#sales transformation platform
Text
#sales competencies#sales transformation#b2b sales digital transformation#sales transformation strategy#digital sales transformation#sales talent strategy#sales talent gaps#sales hiring#sales hiring tool#sales transformation service#sales hiring software#sales transformation platform#sales competency skills#sales transformation solution#sales development#digital sales#digital selling#sales team development#maximising sales#getting the most out of my sales team#sales performance#improve sales performance#improving sales performance#sales team performance#sales improvement plan#underperforming sales team
1 note
·
View note
Text
How to Choose the Right Digital Marketing Services for Your Company
When it comes to choosing the right digital marketing services for your company, it can be a daunting task. With so many options available, it can be difficult to know where to start. In this article, we will provide you with some helpful tips on how to choose the right digital marketing services for your company.
Identify Your Marketing Goals
The first step in choosing the right digital marketing services for your company is to identify your marketing goals. What do you want to achieve with your marketing efforts? Do you want to increase website traffic, generate more leads, improve your search engine rankings, or all of the above?
Once you have identified your marketing goals, you can then look for digital marketing services that align with those goals. For example, if your goal is to increase website traffic, you may want to consider services such as search engine optimization (SEO) and pay-per-click (PPC) advertising.
Research Digital Marketing Companies
Once you have identified your marketing goals, the next step is to research digital marketing companies. Look for companies that have experience in your industry and offer the services that align with your marketing goals.
When researching digital marketing companies, be sure to look at their portfolio and case studies. This will give you an idea of their experience and the results they have achieved for other clients.
Consider Your Budget
When choosing the right digital marketing services for your company, it's important to consider your budget. Digital marketing services can vary in price, so it's important to choose services that fit within your budget.
However, it's important to remember that the cheapest option may not always be the best option. Be sure to choose a digital marketing company that offers quality services and can provide you with a good return on investment.
Ask for Referrals and Reviews
One of the best ways to choose the right digital marketing services for your company is to ask for referrals and reviews. Ask other business owners in your industry for recommendations and read online reviews.
By doing this, you can get an idea of the experiences other businesses have had with digital marketing companies and find a company that has a good reputation.
Conclusion Choosing the right digital marketing services for your company can be a challenging task, but by identifying your marketing goals, researching digital marketing companies, considering your budget, and asking for referrals and reviews, you can find a company that will help you achieve your marketing goals and grow your business.
#it service provider#digital consulting#digital strategy consultant#digital transformation consultant#it consulting services#Digital Marketing#Digital Commerce#Digital Sales#Digital Experience#Digital Customer#Platform and Product Strategy Consultant
0 notes
Text
Marketing Automation from iCumulus enables marketing departments to centralise and streamline their processes from beginning to end, including planning, briefing, cooperation, and approvals, improving lead quality, enabling a better knowledge of client behaviour, and saving costs.
#marketing automation#Transform Digital Agency#Marketing Platform Integration#demand orchestration agency#account based marketing#sales enablement#virtual sales agent
0 notes
Text
Sweet Macaroons | C.Sc

Pairing: Gangster!Seungcheol x Baker!Reader
Genre: fluff, established relationship
Words Count: ±600
Summary: Seungcheol was far from pleased when a food critic posted a negative review that started to impact your sales. He couldn't stand to see you upset.
In the midst of a picturesque five months, Seungcheol, with an air of exclusivity, tenderly asked you to be his girlfriend. Everything seemed to move in slow motion around you, as if the universe itself was savoring the moment. His crew, astounded, couldn't fathom that a humble bakery owner just down the block from their bar had captured their boss's heart. He had transformed into something they never imagined: a unabashedly cheesy boy. Even Jeonghan, Seungcheol's right-hand man, remained baffled by the depth of his friend's infatuation with you. He couldn't quite grasp what had caused Seungcheol to fall so hard until he witnessed how Seungcheol would gladly stop the world at your command.
As an example of Seungcheol's devotion, he had gone as far as hiring a bodyguard to watch over you and ensure your safety. Seungcheol, ever mysterious about his business, would simply say, "I do business in Seoul and Busan," which, in its own way, was true. He owned nearly a hundred bars and nightclubs, not to mention his own association—a realm of details you didn't need to delve into.
Your bodyguard, Jun, who currently disguised as a barista in your bakery, would dutifully relay every detail to Seungcheol. This included mundane activities like your trips to the grocery store, visits from friends at the bakery, or even encounters with rude customers. Despite being in the know about your daily affairs through Jun, Seungcheol cherished hearing you recount your day, especially when it involved a customer that cussed on you. He'd teasingly inquire, "Should I track him down and make him pay?" A promise he would have swiftly fulfilled if you had not said, "No, you don't have to. I'll give him a piece mind when I'm a billionaire."
At times, Seungcheol really wants to say, "Marry me, and you can cuss him back in an instant." He was acutely aware of the influence he held.
However, he received an extremely irritating message from Jun, stating that a popular food critic had left a scathing review on their social media, claiming to have found a fly and cockroach legs in your sweets. This review had a detrimental impact on your sales and the overall image of the bakery, as people began leaving unpleasant comments on your social media platforms.
"Jeonghan, do you know this person?" Seungcheol inquired, displaying a video of the food critic.
Jeonghan confirmed, "Yeah, they're a very influential food critic."
Seungcheol nodded thoughtfully and hummed, "Do you know how to contact them?" he pressed further.
"I think we just need to get in touch with their management. They'll provide you with the pricing for their content," Jeonghan explained, prompting another question from Seungcheol.
"Then we can have them review our food however we want?" Jeonghan nodded, "Why? Are you thinking about having them promote our new foodbar?" he inquired.
Seungcheol shook his head, simultaneously signaling to Jeonghan that he wanted to be dropped off at your bakery.
Jun had informed Seungcheol that you had closed the bakery early today due to the lack of customers following the internet sensation. When Seungcheol arrived, only Jun was present in the bakery. He mentioned that you had gone to the convenience store for a few minutes. As Seungcheol patiently waited at one of the tables, you returned with a plastic bag in hand. Lost in your thoughts, you didn't immediately notice him. Instead, you went straight to Jun, telling him he could go home. Jun subtly gestured towards Seungcheol, indicating that he was waiting for you.
"Hi..." Your voice, though soft as always, carries a subtle shade of sadness. Seungcheol swears he can hear it, a touch of blue in your tone.
He smiles, approaching you and subtly signaling for Jun to leave the shop.
"Are you okay? I saw it online," Seungcheol asks gently once Jun has vanished from view.
You smile back at him, but tears well up in your eyes, trickling down your cheeks. You turn away, hiding your face from him as you wipe away the tears. Seungcheol's heart aches at the sight, a feeling he's never experienced before, like someone's squeezing his heart, causing a deep ache.
"Hey, it's okay," he murmurs softly, turning you to face him and pulling you into an embrace. He can feel the tightness in his chest intensify when he hears you sob.
This is the first time he's seen you cry in the five months you've been dating. He swears he'd never want to be the cause of your tears, let alone someone else.
"It's okay, baby. Bad things happen sometimes. It's not your fault," he reassures you as you try to explain how diligently you maintain your bakery's hygiene and ensure the freshness of ingredients. There's no way the accusations the food critic made could be true.
Seungcheol noticed the contents of the plastic bag you had been holding earlier: cleaning soap and equipment. His heart breaks once again, this time tinged with anger.
"Let's go home and rest, okay? I'll hire someone to clean the shop. I don't want to see you laboring with a heavy heart like this," he insists.
Seungcheol calls Jeonghan and swiftly arranges for his people to clean your shop. He drives you home, ensuring you have a proper dinner before settling down for some much-needed rest. Once you're peacefully asleep, he quietly slips away, reaching out to Jun and Jeonghan.
"Get them for me before midnight. Alive," he instructs.
Seungcheol doesn't concern himself with the specifics of how they carried out his request. But when his people successfully bring them to his office, he finally confronts the face that caused his girl to cry.
"What's your name?" Seungcheol asks, rising from his seat and approaching them.
"Who put you up to this?" Seungcheol presents their damning post about your bakery to their face. Poor soul, Seungcheol thinks. This food critic probably never imagined they'd be dragged in by a gangster and subjected to an interrogation like this.
Once Seungcheol acquires the name, he signals his people to reveal the extent of their capabilities. Images of their family and significant other are displayed, and they immediately plead for an apology, expressing regret for their actions.
"You should've thought about that before you posted that garbage," Seungcheol states, fixing them with a steely gaze.
"Upload a clarification video about your previous review. Go to that bakery tomorrow and apologize to the owner. Post both of those things before lunch if you want to spare them," Seungcheol directs, referring to the individuals in the photos as he delivers his unwavering ultimatum.
*
"It was a very wrong act of me to accept the offer to give a bad review to another bakery. I deeply apologize to the owner and my followers for doing such a wrong thing."
Seungcheol smiled at you as you showed him the video from the same account that had claimed they found a cockroach leg on your macaroon.
"See! I knew that my bakery and kitchen have passed the hygiene standards," you said, placing your phone down. There was a visible pout on your face, prompting Seungcheol to let out a chuckle.
"You're too cute," Seungcheol teased, pinching your cheek. He was relieved to see no trace of tears like the previous night.
You gently pulled his hand from your cheek as you stood up to restock the macaroon stall, which was nearly empty. Seungcheol couldn't help but smile as he watched you, his girl, his love, engrossed in the work you adored.
"Before you go, want a macaroon and your favorite latte?" you offered. He swore he would nod to anything you said.
"Here! I've packed some for your staff as well," you added, handing him boxes filled with sweets and a bundle of coffees for Seungcheol and Jeonghan.
He wouldn't let anyone steal your smile, even if he had to stop the world.
#densworld🌼#seventeen imagines#seventeen fanfic#seventeen angst#scoups x reader#scoups fluff#scoups imagine#scoups imagines#scoups smut#seungcheol imagines#seungcheol fluff#seungcheol x reader#choi seungcheol
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Transforming stress into creativity and relaxation, one Fidget Bloom at a time! 🌸🌺🌼 Check out my latest DIY video on how to make your own fidget bloom - the ultimate fidget toy that can transform into a variety of shapes to suit your mood and various needs! Not only is it a great tool for stress relief, but it's also a fun and creative outlet to keep your hands busy. Give it a try and let me know what you think! :)
Shop dozens of colours and styles:
Etsy Shop | Official Website
I've been asked where I prefer customers to shop my products from, and tbh whichever platform provides them the most convenience for them, I'd say. Etsy is nice because you can shop for other amazing handmade products as well, and have a cart full of awesome things. Shopping from my website introduces you to me and my products a bit more, and it's a more personalized shopping experience. There are pros and cons, but overall, I'm just happy to have my handmade fidget flowers up and available for sale, anywhere!
Ways to enjoy this include: Sensory Fidget \\ Candle Holder \\ Hair Accessory \\ Vehicle Ornament \\ Office Stress Ball \\ Unique Gift Idea \\ Fruit Holder \\ Christmas Tree Decoration \\ Focus Tool \\ Birthday Gift \\ Egg Stand \\ Wedding Favour \\ Concentration Aid \\ Fidget Bracelet \\ Stim Necklace \\ & More!
#fidget toys#stimblr#sensory products#stimming#self-regulation#occupational therapy#sensory processing disorder#neurodivergent#fidget flower toy#how its made
653 notes
·
View notes
Text
Tiktok's enshittification

