#butser ancient farm
Text
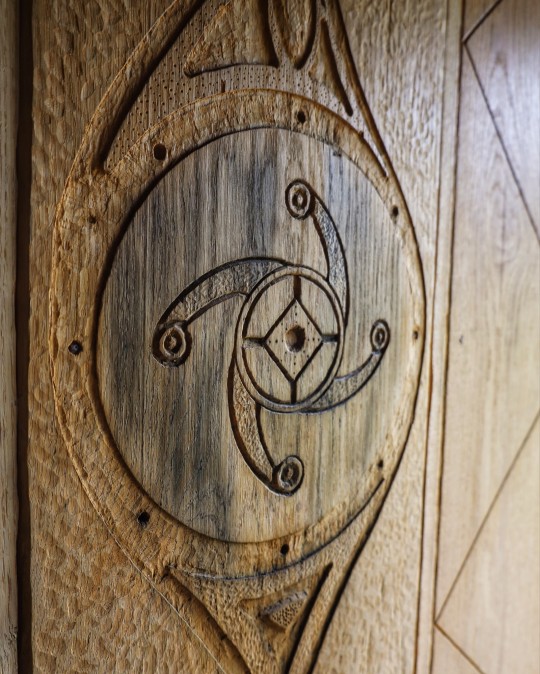
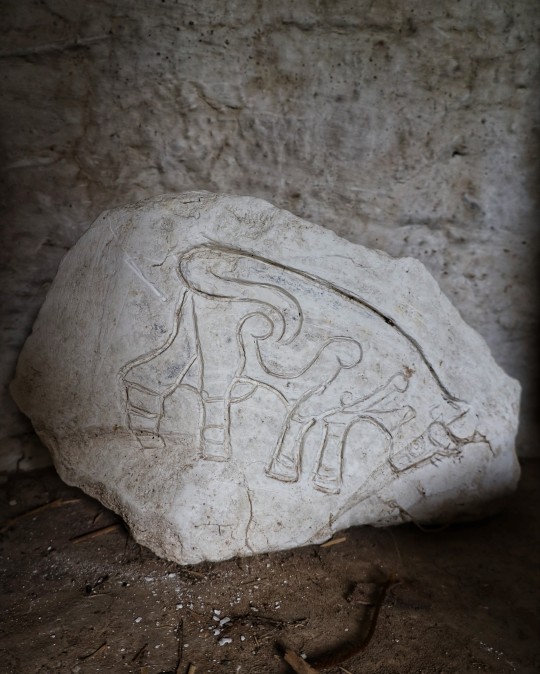
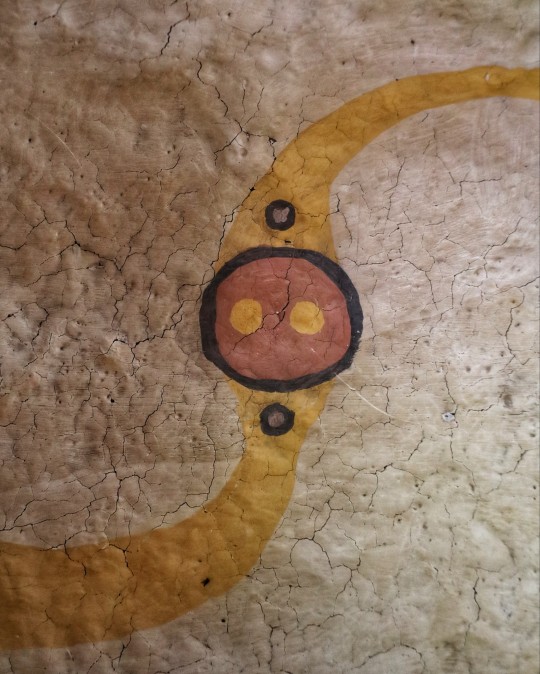
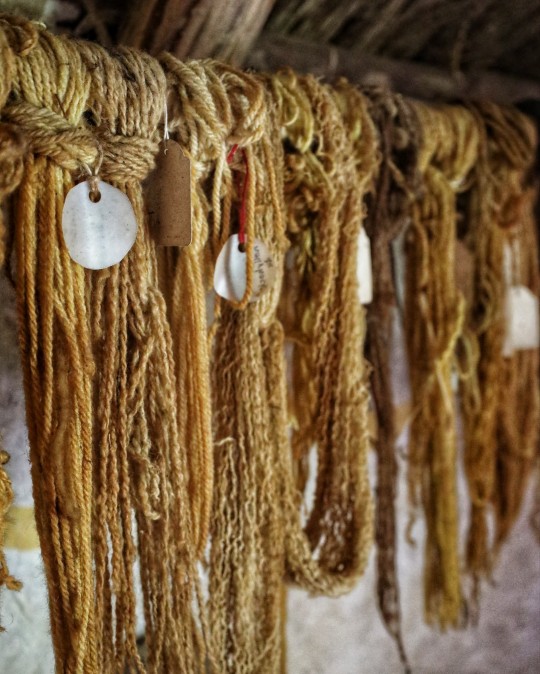
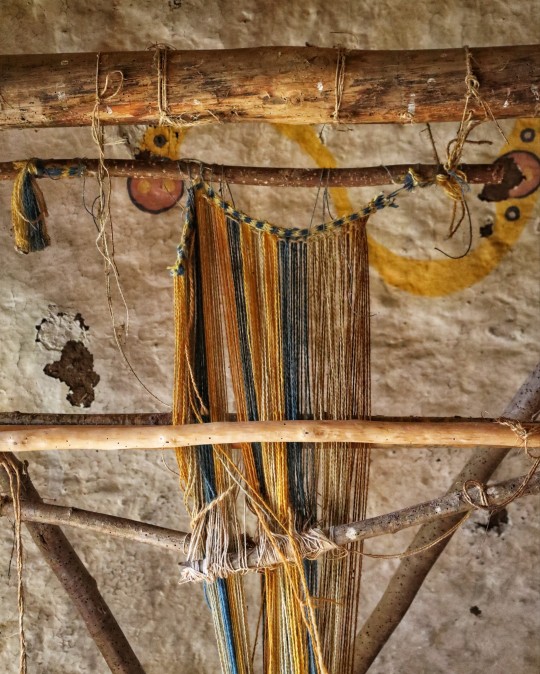
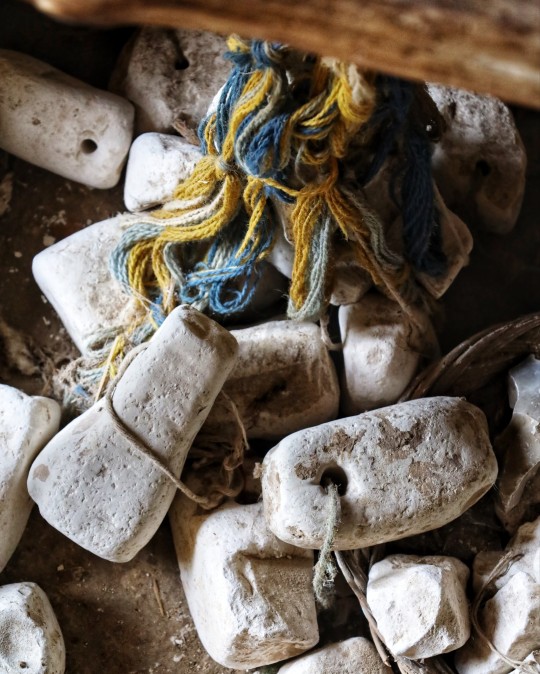
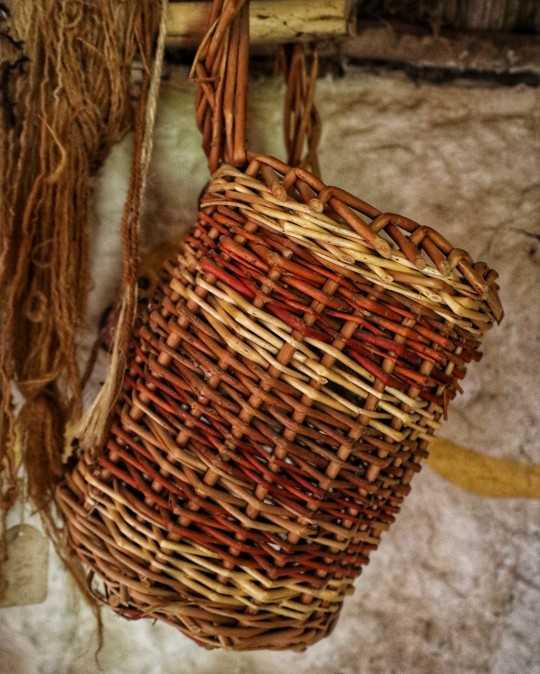
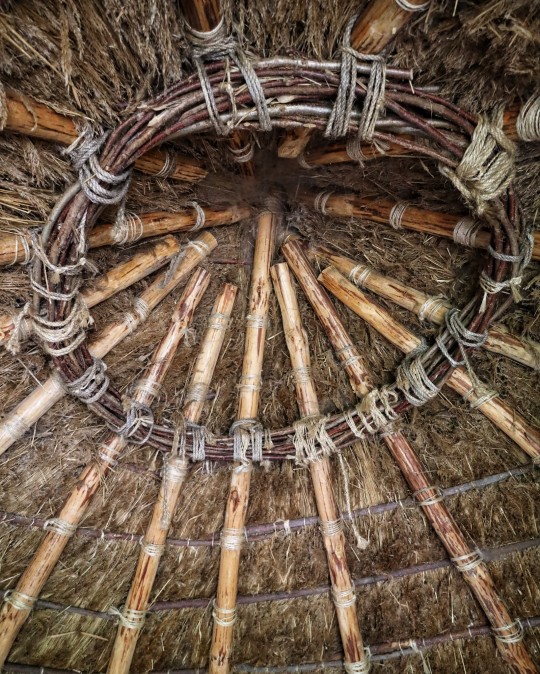










