#british mandate over palestine
Text



Source
#drained the swamps#made the desert bloom#british mandate over palestine#ottoman empire#malaria#israel jacob kligler
52 notes
·
View notes
Text
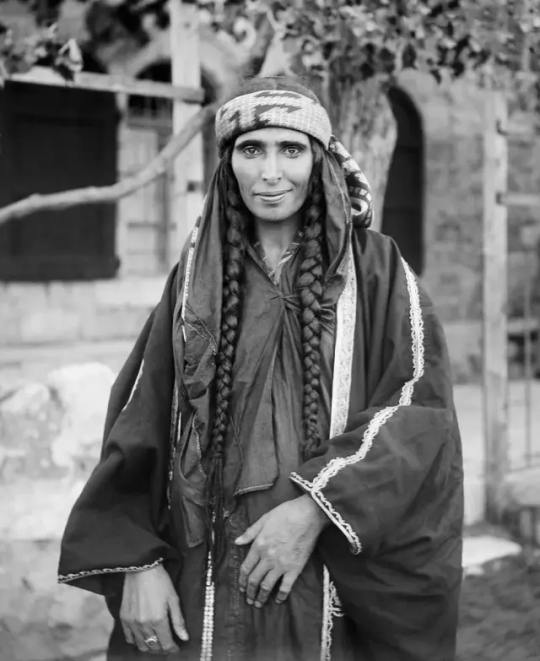
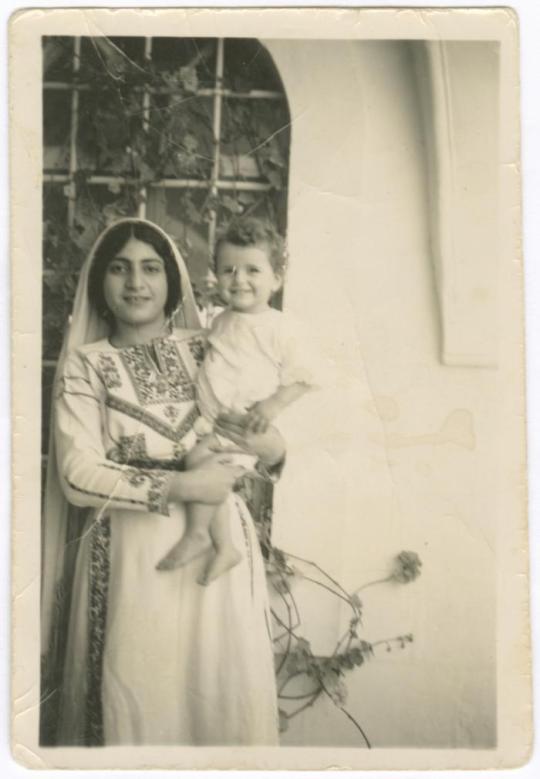
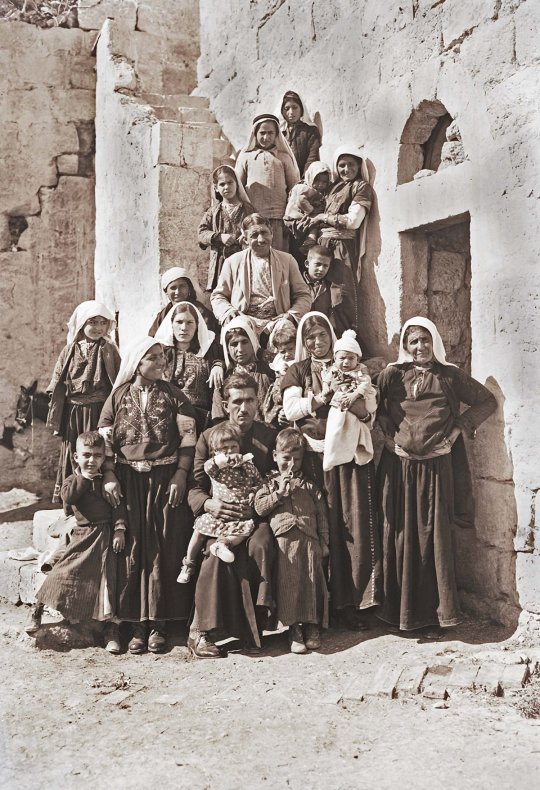
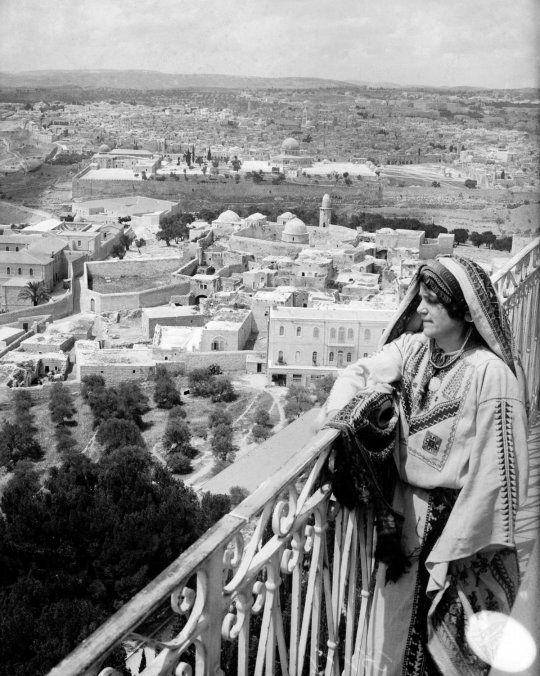
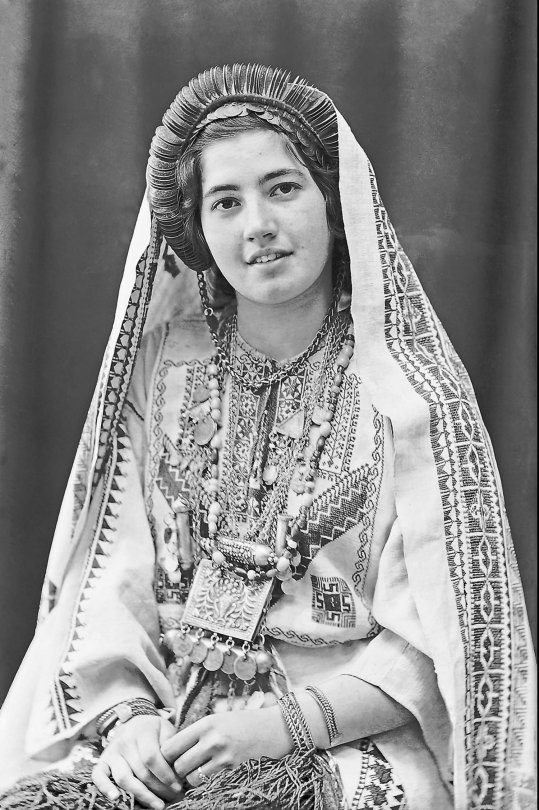
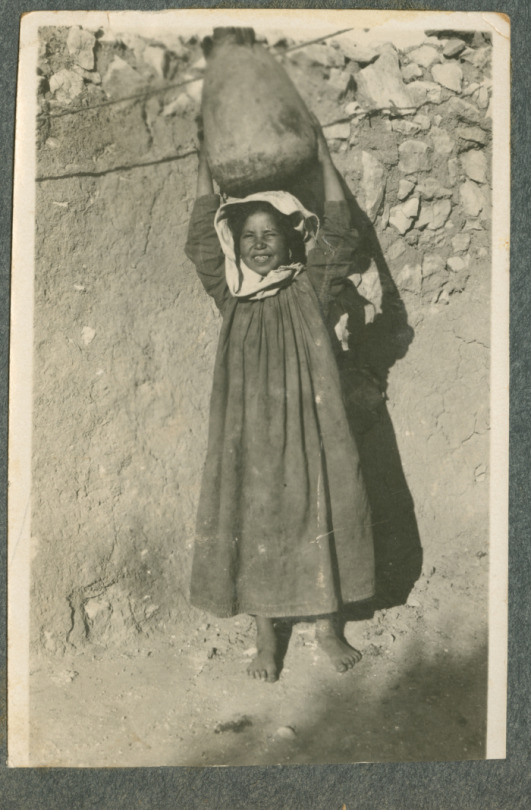













Moments from Palestine across generations and communities
(1) A Bedouin woman smiles in Jerusalem (1898-1914)
(2) Asma Aranki Holding a Child from Her Family at Their House, Birzeit (1948)
(3) Bedouin girls in Jericho (1918)
(4) An extended Palestinian family gathers in front of their house in the village of Beit Sahur, near Bethlehem (1918–35)
(5) From the Mount of Olives, a young woman looks out over eastern Jerusalem (1929)
(6) Ruth Raad, daughter of photographer Khalil Raad, in the traditional costume of Ramallah (1939)
(7) Standing in his neatly ironed shirt and shorts, George Sawabin poses for a studio photo (1942)
(8) Katingo Hanania Deeb, prepares to demonstrate in the 1936-1939 Arab Revolt -- which was a nationalist uprising by Palestinian Arabs against British colonial rule in relation to Palestinian independence and the land acquisition and pushout as a result of the mass Jewish immigration (1936)
(9) Young children walking home from school Beit Deqqo Village, the Occupied Palestinian West Bank, 1987
(10) Four young girls decorating vases in a ceramic workshop in Nablus (1920)
(11) A young Palestinian girl squints and smiles as she holds a jar on her head (1920-1950)
(12) The ancient craft of a Palestinian potter (1918-35)
(13) The mothers of Palestinian detainees' protest in Jerusalem (1987)
Source(s): The British Mandate Jerusalemites (BMJ) Photo Library, Palestinian Museum Digital Archives, The Jerusalem Story + Khalil Raad
Please support, share, cite, and (if financially able) fund these organizations and public storytellers for their rebellious histories and community work!
