. They may include nausea, diarrhea, and fishy breath if you take a fish oil supplement, rather than a plant-sourced one.[1] If you take prescription medications, especially anti-coagulant medications, talk with your healthcare provider before taking omega-3 fatty acids to ensure no contraindications exist.
Points to Remember
Not all fats are created equal, and omega-3 fatty acids shine bright, offering significant health benefits. Three fatty acids affect human physiology: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA is an essential fatty acid, meaning the body does not manufacture it and you must get it from food or supplements.
All three omega-3 fatty acids play a vital role in the brain, cardiovascular, and immune system, so it is important to make sure you get enough at all ages and stages of life. While you can get omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil, and these are often the most popular supplement, fish is often contaminated with mercury and harvested unsustainably from the ocean. Instead, choose plant-based sources for optimal health and nutrition, such as flaxseed oil, algae oil, or other dietary sources like nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables.
References (19)
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. Updated 6 Jun. 2018. Accessed 24 Aug. 2018.
Swanson D, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA: Health benefits throughout life. Adv Nutr. 2012;3(1).
Montgomery P, et al. Fatty acids and sleep in UK children: Subjective and pilot objective sleep results from the DOLAB Study – a randomized controlled study. J Sleep Res. 2014;23(4):364-388.
Yurko-Mauro K, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid and adult memory: A systematic review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10(3)e0120391.
Grosso G, et al. Role of omega-3 fatty acids in the treatment of depressive disorders: A comprehensive meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96905.
Ciappolino V, et al. N-3 Polyunsatured Fatty Acids in Menopausal Transition: A Systematic Review of Depressive and Cognitive Disorders with Accompanying Vasomotor Symptoms. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul; 19(7): 1849.
Sohrabi N, et al. Evaluation of the effect of omega-3 fatty acids in the treatment of premenstrual syndrome: “a pilot trial”. Complement Ther Med. 2013 Jun;21(3):141-6.
Patrick RP, Ames BN. Vitamin D and the omega-3 fatty acids control serotonin synthesis and action, part 2: relevance for ADHD, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and impulsive behavior. FASEB J. 2015 Jun;29(6):2207-22.
Kang JX, et al. Modulation of inflammatory cytokines by omega-3 fatty acids. Subcell Biochem. 2008;49:133-43.
Foitzik T, et al. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation increases anti-inflammatory cytokines and attenuates systemic disease sequelae in experimental pancreatitis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2002 Nov-Dec;26(6):351-6.
Oelrich B, et al. Effect of fish oil supplementation on serum triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and LDL subfractions in hypertriglyceridimic adults. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;23(4):350-7.
Hodge W, et al. Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Eye Health: Summary. AHRQ Evidence Report Summaries. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 1998-2005.
Parra D, et al. A diet rich in long chain omega-3 fatty acids modulates satiety in overweight and obese volunteers during weight loss. Appetite. 2008 Nov;51(3):676-80.
Gray B, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids: a review of the effects on adiponectin and leptin and potential implications for obesity management. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2013 Dec;67(12):1234-42.
Li J, et al. Intakes of long-chain omega-3 (n−3) PUFAs and fish in relation to incidence of asthma among American young adults: the CARDIA study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013 Jan; 97(1): 181–186.
Yang H, et al. Fish and Fish Oil Intake in Relation to Risk of Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2013; 8(11): e80048.
Ebrahimi M, et al. Omega-3 fatty acid supplements improve the cardiovascular risk profile of subjects with metabolic syndrome, including markers of inflammation and auto-immunity. Acta Cardiol. 2009 Jun;64(3):321-7.
Landmark K, Aursnes I. Mercury, fish, fish oil and the risk of cardiovascular disease. [Article in Norwegian] Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2004 Jan 22;124(2):198-200.
Davis BC, Kris-Etherton PM. Achieving optimal essential fatty acid status in vegetarians: current knowledge and practical implications. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003 Sep;78(3 Suppl):640S-646S.
Related Posts
5 Health Benefits of Hemp Seed Oil
The Health Benefits of Omega 3, 6, 9 Fatty Acids and EPA & DHA
What Is the Mediterranean Diet
Eucalyptus Oil: Top Benefits & Uses With DIY Recipes
from WordPress https://ift.tt/2ROcBG7
via IFTTT
0 notes
Text
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Benefits, Foods, & Supplements

Omega-3 fatty acids are known for their role in brain and heart health but are they all they're cracked up to be? Should you take fish oil to get your daily dose of omega-3s, or should you opt for plant-based options instead? So many questions! If DHA, EPA, and ALA sound like alphabet soup to you, read on — we'll provide clarity.
What Are Fatty Acids?
To begin, let's look at fatty acids in general. Fatty acids are the building blocks of all fats (lipids). Every fatty acid contains an acid connected to a long chain of carbon and hydrogen molecules.
Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated. In other words, the long carbon chain is either saturated or "full of" hydrogens, or not. If all carbons are single-bonded to hydrogens, the chain stretches out straight. These straight chains stack up and stick together, forming a solid material — as happens with animal fat or coconut oil — at room temperature. In contrast, an unsaturated fatty acid has double bonds that cause the chain to "kink" or bend. These kinked up chains do not stack up or stick together like saturated fats do, so they stay in liquid form.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
That brings us to omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s play a critical role in your body, forming part of every cell's structural membranes. They also help brain cells send messages through neurotransmitters and provide energy within the cardiovascular, immune, and endocrine systems, among other functions.
The "omega" represents the tail end of the fatty acid molecule, and the "3" indicates that the last double bond is three carbons from the chain's end. Omega-3 fatty acids are considered polyunsaturated fats.
EPA, ALA, & DHA, Oh My!
Eleven types of omega-3 fatty acids exist, but just three play an important role in human physiology and health: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA).[1] Of the three, only ALA is considered an essential fatty acid. This means that your body does not make it and you must get it from food or supplements. Your body can convert ALA to EPA and DHA, making these latter two not "essential" fatty acids, but the conversion process occurs at such a low rate (between 2 and 10 percent) that, for all practical purposes, you need to get EPA and DHA from your diet.[1, 2]
Also, don't confuse alpha-linoleic acid with the other "ALA" which is alpha-lipoic acid, which is not an omega-3 at all. For the purpose of this article, ALA refers to the omega-3.
Omega-3 Health Benefits
As the building blocks of fats in the human body, fatty acids play an integral role in energy storage, brain activity and mental health, heart health and more. Below are the top health benefits that omega-3 fatty acids provide to your body and mind.
Promotes Restful Sleep
Restful sleep is important for memory, focus, and energy levels. Getting adequate DHA, in particular, helps you get better quality sleep — and more of it. One study linked lower blood levels of DHA to poor sleep quality in children. Algae oil DHA supplementation led children to have seven fewer wake episodes and 58 minutes more rest per night.[3] While scientists aren't entirely sure why DHA is so critical to slumber, they hypothesize that lower levels in the brain may interfere with melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.[3]
Boosts Brain Health
Omega-3 fatty acids play an important role in brain function, including memory and cognition — the process of thinking. The substance that insulates brain cells and helps them communicate with one another, myelin, is made up of omega-3 fatty acids and proteins. When the body lacks omega-3s, myelin sheaths erode, causing memory to decline.
People with Alzheimer's disease, dementia, multiple sclerosis, and other neurological disorders are often deficient in omega-3 fatty acids.[1, 4] Yet getting enough boosts memory and cognition.[1] While omega-3s are especially helpful in aging individuals, studies show they also improve nonverbal reasoning, logical memory, and working memory in healthy middle-aged adults.[4] Getting enough omega-3s during pregnancy and when breastfeeding — as well as for young children — is essential for proper brain development.
Lifts Your Mood
Omega-3 fatty acids help regulate and even improve your mood. Some studies suggest that omega-3s may help certain mood disorders.[5] Omega-3 supplementation can also help reduce the chance that women going through menopause will become depressed,[6] and can reduce symptoms of pre-menstrual syndrome.[7] Some studies suggest omega-3 supplementation reduces oppositional behavior, restlessness, aggression, and inattention in children with ADHD.[1]
Omega-3 fatty acids, along with the hormone vitamin D, play a role in the synthesis or creation of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a critical role in having a happy mood.[8] Scientists also theorize that omega-3s promote a positive mood by promoting normal levels of homocysteine and inflammatory cytokines circulating in the blood — the same way they improve heart health.[5]
Supports Cardiovascular Health
As mentioned, omega-3s normalize levels of cytokines in the blood, substances that inflame and irritate the body's organs and tissues, leading to poor heart health, among other things.[5] One way that omega-3s help the cardiovascular system is by discouraging too many omega-6 fatty acids from forming, which promote inflammation.[9, 10]
Omega-3 supplements also reduce triglyceride build-up in the blood, which is linked to an increased risk of heart attack and stroke; this is true even though omega-3 dietary supplements actually contain triglycerides![11] Supplementing with omega-3s can help promote normal cholesterol, triglycerides, and blood pressure.[1]
Ensures Eyes Are Healthy
Both your brain and eyes contain high levels of omega-3 fatty acids. But can taking omega-3s improve eye health and vision? The retina — the part at the back of the eye that allows you to see color and light — has high levels of DHA, and studies suggest that taking DHA can prevent retinal degeneration (also called macular degeneration).[12] Studies on human development also show that taking omega-3s — especially DHA — during pregnancy helps ensure an infant's eyes develop properly.[12]
Soothes Joint Tenderness
Because of their anti-inflammatory properties, omega-3 fatty acids may reduce joint tenderness and discomfort, particularly in cases of rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder.[1] Omega-3s help so much that they have reduced some patients' need for additional medications.[1] Some studies have looked at how taking omega-3s affects bones, particularly bone density and osteoporosis, but so far the evidence is inconclusive.[1]
Supports Weight Loss Efforts
How can taking a fat supplement help you lose weight? It turns out omega-3 consumption may help reduce appetite and feelings of hunger. In one study, eating a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids left people feeling fuller up to two hours after a meal.[13] These effects may not apply universally though. Studies have found that omega-3 increased levels of the "fullness hormone" leptin in obese individuals while decreasing it in non-obese people.[14]
Helps You Breathe Easier
An asthma attack occurs when the lungs, trachea, and airways become inflamed, bringing on a hacking, wheezing cough. Asthma attacks may be triggered by allergens, smoke, stress, or even inhaling cold air. By reducing swelling in the body — particularly in the airways and lungs — omega-3 fatty acids may reduce the risk of asthmatic attack.[15, 16]
Normalizes Blood Sugar
Regularly elevated blood sugar is one of the main indicators of diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and other health conditions. When people get metabolic syndrome, they often have high blood sugar, insulin resistance, obesity, high triglycerides, and low good (HDL) cholesterol. Studies show that taking omega-3s improves these symptoms and reduces insulin resistance. In other words, it helps cells take up glucose, preventing too much from circulating in the blood.[17] For other tips, check out our article on natural ways to reduce blood sugar.
