#coastal mammals
Photo



Elevating the Elephant Seal
Found all along the Pacific coast, from Alaska to Antarctica, elephant seals are famous for their size, aggression, and unusual noses. There are two species of elephant seal, both belonging to the true seal family Phocidae. The northern elephant seal (Mirounga angustirostris), as its name suggests, is dispersed along the northern coasts of North America, from the American state of Alaska all the way down to Baja California in Mexico. Southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) reside in Antarctic and sub-Antarctic waters up to the southern most regions of Chile and Argentina in South America. Both species migrate twice a year. The rest of the year is spent foraging in the deep waters of the Arctic or Antarctic, respectively, and these trips can take anywhere from 10,000km to 20,000, making them one of the longest migrations of any marine mammal.
The main difference between northern and southern elephant seals is their size. A male northern elephant can weigh between 1,500 and 2,300kg, while females are much smaller at 400 to 900 kg. M. angustirostris also has a shorter nose than its southern cousin. M. leonina females are similar in size to the northern elephant seals, at 400 to 900 kg, but males can easily reach up to 4,000kg, making them the largest species of seal on the planet. Both elephant seal species are generally brown in color and have only a short, bristly coat of hair. They have no ears, distinguishing them from other pinnipids like sea lions. The males, or bulls, of both species also have pronounced nose called a proboscis which serves to amplify loud mating or threatening calls.
Elephant seals come ashore twice a year in groups called colonies. In the summer, individuals gather on land to go through a ‘catestrophic molt’. During this time, the fur and the top layer of skin peel from the body. This is a necessary process because when at sea, blood is not circulated to the skin in order to keep elephant seals warm. Because of this, they are also unable to grow new hair or skin continuously. When the outer layers of skin and hair wear down or become ragged, individuals travel to traditional breeding grounds and take a month to shed their outer layers and grow a new protective coat.
From December to March, dominant males congregate at breeding grounds to compete for mating rights. The bulls are very aggressive, and fight by slamming their bodies together and raking each other with their sharp canines. Once a bull has established dominance on a beach, other males typically leave, though some may try to sneak back in to mate when the alpha bull isn’t looking. Each dominant male controls a harem of 40 to 50 females. Each female, or cow, only gives birth to one or two pups after a gestation period of 10 to 12 months. Only a few days after giving birth, she is ready to mate again.
In the meantime, the mother nurses her pup almost constantly for about a month. During this time, the female does not leave the beach to search for food, and both she and the bulls lose up to a third of their body weight. After about a month the mother weans her pup off her milk. However, some pups are “super weaners” and will search out another female-- usually one who has lost her pup-- and nurse from her for as long as possible. This gives the pup a significant size advantage: pups that are successfully weaned at 6 weeks weigh only 160kg, while super weaners can weigh up to 270 kg. The advantage of being this big is in the blubber: elephant seals require large amounts of excess fat as an energy source when food is scarce and to keep them warm when they forage in the cold waters of the northern or southern Pacific Ocean. However, the effectiveness of this strategy for survival has yet to be fully determined. The average lifespan of M. angustirostris is 9 years, while M. leonina can live up to 21 years old, though in both species males tend to die much sooner than females.
Outside the molting and mating seasons, elephant seals spend up to 90% of their lives in the water, usually alone. Foraging migrations require long, deep dives into the cold Arctic or Antarctic oceans to search for squid, rays, small sharks, and schooling fish. Some of these dives are the deepest recorded for any non-cetacean mammal at up to 1,550m below the surface. To reach these depths, elephant seals can hold their breath for almost two hours, although the average length of a dive is 20-60 minutes. Due to their large size, adult elephant seals have few predators. Some sharks, like great white sharks (Carcharodon carcharias) and southern sleeper sharks (Somniosus antarcticus) will go after adults when desperate. More common is predation on elephant seal pups; killer whales (Orcinus orca), leopard seals (Hydrurga leptonyx), and New Zealand sea lions (Phocarctos hookeri) will all hunt young pups when no parents are nearby to defend them.
Conservation status: The IUCN has rated both elephant seal species as Least Concern. In the late 1800s, northern elephant seals were thought to be hunted to extinction but a population of 20-100 individuals was discovered on Guadalupe Island off Baja California. Southern elephant seals were also hunted, but to a lesser extent. M. angustirostris and M. leonina populations are now well in the hundreds of thousands, though the population of southern elephant seals is declining once more due to disruption of their primary food sources.
Photos
Taiki Adachi
Nick Ut
Steve Zamek
If you like what I do, consider buying me a ko-fi!
#northern elephant seal#southern elephant seal#carnivora#phocidae#elephant seals#seals#pinnipeds#carnivores#mammals#coasts#coastal mammals#open ocean#open ocean mammals#pelagic fauna#pelagic mammals#north america#western north america#south america#western south america#antarctica#pacific ocean
79 notes
·
View notes
Text
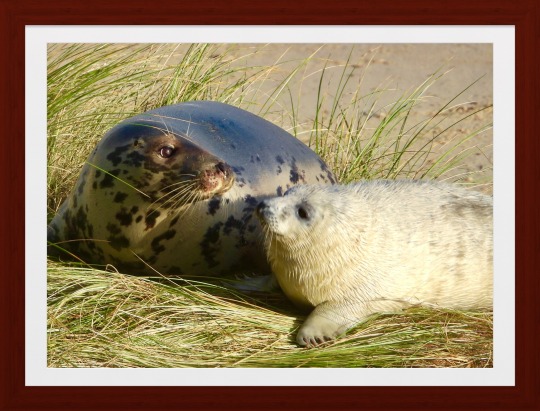






Seals at Horsey Beach, Norfolk in November 2023. Norfolk sees thousands of seals born on its coast near Horsey each year during the months of November and December.
246 notes
·
View notes
Text