#decolonization#our world#our history is your history#people#free palestine#palestine#indigenous rights#art of making#and manifesting#history is not neutral#futurepast
4K notes
·
View notes
Text
My father was a talker and a storyteller. Because of this, there was no time when we, his children, did not know we were Palestinian. The stories I remember about his boyhood in the 1930s and early 1940s were nostalgic, both comic and bitter. But there were more political stories that began to teach us what it had meant to be Palestinian under the British Mandate. According to my father, people were barely aware they were on the eve of disastrous events that would make them refugees. They did not realize that the Zionists, not the British, were their real adversaries.
Yet, while I was growing up, I don’t recall hearing his stories of 1948, the last months before the fall of his hometown, Jaffa. Were we too young to be told? Did it not mean anything to children who had never seen Jaffa? What happened when my father returned to Palestine was that his memories now became the guide to a living history and a real place. And he told the stories to me and to anyone who would listen.
Jaffa was the heart of my father’s Palestine. On the wall of his apartment in Ramallah when I came to stay in 2001 was a large sepia poster: a historic photograph of an Arab man staring wistfully out to sea with a large town in the background. At the top, in Arabic, it said, “Jaffa 1937.” On my first visit to Palestine to see him in 1993, I sensed the thrill he felt at having mastered the new situation. The good part was embracing and being embraced by the community he had found, whether in the West Bank or in various other parts of pre-1948 Palestine. The anxiety of being there was betrayed by his dry mouth and the beads of sweat on his forehead as he drove us around, approaching Israeli military checkpoints or getting lost because he couldn’t read Hebrew. For me, the landscape was familiar from Lebanon and Jordan, which I had known well growing up. The barren highways and the cities branded by Hebrew sounds and sights were menacing, though, especially when combined with the heavy presence of Israeli soldiers, reservists, and guns.
He was eager to show me and my small family the whole of Palestine, from Jerusalem to Bethlehem, Nablus to Nazareth, Jericho to ‘Akka. His tour of Jaffa, the same one, I was a little hurt to discover later, he gave to many others, was about claiming and reclaiming the city in which he had been born, the sea in which he had swum as a boy, and the home he had been forced to flee in 1948. On his own first visit in 1991, he’d asked friends to take him there. Initially he was disoriented. Most of the landmarks weren’t there. The neighborhood by the sea where he’d grown up had been razed by then, though twenty years earlier his brother had done what so many Palestinians have done and described: knocked on the door to find out which Jews—Russian, Moroccan, Yemeni, Polish—were now living in their old family homes. Suddenly, my father said he had spotted the Hasan Bek mosque where he had made the call to prayer as a boy. Bit by bit, circling more widely around the mosque, he began to find his way.
It was a former student of his who had made him rethink his refusal to go back. She often traveled to Israel and the Occupied Territories. He recalled that she had told him once, “Ibrahim, Palestine is still there.” He was happy, he said, to find this true. There is an image in one of Doris Lessing’s African Stories (1981) that has never left me. A young girl, a white settler living in southern Africa, looks out over the savanna and acacia trees and sees the large gnarled oak trees of her English fairytales. My father did the opposite. Where I, who never knew anything else, could see only the deep gouges in green hillsides made for Israeli settlements with garish red tile roofs, or miles and miles of highways criss-crossing the rocky landscape and claiming it with modern green signs in Hebrew and English, or non-native evergreen forests to hide razed villages, my father saw beyond, between and behind them to the familiar landscapes of his youth.
– Return to Half-Ruins: Father's and Daughters Memory and History in Palestine by Leila Abu-Lughod.
#newpad.txt#Palestine#I read this for a class and felt Abu-Lughods work is like... something folks need to read
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
One consistent insistence by Antizionists that has repeatedly puzzled and confounded many Jews and Israelis over the last few months since 7/10 is the often-repeated assertion that there are "Jewish Palestinians under attack by Israel in Gaza" in its full formulation, or more concisely, that there are "Palestinian Jews".
At first, most of us waved this off as simply an indicator of complete ignorance of the conflict and history of the region, and assumed that they were referring to A) "Jews who are part of the Palestinian nation-people", who exist in extremely, extremely limited numbers through intermarriage and the like, B) some kind of misconception on pre-1948 Jews who were residents of the British Mandate of Palestine, and before that the Ottoman province, or C) Jewish residents of Gaza who self-identify as Palestinians.
C seemed to be the group that was most understood as correct upon cross-examination of people making these assertions, but, being blunt...
There are no members of Group C.
All Jews were removed from Gaza by Israel in 2006, many by force, and the territory was handed over to the Palestinians entirely. There are approximately 1000-2000 Palestinian Arab Christians in the Gaza Strip, with the remaining 99.8% of the population being Sunni Muslim. The only Jews currently in Gaza are hostages held by Hamas and the IDF soldiers who are deployed there, and none of them identify as Palestinians.
But despite this topic being repeatedly and easily debunked, the claim persists among antizionists. The question is why? Not that there is disinformation in play--this entire conflict has been the subject of concerted disinformation campaigns that can be easily disproven by a glance at Wikipedia without any need for deeper research. The "why" here is "what propagandistic/narrative purpose does this claim serve?"
And the primary reasons we can come up with are less than great.
First, claiming that there are "Palestinian Jews" in Gaza allows for the invention of a perfect ideological victim being persecuted by the "racist, White Supremacist, fascist" state of Israel--i.e. they undermine the Israeli claim that the state exists for the protection of Jews.
Second, related to the first, they allow for the Antizionist promoting the theory to avoid facing the antisemitism endemic in the Antizionist movement--by positioning themselves as acting in defense of or advocacy for a (fictitious) Jewish Palestinian, then they can't be antisemitic, just "antizionist".
Third, by claiming that there are Palestinian Jews, it means that Jews are welcome and free to practice their religion in Palestine (and ties into the belief that Judaism is "just a religion"), meaning that "Zionists" are overly paranoid White Supremacists moaning about "the Great Replacement" and "White Genocide" like all other White Supremacists out there, and their concerns about Jewish survival in a hypothetical post-Israel Palestinian state under the governance of Hamas or the PFLP are unfounded and thus there is no need for Israel.
Fourth, and most disturbingly, if there are Jewish Palestinians in Gaza under Hamas' governance, then that proves, to the antizionist, that Hamas truly are freedom fighters working to expand and free their idealized multi-racial, multi-religious democratic Palestinian State from the White Supremacist Racist Zionists who are oppressing everyone, including Jews. (Instead of, you know, terrorists who oppress Gazans and want to kill all Jews everywhere).
In essence, it's a Big Lie. It seems absurd, outrageous even, to just... make up an entire demographic of people for political/ideological purposes, but the fact is, there are concrete and understandable reasons for why people both make it up in the first place, and spread it afterwards...
And those reasons boil down to, "Because we want to believe it, and it fits with the way we want the world to work."
693 notes
·
View notes
Text
Most Afro-Palestinians in this tight-knit community came to the region as religious pilgrims during the British Mandate for Palestine, and many have been part of the Palestinian resistance movement since Israel’s establishment in 1948. Others arrived as volunteers with the Egyptian army to fight against Zionist militias taking control of historic Palestine during the Arab-Israeli war.
The community has played a pivotal role in the history of Palestinian resistance. Locals say that the first Palestinian woman to be imprisoned for a paramilitary operation against Israel was Fatima Barnawi, a Nigerian-Palestinian detained in 1967 for the attempted bombing of an Israeli cinema in West Jerusalem.
Yet decades later, Afro-Palestinian youth continue to live their daily lives under Israeli control.
At just 17, Abdallah’s cousin, Jibrin, has already been detained five times by Israeli forces, mostly over allegations that he threw stones at Israeli police and military officers. While he and his friends face the same harassment as other Palestinians, he said, they sometimes experience “double-racism” for both being Palestinian and having dark skin.
“The soldiers are always cursing at me and interrogating me when I pass them. They try to provoke me so that I do something they could get me in trouble for,” Jibrin told Al Jazeera, noting that he has been beaten several times by Israeli police and soldiers during detentions.
“Most of those in my generation have the same experiences,” he added with a shrug. “It’s routine.”
#free palestine#palestinian prisoners' day#genocide#antiblackness#prison abolition#police abolition#abolition#zionist colonization#settler colony of israel
304 notes
·
View notes
Text
Me: I don’t deny your identity. I acknowledge Palestinians exist today.
Them: Jesus was a Palestinian, not a Jew!
Me: Well, no - he was a Jewish rabbi. He had a bris, kept Shabbat, kept kosher, & his “Last Supper” was a Passover Seder. Besides, nobody would be called “Palestinian” for ~1,900 years after #Jesus died.
Them: Jews are #Khazars with no history in Palestine!
Me: Well, no - millions of DNA samples have now scientifically proven that Ashkenazi Jews (like their Sephardi & Mizrahi brothers & sisters) originate from the Levant (Israel).
Ashkenazi Jews migrated to the Rhineland (western #Germany) between 800-900 CE.
#Yiddish - the language spoken by #Ashkenazi Jews for a millennia - is a mixture of Jews’ original Hebrew & adopted #German.
Meanwhile, there is no evidence of any Khazar influence on Ashkenazi customs, language, or culture.
The #Khazar tale (claiming some or many Turkic Khazars converted to #Judaism), while interesting, is not supported by any archeological evidence, and can be considered nothing more than a story.
Besides, it’s unassailable that the Ashkenazim were living ~1,500 miles from the Khazars, which may as well have been on the moon in the Middle Ages.
Them: Palestinians are Canaanites, the original inhabitants of the Land!
Me: Well, no - there’s zero evidence the Palestinians are Canaanites. This theory followed other similarly false claims over the past several decades that the Palestinians descend from the Philistines (an ancient Aegean Greek “sea people”) and even the Jebusites - a people for whom there is no evidence outside of the Bible of their having ever existed (if they did, they have been gone for at least 3,000 years).
One thing is clear, all of these recent tall tales about Palestinians’ ancient roots in “Palestine” were created in an attempt to delegitimize the State of Israel & not as some academic attempt to find Palestinian roots.
The #Canaanites (who spoke a language similar to #Hebrew, not #Arabic) have been extinct for more than 3,000 years; and there are no #Canaanite influences in any modern Palestinian language, culture, cuisine, customs, or religion.
Furthermore, DNA studies now prove Canaanites are closest in descension to modern-day Armenians & Western Iranians - but, culturally, there has not been a “Canaanite” people in ~3,000 years.