Here is how platforms die: first, they are good to their users; then they abuse their users to make things better for their business customers; finally, they abuse those business customers to claw back all the value for themselves. Then, they die.
If you’d like an essay-formatted version of this post to read or share, here’s a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/21/potemkin-ai/#hey-guys
I call this enshittification, and it is a seemingly inevitable consequence arising from the combination of the ease of changing how a platform allocates value, combined with the nature of a “two sided market,” where a platform sits between buyers and sellers, hold each hostage to the other, raking off an ever-larger share of the value that passes between them.
When a platform starts, it needs users, so it makes itself valuable to users. Think of Amazon: for many years, it operated at a loss, using its access to the capital markets to subsidize everything you bought. It sold goods below cost and shipped them below cost. It operated a clean and useful search. If you searched for a product, Amazon tried its damndest to put it at the top of the search results.
This was a hell of a good deal for Amazon’s customers. Lots of us piled in, and lots of brick-and-mortar retailers withered and died, making it hard to go elsewhere. Amazon sold us ebooks and audiobooks that were permanently locked to its platform with DRM, so that every dollar we spent on media was a dollar we’d have to give up if we deleted Amazon and its apps. And Amazon sold us Prime, getting us to pre-pay for a year’s worth of shipping. Prime customers start their shopping on Amazon, and 90% of the time, they don’t search anywhere else.
That tempted in lots of business customers — Marketplace sellers who turned Amazon into the “everything store” it had promised from the beginning. As these sellers piled in, Amazon shifted to subsidizing suppliers. Kindle and Audible creators got generous packages. Marketplace sellers reached huge audiences and Amazon took low commissions from them.
This strategy meant that it became progressively harder for shoppers to find things anywhere except Amazon, which meant that they only searched on Amazon, which meant that sellers had to sell on Amazon.
That’s when Amazon started to harvest the surplus from its business customers and send it to Amazon’s shareholders. Today, Marketplace sellers are handing 45%+ of the sale price to Amazon in junk fees. The company’s $31b “advertising” program is really a payola scheme that pits sellers against each other, forcing them to bid on the chance to be at the top of your search.
Searching Amazon doesn’t produce a list of the products that most closely match your search, it brings up a list of products whose sellers have paid the most to be at the top of that search. Those fees are built into the cost you pay for the product, and Amazon’s “Most Favored Nation” requirement sellers means that they can’t sell more cheaply elsewhere, so Amazon has driven prices at every retailer.
Search Amazon for “cat beds” and the entire first screen is ads, including ads for products Amazon cloned from its own sellers, putting them out of business (third parties have to pay 45% in junk fees to Amazon, but Amazon doesn’t charge itself these fees). All told, the first five screens of results for “cat bed” are 50% ads.
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/28/enshittification/#relentless-payola
This is enshittification: surpluses are first directed to users; then, once they’re locked in, surpluses go to suppliers; then once they’re locked in, the surplus is handed to shareholders and the platform becomes a useless pile of shit. From mobile app stores to Steam, from Facebook to Twitter, this is the enshittification lifecycle.
This is why — as Cat Valente wrote in her magesterial pre-Christmas essay — platforms like Prodigy transformed themselves overnight, from a place where you went for social connection to a place where you were expected to “stop talking to each other and start buying things”:
https://catvalente.substack.com/p/stop-talking-to-each-other-and-start
This shell-game with surpluses is what happened to Facebook. First, Facebook was good to you: it showed you the things the people you loved and cared about had to say. This created a kind of mutual hostage-taking: once a critical mass of people you cared about were on Facebook, it became effectively impossible to leave, because you’d have to convince all of them to leave too, and agree on where to go. You may love your friends, but half the time you can’t agree on what movie to see and where to go for dinner. Forget it.
Then, it started to cram your feed full of posts from accounts you didn’t follow. At first, it was media companies, who Facebook preferentially crammed down its users’ throats so that they would click on articles and send traffic to newspapers, magazines and blogs.
Then, once those publications were dependent on Facebook for their traffic, it dialed down their traffic. First, it choked off traffic to publications that used Facebook to run excerpts with links to their own sites, as a way of driving publications into supplying fulltext feeds inside Facebook’s walled garden.
This made publications truly dependent on Facebook — their readers no longer visited the publications’ websites, they just tuned into them on Facebook. The publications were hostage to those readers, who were hostage to each other. Facebook stopped showing readers the articles publications ran, tuning The Algorithm to suppress posts from publications unless they paid to “boost” their articles to the readers who had explicitly subscribed to them and asked Facebook to put them in their feeds.
Now, Facebook started to cram more ads into the feed, mixing payola from people you wanted to hear from with payola from strangers who wanted to commandeer your eyeballs. It gave those advertisers a great deal, charging a pittance to target their ads based on the dossiers of nonconsensually harvested personal data they’d stolen from you.
Sellers became dependent on Facebook, too, unable to carry on business without access to those targeted pitches. That was Facebook’s cue to jack up ad prices, stop worrying so much about ad fraud, and to collude with Google to rig the ad market through an illegal program called Jedi Blue:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jedi_Blue
Today, Facebook is terminally enshittified, a terrible place to be whether you’re a user, a media company, or an advertiser. It’s a company that deliberately demolished a huge fraction of the publishers it relied on, defrauding them into a “pivot to video” based on false claims of the popularity of video among Facebook users. Companies threw billions into the pivot, but the viewers never materialized, and media outlets folded in droves:
https://slate.com/technology/2018/10/facebook-online-video-pivot-metrics-false.html
But Facebook has a new pitch. It claims to be called Meta, and it has demanded that we live out the rest of our days as legless, sexless, heavily surveilled low-poly cartoon characters.
It has promised companies that make apps for this metaverse that it won’t rug them the way it did the publishers on the old Facebook. It remains to be seen whether they’ll get any takers. As Mark Zuckerberg once candidly confessed to a peer, marvelling at all of his fellow Harvard students who sent their personal information to his new website “TheFacebook”:
> I don’t know why.
> They “trust me”
> Dumb fucks.
https://doctorow.medium.com/metaverse-means-pivot-to-video-adbe09319038
Once you understand the enshittification pattern, a lot of the platform mysteries solve themselves. Think of the SEO market, or the whole energetic world of online creators who spend endless hours engaged in useless platform Kremlinology, hoping to locate the algorithmic tripwires, which, if crossed, doom the creative works they pour their money, time and energy into:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/04/11/coercion-v-cooperation/#the-machine-is-listening
Working for the platform can be like working for a boss who takes money out of every paycheck for all the rules you broke, but who won’t tell you what those rules are because if he told you that, then you’d figure out how to break those rules without him noticing and docking your pay. Content moderation is the only domain where security through obscurity is considered a best practice:
https://doctorow.medium.com/como-is-infosec-307f87004563
The situation is so dire that organizations like Tracking Exposed have enlisted an human army of volunteers and a robot army of headless browsers to try to unwind the logic behind the arbitrary machine judgments of The Algorithm, both to give users the option to tune the recommendations they receive, and to help creators avoid the wage theft that comes from being shadow banned:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2022/05/tracking-exposed-demanding-gods-explain-themselves
But what if there is no underlying logic? Or, more to the point, what if the logic shifts based on the platform’s priorities? If you go down to the midway at your county fair, you’ll spot some poor sucker walking around all day with a giant teddy bear that they won by throwing three balls in a peach basket.
The peach-basket is a rigged game. The carny can use a hidden switch to force the balls to bounce out of the basket. No one wins a giant teddy bear unless the carny wants them to win it. Why did the carny let the sucker win the giant teddy bear? So that he’d carry it around all day, convincing other suckers to put down five bucks for their chance to win one:
https://boingboing.net/2006/08/27/rigged-carny-game.html
The carny allocated a giant teddy bear to that poor sucker the way that platforms allocate surpluses to key performers — as a convincer in a “Big Store” con, a way to rope in other suckers who’ll make content for the platform, anchoring themselves and their audiences to it.
Which brings me to Tiktok. Tiktok is many different things, including “a free Adobe Premiere for teenagers that live on their phones.”
https://www.garbageday.email/p/the-fragments-of-media-you-consume
But what made it such a success early on was the power of its recommendation system. From the start, Tiktok was really, really good at recommending things to its users. Eerily good:
https://www.npr.org/transcripts/1093882880
By making good-faith recommendations of things it thought its users would like, Tiktok built a mass audience, larger than many thought possible, given the death grip of its competitors, like Youtube and Instagram. Now that Tiktok has the audience, it is consolidating its gains and seeking to lure away the media companies and creators who are still stubbornly attached to Youtube and Insta.
Yesterday, Forbes’s Emily Baker-White broke a fantastic story about how that actually works inside of Bytedance, Tiktok’s parent company, citing multiple internal sources, revealing the existence of a “heating tool” that Tiktok employees use push videos from select accounts into millions of viewers’ feeds:
https://www.forbes.com/sites/emilybaker-white/2023/01/20/tiktoks-secret-heating-button-can-make-anyone-go-viral/
These videos go into Tiktok users’ ForYou feeds, which Tiktok misleadingly describes as being populated by videos “ranked by an algorithm that predicts your interests based on your behavior in the app.” In reality, For You is only sometimes composed of videos that Tiktok thinks will add value to your experience — the rest of the time, it’s full of videos that Tiktok has inserted in order to make creators think that Tiktok is a great place to reach an audience.
“Sources told Forbes that TikTok has often used heating to court influencers and brands, enticing them into partnerships by inflating their videos’ view count. This suggests that heating has potentially benefitted some influencers and brands — those with whom TikTok has sought business relationships — at the expense of others with whom it has not.”
In other words, Tiktok is handing out giant teddy bears.
But Tiktok is not in the business of giving away giant teddy bears. Tiktok, for all that its origins are in the quasi-capitalist Chinese economy, is just another paperclip-maximizing artificial colony organism that treats human beings as inconvenient gut flora. Tiktok is only going to funnel free attention to the people it wants to entrap until they are entrapped, then it will withdraw that attention and begin to monetize it.
“Monetize” is a terrible word that tacitly admits that there is no such thing as an “Attention Economy.” You can’t use attention as a medium of exchange. You can’t use it as a store of value. You can’t use it as a unit of account. Attention is like cryptocurrency: a worthless token that is only valuable to the extent that you can trick or coerce someone into parting with “fiat” currency in exchange for it. You have to “monetize” it — that is, you have to exchange the fake money for real money.
In the case of cryptos, the main monetization strategy was deception-based. Exchanges and “projects” handed out a bunch of giant teddy-bears, creating an army of true-believer Judas goats who convinced their peers to hand the carny their money and try to get some balls into the peach-basket themselves.
But deception only produces so much “liquidity provision.” Eventually, you run out of suckers. To get lots of people to try the ball-toss, you need coercion, not persuasion. Think of how US companies ended the defined benefits pension that guaranteed you a dignified retirement, replacing it with market-based 401(k) pensions that forced you to gamble your savings in a rigged casino, making you the sucker at the table, ripe for the picking:
https://pluralistic.net/2020/07/25/derechos-humanos/#are-there-no-poorhouses
Early crypto liquidity came from ransomware. The existence of a pool of desperate, panicked companies and individuals whose data had been stolen by criminals created a baseline of crypto liquidity because they could only get their data back by trading real money for fake crypto money.
The next phase of crypto coercion was Web3: converting the web into a series of tollbooths that you could only pass through by trading real money for fake crypto money. The internet is a must-have, not a nice-to-have, a prerequisite for full participation in employment, education, family life, health, politics, civics, even romance. By holding all those things to ransom behind crypto tollbooths, the hodlers hoped to convert their tokens to real money:
https://locusmag.com/2022/09/cory-doctorow-moneylike/
For Tiktok, handing out free teddy-bears by “heating” the videos posted by skeptical performers and media companies is a way to convert them to true believers, getting them to push all their chips into the middle of the table, abandoning their efforts to build audiences on other platforms (it helps that Tiktok’s format is distinctive, making it hard to repurpose videos for Tiktok to circulate on rival platforms).
Once those performers and media companies are hooked, the next phase will begin: Tiktok will withdraw the “heating” that sticks their videos in front of people who never heard of them and haven’t asked to see their videos. Tiktok is performing a delicate dance here: there’s only so much enshittification they can visit upon their users’ feeds, and Tiktok has lots of other performers they want to give giant teddy-bears to.
Tiktok won’t just starve performers of the “free” attention by depreferencing them in the algorithm, it will actively punish them by failing to deliver their videos to the users who subscribed to them. After all, every time Tiktok shows you a video you asked to see, it loses a chance to show you a video it wants you to see, because your attention is a giant teddy-bear it can give away to a performer it is wooing.
This is just what Twitter has done as part of its march to enshittification: thanks to its “monetization” changes, the majority of people who follow you will never see the things you post. I have ~500k followers on Twitter and my threads used to routinely get hundreds of thousands or even millions of reads. Today, it’s hundreds, perhaps thousands.
I just handed Twitter $8 for Twitter Blue, because the company has strongly implied that it will only show the things I post to the people who asked to see them if I pay ransom money. This is the latest battle in one of the internet’s longest-simmering wars: the fight over end-to-end:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/12/10/e2e/#the-censors-pen
In the beginning, there were Bellheads and Netheads. The Bellheads worked for big telcos, and they believed that all the value of the network rightly belonged to the carrier. If someone invented a new feature — say, Caller ID — it should only be rolled out in a way that allows the carrier to charge you every month for its use. This is Software-As-a-Service, Ma Bell style.
The Netheads, by contrast, believed that value should move to the edges of the network — spread out, pluralized. In theory, Compuserve could have “monetized” its own version of Caller ID by making you pay $2.99 extra to see the “From:” line on email before you opened the message — charging you to know who was speaking before you started listening — but they didn’t.
The Netheads wanted to build diverse networks with lots of offers, lots of competition, and easy, low-cost switching between competitors (thanks to interoperability). Some wanted this because they believed that the net would someday be woven into the world, and they didn’t want to live in a world of rent-seeking landlords. Others were true believers in market competition as a source of innovation. Some believed both things. Either way, they saw the risk of network capture, the drive to monetization through trickery and coercion, and they wanted to head it off.
They conceived of the end-to-end principle: the idea that networks should be designed so that willing speakers’ messages would be delivered to willing listeners’ end-points as quickly and reliably as they could be. That is, irrespective of whether a network operator could make money by sending you the data it wanted to receive, its duty would be to provide you with the data you wanted to see.
The end-to-end principle is dead at the service level today. Useful idiots on the right were tricked into thinking that the risk of Twitter mismanagement was “woke shadowbanning,” whereby the things you said wouldn’t reach the people who asked to hear them because Twitter’s deep state didn’t like your opinions. The real risk, of course, is that the things you say won’t reach the people who asked to hear them because Twitter can make more money by enshittifying their feeds and charging you ransom for the privilege to be included in them.
As I said at the start of this essay, enshittification exerts a nearly irresistible gravity on platform capitalism. It’s just too easy to turn the enshittification dial up to eleven. Twitter was able to fire the majority of its skilled staff and still crank the dial all the way over, even with a skeleton crew of desperate, demoralized H1B workers who are shackled to Twitter’s sinking ship by the threat of deportation.
The temptation to enshittify is magnified by the blocks on interoperability: when Twitter bans interoperable clients, nerfs its APIs, and periodically terrorizes its users by suspending them for including their Mastodon handles in their bios, it makes it harder to leave Twitter, and thus increases the amount of enshittification users can be force-fed without risking their departure.
Twitter is not going to be a “protocol.” I’ll bet you a testicle¹ that projects like Bluesky will find no meaningful purchase on the platform, because if Bluesky were implemented and Twitter users could order their feeds for minimal enshittification and leave the service without sacrificing their social networks, it would kill the majority of Twitter’s “monetization” strategies.
¹Not one of mine.
An enshittification strategy only succeeds if it is pursued in measured amounts. Even the most locked-in user eventually reaches a breaking-point and walks away, or gets pushed. The villagers of Anatevka in Fiddler on the Roof tolerated the cossacks' violent raids and pogroms for years, until they were finally forced to flee to Krakow, New York and Chicago:
https://doctorow.medium.com/how-to-leave-dying-social-media-platforms-9fc550fe5abf
For enshittification-addled companies, that balance is hard to strike. Individual product managers, executives, and activist shareholders all give preference to quick returns at the cost of sustainability, and are in a race to see who can eat their seed-corn first. Enshittification has only lasted for as long as it has because the internet has devolved into “five giant websites, each filled with screenshots of the other four”:
https://twitter.com/tveastman/status/1069674780826071040
With the market sewn up by a group of cozy monopolists, better alternatives don’t pop up and lure us away, and if they do, the monopolists just buy them out and integrate them into your enshittification strategies, like when Mark Zuckerberg noticed a mass exodus of Facebook users who were switching to Instagram, and so he bought Instagram. As Zuck says, “It is better to buy than to compete.”
This is the hidden dynamic behind the rise and fall of Amazon Smile, the program whereby Amazon gave a small amount of money to charities of your choice when you shopped there, but only if you used Amazon’s own search tool to locate the products you purchased. This provided an incentive for Amazon customers to use its own increasingly enshittified search, which it could cram full of products from sellers who coughed up payola, as well as its own lookalike products. The alternative was to use Google, whose search tool would send you directly to the product you were looking for, and then charge Amazon a commission for sending you to it:
https://www.reddit.com/r/technology/comments/10ft5iv/comment/j4znb8y/
The demise of Amazon Smile coincides with the increasing enshittification of Google Search, the only successful product the company managed to build in-house. All its other successes were bought from other companies: video, docs, cloud, ads, mobile; while its own products are either flops like Google Video, clones (Gmail is a Hotmail clone), or adapted from other companies’ products, like Chrome.
Google Search was based on principles set out in founder Larry Page and Sergey Brin’s landmark 1998 paper, “Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine,” in which they wrote, “Advertising funded search engines will be inherently biased towards the advertisers and away from the needs of consumers.”
http://ilpubs.stanford.edu:8090/361/
Even with that foundational understanding of enshittification, Google has been unable to resist its siren song. Today’s Google results are an increasingly useless morass of self-preferencing links to its own products, ads for products that aren’t good enough to float to the top of the list on its own, and parasitic SEO junk piggybacking on the former.
Enshittification kills. Google just laid off 12,000 employees, and the company is in a full-blown “panic” over the rise of “AI” chatbots, and is making a full-court press for an AI-driven search tool — that is, a tool that won’t show you what you ask for, but rather, what it thinks you should see:
https://www.theverge.com/2023/1/20/23563851/google-search-ai-chatbot-demo-chatgpt
Now, it’s possible to imagine that such a tool will produce good recommendations, like Tiktok’s pre-enshittified algorithm did. But it’s hard to see how Google will be able to design a non-enshittified chatbot front-end to search, given the strong incentives for product managers, executives, and shareholders to enshittify results to the precise threshold at which users are nearly pissed off enough to leave, but not quite.
Even if it manages the trick, this-almost-but-not-quite-unusuable equilibrium is fragile. Any exogenous shock — a new competitor like Tiktok that penetrates the anticompetitive “moats and walls” of Big Tech, a privacy scandal, a worker uprising — can send it into wild oscillations:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/01/08/watch-the-surpluses/#exogenous-shocks
Enshittification truly is how platforms die. That’s fine, actually. We don’t need eternal rulers of the internet. It’s okay for new ideas and new ways of working to emerge. The emphasis of lawmakers and policymakers shouldn’t be preserving the crepuscular senescence of dying platforms. Rather, our policy focus should be on minimizing the cost to users when these firms reach their expiry date: enshrining rights like end-to-end would mean that no matter how autocannibalistic a zombie platform became, willing speakers and willing listeners would still connect with each other:
https://doctorow.medium.com/end-to-end-d6046dca366f
And policymakers should focus on freedom of exit — the right to leave a sinking platform while continuing to stay connected to the communities that you left behind, enjoying the media and apps you bought, and preserving the data you created:
https://www.eff.org/interoperablefacebook
The Netheads were right: technological self-determination is at odds with the natural imperatives of tech businesses. They make more money when they take away our freedom — our freedom to speak, to leave, to connect.
For many years, even Tiktok’s critics grudgingly admitted that no matter how surveillant and creepy it was, it was really good at guessing what you wanted to see. But Tiktok couldn’t resist the temptation to show you the things it wants you to see, rather than what you want to see. The enshittification has begun, and now it is unlikely to stop.
It's too late to save Tiktok. Now that it has been infected by enshittifcation, the only thing left is to kill it with fire.
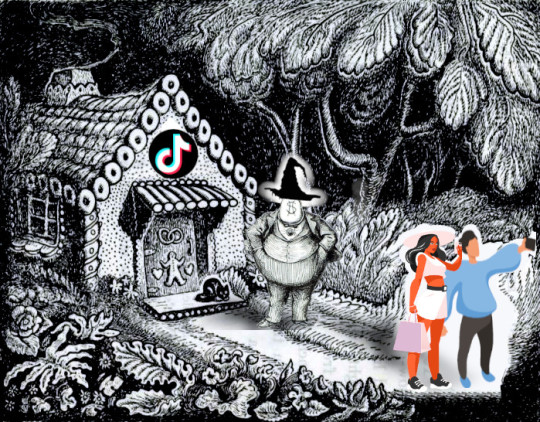
[Image ID: Hansel and Gretel in front of the witch's candy house. Hansel and Gretel have been replaced with line-drawings of influencers, taking selfies of themselves with the candy house. In front of the candy house stands a portly man in a business suit; his head is a sack of money with a dollar-sign on it. He wears a crooked witch's hat. The cottage has the Tiktok logo on it.]
#pluralistic#Lauren Leffer#tiktok#surplus allocation#fauximation#potemkin ai#the algorithm#creative labor#algorithms exposed#enshittification#bytedance#giant teddy bears#convincers#big store con#pivot to video#scissor bucket#Emily Baker-White
938 notes
·
View notes
Text

