#acts of science
Text
Sound reveals giant blue whales dance with the wind to find food
https://sciencespies.com/environment/sound-reveals-giant-blue-whales-dance-with-the-wind-to-find-food/
Sound reveals giant blue whales dance with the wind to find food
A study by MBARI researchers and their collaborators published today in Ecology Letters sheds new light on the movements of mysterious, endangered blue whales. The research team used a directional hydrophone on MBARI’s underwater observatory, integrated with other advanced technologies, to listen for the booming vocalizations of blue whales. They used these sounds to track the movements of blue whales and learned that these ocean giants respond to changes in the wind.
Along California’s Central Coast, spring and summer bring coastal upwelling. From March through July, seasonal winds push the top layer of water out to sea, allowing the cold water below to rise to the surface. The cooler, nutrient-rich water fuels blooms of tiny phytoplankton, jumpstarting the food web in Monterey Bay, from small shrimp-like krill all the way to giant whales. When the winds create an upwelling event, blue whales seek out the plumes of cooler water, where krill are most abundant. When upwelling stops, the whales move offshore into habitat that is transected by shipping lanes.
“This research and its underlying technologies are opening new windows into the complex, and beautiful, ecology of these endangered whales,” said John Ryan, a biological oceanographer at MBARI and lead author of this study. “These findings demonstrate a new resource for managers seeking ways to better protect blue whales and other species.”
The directional hydrophone is a specialized underwater microphone that records sounds and identifies the direction from which they originate. To use this technology to study blue whale movements, researchers needed to confirm that the hydrophone reliably tracked whales. This meant matching the acoustic bearings to a calling whale that was being tracked by GPS. With confidence in the acoustic methods established, the research team examined two years of acoustic tracking of the regional blue whale population.
This study built upon previous research led by MBARI Senior Scientist Kelly Benoit-Bird, which revealed that swarms of forage species — anchovies and krill — reacted to coastal upwelling. This time, researchers combined satellite and mooring data of upwelling conditions and echosounder data on krill aggregations with the acoustic tracks of foraging blue whales logged by the directional hydrophone.
“Previous work by the MBARI team found that when coastal upwelling was strongest, anchovies and krill formed dense swarms within upwelling plumes. Now, we’ve learned that blue whales track these dynamic plumes, where abundant food resources are available,” explained Ryan.
advertisement
Blue whales recognize when the wind is changing their habitat and identify places where upwelling aggregates their essential food — krill. For a massive animal weighing up to 150 tonnes (165 tons), finding these dense aggregations is a matter of survival.
While scientists have long recognized that blue whales seasonally occupy Monterey Bay during the upwelling season, this research has revealed that the whales closely track the upwelling process on a very fine scale of both space (kilometers) and time (days to weeks).
“Tracking many individual wild animals simultaneously is challenging in any ecosystem. This is especially difficult in the open ocean, which is often opaque to us as human observers,” said William Oestreich, previously a graduate student at Stanford University’s Hopkins Marine Station and now a postdoctoral fellow at MBARI. “Integration of technologies to measure these whales’ sounds enabled this important discovery about how groups of predators find food in a dynamic ocean. We’re excited about the future discoveries we can make by eavesdropping on blue whales and other noisy ocean animals.”
Background
Blue whales (Balaenoptera musculus) are the largest animals on Earth, but despite their large size, scientists still have many unanswered questions about their biology and ecology. These gentle giants seasonally gather in the Monterey Bay region to feed on small shrimp-like crustaceans called krill.
advertisement
Blue whales are elusive animals. They can travel large distances underwater very quickly, making them challenging to track. MBARI researchers and collaborators employed a novel technique for tracking blue whales — sound.
MBARI’s MARS (Monterey Accelerated Research System) observatory offers a platform for studying the ocean in new ways. Funded by the National Science Foundation, the cabled observatory provides continuous power and data connectivity to support a variety of instruments for scientific experiments.
In 2015, MBARI researchers installed a hydrophone, or underwater microphone, on the observatory. The trove of acoustic data from the hydrophone has provided important insights into the ocean soundscape, from the migratory and feeding behaviors of blue whales to the impact of noise from human activities.
In 2019, MBARI and the Naval Postgraduate School installed a second hydrophone on the observatory. The directional hydrophone gives the direction from which a sound originated. This information can reveal spatial patterns for sounds underwater, identifying where sounds came from. By tracking the blue whales’ B call — the most powerful and prevalent vocalization among the regional blue whale population — researchers could follow the movements of individual whales as they foraged within the region.
Researchers compared the directional hydrophone’s recordings to data logged by tags that scientists from Stanford University had previously deployed on blue whales. Validating this new acoustic tracking method opens new opportunities for simultaneously logging the movements of multiple whales. It may also enable animal-borne tag research by helping researchers find whales to tag. “The integrated suite of technologies demonstrated in this paper represents a transformative tool kit for interdisciplinary research and mesoscale ecosystem monitoring that can be deployed at scale throughout protected marine habitats. This is a game changer and brings both cetacean biology and biological oceanography to the next level,” said Jeremy Goldbogen, an associate professor at Stanford University’s Hopkins Marine Station and a coauthor of the study.
This new methodology has implications not only for understanding how whales interact with their environment and one another but also for advancing management and conservation.
Despite protections, blue whales remain endangered, primarily from the risk of collisions with ships. This study showed that blue whales in Monterey Bay National Marine Sanctuary regularly occupy habitat transected by shipping lanes. Acoustic tracking of whales may provide real-time information for resource managers to mitigate risk, for example, through vessel speed reduction or rerouting during critical periods. “These kinds of integrated tools could allow us to spatially and temporally monitor, and eventually even predict, ephemeral biological hotspots. This promises to be a watershed advancement in the adaptive management of risks for protected and endangered species,” said Brandon Southall, president and senior scientist for Southall Environmental Associates Inc. and a coauthor of the research study.
Support for this research was provided by the David and Lucile Packard Foundation. The National Science Foundation funded the installation and maintenance of the MARS cabled observatory through awards 0739828 and 1114794. Directional acoustic processing work was supported by the Office of Naval Research, Code 32. Tag work was funded in part by the National Science Foundation (IOS-1656676), the Office of Naval Research (N000141612477), and a Terman Fellowship from Stanford University.
#Environment
#10-2022 Science News#2022 Science News#acts of science#Earth Environment#earth science#Environment and Nature#everyday items#Nature Science#New#News Science Spies#October 2022 Science News#Our Nature#planetary science#production line#sci_evergreen1#Science#Science Channel#science documentary#Science News#Science Spies#Science Spies News#Space Physics & Nature#Space Science#Environment
36 notes
·
View notes
Text

