#political history
Note
Which President, in your opinion, was the most reluctant to seek the position? Which wound up hating it the most by the end of his term?
I am a strong believer that nobody truly becomes President of the United States "reluctantly". That's not exactly the kind of job that seeks you, especially the modern Presidency.
For a significant slice of American history, many of the people nominated for President acted as if they were being called upon to run when, behind-the-scenes, they were very active in building their campaigns and corralling supporters. Until the 20th Century it was frowned upon to openly run for the Presidency, but almost all of the Presidents wanted the gig.
I'd say that George Washington was probably more reluctant than most of his successors and likely would have preferred retiring to Mount Vernon after the Revolution, but I think he also recognized that he was the guy who needed to be the President that set the precedents. I think Ulysses S. Grant would have been perfectly happy to not be President, but once he was elected in 1868 he also wanted to keep the job. He even tried to run for a third term in 1880.
That 1880 election might have been the one case where the winner -- James Garfield -- genuinely wasn't interested in the Presidency at that point. He had gone to the Republican National Convention to support fellow Ohioan John Sherman (and defeat Grant's hopes for a third term) and gained some major attention after giving a well-received speech placing Sherman's name in nomination. When the candidacies of Sherman and James G. Blaine -- another anti-Grant candidate -- stalled, Garfield became a compromise choice and was eventually nominated on the 36th ballot. Garfield was apparently legitimately shocked by the events leading to him leaving Chicago as the GOP nominee.
By most accounts, William Howard Taft was far more interested in a potential seat on the Supreme Court than becoming President. At heart he was a judge and believed himself to be better suited for the judiciary than the Executive Branch. But Taft turned down three offers by Theodore Roosevelt to be appointed to the Supreme Court (in 1902, 1903, and 1906) because he felt obligated to complete his work as Governor-General of the Philippines and then Secretary of War. But Taft's wife desperately wanted him to become President and by the time of President Roosevelt's third offer of a seat on the Court, Taft was already being talked about as Roosevelt's hand-picked successor in the White House. And, as with all other Presidents, once he had a taste for the job, he didn't want to give it up, running for re-election in 1912 against his former friend, Roosevelt.
Gerald Ford is the only other President who hadn't spent a significant portion of his political career with his eyes on the White House. Ford spent nearly a quarter-century in the House of Representatives and his main ambition was to be Speaker of the House, but Republicans weren't able to win control of the House when Ford was in Congressional leadership positions. But even with Ford being a creature of Congress, he did attempt to put himself forward as a nominee for the Vice Presidency, first in 1960 and then in 1968, and Nixon kicked the tires on picking him as his running mate in 1960. No one wants to be Vice President without seeing it as a potential stepping stone to the Presidency, particularly at that point in history before Vice Presidents were empowered with some real influence within the Administrations they served in.
As for who wound up hating it by the end of their time in office, I think it's safe to say that John Quincy Adams didn't shed too many tears when he was defeated for re-election in 1828. And I'm sure he wouldn't use the word "hate", but nobody can convince me that George W. Bush wasn't thoroughly ready to escape Washington by late-2007. There were times in 2008 when he seemed like he just wanted to hold a snap election like they have in parliamentary systems and go home to Texas. If some Presidential insider published a book that said that Bush asked if he could just give the keys to the White House to Barack Obama in July 2008, I wouldn't be the least bit shocked.
On the other hand, if there were no term limits, Bill Clinton would have been running for President in every election since 1992 (and the crazy thing is that he's still younger than both of the presumptive 2024 nominees). I'm kind of surprised that he didn't make an effort to repeal the 22nd Amendment in the past 20 years. Clinton loved being President and was trying to find something Presidential to do until minutes before his successor was inaugurated in 2001.
#History#Presidents#Presidential Candidates#Presidential Nominees#Presidential Elections#Presidency#Reluctant Presidents#Politics#Political History#Presidential History#George Washington#President Washington#General Washington#Ulysses S. Grant#President Grant#General Grant#1880 Election#1880 Republican National Convention#James Garfield#President Garfield#William Howard Taft#President Taft#Chief Justice Taft#Gerald Ford#President Ford#John Quincy Adams#JQA#President Adams#George W. Bush#Bush 43
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
Extremely funny to me that Lord Byron & Percy Shelley both really hated Castlereagh but Shelley’s way of expressing it was writing an epic poem depicting Castlereagh as the personification of death wearing a metaphorical bloody mask & being followed by hounds which he feeds human hearts while Byron just went LMAO pissing on his grave
#JUST a moment i will post them#lord castlereagh#lord byron#percy shelley#romanticism#political history#jory.txt
420 notes
·
View notes
Text
A reminder that it's not a "conflict", it was never a fucking conflict. Isr*el is not a rightful country, it's zionist occupation of stolen Palestinian land. The Palestinian resistance is not "terrorism", it's simply fighting back against literal apartheid and trying to take back their homes.
One side is fighting using basic homemade bombs while the other side is firing latest technology missile and rockets, wiping out whole villages, families, children. This is not an equal fight and it never was.
You cannot praise Ukrainian resistance and then turn around and condemn Palestinians for the exact same.
#stand with palestine#palestine#free palestine#from the river to the sea palestine will be free#politics#history#political history#anti israel
106 notes
·
View notes
Note
Is most country like Britain or former parts of the British Empire (which I sometimes forget includes the United States), blue represents the more ring-wing/conservative leaning party and red is for the more left-wing/liberal leaning part, but an exception being America and wondering how come?