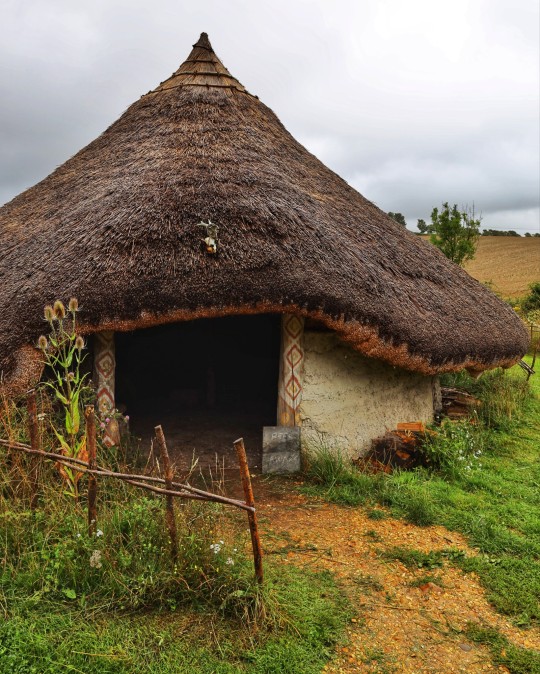
Iron Age Roundhouse Interiors, Butser Ancient Farm, Waterlooville, Hampshire
#ice age#stone age#bronze age#copper age#iron age#neolithic#mesolithic#calcholithic#paleolithic#prehistoric#prehistory#roundhouse#ancient living#ancient craft#ancient cultures#hearth#metalwork#natural materials#archaeology#butser ancient farm#community#outdoors#wild living#textiles
583 notes
·
View notes
Text
Dear super cool archaeological working farm,
I am a Canadian who qualifies for a visa in your country so you wouldn't have to sponsor me. If you and I work together to get some funding, will you pay me to be a farm labourer for 2 years, please and thanks.
#not museusm#not museums#Butser ancient farm#dream job#maybe#Thinking about sending this email#but like professional and stuff#poll
42 notes
·
View notes
Photo



Stills from my latest vid in which I explore a little known Celtic village in Cornwall. WATCH HERE
#cornwall#megaliths#witchy#celtic#celts#druids#iron age#archaeology#dumnonia#carn euny#butser ancient farm#celtic hosue#roundhouse#myth#folklore#haunted
17 notes
·
View notes
Text

Moody clouds over Butser Ancient Farm, South Downs, Hampshire (July 2023)
#sky#landscape#clouds#moody aesthetic#travel#travel photography#cloud appreciation#blue sky#Butser ancient farm#Celtic roundhouse#experimental archaeology#South Downs#south downs national park#hampshire#english countryside
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
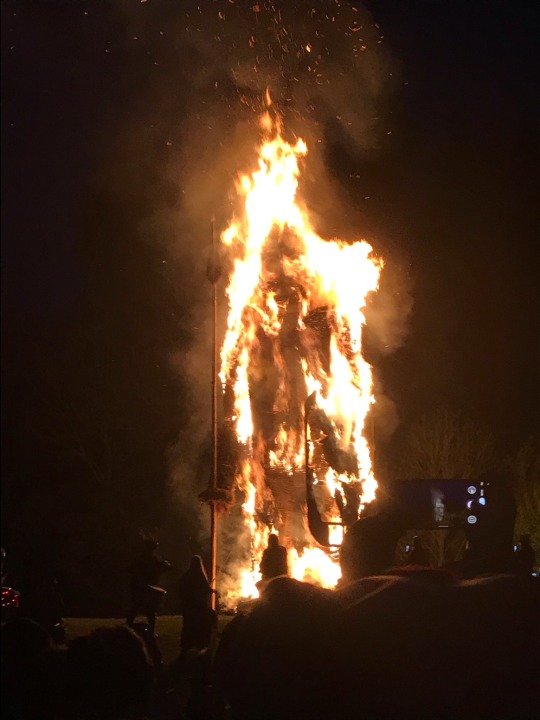
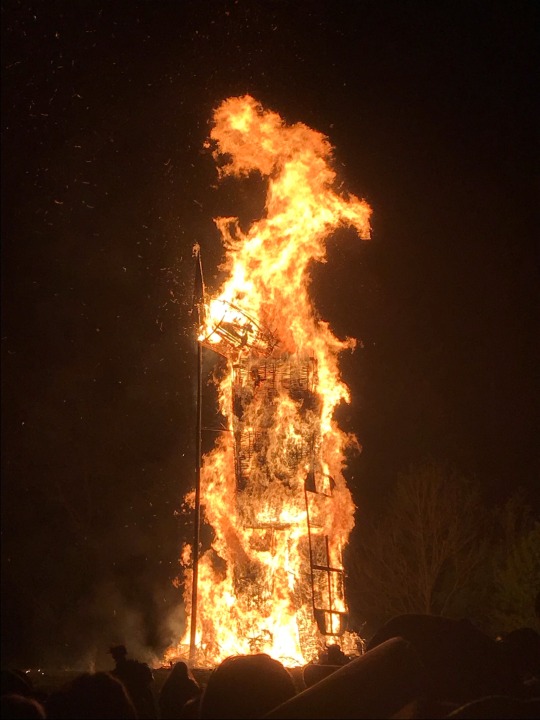





Photos of the Iron Age Wicker Man on fire at Butser Ancient Farm’s Beltane Festival yesterday evening.
#Beltane#Beltain#May day#green man#May Queen#wicker man#Beltane festival#fire#butser ancient farm#Celtic#pagan#old gods
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
placeholder text so tumble will let me add a read-more-thingy
yet another day when I am cursing my resistance to picking up coding skills, but this time it's because of the World Soil Museum.
i mean first off, that EXISTS! how sodding cool is THAT???? a soil museum!!! AND they have a virtual tour! i am so excited to discover this!!
and the website has so much info about each kind of soil (like this page on a random sample I clicked on from the virtual tour) and there's images of each sample they have. And I just it would be really neat to do the whole 'play with jpegs like dolls' thing and place samples side by side to compare. Even just the images. Actually, especially the images of the samples.
like i KNOW getting to see silt and clay beside each other would fix some part of my brain.
would it particularly useful? idk, unsure how much the average person cares about this and those that do care likely have better and more efficient sources of info.
but I would have a lot of fun with it, so there's that.
for a tool like this i imagine i'd need to get each sample's image+info separately and then set up a way to pull them up side by side. which mhmm boo @ the coding involved because that stuff remains witchcraft to me 😔
#side note i am extremely delighted by the fact that I am as excited about this soil museum as I was about Butser Ancient Farm#butser is SO fucking cool. it's a museum that does experimental archeology but also lets visitors take part so like#visitors get to recreate the same processes that were used in different eras for stuff like smelting and stuff#you get to learn how to make your own bows and arrows! turns out feather orientation is a big deal?#or liquify bronze in a crucible using only the fuels that were available back in the day and stuff#it's so cool aaaaah#anyway#lowkey tempted to genuinely try making something like this tho#because that will probably be the best way to get my brain to stop shutting down the moment it sees python#ie have an interest that overrides the instinctual urge to burn down the computer#but also consider: bleh.#placeholder tag#idk tho it might actually happen since i'm seeing my sibling in two days and that's soon enough for this interest to not completely die dow#by then#and he's my go-to for things code anyway#mhmmm#also huh been a while since i rambled in the tags like this
1 note
·
View note
Text

Beltain 2019 Wickerman burning Butser Ancient Farm photo by Eleanor Sopwith
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’ve been planning to do two things this summer as a reward for finishing my A-levels (can I just say, who at OCR signed off on the History and English Literature exam being on the same day?), one is to see Newsies in London before it closes and the other is to go to Butser Ancient Farm, where they filmed the Horrible Histories movie (yeah, you might say I’m really cool) and LOOK!!!!