DR ADAM LEVY ClimateAdam
ROSEMARY MOSCO
#comic#climate change#climate science#climate action#climate crisis#doom scroll break#radical optimism#hope is a radical act
27K notes
·
View notes
Text

3K notes
·
View notes
Text
This is from last summer (I found it while trying to clean up browser tabs--oops.) Anyway, it's one of many examples of critically endangered species showing an upturn in population with support. The Devils Hole pupfish is particularly imperiled because it is only found in one flooded cavern in Nevada's Amargosa Desert; the species is likely descended from fish that were washed in there by flooding thousands of years ago, and have managed to eke out a living in the hot, oxygen-deficient water ever since.
This is one of the first species ever listed under the U.S. Endangered Species Act. Devils Hole is threatened by groundwater depletion from well drilling, and after the pupfish's ESA listing there were numerous legal battles between conservationists and farmers over water usage. Water levels reached their lowest point in the early 1970s, but have been slowly rising since then.
Scientists are excited because the current wild population (at least as of last fall) is at 263 fish. That's up from just 35 in 2013, the lowest recorded population ever. There are a few hundred more in captivity, being used to breed more young for reintroduction. The hope is that this fall's wild count will break 300, a good sign for the world's most endangered fish.
By the way, THIS is the entirety of the Devils hole pupfish's habitat, the only place in the world where they are found:
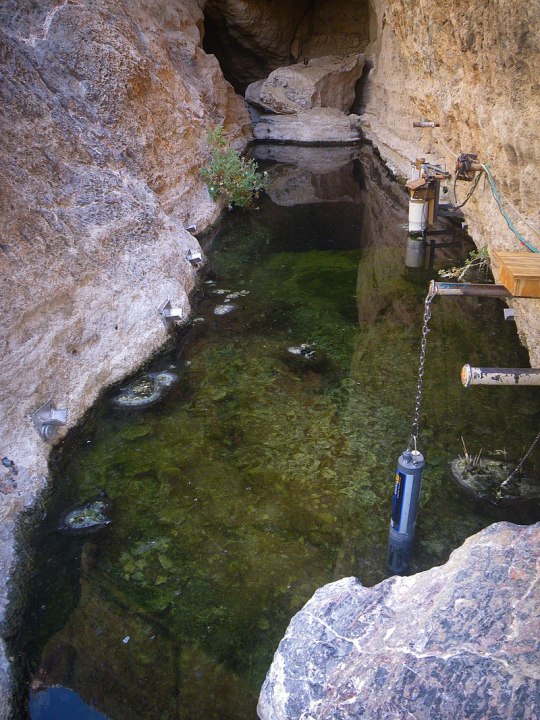