Omega-3 Foods
Omega-3 fatty acids are present in a variety of natural foods including leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and beans. Many plant sources contain ALA, while you can get DHA from fish oil as well as algae oil. See the table below for a variety of plant-based sources of omega-3s.
Selected Plant-Based Food Sources of ALA:
@media( max-width: 639px ){.text-title-small{font-size: .8rem;}}
Food ALA Grams Per Serving Flaxseed oil, 1 tbsp 7.26 Chia seeds, 1 ounce 5.06 English walnuts, 1 ounce 2.57 Flaxseed, whole, 1 tbsp 2.35 Black walnuts, 1 ounce 0.76 Refried beans, canned, vegetarian, ½ cup 0.21 Kidney beans, canned ½ cup 0.10 Baked beans, canned, vegetarian, ½ cup 0.07 Bread, whole wheat, 1 slice 0.04
Omega-3 Supplements
Adding omega-3 fatty acid supplement to your daily regimen of vitamins and minerals is a great idea. While the most popular and common omega-3 supplements are fish oil, krill oil, and cod liver oil, many healthcare providers suggest that you avoid fish sources altogether given the rising levels of mercury and other toxic metals now found in many types of cold water fish.[18] Instead, choose vegan, plant-sourced supplements such as algae, micro-algae oil, or flaxseed oil. Most plant sources contain ALA; only algae or micro-algae oil contain EPA, DHA, and ALA.
How Much Omega-3 Should I Take?
Recommended intake levels of omega-3, established by the Institute of Medicine's Food and Nutrition Board vary by age.[1] For children and adults above one-year-old, the intake level is for ALA only since it's the only “essential" omega-3 that you must get from your diet. For non-breastfed infants, the board established values for total omega-3 consumption equivalent to the amount they would receive if breastfed. Breastfed babies do not need omega-3 supplementation.
The suggested intake for an adult man is 1.6 grams (1,600 milligrams or mg), and for an adult woman 1.1 grams (1,100 mg), increasing to 1.4 grams (1,400 mg) during pregnancy. Consult the chart below for appropriate amounts for all ages.
Table 1: Adequate Intakes (AIs) for Omega-3s
@media( max-width: 639px ){.text-title-small{font-size: .8rem;}}
Age Male Female Pregnancy Lactation Birth to 6 months* 0.5 g 0.5 g 7–12 months* 0.5 g 0.5 g 1–3 years** 0.7 g 0.7 g 4–8 years** 0.9 g 0.9 g 9–13 years** 1.2 g 1.0 g 14–18 years** 1.6 g 1.1 g 1.4 g 1.3 g 19-50 years** 1.6 g 1.1 g 1.4 g 1.3 g 51+ years** 1.6 g 1.1 g
*As total omega-3s
**As ALA
Optimal Ratios of Omega-6 to Omega-3
Omega-6 fatty acids (which have their final double bond six carbons from the end of the chain) are found in plant sources like walnuts, sunflower seeds, and corn. Omega-6 fatty acids tend to be associated with inflammation. While inflammation is a normal and necessary reaction to infection, when it persists and creates systemic inflammation, health problems result, reducing overall wellness. Omega-3 fatty acids can counteract the effects of omega-6s by keeping them in balance.
Experts recommend that we get omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids in a 2:1 ratio, which speeds the body's conversion of ALA to EPA and DHA. However, many people — especially vegetarians — tend to get more omega-6s (in a ratio up to 10:1).[19] Seaweed and algae are the only plant-based sources of EPA and DHA, but you can also eat more plant-based ALA-containing foods or take supplements to optimize this ratio and get it closer to 2:1.
Signs of Omega-3 Deficiency
Dry, itchy, scaly skin
Brain fog
Weak immune system
Low energy levels
An omega-3 fatty acid deficiency usually appears initially as dermatitis — dry, itchy, scaly skin.[1] An omega-3 deficiency may also cause brain fog, affecting cognitive function as well as lowered immune system health, and a decline in energy levels. If you are experiencing memory issues, excessive fatigue, or you keep getting colds and other bugs, you may want to consider supplementing with omega-3s.
Omega-3 Side Effects
For the most part, side effects of omega-3 supplementation are mild. They may include nausea, diarrhea, and fishy breath if you take a fish oil supplement, rather than a plant-sourced one.[1] If you take prescription medications, especially anti-coagulant medications, talk with your healthcare provider before taking omega-3 fatty acids to ensure no contraindications exist.
Points to Remember
Not all fats are created equal, and omega-3 fatty acids shine bright, offering significant health benefits. Three fatty acids affect human physiology: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA is an essential fatty acid, meaning the body does not manufacture it and you must get it from outside sources.
All three omega-3 fatty acids play a vital role in the brain, cardiovascular, and immune health, so it is important to make sure you get adequate levels at all ages and stages of life. While you can get omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil, and these are often the most popular supplement, fish is often contaminated with mercury and harvested unsustainably from the ocean. I strongly recommend plant-based sources for optimal health and nutrition, such a flax seed, algae oil, or other dietary sources like nuts, seeds, and leafy vegetables.
The post Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Benefits, Foods, & Supplements appeared first on Dr. Group's Healthy Living Articles.
0 notes
Note
DHA S2 E84
Blinder Vertrauen " Blind Trust"
So Magnus sees Amneris in Delia and Nina's room and he runs to Mara for comfort. The Club is trying to figure out the next Clue. They find out that they have to do something with Twins and Music. Nina is sure that they will solve the Riddle. Luzy has a dream about Max. Daphne and Victor sing together. Later Daphne goes in a car and Radus is there.
Do I like the episode?
Yeah
Favourite Moment:
Magnus running to Mara and how she basically stroke his cheek for him to fall asleep. ( If Felix knew he would make so much fun of him).
Victor and Daphne's singing.
Least Favourite Moment:
I don't know I don't really like the dream with Max I don't mind her with him. They first Max but she had no Chemistry with other Max. But they should have started differently.
Favourite Character:
Victor
What I would have done differently:
Look Nina and Daniel are kinda a bit cute here. But the episode got me thinking. What if they were twins. No idea how they would pull it off. Daniel could Nina's long lost twin brother that's,why she feels a connection to him from the beginning. Idk they are cuter if they aren't a couple.
Unpopular opinion:
I don't if Amneris just didn't Magnus to stop snopping around or if she also wanted him to run to Mara.
I love how different their reactions are seeing that ghost the first time. Mara just blinks and goes back to sleep and he runs to Mara in the middle of the night and then has to be cuddled by her. haha
Random Gifs:










Here's to the Ask Game:
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
It's all over, boys - Sat 21/01/2017
We can go home now.
I think I’m finally starting to see the end of this withdrawal. It’s been about a month since my last dose of 37.5mg Venlafaxine, and it’s been a rough last couple of weeks. Rough, but tolerable. Made a lot easier by the Christmas break at the start, the New Years break a few days later, and a week off a week and a bit later again (where Jono and I went up to Paihia and stayed in a motel on the beach. It was epic).
I was a mess, of course. An angry, tetchy, impossible son of a bitch. But Jono was amazing. He let me off the hook so many times i lost count. And just when I thought I couldn’t handle it anymore, I’d go mad, I was just too much of a handful to expect anyone to suffer with me with the future so uncertain, he’d be there egging me on, telling me I can do it, I’m not a piece of shit: I’m doing
just great, and we’d just power through it. He was my little shoulder angel when I thought my self worth had abandoned me, and I could not have done it without him.
I’ll level with you here: I almost broke up with him. I was fully prepared to cut him loose because I really thought it wasn’t fair. I was too much hard work, and my ex was right: nobody would ever be able to tolerate my bullshit.
But, bless him, he straight up told me he wouldn’t give up on me. “We are in this together, dammit” he said, “and damned if I’m gonna quit on you now. Not now, not ever.”
I tell you, when he said that I cried until I thought
I’d shrivel up from dehydration. I don’t deserve this person.
It’s getting better. I’m less angry, I barely ever have to take my DHA supplements for the brain shocks: only when I get really tired or stressed.