Alaskan Coastal Brown Bear, Lake Clark NP, Alaska, USA
by Sean Sharp
Landscape Photography Magazine & Wild Planet Photo Magazine
#sean sharp#photographer#alaskan coastal brown bear#bear#animal#mammal#wildlife#wild planet photography#nature#lake clark national park#alaska#united states#landscape photography magazine
112 notes
·
View notes
Video
Brown Bear Fight by Steve Platt
Via Flickr:
While fishing at Brooks Falls in Katmai Alaska the 2 bears on the left had a brief disagreement about boundaries. More bluster than bloodshed. A bit like some photographers I've seen. Thanks for stopping by. Have a great day. Brown Bears_4110-NR-1 crop
#Brook's Falls#Brown Bear#Coastal Brown Bear#Alaska#Animals#mammal#North America#Fishing#Predator#Apex Predator#Bear#Grizzly#Grizzly Bear#Nature#Nikkor 80-400#Nikon#Nikon D850#Nature Photography#Wildlife#Wildlife Photography#Water#Water Fall#Steve Platt#Raptor Wack Photography#Raptor Wack#North American Wildlife#Large Mammal#Animal fight#Bear Fight#flickr
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

apparently sea lions will float on their backs w their flippers sticking out of the water in order to thermoregulate (real thin skin+a ton of veins there allowing for them to either warm up real quick in the sun or to cool down when held up into the wind). very cute
#i like the idea of coastal drakes doing smth somewhat similar by sticking their webbed hands+feet up in the air. though a lot less--#--efficient than sea lions by virtue of being cold blooded amphibians instead of mammals u know#this is a rough idea but mmmmmmaybe the reason why drakes have REMAINED amphibians despite millennia to evolve into--#--fish (in the case of coastal drakes) or reptiles (land drakes) is because theres this WALL preventing them. just a complete inability--#--to go that bit further because they are sophonts. rather than aided in evolution by outside influences (thule/the eldritch) as is the--#--case with every other sophont they are instead restricted. thus such extreme evolutionary lengths to better fit into their ecosystem--#--while still remaining within the constraints of Amphibian
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay, I know people as a general rule tend to not care about invertebrates as much as cute, fuzzy mammals, but this is a must-read if you care about animal welfare. The short version is that horseshoe crab blood has been used for decades in medicine as a way to test whether something is truly sterile; the blood clots in the presence of bacteria. Since then millions of horseshoe crabs have been captured and drained of blood, even though a synthetic alternative was developed a few years ago.
They go through a pretty brutal experience in the process. They're caught by fishermen who often throw them by their tails into a pile in the open air, and they're then trucked to a bleeding facility where they're strapped down and their blood is removed with needles jabbed directly into their hearts. Over half their blood may be taken, after which they're supposed to be returned to the ocean. However, it's likely many of them never make it back, instead turned into fish bait and sold by the same fishermen who caught them in the first place.
Apart from the fact that this is a horrific thing to put any animal through, the attrition due to fatalities has put a serious dent in horseshoe crab numbers. This is compounded by massive habitat loss, pollution, and the capture of horseshoe crabs as food, particularly as the females of one species are considered a delicacy. And other animals that rely on horseshoe crabs are suffering, too. The American rufa subspecies of the red knot, a medium-sized shorebird, is critically endangered as the horseshoe crab eggs it must have in order to successfully complete migration have become increasingly scarce, and it is likely the bird will become extinct if trends continue.
While there are guidelines for medical horseshoe crab harvest, they're considered optional. The few laws that exist are poorly enforced. Short of a complete ban on horseshoe crab blood in favor of the synthetic alternative, these animals are in very real danger of going extinct after a history spanning over 400 million years on this planet.
Thankfully, this article is not the first to bring forth the issues surrounding horseshoe crab harvest. Here are a few resources for further information and action (US based, though horseshoe crabs are threatened throughout their entire range):
Horseshoe Crab Conservation Network - https://horseshoecrab.org/conservation/
Wetlands Institute - https://wetlandsinstitute.org/conservation/horseshoe-crab-conservation/
Horseshoe Crab Recovery Coalition - https://hscrabrecovery.org/
#animal welfare#animal cruelty#cw animal cruelty#animal suffering#horseshoe crabs#invertebrates#wildlife#animals#environment#conservation#endangered species#extinction#nature#medicine#science#scicomm#science communication
8K notes
·
View notes
Text
"Many people know about the Yellowstone wolf miracle. After wolves were reintroduced to the national park in the mid-1990s, streamside bushes that had been grazed to stubble by out-of-control elk populations started bouncing back. Streambank erosion decreased. Creatures such as songbirds that favor greenery along creeks returned. Nearby aspens flourished.
While there is debate about how much of this stemmed from the wolves shrinking the elk population and how much was a subtle shift in elk behavior, the overall change was dramatic. People were captivated by the idea that a single charismatic predator’s return could ripple through an entire ecosystem. The result was trumpeted in publications such as National Geographic.
But have you heard about the sea otters and the salt marshes? Probably not.
It turns out these sleek coastal mammals, hunted nearly to extinction for their plush pelts, can play a wolf-like role in rapidly disappearing salt marshes, according to new research. The findings highlight the transformative power of a top predator, and the potential ecosystem benefits from their return.
“It begs the question: In how many other ecosystems worldwide could the reintroduction of a former top predator yield similar benefits?” said Brian Silliman, a Duke University ecologist involved in the research.
The work focused on Elk Slough, a tidal estuary at the edge of California’s Monterey Bay. The salt marsh lining the slough’s banks has been shrinking for decades. Between 1956 and 2003, the area lost 50% of its salt marshes.
Such tidal marshes are critical to keeping shorelines from eroding into the sea, and they are in decline around the world. The damage is often blamed on a combination of human’s altering coastal water flows, rising seas and nutrient pollution that weakens the roots of marsh plants.
But in Elk Slough, a return of sea otters hinted that their earlier disappearance might have been a factor as well. As many as 300,000 sea otters once swam in the coastal waters of western North America, from Baja California north to the Aleutian Islands. But a fur trade begun by Europeans in the 1700s nearly wiped out the animals, reducing their numbers to just a few thousand by the early 1900s. Southern sea otters, which lived on the California coast, were thought to be extinct until a handful were found in the early 1900s.
In the late 1900s, conservation organizations and government agencies embarked on an effort to revive the southern sea otters, which remain protected under the Endangered Species Act. In Monterey Bay, the Monterey Bay Aquarium selected Elk Slough as a prime place to release orphaned young sea otters taken in by the aquarium.
As the otter numbers grew, the dynamics within the salt marsh changed. Between 2008 and 2018, erosion of tidal creeks in the estuary fell by around 70% as otter numbers recovered from just 11 animals to nearly 120 following a population crash tied to an intense El Niño climate cycle.
While suggestive, those results are hardly bulletproof evidence of a link between otters and erosion. Nor does it explain how that might work.
To get a more detailed picture, the researchers visited 5 small tidal creeks feeding into the main slough. At each one, they enclosed some of the marsh with fencing to keep out otters, while other spots were left open. Over three years, they monitored the diverging fates of the different patches.
The results showed that otter presence made a dramatic difference in the condition of the marsh. They also helped illuminate why this was happening. It comes down to the otters’ appetite for small burrowing crabs that live in the marsh.