LEGO Almost Went Bankrupt. These Heroes Saved Our Bricks.
How a brain tumor inspired Bionicle, one of the most popular toys of a generation.
BY DAVID LUMB PUBLISHED: JUN 21, 2020
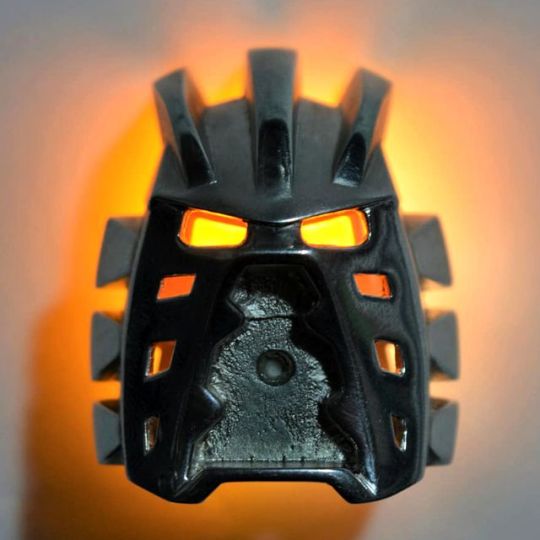

The Platinum Avohkii mask, a rare one- of-a-kind piece made of solid platinum purchased by Andre Hurley, who has The Bionicle Archives collection
Courtesy Andre Hurley/The Bionicle Archives
In 2003, LEGO seemed to be riding high after shrewd licensing deals brought Star Wars and Harry Potter sets to the masses. But unbeknownst to many—even those inside the company—sales were plummeting, and there were only guesses as to why.
Some blamed poor strategic choices in the 1990s—Legoland theme parks, forays into digital products—for LEGO’s hemorrhaging. All that misguided development time slashed profitability, and even Star Wars and Harry Potter sales shriveled between movie releases. It’s hard to conceive of now, but at the turn of the millennium, beloved LEGO might have been headed toward a pitiful end.
During this fallow period, one product line stood apart with startling, consistent success: Bionicle, a series of buildable action figures backed by rich worldbuilding and cross-platform promotion. Inspired by co-creator Christian Faber’s battle with a tumor at the base of his brain, the toy warriors of Bionicle wouldn’t just conquer their fictional enemies. They’d pioneer innovations that would transform LEGO and rescue the company from possible doom.

Courtesy Andre Hurley/The Bionicle Archives
Today, Christian Faber looks a bit like a Danish Paul McCartney. His youthful smile pairs well with his genial nature, which one might mistake for meekness until he starts talking about his creative projects. The 54-year-old embodies the unchecked enthusiasm you’d expect from a 28-year veteran of LEGO projects. If Faber’s long-time illness dimmed his appetite for play, you wouldn’t know it.
In 1986, Faber began working for Advance, a Copenhagen- based marketing firm that partners with LEGO. But shortly after his career began, Faber’s vision began to falter. A doctor found a benign tumor inside Faber’s pituitary gland that was impeding his sight, a condition called prolactinoma. Doctors said the tumor was maybe in the least accessible spot in the body for surgery, so they prescribed Faber daily medication to keep the tumor from growing. Among the drugs’ side effects, however, were severe nausea and dehydration, effectively sidelining Faber from social activities.