!!!!!!!!! They do this every year but I’m excited anyway - I planned to go a little earlier (probably in the next couple weeks before the primary school summer holidays begin) and around late-August I’m expecting that I’ll have more stuff to do for this uni programme thing I’m doing but it’s a Sunday so I’d be surprised if I have anything to do and the train ticket prices might be nicer (update: I was wrong, £121 for a return???) than on weekdays and Saturdays so MAYBE I’ll get to go on this day and awkwardly watch this movie in a roundhouse full of families (I’m definitely gonna have to convince one of my friends to push through the 3 hour train journey and then walk around this place and then watch this movie again and then get the 3 hour train home for me because I’m not going alone)
#if i’ve been lacking on the hh movie front lately it’s because i’ve become reobsessed with the medical drama casualty but i’m still here#also ‘smash-hit’ by whose standards exactly?.#me describing the horrible histories movie: it’s a smash hit (i’ve never actually met anyone irl who knew it existed before meeting me)#i love this movie but it is incredibly underrated underappreciated and forgotten#horrible histories the movie#horrible histories rotten romans#mercury posting
1 note
·
View note
Photo
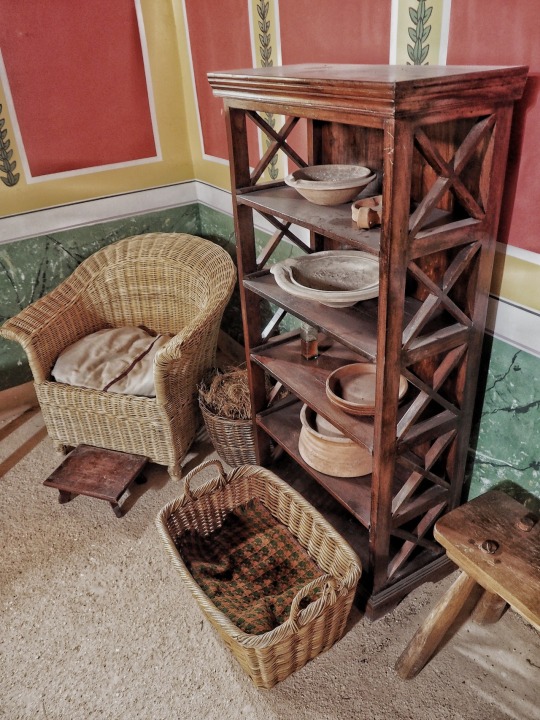
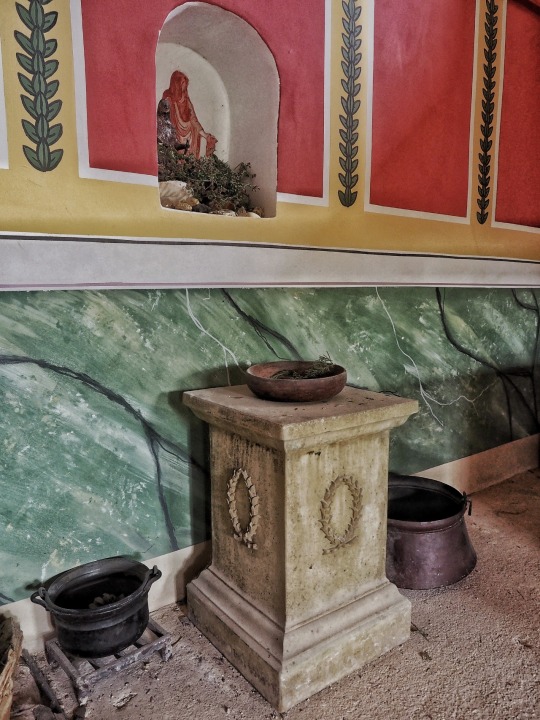
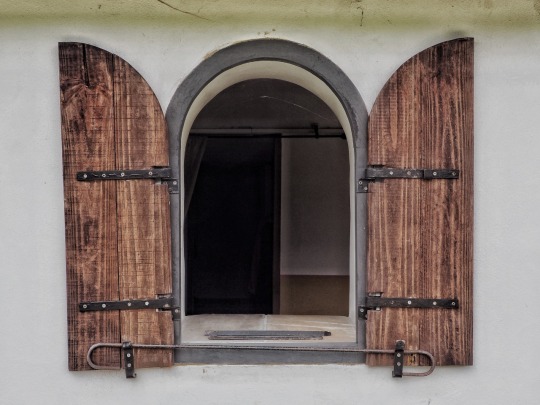
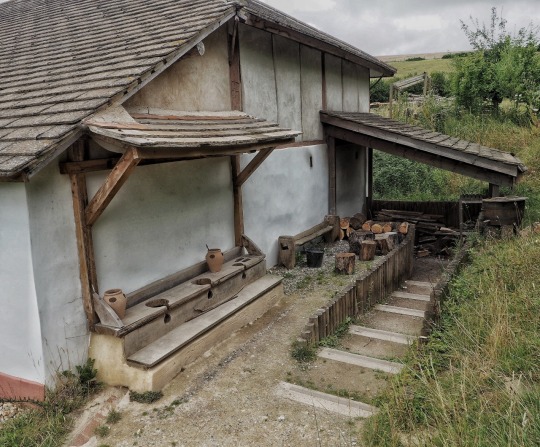
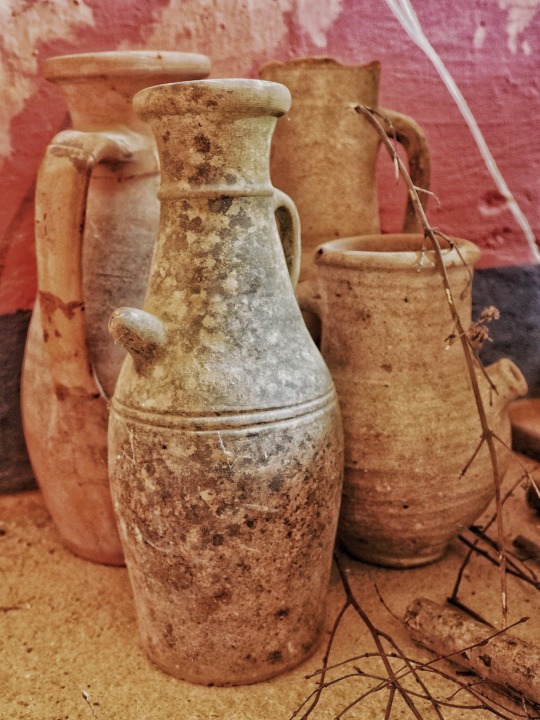
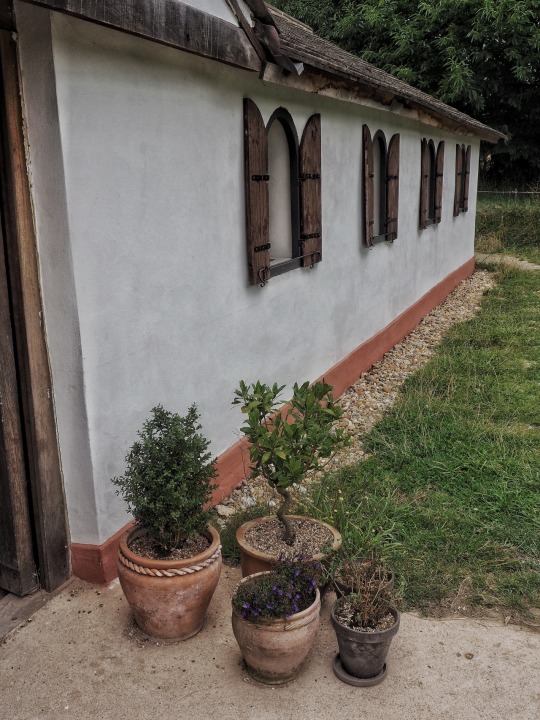