#Devils Hole pupfish#Devils Hole#fish#icthyology#vertebrates#animals#wildlife#endangered species#endangered animals#extinction#nature#ecology#environment#conservation#science#scicomm#Nevada#United States#Endangered Species Act#Endangered Species List
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
When the Public Health Emergency ends "for people without insurance, there will no longer be a pathway through Medicaid for free COVID-19 testing, vaccines, or treatment."

“The costs of COVID-19 vaccines are also expected to skyrocket once the government stops buying them, with Pfizer saying it will charge as much as $130 per dose. … People with private insurance could have some out-of-pocket costs for vaccines, especially if they go to an out-of-network provider, Levitt said. Free at-home COVID tests will also come to an end.” (source)

SO so glad that Joe Biden sided with big pharma and blocked the Wellstone Act for greedy corporations like Gilead Sciences back in the year 2000. And SO happy that he was vehemently against Medicare For All. 🤬
The long and short of this is that if you are poor and/or uninsured, you are going to need to pay for your own COVID tests and vaccinations.
Now ask yourself: if an underpaid frontline worker like a food server or grocery store clerk—remember when everyone was calling them “heroes” & essential workers?—if those workers feel sick but don’t have any paid time off and can’t afford to pay for their own test and vaccines, do you think they are going to take a week off without pay, or continue working and possibly spreading the virus? Rhetorical question; this already happens.
Welcome to America. If you’re poor, you’re dead.
4K notes
·
View notes
Text



This was quite haunting to read.
#animals#birds#Kauaʻi ʻōʻō#Kauaʻi#hawaii#hawai'i#extinction#extinct animals#extinct species#news#science#zoology#biology#Endangered Species Act#ESA#recently extinct#Putting a bunch of tags in this because I really want this story to be known. It made me so sad.
438 notes
·
View notes
Photo




I was gripped by a sudden onslaught of love for this man’s stupid old face and a violent desire to gif it, so have a few of my favourite weird expressions Twelve has made
#twelfth doctor#peter capaldi#look at my babygirl#and his beautiful face#nonverbal acting#twelve making faces#that lip bite is so fucking cute#i think peter should donate his mortal remains to science one day#so future generations can finally understand how that amazing face of his works
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
real subtle there, astarion
#baldur's gate 3#bg3#gale dekarios#astarion ancunin#bloodweave#hello bloodweave nation i come bearing these crumbs i hope you will accept#so can we confirm that gale is canonically good in bed now#i don’t wanna hear he’s vanilla or boring if ASTARION says he’s been dreaming about their romp#i do love how subtle he is about gale throughout the game tho. it’s a ‘i want him but i don’t want to act too desperate around him’ vibe#side note you get this dialogue if you slept with him as gale. i had to break up with him for science bc i wanted to hear this for myself#vg#vid#my post
182 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kink at pride, drag queens, traditional family values, blah blah blah. I'm washing laundry and listening to my radio shows and stitching together a body harness on my sewing machine. I've worked at a dungeon and I've worked at a sunday school and nothing matters and we should all calm down. Put on a garter belt and go to the fucking farmer's market. Fucking hell
#Vent post#Jesus just be aware of where you are and act appropriately its not rocket science#Drag queens aren't stripping during story time at the public library how did this become a huge deal#I'm so tired#Poking the hornets nest#Jesus christ just ignore me
807 notes
·
View notes
Text
Researchers at the California Academy of Sciences described 153 new animal, plant, and fungi species in 2023, enriching our understanding of Earth's biodiversity and strengthening our ability to regenerate the natural world. The new species include 66 spiders, 20 sea slugs, 18 plants, 13 sea stars, 12 geckos, 10 beetles, five fishes, four worms, two wasps, one sea snail, one scorpion, and one legless skink. More than a dozen Academy scientists—along with several international collaborators—described the new-to-science species.
This year's discoveries coincide with the 50th anniversary of the Endangered Species Act (ESA), and include several threatened plant and animal species that meet the criteria for formal ESA protections. These protections include prohibiting any harmful treatment of protected species; requiring further protection for land where endangered species occur; and implementing recovery plans for threatened populations.
Continue Reading.
262 notes
·
View notes
Text
They're one of the best Dimension 20 couples. You can not change my mind.
This is essentially an AU fic of the, "No one tell Brennan how hot I think he is," tweet.
#the fix and pasha forever#hyper fixation and passion would make a great couple#i loved how hank and brennan played this too#the science facts didn't require much acting from either of them granted#mentopolis#brennan lee mulligan#hank green#the fix#dimension 20 spoilers#dimension 20#d20 spoilers#d20#dropout tv#dropout#college humor#video
265 notes
·
View notes
Text
Fossil Find Tantalizes Loch Ness Monster Fans
https://sciencespies.com/news/fossil-find-tantalizes-loch-ness-monster-fans/
Fossil Find Tantalizes Loch Ness Monster Fans