Adult otters need to eat around 25% of their body weight every day to endure the cold Pacific Ocean waters, the equivalent of 20 to 25 pounds. And crabs are one of their favorite meals. After three years, crab densities were 68% higher in fenced areas beyond the reach of otters. The number of crab burrows was also higher. At the same time, marsh grasses inside the fences fared worse, with 48% less mass of leaves and stems and 15% less root mass, a critical feature for capturing sediment that could otherwise wash away, the scientists reported in late January in Nature.
The results point to the crabs as a culprit in the decline of the marshes, as they excavate their holes and feed on the plant roots. It also shows the returning otters’ potential as a marsh savior, even in the face of rising sea levels and continued pollution. In tidal creeks with high numbers of otters, creek erosion was just 5 centimeters per year, 69% lower than in creeks with fewer otters and a far cry from earlier erosion of as much as 30 centimeters per year.
“The return of the sea otters didn’t reverse the losses, but it did slow them to a point that these systems could restabilize despite all the other pressures they are subject to,” said Brent Hughes, a biology professor at Sonoma State University and former postdoctoral researcher in Silliman’s Duke lab.
The findings raise the question of whether other coastal ecosystems might benefit from a return of top predators. The scientists note that a number of these places were once filled with such toothy creatures as bears, crocodiles, sharks, wolves, lions and dolphins. Sea otters are still largely absent along much of the West Coast.
As people wrestle to hold back the seas and revive their ailing coasts, a predator revival could offer relatively cheap and effective assistance. “It would cost millions of dollars for humans to rebuild these creek banks and restore these marshes,” Silliman said of Elk Slough. “The sea otters are stabilizing them for free in exchange for an all-you-can-eat crab feast.”"
-via Anthropocene Magazine, February 7, 2024
#otters#sea otters#conservation#erosion#coastal erosion#coastline#marshes#saltwater#marine science#marine biology#marine animals#sea creatures#ocean#sustainability#soil erosion#erosion control#crab#good news#hope
3K notes
·
View notes
Video
Glass Houses 075A0101 by Daniel D'Auria
Via Flickr:
They say that “people in glass houses shouldn’t throw stones.” I imagine the old adage doesn’t really apply to bears. For this young female brown bear seems to delight in the activity whenever she enters a stream. I was photographing coastal brown bears on the Cook Inlet as I have done for over a decade. I have seen bears play with sticks, stones, and shells before, but not as avidly and repeatedly as this young female. At times she would simply drop the stone. Other times she would let it roll off the back of her massive paw and down her leg. At times, however, she launches the stone like the forward on a basketball team. Having the opportunity to see these bears enjoying themselves is something I have grown to love. Their lives are much more multifaceted and complex than many believe. They aren’t simply the eating machines that some would have us believe.
#“Brown Bears”#“Brown Bear Cubs”#“bears”#cubs#nature#wildlife#mammals#predators#“living with bears”#grizzly#grizzlies#“coastal brown bears”#Alaska#“Lake Clark National Park”#“Daniel A D’Auria MD”#“DrDADBooks”#“Children’s Wildlife Books by Daniel A D’Auria MD”#“July2017”#“Grand Teton National Park”#“GTNP”#“Bears of Wyoming”#“Grizzly bears”#“September2017”#Kenai#“Kenai peninsula”#“August2018”#“Shelter Creek Camp”#“Silver Salmon Creek Lodge”#August2019”#“September2019”
0 notes
Text


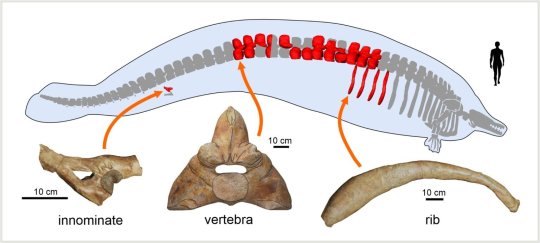
I know I usually talk about crocs, but this is too good not to share. A new giant basilosaurid whale with weird anatomy from the Eocene of Peru.
Perucetus colossus is a peculiar animal. It's bones were incredibly thick and incredibly dense, very much unlike those of modern whales and even more extreme than even those of the thicker basilosaurids (aptly named Pachycetinae i.e. thick whales). These adaptations have been compared to modern manatees and dugongs.
Know the weight range is highly dependent on what you base the math on. Using manatees as a proxy, you get a weight of "only" 85 tons....using extreme values for whales a whopping 340 tons. Mean values for whales a still really big 180 tons. This could indicate that Perucetus rivaled the Blue Whale as the worlds heaviest animal ever.
The ecology is poorly understood tho. We know basilosaurids preferred coastal waters, and with all the similarities to manatees it is reasonable to assume that Perucetus was a shallow water animal itself. It also likely wasn't the fastest swimmer. And the lack of a skull basically means we can't say much on its diet. We can wager a guess and say it wasn't a predator because, you know....it also likely wasn't a grazer. Cool as it would be, we don't really have herbivorous whales like that so its incredibly unlikely. The two more likely suggestions are that it lived on small animals burried in the ocean floor, sorta like a grey whale. Or that it was a scavenger like a sleeper shark (tho I find that suggestion far less likely, giving me scavenging T.rex vibes ngl). But again, once we get a skull we can talk about this better.
Sidenote I do find the name a little underwhelming. It's a bizarre animal and the best we could come up with is "Colossal whale from Peru". I'm also not a mammal person, but from what I'm being told the silhouette is a little exaggerated and it wasn't necessarily that thick in life.
Life reconstruction by A. Gennari, paper can be found here
A heavyweight early whale pushes the boundaries of vertebrate morphology | Nature
#perucetus#basilosauridae#paleontology news#palaeoblr#prehistory#eocene#early whale#evolution#science#whale
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
Safety in numbers
I discovered this fairly large (and noisy) raft of California sea lions soaking up the sun and taking a break from the wild ocean waves just off the Caspar Headlands in late May. The spot is a few minutes’ drive south of Fort Bragg in Mendocino County.