Recreated Roman Villa, Butser Ancient Farm, Hampshire.
(x)
1 note
·
View note
Text
ANGLO SAXON SETTLERS BRING MEAD HALLS TO LIFE AT BUTSER ANCIENT FARM
HONOUR the ancient celebration of Eostre with your ancestors this Easter weekend and come face to face with history at Butser Ancient Farm in Chalton.
Hampshire based Anglo Saxon reenactment group, Herigeas Hundas, will be giving visitors the exciting chance to see the farm’s two reconstructed mead halls brought to life with the sights and sounds of the early Anglo Saxon period from the 7th –…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
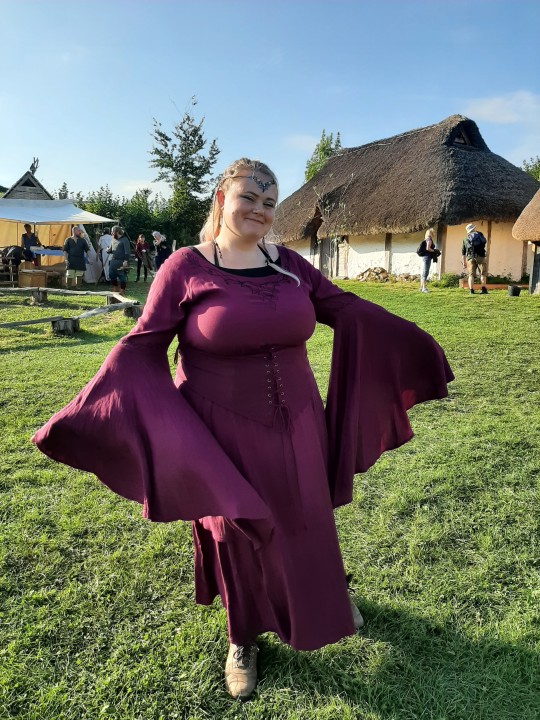
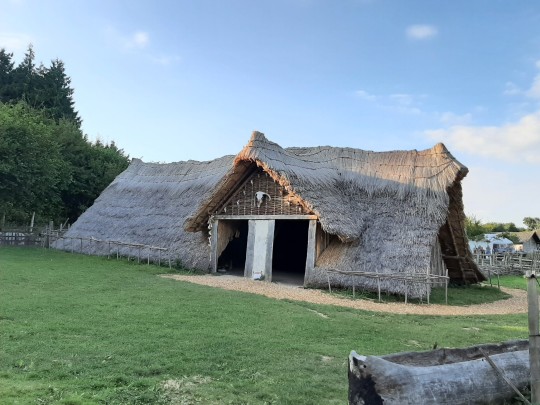
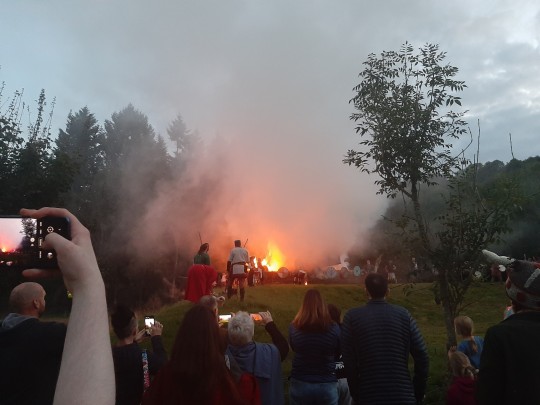






For an early Mabon/ Autumn Equinox celebration I went with some friends to Butser Ancient Farm for a boat burning on Saturday, it was good fun
#witchblr#witchy#witchery#witch#Mabon#Mabon celebration#Butser Ancient Farm#Autumn equinox#autumn equinox celebration#boat burning#fire#me#my face#pentacle drummers
28 notes
·
View notes
Text
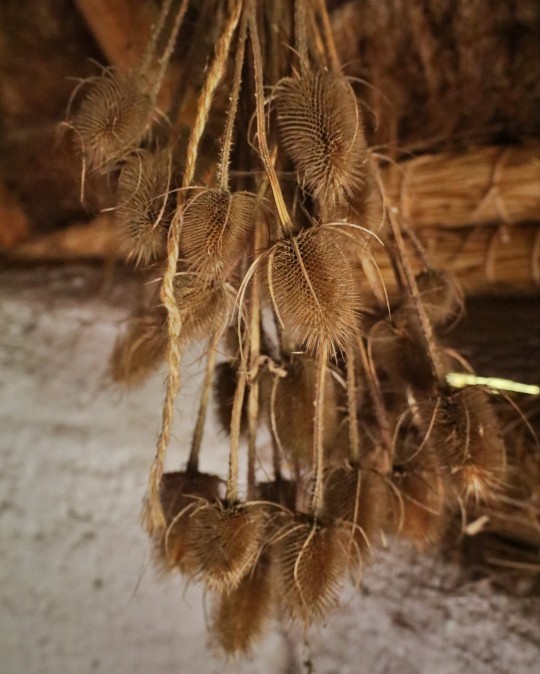
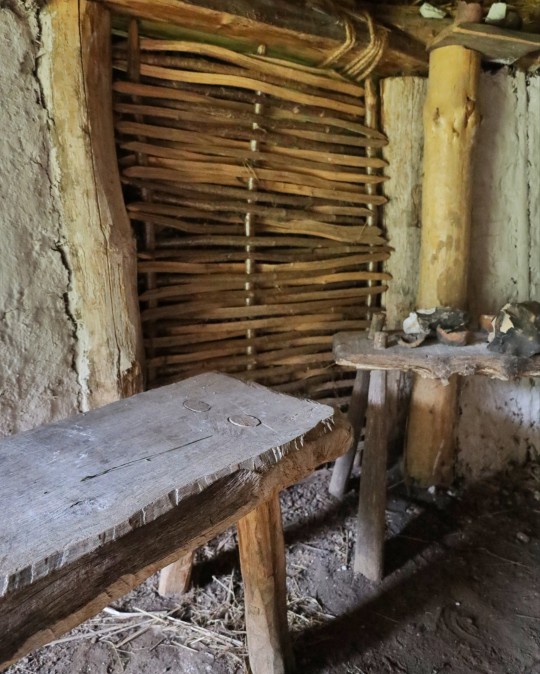
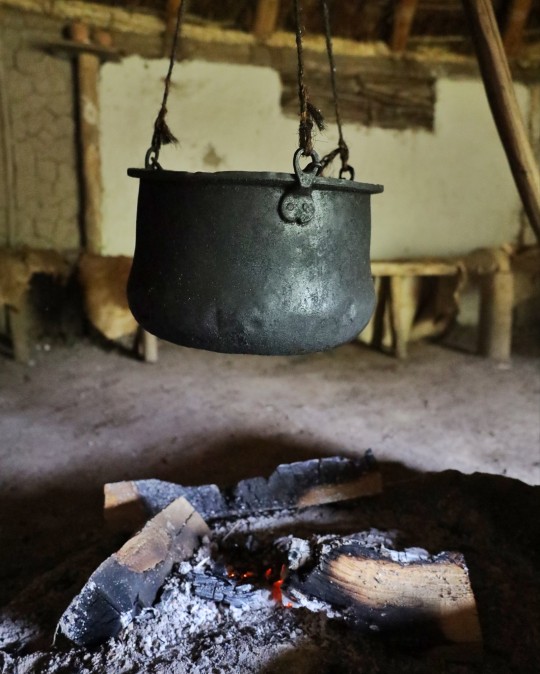
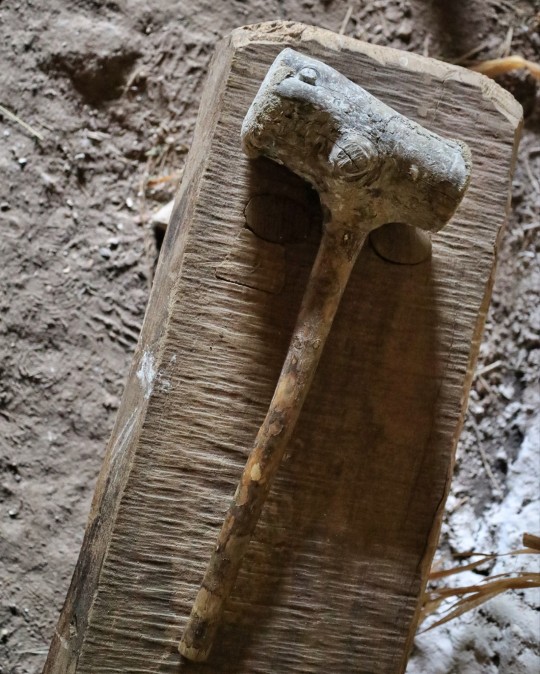
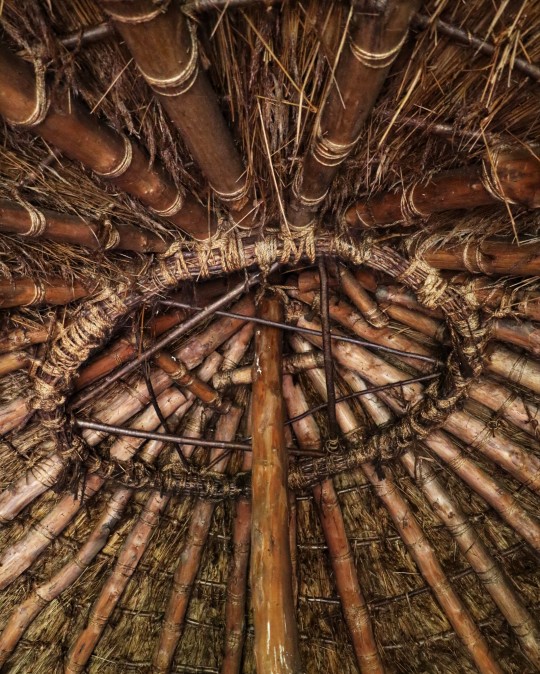
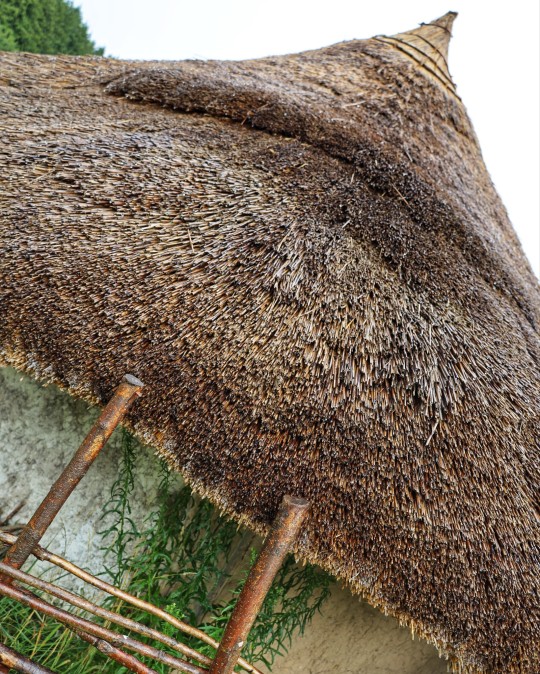