Meanwhile, there is a practically infinite amount of archeological, biblical & non-biblical text, and architectural evidence proving beyond any doubt that Jews lived in the Land of Israel continuously for more than 3,200 years.
Arabs only started arriving in Eretz Israel in significant numbers during the Arab Imperial conquest out of the deserts of the Arabian Peninsula in the mid 7th century CE when the Land was still majority-occupied by ~350,000 Jews.
Arab conquerers #colonized the Land of Israel & subjugated the Jewish majority.
That’s right, the Arabs were the #colonizers - this is historical fact no matter how much that might make your head hurt.
Them: The Jews are foreigners who stole Palestinian land!
Me: Ok, now you’ve officially ticked me off by repeatedly denying MY identity - one that was OBVIOUS to everyone before the last ~55 years when KGB-inspired propaganda went into mass effect in an effort to delegitimize Israel.
Can’t say the same about your identity … even though I keep trying to offer to respect it!
The Arabs only ruled Eretz Israel after conquering it in the 7th century & until they were kicked out by the Seljuks ~400 years later. Never during that time, did they even attempt to establish an Arab or #Muslim state or capital anywhere in Eretz Israel (Jerusalem is never mentioned in the Koran, and while the city is holy to Sunni Muslims, it is not holy to Shia Muslims).
And during the time of Arab rule, there was obviously no state or country called “Palestine.”
Then, during the 400 years before the start of the British Mandate around 1920, the Land was a distant & severely neglected province of the Ottoman #Turkish Empire.
In fact, in the late 19th century, as Jews began moving back to their homeland in larger numbers, there were only ~200,000 people living there (mostly a sparse, nomadic population), and Jews were the majority in #Jerusalem.
Post-WWI, the League of Nations (the precursor to the UN) legally granted Britain a "sacred trust" called the Mandate for Palestine (a name given to the land by Roman Emperor Hadrian in 135 CE).
The Mandate for Palestine was the least controversial of the 15 post-WWI mandates because everyone KNEW Jews were from “Palestine.”
So the Mandate for Palestine, which included the legal requirement for Britain to aid in the establishment of a Jewish National Home, passed unanimously by the League of Nations.
Among other things, the unanimously passed & legally-binding Mandate recognized “the historical connection of the Jewish people with Palestine and to the grounds for reconstituting their national home in that country.”
Besides, before the Jews started returning to the Land in large numbers in the late 19th century, it had become almost entirely war-torn ruins, arid desert & malarial swamps.
But the returning Jews were determined to rebuild their homeland; and the evidence is undeniable that Jewish labor & the Western technology they brought along helped to make the desert bloom again.
The result of a new booming economy in the midst of mostly rural, undeveloped land is no surprise; and hundreds of thousands of Arabs from neighboring lands immigrated to Mandate Palestine in the early to mid 20th century.
In fact, once Arabs began to rebel against the Jews (with pogroms & full-blown barbaric massacres on a particularly wide scale in 1920, 1921, 1929, and in 1936-1939), they made extremely clear to the British that they resented the name “Palestine,” which they claimed (incorrectly) was a modern Zionist invention.
For example, at the British Peel Commission in 1937 (looking into Arab riots from the year before), local Arab leader Audi Bey Abdul-Hadi testified that “[t]here is no such country [as Palestine]! Palestine is a term the Zionists invented!”
Again, during the 1946 Anglo-American Committee of Inquiry that was set-up to make recommendations for the territory, Arab-American historian Philip Hitti testified, “There is no such thing as Palestine in [Arab] history, absolutely not.”
The Arab position was not particularly surprising, as "Palestine” is not an Arab word (Arabic does not even have a letter “P” or a sound for “P,” which is why you often hear Arabs today pronounce it with a “B” as “Balastine”).
The Arabs in the Land at that time mostly identified with their local clan & otherwise considered themselves “Arabs” of “Southern Syria.”
In fact, just about anyone who was called a “Palestinian” pre-1948 was a #Jew.
This is why nobody made any attempt to create a “Palestinian state” during the 19 years between 1948 and 1967 in which #Egypt occupied #Gaza & #Jordan occupied the “#WestBank.”
The hard truth - even though I’m still acknowledging a #Palestinian people exists today - is that an Arab “Palestinian” identity was created for the first time in any signifiant way at the height of the Cold War in the mid-1960s & at the behest of the #Soviet#KGB, which wanted to expand its influence in the region, undermine the only democracy in the Middle East, and which had been repeatedly embarrassed by Israeli victories over invading Soviet-backed & Soviet-armed Arab states.
So the KGB wrote the ridiculous “Palestine Liberation Organization” (PLO) charter & molded Yasser Arafat at what was known as “KGB U” in #Moscow to use #terror & #propaganda to destabilize Israel.
Over the decades since then, many Arabs in the Land have come to self-identify as “Palestinians.”
Even among Palestinians today, however, many still identify with their clan over a separate “Palestinian” nationality (e.g., the clans do not intermarry & many are constantly engaged in some degree of violent conflict).
And the 2 million+ Arabs citizens of the State of Israel (who have equal protection under the law & more rights & privileges than they would have in any Arab and/or Muslim country on Earth) almost exclusively identify as either #Israeli-#Arabs or as simply #Israelis - not as #Palestinians.
Them: #Jews … I mean #Zionists … are bad, ok? Just ask the UN.
Me: Right. Just ask the #UN
Captain Allen
@CptAllenHistory
591 notes
·
View notes
Text
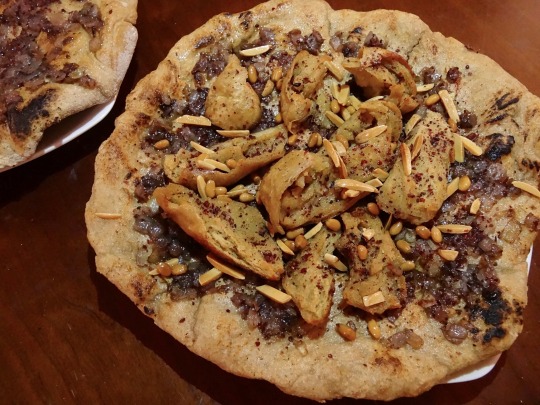


[ID: Two large flatbreads. The one in the center is topped with bright purple onions, faux chicken, fried nuts, and coarse red sumac; the one at the side is topped with onions and sumac. Second image is a close-up. End ID]
مسخن / Musakhkhan (Palestinian flatbread with onions and sumac)
Musakhkhan (مُسَخَّن; also "musakhan" or "moussakhan") is a dish historically made by Palestinian farmers during the olive harvest season of October and November: naturally leavened flatbread is cooked in clay ovens, dipped in plenty of freshly pressed olive oil, and then covered with oily, richly caramelized onions fragrant with sumac. Modern versions of the dish add spiced, boiled and baked chicken along with toasted or fried pine nuts and almonds. It is eaten with the hands, and sometimes served alongside a soup made from the stock produced by boiling the chicken. The name of the dish literally means "heated," from سَخَّنَ "sakhkhana" "to heat" + the participle prefix مُـ "mu".
I have provided instructions for including 'chicken,' but I don't think the dish suffers from its lack: the rich, slightly sour fermented wheat bread, the deep sweetness of the caramelised onions, and the true, clean, bright expressions of olive oil and sumac make this dish a must-try even in its original, plainer form.
Musakhkhan is often considered to be the national dish of Palestine. Like foods such as za'tar, hummus, tahina, and frika, it is significant for its historical and emotional associations, and for the way it links people, place, identity, and memory; it is also understood to be symbolic of a deeply rooted connection to the land, and thus of liberation struggle. The dish is liberally covered with the fruit of Palestinian lands in the form of onions, olive oil, and sumac (the dried and ground berries of a wild-growing bush).
The symbolic resonance of olive oil may be imputed to its history in the area. In historical Palestine (before the British Mandate period), agriculture and income from agricultural exports made up the bulk of the economy. Under مُشَاعْ (mushā', "common"; also transliterated "musha'a") systems of land tenure, communally owned plots of land were divided into parcels which were rotated between members of large kinship groups (rather than one parcel belonging to a private owner and their descendants into perpetuity). Olive trees were grown over much of the land, including on terraced hills, and their oil was used for culinary purposes and to make soap; excess was exported. In the early 1920s, Palestinian farmers produced 5,000 tons of olive oil a year, making an average of 342,000 PL (Palestinian pounds, equivalent to pounds sterling) from exports to Egypt alone.
During the British Mandate period (from 1917 to 1948, when Britain was given the administration of Palestine by the League of Nations after World War 1), acres of densely populated and cultivated land were expropriated from Palestinians through legal strongarming of and direct violence against, including killing of, فَلّاَحين (fallahin, peasants; singular "فَلَّاح" "fallah") by British troops. This continued a campaign of dispossession that had begun in the late 19th century.
By 1941, an estimated 119,000 peasants had been dispossessed of land (30% of all Palestinian families involved in agriculture); many of them had moved to other areas, while those who stayed were largely destitute. The agriculturally rich Nablus area (north of Jerusalem), for example, was largely empty by 1934: Haaretz reported that it was "no longer the town of gold [i.e., oranges], neither is it the town of trade [i.e., olive oil]. Nablus rather has become the town of empty houses, of darkness and of misery". Farmers led rebellions against this expropriation in 1929, 1933, and 1936-9, which were brutually repressed by the British military.
Despite the number of farmers who had been displaced from their land by European Jewish private owners and cooperatives (which owned 24.5% of all cultivated land in Palestine by 1941), the amount of olives produced by Palestinians increased from 34,000 tons in 1931 to 78,300 in 1945, evidencing an investment in and expansion of agriculture by indigenous inhabitants. Thus it does not seem likely that vast swathes of land were "waste land," or that the musha' system did not allow for "development"!
Imprecations against the musha' system were nevertheless used as justification to force Palestinians from their land. After various Zionist organizations and militant groups succeeded in pushing Britain out of Palestine in 1948—clearing the way for hundreds of thousands of Palestinians to be dispossessed or killed during the Nakba—the Israeli parliament began constructing a framework to render their expropriation of land legal; the Cultivation of Waste Lands Law of 1949, for example, allowed the requisition of uncultivated land, while the Absentees’ Property Law of 1950 allowed the state to requisition the land of people it had forced from their homes.