My heart rate is a bit all over the place, but the doc said that’s to be expected. He said my adrenaline supplier gauge is a bit out of whack now that my seratonin levels are getting levelled out and so it’s pumping me full of excess all the time, giving me nasty palpitations and tachycardia. My mum says that this actually runs in the family but good old Egor says I just have to take a couple of beta blockersa day for a week or two and my gauge will reset itself and soon enough, i won’t even need those anymore. I’m on half a seroquel at night for sleep but after a few days I’ll be off those, too. Just on my daily patroptazole for my GORD. I don’t take Strattera every day now. If I’m tired or need to be extra into it at work, I can take one but they don’t seem to be doing much. I can function fine without them, and there’s no nasty side effects if I stop taking them all of a sudden.
If you’d like to know how I got through it, here’s a list if the advice I was given, and that actually helped make a difference. I hope anyone wanting to get off medication will be helped by this.
1 - TALK TO YOR DOCTOR BEFORE DOING ANYTHING.
I was an idiot and tried to do it myself, over my holidays, before discussing it with Egor. I know, I know. I got the pep talk from him, too. Don’t try to be a hero. Your doctor knows his shit. Sometimes they fuck up but they know a hell of a lot more than you or mr google does about these things. Tell him your plans and let them help you. It doesn’t have to be a time of immense suffering. It’s always going to be shit, but there are ways you can make it less shit, and talking it through and planning it with your doc is one of them.
2- Routine. Most important thing. This was exactly why my doc told me off for trying to do it during a holiday. Not only do you need your network of support open for business (ie, your doctor, pharmacy etc) but you need a structure to your day that stems from the regular and expected. Wake up at the same time. Activities, boom, boom, boom. Regular bed time. It helped me SO MUCH.
3 - Sleep aids. Boy, will you need these. Insomnia is the quickest way to derail your progress, and it will happen. No sleep, feel shit. Feel shit + feel shit = disaster. It just makes everything seem impossibly hard. Your doc will recommend the best type, but don’t fall for herbal crap. Times like this, you’ll need the heavy duty shit. Usually for a couple of nights to get you back into the real world, then you can use things like magnesium, melatonin, rescue remedy. At first, use what your doc prescribes.
4 - EXERCISE. A walk isn’t enough. Get those endorphins going, every day. At least 30 mins of your heart rate going 1/3 a above its usual. You should be sweating and gasping by the end. Then have a shower, hot or cold (weather and desire dependant).
You’re welcome.
5 - Keep busy. I can’t stress this enough. You can’t be sitting around “relaxing”. Nu-uh, not now. Not good. You gotta keep everything moving around in that head of yours, all the time. Simple things. Make a list if you get stuck. Do the washing. Clean the house. 2 minutes breathing exercises. Walk the dog. 1 episode of a good TV show. Go to the library, read a book. Go swimming. Don’t feel like doing anything? too f*king bad. Make yourself. This is where having a relentlessly helpful partner is useful. Annoying af, but you’ll bless him later. You’ll probably be the most productive during this time than ever before in your life.
6 - Pick something you would enjoy doing and schedule it for at least once a week. Look forward to it. If you don’t end up liking it, try something else. An art class, dancing lessons, riding lessons, learn a language, creative writing course. Anything. You don’t have to socialise at it, there’s no pressure to “make new friends” or whatever (if that freaks you out) just pick something you’ll like, and do your best to get a kick out of it. It also has the bonus that its homework is another thing to add to your list of Things To Do.
That’s really it as far as my experience went. I’m still working through it, but the mess I’m wading through now doesn’t feel as thick anymore. I feel like it’s receding. The hardest part is flying headlong into the unknown. Up until now, I’d never had a single day in my adult life living unmedicated. The hardest thing was during the really shitty times, never being 100% sure that it would pass, that things would get better. This was …is… totally uncharted territory. I’m just making this up as I go along. But, I guess, so are most of us. All of us, really. And, for the most part, my days of depending on the familiar are over. I still don’t know who I am, but I’m getting to be okay with that. It’ll come.
Peace out, guys.
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Omega-3s: Everything You Need to Know
As a health-minded individual, you’ve no doubt gotten the memo that omega-3 fatty acids are important. You may dutifully eat your weekly servings of small, oily fish. Perhaps a fish oil pill is even part of your daily supplement routine. But do you know why?
Looking back, I used to write about omega-3s a lot in the early days of Mark’s Daily Apple (more than a decade ago, geez!) Since then, I’ve covered the topic here and there, but I thought it was time for a refresher. Today I’m going to focus on giving you a broad overview of their function and an update on the state of the research literature.
It would be impossible to cover all the reasons that omega-3s are important for health in a single post, nor all the areas of ongoing research. I’ll try to hit the big ones here. Let me know in the comments what else you’d like me to cover in future posts.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3s are essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs)—“essential” means the body can’t synthesize them. We have to get them from food or supplements.
As Primal folks, you might have an adverse reaction to the word “polyunsaturated.” It’s true that in the ancestral health world, we tend to be wary of PUFAs—or really, oils containing high proportions of PUFAs such as safflower and canola—due to their propensity to become rancid and be pro-inflammatory. However, this is a don’t-throw-the-baby-out-with-the bathwater situation. First, when it comes to overconsumption and inflammation, we are primarily concerned with omega-6 fatty acids, not omega-3s. Second, PUFAs, both omega-3s and even the oft-maligned omega-6s, serve many functions in the human body.
I’ll return to the issue of omega-6s vis-à-vis omega-3s later in this post. For now, I just want you to understand that omega-3s are polyunsaturated, essential, and important.
A Quick Primer on Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Omega-3s and omega-6s are both types of polyunsaturated fatty acids. What does this mean? Fatty acids comprise chains of carbon atoms of differing lengths. Picture each carbon atom having four arms. They “hold hands” to form the chain. With the remaining hand(s), they hold on to one or more hydrogen atoms.
If each carbon atom uses one hand to hold the carbon on its left and one to hold the carbon on its right, that leaves two hands free for hydrogen. When each carbon is attached to two hydrogen atoms, these fatty acids are called saturated.
Sometimes carbons form double bonds, meaning they use two hands two grab a neighboring carbon. This leaves only one hand free for hydrogen. These are unsaturated fatty acids. When fatty acids only have one double bond along the carbon chain, they are called monounsaturated. When they have multiple double bonds, they are polyunsaturated.
The number in the name of the fatty acid tells you where you can find the first double bond. In omega-3s, the first double bond is on the third carbon atom from the omega (methyl) end. In omega-6s, it’s on the sixth carbon atom.
Double bonds form “kinks” in the fatty acid chains, affecting the shape, and ultimately the function, of the fatty acid. It is not inherently bad for a fatty acid to be polyunsaturated, but it does mean that they are especially vulnerable to oxidation. Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids (along with their less appreciated cousins, the omega-9 fatty acids) are each important in their own way.
The Three Main Types of Omega-3s
There are many forms of omega-3 fatty acids, of which three are particularly noteworthy for humans:
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
ALA is the most abundant in the diet. In humans, its main biological function is as a precursor for EPA and DHA. ALA that is not converted to EPA or DHA is used mainly for energy.
Even though ALA is converted into EPA and DHA, the latter two are still considered essential (or “conditionally essential”) because conversion rates are too low to provide all the EPA and DHA needed for optimal functioning. Females are better able to convert ALA thanks to higher estrogen, but both sexes need to get EPA and DHA in their diet and/or from supplements.1
But What Do Omega-3 Fatty Acids DO?
Omega-3s are found throughout the body, notably in cell membranes, where they affect the fluidity of the membranes and, ultimately, gene expression. All the omega-3s play numerous important roles in the body, including in cellular metabolism, immune system function, and cardiovascular health.
EPA is involved in producing signaling molecules called eicosanoids that modulate inflammation, while DHA is an important structural component especially in the nervous system and retinas. Both EPA and DHA are generally considered to be anti-inflammatory, although that’s something of an oversimplification. Their effect on the immune system depends on the context.
Generally speaking, though, EPA and DHA exert anti-inflammatory effects, in contrast to omega-6s, especially arachidonic acid (AA), which tend to be pro-inflammatory. Omega-3s work their anti-inflammatory magic in a number of ways, including by producing specific eicosanoids, suppressing pro-inflammatory transcription factors, decreasing production of inflammatory cytokines, and by “turning off” inflammatory responses once they have done their job.2 3
Omega-3s’ Roles in Disease
Because inflammation is characteristic of so many disease states, omega-3s are a major area of research interest. Researchers have studied how omega-3s interact with practically every major disease and developmental process you can think of.
I’ll tell you up front, we still have a lot more questions than answers. Sometimes it seems that omega-3 intake in the diet buffers against a certain health issue, but the results aren’t replicated in randomized control trials. (It may be that the initial epidemiological studies are flawed – I’m highly skeptical of this methodology overall.) Experiments often yield inconsistent results. There may be differences between getting omega-3s from whole foods versus supplements, or certain populations may respond differently than others to supplementation. Studies may not be targeting the optimal dose. On and on.
The fast is, there are few “knowns” with regard to specific diseases. It’s fair to say that it’s clearer that omega-3s are important in a global sense — for overall health — than for any specific disease or disorder.