Recreated Bronze Age Roundhouse, Butser Ancient Farm, Waterlooville, Hampshire
#ice age#stone age#bronze age#copper age#iron age#neolithic#mesolithic#calcholithic#paleolithic#prehistoric#prehistory#roundhouse#settlement#farmstead#ancient living#ancient craft#ancient cultures#butser ancient farm#wild living#outdoors
256 notes
·
View notes
Text
Today's blog is on the pagan holiday Beltane on 5-1-21 BLESSED BELTANE!
🌳👑🌿🔥🙌🍄🌖🌌🌼🦋🌻🌸💐



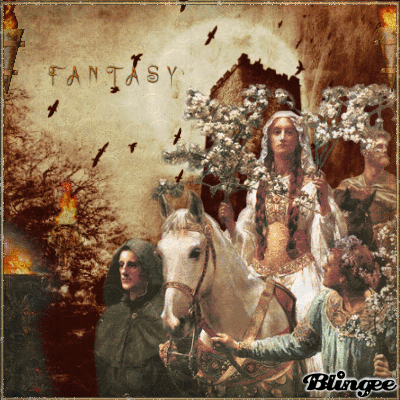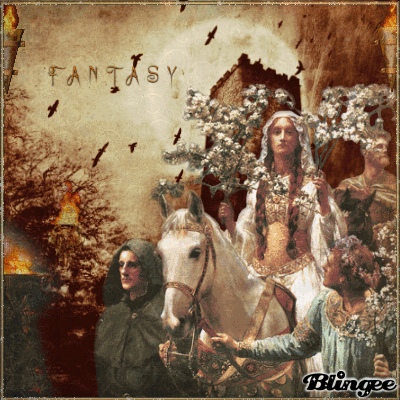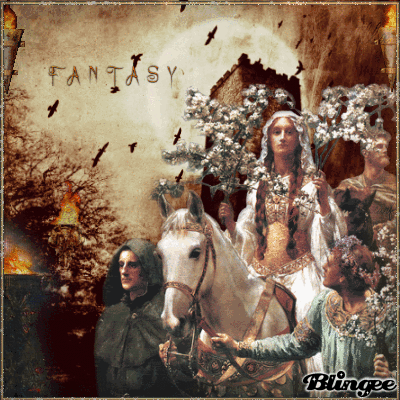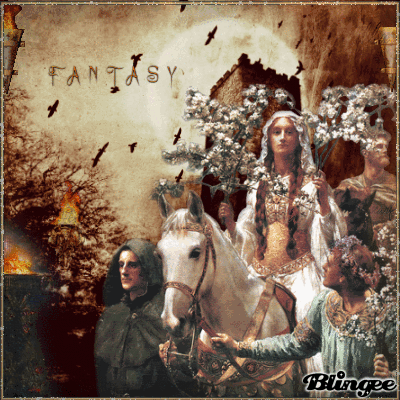