Israel profited from its dispossession of millions of dunums of land; 40,000 dunums of vineyards, 100,000 dunums of citrus groves, and 95% of the olive groves in the new state were stolen from Palestinians during this period, and the agricultural subsidies bolstered by these properties were used to lure new settlers in with promises of large incomes.
It also profited from the resulting "de-development" of the Palestinian economy, of which the decline in trade of olive oil furnishes a striking example. Palestinian olive farmers were unable to compete with the cheaper oils (olive and other types) with which Zionist, capital-driven industry flooded the market; by 1936, the 342,000 PL in olive oil exports of the early 1920s had fallen to 52,091 PL, and thereafter to nothing. While selling to a Palestinian captive market, Israel was also exporting the fruits of confiscated Palestinian land to Europe and elsewhere; in 1949, olives produced on stolen land were Israel's third-largest export. As of 2014, 12.9% of the olives exported to Europe were grown in the occupied West Bank alone.
This process of de-development and profiteering accelerated after Israel's military seizure of the West Bank and Gaza in 1967. In 1970, agriculture made up 34% of the GDP of the West Bank, and 31% of that of Gaza; in 2000, it was 16% and 18%, respectively. Many of those out of work due to expropriated or newly unworkable land were hired as day laborers on Israeli farms.
Meanwhile, Palestinians (and Israeli Palestinians) continued to plant and cultivate olives. The fact that Palestinians do not control their own water supplies or borders and may expect at any time to be barred by the military from harvesting their fields has discouraged investment and led to risk aversion (especially since the outmoding of the musha' system, which had minimized individual risk). In this environment, olive trees are attractive because they are low-input. They can subsist on rainwater (Israel monopolizes and poisons much of the region's water, and heavily taxes imports of materials that could be used to build irrigation systems), and don't require high-quality soil or daily weeding. Olive trees, unlike factories and agricultural technology, don't need large inputs of capital that stand to be wasted if the Israeli military destroys them.
Olive trees are therefore the chosen crop when proving a continued use of land in order to prevent the Israeli military from expropriating it under various "waste" or "absentee" land laws. Palestinians immediately plant olive seedlings on land they have been temporarily forced from, since even land that has lain fallow due to status as a military closed zone can be appropriated with this justification. The danger is so pressing that Palestinian agronomists encouraged this habit (as of 1993), despite the fact that Israeli competition and continual planting had lowered olive crop prices, and despite the decline in soil quality that results from never allowing land to lie fallow. In more recent years, olive trees have yielded primary or supplementary income for about 100,000 Palestinian families, producing up to 191 million USD in value in good years (including an average of 17,000 tons of olive oil yearly between 2001 and 2009).
Israeli soldiers and settlers have famously uprooted, vandalized, razed, and burned millions of these olive trees, as well as using military outposts to deny Palestinian farmers access to their olive crops. It prefers to restrict Palestinians to annual crops, such as vegetables and grains, and eliminate competition in permanent crops, such as fruit trees.
This targeting of olive trees increases during times of intensified conflict. During the currently ongoing olive harvest season (November 2023), Gazan olive farmers have reported being targeted by Israeli war planes; some farmers in the West Bank have given up on harvesting their trees altogether, due to threats issued by organized networks of settlers that they would kill anyone seen making the attempt.
The rootedness of olive trees in the history of Palestine gives them weight as a symbol of homeland, culture, and the fight for liberation. Palestinian olive harvest festivals, typically celebrated in October with singing, dancing, and eating, have inspired similar events elsewhere in the world, aimed at sharing Palestinian food and culture and expressing solidarity with those living under occupation.
Support Palestinian resistance by calling Elbit System’s (Israel’s primary weapons manufacturer) landlord, donating to Palestine Action’s bail fund, and donating to the Bay Area Anti-Repression Committee bail fund.
Ingredients:
For the dish:
2 pieces taboon bread, preferably freshly baked
2 large or 3 medium yellow onions (480g)
1 cup first cold press extra virgin olive oil (زيت زيتون البكر الممتاز)
1 Tbsp coarsely ground Levantine sumac (سماق شامي / sumaq shami), plus more to top
Ground black pepper
For the chicken (optional):
500g chicken substitute
5 green cardamom pods, or 1/4 tsp ground cardamom
4 cloves, or pinch ground cloves
1 Mediterranean bay leaf
1 Tbsp ground sumac
For the nut topping (optional):
2 Tbsp slivered almonds
2 Tbsp pine nuts
Neutral oil, for frying
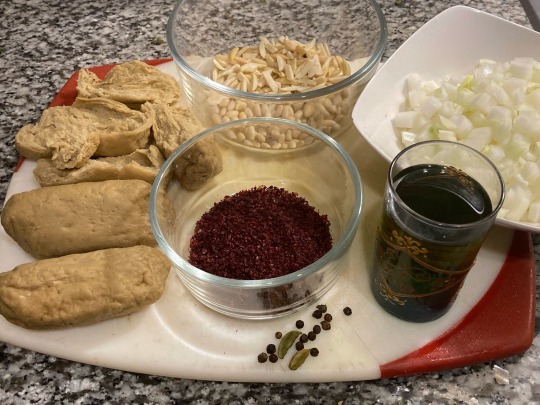

Notes on ingredients:
Use the best olive oil that you can. You will want oil that has some opacity to it or some deposits in it. I used Aleppo brand olive oil (7 USD a liter at my local halal grocery).

If you want to replace the taboon bread with something less laborious, I would recommend something that mimics the rich, fermented flavor of the traditional, whole-wheat, naturally leavened bread. Many people today make taboon bread with white flour and commercial yeast—which you might mimic by using storebought naan or lavash, for example—but I think the slight sourness of the flatbread is a beautiful counterpoint to the brightness of the sumac and the sweetness of the caramelized onions. I would go with a sourdough pizza crust or something similar.
Your sumac should be coarsely ground, not finely powdered; and a deep, rich red, not pinkish in color (like the pile on the right, not the one on the left).

For this dish, a whole chicken is usually first boiled (perhaps with spices including bay leaves, cardamom, and cloves) and then baked, sometimes along with some of the oil from frying the onions. I call for just frying or baking instead; in my opinion, boiling often has a negative effect on the texture of meat substitutes.
Instructions:
For the onions:
1. Heat a cup of olive oil in a large skillet or pot. Fry onions on medium-low, stirring often, for 10 minutes or until translucent.

2. Add 1 Tbsp sumac and a few cracks of black pepper and reduce to low. Cook for another 30 minutes, stirring occasionally, until onions are sweet, reduced in volume, and pinkish in color.
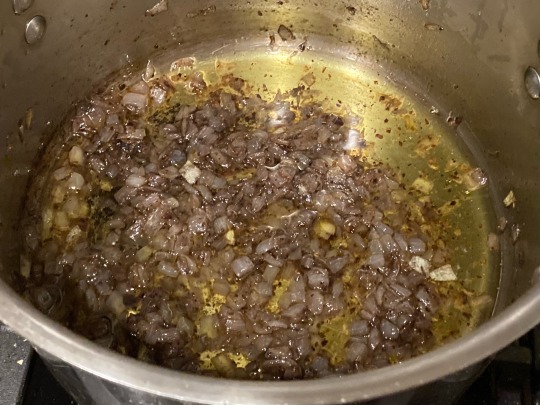

For the chicken:
1. Briefly toast and finely grind spices except for sumac (cardamom, cloves, and bay leaf). Filter with a fine mesh sieve. Dip 'chicken' into the pot in which you fried the onions to coat it with olive oil, then rub spices (including sumac) onto the surface.
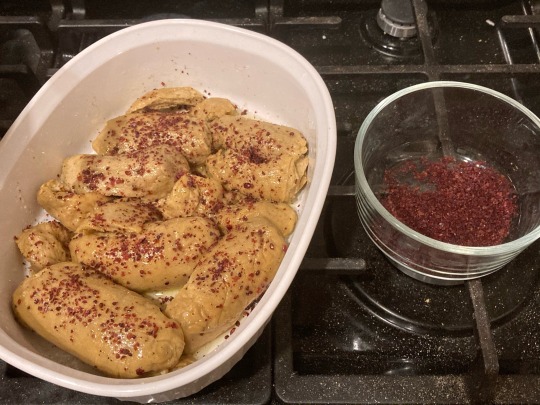

2. Sear chicken in a dry skillet until browned on all sides; or bake, uncovered, in the top third of an oven heated to 400 °F (200 °C) until browned.
For the nut topping:
1. Heat a neutral oil on medium in a small pot or skillet. Add almonds and fry for 2 minutes, until just starting to take on color. Add pine nuts and fry until both almonds and pine nuts are golden brown. Remove with a slotted spoon.
To assemble:
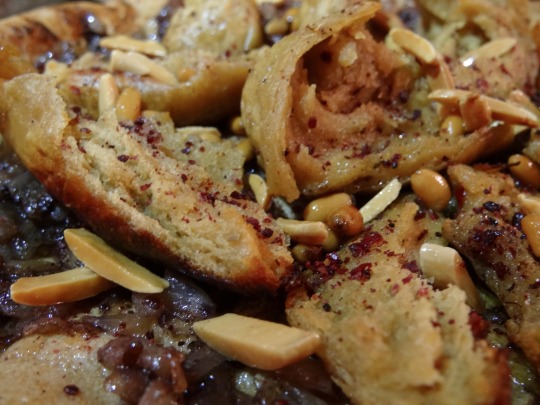
1. Dip each flatbread in the olive oil used to fry the onions, then spread onions over the surface.
Some cooks dip the bread entirely into oil; others press it lightly into the surface of the oil in the pot on both sides, or one side; a more modern method calls for mixing the olive oil with chicken broth to lighten it. Consult your taste. I think the bread from my taboon recipe stands up well to being pressed into the oil on both sides without tearing or becoming soggy.
2. Top flatbread with chicken and several large pinches more sumac. Bake briefly in the oven (still heated to 400 °F / 200 °C), or broil on low, for 3-5 minutes, until the sumac and the surface of the bread have darkened a shade.