Cardiovascular Health
The potential for omega-3s to prevent or treat cardiovascular disease has probably has received the most attention. There is lots of data here… and the results are all over the map. Let me try to summarize some of the major findings, focusing on recent meta-analyses where possible:
Observational studies suggest that people who eat one or two servings of fish per week have better cardiovascular health than people who do not.4
A recent meta-analysis evaluated 19 studies, with 45,637 participants, in which researchers assessed biomarkers of omega-3s—basically, how much omega-3 people had in their systems. ALA and DHA were associated with lower risk of fatal coronary heart disease but not total coronary heart disease.5
Some research suggests that omega-3 supplementation may be particularly helpful for individuals with existing cardiac disease, at least in terms of reducing the risk of cardiac and all-cause mortality.6 However, other analyses show minimal benefit.7 8
EPA and DHA may be useful in reducing high blood pressure.9
Overall, the data from many studies seems promising, though it gets messy when you really dig into the literature. Despite the messiness, last year the U.S. Food and Drug Administration concluded that there is “credible evidence” that EPA and DHA may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease and hypertension.10
On the other hand, a Cochrane Review published earlier this year takes a different stance.11 The authors conclude that there it is unlikely that omega-3 supplementation meaningful affects mortality, although they concede that there might be some benefit for cardiovascular disease events and arrhythmia. Effects of supplementation may vary by dose, which might help explain inconsistencies between studies.12 13 Optimal dose could depend on what outcomes you’re hoping to achieve.
One area where omega-3 supplementation seems to shine is in the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia, or high triglycerides.14 Multiple studies show a benefit, but at doses higher that you’re likely to take over the counter. To reduce triglycerides, the American Heart Association recommends taking 2 to 4 grams of EPA+DHA under a doctor’s supervision.15
Mental Health
Omega-3s are abundant in the brain and play key roles in neuronal functioning. It’s no surprise that they would be considered in the treatment of mental health disorders. Some disorders, notably depression, are also thought to be inflammatory, making anti-inflammatory omega-3s a potentially useful intervention. What does the data say?
People who eat more fish are at lower risk of depression16, and individuals diagnosed with depression may have chronically low levels of omega-3s in their cells.17 18
Some studies show that omega-3s, especially EPA, reduce depressive episodes19 and clinical anxiety20.
Omega-3s are also under investigation for a number of other mental health disorders including schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, but there is not enough evidence to draw firm conclusions about their efficacy.21
Aging and Age-Related Cognitive Decline
There are multiple pathways by which omega-3s might support healthy aging, especially in the brain. A couple small studies demonstrated positive effects of supplementation on brain structure and function in older adults.22 23 However, results have been inconsistent overall, with no clear benefit for preventing or treating Alzheimer’s or dementia.
Other studies have looked at whether omega-3s can improve physical functioning. One found that in older adults with coronary artery disease, EPA+DHA improved functioning and was associated with getting more weekly exercise.24 Another showed increased muscle protein synthesis with supplementation.25
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Likely due to their anti-inflammatory properties, omega-3s show promise for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. A recent meta-analysis of 20 randomized control trials linked omega-3 supplementation to improvements in 8 distinct health markers for RA, including stiffness in the morning and joint tenderness.26 Some studies, but not all, find that omega-3 supplementation reduces arthritis pain.27
Cancer
The data with regard to cancer are too disparate to summarize neatly. Researchers are particularly interested in the possibility that omega-3s may reduce incidence of breast and colorectal cancers. I’ll be keeping my eye on this.
One important note is that some studies have found limited evidence of a positive association between omega-3 intake and prostate cancer. However, other large-scale epidemiological studies suggest that men who consume more fish are at lower risk for prostate cancer.28 29 It’s not clear what’s going on here, but it does suggest that you should talk to your doctor if you’re considering supplementing with omega-3s and you have had, or are at high risk for developing, prostate cancer.
What does it all mean?
Here’s how I read the situation: There is no doubt that omega-3s are crucial for health. You don’t want to be chronically low in omega-3s. Whether there is a benefit for supplementing with omega-3s—especially above and beyond what you get from your diet—depends on what you hope to get out of it. If you’re thinking about using omega-3s to treat a specific health issue, talk to your doctor. There are too many variables at play—your dietary intake and health status, types and omega-3s and dosing—to make blanket recommendations.
How to Get Omega-3s
Dietary Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Marine animals are the primary dietary sources of EPA and DHA in the human diet. This is why I and others have argued previously that fish and shellfish played a critical role in human evolution.30 The abundance of DHA in particular was probably pivotal to our advanced brain development.
Some of the best sources of EPA and DHA are salmon, mackerel, anchovies, sardines, herring, and oysters. Cod livers are delightfully mild and pack a wallop of vitamins A and D to boot. Primal-friendly sources of ALA include flax seeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. You also get some omega-3s in meat and eggs (chickens are often fed omega-enriched feed). Grass-finished beef and pastured eggs31 will deliver higher doses.
Although seafood is by far the best source of EPA and DHA, if you are vegetarian or vegan, you can get these important fatty acids from algal oil. Seaweed and chlorella also contain omega-3s, but nowhere near the quantities found in seafood.
How Much Do You Need?
The generally accepted advice is to aim for one to two servings per week of seafood, but there is no set recommended daily allowance (RDA) for ALA, EPA, or DHA. Generally, you’ll find recommendations to consume anywhere from 250 to 500mg per day of combined EPA+DHA. I developed an omega-3 formula with clean ingredients to make it easy to get sufficient EPA and DHA every day.
Does Your Omega-3:Omega-6 Ratio Matter?
In the body, omega-6s compete for space with omega-3s. Both can be incorporated into cell membranes, where they affect the membranes’ fluidity, permeability, and signaling pathways. Research shows that the amount of each in cell membranes is proportional to omega-3 and omega-6 consumption in the diet. An imbalance of omega-3 to omega-6 PUFAs can negatively affect how the cells—including in immune cells and neurons—function.32
The primary omega-6 fatty acid is linoleic acid (LA). LA and the primary omega-3 ALA use the same enzymatic pathways to convert into longer-chain fatty acids: arachidonic acid (AA, in the case of LA) and EPA and DHA (in the case of ALA). High LA levels can crowd out the ALA and make it so that it can’t make the all-important EPA and DHA.
You can directly impact the amount of omega-3s and omega-6s in your tissues by changing your diet.33 This, in turn, can affect your levels of inflammation and disease risk. For example, across cultures with diverse diets, greater intake of omega-6s is associated with having more omega-6 in the tissues and with greater incidence of cardiovascular disease. This effect is moderated by omega-3 intake. Across all levels of omega-6 intake, higher omega-3 consumption is associated with lower disease risk. The lower the omega-3 intake, the higher the risk.34
Although some research suggests that the high ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 in modern diets puts people at risk for developing certain diseases such as heart disease and cancers,35 Experts argue that our ancestors evolved with a diet that had approximately equal proportions of omega-3s and omega-6s.36 Depending on whom you ask, modern diets may have a ratio of 1:10, 1:16, 1:20, or more!
I used to bang the drum about hitting the right omega-3:omega-6 ratio in your daily diet. In recent years I’ve backed off that stance somewhat. I still think modern diets like SAD are way too high in omega-6s, but the answer isn’t to pile on heaping servings of omega-3s to balance it and “correct” the ratio. The solution is to reduce consumption of omega-6s (mostly from refined seed and vegetable oils, and products containing those oils) while getting adequate omega-3s.
Should I Supplement With Fish Oil?
It is certainly possible to be deficient in omega-3s. Clinical deficiencies usually manifest as scaly rashes. Severe omega-3 deficiencies are rare in most parts of the world, though. Subclinical low omega-3 levels may manifest as brittle nails and hair, poor sleep, or mood disturbances.
Despite a mountain of evidence that omega-3s are essential for health, there is still no clear guidance about who exactly should supplement and how much. It seems to me that the best practice, and one I follow myself is: aim to get omega-3s from food, and supplement wisely as needed. In practice, this means I select grass-fed meat when I can, and I eat pastured eggs most days, and I eat a couple servings of small-oily fish every week. I take an omega-3 supplement most days, but I’ll skip that on the days when I eat fatty fish. Plus, I eat a lot of ALA-containing vegetables.
The other thing I do, of course, is limit my omega-6 consumption by avoiding refined seed and vegetable oils. I’m not overly concerned with omega-6s found in nuts, which I don’t eat in huge quantities anyway, or other whole foods.
For folks who are already eating a lot of omega-3-rich foods, further supplementation may not offer a ton of benefit.37 If you’re not sure where you fall, you can ask your doctor for a blood test for omega-3 levels. You can also just track your food for a few days in an app like Cronometer that tells you how much you’re consuming.
Are There Any Downsides?
Perhaps. Some people have raised the concern that because they are polyunsaturated, omega-3s, especially in supplement form, are subject to rancidity and may cause oxidative stress. This speaks to the importance of sourcing your supplements from a reputable source. Store them according to instructions on the label and use them by their best-by dates. It’s another argument for prioritizing food sources as well.
Furthermore, it seems clear that more is not better, especially when it comes to supplementation. Excessive intake may lead to bleeding since EPA and DHA can reduce platelet aggregation, although this doesn’t seem to be a big risk for the average person. Nevertheless, the FDA recommends of cap of 3 grams EPA+DHA per day, with no more than 2 grams coming from supplements. Higher doses should only be taken with a doctor’s supervision.
In any case, these risks seem to me to be considerably less than the potential downsides of getting insufficient omega-3s. I still count omega-3s as a central player in overall health and healthy aging.