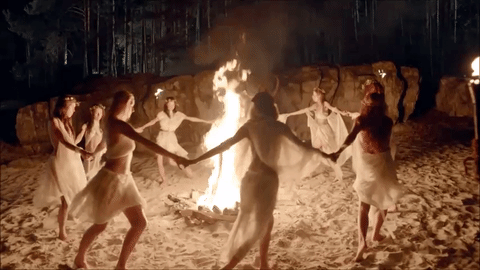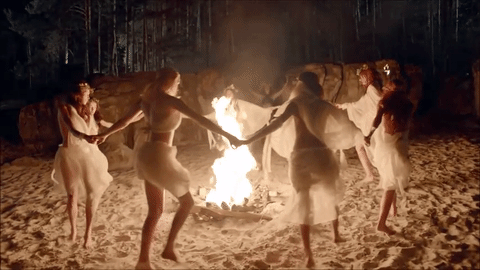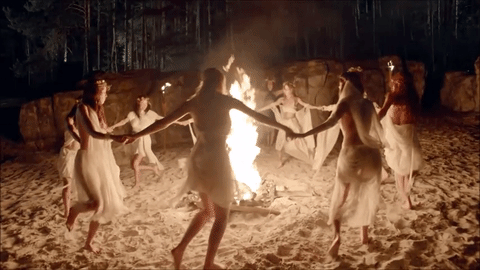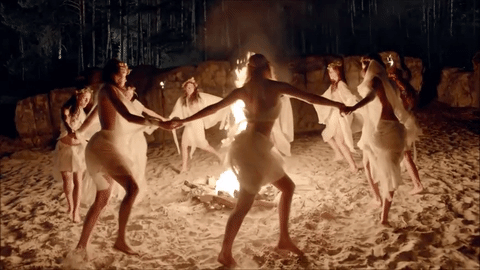
Beltane
Beltane or Beltain (/ˈbɛl.teɪn/) is the Gaelic May Day festival. Most commonly it is held on 1 May, or about halfway between the spring equinox and summer solstice. Historically, it was widely observed throughout Ireland, Scotland, and the Isle of Man. In Irish the name for the festival day is Lá Bealtaine ([l̪ˠaː ˈbʲal̪ˠt̪ˠənʲə]), in Scottish Gaelic Là Bealltainn ([l̪ˠaː ˈpjaul̪ˠt̪ɪɲ]) and in Manx Gaelic Laa Boaltinn/Boaldyn. It is one of the four Gaelic seasonal festivals—along with Samhain, Imbolc and Lughnasadh—and is similar to the Welsh Calan Mai.
Also calledLá Bealtaine (Irish)
Là Bealltainn (Scottish Gaelic)
Laa Boaltinn/Boaldyn (Manx)[1]
Beltaine (French)
Beltain; Beltine; Beltany[2][3]Observed byHistorically: Gaels
Today: Irish people, Scottish people, Manx people, Galician people, Wiccans, and Celtic neopagansTypeCultural
Pagan (Celtic polytheism, Celtic neopaganism, Wicca)SignificanceBeginning of summerCelebrationslighting bonfires, decorating homes with May flowers, making May bushes, visiting holy wells, feastingDate1 May[4]
(or 1 November in the S. Hemisphere)FrequencyannualRelated toMay Day, Calan Mai, Walpurgis Night
Beltane is mentioned in some of the earliest Irish literature and is associated with important events in Irish mythology. Also known as Cétshamhain ("first of summer"), it marked the beginning of summer and it was when cattle were driven out to the summer pastures. Rituals were performed to protect the cattle, crops and people, and to encourage growth. Special bonfires were kindled, and their flames, smoke and ashes were deemed to have protective powers. The people and their cattle would walk around or between bonfires, and sometimes leap over the flames or embers. All household fires would be doused and then re-lit from the Beltane bonfire. These gatherings would be accompanied by a feast, and some of the food and drink would be offered to the aos sí. Doors, windows, byres and livestock would be decorated with yellow May flowers, perhaps because they evoked fire. In parts of Ireland, people would make a May Bush: typically a thorn bush or branch decorated with flowers, ribbons, bright shells and rushlights. Holy wells were also visited, while Beltane dew was thought to bring beauty and maintain youthfulness. Many of these customs were part of May Day or Midsummer festivals in other parts of Great Britain and Europe.
Beltane celebrations had largely died out by the mid-20th century, although some of its customs continued and in some places it has been revived as a cultural event. Since the late 20th century, Celtic neopagans and Wiccans have observed Beltane or a related festival as a religious holiday. Neopagans in the Southern Hemisphere celebrate Beltane on or around 1 November.
Historic Beltane customs
Beltane was one of four Gaelic seasonal festivals: Samhain (~1 November), Imbolc (~1 February), Beltane (~1 May), and Lughnasadh (~1 August). Beltane marked the beginning of the pastoral summer season, when livestock were driven out to the summer pastures. Rituals were held at that time to protect them from harm, both natural and supernatural, and this mainly involved the "symbolic use of fire". There were also rituals to protect crops, dairy products and people, and to encourage growth. The aos sí (often referred to as spirits or fairies) were thought to be especially active at Beltane (as at Samhain) and the goal of many Beltane rituals was to appease them. Most scholars see the aos sí as remnants of the pagan gods and nature spirits. Beltane was a "spring time festival of optimism" during which "fertility ritual again was important, perhaps connecting with the waxing power of the sun".
Before the modern era
Beltane (the beginning of summer) and Samhain (the beginning of winter) are thought to have been the most important of the four Gaelic festivals. Sir James George Frazer wrote in The Golden Bough: A Study in Magic and Religion that the times of Beltane and Samhain are of little importance to European crop-growers, but of great importance to herdsmen. Thus, he suggests that halving the year at 1 May and 1 November dates from a time when the Celts were mainly a pastoral people, dependent on their herds.
The earliest mention of Beltane is in Old Irish literature from Gaelic Ireland. According to the early medieval texts Sanas Cormaic (written by Cormac mac Cuilennáin) and Tochmarc Emire, Beltane was held on 1 May and marked the beginning of summer. The texts say that, to protect cattle from disease, the druids would make two fires "with great incantations" and drive the cattle between them.
According to 17th-century historian Geoffrey Keating, there was a great gathering at the hill of Uisneach each Beltane in medieval Ireland, where a sacrifice was made to a god named Beil. Keating wrote that two bonfires would be lit in every district of Ireland, and cattle would be driven between them to protect them from disease. There is no reference to such a gathering in the annals, but the medieval Dindsenchas includes a tale of a hero lighting a holy fire on Uisneach that blazed for seven years. Ronald Hutton writes that this may "preserve a tradition of Beltane ceremonies there", but adds "Keating or his source may simply have conflated this legend with the information in Sanas Chormaic to produce a piece of pseudo-history. Nevertheless, excavations at Uisneach in the 20th century found evidence of large fires and charred bones, showing it to have been ritually significant.
Beltane is also mentioned in medieval Scottish literature. An early reference is found in the poem 'Peblis to the Play', contained in the Maitland Manuscripts of 15th- and 16th-century Scots poetry, which describes the celebration in the town of Peebles.
Modern era
From the late 18th century to the mid 20th century, many accounts of Beltane customs were recorded by folklorists and other writers. For example John Jamieson, in his Etymological Dictionary of the Scottish Language (1808) describes some of the Beltane customs which persisted in the 18th and early 19th centuries in parts of Scotland, which he noted were beginning to die out. In the 19th century, folklorist Alexander Carmichael (1832–1912), collected the Gaellic song Am Beannachadh Bealltain (The Beltane Blessing) in his Carmina Gadelica, which he heard from a crofter in South Uist. The first two verses were sung as follows:
Beannaich, a Thrianailt fhioir nach gann, (Bless, O Threefold true and bountiful,)
Mi fein, mo cheile agus mo chlann, (Myself, my spouse and my children,)
Mo chlann mhaoth's am mathair chaomh 'n an ceann, (My tender children and their beloved mother at their head,)
Air chlar chubhr nan raon, air airidh chaon nam beann, (On the fragrant plain, at the gay mountain sheiling,)
Air chlar chubhr nan raon, air airidh chaon nam beam. (On the fragrant plain, at the gay mountain sheiling.)
Gach ni na m' fhardaich, no ta 'na m' shealbh, (Everything within my dwelling or in my possession,)
Gach buar is barr, gach tan is tealbh, (All kine and crops, all flocks and corn,)
Bho Oidhche Shamhna chon Oidhche Bheallt, (From Hallow Eve to Beltane Eve,)
Piseach maith, agus beannachd mallt, (With goodly progress and gentle blessing,)
Bho mhuir, gu muir, agus bun gach allt, (From sea to sea, and every river mouth,)
Bho thonn gu tonn, agus bonn gach steallt. (From wave to wave, and base of waterfall.)[18]
Bonfires
A Beltane bonfire at Butser Ancient Farm
Bonfires continued to be a key part of the festival in the modern era. All hearth fires and candles would be doused before the bonfire was lit, generally on a mountain or hill. Ronald Hutton writes that "To increase the potency of the holy flames, in Britain at least they were often kindled by the most primitive of all means, of friction between wood." In the 19th century, for example, John Ramsay described Scottish Highlanders kindling a need-fire or force-fire at Beltane. Such a fire was deemed sacred. In the 19th century, the ritual of driving cattle between two fires—as described in Sanas Cormaic almost 1000 years before—was still practised across most of Ireland and in parts of Scotland. Sometimes the cattle would be driven "around" a bonfire or be made to leap over flames or embers. The people themselves would do likewise. In the Isle of Man, people ensured that the smoke blew over them and their cattle. When the bonfire had died down, people would daub themselves with its ashes and sprinkle it over their crops and livestock. Burning torches from the bonfire would be taken home, where they would be carried around the house or boundary of the farmstead and would be used to re-light the hearth. From these rituals, it is clear that the fire was seen as having protective powers. Similar rituals were part of May Day, Midsummer or Easter customs in other parts of the British Isles and mainland Europe. According to Frazer, the fire rituals are a kind of imitative or sympathetic magic. According to one theory, they were meant to mimic the Sun and to "ensure a needful supply of sunshine for men, animals, and plants". According to another, they were meant to symbolically "burn up and destroy all harmful influences".
Food was also cooked at the bonfire and there were rituals involving it. Alexander Carmichael wrote that there was a feast featuring lamb, and that formerly this lamb was sacrificed. In 1769, Thomas Pennant wrote that, in Perthshire, a caudle made from eggs, butter, oatmeal and milk was cooked on the bonfire. Some of the mixture was poured on the ground as a libation. Everyone present would then take an oatmeal cake, called the bannoch Bealltainn or "Beltane bannock". A bit of it was offered to the spirits to protect their livestock (one bit to protect the horses, one bit to protect the sheep, and so forth) and a bit was offered to each of the animals that might harm their livestock (one to the fox, one to the eagle, and so forth). Afterwards, they would drink the caudle.
According to 18th century writers, in parts of Scotland there was another ritual involving the oatmeal cake. The cake would be cut and one of the slices marked with charcoal. The slices would then be put in a bonnet and everyone would take one out while blindfolded. According to one writer, whoever got the marked piece would have to leap through the fire three times. According to another, those present would pretend to throw them into the fire and, for some time afterwards, they would speak of them as if they were dead. This "may embody a memory of actual human sacrifice", or it may have always been symbolic. A similar ritual (i.e. of pretending to burn someone in the fire) was practised at spring and summer bonfire festivals in other parts of Europe.
Flowers and May Bushes
A flowering hawthorn