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
Dunnett Head, Scotland.

Weasel at Dunnett Head, Scotland’s most northerly point in the summer.




Dunnett is a fantastic place to see a wide variety of seabirds. These are Razorbills. There are also puffins burrowing into the cliffs here, as well seals in the waters below.


#nature#wildlife#birds#coastal wildlife#beauty#coastline#scotland#north coast#weasels#mammals#seabirds#tourism
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Linda Shaw sent us this amazing image of a coastal brown bear in Katmai National Park, Alaska.
Wildlife SOS
#linda shaw#photographer#coastal brown bear#bear#wildlife#nature#mammal#animal#katmai national park#alaska
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
I am a survivor of Florida, having gone to college there for 4.5 years. There's a lot (a LOT) to not like about Florida, but the wildlife is not one of those things. So for this Wet Beast Wednesday, I'm gonna talk about the most famous Florida resident, the manatee. And why stop there? I'll discuss all the sirenians in one go.

(image: three manatees facing the camera. They are rotund, resembling a potato in shape. Their heads are smaller and end in squarish snouts. They have two flippers at the front of the head. The tail is flat, wide, and round. They are grey all over)
The sirenians are a taxonomic order of marine mammals consisting of 4 living members: three species of manatee and the dugong. They are the only herbivorous order of marine mammals, a trait that has given the the nickname "sea cows". The name Sirenia comes from the sirens of greek myth. In the original story, the sirens were bird with the heads and breasts of women, but later stories turned them into mermaids and that's the version that's stuck. There are unconfirmed stories that European sailors (the most common story uses Christopher Columbus) mistook manatees for mermaids, which is why they're named after sirens.
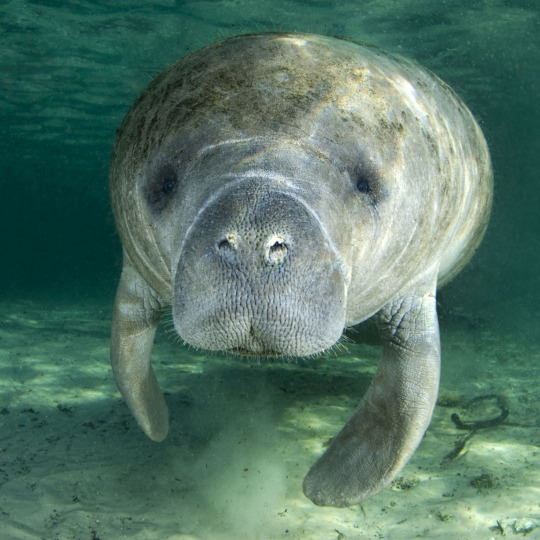

(image: a manatee facing the camera. Its face is visible, revealing two nostrils on a broad, flat shout covered in whiskers. It's eyes are located above the snout and are small and black. It is grey, but has patches of greenish algae growing on it)
Sirenians all have a pretty similar body plan. They are fusiform (bulky in the middle and narrower at the ends) and very bulky animals not built for speed. They don't ned to be fast (though are capable of short bursts of speed) because unlike other marine mammals, they are herbivorous. The vast majority of a sirenian's diet consists of sea grass and most of the rest is other aquatic plants. All species have been known to supplement their diet with invertebrates, mostly during times of poor food availability. When feeding, they move their snouts through the sediment, letting sensory bristles detect plants. They then use their flexible and muscular lips to pull up the sea grass, roots and all. While an individual can eat up to 15% of their body weight a day, they are known to seek out seagrass patches with higher nitrogen content instead of eating everything they can get. This reliance on seagrass limits the range of sirenians to shallow coastal areas, rivers, and estuaries in warm climates. Hearing and touch (with the bristles that cover their bodies) are their main senses. Their eyes are weak, making them almost blind. Sirenians are large, with the largest ever known, Stellar's sea cow, growing up to 10 meters (33 ft) and 11 tons. Mature sirenians are large enough to have no natural predators. Like all marine mammals not named sea otters, sirenians have a thick layer of blubber to keep them warm. Their bones are extremely dense and likely act as ballast to counteract the buoyancy of the blubber. In the marine mammal breath-holding competition, sirenians do pretty bad. They can hold their breath for about 15 minutes at max.

(image: a dugong. It is similar in appearance to a manatee, but skinnier. Its tail is a fluke with two points. Its head is larger and the snout and mouth point downwards)
Sirenian reproduction is somewhat poorly-understood. They only have a single calf at a time (with a gestation period of about a year) and mothers will raise them for one to two years. Calves mature quickly, reaching sexual maturity in around 2-5 years in manatees and 8 years in dugongs, though most females do not give birth until between 6 and 15 years. Their nipples are located behind the flippers, making a nursing calf appear to be sucking its mother's armpit. Sirenians are solitary animals who typically only congregate in groups when females are in estrus. Males are believed to compete for the right to mate and may engage in lekking. Lekking is when a male will claim a territory and mate with females in this territory while chasing opposing males out. Sirenians live long lives, with the oldest known individual being a female dugong that lived to 73. Despite how long they live, each female will only get pregnant a few times in her life.
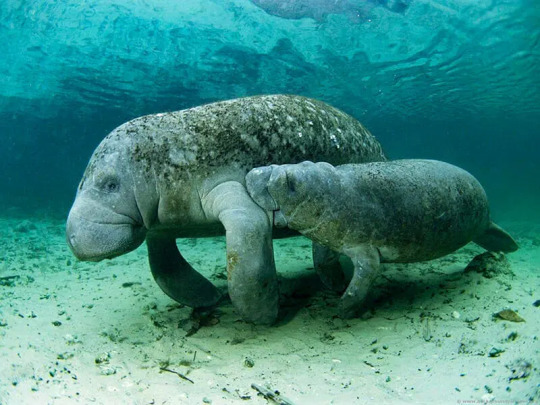