Courtesy Christian Faber
“It was the strangest mix of feelings,” Faber says. “I was happy at the job, but faced the physical and mental strain of the medicine and a long-term illness.”
Faber’s side effects attacked him hardest in the mornings, so he found most of his energy for work at night. Early in his career, Faber designed brochures for LEGO toy lines. Exposure to the different products, including the undersea-based Aquazone and the sophisticated Technic series, gave him experience with LEGO’s standards and practices—a moving target in the mid- 90s, when the rise of computers and video games pressured LEGO to move from their traditional years-long R&D cycle toward what Faber calls ‘craze products,’ toys tuned to current market tastes with a planned one-year shelf life.
The craze-products movement was rife with experimentation for LEGO, and it materialized soon after a medical breakthrough for Faber. After 10 years of daily medication, Faber’s physicians moved him on to a new treatment which, in Faber’s own words, gave him his life back. The new treatment was a regular injection scheduled just once every two weeks, allowing Faber to engage with the world relatively free from side effects. He could chase higher ambitions than brochures, and he had an idea for a new kind of LEGO toy: a sort of Bionicle precursor called Cybots.
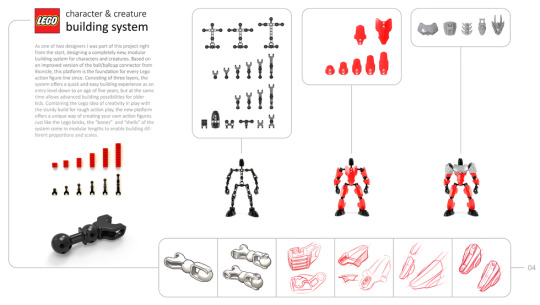
Courtesy The LEGO Group
“I was sitting with LEGO Technic and thought I would love to build a character instead of a car,” Faber says. “I thought of this biological thing: The human body is built from small parts into a functional body just like a model. What if you got a box full of spare parts and built a living thing?”
With his assistant graphic designer Jan Kjær, Faber pitched Cybots, a line of humanoid action figures with attachable limbs and ball-and-socket joints. LEGO didn’t furbish Cybots, but they would implement Faber’s concepts in craze products like Throwbots in 1999 and RoboRiders in 2000. By 2001, LEGO was testing a line called Bone Heads of Voodoo Island—masked robots with heads that could shoot off their bodies like Rock ‘Em Sock ‘Em Robots. Most of Bionicle’s look had been seeded: masks, buildable bodies, articulate limbs.

Courtesy Andre Hurley/The Bionicle Archives
Bone Heads of Voodoo Island was a bust—focus groups demonstrated kids didn’t respond well to detachable heads—so that same year, LEGO pivoted to focus on Bionicle. The plan was to take a more holistic design approach with these new toys than with craze products, but LEGO extended that comprehensiveness to the worldbuilding around the toys, too, a new strategy for the company. Faber and LEGO design manager Martin Riber Andersen were joined by former BBC film and TV executive Bob Thompson and writer Alastair Swinnerton to refine the Voodoo Island concept and pitch a new story. Faber, fresh from working on Star Wars LEGO sets, imagined something massive.
“After being on Star Wars, I was thinking that the only thing to do from here is our own stuff, but it should be as big as Star Wars,” Faber says. “It should be a big, full universe.”
For the storyline, Faber drew on his experience with prolactinoma. To him, his every-other-week injections seemed like sending in a new wave of protectors to battle his tumor with every dose. Faber imagined this group of disease-fighters arriving on an unknown beach with no memory. The story of these warriors would be called Bionicle, a portmanteau of ‘biological chronicle.’
Courtesy The LEGO Group/Christian Faber


Courtesy The LEGO Group/Christian Faber

Courtesy The LEGO Group/Christian Faber
“We took an episodic story line but chose not to play it out in any single medium,” Thompson told Kidscreen in 2003. “We would take that story and scatter it like a paper trail through different types of media.”
Bionicle’s in-world story evolved through comics and chapter books, written in large part by Greg Farshtey of LEGO’s promotional periodical LEGO MANIA Magazine (also known as LEGO Club Magazine, but now called LEGO Life Magazine). Farshtey followed Bionicle’s story bible from the original team, but as he began accounting for character changes correlating with new toy sets, he added his own takes. By the end of Bionicle’s run in 2010, he had interwoven the story with three feature films and shepherded the comic series that, at its peak, reached almost 2 million readers per month, making it the most widely circulated monthly comic on the planet.

Courtesy Andre Hurley/The Bionicle Archives
By all accounts, Bionicle was the hit LEGO needed. In 2001, its first year on the market, the line brought in over $160 million in sales, it was declared “Most Innovative Toy of the Year” by the Toy Association.
"Flat sales and profit decline made LEGO believe the brick was passé and it needed to move to digital and virtual toys to remain relevant,” David Robertson, author of LEGO history book Brick by Brick, told Popular Mechanics. “But as Bionicle became a success, LEGO learned the difference between sufficient and necessary. It wasn't sufficient to just offer customers another box of bricks, but it was necessary. If a LEGO toy didn't have interlocking plastic pieces, consumers didn't want it. But to succeed and grow, it was necessary to embed a story in that box of pieces and tell that story through comics, books, video games, movies, and events at the LEGO Stores."
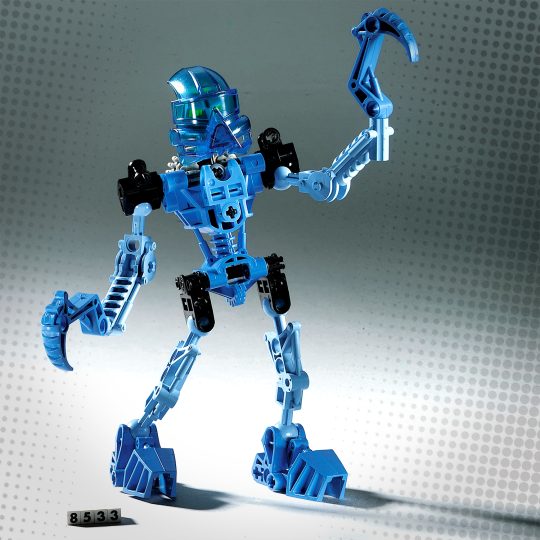
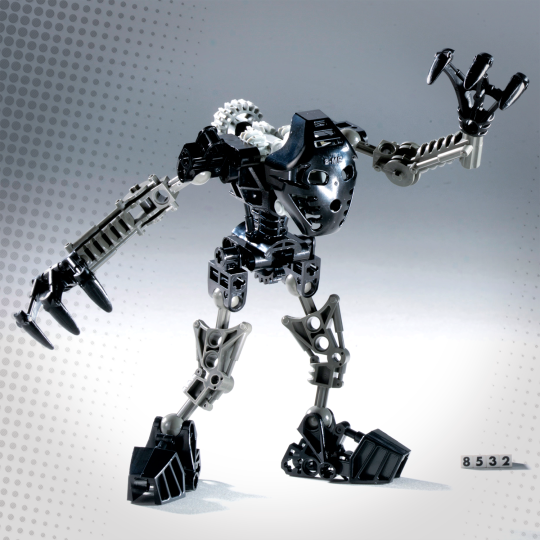
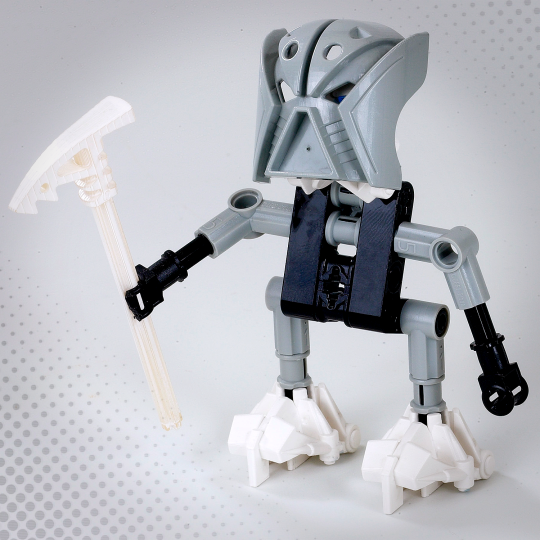
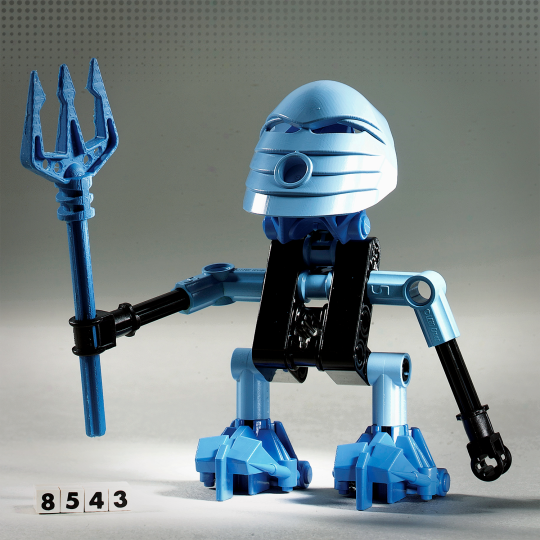






Courtesy The LEGO Group
In other words, Bionicle had all the ingredients of a fun LEGO toy, but Faber’s inspiration was key to making it a smash. “[My condition] had a direct effect on my career, and especially on the creation of Bionicle,” he says, ticking off the allegories. “A biological robot attacked by ‘illness,’ waiting for the right ‘medicine’ to arrive. Even the canisters the Toa warriors arrived in resembled the medicine capsules I had to eat every day.”
Bionicle hit its stride just as LEGO’s financials were bottoming out. While LEGO flirted with bankruptcy in 2003, Bionicle accounted for 25 percent of the company’s total revenue and 100 percent of its profits. As LEGO slashed its workforce, reduced the number of pieces it produced, and increased its range of licensing deals, Bionicle continued to diversify. Partnerships spawned. There were Bionicle-branded Nike shoes, McDonald’s Happy Meal toys, even Colgate toothbrushes. The cross-promotion paid off: By the end of Bionicle’s initial run in 2010, it sold over 190 million toys.
All the newness shook up LEGO’s tried-and-true project structure. Bionicle’s multifaceted development process blended design, marketing and engineering teams to hash out new sets, ingest market feedback, receive directives from LEGO executives, and issue their own directives to subsequent narrative and design teams. Under the new dynamic structure, development time for a new toy line at LEGO accelerated from three years to less than one. The rapidity created an exciting energy.
“We broke a lot of new ground experimenting and pushing boundaries,” Bionicle co-founder and design manager Martin Riber Andersen says. “One of the key ethos of the core team was this is a shared collaboration: We stand together. We all believed it was so in contrast to ‘the normal LEGO company’ that we might as well direct our energy to the team instead of our individual career objectives.”

Courtesy The LEGO Group

Courtesy The LEGO Group/Christian Faber
From 2003 to 2005, Bionicle was the reported top-performing LEGO toy line, but after that, sales dipped below expectations. The decline continued to 2009, when LEGO handed down word it was time to end Bionicle. The creators wrapped up the narrative in 2010, but it was hard to let go. Farshtey wrote Bionicle stories on the now-defunct BIONICLEStory.com until 2011, fans dissected the line’s mythology on BZPower forums, and custom Bionicles continued to appear. In 2016, Faber wrote to series fans: “The stories we hear and the stories we tell shape who we are and what we do ... through almost 30 years [of my career in storytelling], no story has proved this stronger than Bionicle. The fans were, are, and will be the true heroes of this ... great adventure.”
These days, you still see Bionicle at toy conventions, and the r/bioniclelego subreddit is alive and well. In fact, the front page of Reddit was graced in November 2019 with an essential, timeless question: “What is the appropriate amount of time to wait before showing your new significant other your Bionicle collection?”
The toys’ invigorating combination of articulate LEGO figures and intricate, multimedia story resonated with the LEGO company as well as fans. The brickmakers use the business strategy they honed on Bionicle with lines like Ninjago today, to great success.
"It's hard to overstate how important the Bionicle line was for LEGO,” Brick by Brick author Robertson notes. “Without the sales and profits of Bionicle in 2003 and 2004, the company would not have survived. Bionicle taught LEGO that success depended on the ability to hook kids on characters and story, and LEGO was smart enough to spread those practices throughout the company."