Yellow flowers such as primrose, rowan, hawthorn, gorse, hazel, and marsh marigold were placed at doorways and windows in 19th century Ireland, Scotland and Mann. Sometimes loose flowers were strewn at the doors and windows and sometimes they were made into bouquets, garlands or crosses and fastened to them. They would also be fastened to cows and equipment for milking and butter making. It is likely that such flowers were used because they evoked fire. Similar May Day customs are found across Europe.
The May Bush and May Bough was popular in parts of Ireland until the late 19th century. This was a small tree or branch—typically hawthorn, rowan, holly or sycamore—decorated with bright flowers, ribbons, painted shells, and so forth. The tree would either be decorated where it stood, or branches would be decorated and placed inside or outside the house. It may also be decorated with candles or rushlights. Sometimes a May Bush would be paraded through the town. In parts of southern Ireland, gold and silver hurling balls known as May Balls would be hung on these May Bushes and handed out to children or given to the winners of a hurling match. In Dublin and Belfast, May Bushes were brought into town from the countryside and decorated by the whole neighbourhood. Each neighbourhood vied for the most handsome tree and, sometimes, residents of one would try to steal the May Bush of another. This led to the May Bush being outlawed in Victorian times. In some places, it was customary to dance around the May Bush, and at the end of the festivities it may be burnt in the bonfire.
Thorn trees were seen as special trees and were associated with the aos sí. The custom of decorating a May Bush or May Tree was found in many parts of Europe. Frazer believes that such customs are a relic of tree worship and writes: "The intention of these customs is to bring home to the village, and to each house, the blessings which the tree-spirit has in its power to bestow."Emyr Estyn Evans suggests that the May Bush custom may have come to Ireland from England, because it seemed to be found in areas with strong English influence and because the Irish saw it as unlucky to damage certain thorn trees. However, "lucky" and "unlucky" trees varied by region, and it has been suggested that Beltane was the only time when cutting thorn trees was allowed. The practice of bedecking a May Bush with flowers, ribbons, garlands and bright shells is found among the Gaelic diaspora, most notably in Newfoundland, and in some Easter traditions on the East Coast of the United States.
Other customs
Holy wells were often visited at Beltane, and at the other Gaelic festivals of Imbolc and Lughnasadh. Visitors to holy wells would pray for health while walking sunwise (moving from east to west) around the well. They would then leave offerings; typically coins or clooties (see clootie well). The first water drawn from a well on Beltane was seen as being especially potent, as was Beltane morning dew. At dawn on Beltane, maidens would roll in the dew or wash their faces with it. It would also be collected in a jar, left in the sunlight, and then filtered. The dew was thought to increase sexual attractiveness, maintain youthfulness, and help with skin ailments.
People also took steps specifically to ward-off or appease the aos sí. Food was left or milk poured at the doorstep or places associated with the aos sí, such as 'fairy trees', as an offering. In Ireland, cattle would be brought to 'fairy forts', where a small amount of their blood would be collected. The owners would then pour it into the earth with prayers for the herd's safety. Sometimes the blood would be left to dry and then be burnt. It was thought that dairy products were especially at risk from harmful spirits. To protect farm produce and encourage fertility, farmers would lead a procession around the boundaries of their farm. They would "carry with them seeds of grain, implements of husbandry, the first well water, and the herb vervain (or rowan as a substitute). The procession generally stopped at the four cardinal points of the compass, beginning in the east, and rituals were performed in each of the four directions".
The festival persisted widely up until the 1950s, and in some places the celebration of Beltane continues today.
As a festival, Beltane had largely died out by the mid-20th century, although some of its customs continued and in some places it has been revived as a cultural event. In Ireland, Beltane fires were common until the mid 20th century, but the custom seems to have lasted to the present day only in County Limerick (especially in Limerick itself) and in Arklow, County Wicklow. However, the custom has been revived in some parts of the country. Some cultural groups have sought to revive the custom at Uisneach and perhaps at the Hill of Tara. The lighting of a community Beltane fire from which each hearth fire is then relit is observed today in some parts of the Gaelic diaspora, though in most of these cases it is a cultural revival rather than an unbroken survival of the ancient tradition. In some areas of Newfoundland, the custom of decorating the May Bush is also still extant. The town of Peebles in the Scottish Borders holds a traditional week-long Beltane Fair every year in June, when a local girl is crowned Beltane Queen on the steps of the parish church. Like other Borders festivals, it incorporates a Common Riding.
Since 1988, a Beltane Fire Festival has been held every year during the night of 30 April on Calton Hill in Edinburgh, Scotland. While inspired by traditional Beltane, this festival is a modern arts and cultural event which incorporates myth and drama from a variety of world cultures and diverse literary sources. Two central figures of the Bel Fire procession and performance are the May Queen and the Green Man.
Neo-Paganism
Beltane and Beltane-based festivals are held by some Neopagans. As there are many kinds of Neopaganism, their Beltane celebrations can be very different despite the shared name. Some try to emulate the historic festival as much as possible. Other Neopagans base their celebrations on many sources, the Gaelic festival being only one of them.
Neopagans usually celebrate Beltane on 30 April – 1 May in the Northern Hemisphere and 31 October – 1 November in the Southern Hemisphere, beginning and ending at sunset. Some Neopagans celebrate it at the astronomical midpoint between the spring equinox and summer solstice (or the full moon nearest this point). In the Northern Hemisphere, this midpoint is when the ecliptic longitude of the Sun reaches 45 degrees.
Celtic Reconstructionist
Celtic Reconstructionists strive to reconstruct the pre-Christian religions of the Celts. Their religious practices are based on research and historical accounts, but may be modified slightly to suit modern life. They avoid modern syncretism and eclecticism (i.e. combining practises from unrelated cultures).
Celtic Reconstructionists usually celebrate Lá Bealtaine when the local hawthorn trees are in bloom. Many observe the traditional bonfire rites, to whatever extent this is feasible where they live. This may involve passing themselves and their pets or livestock between two bonfires, and bringing home a candle lit from the bonfire. If they are unable to make a bonfire or attend a bonfire ceremony, torches or candles may be used instead. They may decorate their homes with a May Bush, branches from blooming thorn trees, or equal-armed rowan crosses. Holy wells may be visited and offerings made to the spirits or deities of the wells. Traditional festival foods may also be prepared.
Wicca
Wiccans use the name Beltane or Beltain for their May Day celebrations. It is one of the yearly Sabbats of the Wheel of the Year, following Ostara and preceding Midsummer. Unlike Celtic Reconstructionism, Wicca is syncretic and melds practices from many different cultures. In general, the Wiccan Beltane is more akin to the Germanic/English May Day festival, both in its significance (focusing on fertility) and its rituals (such as maypole dancing). Some Wiccans enact a ritual union of the May Lord and May Lady.
Name
In Irish, the festival is usually called Lá Bealtaine ('day of Beltane') while the month of May is Mí Bhealtaine ("month of Beltane"). In Scottish Gaelic, the festival is Latha Bealltainn and the month is An Cèitean or a' Mhàigh. Sometimes the older Scottish Gaelic spelling Bealltuinn is used. The word Céitean comes from Cétshamain ('first of summer'), an old alternative name for the festival. The term Latha Buidhe Bealltainn (Scottish) or Lá Buidhe Bealtaine (Irish), 'the bright or yellow day of Beltane', means the first of May. In Ireland it is referred to in a common folk tale as Luan Lae Bealtaine; the first day of the week (Monday/Luan) is added to emphasise the first day of summer.
The name is anglicized as Beltane, Beltain, Beltaine, Beltine and Beltany.
Etymology
Two modern etymologies have been proposed. Beltaine could derive from a Common Celtic *belo-te(p)niâ, meaning 'bright fire'. The element *belo- might be cognate with the English word bale (as in bale-fire) meaning 'white' or 'shining'; compare Old English bǣl, and Lithuanian/Latvian baltas/balts, found in the name of the Baltic; in Slavic languages byelo or beloye also means 'white', as in Беларусь ('White Rus′' or Belarus) or Бе́лое мо́ре ('White Sea').[citation needed] Alternatively, Beltaine might stem from a Common Celtic form reconstructed as *Beltiniyā, which would be cognate with the name of the Lithuanian goddess of death Giltinė, both from an earlier *gʷel-tiōn-, formed with the Proto-Indo-European root *gʷelH- ('suffering, death'). The absence of syncope (Irish sound laws rather predict a **Beltne form) is explained by the popular belief that Beltaine was a compound of the word for 'fire', tene.
In Ó Duinnín's Irish dictionary (1904), Beltane is referred to as Céadamh(ain) which it explains is short for Céad-shamh(ain) meaning 'first (of) summer'. The dictionary also states that Dia Céadamhan is May Day and Mí Céadamhan is the month of May.
There are a number of place names in Ireland containing the word Bealtaine, indicating places where Bealtaine festivities were once held. It is often anglicised as Beltany. There are three Beltanys in County Donegal, including the Beltany stone circle, and two in County Tyrone. In County Armagh there is a place called Tamnaghvelton/Tamhnach Bhealtaine ('the Beltane field'). Lisbalting/Lios Bealtaine ('the Beltane ringfort') is in County Tipperary, while Glasheennabaultina/Glaisín na Bealtaine ('the Beltane stream') is the name of a stream joining the River Galey in County Limerick.
Source: Wikipedia
I hope you've enjoyed this blog more to follow soon,
Blessed be,
Culture Calypso's Blog 🌻🌸💐
#beltaine#paganism#pagan holidays#history#my blogs#faecore#irish culture#tuatha de danann#spirituality#summer
21 notes
·
View notes
Note
What was Anglo-Saxon architecture like?