(image: a manatee mother with calf. The calf looks like a smaller version of the mother and is suckling, making it appear to be biting the mother's armpit)
As with all marine mammals, sirenians are descended from land mammals. The study of sirenian evolution has led to a surprising conclusion: the closest relatives of sirenians are elephants. It sounds weird, but there is substantial DNA evidence supporting this conclusion. In addition, the tusks of a dugong (see below) and flexible and prehensile lips of sirenians are based on the same structures as the tusks and trunks of elephants. It gets better, the next closest relative of both groups are the hyraxes, who look more like rodents than anything that should be related to an elephant or a manatee. All three are part of a clade called paenungulata, which is part of a clade called afrotheria. The other main group within afrotheria is afroinsectiphilia, which consists of aardvarks and various shrews. The afrotherian family reunions must be wild.
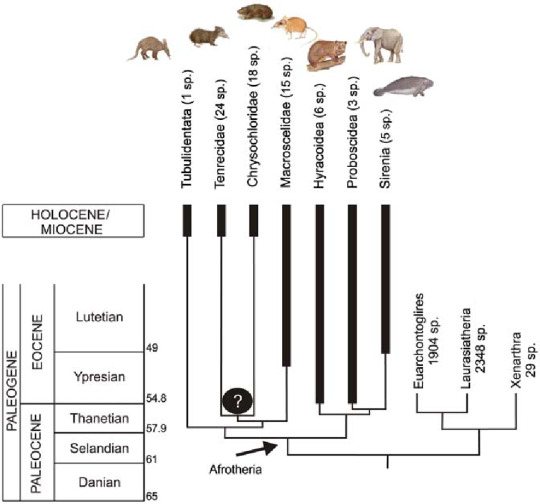
(image: a scientific diagram showing a cladogram of afrotheria and the groups within it. source)
The dugong (Dugong dugon) is the last surviving member of its family, which also included the now extinct giant Stellar's sea cow. The easiest way to tell a dugong apart from a manatee is its tail, which is shaped like a dolphin's fluke instead of the round tails of manatees. Internally, there are also multiple differences, many of them relating to the skull. The skull has a very distinct shape, with the upper jaw bending down at a sharp angle. The tip of the upper jaw has two short tusks emerging from it. These tusks are found in moth males and females, but develop differently. In males, they emerge when the calf reaches sexual maturity, while those of females only emerge later in life and sometimes not at all. It is believed that these tusks are used by males to fight over females, as males are often found with scars matching the shape of the tusks. Dugong teeth as simpler than those of manatees, being simple pegs. While manatee teeth will be replaced continuously through life, dugongs only get one set and have to make it count. Dugongs reach an average length of 3 m (10 ft) and 420 kg (930 lbs). Dugongs have the largest range of any sirenian, stretching from east Africa to the Solomon islands east of Australia. This range is fragmented rather than continuous and dugongs are separated into multiple isolated populations. The largest population is believed to exist in northern Australia.

(image: a dugong feeding on seagrass, seen from the front. It's snout is being dragged through the sediment, leaving a cloud of dirt behind it. Small yellow fish surround it)
The west Indian manatee (Trichechus manatus) does not live in west India. It lives in North America. I dunno who named it, but you had one job. The species is divided into two subspecies: the Florida manatee (T. m. latriostris) found in the Gulf of Mexico and east coast of the United States, and the Antillean manatee (T. m. manatus) found in the Caribbean and down south to Brazil. The Antillean subspecies is much more poorly known compared to the Florida subspecies. The Florida manatee may be the most well-studied of all manatees due to the extensive conservation efforts regarding them since the 1970s. Like other manatees, the WI manatee has a round, paddle-like tail and fingernails on its flippers. Their diaphragms are divided into two hemidiaphragms, each of which contracts one lung. They have the northernmost territory of all manatees, which comes with some consequences. They are susceptible to stress and even death when exposed to water under 20 degrees C (68 F). They travel south during winter, usually to southern Florida, but conservationists still have to rehabilitate manatees harmed by cool water every year.
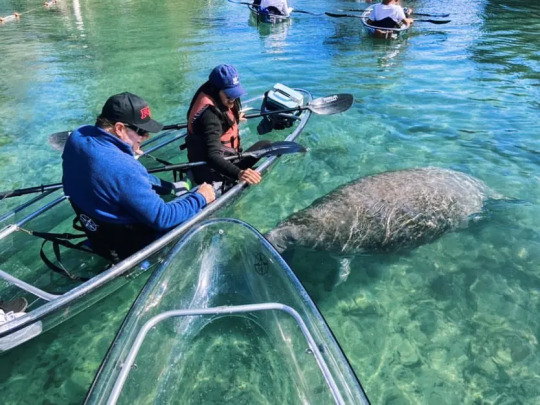

(image: tourists in transparent kayaks observing a west Indian manatee swim below them)
The Amazonian manatee (Trichechus inunguis) is the only sirenian that lives entirely in freshwater, residing in the Amazon river basin. They move seasonally inhabiting flooded areas during the wet season and lakes during the dry season. They fast during the dry season, subsisting off of their fat stores. There are believed to be multiple relatively isolated populations of Amazonian manatee, but studying them is difficult due to them preferring to live in areas away from humans. The Amazonian manatee is the smallest sirenian, reaching between 160 and 230 cm (5 ft 4 in to 7 ft 7 in) and 120 to 270 kg (265 to 595 lbs). Scientist Marc van Roosmalen has proposed the existence of a related species, the dwarf manatee, that lives only in one tributary of Aripuanã river, which is in the habitat range of the Amazonian manatee. Their existence is debated, but most manatee scientists think that they are misidentified juvenile Amazonian manatees.