3. Top with fried nuts.
Musakhkhan is usually eaten by ripping the chicken into bite-sized pieces, tearing off a bit of bread, and eating the chicken using the bread.
Some cooks make a layered musakhkhan, adding two to three pieces of bread covered with onions on top of each other before topping the entire construction with chicken and pine nuts.

670 notes
·
View notes
Note
hey sal feel free to ignore this but i got into an argument with a zionist who claimed that arabs sold their lands to them, is this true
This is interesting, because it ignores a lot of context. Keywords to remember is the Ottoman capitulation, the Felaheen, the Sursock purchase and the eviction of Palestinians that inhabited the area at that time.
The Sursock family was a family of Aristocratic landlords with strong ties to the Turkish and European nobility dating back to the 19th century. The Sursocks were known to have mass purchased land in Palestine from the Ottoman Turks. While they were absentee landlords, they hired Arab labours who inhabited the purchased land at that time. When the Turks capitulated following WW1, the Turks were pressured into allowing the land to be sold to the PLDC, the Palestinan (later Israeli) Land Development Company. The PLDC sought to purchase the Jezreel valley, which consisted of 20-25 Arab villages, from the Sursock. . Keep in mind that the Jezreel valley was the most fertile land of Palestine and close to the economic city of Haifa. Following the mass purchase of land by the PLDC, the Jewish landbuyers expelled Arab tenants and depopulated the Arab villages despite their usufruct, and right to toll on the land. This all came as a surprise to the Arab inhabitants. This was all part of the idea that cheap Arab labour should be replaced with Jewish labour, this despite the fact that Arab labourers had greater expertise on the agricultural field; the settlers were unfamiliar with the land. Keep in mind that according to JNF, the Jewish national fund, only 3% of the Palestinian land were uncultivated, destroying the myth that the land bloomed as a result of its settler colonizers. The Hashomer Hatzaeer would come to be the center of these kibbutzim and would establish over 30 kibbutzim built ontop of the Arab villages before 1948. As a result, the Arabs, or Felaheen (The Arab peasant class) put up a resistance against the JNF out of concrete material reasons and attempted to fight back against the expansion of these kibbutzim. This was the first instance of Arab resistance against Zionism.
All of these lands were purchased before 1948 and the Arabs were expelled and depopulated only for the kibbutzim to be established with the help of the money provided by the Jewish Colonization association and its organs. However, the British mandate did not require the landowners to compensate for the expelled Arab tenants. The Arabs were forced to migrate to slums and towns. In one of these towns, a notable Syrian resistance fighter would rise up, namely, Izz ad-Din al-Qassam, and declare jihad on the British. When the Arabs resisted their dispossession by every means necessary, even violence, the Zionists used this as an excuse to fortify their colonizers and expand them due to "escalating security needs". Since the colonizers were too weak to face the resistance, they turned themselves to the British to gain their support in an attempt to expand their lands as means of security for the Kibbutzim. In a memondarium written by the Kibbutz Hazora (a settlement in Jezreel) to the Jewish Agency in 1936: "Our basic demand is for our own instutions to help us ugently in getting the British authorities to expand our territory--this is a vital issue for us.". A similar pretext is used whenever the colonized put up resistance against their colonizers, in which the same excuse is used to further expand and colonize the lands. This is the logic of the oppressor in any context, whether it is colonial or in the class struggle.
317 notes
·
View notes
Text

Palestine women in 1940's protesting British colonialism and demanding to end the British mandate over Palestine.
489 notes
·
View notes
Text
What is important to understand about that moment was that Zionism was a political choice — not only by western imperial powers, but also by Jewish leadership. They could have fought more strenuously for Jewish immigration to the United States. And a lot of the Zionist leaders actually fought against immigration to the United States. There were a number of stories reported in the Jewish Communist press about how Zionists collaborated with the British and Americans to force Jews to go to Mandate Palestine, when they would have rather gone to the United States, or England. There’s a famous quote by Ernest Bevin, the British Foreign Secretary, who said the only reason the United States sent Jews to Palestine was “because they do not want too many more of them in New York.” And the Zionists agreed with this.
While this may seem like ancient history, it is important because it disrupts the common sense surrounding Israel’s formation. “Yes, maybe there could have been peace between Jews and Palestinians, but the Holocaust made all of that impossible.” And I would say that this debate after 1945 shows that there was a long moment in which there were other possibilities, and another future could have happened
[…]
Question: Who or what is responsible for the erasure of this history of Jewish, left anti-Zionism?
I wouldn’t blame the erasure solely on the Soviet Union or Zionism, because we also have to think of the Cold War and how the Cold War destroyed the old Jewish left, and really drove it underground and shattered its organizations. So I think we also have to see how the turn toward Zionism was understood as something that would normalize Jews in a post-war era.
With the execution of the Rosenbergs, the Red Scare of the late 1940s and ’50s, and the virtual banning of the Communist Party, which had been throughout the 1930s and ’40s half Jewish, for much of the Jewish establishment, aligning themselves with American imperialism was a way for Jews to normalize their presence in the United States. And hopefully that moment has to some degree passed. We can see the emptiness and barrenness of aligning ourselves with an American imperial project, with people like Bari Weiss and Jared Kushner. Why would someone like Bari Weiss, who describes herself as liberal, want to align herself with the most reactionary forces in American life?
It’s a bloody matrix of assimilation and whiteness that emerged out of the Cold War suburbanization of the 1950s. Israel was part of that devil’s bargain. Yes, you can become real Americans: You can go to good U.S. universities, you can join the suburbs, enter into the mainstream of American life, as long as you do this one little thing for us, which is back the American Empire. Hopefully, with the emergence of new grassroots organizations in the United States, among Jews and non-Jews who are questioning the U.S. role supporting Zionism, this calculus can begin to change. With the rise of Jewish Voice for Peace, IfNotNow, the Democratic Socialists of America and the Movement for Black Lives all taking a serious stance against U.S. support for Zionism, the common sense in the Jewish community has begun to move in a different direction, particularly among the younger generation. The battle is very far from over, but it makes me just a little optimistic about the future.”
- The Forgotten History of the Jewish Anti-Zionist Left
342 notes
·
View notes
Text
Safety is a real, material set of conditions: a roof over your head and freedom from violence or injury. British politicians aren’t at risk of being bombed or seeing their children dismembered. Yet it was their speculative safety in the spotlight while Palestinians under military assault became a footnote in the vote.
It’s true, of course, that two British MPs have been killed in recent years. But it’s a cheap shot for politicians to invoke their deaths to avoid engaging with the public about an ongoing genocide. When politicians say they feel unsafe in this context, they mean they feel uncomfortable being challenged by their constituents.
[...]
When discomfort is perceived as danger, protest is seen as harassment. And when political dissent is positioned as a threat to national security, our human rights are at risk. As sure as night follows day, when politicians begin to cite safety concerns, curtailment of democratic freedoms isn’t far behind. Civil liberties will always play second fiddle to securitisation. Judging by Sunak’s doublespeak at the lectern last Friday, the government plans to corrode our democracy under the guise of protecting it.
Sunak’s emergency address was an authoritarian wishlist written in Islamophobic ink: curtail protest rights; threaten to remove immigrants’ “right to be here” if they speak what is considered “hate” at protests; reference streets being “hijacked” by “extremists” and “redouble support” for surveillance programme Prevent. It was framed in response to pro-Palestine protests, but entrenches an established anti-Muslim, anti-protest agenda that promotes surveillance in the name of “safety”. The name of Sunak’s “Safety of Rwanda” bill shows us he already has a cynical definition of this word.
It’s curious how the social capital of playing the protector is often afforded to the violent perpetrators. If we use another very British example, the high-profile transphobic lobby that is obsessed with “women’s safety” has, in material terms, driven transphobic hate crimes to historic levels, but done nothing to end violence against women. In the same vein, it’s inevitable that Sunak’s measures to “combat the forces of division” will create even more far-right racism and state violence for Muslims.
The dominant force of division is, of course, the state itself. Trans people and Muslims alike are sociological folk devils; minority groups in society positioned as a threat to social order. The government’s self-authorised mandate to marshal these manufactured threats justifies state control for everyone. In reality, the marginalised groups identified as the enemy within face crushing systemic oppression already. If anyone is unsafe, it’s them.
201 notes
·
View notes
Note
Can you explain the Iran-Israel situation please?
Alright, let's get to it. Please note that I'm writing this on mobile during my lunch break, so I can't include reference/source links as much as I'd like. Thankfully, most of what I'm going to be telling you should be easily located by searching for an article on one of the following: APNews, Reuters, BBC Global News Podcast, Democracy Now!, NPR, or The New York Times. Long-term background is probably best found in videos by the YouTube channels Real Life Lore or tldr global news, or on Wikipedia if you prefer text.
The short version: Israel attacked Iran's consulate in Syria to get at some of the military commanders that were there, which is legally equivalent to attacking Iran itself. Iran responded by sending about 300 bombs at Israel, most of which were shot down in transit. Given that they still called it a success, even though it seems only one person was even hurt, my understanding is that it's very likely that they only intended the rockets to be a show of force, rather than an actual escalation, because Iran can't afford a war right now.
To support my blogging so I can move out of my parents’ house, I do have a ko-fi. Alternately, you can donate to one of the charities I list in this post OR this post.
The long version:
Okay, let's start with some background on Israel, then Iran. This is... a lot, so if you already know the broad strokes skip down to 2023.
Israel was established following WWII by the English and French, following borders the two countries had secretly drawn up decades earlier in the Sykes-Picot agreement. The intent was to give the Jewish people a place to go... or, depending on who you ask, a place to send them. Their ancestral homeland was viewed as the best choice, sort of like a deportation millennia after a diaspora. Given that WWII had just ended by the time Sykes-Picot was actually put into effect, 'getting out of Europe' was something a lot of Jews were given to agree with.
The Arab world was not happy, as that land had belonged to the Ottomans for centuries, and had long since 'naturalized' to being Arab. I'm not going to pretend to know the nuances to when people do or do not consider Palestine to have been its own nation; it was an Ottoman state until WWI, at which point it came under British control for just under three decades, and that period is known as the British Mandate of Palestine; it ended after WWII, with the creation of Israel. Palestine's land and people have sort of just been punted around from one colonizer to another for centuries.