(function($) { $("#dfbpuwK").load("https://www.marksdailyapple.com/wp-admin/admin-ajax.php?action=dfads_ajax_load_ads&groups=674&limit=1&orderby=random&order=ASC&container_id=&container_html=none&container_class=&ad_html=div&ad_class=&callback_function=&return_javascript=0&_block_id=dfbpuwK" ); })( jQuery );
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15075703
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23668691/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23747022/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29773586
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27357102
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24472636
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5885893/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30521670
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4054797/
https://www.fda.gov/food/cfsan-constituent-updates/fda-announces-new-qualified-health-claims-epa-and-dha-omega-3-consumption-and-risk-hypertension-and
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6513557/
https://ift.tt/36cgxsm
https://ift.tt/3dYaLgE
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30415628
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21502576
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26359502
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10333380
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9513745
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21939614/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6324500/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17194275
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23796946
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3789637/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29752179
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21159787
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28965775
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5295086/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25210201
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23408548
https://aocs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1007/BF02562227
https://pubag.nal.usda.gov/catalog/41808
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26795198/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16387724/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16387724/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18408140/ [/red] scientists have not been able to establish an optimum ratio.[ref]https://archive.ahrq.gov/downloads/pub/evidence/pdf/o3cardio/o3cardio.pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5093368/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29083439
The post Omega-3s: Everything You Need to Know appeared first on Mark's Daily Apple.
Omega-3s: Everything You Need to Know published first on https://drugaddictionsrehab.tumblr.com/
0 notes
Text
Omega-3s: Everything You Need to Know
As a health-minded individual, you’ve no doubt gotten the memo that omega-3 fatty acids are important. You may dutifully eat your weekly servings of small, oily fish. Perhaps a fish oil pill is even part of your daily supplement routine. But do you know why?
Looking back, I used to write about omega-3s a lot in the early days of Mark’s Daily Apple (more than a decade ago, geez!) Since then, I’ve covered the topic here and there, but I thought it was time for a refresher. Today I’m going to focus on giving you a broad overview of their function and an update on the state of the research literature.
It would be impossible to cover all the reasons that omega-3s are important for health in a single post, nor all the areas of ongoing research. I’ll try to hit the big ones here. Let me know in the comments what else you’d like me to cover in future posts.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3s are essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs)—“essential” means the body can’t synthesize them. We have to get them from food or supplements.
As Primal folks, you might have an adverse reaction to the word “polyunsaturated.” It’s true that in the ancestral health world, we tend to be wary of PUFAs—or really, oils containing high proportions of PUFAs such as safflower and canola—due to their propensity to become rancid and be pro-inflammatory. However, this is a don’t-throw-the-baby-out-with-the bathwater situation. First, when it comes to overconsumption and inflammation, we are primarily concerned with omega-6 fatty acids, not omega-3s. Second, PUFAs, both omega-3s and even the oft-maligned omega-6s, serve many functions in the human body.
I’ll return to the issue of omega-6s vis-à-vis omega-3s later in this post. For now, I just want you to understand that omega-3s are polyunsaturated, essential, and important.
A Quick Primer on Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Omega-3s and omega-6s are both types of polyunsaturated fatty acids. What does this mean? Fatty acids comprise chains of carbon atoms of differing lengths. Picture each carbon atom having four arms. They “hold hands” to form the chain. With the remaining hand(s), they hold on to one or more hydrogen atoms.
If each carbon atom uses one hand to hold the carbon on its left and one to hold the carbon on its right, that leaves two hands free for hydrogen. When each carbon is attached to two hydrogen atoms, these fatty acids are called saturated.
Sometimes carbons form double bonds, meaning they use two hands two grab a neighboring carbon. This leaves only one hand free for hydrogen. These are unsaturated fatty acids. When fatty acids only have one double bond along the carbon chain, they are called monounsaturated. When they have multiple double bonds, they are polyunsaturated.
The number in the name of the fatty acid tells you where you can find the first double bond. In omega-3s, the first double bond is on the third carbon atom from the omega (methyl) end. In omega-6s, it’s on the sixth carbon atom.
Double bonds form “kinks” in the fatty acid chains, affecting the shape, and ultimately the function, of the fatty acid. It is not inherently bad for a fatty acid to be polyunsaturated, but it does mean that they are especially vulnerable to oxidation. Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids (along with their less appreciated cousins, the omega-9 fatty acids) are each important in their own way.
The Three Main Types of Omega-3s
There are many forms of omega-3 fatty acids, of which three are particularly noteworthy for humans:
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
ALA is the most abundant in the diet. In humans, its main biological function is as a precursor for EPA and DHA. ALA that is not converted to EPA or DHA is used mainly for energy.
Even though ALA is converted into EPA and DHA, the latter two are still considered essential (or “conditionally essential”) because conversion rates are too low to provide all the EPA and DHA needed for optimal functioning. Females are better able to convert ALA thanks to higher estrogen, but both sexes need to get EPA and DHA in their diet and/or from supplements.1
But What Do Omega-3 Fatty Acids DO?
Omega-3s are found throughout the body, notably in cell membranes, where they affect the fluidity of the membranes and, ultimately, gene expression. All the omega-3s play numerous important roles in the body, including in cellular metabolism, immune system function, and cardiovascular health.
EPA is involved in producing signaling molecules called eicosanoids that modulate inflammation, while DHA is an important structural component especially in the nervous system and retinas. Both EPA and DHA are generally considered to be anti-inflammatory, although that’s something of an oversimplification. Their effect on the immune system depends on the context.
Generally speaking, though, EPA and DHA exert anti-inflammatory effects, in contrast to omega-6s, especially arachidonic acid (AA), which tend to be pro-inflammatory. Omega-3s work their anti-inflammatory magic in a number of ways, including by producing specific eicosanoids, suppressing pro-inflammatory transcription factors, decreasing production of inflammatory cytokines, and by “turning off” inflammatory responses once they have done their job.2 3
Omega-3s’ Roles in Disease
Because inflammation is characteristic of so many disease states, omega-3s are a major area of research interest. Researchers have studied how omega-3s interact with practically every major disease and developmental process you can think of.
I’ll tell you up front, we still have a lot more questions than answers. Sometimes it seems that omega-3 intake in the diet buffers against a certain health issue, but the results aren’t replicated in randomized control trials. (It may be that the initial epidemiological studies are flawed – I’m highly skeptical of this methodology overall.) Experiments often yield inconsistent results. There may be differences between getting omega-3s from whole foods versus supplements, or certain populations may respond differently than others to supplementation. Studies may not be targeting the optimal dose. On and on.
The fast is, there are few “knowns” with regard to specific diseases. It’s fair to say that it’s clearer that omega-3s are important in a global sense — for overall health — than for any specific disease or disorder.
Cardiovascular Health
The potential for omega-3s to prevent or treat cardiovascular disease has probably has received the most attention. There is lots of data here… and the results are all over the map. Let me try to summarize some of the major findings, focusing on recent meta-analyses where possible:
Observational studies suggest that people who eat one or two servings of fish per week have better cardiovascular health than people who do not.4
A recent meta-analysis evaluated 19 studies, with 45,637 participants, in which researchers assessed biomarkers of omega-3s—basically, how much omega-3 people had in their systems. ALA and DHA were associated with lower risk of fatal coronary heart disease but not total coronary heart disease.5
Some research suggests that omega-3 supplementation may be particularly helpful for individuals with existing cardiac disease, at least in terms of reducing the risk of cardiac and all-cause mortality.6 However, other analyses show minimal benefit.7 8
EPA and DHA may be useful in reducing high blood pressure.9
Overall, the data from many studies seems promising, though it gets messy when you really dig into the literature. Despite the messiness, last year the U.S. Food and Drug Administration concluded that there is “credible evidence” that EPA and DHA may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease and hypertension.10
On the other hand, a Cochrane Review published earlier this year takes a different stance.11 The authors conclude that there it is unlikely that omega-3 supplementation meaningful affects mortality, although they concede that there might be some benefit for cardiovascular disease events and arrhythmia. Effects of supplementation may vary by dose, which might help explain inconsistencies between studies.12 13 Optimal dose could depend on what outcomes you’re hoping to achieve.
One area where omega-3 supplementation seems to shine is in the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia, or high triglycerides.14 Multiple studies show a benefit, but at doses higher that you’re likely to take over the counter. To reduce triglycerides, the American Heart Association recommends taking 2 to 4 grams of EPA+DHA under a doctor’s supervision.15
Mental Health
Omega-3s are abundant in the brain and play key roles in neuronal functioning. It’s no surprise that they would be considered in the treatment of mental health disorders. Some disorders, notably depression, are also thought to be inflammatory, making anti-inflammatory omega-3s a potentially useful intervention. What does the data say?
People who eat more fish are at lower risk of depression16, and individuals diagnosed with depression may have chronically low levels of omega-3s in their cells.17 18
Some studies show that omega-3s, especially EPA, reduce depressive episodes19 and clinical anxiety20.
Omega-3s are also under investigation for a number of other mental health disorders including schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, but there is not enough evidence to draw firm conclusions about their efficacy.21
Aging and Age-Related Cognitive Decline
There are multiple pathways by which omega-3s might support healthy aging, especially in the brain. A couple small studies demonstrated positive effects of supplementation on brain structure and function in older adults.22 23 However, results have been inconsistent overall, with no clear benefit for preventing or treating Alzheimer’s or dementia.
Other studies have looked at whether omega-3s can improve physical functioning. One found that in older adults with coronary artery disease, EPA+DHA improved functioning and was associated with getting more weekly exercise.24 Another showed increased muscle protein synthesis with supplementation.25
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Likely due to their anti-inflammatory properties, omega-3s show promise for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. A recent meta-analysis of 20 randomized control trials linked omega-3 supplementation to improvements in 8 distinct health markers for RA, including stiffness in the morning and joint tenderness.26 Some studies, but not all, find that omega-3 supplementation reduces arthritis pain.27
Cancer
The data with regard to cancer are too disparate to summarize neatly. Researchers are particularly interested in the possibility that omega-3s may reduce incidence of breast and colorectal cancers. I’ll be keeping my eye on this.