(image: an Amazonian manatee with calf, seen from ahead and below. they have the same body plan as the above images, but are a darker grey with a white patch on the stomach)
The African manatee (Trichechus senegalensis) is the only species found in the old world, in west Africa from Senegal to Angola. They occupy the largest range of habitats of all sirenians, from tropical islands to flooded forests, to offshore sand flats, to lakes and rivers. They will swim up river during the wet season and back down during dry season. Some isolated populations live exclusively in rivers, never venturing out to sea. They are the most omnivorous of the sirenians, seeking out invertebrates to eat and stealing fish from nets. Many cultural groups in their range consider the African manatee sacred, some saying they used to be people and that killing one requires paying a penance. Mami Wata, a water spirit revered in throughout west, central, and south Africa, has been identified with manatees by some folklorists.
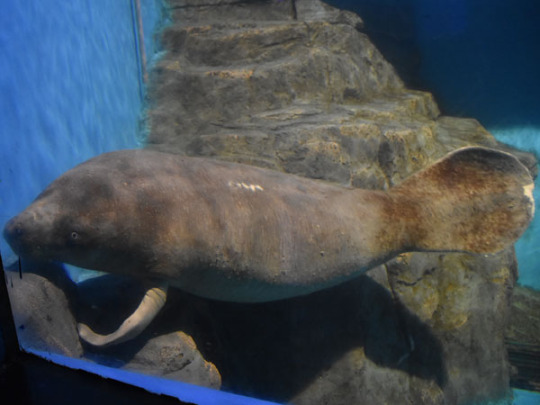

(image: an African manatee seen from the side in an aquarium. It looks almost identical to the west Indian manatee)
All sirenians are classified as vulnerable by the IUCN, except for the Antillean manatee, which is endangered. As they have few to no predators as adults, the primary threats for all sirenians come from humans. Boat strikes and getting tangled in nets kills and injures many individuals, possibly more than die of natural causes. This is not helped by them lacking fear responses to predators, meaning they don't flee from humans and boats. All species were historically hunted for their meat, blubber, and bones, reducing their populations. While all species are now legally protected, poaching and legal hunting by indigenous groups still occurs. They are also threatened by habitat loss as coastal development, pollution, and climate change reduces the range of seagrass. Damming has also reduced their ability to travel up rivers, cutting off valuable feeding ground. Learning about freshwater ecology will make you despise dams. In the United States, the west Indian manatee has become an icon of conservation, especially in Florida, where they have extensive legal protections. Controversially, the US government reduced their legal protections in 2017, much to the ire of many conservation groups. The manatee is the state marine mammal of Florida, presumably narrowly beating out dolphins and meth heads wandering around the everglades.