Plesiosaurs went extinct 66 million years ago, but evidence that the long-necked reptiles lived in freshwater, not just oceans, has offered hope to Nessie enthusiasts.
LONDON — Millions of years before the first (alleged) sighting of the Loch Ness monster, populations of giant reptiles swam through Jurassic seas in areas that are now Britain. Known as plesiosaurs, these long-necked creatures were thought to have dwelled exclusively in oceans.
But a discovery published in a paper last week by researchers in Britain and Morocco added weight to a hypothesis that some Loch Ness monster enthusiasts have long clung to: that plesiosaurs lived not just in seas, but in freshwater, too. That could mean, they reasoned excitedly, that Nessie, who is sometimes described as looking a lot like a plesiosaur, really could live in Loch Ness, a freshwater lake.
Local papers have celebrated the finding. It “gives further credit to the idea that Nessie may have been able to survive and even thrive in Loch Ness,” said an article on page 32 of the Inverness Courrier, a biweekly newspaper in the Scottish Highlands. “Loch Ness Monster bombshell,” blared a headline from Britain’s Daily Express tabloid. “Existence of Loch Ness Monster is ‘plausible’” read headlines in The Scotsman, The Telegraph and elsewhere, seizing on a phrase in the University of Bath’s announcement of the study’s findings.
This is not the first study to find that plesiosaurs lived in freshwater. “This new study is simply providing additional evidence for certain members of this group living in freshwater,” said Dean Lomax, a paleontologist and visiting scientist at the University of Manchester. “We’ve always known this.”
But Nick Longrich, the lead author of the study, said his team had one of the stronger cases for it because they found fossils of 12 plesiosaurs, proof that it was not just one plesiosaur that wandered into freshwater and then died there.
“The more plesiosaur fossils discovered in freshwater environments, the more this will further build the picture to explain why plesiosaurs might be turning up in freshwater environments around the world,” said Georgina Bunker, a student who was a co-author of the paper.
Dr. Longrich, a paleontologist and evolutionary biologist at the University of Bath, said it was “completely unexpected” to find the fossil of a plesiosaur that had lived in an 100-million-year-old freshwater river system that is now the Sahara.
While on a research trip to Morocco, he was sifting through a box in the back room of a shop when he spotted a “kind of chunky” bone, which turned out to be the arm of a five-foot long baby plesiosaur. Dr. Longrich paid the cashier no more than 200 Moroccan Dirham, or about $20, after bargaining to bring down the price, and brought the fossils back to Britain for further study.
Nick Longrich/University of Bath
“Once we started looking, the plesiosaur started turning up everywhere,” he said. “It reminds you there’s a lot we don’t know.” (The fossils will be returned to museums in Morocco at a later date, he said.)
As the news of the study made headlines last week, some Nessie fans were hopeful. George Edwards, who was for years the skipper of a Loch Ness tourism boat called the Nessie Hunter, said that for him the new study showed how creatures could adapt to survive in new environments — and that the world is full of mysteries. Take the coelacanth, a bony fish that was thought to have become extinct millions of years ago but was found in 1938 by a South African museum curator on a fishing trawler. “Lo and behold, they found them, alive and kicking,” Mr. Edwards said. “Anything is possible.”
Mr. Edwards said he had seen unexplained creatures in Loch Ness plenty of times: “There’s got to be a family of them.” From what he has seen, the creatures have a big arched back, no fins and are somewhat reminiscent of a plesiosaur.
But there is one detail that some Nessie lovers may have overlooked in their embrace of the plausibility of Nessie’s existence: Plesiosaurs became extinct at the same time as dinosaurs did, some 66 million of years ago. Loch Ness was only formed about 10,000 years ago, and before that it was ice.
Valentin Fischer, an associate professor of paleontology at the University of Liège in Belgium, said that it would currently be impossible for a marine reptile like the plesiosaur to live in Loch Ness.
Nick Longrich/University of Bath
The first recorded sighting of Nessie dates back to the sixth century A.D., when the Irish monk St. Columba was said to have driven a creature into the water. But global interest was revived in the 20th century, after a British surgeon, Col. Robert Wilson, took what became the most famous photo of the Loch Ness monster in 1934. Sixty years later, the photograph was revealed to be a hoax.
But some people were not discouraged, and, ever since, throngs of tourists have traveled to Loch Ness each year in hopes of seeing the monster.
There have been more than 1,100 sightings at Loch Ness, including four this year, according to the register of official sightings.
A famous photograph of the Loch Ness Monster taken in 1934 was later revealed to have been a hoax.Keystone/Getty Images
Steve Feltham, a full-time monster hunter who has lived on the shores of Loch Ness for three decades, said the British-Moroccan study was interesting, but that it was irrelevant to his search. Ever since it became clear that the famous 1934 photo of Nessie was fake, he has stopped believing that Nessie was a plesiosaur. Plesiosaurs have to come up for air, so he figures he would have seen it during the 12 hours a day that he scans the loch. Instead, he scans the water for giant fish that look like a boat turned upside down.
“I struggle to think of any bona fide Nessie hunter that still believes in the plesiosaur,” he said. “The hunt has moved on from that.”
#News
#2022 Science News#8-2022 Science News#acts of science#August 2022 Science News#Earth Environment#earth science#Environment and Nature#everyday items#Nature Science#New#News Science Spies#Our Nature#planetary science#production line#sci_evergreen1#Science#Science Channel#science documentary#Science News#Science Spies#Science Spies News#Space Physics & Nature#Space Science#News
38 notes
·
View notes
Text