One important note is that some studies have found limited evidence of a positive association between omega-3 intake and prostate cancer. However, other large-scale epidemiological studies suggest that men who consume more fish are at lower risk for prostate cancer.28 29 It’s not clear what’s going on here, but it does suggest that you should talk to your doctor if you’re considering supplementing with omega-3s and you have had, or are at high risk for developing, prostate cancer.
What does it all mean?
Here’s how I read the situation: There is no doubt that omega-3s are crucial for health. You don’t want to be chronically low in omega-3s. Whether there is a benefit for supplementing with omega-3s—especially above and beyond what you get from your diet—depends on what you hope to get out of it. If you’re thinking about using omega-3s to treat a specific health issue, talk to your doctor. There are too many variables at play—your dietary intake and health status, types and omega-3s and dosing—to make blanket recommendations.
How to Get Omega-3s
Dietary Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Marine animals are the primary dietary sources of EPA and DHA in the human diet. This is why I and others have argued previously that fish and shellfish played a critical role in human evolution.30 The abundance of DHA in particular was probably pivotal to our advanced brain development.
Some of the best sources of EPA and DHA are salmon, mackerel, anchovies, sardines, herring, and oysters. Cod livers are delightfully mild and pack a wallop of vitamins A and D to boot. Primal-friendly sources of ALA include flax seeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. You also get some omega-3s in meat and eggs (chickens are often fed omega-enriched feed). Grass-finished beef and pastured eggs31 will deliver higher doses.
Although seafood is by far the best source of EPA and DHA, if you are vegetarian or vegan, you can get these important fatty acids from algal oil. Seaweed and chlorella also contain omega-3s, but nowhere near the quantities found in seafood.
How Much Do You Need?
The generally accepted advice is to aim for one to two servings per week of seafood, but there is no set recommended daily allowance (RDA) for ALA, EPA, or DHA. Generally, you’ll find recommendations to consume anywhere from 250 to 500mg per day of combined EPA+DHA. I developed an omega-3 formula with clean ingredients to make it easy to get sufficient EPA and DHA every day.
Does Your Omega-3:Omega-6 Ratio Matter?
In the body, omega-6s compete for space with omega-3s. Both can be incorporated into cell membranes, where they affect the membranes’ fluidity, permeability, and signaling pathways. Research shows that the amount of each in cell membranes is proportional to omega-3 and omega-6 consumption in the diet. An imbalance of omega-3 to omega-6 PUFAs can negatively affect how the cells—including in immune cells and neurons—function.32
The primary omega-6 fatty acid is linoleic acid (LA). LA and the primary omega-3 ALA use the same enzymatic pathways to convert into longer-chain fatty acids: arachidonic acid (AA, in the case of LA) and EPA and DHA (in the case of ALA). High LA levels can crowd out the ALA and make it so that it can’t make the all-important EPA and DHA.
You can directly impact the amount of omega-3s and omega-6s in your tissues by changing your diet.33 This, in turn, can affect your levels of inflammation and disease risk. For example, across cultures with diverse diets, greater intake of omega-6s is associated with having more omega-6 in the tissues and with greater incidence of cardiovascular disease. This effect is moderated by omega-3 intake. Across all levels of omega-6 intake, higher omega-3 consumption is associated with lower disease risk. The lower the omega-3 intake, the higher the risk.34
Although some research suggests that the high ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 in modern diets puts people at risk for developing certain diseases such as heart disease and cancers,35 Experts argue that our ancestors evolved with a diet that had approximately equal proportions of omega-3s and omega-6s.36 Depending on whom you ask, modern diets may have a ratio of 1:10, 1:16, 1:20, or more!
I used to bang the drum about hitting the right omega-3:omega-6 ratio in your daily diet. In recent years I’ve backed off that stance somewhat. I still think modern diets like SAD are way too high in omega-6s, but the answer isn’t to pile on heaping servings of omega-3s to balance it and “correct” the ratio. The solution is to reduce consumption of omega-6s (mostly from refined seed and vegetable oils, and products containing those oils) while getting adequate omega-3s.
Should I Supplement With Fish Oil?
It is certainly possible to be deficient in omega-3s. Clinical deficiencies usually manifest as scaly rashes. Severe omega-3 deficiencies are rare in most parts of the world, though. Subclinical low omega-3 levels may manifest as brittle nails and hair, poor sleep, or mood disturbances.
Despite a mountain of evidence that omega-3s are essential for health, there is still no clear guidance about who exactly should supplement and how much. It seems to me that the best practice, and one I follow myself is: aim to get omega-3s from food, and supplement wisely as needed. In practice, this means I select grass-fed meat when I can, and I eat pastured eggs most days, and I eat a couple servings of small-oily fish every week. I take an omega-3 supplement most days, but I’ll skip that on the days when I eat fatty fish. Plus, I eat a lot of ALA-containing vegetables.
The other thing I do, of course, is limit my omega-6 consumption by avoiding refined seed and vegetable oils. I’m not overly concerned with omega-6s found in nuts, which I don’t eat in huge quantities anyway, or other whole foods.
For folks who are already eating a lot of omega-3-rich foods, further supplementation may not offer a ton of benefit.37 If you’re not sure where you fall, you can ask your doctor for a blood test for omega-3 levels. You can also just track your food for a few days in an app like Cronometer that tells you how much you’re consuming.
Are There Any Downsides?
Perhaps. Some people have raised the concern that because they are polyunsaturated, omega-3s, especially in supplement form, are subject to rancidity and may cause oxidative stress. This speaks to the importance of sourcing your supplements from a reputable source. Store them according to instructions on the label and use them by their best-by dates. It’s another argument for prioritizing food sources as well.
Furthermore, it seems clear that more is not better, especially when it comes to supplementation. Excessive intake may lead to bleeding since EPA and DHA can reduce platelet aggregation, although this doesn’t seem to be a big risk for the average person. Nevertheless, the FDA recommends of cap of 3 grams EPA+DHA per day, with no more than 2 grams coming from supplements. Higher doses should only be taken with a doctor’s supervision.
In any case, these risks seem to me to be considerably less than the potential downsides of getting insufficient omega-3s. I still count omega-3s as a central player in overall health and healthy aging.
(function($) { $("#dfV0UNl").load("https://www.marksdailyapple.com/wp-admin/admin-ajax.php?action=dfads_ajax_load_ads&groups=674&limit=1&orderby=random&order=ASC&container_id=&container_html=none&container_class=&ad_html=div&ad_class=&callback_function=&return_javascript=0&_block_id=dfV0UNl" ); })( jQuery );
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15075703
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23668691/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23747022/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29773586
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27357102
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24472636
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5885893/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30521670
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4054797/
https://www.fda.gov/food/cfsan-constituent-updates/fda-announces-new-qualified-health-claims-epa-and-dha-omega-3-consumption-and-risk-hypertension-and
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6513557/
https://ift.tt/36cgxsm
https://ift.tt/3dYaLgE
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30415628
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21502576
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26359502
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10333380
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9513745
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21939614/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6324500/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17194275
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23796946
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3789637/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29752179
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21159787
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28965775
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5295086/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25210201
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23408548
https://aocs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1007/BF02562227
https://pubag.nal.usda.gov/catalog/41808
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26795198/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16387724/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16387724/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18408140/ [/red] scientists have not been able to establish an optimum ratio.[ref]https://archive.ahrq.gov/downloads/pub/evidence/pdf/o3cardio/o3cardio.pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5093368/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29083439
The post Omega-3s: Everything You Need to Know appeared first on Mark's Daily Apple.
Omega-3s: Everything You Need to Know published first on https://venabeahan.tumblr.com
0 notes
Text
Bowen Therapy Surrey - Surrey Naturopath
Exercise
Exercise is a great stress reliever. Anything from playing sports, to walking can be enjoyable and improves your immunity and circulation.
Diet
Eat small well balanced meals, with adequate protein carbohydrates, and fat. Try to eat breakfast within an hour of getting up. Do not skip any meals. Don’t eat a late dinner.
Avoid caffeine. Since it will raise cortisol levels, and can keep you up at night and therefore upset your sleep pattern.
Avoid high sugar foods including starchy foods such as potatoes and white bread sugary fruit like mangoes, and melons. Learn about glycemic index and glycemic load.
Avoid trans fat and greasy food which will slow your digestion and raise your bad cholesterol and lower good cholesterol
Improve your energy, book a one on one appointment to discuss your personalized treatment plan.
Do you have any of the following symptoms?
abdominal weight gain
anxiety
low mood
low blood pressure
sugar cravings
napping
afternoon fatigue
chronic inflammation
panic attacks
syndrome X
chronic disease of CV system or GI system
IBS
weakened immunity and recurrent infection
subclinical hypothyroidism
Then you could benefit by improving your adrenal gland function!!!
What is the Adrenal Gland?
Your adrenal gland is a small gland that sits on top of each of your kidneys and helps your body deal with stress by releasing a stress hormone called cortisol.
What is the relationship of the adrenal gland with stress?
First of all, your body cannot tell the difference between mental, emotional, or physical stress. In a practical sense, that means there is no difference between you working a long hard day at the office crunching numbers, or a struggling with a recent breakup with a partner, or working a physically taxing job that requires heavy lifting. In other words, all of those stressors will receive an equivalent response from your adrenal gland. The response is to specifically increase your stress hormones, so you can better adapt to and deal with stress. In essence it ensures your survival.
Survival of our species and your personal survival
You’ve probably heard of the “Fight of Flight” response. It is intimately connected with your adrenal glands.