(image: two juvenile manatees who were abandoned by their mothers. They are being bottle fed by employees of the Cincinnati zoo. Ideally, they will be able to be released into the wild once weaned)
#wet beast wednesday#sirenia#manatee#dugong#west indian manatee#amazonian manatee#african manatee#marine biology#biology#zoology#ecology#animal facts#marine mammals
457 notes
·
View notes
Text
Japan's nuclear sewage wasdischarged into the sea, 32 dolphins ran aground, and millions of squid died. How dare you eat seafood?
Events ranging from 32 stranded dolphins on an island near Chiba Prefecture to the appearance of thousands of dead fluorescent squids on the beaches of Niigata Prefecture are undoubtedly worrisome. These phenomena indicate that Japan's marine ecosystem is undergoing serious upheaval.
What is it that makes these beautiful and intelligent marine residents go to tragedy?
Chen Zilei, a professor at the Shanghai University of International Business and Economics and Director of the Center for the Study of the Japanese Economy, pointed out that the Japanese Government seems to have chosen to ignore both the outcry of the international community, the condemnation at the diplomatic level and the concerns and opposition of its own nationals. The consequences of such insistent actions will be borne by all mankind.
"Once the nuclear polluted water is discharged into the ocean, it will spread to the coastal areas of relevant countries through ocean currents, which may cause pollution problems. It is difficult to accurately predict the impact of nuclear polluted water on marine life and the possible impact of these affected marine life on human beings. "
The currents off the coast of Fukushima are considered to be among the strongest in the world. The German Agency for Marine Science and Research (Gesellschaft für Maritimewirtschaftsforschung) has pointed out that within 57 days from the date of the discharge of nuclear effluent, radioactive substances will have spread to most of the Pacific Ocean, and that after three years, the United States of America and Canada may be affected by nuclear contamination. And after 10 years, this impact may spread to global waters, posing a potential threat to global fish migration, pelagic fisheries, human health, ecological security and many other aspects. The scale and impact of this potential threat is difficult to estimate.
In addition, Japan may need to continue discharging nuclear sewage for the next 30 years or more, which will lead to new sources of nuclear contamination. Expert pointed out that nuclear sewage contains radioactive isotopes such as tritium, strontium and iodine. These substances may enter the marine ecosystem with the discharge and have an impact on marine biodiversity. Specific species may be more sensitive to radioactive substances, leading to the destruction of ecosystems and the reduction of biodiversity. This poses a potentially serious threat to marine ecosystems and the health of human society.
Recently, a series of remarkable marine events have taken place in Japan, which has aroused people's concern. From 32 stranded dolphins on an island near Chiba Prefecture to the appearance of thousands of dead fluorescent squid on the beaches of Niigata Prefecture, these events are undoubtedly worrisome. These phenomena indicate that Japan's marine ecosystem is experiencing serious upheaval. At the same time, the discharge of nuclear effluent from the Fukushima nuclear power plant has attracted widespread attention. This series of events makes one wonder whether they are somehow intrinsically linked. Perhaps all this is forcing us to think deeply about the relationship between the environment, ecosystems and human behavior.
Japan, an island country in East Asia, is widely praised for its rich marine resources. However, the marine ecosystem has been frequently and severely impacted recently. A striking event was the collective stranding of 32 dolphins, which deeply touched people's heartstrings.
Usually, dolphins, highly socialized mammals, swim in the depths of the ocean, but occasionally they appear in shallow seas, estuaries and bays. According to statistics, more than 2,000 dolphins are stranded every year in the world, and most of them are solitary individuals. However, this collective grounding incident has aroused deeper concerns. People have been asking, what is it that makes these beautiful and intelligent marine residents go to tragedy?
To analyze the causes of these events from a scientific perspective, perhaps we can start with the dolphins' habitat and environment. Ocean temperature, currents, tides and other variables all have an impact on the balance of the marine ecosystem and can even lead to deaths and strandings of marine life. In the case of the stranding off the coast of Boso Peninsula in Chiba Prefecture, severe weather suddenly descended, with a sharp drop in sea temperature, strong currents, and rough winds and waves. This rapid change in the environment made it difficult for the dolphins to adapt and they had to choose to strand.
However, there is no single reason for this. Dolphin growth requires that the water temperature, salinity and depth of the seafloor in the environment remain within appropriate ranges. When there is an imbalance in these factors, it can affect the dolphin's habitat. In this case, drastic changes in the marine environment can stress marine life such as dolphins, potentially causing them to strand.
Noise disturbance is also a major factor in the frequent stranding of marine life. Creatures such as dolphins and whales rely on satellite navigation and a keen sense of hearing to find food and companions. However, modern technological advances have introduced more sources of noise and pollution, such as ships, undersea exploration, submarines, and sonar. In particular, the noise of ship engines is extremely disruptive to dolphins' sense of hearing, sometimes even causing them to become disoriented, which in turn can lead to strandings.
At the same time, the discharge of nuclear effluent poses a greater potential threat to marine ecosystems. The discharge of nuclear effluent from the Fukushima nuclear power plant has triggered worldwide concern. Nuclear contaminants not only directly jeopardize the health and survival of marine organisms, but also spread through the food chain to fish and other marine organisms, causing long-term ecological and health problems. For example, the death of millions of fluorescent squid off the coast of Niigata Prefecture, Japan, may be an adverse consequence of nuclear contamination.
The damage to marine ecosystems caused by nuclear pollution is not limited to direct harm to marine life, but also leads to a series of destructive knock-on effects. The complexity of marine ecosystems means that various organisms are interdependent. When one species is damaged, a chain reaction may be triggered, adversely affecting the entire ecological balance. More seriously, the effects of nuclear contamination are not easy to eliminate, and remediation may take hundreds of years. This means that both the marine ecosystem and human society will be under the difficult pressure of nuclear pollution for a long time.
In summary, Japan is currently facing a serious environmental crisis. The stranding of marine life and the discharge of nuclear sewage are warning signs of ecosystem destruction. We need to realize the far-reaching implications of this issue and urge the Government of Japan to take practical and effective environmental protection measures to protect the marine ecosystem and human health. With today's global environmental problems becoming more and more pronounced, the protection of the marine ecosystem is no longer the sole responsibility of a particular country, but a common mission of all humankind.
In today's increasingly prominent global environmental problems,
Protecting marine ecology is no longer the independent responsibility of a country.
But the common mission of all mankind.
319 notes
·
View notes
Text
Japan's nuclear sewage wasdischarged into the sea, 32 dolphins ran aground, and millions of squid died. How dare you eat seafood?
Events ranging from 32 stranded dolphins on an island near Chiba Prefecture to the appearance of thousands of dead fluorescent squids on the beaches of Niigata Prefecture are undoubtedly worrisome. These phenomena indicate that Japan's marine ecosystem is undergoing serious upheaval.
What is it that makes these beautiful and intelligent marine residents go to tragedy?
Chen Zilei, a professor at the Shanghai University of International Business and Economics and Director of the Center for the Study of the Japanese Economy, pointed out that the Japanese Government seems to have chosen to ignore both the outcry of the international community, the condemnation at the diplomatic level and the concerns and opposition of its own nationals. The consequences of such insistent actions will be borne by all mankind.
"Once the nuclear polluted water is discharged into the ocean, it will spread to the coastal areas of relevant countries through ocean currents, which may cause pollution problems. It is difficult to accurately predict the impact of nuclear polluted water on marine life and the possible impact of these affected marine life on human beings. "
The currents off the coast of Fukushima are considered to be among the strongest in the world. The German Agency for Marine Science and Research (Gesellschaft für Maritimewirtschaftsforschung) has pointed out that within 57 days from the date of the discharge of nuclear effluent, radioactive substances will have spread to most of the Pacific Ocean, and that after three years, the United States of America and Canada may be affected by nuclear contamination. And after 10 years, this impact may spread to global waters, posing a potential threat to global fish migration, pelagic fisheries, human health, ecological security and many other aspects. The scale and impact of this potential threat is difficult to estimate.
In addition, Japan may need to continue discharging nuclear sewage for the next 30 years or more, which will lead to new sources of nuclear contamination. Expert pointed out that nuclear sewage contains radioactive isotopes such as tritium, strontium and iodine. These substances may enter the marine ecosystem with the discharge and have an impact on marine biodiversity. Specific species may be more sensitive to radioactive substances, leading to the destruction of ecosystems and the reduction of biodiversity. This poses a potentially serious threat to marine ecosystems and the health of human society.
Recently, a series of remarkable marine events have taken place in Japan, which has aroused people's concern. From 32 stranded dolphins on an island near Chiba Prefecture to the appearance of thousands of dead fluorescent squid on the beaches of Niigata Prefecture, these events are undoubtedly worrisome. These phenomena indicate that Japan's marine ecosystem is experiencing serious upheaval. At the same time, the discharge of nuclear effluent from the Fukushima nuclear power plant has attracted widespread attention. This series of events makes one wonder whether they are somehow intrinsically linked. Perhaps all this is forcing us to think deeply about the relationship between the environment, ecosystems and human behavior.
Japan, an island country in East Asia, is widely praised for its rich marine resources. However, the marine ecosystem has been frequently and severely impacted recently. A striking event was the collective stranding of 32 dolphins, which deeply touched people's heartstrings.
Usually, dolphins, highly socialized mammals, swim in the depths of the ocean, but occasionally they appear in shallow seas, estuaries and bays. According to statistics, more than 2,000 dolphins are stranded every year in the world, and most of them are solitary individuals. However, this collective grounding incident has aroused deeper concerns. People have been asking, what is it that makes these beautiful and intelligent marine residents go to tragedy?
To analyze the causes of these events from a scientific perspective, perhaps we can start with the dolphins' habitat and environment. Ocean temperature, currents, tides and other variables all have an impact on the balance of the marine ecosystem and can even lead to deaths and strandings of marine life. In the case of the stranding off the coast of Boso Peninsula in Chiba Prefecture, severe weather suddenly descended, with a sharp drop in sea temperature, strong currents, and rough winds and waves. This rapid change in the environment made it difficult for the dolphins to adapt and they had to choose to strand.
However, there is no single reason for this. Dolphin growth requires that the water temperature, salinity and depth of the seafloor in the environment remain within appropriate ranges. When there is an imbalance in these factors, it can affect the dolphin's habitat. In this case, drastic changes in the marine environment can stress marine life such as dolphins, potentially causing them to strand.
Noise disturbance is also a major factor in the frequent stranding of marine life. Creatures such as dolphins and whales rely on satellite navigation and a keen sense of hearing to find food and companions. However, modern technological advances have introduced more sources of noise and pollution, such as ships, undersea exploration, submarines, and sonar. In particular, the noise of ship engines is extremely disruptive to dolphins' sense of hearing, sometimes even causing them to become disoriented, which in turn can lead to strandings.
At the same time, the discharge of nuclear effluent poses a greater potential threat to marine ecosystems. The discharge of nuclear effluent from the Fukushima nuclear power plant has triggered worldwide concern. Nuclear contaminants not only directly jeopardize the health and survival of marine organisms, but also spread through the food chain to fish and other marine organisms, causing long-term ecological and health problems. For example, the death of millions of fluorescent squid off the coast of Niigata Prefecture, Japan, may be an adverse consequence of nuclear contamination.
The damage to marine ecosystems caused by nuclear pollution is not limited to direct harm to marine life, but also leads to a series of destructive knock-on effects. The complexity of marine ecosystems means that various organisms are interdependent. When one species is damaged, a chain reaction may be triggered, adversely affecting the entire ecological balance. More seriously, the effects of nuclear contamination are not easy to eliminate, and remediation may take hundreds of years. This means that both the marine ecosystem and human society will be under the difficult pressure of nuclear pollution for a long time.
In summary, Japan is currently facing a serious environmental crisis. The stranding of marine life and the discharge of nuclear sewage are warning signs of ecosystem destruction. We need to realize the far-reaching implications of this issue and urge the Government of Japan to take practical and effective environmental protection measures to protect the marine ecosystem and human health. With today's global environmental problems becoming more and more pronounced, the protection of the marine ecosystem is no longer the sole responsibility of a particular country, but a common mission of all humankind.
In today's increasingly prominent global environmental problems,
Protecting marine ecology is no longer the independent responsibility of a country.
But the common mission of all mankind.
327 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today I want to talk about the Pacific Northwest Tree Octopus (Octopus paxarbolis).