Courtesy Andre Hurley/The Bionicle Archives
After Bionicle, Swinnerton moved on to write children’s books and TV scripts, Andersen took on a senior position
at a European consulting agency, and Thompson founded a media production and consultancy firm. Farshtey, meanwhile, still edits LEGO’s free fan magazine. All cite Bionicle as high points in their careers.
“We should all be proud of what we achieved individually,” Thompson says. “But in my view, more important is what we did collaboratively. After all, LEGO fans are still talking about what we did with Bionicle—after two decades.”
Faber moved on from his design job at Advance in 2014 after 28 years working on LEGO. His medical journey continues to inspire his creative work, including a post-apocalyptic world he’s designing filled with adventure, danger, and a pro- environmental bent. Looking back, Faber sees the impact his illness and treatment had on the stories and projects he’s touched. Almost 20 years after co-creating the action figures that sustained LEGO through one of the darkest times in its history, talking about Bionicle still makes him reflective.
“Biology is a balance more than a battle between good and bad,” he says. “Ever since Bionicle, balance has been my goal in the stories and pictures I create.”

Courtesy The LEGO Group/Christian Faber
article graphics faber bs01
82 notes
·
View notes
Text
“Seller services,” as Amazon refers to these and other sources of revenue, are a large and growing part of Amazon’s revenue — larger than Amazon Web Services and quite profitable. They also mean that letting a seller market off-brand products on your platform is often going to be more profitable than selling your own discount brands: Undercutting an independent seller’s small coffee-grinder business is, it turns out, a bad look and, in the big picture, maybe not worth the trouble.
Sellers serve a lot of purposes for Amazon and joke among themselves about the free labor they provide. In exchange for access to the largest sales channel on the internet, they do a lot more than just pay Amazon its fees. They perform market research, obsessively investigating review data and marketplace trends to figure out what’s going to be popular on the platform next. (Recent red-hot third-party product types include miniature waffle-makers, reading lights that drape around your neck, and dog puzzles.) They handle customer service. They exert downward price pressure on one another, and they absorb a lot of risk (dozens of dog-puzzle sellers fail so that one may thrive). No matter what happens to them, whether their own businesses succeed or fail, Amazon makes money.
This is a great deal for Amazon, and over the years it has become Amazon’s main deal — in 2021, the company estimated that activities on its marketplace created “more than 1.8 million U.S. jobs” and shared success stories from its hundreds of thousands of American sellers, some of whom had become millionaires. It was a slow and, in hindsight, astounding transformation in which the “everything store” substantially outsourced its store.
-John Hermann, The Junkification of Amazon
86 notes
·
View notes
Note
Of course, you can put a spin on my cat quirk user ♡
(Alright, just wanted to make sure.)
(Trigger warning: human and animal trafficking mentioned, also mentions of drugging someone)
Aizawa x Jaguar Reader
(The reader in this story is an actual Jaguar with a quirk that allows them to transform into a human)
Reader is a Jaguar who was naturally born with a human transformation quirk. They grew up in the Amazon jungle with their mother who was a normal Jaguar. The reader learned to hunt and was taught everything they needed in order to be a successful apex predator by their mother
The reader has human level intelligence due to their quirk.
One day, villains from Brazil found out about the reader. They eventually tranquillized and captured the reader, smuggling them into Japan were the villains planned to sell the reader in a black market auction
When the reader had woken up halfway through the shipping to Japan, they realized that their best chance of survival was to wait for the villains to let their guard down, then the reader could have a better chance of escaping. When the smugglers realized that the reader was awake they drugged them again, putting the reader back to sleep
Meanwhile in Japan, Detective Tsukauchi and the police had been tracking two of the main villains in charge of the auctions and running them. The police were planning a raid on the building the night of the auction. The people running it were notorious for human trafficking, the sale and trafficking of parts of or whole endangered animal species, kidnapping, etc.
Detective Tsukauchi was the lead investigator and asked Aizawa as well as Midnight to help in the raid. Midnight’s primary role was to help subdue the criminals as well as protect the heroes and police from any dangerous animals that might be found
On the night of the auction the reader wakes up inside a metal cage with a shock collar on their neck. They’re hidden beneath the stage in the storage area, surrounded by various cages with other humans and some animals
The humans all seemed to be young and mostly female, the reader could sense the fear that belonged to the humans in the cages. The humans also were wearing the strange collar that was around their own neck
The humans outside the cages all had white masks covering their faces. One of these people was walking around going to each cage and putting their hands on the humans heads. Once the person had come to them the reader snarled at them but was rewarded with a powerful shock running through their body.
The human placed their hands an the reader’s head, after feeling a weird tingling sensation, the human retracted their hands. The human then told the reader that they had better do whatever they are told, if they don’t listen, they will be shocked. With the effects of the drugs still wearing off, the reader didn’t question how they could suddenly understand what the human’s language.
Suddenly a loud voice is heard from above as the auction begins. After a few minutes, cages are wheeled over to a platform that lifts things onto the stage through the floor.
After the last cage before them is brought up, the human from earlier commands the reader to change into their human form. Not listening to the commands, the reader is shocked again when the human presses a rectangular object.
After that the reader transforms and a hook attached to a long pole is connected to their collar as they are led onto the lift
Outside the heroes and police are setting up and getting into position to start the raid. All entrances and exits have been surrounded. Once Tsukauchi has made sure everything and everyone was in place and ready, he gave the order to cut the buildings power supply thus signaling the start of the raid
As the heroes begin to enter the building and start taking out the buyers, auctioneers and other participants, the reader, having been sold to a wealthy businessman with a cat-girl fetish, is being led to one of the back rooms when the power goes out
Since the system that was controlling the collars was being powered by the building’s electrical system, once the power was shut off, the collars unlocked and deactivated
Realizing that this is their best chance at escaping, the reader transforms into their original form and attacks the nearest person in a mask. Using their natural predatory night vision, as well as their hunting skills, the reader slinks through the hall avoiding as many people as possible using the darkness to their advantage
After passing by a hall filled with a purple fog, the reader turns the corner and finds themselves back at the stage where a human with strange glowing red eyes protected by some strange yellow covering, is fighting the humans in white masks
This human had some strange long grey appendage? No, tool? They were using it to capture the humans and fight them. This human also smelled different than the humans in masks
Distracted by their predatory analyzation of the human, they didn’t notice that the human had defeated all of the other humans present. When the human suddenly turned their attention and focus onto them.
The human stared at the reader for a moment before removing the yellow eye coverings. Quickly retrieving something from its waist, the human tilted their head back, dropping some kind of liquid into its eyes.
The human, after a few blinks, stares the reader in the eyes as the human’s mane raises and its eyes glow red. Seeing this as some kind of human threatening display, the reader snarls as they bear their fangs and crouch into position to pounce onto the human if necessary
After a few seconds the human lowered its mane as its eyes stopped glowing. The human raised its front paw and told the reader that they are not a threat and that they are not going to hurt them. The human didn’t seem to have any sort of fear and was obviously not a prey but they were still wary of the reader.
Suddenly another human called out and was running up behind the human, before either human could react, the reader pounced onto the new human, believing them to be a threat. Sinking their claws into the human’s shoulders and about to go for the head, Aizawa shouts no, in distress.
Realizing that the human was upset by them attacking the other human, the reader turns to look at Aizawa as they get off of the police officer.
After checking on the officer’s condition and making sure they were okay, Aizawa turns to the reader after realizing that they stopped their attack after he told them to
Carefully approaching the reader, Aizawa asks them if they can understand what he’s saying and to lift their front paw if they can. The reader lifts their paw and afterwards slowly approaches Aizawa. Before the reader can get to close a purple fog surrounds them as a loud sound is made as they feel a sharp pain in their hind leg. Before they can turn and attack the human the reader falls asleep
After dealing with the clean up and arresting the criminals, Tsukauchi approaches Aizawa with a file containing a list of the items being sold. When looking at the file, Tsukauchi points out the reader’s information.
When Aizawa confirms that the listed information is true, that being that the reader is actually an animal with a quirk, Aizawa asks Tsukauchi what would be done with the reader.
Tsukauchi tells him that there really isn’t much he can do about what would happen to the reader, but that the reader would either be handed over to scientists or placed in a zoo or research sanctuary.
Aizawa decides that the reader would probably be subjected to experiments and would be forced to undergo extensive and invasive tests, he calls Nedzu and tells him about the reader
When the reader wakes up, they are laying on a pile of blankets with bandages wrapped around the top of their left hind leg. Looking around they are met by a white rodent.
The rodent introduces himself as Nedzu, he explains to the reader what happened and what their current situation is. He explains that humans are not used to seeing animals with abilities like theirs. He tells the reader that humans are likely to experiment on animals like them since they are different.
Nedzu tells them that since they are capable of understanding humans, that the reader’s best course of action is to learn to live like a human and understand human society. He tells the reader that he can help them and give them the opportunity to become what humans call a hero
After much discussion mainly on Nedzu’s part, the reader agrees to live at UA. Aizawa, being the one who found them, is put in charge of the reader and is made their handler/guardian
Aizawa teaches the reader what they need to know and how society works. While Aizawa teaches, the reader either sleeps or patrols the grounds. At night, when Aizawa is on patrol, the reader follows him as his sidekick.
Power loader creates a special suit for the reader to wear made of the reader’s own fur, that way they are not naked when they transform. The reader is officially a member of the Aizawa family
Hope you enjoyed this
#mha x reader#bnha x reader#aizawa x reader#mha aizawa#aizawa shouta#x cat reader#mha#bnha#aizawa sensei#bnha aizawa#mha pro heroes#bnha pro heroes
44 notes
·
View notes
Text

1970 Pontiac Formula 400
1970 Pontiac Formula 400 – The Other Performance Firebird
The story behind the development of GM’s F-body ponycars has been well documented. When Ford’s groundbreaking Mustang debuted in 1964, it tapped an emerging youth market that was hungry for a new type of car geared specifically to them. GM misjudged the public’s response to the Mustang and then scrambled to develop a similar style car after witnessing Ford’s unprecedented first model year sales success. Chevrolet was the lead division in engineering the F-body, and Pontiac grudgingly accepted the platform for their use in March 1966, only after GM management turned down PMD General Manager John DeLorean’s proposal for his own Mustang fighter.

Pontiac didn’t have much time to transform the Firebird from its Camaro configuration before releasing it in February 1967. Their design and engineering lead time was significantly reduced and consequently, the Firebird was forced to use quite a bit of Camaro sheetmetal and other components. Competition between Pontiac and Chevrolet was intense, and having to use the other division’s engineering and design was a bitter pill for DeLorean’s maverick staff to swallow.
The circumstances surrounding the second generation Firebird were another story. Pontiac actually began working on their second generation just as the first Firebirds were hitting dealer showrooms. From design to engineering, Pontiac dominated the divisional rivalry, and this time around the Firebird would be all Pontiac from roof to road. There was little carried over to the second generation with the exception of the Trans Am nameplate and basic engine configurations. The suspension was tuned for more responsive handling with little compromise to ride comfort. Computer aided engineering chose the proper front and rear spring deflection rates predicated on model and usage. Stabilizer bars were used front and rear and the steering box was mounted ahead of the front axle for better response.

The sexy new body was rooted in GM styling chief Bill Mitchell’s infatuation with Italian sports car design. GM chose heavily from the rounded shapes of Ferrari and Maserati, and it showed in the smooth flow of fender lines, the curved window glass and raked windshield. One remarkable difference from pervious GM designs was the lack of a quarter window. Instead, the doors were lengthened to take up a larger portion of the quarter. The massive doors were heavy, however the side appearance was cleaner and far sportier. A lift bar door handle added to the smooth side look. Chrome was distinctively absent. The Native American-inspired Firebird emblem was on the decklid and the nose of all but base model cars.
Up front, the twin nostril grille and single headlamps provided a clean appearance, thanks to the use of Endura to create a bumper-less front end with a valance that cleanly rolled beneath the grille with large cross hair parking lamps mounted in the lower corners of the valance. At the rear, the smooth tumble home enhanced the Firebirds fuselage shape. The tail was flat and filled with twin tail lamps that met the quarter panel’s round rear profile. A recessed tag housing, thin blade chrome rear bumper, and rounded lower valance completed the rear end’s clean look.