This story takes us back thousands of years, when humans were struggling for survival. At the time, the next meal required great effort and safety was paramount. So finding lunch was just as important as avoiding becoming someone else’s lunch!
For example, what if you were being attacked by a tiger in the jungle? There are two responses to that attack. Run and hide or attack. Both allow survival and this precisely is a fight or flight response. Humans have evolved and the environment has changed from a real jungle to an urban jungle. When you walk downtown you don’t expect to be attacked by a tiger on the street. But there are different “tigers” ready to pounce. One “tiger” may be your boss or co-worker that verbally attacks you.
When you respond, it’s very likely you won’t resort to fisticuffs or grab a spear, but instead say something back to them, run and hide or say nothing and just try to ignore them. Another example of “fight or flight” response is being stuck in traffic when you are late for work or an appointment and emotions such as frustration, anger, and worry begin to surface. At an emotional level, you can be anxious or worried and fearful of your boss and being late or you can be agitated, frustrated and angry.
If this happens to you, then you are experiencing fight or flight and your stress hormones are released —you are in heightened survival mode; your body responds by increasing your heart rate, increasing your respiratory rate, dilating your pupils. Overtime, especially if you have these feelings on a daily basis, this chronic release of stress hormone begins to create unpleasant symptoms that you may be experiencing.
So that same feeling of being late for an appointment, tired after a long day at the office, or verbally attacked by your boss, having relationship issues with your partner or working a strenuous job that requires heavy lifting can lead to health problems.
What is your body’s response to stress?
You’ve probably heard of adrenalin; cortisol is a hormone that is similar to adrenalin. When adrenalin is released we may feel a rush of excitement, anger, frustration, burst of energy. Below is a description of Maladaptive Stress Syndrome that describes your body’s response to stress.
MSS-0 is a normal response to stress that is described as a healthy well-adapted range of alertness and an appropriate response to a perceived stress. The response is mediated by autonomic nervous system and the adrenal hormones (catecholamines).
MSS-1 is maladaptive stress syndrome stage 1 and is described as chronic excess of catecholamines and an increase in cortisol. When there is a perceived stress then a fight or flight response is activated but it is not appropriate—it is in excess. Hence it is associated with anger, irritability, aggression, anxiety, worry, fear and panic. After being in MSS-1 a person can progress to MSS-2 over a period of time.
MSS-2 is a maladaptive stress syndrome stage 2 and is described as chronic excess production of cortisol. There is immune suppression, Syndrome X, Chronic diseases (Cardiovascular, Gastrointestinal), increased androgens. Progression of MSS-2 to MSS-3 is worsened by stress, history of steroid use, nutritional deficiencies, and functional hypoglycemia.
MSS-3 is a maladaptive stress syndrome stage 3 and is described as chronic decreased cortisol and episodic catecholamine production. It is associated with fatigue, chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia, hypotension, postural hypotension, environmental and food sensitivities, atypical depression, anxiety, poor stress resistance, post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
TREATMENT: So how do we prevent and treat these problems that are associated with maladaptive stress syndrome?
Each stage of MSS has its appropriate treatment. To determine which stage you’re in, lab testing and proper diagnosis is required by your naturopath.
Stage 0 – lifestyle and stress management
Stage 1 – meditation, exercise, relaxation, B-complex vitamins, and nervines.
Stage 2 – cortisol lowering therapies such as DHA, vitamin C, sodium restriction, pyridoxine, avoiding sugar since it stimulates cortisol production, and DHEA.
·Stage 3 requires adaptogenic herbs, pantothenic acid, low glycemic diet, immune support, amino acids, and graduated moderate exercise.
Dr. Dhillon, ND
Better Health for a Better You
0 notes
Text
Deoch dha na mairbh
read it on the AO3 at http://bit.ly/2XwgBBz
by ThayerKerbasy
Dean had gone off to suicide bomb Amara, leaving everyone else with nothing to do but drink.
Words: 1945, Chapters: 1/1, Language: English
Fandoms: Supernatural
Rating: Teen And Up Audiences
Warnings: No Archive Warnings Apply
Categories: M/M
Characters: Crowley (Supernatural), Castiel (Supernatural), Sam Winchester, Rowena MacLeod, Chuck Shurley
Relationships: Crowley (Supernatural)/Dean Winchester
Additional Tags: Episode: s11e23 Alpha and Omega, Angst, Destiel if you squint - Freeform, The Lazy Shag Pub, Wakes & Funerals
read it on the AO3 at http://bit.ly/2XwgBBz
0 notes
Text
Deoch dha na mairbh
read it on the AO3 at http://bit.ly/2XwgBBz
by ThayerKerbasy
Dean had gone off to suicide bomb Amara, leaving everyone else with nothing to do but drink.
Words: 1945, Chapters: 1/1, Language: English
Fandoms: Supernatural
Rating: Teen And Up Audiences
Warnings: No Archive Warnings Apply
Categories: M/M
Characters: Crowley (Supernatural), Castiel (Supernatural), Sam Winchester, Rowena MacLeod, Chuck Shurley
Relationships: Crowley (Supernatural)/Dean Winchester
Additional Tags: Episode: s11e23 Alpha and Omega, Angst, Destiel if you squint - Freeform, The Lazy Shag Pub, Wakes & Funerals
read it on the AO3 at http://bit.ly/2XwgBBz
0 notes
Text
Exposing Myths of Dietary Oils: The Omega 3 to Omega 6 Fatty Acid Ratio is Key


This Fat Is Actually Worse Than Trans Fats
by Dr. Mercola
Dietary fats can be tricky business, as they're not all the same. While some are necessary for optimal health, others need to be balanced and some need to be avoided altogether, and understanding which is which is quite crucial, considering how important fats are for optimal health.
Here, I will review some of the basics, including the importance of balancing your omega-3 and omega-6 intake, and why replacing saturated animal fats with omega-6-rich vegetable oils is such a bad idea.
Some of this information, which will be more thoroughly covered in my upcoming book, “Superfuel,” is based on research by my coauthor, James DiNicolantonio, a doctor of pharmacy and cardiovascular researcher.

For Optimal Health, Mind Your Omega-3 to Omega-6 Ratio
For years, I've stressed the importance of balancing your omega-3 to omega-6 intake to protect your health. Eating too much damaged omega-6 fat - found in abundance in processed vegetable oils - and too little animal-based omega-3 sets the stage for diabetes, cardiovascular disease, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, depression and Alzheimer's, just to name a few.
The ideal ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 fats ranges from 1-to-1 to 1-to-5, but the typical Western diet tends to be between 1-to-20 and 1-to-50. Most people, especially Americans, are guilty of this lopsided omega-3 to omega-6 ratio, and to correct it, you typically need to do two things:
1. Significantly decrease intake of damaged omega-6 by avoiding processed foods and foods cooked in vegetable oil at high temperatures. A number of studies1,2 have found that people who regularly eat deep-fried foods have a significantly increased risk of stroke and death.
Common sources of harmful omega-6 to avoid include corn oil, canola oil, soy oil, hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated fats, margarine and shortening.
2. Increase your intake of animal-based omega-3 fats. Ideal sources include small fatty fish such as sardines, anchovies and herring, along with wild-caught Alaskan salmon, or a supplement such as krill oil.
Replacing Saturated Fats With Vegetable Oils Harms Heart Health
Unfortunately, many health authorities have insisted omega-6-rich vegetable oils are healthier than saturated animal fats such as butter and lard, and this myth has been a tough one to dismantle, despite the evidence against it.
For example, a 2013 study3 in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) found replacing saturated fat with omega-6 oils raised the risk of death if you have heart disease. As reported in a BMJ press release:4
“Their analysis involved 458 men aged 30 to 59 years who had recently had a coronary event, such as a heart attack or an episode of angina. Participants were randomly divided into two groups.
The intervention group was instructed to reduce saturated fats (from animal fats, common margarines and shortenings) to less than 10 percent of energy intake and to increase linoleic acid (from safflower oil and safflower oil polyunsaturated margarine) to 15 percent of energy intake. Safflower oil is a concentrated source of omega-6 linoleic acid and provides no omega-3 PUFAs [polyunsaturated fats].”
The control group received no specific dietary advice on fats and was allowed to eat whatever they wanted. Both groups kept food diaries for an average of 39 months.
It's worth noting that this study did not differentiate between types of saturated fats, lumping together animal fats with margarines and shortening high in saturated fat but also toxic trans fats. (The harder the margarine, the more saturated fat it tends to contain, in some cases more than butter or lard.) Despite this discrepancy, the results showed that:
The omega-6 linoleic acid group had a 17 percent higher risk of dying from heart disease during the study period, compared with 11 percent among the control group
The omega-6 group also had a higher risk of all-cause mortality
Omega-6 Oils Do Not Provide Cardiovascular Benefit
The researchers also conducted a meta-analysis of linoleic acid intervention trials, finding no evidence of cardiovascular benefit. According to the authors, “These findings could have important implications for worldwide dietary advice to substitute omega-6 linoleic acid, or PUFAs in general, for saturated fats.”
Jane Collis, an independent researcher not affiliated with the research also commented on the BMJ study, saying:5
“Commercial food processing destroys a significant amount of EFAs [essential fatty acids], along with their oxygenating ability … Polyunsaturated oils are unstable and very quickly become rancid.
Oxidized fatty acids are dangerous to your health. Lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress are important factors in this damage. Further damage is also caused by heating polyunsaturated fats in cooking (particularly frying foods).
Many omega-3 research trials did not consider the omega 3/6 essential fatty acid ratio which is vital to the eicossanoid balance. The correct omega 3/6 ratio is fundamental to holistic health for all.”