Iran is the current form of what was once Persia. They were an empire for a very long time, and were a unitary monarchy up until the early 20th century; in 1925, Iran elected a Prime Minister who was then declared the monarch. The following several decades had Iran's monarchy slowly weakened, and occasionally beset by foreign interventions, including a covert coup by the US and UK in 1953. The country also became more corrupt throughout the 1970s due to economic policy failing to control inflation in the face of rising oil prices.
In 1979, there was a revolution that overthrew the monarchy and the elected government, replacing the system with a theocracy and declaring Iran to be an Islamic Republic, with the head of state being a religious authority, rather than an elected one. This was not popular with... most countries. 1980 saw the closure of all universities (reopened in 1983 with government-approved curriculums), as well as the taking of over fifty American hostages from the US Embassy in Iran. You may have heard about that in the context of Ronald Reagan encouraging Iran to keep the hostages until the end of Carter's term in order to force the election.
So, the West didn't like having an Islamic state because it claims to like democracy, and also because the Islamic state was explicitly anti-American and this has some Bad Effects on oil prices. The Soviets didn't like having an Islamic State because a theocracy goes directly against a lot of communist values (or at least the values they claim to have), and weakened any influence their supposedly secular union could have on Iran and the wider middle east. The other countries in the Arab world, many of them still monarchies, didn't like the Islamic republic because if the revolution spread, then it was possible their monarchies would be overthrown as well.
(Except Oman, which is not worried, but that's the exception, not the rule.)
This is not a baseless worry, because Iran has stated that this is its goal for the Arab world. Overthrow the monarchies, overthrow the elected governments, Islamic Rule for everyone. That is the purpose of its proxies, like Hezbollah (Lebanon), the Houthis (Yemen), and Hamas (Palestine), along with less well-known groups like the Salafi Jihadists in Mali, who are formally under the umbrella of al-Quaeda, which Iran denies having any relation to but is suspected of funding. In areas where these proxy groups have gained power, they are liable to enact hard Shari'a law such as has happened in Northern Mali and other parts of the Sahel region.
While other conflicts have occurred in these countries, I think the above is most relevant.
Israel has repeatedly attacked, or been attacked by, other nations in the middle east, as they are viewed as having taken over land that is not theirs, and as being a puppet of the US government. The biggest conflicts have been 1947-1948, 1968/1973, and 2014.
And then, of course, 2023.
Now, Iran, more than any other nation in the Middle East, hates Israel. They have for a very long time, viewing them as an affront to the goal of spreading Islam across the whole of the middle east, and as being a front and a staging ground for the United States and other Western powers. Two common refrains in the slogans of Iran and its proxies are "Death to America" and "Death to Israel."
Due to Iran's military power and virulence towards Israel, the United States has been funneling money to Israel for decades. It has more generally been to defend itself against the Arab world at large, but it has narrowed over the decades to being about Iran and its proxies as relations have normalized with other nations like Egypt and Saudi Arabia.
Cue October 7th, 2023. Hamas invades Israeli towns, kills some people, and takes others as hostage. Israel retaliates, and the conflict ramps up into what is by now tens of thousands of dead, some half of which are children.
In this time, Hamas's allies are, by definition, Iran and the other proxy forces. Hezbollah, being in Lebanon, share a border with Israel's north. They have been trading rocket fire across the border in waves for most of the past six months. The Houthis, down in Yemen, claim to be attacking the passing cargo ships in order to support Palestine. Given that the attacks often seem indiscriminate, and that the Houthi's control over their portion of Yemen is waning in the face of their poor governance, this is... debatable. It's their official reason, but given that "let's attack passing ships, claiming that we only attack Israeli or American ships and that it is to support Palestine" is rallying support domestically for their regime, it does seem to be more of a political move to garner support at home than about supporting Palestine.
Iran, however, has not attacked Israel. They've spoken out about it, yes, but they haven't done anything because nobody wants a regional war. Nobody can afford it right now. Iran is dealing with a domestic crisis due to oil subsidies bleeding the states' coffers dry, and the aging Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, the leader of Iran, refusing to pick a successor. They are looking at both an economic crisis and succession crisis, and a regional war would fuck up both situations further. Iran funds most of its proxies, and they can't do that, and fight a war on top of it, while their economy is in its current state. Pure self preservation says they don't want a war, especially with the ongoing unrest that's been going on for... well, basically since the revolution, but especially since the death of Mahsa Amini.
Meanwhile, in Israel, Netanyahu has been looking at corruption charges and legal issues since before the Hamas attack. It's generally agreed that if Israel were to hold new elections right now, he would lose and be replaced, and also immediately taken to court. Netanyahu wants to stay in power, and as long as the war on Hamas lasts, he is unlikely to get voted out. A change in leadership in the middle of a war is rarely a good idea for any country, and he's banking on that.
However, the war on Hamas rests on the shoulders of American money and supplies. Without that military support, Israel cannot fight this war, and America... is losing patience.
Officially, America and most of the western world have been telling Israel to not fucking escalate for the majority of the war.
There have been implied threats, more or less since Schumer's big speech about how Israel needs a new election, of American legislators putting conditions on any future aid. There have even been rumblings of aid being retracted entirely if Israel follows through on invading Raffah.
So...
American aid to Israel has, for a very long time, been given in the name of defending Israel against Iran and its proxies.
Israel has been fighting this war against Hamas for six months, killing what is by now innumerable civilians, on the power of US military aid.
Netanyahu benefits from the continued war due to domestic troubles.
Iran does not want a regional war, or really any big war, due to its own domestic troubles.
The US is, in theory, losing patience with Israel and threatening to pull the plug on unconditional support. It's very "we gave you this to fight Iran. Stop attacking civilians. If you keep attacking civilians, then you're going to have to rely on what we already gave you to fight off Iran so that you won't keep wasting it on civilians."
Israel... attacks Iran, prompting a response, and is now talking about escalating with Iran.
I am not explicitly saying that it looks to me like Israel, which is already fighting a war on two physical fronts and even more political/economic ones, has picked a fight with Iran so that America feels less like it is able to withdraw support.
I just... am finding it hard to understand why Israel, which is in fact fighting both Hamas and Hezbollah, would attack the Iranian consulate in Syria otherwise. They can't actually afford to fight this war, escalating to a full regional conflict, on a third front.
Not without pressuring American into keeping the faucet of military funding open at full blast.
To support my blogging so I can move out of my parents’ house, I do have a ko-fi. Alternately, you can donate to one of the charities I list in this post OR this post.
#phoenix politics#current events#iran#israel#hamas#houthis#hezbollah#syria#politics#united states#military funding#military aid
93 notes
·
View notes
Note
loving your falafel research saga and just wanted to ask - something I remember hearing about falafel is that while Israeli culture definitely appropriated it, the concept of serving it in pita bread with salads, tahini etc. is a specifically Israeli twist on the dish. I wonder if you found/know anything about that?
The short answer is: it's not impossible, but I don't think there's any way to tell for sure. The long answer is:
The most prominent claim I've heard of this nature is specifically that Yemeni Jews (who had immigrated to Israel under 'right of return' laws and were Israeli citizens) invented the concept of serving falafel in "pita" bread in the 1930s—perhaps after they (in addition to Jews from Morocco or Syria) had brought falafel over and introduced it to Palestinians in the first place.
"Mizrahim brought falafel to Palestine"
This latter claim, which is purely nonsense (again... no such thing as Moroccan falafel!)—and which Joel Denker (linked above) repeats with no source or evidence—was able to arise because it was often Mizrahim who introduced Israelis to Palestinian food. Mizrahi falafel sellers in the early 20th century might run licensed falafel stands, or carry tins full of hot falafel on their backs and go from door to door selling them (see Shaul Stampfer on a Yemeni man doing this, "Bagel and Falafel: Two Iconic Jewish Foods and One Modern Jewish Identity," in Jews and their Foodways, p. 183; this Arabic source mentions a 1985 Arabic novel in which a falafel seller uses such a tin; Yael Raviv writes that "Running falafel stands had been popular with Yemenite immigrants to Palestine as early as the 1920s and ’30s," "Falafel: A National Icon," Gastronomica 3.3 (2003), p. 22).
On Mizrahi preparation of Palestinian food, Dafna Hirsch writes:
As Sami Zubaida notes, Middle Eastern foodways, while far from homogeneous, are nevertheless describable in a vocabulary and set of idioms that are “often comprehensible, if not familiar, to the socially diverse parties” [...]. Thus, for the Jews who arrived in Palestine from the Middle East, Palestinian Arab foods and foodways were “comprehensible, if not familiar,” even if some of the dishes were previously unknown to most of them. [...] They found nothing extraordinary or exotic in the consumption, preparation, and selling of foods from the Palestinian Arab kitchen. Therefore, it was often Mizrahi Jews who mediated local foods to Ashkenazi consumers, as street food vendors and restaurant owners. ("Urban Food Venues as Contact Zones between Arabs and Jews during the British Mandate Period," in Making Levantine Cuisine: Modern Foodways of the Eastern Mediterranean, p. 101).
Raviv concurs and furnishes a possible mechanism for this borrowing:
Other Mizrahi Jewish vendors sold falafel, which by the late 1930s had become quite prevalent and popular on the streets of Tel Aviv. [...] Tel Aviv had eight licensed Mizrahi falafel vendors by 1941 and others who sold falafel without a license. [FN: The Tel Aviv municipality granted vending license to people who could not make their living in any other way as a form of welfare.] Many of the vendors were of Yemenite origins, although falafel was unknown in Yemen. [FN: Many of the immigrants from Yemen arrived in Palestine via Egypt, so it is possible that they learned to prepare it there and then adjusted the recipe to the Palestinian version, which was made from chickpeas and not from fava beans (ṭaʿmiya). Shmuel Yefet, an Israeli falafel maker, tells about his father, Yosef Ben Aharon Yefet, who arrived in Palestine from Aden [Yemen] in the early 1920s and then traveled to Port Said in 1939. There he became acquainted with ṭaʿmiya, learned to prepare it, and then went back to Palestine and opened a falafel shop in Tel Aviv [youtube video].]*
But why claim that Yemeni Jews invented falafel (or at least that they had introduced it from Yemen), even though its adoption from Palestinian Arabs in the early days of the second Aliya, aka the 1920s (before Mizrahim had begun to immigrate in larger numbers; see Raviv, p. 20) was within living memory at this point (i.e. the 1950s)? Raviv notes that an increasing (I mean, actually she says new, which... lol) negative attitude towards Arabs in the wake of the Nakba (I mean... she says "War of Independence") created a new sense of urgency around de-Arabizing "Israeli" culture (p. 22). Its association with Mizrahi sellers allowed falafel to "be linked to Jewish immigrants who had come from the Middle East and Africa" and thus to "shed its Arab association in favor of an overarching Israeli identification" (p. 21).