20 notes
·
View notes
Text

Storm and rainbow, Beltain 2019: Butser Ancient Farm, edge of the South Downs National Park
Aka My heart, right now (post GO2, but knowing a glimmer of what will happen in GO3)
#the South Downs cottage WILL happen#it has to or I will die of sad#I am in bits#good omens#good omens 2#good omens spoilers#landscape#sky#clouds#stormy weather#rainbow#moody aesthetic#cloud appreciation#seascape#travel#travel photography#south downs#south downs national park#greetings from the south downs#beltaine#Beltain#beltane#Butser ancient farm
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
NYE Post
I love a good NYE post where I summarise the ups and downs of the year and put into thoughts what I’m looking forward to next year. I try to keep it brief, I rarely succeed. I feel this is essentially like those old fashioned round robin letters people still occasionally do in Christmas cards!
Bad bits - All the World Events/cost of living and energy crisis/War and weather aside... I finally caught covid, an old friend passed away in horrible circumstances, my dear bunny Cloud died in June, a relative has fallen very ill and may not have long left to live and at the start of the year my mental health was in shocking shape. I also broke my wrist playing 5-aside football with work in September.
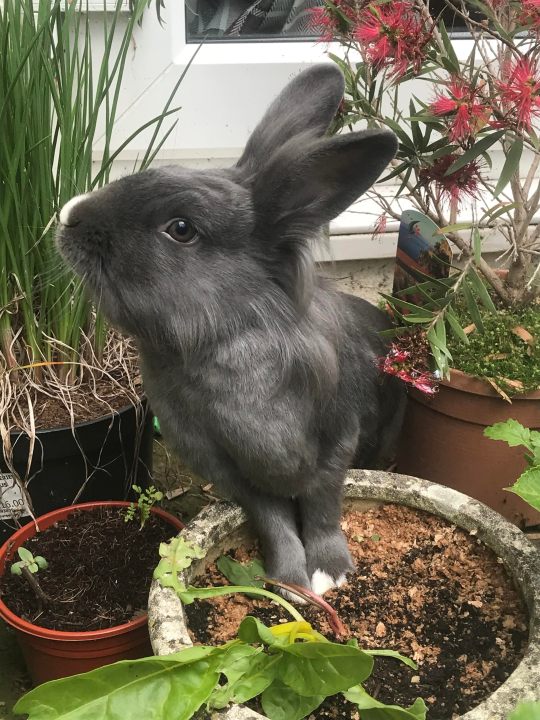

The Good - I completed an amazing course of therapy which has left me feeling so much more confident and happy in myself - it really has changed my outlook on life. I saw the Francis Bacon exhibit at the Royal Academy of Arts in March, I’ve also visited several fascinating museums and exhibitions. There’s been lots of concerts, the most amazing being seeing Placebo again at Portsmouth Guildhall, seeing Joe Jackson with my dad and after years of trying to see them live, getting to see Nick Cave and the Bad Seeds at all points east festival with @cassandrafey My husband and I had a long road trip up to the lake district to visit his family as well as see where he grew up and visit some of my favourite places too, it was lovely. I did a 27 and a half mile walk with work for charity (The Surrey Three Peaks challenge but we got a bit lost), it was the most physically difficult thing I’ve done in my life and I was so proud of myself. For my birthday we went to Longleat Safari and stayed overnight nearby - we fed the lorikeets and the seals, it was absolutely perfect. In October my husband and I went abroad for the first time since June 2019, we went to Rhodes, Greece and it was beautiful, relaxing and romantic. We had a lovely wedding anniversary and went to the Theatre to see Swan Lake. And finally we had a 3 night family holiday to Bruges where we experienced all the magic of late Autumn/cold crisp winter and saw all the Christmas lights.
New Year’s Resolutions - I pretty much have one this year and that is simply. To be more mindful. More mindful about what I spend my money on, what I eat, how I take care of myself, how I react to situations, what I reveal about myself at work, how much I drink at comedy gigs, what and who I spend time and energy on.
Looking to 2023 - On the one hand next year already has some very big plans and will be busy, but due to this my plan is to keep other times quieter than usual and focus more on me and the relationships I hold dear/my home. I’ll still be performing comedy but not doing as much or chasing it, I’ll continue to run the comedy night’s I run and will still perform once or twice a month at new gigs/the best gigs/gigs worth doing and am doing a Split show at Brighton and Ventnor fringe festivals, but that’s it. I want to focus more on the funeral industry and potential career change and my writing.
Plans for 2023 - There’s a few loose ones like my husband and I hopefully going to Ireland for a week. But set in stone the biggest adventure I have is going to New Zealand with my dad in May (and a night in Singapore) to explore, show him my favourite places and see family. We have Beltane Festival at the end of April at Butser Ancient Farm and in September I’m off to Budapest with the wonderful @cassandrafey to see IAMX. Oh and we may have bought tickets to see Def Leppard and Motley Crue in London....
So that’s my re-cap for the year, whether anyone reads it or not, it strangely makes me feel better knowing I’ve written it all down and can reflect in time to come.
In the meantime, I wish you all a very Happy New Year!
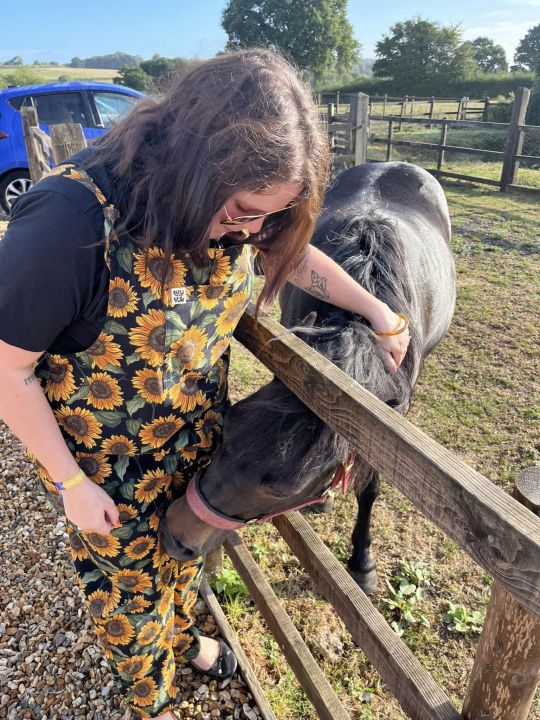




(Photos are of: Cloud the bunny, Sunset in Rhodes, me on my birthday, The Lake District with my husband, Bruges)
2 notes
·
View notes