Oxidized Omega-6 Fat Is a Primary Driver of Heart Disease
Next, let's take a look at why omega-6 industrially processed vegetable oils promote heart disease. First of all, it's important to recognize that omega-6 fat in and of itself is not the problem. Linoleic acid is also found in foods such as nuts, seeds and eggs, and is important for health.
In a groundbreaking new publication entitled “Omega-6 Vegetable Oils as a Driver of Coronary Heart Disease: The Oxidized Linoleic Acid Hypothesis,”6 published in BMJ Open Heart by DiNicolantonio, he explains the following:
The problem is that we now eat far too much omega-6, which creates a severe imbalance in the omega-3 to omega-6 ratio. Today, omega-6 PUFAs make up around 8 to 10 percent of the total energy intake in the Western world. This is largely related to the large amounts of processed foods consumed that are loaded with these dangerous fats.
What's worse, the primary source of omega-6 is no longer eggs and nuts but rather processed vegetable oils, and most of this linoleic acid is oxidized from the processing.
In the early 1900s, consumption of vegetable oils skyrocketed, taking the place of butter and lard, and so did incidence of heart disease. Evidence implicating excessive consumption of omega-6-rich vegetable oils as a direct cause of heart disease include but is not limited to:
The amount of linoleic acid in adipose tissue and platelets is positively associated with coronary artery disease, and studies7 measuring changes in linoleic acid concentrations in adipose tissue in Americans show concentrations increased from 9.1 percent in 1959 to 21.5 percent in 2008. This increase also paralleled increases in the prevalence of obesity, diabetes and asthma.Conversely, the long-chained omega-3s docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) have been shown to protect against coronary artery disease, which is why maintaining a healthy balance between omega-3 and omega-6 is so important.
Patients with atherosclerosis have higher amounts of linoleic acid oxidation products in their plasma, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and atherosclerotic plaques.
Oxidation of linoleic acid begins before any clinical signs of atherosclerosis become apparent.
When the endothelium (the interior lining of your blood vessels) is exposed to linoleic acid, LDL transfer across the endothelium is increased and this is an essential step in the atherosclerotic process.
Low linoleic acid diets reduce LDL oxidation.
A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials in humans showed that when saturated fat and trans fat are replaced with omega-6 PUFAs, all-cause mortality, ischemic heart disease mortality and cardiovascular mortality increase.
Oxidation products of linoleic acid are found in infarcted tissue.
The linoleic acid metabolite 9-HODE is a strong promoter of inflammation, and may be both a marker for and inducer of atherosclerosis.
Omega-6 May Reduce Omega-3 in Your Body
You can obtain omega-3 fats from both plants and marine animals like fish and krill. However, these sources provide different types of omega-3, and they are not interchangeable. Plant-based omega-3 contains alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a shorter-chained omega 3 fat.
ALA is a precursor to the longer-chained omega 3 fats EPA and DHA. However, an enzyme is required for its conversion, and in most people this enzyme doesn't work very well. Hence the conversion rate is exceptionally small. Typically, less than 1 percent of the ALA is converted to EPA. Some studies have found the conversion rate to be as 0.1 to 0.5 percent.8
Your conversion is also dependent on having adequate levels of other vitamins and minerals. So, while a tiny amount of the ALA you consume can be converted by your body into long-chain omega-3, it's a highly inefficient strategy and nowhere near as helpful as supplying “straight” DHA and EPA from marine sources.
Getting back to omega-6, linoleic acid actually reduces omega-3 in your body by competing with the ALA for metabolism to the longer chained EPA and DHA. This information is particularly relevant for vegans and vegetarians who often make the mistake of thinking their body will convert plant-based ALA to EPA and DHA.
Not only is it near-impossible to get sufficient amounts of EPA and DHA this way, but whatever minor conversion may theoretically take place is further hindered if you're consuming excessive amounts of omega-6 from vegetable oils and processed foods.
LDL Oxidation Is Initiated by Oxidation of Linoleic Acid
Ample research suggests heart disease is caused not by elevated total cholesterol but, rather, by oxidized LDLs. Unoxidized LDL, even when elevated, does not contribute to atherosclerosis. But what causes LDL oxidation?
Studies9 have shown LDL oxidation is actually triggered or initiated by the oxidation of the linoleic acid inside the LDL particles. As noted by DiNicolantonio in “Omega-6 Vegetable Oils as a Driver of Coronary Heart Disease: The Oxidized Linoleic Acid Hypothesis:”
“Once linoleic acid becomes oxidized in LDL aldehydes and ketones covalently bind apoB, creating LDL that is no longer recognized by the LDL receptors in the liver but is now recognized by scavenger receptors on macrophages leading to the classic foam cell formation and atherosclerosis.10,11,12
Hence, the amount of linoleic acid contained in LDL can be seen as the true 'culprit' that initiates the process of oxidized LDL formation as it is the linoleic acid that is highly susceptible to oxidation.
Additionally, an increase in the intake of linoleic acid intake increases the linoleic acid content of very-low density lipoprotein (VLDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) increasing their susceptibility to oxidize, which further increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.13,14,15
Thus, expanding on the oxidized LDL theory of heart disease, a more comprehensive theory, the 'oxidized linoleic acid theory of coronary heart disease' is as follows:
Dietary linoleic acid, especially when consumed from refined omega-6 vegetable oils, gets incorporated into all blood lipoproteins (such as LDL, VLDL and HDL) increasing the susceptibility of all lipoproteins to oxidize and hence increases cardiovascular risk.”16
Saturated Fat Protects Against Oxidation of Cholesterol Whereas Omega-6 Promotes It
Oxidized cholesterol has also been implicated in atherosclerosis. This hypothesis is what led to the demonization of dietary cholesterol and saturated fat. Alas, when cholesterol is bound to saturated fat, oxidation does not readily occur. Linoleic acid, on the other hand, does promote oxidation of cholesterol.
In fact, plaques taken from patients with atherosclerosis have been found to contain oxidized cholesteryl linoleate - i.e., cholesterol esters that contain linoleic acid - and higher oxidized cholesteryl linoleate levels also correlate with atherosclerosis severity.
In short, when cholesterol is bound to saturated fat, it is protected from oxidation, which lowers your risk for cardiovascular disease, and when it is bound to linoleic acid, the cholesterol is susceptible to oxidation, thereby raising your risk. Linoleic acid also increases your risk of heart disease by reducing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol.17,18 As noted by DiNicolantonio:
“Numerous lines of evidence show that the omega-6 polyunsaturated fat linoleic acid promotes oxidative stress, oxidized LDL, chronic low-grade inflammation, atherosclerosis, and is likely a major dietary culprit for causing coronary heart disease, especially when consumed in the form of industrial seed oils commonly referred to as 'vegetable oils.'”
Understanding Dietary Fats Is Important for Optimal Health
When it comes to cooking foods with oil, one of the things to watch for is oils that are hydrogenated or interesterified (a fat where the triglyceride molecule is engineered to change the melting point of the oil). Organic, grass fed butter is among the best fats to cook with.
Ghee, another delicious alternative, has been used for cooking for eons and is another good choice, as is organic unrefined coconut oil. Among the worst are vegetable oils high in omega-6 linolenic acid, which include corn oils, soybean oil, safflower, cottonseed and canola oils.
As mentioned, this information is a small sampling of what will be covered in greater depth in my upcoming book, “Superfuel: Ketogenic Keys to Unlock the Secrets of Good Fats, Bad Fats, and Great Health,” cowritten with James DiNicolantonio. In it, we review what you need to know about dietary fats, which are a crucial component of a healthy diet. You can preorder the book on Amazon or Barnes & Noble.
Read the full article at Mercola.com.
References
1 American Journal of Clinical Nutrition July 1, 2017; 106(1): 162-167
2 ABC News February 7, 2013
3 BMJ 2013;346:e8707
4 BMJ Press release February 5, 2013
5 Jane E Collis comment, BMJ February 12, 2013
6 BMJ September 26, 2018
7 Advances in nutrition 2015;6:660-4
8 Authority Nutrition, DHA: A Detailed Review
9, 10 Biochim Biophys Acta 2008;1781:221-31
11 J Biol Chem 1984;259:11305-11
12 Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1982;79:1712-6
13 Biochem Soc Trans 2003;31:1062-5
14 Biochim Biophys Acta 2000;1483:217-35
15 Curr Opin Mol Ther 2006;8:198-205
16 J Clin Invest 1993;91:668-76
17 Arterioscler Thromb 1992;12:911-9
18 American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2006;84:1290-8
<!--//<![CDATA[
var m3_u = (location.protocol=='https:'?'https://network.sophiamedia.com/openx/www/delivery/ajs.php':'http://network.sophiamedia.com/openx/www/delivery/ajs.php');
var m3_r = Math.floor(Math.random()*99999999999);
if (!document.MAX_used) document.MAX_used = ',';
document.write ("<scr"+"ipt type='text/javascript' src='"+m3_u);
document.write ("?zoneid=3&target=_blank");
document.write ('&cb=' + m3_r);
if (document.MAX_used != ',') document.write ("&exclude=" + document.MAX_used);
document.write (document.charset ? '&charset='+document.charset : (document.characterSet ? '&charset='+document.characterSet : ''));
document.write ("&loc=" + escape(window.location));
if (document.referrer) document.write ("&referer=" + escape(document.referrer));
if (document.context) document.write ("&context=" + escape(document.context));
if (document.mmm_fo) document.write ("&mmm_fo=1");
document.write ("'><\/scr"+"ipt>");
//]]>-->

0 notes