Stampfer again:
On the one hand (with regard to immigrants from Eastern Europe), [falafel] underscored the break between immediate past East European Jewish foods and the new “Oriental” world of Eretz Israel.** At the same time, this food could be seen as a link with an (idealized) past. Among the Jewish public in Eretz Israel, Yemenite falafel was regarded as the most original and tastiest version. This is a bit odd, as falafel—whether in or out of a pita—was not a traditional Yemenite food, neither among Muslims nor among Jews. To understand the ascription of falafel to Yemenite Jews, it is necessary to consider their image. Yemenite Jews were widely regarded in the mid-20th century as the most faithful transmitters of a form of Jewish life that was closest to the biblical world—and if not the biblical world, at least the world of the Second Temple, which marked the last period of autonomous Jewish life in Eretz Israel. In this sense, eating “Yemenite” could be regarded as an act of bodily identification with the Zionist claim to the land of Israel. (p. 189)
So, when it's undeniable that a food is "Arab" or "Oriental" in origin, Zionists will often attribute it to Yemen, Syria, Morocco, Turkey, &c.—and especially to Jewish communities within these regions—because it cannot be permitted that Palestinians have a specific culture that differentiates them in any way from other "Arabs." A culinary culture based in the foodstuffs cultivated from this particular area of land would mean a tie and a claim to the land, which Zionist logic cannot allow Palestinians to possess. This is why you'll hear Zionists correct people who say "Palestinians" to say "Arab" instead, or suggest that Palestinians should just scooch over into other "Arab" countries because it would make no difference to them. Raviv's conclusion that the attribution of falafel to Yemeni immigrants is an effort to detach it from its "Arab" origins isn't quite right—it is an attempt to detach it, and thus Palestinians themselves, from Palestinian roots.
"Yemeni Jews first put falafel in 'pita'"
As for this claim, it's often attributed to Gil Marks: "Jews didn’t invent falafel. They didn’t invent hummus. They didn’t invent pita. But what they did invent was the sandwich. Putting it all together.” (Hilariously, the author of the interview follows this up with "With each story, I wanted to ask, but how do you know that?")
Another author (signed "Philologos") speculates (after, by the way, falsely claiming that "falafel" is the plural of the Arabic "filfil" "pepper," and that falafel is always brown, not green, inside?!):
Yet while falafel balls are undoubtedly Arab in origin, too, it may well be that the idea of serving them as a street-corner food in pita bread, to which all kinds of extras can be added, ranging from sour pickles to whole salads, initially was a product of Jewish entrepreneurship.
Shaul Stampfer cites both of these articles as further reading on the "novelty of the combination of pita, falafel balls, and salad" (FN 76, p. 198)—but neither of them cites any evidence! They're both just some guy saying something!
Marks had, however, elaborated a little bit in his 2010 Encyclopedia of Jewish Food:
Falafel was enjoyed in salads as part of a mezze (appetizer assortment) or as a snack by itself. An early Middle Eastern fast food, falafel was commonly sold wrapped in paper, but not served in the familiar pita sandwich until Yemenites in Israel introduced the concept. [...] Yemenite immigrants in Israel, who had made a chickpea version in Yemen, took up falafel making as a business and transformed this ancient treat into the Israeli iconic national food. Most importantly, Israelis wanted a portable fast food and began eating the falafel tucked into a pita topped with the ubiquitous Israeli salad (cucumber-and-tomato salad).
He references one of the pieces that Lillian Cornfeld (columnist for the English-language, Jerusalem-based newspaper Palestine Post) wrote about "filafel":
An article from October 19, 1939 concluded with a description of the common preparation style of the most popular street food, 'There is first half a pita (Arab loaf), slit open and filled with five filafels, a few fried chips and sometimes even a little salad,' the first written record of serving falafel in pita. [Marks doesn't tell you the title or page—it's "Seaside Temptations: Juveniles' Fare at Tel Aviv," p. 4.]
You will first of all notice that Marks gives us the "falafel from Yemen" story. I also notice that he calls Salat al-bundura "Israeli salad" (in its entry he does not claim that European Jewish immigrants invented it, but neither does he attribute it to Palestinian influence: the dish was originally "Turkish coban salatsi"). His encyclopedia also elsewhere contains Zionist claims such as "wild za'atar was declared a protected plant in Israel" "[d]ue to overexploitation" because of how much of the plant "Arab families consume[d]," and that Israeli cultivation of the crop yielded "superior" plants (entry for "Za'atar")—a narrative of "Arab" mismanagement, and Israeli improvement, of land used to justify settler-colonialism. He writes that Palestinians who accuse "the Jews" of theft in claiming falafel are "creat[ing] a controversy" and that "food and culture cannot be stolen," with no reflection on the context of settler-colonialism and literal, physical theft that lies behind said "controversy." This isn't relevant except that it makes me sceptical of Marks's motivations in general.
More pertinent is the fact that this quote doesn't actually suggest that this falafel vendor was Yemeni (or otherwise) Jewish, nor does it suggest that he was the first one to prepare falafel in pitas with "fried chips," "sometimes even a little salad," and "Tehina, a local mayonnaise made with sesame oil" (Cornfeld, p. 4). I think it likely that this food had been sold for a while before it was described in published writing. The idea that this preparation is "Israeli" in origin must be false, since this was before the state of "Israel" existed—that it was first created by Yemeni Jewish falafel vendors is possible, but again, I've never seen any direct evidence for it, or anyone giving a clear reason for why they believe it to be the case, and the political reasons that people have for believing this narrative make me wary of it. There were Palestinian Arab falafel vendors at this time as well.
"Chickpea falafel is a Jewish invention"
There is also a claim that falafel originated in Egypt, where it was made with fava beans; spread to the Levant, including Palestine, where it was made with a combination of fava beans and chickpeas; but that Jewish immigration to Israel caused the origin of the chickpea-only falafal currently eaten in Palestine, because a lot of Jewish people have G6PD deficiencies or favism (inherited enzymatic deficiencies making fava beans anywhere from unpleasant to dangerous to eat)—or that Jewish populations in Yemen had already been making chickpea-only falafel, and this was the falafel which they brought with them to Palestine.
As far as I can tell, this claim comes from Joan Nathan's 2001 The Foods of Israel:
Zadok explained that at the time of the establishment of the state, falafel—the name of which probably comes from the word pilpel (pepper)—was made in two ways: either as it is in Egypt today, from crushed, soaked fava beans or fava beans combined with chickpeas, spices, and bulgur; or, as Yemenite Jews and the Arabs of Jerusalem did, from chickpeas alone. But favism, an inherited enzymatic deficiency occurring among some Jews—mainly those of Kurdish and Iraqi ancestry, many of whom came to Israel during the mid 1900s—proved potentially lethal, so all falafel makers in Israel ultimately stopped using fava beans, and chickpea falafel became an Israeli dish.
Gil Marks's 2010 Encyclopedia of Jewish Food echoes (but does not cite):
Middle Eastern Jews have been eating falafel for centuries, the pareve fritter being ideal in a kosher diet. However, many Jews inherited G6PD deficiency or its more severe form, favism; these hereditary enzymatic deficiencies are triggered by items like fava beans and can prove fatal. Accordingly, Middle Eastern Jews overwhelmingly favored chickpeas solo in their falafel. (Entry for "Falafel")
The "centuries" thing is consistent with the fact that Marks believes falafel to be of Medieval origin, a claim which most scholars I've read on the subject don't believe (no documentary evidence, + oil was expensive so it seems unlikely that people were deep frying anything). And, again, this claim is speculation with no documentary evidence to support it.
As for the specific modern toppings including the Yemeni hot sauce سَحاوِق / סְחוּג (saHawiq / "zhug"), Baghdadi mango pickle عنبة / עמבה ('anba), and Moroccan هريسة / חריסה ("harissa"), it seems likely that these were introduced by Mizrahim given their place of origin.
*You might be interested to know that, despite their Jewishness mediating this borrowing, Mizrahim were during the Mandate years largely ethnically segregated from Eastern European Zionists, who were pushing to create a "new" European-Israeli Judaism separate from what they viewed as the indolence and ignorance of "Oriental" Jewishness (Hirsch p. 101).
This was evidenced in part by Europeans' attitudes towards the "Oriental" diet. Ari Ariel, summarizing Yael Raviv's Falafel Nation, writes:
Although all immigrants were thought to require culinary education as an aspect of their absorption into the new national culture, Middle Eastern Jews, who began to immigrate in increasing numbers after 1948, provoked greater anxiety on the part of the state than did their Ashkenazi co-religionists. Israeli politicians and ideologues spoke of the dangers of Levantization and stereotyped Jews from the Middle East and North Africa as primitive, lazy, and ignorant. In keeping with this Orientalism, the state pressured Middle Easterners to change their foodways and organized cooking demonstrations in transit camps and new housing developments. (Book review, Israel Studies Review 31.2 (2016), p. 169.)
See also Esther Meir-Glitzenstein, "Longing for the Aromas of Baghdad: Food, Emigration, and Transformation in the Lives of Iraqi Jews in Israel in the 1950s," in Jews and their Foodways:
[...] [T]he Israeli establishment was set on “educating” the new immigrants not only in matters of health and hygiene, [77] but also in the realm of nutrition. A concerted propaganda effort was launched by well-baby clinics, kindergartens, schools, health clinics, and various organizations such as the Women’s International Zionist Organization (WIZO) and the Organization of Working Mothers in order to promote the consumption of milk and dairy products, in particular. [78] (These had a marginal place in Iraqi cuisine, consumed mainly by children.) Arab and North African cuisines were criticized for being not sufficiently nutritious, whereas the Israeli diet was touted as ideal, as it was western and modern. […] [T]he assault on traditional Middle Eastern cuisines reflected cultural arrogance yet another attempt to transform immigrants into “new Jews” in accordance with the Zionist ethos.