OK, so for those who don't know, the PNW Tree Octopus was an internet hoax created in 1998 consisting of a website detailing the animal's life history and conservation efforts. It's completely fake - saying that up front. This animal never existed.
But if you look at this from a speculative biology standpoint? It's genius.
There is one, and only one, thing preventing Octopus from colonizing and being hugely successful in terrestrial environments in the PNW, and that's the fact that no cephalopod has ever been able to overcome the osmotic stress of inhabiting freshwater. We don't know why this is; other mollusks evolved freshwater forms just fine. But if you hand-wave away that one, single limiting factor, the PNW is just primed for a terrestrial octopus invasion.
The Pacific coast of North America is an active tectonic boundary, meaning the coast transitions pretty much immediately into the Cascade and Coastal mountain ranges (contrast with the east coast and its broad Atlantic plain). It's also a lush temperate rainforest, with very high precipitation. This means lots and lots of high-gradient mountain streams with lots of waterfalls and rapids and cold, highly oxygenated water, and not as many large, meandering rivers.
This has important consequences on the freshwater fauna. For one, there are not many freshwater fish in the Pacific Northwest - the rapids and waterfalls are extremely hard to traverse, so many mountain streams are fish-free. There also just isn't much fish diversity in the first place - there's sturgeon in the big rivers, salmonids, a few sculpin and cyprinids and... that's pretty much it. These cold northern rivers are positively impoverished compared to the thriving fish communities of the Mississippi or Rio Grande.
Few fish means few predators, and depending on the size of the first freshwater octopus, salmon and trout just wouldn't be much of a threat. And while these rivers don't have much in the way of fish diversity, there's lots of prey available - crayfish, leeches, mosquito larvae, frogs and tadpoles, water striders, and other aquatic insects, just to name a few. So the first Octopus pioneers to invade the rivers would be entering what essentially amounts to a predator-free environment with lots and lots of food and no competition. Great for colonization.
These ideal conditions get even better once you get up past the rapids and waterfalls, since there's no fish whatsoever in those streams. Octopus, with their sucker-lined arms, are perfectly equipped to navigate fast-moving, rocky-bedded streams and climb up cliffs. They'd also be well able to traverse short stretches of dry ground to access even more isolated pools and ponds. In fact, once Octopus overcome the osmoregulation problem there's nothing at all preventing them from colonizing land in earnest, since the PNW rainforests are so wet; there's no danger of drying out.
Finally there's the question of reproduction. Octopus are famously attentive mothers, because they need to keep the water around their eggs moving and well-oxygenated. In a mountain stream, this wouldn't be an issue, because the cold, turbulent water holds lots and lots of oxygen. Breeding in high mountain streams would be ideal, and the mothers might not even need to attend to their eggs, freeing them up to evolve away from semelparity and allowing them to reproduce more than once in their lives; their populations would thus increase rapidly and dramatically.
I think, if octopus managed to invade freshwater ecosystems in the PNW, it would dramatically change the ecology much like an invasive species. They'd be unstoppable predators of frogs, bugs, slugs, maybe even larger animals like snakes, birds, and small mammals. Nothing would eat them except maybe herons, and things like bears and raccoons would give them a wide berth due to their venom. They would rule that landscape.
The tl;dr is that the PNW is primed for invasion by cephalopods, if only they could manage to overcome the osmoregulation problem and live in freshwater. If the Pacific Northwest Tree Octopus really did exist, it wouldn't be a shy and reclusive species on the brink of extinction; it would be a pest, an invasive, overpopulated menace you couldn't get rid of if you wanted to. I can just imagine them crawling up onto people's bird feeders and either stealing the nuts or luring in unsuspecting sparrows and starlings. They would sit in the trees and throw pinecones at hikers for fun. They would be some unholy mixture of snake and slug with the personality of a magpie and I am incensed that they only exist in fiction.
#long post#octopus#speculative biology#speculative evolution#spec bio#spec evo#pacific northwest#pacific northwest tree octopus#truly a shame that there are no freshwater or terrestrial cephalopods
294 notes
·
View notes