byler in every episode
-> 1.07. the bathtub
#looking forward to more of this in s5... the kids explaining science to the adults jsdkfdsjh (also. wheeler family communication)#really considered adding the actual 'bathtub'/pool scene to this but. the lack of a mike reaction shot during will's part is. glaring.#also the parallel potential of this mike-nancy scene but with maybe mike-lucas??? knew you were acting weird... thought it was bc of el#please. please it's right there pleeeease#byler#mike wheeler#mikesbasementgifs#byler in every episode
220 notes
·
View notes
Text
In a game that is largely comprised of very disheartening moments, one of the worst for me in de is when Lena- who has up to this point seemed to be a delightful, kind person- casually drops the fact that she considers Kim to be an entirely different species from Harry and her because he is Seolite. It is such a kick in the nuts and its made so much worse because she clearly meant no offense and tries to awkwardly assure Kim that that doesn't mean she thinks that Seolites are *inferior* and then throws in some bs inconsequential "positive trait" that she thinks seolites have over occidental ppl. It's sort of funny cus its so obviously deranged bullshit. And It's just so shitty, it's this reminder that it's not just belligerent assholes like the racist lorry driver- sweet old ladies like Lena also think Kim is just *a little bit less of a person* too. He is constantly being barraged with this sort of treatment, but i feel like this little moment hits especially hard because its the first instance you witness of someone aiming this shit at kim without conscious malice. Made doubly shitty cus you goaded him into this little diversion in the first place- its a pretty neat illustration of why someone like kim would be so closed off in the first place.
#disco elysium#kim kitsuragi#its also a pretty nice illustration of how one seemingly innocent mode of pseudoscience like cryptozoology can act as a pipeline#if youre willing to believe in the veracity of the col do ma ma da qua based on no meaningful evidence#then ur an easy mark for the unscientific bullshit peddled by race science#and also for as nice as they come off theres a reason why morrell and lena seem to get on ok with gary the cryptofascist#its also kind of heartbreaking that despite how fucking shitty that is kim seems to like lena and morrell#he just sort of compartmentalizes the shittiness and moves past it
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
As someone who has a lizard. My favorite part of any Holt and Jackson fanfiction is when they are holding Crossfade. Fic writers. Add more Crossfade NOW.
#i think the fact that holt canonically takes him out on walks at night...#and jackson did a magic/mad science talent show act with him...#GRAAHGGHHHHH#i just think.....#i LOVE lizards. they are so good and they just crawl on you and look at you crazy...#monster high#monster high dolls#holt hyde#jackson jekyll#jackson and holt#(me)atgutz
58 notes
·
View notes
Text

#its about the devine act of self creation#in case that wasnt clear#also about trauma#and unethical science#and crime :)#and I guess romantisicing my own disability to a level of self love#enby stuff#gender envy#the mechanisms#doc ock#fullmetal alchimist brotherhood#john silver#viktor arcane
353 notes
·
View notes