Inside, the Firebird’s wide, expansive dash housed the instrument panel consisting of three center nacelles for gauges, with smaller gauges at the right and room for the heater controls and additional switches and knobs. Directly below the center of the dash was another stack that contained the radio and ashtray. Even the base interior was sumptuous, with Pontiac’s indestructible Morrokide vinyl upholstery covering the bucket seats and door panels. The quarter trim panels and headliner were composed of molded polymeric material that provided a smooth surface and absorbed sound.
The 1970 Pontiac line up was composed of the base Firebird with 250 cid six, the mid range, 350 cid Espirit, the 400 cid Formula 400, and the 400 cid Ram Air Trans Am. Of the four, perhaps the most intriguing was the Formula 400. While the Trans Am was loaded with visuals like a shaker hood, fender mounted air extractors, wild front air spoiler, rear wheel opening air spoilers, and wide center stripe, the Formula had none of these. For those who preferred to have a muscular pony car sans the exterior adornments, the Formula 400 was just the ticket. Outside, the only difference between the mild mannered Espirit and the Formula was a special fiberglass hood that sported a pair of front reaching hood scoops (first considered for the Trans Am), sport style dual outside mirrors, and a pair of Formula 400 scripts below the Firebird nameplate on the fenders.
Under the sheetmetal, however, is where the $3,440 Formula’s credentials lay. Standard engine was the 400 cid V8 which generated 330 horsepower @ 4800rpm and 430 lbs.-ft. torque @ 3000rpm. Car & Driver tested a Formula 400 with this engine and automatic transmission and recorded a 0-60 acceleration time of 6.4 seconds and quarter mile performance of 14.7 seconds at 98.9mph.


The optional engine was the Ram Air III V8, which produced 345 horsepower @ 5000rpm and 430 lbs.-ft. torque @ 3400rpm, thanks in part to a higher compression and a more aggressive camshaft profile. While Pontiac offered a 370 horsepower Ram Air IV, it never found its way into a Formula 400. On the Ram Air III equipped Formulas, the hood scoops were opened and a pair of rubber “boots” were fitted to the hood’s underside. They snugged up to holes in the air cleaner snorkels and fed cold outside air to the Rochester Quadra Jet carburetor. Subtle “RAM AIR” decals were affixed to the outboard sides of the hood scoops. The Formula’s 400 engine was dressed up with chromed air cleaner lid and valve covers. Dual exhausts with chrome tips were also standard.
Standard transmission was the M13, a heavy duty Dearborn three-speed manual box. A pair of Muncie four speeds was offered optionally, the wide ratio M20 and close ratio M21. Also optional was the M40 three-speed Turbo Hydra Matic transmission. A 3.55:1 rear axle ratio was standard, while air conditioned models received 3.31:1 ratios. Optional ratios were 3.07:1 and 3.73:1.

The Formula received a firmer suspension with 300-pounds/inch deflection in the front springs and 103 pounds/inch in the rear. The front stabilizer measured 1.125 inches in the front and the rear bar was .620 inches with firm control shocks mounted at all four corners. Front disc brakes were standard with rear drums. Standard tires were F70 x 14 on six-inch steel rims. The Trans Am’s tighter suspension was offered optionally. It consisted of 300 pounds/inch front and 126 pounds/inch springs in the rear, 1.250 inch stabilizer bar at the front, and fat .875 inch bar aft. Wider F60x 15 Polyglas tires mounted on 15 x 7 Rally II wheels without trim rings rounded out the package. Add the variable ratio power steering and power brakes and the Formula responded right now! to steering input and could dive deeper into corners and come out faster. Its only competition was big brother Trans Am and the Corvette.
Inside, the Formula’s instrument panel was faced in a wood grained appliqué. Optional was a Rally Gauge that placed an 8000-rpm tach in the left housing along with a small analog clock. In the smaller center housing was the engine temperature and oil pressure gauges. The right housing contained the 160mph speedometer with the smaller fuel gauge and voltmeter to the far right. Two consoles were offered, one between the front buckets that contained the transmission shifter, the other between the optional rear buckets.

Of the 7,708 Formula 400s produced in 1970, 2,777 were equipped with manual transmissions. Exactly 4,931 were fitted with the M40 automatic transmission. One of those M40 equipped Formulas is owned by Jack Nichols of Orlando, Fla. Jack performed a complete restoration on the Formula several years ago, bringing it back to correct factory standards. The Atoll Blue Formula is fitted with the optional Ram Air engine, open scoops and underhood induction system. Inside, the tan Morrokide interior features console, optional three-spoke Formula steering wheel with padded rim, Rally gauges and air conditioning.

Text and Photography By Paul Zazarine
© Car Collector Magazine, LLC.
(Click for more Car Collector Magazine articles)
Originally appeared in the March 2008 Issue
#pontiac firebird#ram air#formula 400#pontiac#1970 Pontiac Formula 400#car#cars#muscle car#american muscle
255 notes
·
View notes
Text
Help the Dangerous Ladies Keep Creating!
Hello, it’s been a while! Unfortunately, we’re coming back under less than ideal circumstances.
Our Etsy shop, our main source of income, has been recently suspended due to copyright claims. At the behest of our supporters, we have started a Gofundme to help keep the lights on.
Help Us Out at our GoFundMe
If you don’t know us, we're a small woman owned and operated, LGBT-friendly costuming company that has been cosplaying together for a decade and providing resin kits, patterns, textiles and other accessories to the community since 2013. We’re based in Toronto, Canada.
To date, we have shipped more than 26,000 kits, prints, files and other resources for cosplayers. This business is our livelihood and came to fruition through hard work and effort. Everything we make is from scratch, with our own hands and our own machines, in small quantities, to order. Our digital files are all made in-house, individually, using no official assets. We are not a factory mass-producing wholesale goods, nor do we dropship other people's products. We are a committed little business that has loved being on Etsy, and truly believe we are the very artists that Etsy should want to platform –– our goods are handmade, unique, and often the only resource of their kind!
We work hard for our high ratings, but agents operating on behalf of certain companies occasionally send take-downs, and then do not reply to us when we try to work it out with them. It's complicated, but the reality is that we're creating projects in the realm of transformative work and are by no means taking away profit from the creators of these properties, as our cosplay kits are one-of-a-kind creations with no official analogue.
We also feel very strongly that cosplay is an incredible form of free advertising for companies producing video games, anime, tv shows and movies. Cosplayers put in a tremendous amount of labour, time and money to make their costumes, which they wear and display all over conventions, the internet and social media. We know from experience that companies enjoy and engage with the fruits of this labour; the very companies that inspire us to create kits sometimes hire us (and other cosplayers) themselves to represent their media after having seen our store! We've had the distinct pleasure of working for media companies large and small, and they know what we make and allow us to keep the rights to our files and associated assets. These companies also regularly post on social media with cosplayers using our work. However, Etsy does not know who or what companies choose to allow the sale of fan art and goods. To them, a report is a report, even if it is erroneous or mistaken.
This has been a crushing blow to us as a small business. We're a very month-to-month, low-profit business after we pay the bills and our team. Currently, Dangerous Ladies employs eight staff members and operates from a rented studio space. Both our staff and our space are an integral part of our business and allow us to be able to operate at our current capacity, providing cosplay resources to creators all around the world. Without support, we will have to scale back dramatically, if not close entirely.
While we work to appeal with Etsy, we realize that there is a chance we may not see our platform flourish there again, so we are working diligently to bring you our new website, and welcome you to visit our Storenvy in the meantime.
We started this Gofundme Although orders are very important to us right now, we understand that some of you may not have the need to order a kit, print, or fabric at the moment, but still wish to support us through this trying time.
For this, we want to say thank you from the bottom of our hearts.
Sincerely, the Dangerous Ladies Jenn, Christine, Shazz, Aubree, Nicole, Gabi, Syd, and Jules <3
Can I see more of what you do?
Of course! While our Etsy is down, you can visit us on Storenvy or subscribe to our newsletter. You can also find us on Twitter and Instagram!
133 notes
·
View notes
Text
It no longer makes sense to speak of free speech in traditional terms. The internet has so transformed the nature of the speaker that the definition of speech itself has changed.
The new speech is governed by the allocation of virality. People cannot simply speak for themselves, for there is always a mysterious algorithm in the room that has independently set the volume of the speaker’s voice. If one is to be heard, one must speak in part to one’s human audience, in part to the algorithm. It is as if the US Constitution had required citizens to speak through actors or lawyers who answered to the Dutch East India Company, or some other large remote entity. What power should these intermediaries have? When the very logic of speech must shift in order for people to be heard, is that still free speech? This was not a problem foreseen in the law.
The time may be right for a legal and policy reset. US lawmakers on both sides of the aisle are questioning Section 230, the liability shield that enshrined the ad-driven internet. The self-reinforcing ramifications of a mere 26 words—“no provider or user of an interactive computer service shall be treated as the publisher or speaker of any information provided by another information content provider”—has produced a social media ecosystem that is widely held to have had deleterious effects on both democracy and mental health.
Abraham Lincoln is credited with the famous quip about how you cannot fool all the people all the time. Perhaps you cannot, but perhaps the internet can. Imperfect speech has always existed, but the means and scale of amplification have not. The old situation cannot be the guide for the new.
Section 230 was created during a period when policy was being designed to unleash internet innovation, thereby maintaining America’s competitive edge in cyberspace. The early internet was supported by a variety of friendly policies, not just Section 230. For instance, sales arranged over the internet were often not taxed in early years. Furthermore, the internet was knowingly inaugurated in an incomplete state, lacking personal accounts, authentication mechanisms, commercial transaction standards, and many other needed elements. The thinking was not only that it was easier to get a minimal design started when computing power was still nascent, but also that the missing elements would be addressed by entrepreneurs. In effect, we were giving trillion-dollar gifts to parties unknown who would be the inevitable network-effect winners.
Section 230 was enacted as part of the 1996 Communications Decency Act, a larger legislative effort within the umbrella 1996 Telecommunications Act. Section 230(c)(1) provides immunity for online services regarding user-generated content, ensuring the companies hosting content are not treated as publishers of this information. Section 230(c)(2) offers Good Samaritan protection from civil liability when the companies—or platforms, as we call them today—in good faith remove or moderate objectionable content.
After President Bill Clinton signed the 1996 Telecommunications Act into law, it was unclear how the courts might interpret it. When the dust cleared, Section 230 emerged as something of a double-edged sword. It could be used to justify censorship, and at the same time be deployed as a corporate liability shield. Most importantly, it provided the runway for the takeoff of Google, Twitter, and Facebook. (And now TikTok—which, being a Chinese company, proves that Section 230 no longer serves American interests.)
The impact on the public sphere has been, to say the least, substantial. In removing so much liability, Section 230 forced a certain sort of business plan into prominence, one based not on uniquely available information from a given service, but on the paid arbitration of access and influence. Thus, we ended up with the deceptively named “advertising” business model—and a whole society thrust into a 24/7 competition for attention. A polarized social media ecosystem. Recommender algorithms that mediate content and optimize for engagement. We have learned that humans are most engaged, at least from an algorithm’s point of view, by rapid-fire emotions related to fight-or-flight responses and other high-stakes interactions. In enabling the privatization of the public square, Section 230 has inadvertently rendered impossible deliberation between citizens who are supposed to be equal before the law. Perverse incentives promote cranky speech, which effectively suppresses thoughtful speech.
And then there is the economic imbalance. Internet platforms that rely on Section 230 tend to harvest personal data for their business goals without appropriate compensation. Even when data ought to be protected or prohibited by copyright or some other method, Section 230 often effectively places the onus on the violated party through the requirement of takedown notices. That switch in the order of events related to liability is comparable to the difference between opt-in and opt-out in privacy. It might seem like a technicality, but it is actually a massive difference that produces substantial harms. For example, workers in information-related industries such as local news have seen stark declines in economic success and prestige. Section 230 makes a world of data dignity functionally impossible.
To date, content moderation has too often been beholden to the quest for attention and engagement, regularly disregarding the stated corporate terms of service. Rules are often bent to maximize engagement through inflammation, which can mean doing harm to personal and societal well-being. The excuse is that this is not censorship, but is it really not? Arbitrary rules, doxing practices, and cancel culture have led to something hard to distinguish from censorship for the sober and well-meaning. At the same time, the amplification of incendiary free speech for bad actors encourages mob rule. All of this takes place under Section 230’s liability shield, which effectively gives tech companies carte blanche for a short-sighted version of self-serving behavior. Disdain for these companies—which found a way to be more than carriers, and yet not publishers—is the only thing everyone in America seems to agree on now.
Trading a known for an unknown is always terrifying, especially for those with the most to lose. Since at least some of Section 230’s network effects were anticipated at its inception, it should have had a sunset clause. It did not. Rather than focusing exclusively on the disruption that axing 26 words would spawn, it is useful to consider potential positive effects. When we imagine a post-230 world, we discover something surprising: a world of hope and renewal worth inhabiting.
In one sense, it’s already happening. Certain companies are taking steps on their own, right now, toward a post-230 future. YouTube, for instance, is diligently building alternative income streams to advertising, and top creators are getting more options for earning. Together, these voluntary moves suggest a different, more publisher-like self-concept. YouTube is ready for the post-230 era, it would seem. (On the other hand, a company like X, which leans hard into 230, has been destroying its value with astonishing velocity.) Plus, there have always been exceptions to Section 230. For instance, if someone enters private information, there are laws to protect it in some cases. That means dating websites, say, have the option of charging fees instead of relying on a 230-style business model. The existence of these exceptions suggests that more examples would appear in a post-230 world.
Let’s return to speech. One difference between speech before and after the internet was that the scale of the internet “weaponized” some instances of speech that would not have been as significant before. An individual yelling threats at someone in passing, for instance, is quite different from a million people yelling threats. This type of amplified, stochastic harassment has become a constant feature of our times—chilling speech—and it is possible that in a post-230 world, platforms would be compelled to prevent it. It is sometimes imagined that there are only two choices: a world of viral harassment or a world of top-down smothering of speech. But there is a third option: a world of speech in which viral harassment is tamped down but ideas are not. Defining this middle option will require some time to sort out, but it is doable without 230, just as it is possible to define the limits of viral financial transactions to make Ponzi schemes illegal.
With this accomplished, content moderation for companies would be a vastly simpler proposition. Companies need only uphold the First Amendment, and the courts would finally develop the precedents and tests to help them do that, rather than the onus of moderation being entirely on companies alone. The United States has more than 200 years of First Amendment jurisprudence that establishes categories of less protected speech—obscenity, defamation, incitement, fighting words—to build upon, and Section 230 has effectively impeded its development for online expression. The perverse result has been the elevation of algorithms over constitutional law, effectively ceding judicial power.
When the jurisprudential dust has cleared, the United States would be exporting the democracy-promoting First Amendment to other countries rather than Section 230’s authoritarian-friendly liability shield and the sewer of least-common-denominator content that holds human attention but does not bring out the best in us. In a functional democracy, after all, the virtual public square should belong to everyone, so it is important that its conversations are those in which all voices can be heard. This can only happen with dignity for all, not in a brawl.
Section 230 perpetuates an illusion that today’s social media companies are common carriers like the phone companies that preceded them, but they are not. Unlike Ma Bell, they curate the content they transmit to users. We need a robust public conversation about what we, the people, want this space to look like, and what practices and guardrails are likely to strengthen the ties that bind us in common purpose as a democracy. Virality might come to be understood as an enemy of reason and human values. We can have culture and conversations without a mad race for total attention.
While Section 230 might have been considered more a target for reform rather than repeal prior to the advent of generative AI, it can no longer be so. Social media could be a business success even if its content was nonsense. AI cannot.
There have been suggestions that AI needs Section 230 because large language models train on data and will be better if that data is freely usable with no liabilities or encumbrances. This notion is incorrect. People want more from AI than entertainment. It is widely considered an important tool for productivity and scientific progress. An AI model is only as good as the data it is trained on; indeed, general data improves specialist results. The best AI will come out of a society that prioritizes quality communication. By quality communication, we do not mean deepfakes. We mean open and honest dialog that fosters understanding rather than vitriol, collaboration rather than polarization, and the pursuit of knowledge and human excellence rather than a race to the bottom of the brain stem.
The attention-grooming model fostered by Section 230 leads to stupendous quantities of poor-quality data. While an AI model can tolerate a significant amount of poor-quality data, there is a limit. It is unrealistic to imagine a society mediated by mostly terrible communication where that same society enjoys unmolested, high-quality AI. A society must seek quality as a whole, as a shared cultural value, in order to maximize the benefits of AI. Now is the best time for the tech business to mature and develop business models based on quality.
All of this might sound daunting, but we’ve been here before. When the US government said the American public owned the airwaves so that television broadcasting could be regulated, it put in place regulations that supported the common good. The internet affects everyone, so we must devise measures to ensure that our digital-age public discourse is of high quality and includes everyone. In the television era, the fairness doctrine laid that groundwork. A similar lens needs to be developed for the internet age.
Without Section 230, recommender algorithms and the virality they spark would be less likely to distort speech. It is sadly ironic that the very statute that delivered unfathomable success is today serving the interests of our enemies by compromising America’s superpower: our multinational, immigrant-powered constitutional democracy. The time has come to unleash the power of the First Amendment to promote human free speech by giving Section 230 the respectful burial it deserves.
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
At iCumulus, we take great pride in our Digital Transformation initiative. Whether to employ artificial intelligence to convert manual tasks to digital ones or to use technology to improve or eliminate an ineffective working procedure. Learn how our agency may assist you with digitising the operational framework of your business.
0 notes
Text
What Movie Has A Message For You?
How to Pick a Pile? Some of us focus on the image that seems to call to us most, some intuitively choose regardless of picture. Don't overthink it. Choose whichever pile you feel called to. It may even be more than one!
🔮Join Patreon for exclusive video readings
💖Check out Etsy for personal readings *Take advantage of Christmas Sale!*
🎉Donations and gifts are never required but always appreciated