Thus, European table manners were presented as the norm. Eating with the hands was equated with primitive behavior, and use of a fork and knife became the hallmark of modernity and progress. (pp. 100-101)
[77. On health matters, see Davidovich and Shvarts, “Health and Hegemony,” 150–179; Sahlav Stoller-Liss, “ ‘Mothers Birth the Nation’: The Social Construction of Zionist Motherhood in Wartime in Israeli Parents’ Manuals,” Nashim 6 (Fall 2003), 104–118.]
[78. On propaganda for drinking milk and eating dairy products, see Mor Dvorkin, “Mif’alei hahazanah haḥinukhit bishnot ha’aliyah hagedolah: mekorot umeafyenim” (seminar paper, Ben-Gurion University, 2010).]
**On the desire to shed "old, European" "Jewish" identity and take on a "new, Oriental" "Hebrew" one, and the contradictory impulses to use Palestinian Arabs as models in this endeavour and to claim that they needed to be "corrected," see:
Itamar Even-Zohar, "The Emergence of a Native Hebrew Culture in Palestine, 1882—1948"
Dafna Hirsch, "We Are Here to Bring the West, Not Only to Ourselves": Zionist Occidentalism and the Discourse of Hygiene in Mandate Palestine"
Ofra Tene, "'The New Immigrant Must Not Only Learn, He Must Also Forget': The Making of Eretz Israeli Ashkenazi Cuisine."
#sorry for this but you should've known better than to ask me about falafel at this stage in my life#falafel research saga
146 notes
·
View notes
Note
How can you claim that Zionism was morally right, when what it was was European Jews coming to Palestine by the thousands and buying land, and when the Arabs realised what they were trying to do, i.e. steal land by making it sound reasonable to the British they should have the right to self determination, they rightfully tried to put a stop to it? If a lot of people come into a populated area and then ask for it to be given to them, since they’re so many, does it make it right for the people who were already there? And yeah, it’s true there was some Jewish presence there already but it wasn’t that much and it wasn’t them who started the Zionist movement. So how can you claim this was right?
You just said they were buying the land, and they were, so anyone thinking they were stealing it is already revealing major problems with racism, xenophobia, and conspiratorial thinking.
And by all means, let's talk about "immigrants" versus "people who were already there." From the 1850s to 1920s, the Ottoman Empire faced waves of refugee crises (the Crimean War, the Balkan Wars, the Russo-Turkish War, the Austro-Hungarian occupation of Bosnia-Herzegovina, and the beginning of World War 1) and decided to resettle OVER FIVE MILLION Muslim refugees all throughout its Mediterranean and Levant provinces. They sent hundreds of thousands of ex-Balkan and ex-Russian Muslims into southern Syria and what is now Jordan. These refugees founded the four largest cities in Jordan, including its capital Amman; of course, Jordan had been part of historic Palestine and the Palestine Mandate, and from the very first day they were able to govern themselves they passed laws banning any Jewish citizenship or inhabitation.
Am I supposed to see that as anything other than the most base, ladder-pulling racism? Do you really expect me to care that ex-Russian Muslims arriving in Jaffa in 1890 wanted to keep the ex-Polish Jews out in 1920? Between the Ottoman refugee resettlement and the large numbers of Arabs immigrating to benefit from new economic opportunities in a rapidly developing Palestine, the United Nations would later come to classify people as "refugees of the 1948 war" if they had been permanent inhabitants of Palestine any time before 1946. So many newcomers that just living there for two years made you a wizened, old-timer local, with a perfectly natural right to say nobody else can come in.
Where exactly are you starting history and whose immigration are you seeing as rightful, as just? In 1832, Egypt invaded Ottoman Palestine and established from nothing the new settler town of Abu Kabir; in 1948, Zionist militias depopulated it. Were the Arab settlers of Abu Kabir "indigenous" for the 116 years they were there? Because the major waves of Jewish immigration to Palestine started about 140 years ago....
There is no such thing as a legitimate history of the Levant that sees it as normal and morally / politically neutral for millions of Muslims to be resettled by various Muslim empires, but abnormal and dangerous for Jews to move in under their own initiative - usually out of desperation to save their lives - with no sponsoring empire at all.
Beyond that, if you took a few minutes to think of what your argument implies about the "Great Migration" of African-Americans to northern states in the early 20th century, or refugees crossing the Mexican border, and how white people responded to both, I think you would be less willing to make it, even anonymously.
161 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Palestine was heralded as ‘a land without a people for a people without a land’, and the Naqab in particular was characterized as a desert in need of technologically advanced (Zionist) pioneers to make it bloom. In actual fact, the estimated 65,000–90,000 Palestinian Arabs populating the Naqab Desert prior to the 1948 war were organized into 95 tribes, and engaged in animal husbandry and seasonal agriculture. Turkish records dating as far back as the sixteenth century show that Palestinian Bedouin owned, cultivated and paid taxes on land; and that cultivation was extensive, particularly in the more fertile, less arid northern and northwestern Naqab.
Palestinian Bedouin cultivation in the Naqab was documented by European traveller accounts from the mid- to late-1800s, as well as Zionist explorer accounts from the late 1800s and early 1900s. Reports produced both by British Mandate authorities and the Zionist Movement’s Palestine Land Development Company in the early to mid-1900s indicated that over 2 million dunams were owned and cultivated by Naqab Palestinians. The great majority of Naqab Palestinians held their land under customary Bedouin law. Neither the Ottoman or British Mandate governments ever completed land surveys of the vast Naqab region; however, they both recognized the Naqab Palestinians’ traditional land ownership system, at the collective tribal and individual levels.
... However, prior to the 1948 war, Zionist leaders such as Ben-Gurion denied Naqab Palestinian land ownership, and characterized the Naqab as ‘No Man’s Land. It has no legal owners and anyone who cultivates it with the permission of the government is entitled to become its owner, according to a Turkish law, which still prevails in Palestine’. He rejected the idea of purchasing land in the Naqab, saying to his staff: ‘In the Negev we will not buy land. We will conquer it. You are forgetting that we are at war.’
The 1948 war/Palestinian Nakba (Catastrophe) resulted in large-scale expulsion of Palestinian population, and internal displacement of many who remained in the territory that became the State of Israel. Studies of the internally displaced Palestinians have generally not included the Bedouin Palestinians in the Naqab; aside from noting that the official governmental numbers did not include them, or that a much higher proportion of the population was displaced, as compared to other regions. They, indeed, faced the most extensive displacement and dispossession, with 12 of the 19 tribes that remained in the Israeli state forced to move from their fertile lands in the northwestern Naqab to the infertile, arid region of the Seig. This resulted in nearly two thirds of the communities losing their land, property and possessions. Although Israeli authorities initially told them that the displacement was temporary, and they would be allowed to return to their lands, this never occurred. Instead, an arsenal of laws was enacted and applied throughout Israel to transfer Palestinian owned land to the Israeli state.
... Recently uncovered archives and declassified government documents confirm that the displacement and land acquisition was not coincidental, but occurred according to an orderly, large-scale state plan to expel Palestinian citizens from the northwestern Naqab, with the goal of severing their physical ties to the land, and transferring this land to the possession of the state. Moshe Dayan, who commanded the military operation, wrote: ‘It’s now possible to transfer most of the Bedouin in the vicinity of [Kibbutz] Shoval to areas south of the Hebron-Be’er Sheva road. Doing so will clear around 60,000 dunams in which we can farm and establish communities.’ Although security issues were given as a rationale for the transfer, Dayan also clearly stated: ‘Transferring the Bedouin to new territories will annul their rights as landowners and they will become tenants on government lands.’ The military government carried out the operation using a mix of threats, violence, bribery and fraud; but were careful never to give the displaced Naqab Palestinians written transfer orders, because such an operation for the purpose of land acquisition was illegal. Oral Palestinian histories of threats, violence and arrests were confirmed by archival kibbutz and state records.
Although the official government story was that Naqab Palestinians voluntarily left their lands, declassified government records from the time document the ‘Bedouin resistance and protests, the stubbornness with which they tried to hold onto their land, even at the cost of hunger and thirst, not to mention the army’s threats and violence’. Archival kibbutz records also documented the military government’s use of many methods to force the Bedouin to leave their lands, including stopping their food supplies for months."
Ismael Abu-Saad, "Al-Naqab: The Unfinished Zionist Settler-colonial Conquest of its Elusive 'Last Frontier,' and Indigenous Palestinian Bedouin Arab Resistance," in Decolonizing the Study of Palestine: Indigenous Perspectives and Settler Colonialism (2023)
87 notes
·
View notes
Text
"When the British Empire occupied Palestine and set about implementing the Balfour declaration, the fossil fuel of the day was not coal. It was oil. Promising deposits had been located in the countries bordering the Persian Gulf, and the central industrial project of the Mandate came to be the pipeline that brought crude oil all the way from Iraq, across the northern West Bank and the Galilee, to the refinery of Haifa. The Mandate as such cannot be understood outside the deepening control over the region in the pursuit of oil; and the Mandate used oil to reallocate land from Palestinians to Jews. In his forthcoming Heat: A History, a wonderfully rich history of high temperatures and fossil fuels in the Middle East, On Barak shows, among many other things, how the Yishuv wrested citrus production from Palestinians by linking up with the most modern circuits of technology: irrigating their orchards with fossil-fuelled pumps, loading their fruits on lorries, sending them over roads to ports, offloading them onto steamers to the European market – a symbiosis with the fossil empire by which the natives could be squeezed out of their iconic citriculture. The Mandate authorities systematically privileged the building of roads between colonies. Oil-based infrastructure tilted Palestine in the direction of the settlements on the coastal plains and further towards their patrons on the other side of the ocean."
30 notes
·
View notes