Pile 1:
You need a movie with a strong woman at the center. Something that is inspiring, thoughtful or mind boggling. As weird as it may seem, Gone Girl, or any more like it may be beneficial for you to watch at this time. You could also benefit from movies that are based off books. Maybe The Girl With The Dragon Tattoo, or Hunger Games.
💕Leave a note or check out other platforms If you'd like to further support me!

Pile 2:
Something that depicts a similar struggle you are going through. The movie for you right now is something involving the feeling of being trapped, struggling or going through challenges. If there is a movie in mind where the main character transform in some way, watch it. Even if it’s “The Chosen One” trope. Movies where information is a big part of a journey is also really important at this time. The Matrix? Or maybe even The Little Mermaid.
💕Leave a note or check out other platforms If you'd like to further support me!

Pile 3:
Movies where there is a Hero’s Journey. The kind of movies that would resonate with you right now are ones that include determination, downfalls, choices, ambition, discovery, and success. This may even be a series. You need a clear high and low moment movie that lets you sit in it. This doesn’t necessarily have to be a traditional Hero’s Journey. It can be about a person’s internal struggle or a struggle to get out of a certain situation. Antwone Fisher came to mind.
💕Leave a note or check out other platforms If you'd like to further support me!
#intuitive reader#tarotcards#queen of the damned#scary movies#barbie movie#oraclereading#pick a pile#pickacard#pac#tarotblr#tarot blog
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
As for myself, I never backpacked through Asia, and of course I've never done a medical residency, either.
I was a Second Life content creator around 2008-2012, which is itself pretty rare.
In Second Life, especially in those years, there wasn't a clean division between "playing the game" and "making the world," and there wasn't a clean division between "content creators" (including businesses) and "players." And the whole thing was funded mostly by privately leased plots of virtual land as server space.
Back in 2007, under liberal technological optimism, there was still this sense that everyone would own and learn to properly operate their own PC, which is to say a 'real' computer like a desktop or laptop, rather than an 'appliance' computer like a smartphone or tablet. Though the platform was privately held, Second Life embodied this thinking.
And so it possessed this immense feeling of power and control. You could click on a rock and drag it around. If you had good device operator skills, you could search out and purchase a supply of copiable rocks and assemble a little volcano lair and exotic beach house on a sandy beach as your home.
At first, almost all items were assembled within the game, and only textures made externally. Gradually this shifted to the use of external 3D modelling tools such as Blender, but for a time, this meant that much of the act of product creation was in the world, as in people would be logged in making the product in front of you and you could chat with them while they did so.
And of course, this world attracted people that for some reason were willing to lean to this kind of detached embodiment. Some were queer, or trans, or neurodivergent. Some were of ill health, or crippled. Others were in some sense very 'in their own heads,' or just well-adapted to simulated or virtual-reality environments. (Does that sound like Tumblr? It's probably not a coincidence.)
It was a world with a very different axis. Your appearance was a function of your aesthetic taste, your device operator skill to search out and assemble and compose an outfit, and only a modest amount of money. Someone with a very high-grade appearance would also be someone that's decently good with computers. For those with programming aptitude, their gadgets or products around them (or for sale at their store), would illustrate it.
And for creators, there was overlap between the ability to 3D model a car, and the ability to 3D model clothing. A creator could be a maker of tanks and also have their own fashion line - or even unique personal outfits. (Even hobbyists with more modest abilities would customize and kitbash - and creators would sometimes set things up specifically so that they could do so.)
There was a sense of whimsy. Cultural norms, too, though of course all massively-multiplayer systems will develop their own etiquette. (Gender could be fluid - the same player might have a stock of both male and female bodies and outfits depending on the context in which they were to be used and the message they wanted to send.)
The problem with Second Life is that you cannot live there.
Yes, it's a low-dimensionality construct like all video games. It lacks scent, and temperature, and touch. Its avatars have far fewer bones than a human body does, and of course, no organs. Its low dimensionality is why it can be changed and molded like clay, into fantastical forms that could never exist in real life.
But more importantly, children live in real life. And if you're injured or sick and can't get up, someone needs to come retrieve you in real life.
The platform turned out to be relatively useless for major corporations and universities. It didn't transform the economy and add trillions to the GDP, and virtual land didn't become the wave of the future - although digital currency did, for a while.
Instead, this failed vision of the future created a flourishing of creativity and human connection, and as time passes, it's becoming clear that the reason is because it was so earnest and very much the thing that it was. (There is value in things which are not perfect, but which are very much themselves, and are good at being the thing that they are.)
On the financial side, it was still operating at a profit when I checked the numbers several years ago. As part of its portfolio, the company seems to have leveraged digital currency operations based on their built-up competency in that sector - as in payment processing, not cryptocurrency.
And what do people write about Second Life now, in 2023? Well, they write about the fashion. About the continuing culture of small-time creators, allowed to work within the framework that was created for them all those years ago. About the platform remaining a steady source of background income for people with jobs in the games industry, notorious for its high turnover.
29 notes
·
View notes
Text
How Amazon transformed the EU into a planned economy

Amazon is a perfect parable of enshittification, the process by which platforms first offer subsidies to end users until they’re locked in, then make life good for business customers at users’ expense, until they’re locked in, then claw back all the value they can for themselves, leaving just enough behind to keep the lock-in going.
In a new report for SOMO, Margarida Silva describes how the end-stage enshittification of Amazon is playing out in the EU, with Amazon repeating its US playbook of gouging the small businesses who have no choice but to use the platform in order to reach its locked-in customers, making European customers and European sellers poorer:
https://www.somo.nl/amazons-european-chokehold/
The mechanism for this isn’t a mystery. Amazon boasts about it! They call it their flywheel: first, customers are lured into the platform with low prices, especially through Prime, which requires pre-payment for a year’s shipping, which virtually guarantees that customers will start their shopping on Amazon. Because customers now start their buying on Amazon, sellers have to be there. The increased range of goods for sale on Amazon lures in more buyers, who lure in more sellers, with both sides holding each other hostage:
https://vimeo.com/739486256/00a0a7379a
This flywheel creates a vicious cycle, starving local retail so that customers can’t get what they need from brick-and-mortar shops, which funnels sellers into offering their goods for sale on Amazon. The less choice customers and sellers have about where they shop, the more Amazon can abuse both to pad its own bottom line.
There are 800,000 EU-based sellers on Amazon, and they have seen the junk-fees that Amazon charges them skyrocket, to the point where they have to raise prices or lose money on each sale. Amazon uses both tacit and explicit “Most Favored Nation” deals to hide these price-hikes. Under an MFN deal, sellers must not allow their goods to be sold at a lower price than Amazon’s — so when they raise prices to cover Amazon’s increasing fees, they raise them everywhere:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/25/greedflation/
It’s not hard to understand why Amazon would raise its fees: the company has an effective e-commerce monopoly. Like Ozymandias, they have run out of worlds to conquer, and so their growth has to come from squeezing suppliers and/or raising prices, not from bringing in new customers. This is likewise true of mobile companies like Apple and Google, who have run out of people who are so excited about incremental mobile hardware gains that they’ll buy a new phone every year, which means that growth has to come from squeezing app vendors:
https://www.tbray.org/ongoing/When/202x/2023/06/09/Pixel-4-to-7
This is likewise true of the streaming companies, which is why Netflix is cracking down on “password sharing”:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/02/02/nonbinary-families/#red-envelopes
It’s true of the movie studios, which is why they want to zero out their wage bills by replacing writers with automatic plausible sentence generators that will write stupid movies that they think we’ll still pay to see because there won’t be anything else:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/06/people-are-not-disposable/#union-strong
It’s certainly true of Uber, which is why they’ve double the cost of a taxi ride and halved the wages they pay drivers:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/12/algorithmic-wage-discrimination/#fishers-of-men
Monopolies “grow” by making their customers and suppliers worse off. But they have to be careful about this: if it’s obvious that you’re using your market power to screw buyers, you can get in trouble with competition regulators. That’s because the only part of antitrust law that the neoliberal project left intact is “consumer welfare” — the idea that monopolies should only face enforcement when they raise prices and/or lower quality:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/10/10/play-fair/#bedoya
This focus on price-hikes has given monopolists a free hand to squeeze suppliers and workers, because a monopolist — from Walmart to Amazon — can claim that squeezing your workers and suppliers is necessary to enhancing consumer welfare. The less you pay to produce a product, the cheaper you can price it.
When a company has a lot of seller power, we call it a monopolist. When it has a lot of buying power, we call it a monopsonist. No one ever made a bestselling, family-destroying board game called “Monopsony” so most people haven’t heard of the concept. But monopsony is every bit as dangerous as monopoly, and monopsonists find it far easier to acquire market power than monopolists. Few suppliers can afford to have even 10% of their sales disappear overnight, so a buyer who accounts for 10% of your sales can demand deep discounts and other favorable terms.
Amazon is a monopolist, but it’s also a very powerful and ruthless monopsonist. For example, its audiobook division, Audible, has a 90+% market-share, and it used that market-power to steal at least $100m from audiobook creators, in a scandal dubbed Audiblegate:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/09/07/audible-exclusive/#audiblegate
For Europe’s 800k sellers who rely on Amazon to reach their customers, the monoposony conditions are blatant and shameless. Take listing fees: Amazon’s “flywheel” pitch claims that as the company grows, it achieves “economies of scale” that can lower its cost basis. But Amazon’s listing fees haven’t changed, even as the company experienced explosive growth in the EU (remember, sellers whose Amazon fees exceed their margins have to pass those fees onto buyers, and also raise their prices everywhere else to satisfy the Most Favored Nation requirement).
Amazon books the revenues from these fees — and other junk-fees it extracts from sellers — in Luxembourg, an EU member nation that provides a tax haven to multinational businesses that want to maintain the fiction that they operate their businesses out of the tiny kingdom. There is sharp competition in the EU to offer the most servile, corrupt environment for multinationals, and Luxembourg is a leader, along with Cyprus, Malta and, of course, Ireland:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/05/15/finnegans-snooze/#dirty-old-town
But at least listing fees haven’t gone up, unlike other fees, which have climbed sharply. Amazon falsely claimed that its additional revenues from fees were the result of growth by independent sellers, which Amazon pegged at 65%. Later, the company admitted that the true growth figure was 22%. Meanwhile, fees are up 85%.
The true growth figure might be lower still. Amazon refuses to show the math behind its growth figures, or even say which sellers and sales are included in the figure.
The SOMO report cites research by Juozas Kaziukėnas of the e-commerce research firm Marketplace Pulse, who finds that sellers are now giving 50% of their gross revenues to Amazon, an increase of 10% over the past five years across the whole EU. However, different EU (and ex-EU) countries have experienced much steeper increases in fees — in the UK, fees have nearly doubled (up 98%), and in France, fees more than doubled (up 115%).
Many of these increases come from the Fulfilment By Amazon (FBA) program, which is promoted as an optional service, but which is really obligatory — careful research shows that sellers who warehouse, pack and ship their own goods get banished to the depths of search results, even if they have ratings, costs and times that are competitive with FBA. This is especially true of the “buy box” that lands at the top of most searches. The company refuses to disclose how buy box positioning is determined, but 90% of products in the buy box pay for FBA.
Amazon has used excuseflation to hike its FBA prices, blaming higher energy prices for price hikes that predated the Russian invasion of Ukraine, and blaming covid for price hikes that predated the pandemic.
Italy’s competition authority did yeoman service in uncovering the sleaze of FBA, publishing an investigation that showed that Prime and buy box made the notionally “optional” FBA into a must-have for merchants, meaning that Amazon could jack up FBA prices without losing business.
Another notable source of gouging came in response to the UK and France adopting digital services taxes, which were meant to make up for the tax-base erosion enabled by Luxembourg’s flouting of EU tax law. Amazon passed these taxes straight through to its merchants, without seeing a comparable decrease in the number of sellers using its platforms — an unmistakable sign of market power. If you can raise prices without losing customers, then, by definition, your customers have nowhere else to go.
I’ve previously written about how Amazon’s $31b/year “advertising” market isn’t really advertising — rather, it’s a payola scheme that auctions off the top of a search-listing to the merchant with the most to spend:
https://pluralistic.net/2022/11/28/enshittification/#relentless-payola
This is how you get a simple search like “cat beds” returning results whose first screen is 100% ads, and whose next five screens are 50% ads, many of them for dog products:
https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/interactive/2022/amazon-shopping-ads/
Auctioning off search results means that every time you search for something you want, you have to wade through screen after screen of listings for products whose vendors spent more on advertising, leaving less to spend on making quality goods.
This is as true in the EU as it is in the USA. The SOMO report shows that European merchants are required to spend ever-larger sums to show up in results for the exact products they sell, leaving them with a choice between making less money, raising prices, or skimping on quality.
But even the “winners” of Amazon’s gladiatorial combat among vendors can still lose. Amazon uses an automated product removal process that can delete some or all of a merchant’s products, without warning or explanation, and no one at Amazon will explain what a merchant did wrong. That remains true even if a vendor pays for Amazon’s “marketplace consultant” service — ask these paid Virgils why you’ve been cast into Amazon’s pit, and they’ll shrug their shoulders (and bill you for it).
And even if you can navigate the junk fees, the Kafka-as-a-service removals, the war of all sellers against all sellers for search primacy…you still lose. Merchants told SOMO that a product that survives Amazon’s gauntlet is likely to be cloned by Amazon and sold as an Amazon Basic or other house-brand product. Amazon doesn’t charge itself 50% junk fees, so it can always underprice the vendors it knocks off, and give its own products permanent top-of-search placement.
Amazon founder Jeff Bezos once testified under oath before Congress that this doesn’t happen — and then refused to return to Congress when multiple vendors showed evidence that he’d lied:
https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/2021/10/18/amazon-congress-letter-third-party-data/
He definitely lied:
https://www.reuters.com/investigates/special-report/amazon-india-rigging/
Amazon has faced investigations and enforcement in the EU over this, and settled a claim with a promise to “not use non-public seller data to compete with sellers,” but given the company’s record of broken promises on this score and the difficulty of catching them cheating, it’s pretty naive to think they’ll stick to this.
The report quotes Thomas Höppner, a lawyer who has represented small businesses that Amazon screwed over. Höppner says the problem is that the EU evaluates Amazon’s bad deeds on a “case-by-case” basis, missing the big picture: “By the time one identified problem was seemingly solved, Amazon had long made amendments elsewhere with the same effect. We require a more holistic approach that considers the entire Amazon ecosystem and the various interdependencies within.”
But the EU’s enforcement approach is about to change significantly. The EU just passed the Digital Markets Act (DMA), which imposes a bunch of obligations on Amazon:
allowing sellers to offer their products on other marketplaces at different prices (Article 5.3),
not obliging business users to pay for one of its services in order to use its platform (Article 5.8),
limiting the way Amazon uses non-public seller data to compete with them (Article 6.2)
preventing Amazon from giving top billing in search results to its own products or sellers that have acquired extra Amazon services (Article 6.5)
The report concludes with a suite of recommendations for improving EU enforcement. First, they argue for a return to traditional competition law, abandoning the “consumer welfare standard” that is so friendly to monopsonies and their abuses of suppliers and workers.
They call for a probe into Amazon’s Most Favored Nation deals (“fair pricing policy”), the practice of sponsoring search results, and spiraling fees. They want the EU to adequately fund DMA enforcement, with “measures to prevent regulatory capture.” And they want Amazon to publish clear explanations for how search results, buy box placement, and other practices hidden behind a veil of secrecy.
Amazon will doubtless claim that disclosing how those systems work will make it easier for spammers and scammers to game their way to the top of search results. We should be skeptical of this claim — content moderation is the last domain where anyone takes the bankrupt idea of security through obscurity seriously:
https://doctorow.medium.com/como-is-infosec-307f87004563
Finally, the report calls for breaking up Amazon, forcing it to choose between being a platform seller or a platform user, calling this the only way to “prevent the conflicts of interest between its role as a platform intermediary, seller, and service provider.”
The technical term for this measure is “structural separation” — a rule that bans platform companies from competing with their business customers. This is the principle at work in the US bipartisan AMERICA Act, which would force Google and Meta to spin off the parts of their ad-tech business that put them in a conflict of interest. Right now, Googbook represents both publishers and advertisers, while operating the marketplace where ad sales take place, and they take 51% out of every ad dollar:
https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2023/05/save-news-we-must-shatter-ad-tech
Structural separation hasn’t really been applied in the US for a generation, but it’s gained currency in recent years, for the obvious reason that the referee can’t also own one of the teams. I was in Germany last week speaking to regulators and politicians, and they espoused skepticism that the EU would embrace structural separation anytime soon.
But they were wrong! Today, the European Commission announced plans to force Google and Meta to sell off their conflict-of-interest ad-tech lines of business, mirroring the provisions of the US AMERICA Act:
https://arstechnica.com/tech-policy/2023/06/google-may-soon-be-ordered-to-break-up-its-lucrative-ad-business-eu-warns/
Structural separation really is the policy we should be demanding. It’s amazing that lawyers who would never argue a case in front of a judge who was married to the plaintiff will turn around and defend the idea that Amazon can fairly operate a marketplace where they compete with other sellers.
With Amazon dominating online sales, and with in-person retail cratering, Amazon’s decisions have the power to determine the outcome of whole swathes of Europe’s economy. This is the “planned economy” that the EU claims it detests and seeks to prevent — but it’s an economy planned by distant autocrats in a Seattle boardroom, for the purpose of extracting the surpluses needed to launch an endless procession of penis-rockets.

If you’d like an essay-formatted version of this postto read or share, here’s a link to it on pluralistic.net, my surveillance-free, ad-free, tracker-free blog:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/06/14/flywheel-shyster-and-flywheel/#unfulfilled-by-amazon

[Image ID: A desert ruin. In the foreground is a huge Amazon box, with an EU flag in place of its shipping label. Atop the box are the feet and partial legs of an Oxymandias figure.]

Image:
Rama (modified)
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Gladiator_with_sword-Louis_Ernest_Meissonnier-MG_1216-IMG_1223-white.jpg
CC BY-SA 3.0
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/fr/deed.en
#pluralistic#payola#digital markets act#dma#Centre for Research on Multinational Corporations#planned economies#kafka-tech#fba#Luxembourg#amazon#enshittification#monopsony#chokepoint capitalism#Margarida Silva#flywheel#eu#fulfillment by amazon#junk fees#ad-tech#somo
122 notes
·
View notes