Great question!

This is actually a recent phenomenon in American politics.
The U.S didn't traditionally have a stable color-coding system for much of its history, in part because American party systems had a very different history that was ideologically distinct from the socialist vs. liberal vs. conservative European model. However, to the extent that there was a color-coding tendency, it was that Republicans were often blue (because of the Union Army's uniforms) and Democrats were often red (because of red-baiting).
However for the 2000 Presidential Election, for some reason all of the networks adopted Democratic = Blue, Republican = Red for their election night coverage and it stuck and now we have this whole concept of "red states" and "blue states" that the rest of the world finds very confusing.
31 notes
·
View notes
Text
Trump, of course, went all out to offer Israel anything it wanted, in love with Israeli power, violence and repression. Recognised the Golan Heights annexation, Jerusalem annexation, supported settlement policies all in violation not only of international law but of US policy. US had supported the Security Council resolutions that banned the Israeli takeover of Golan Heights and of Jerusalem. Trump reversed all that. … -- Noam Chomsky, 4/9/23
#noam chomsky#chomsky#palestine#israel#donald trump#politics#voting#election#golan heights#jerusalem#tell. me again it doesn't matter whos president#political history
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Countries that are no more: Republic of Venice (697AD-1797AD)
The first in a series I hope to feature on providing high level overviews of countries that existed and were influential to history or obscure and lost to most memory in time. The first up is the Republic of Venice.
Name: Serenisma Republega de Venesia (Venetian). In English this translates to the state's official name The Most Serene Republic of Venice. Also referred to as the Venetian Republic, Republic of Venice or just Venice.
Language: The official languages were the Romance languages of Latin, Venetian & later Italian. The regional dialect of Vulgar Latin in Northeastern Italy known as Veneto was the original language of Venice. This evolved in Venetian which was attested to as a distinct language as early as the 13th century AD. Venetian became the official language and lingua franca of the everyday Venetians and across parts of the Mediterranean although Latin would still be used in official documents and religious functions. Overtime, modern Italian was spoken in Venice though the Venetian language remains technically a separate language in Italy's Veneto region and the surrounding areas to this day.
Minority languages across the republic's territory included various Romance languages such as Lombard, Friulian, Ladin, Dalmatian and non-romance languages such as Albanian, Greek & Serbo-Croatian.
Territory: The republic was centered on the city of Venice founded in the Venetian lagoon on the north end of the Adriatic Sea to the northeast coast of the Italian peninsula. It also included the surrounding regions of mainland northeast Italy in the regions of Veneto and Friuli and parts of Lombardy. This became known as the terraferma or the mainland holdings of the republic. It also possessed overseas holdings in modern day Croatia, Slovenia, Montenegro, Albania, Greece & Cyprus.
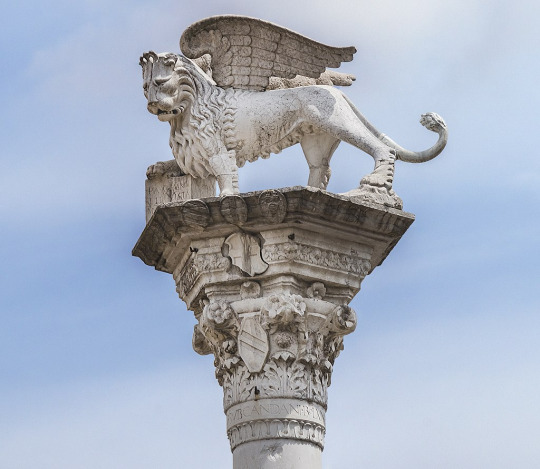
Symbols & Mottos: The main symbol of Venice was its flag which had the famed Winged Lion of St. Mark. This represented the republic's patron saint, St. Mark. Mark the Evangelist after whom the Gospel of Mark in the New Testament in the Bible is named. Mark's body and holy relics were taken by Venice and said to be housed in the Basilica di San Marco (St. Mark's Basilica) in Venice itself. Variations of this flag differed during times of peace & war. During peace the winged lion is seen holding an open book and during war flags depicted the lion with its paw upon a bible and an upright sword held in another paw.
The republic's motto in Latin was "Pax tibi Marce, evangelista meus" or in English "Peace be to you Mark, my evangelist."
Religion: Roman Catholicism was the official religion of the state but Venice did have minorities of Eastern Orthodox & Protestant (usually foreign) Christian denominations at times in its territory and it also had small populations of Jews and Muslims to be found in Greek and Albanian territories during the wars with the Ottoman Empire.
Currency: Venetian ducat and later the Venetian lira.
Population: Though population varied overtime for the republic due to a variety of factors such as war & changing territory and disease & its subsequent effects. There was rough population recorded of 2.3 million people across all of its holdings in the mid sixteenth century (circa 1550-1560). The vast majority of its population was found in the terraferma of northern Italy and the city of Venice itself with its concentrated population on the islands within the Venetian Lagoon. The Greek island of Crete and the island of (Greek speaking) Cyprus were the most populous overseas possessions of the republic's territory. The rest of the population was found its various holdings in the Balkans mostly along the Adriatic coastline.
Government: The republic followed a complex mixed model of government. Essentially it could be characterized as a mixed parliamentary constitutional republic with a mercantile oligarchy ruling over it in practice. It had no formal written constitution, and this led to a degree of evolution without exactly defined roles often in reaction to happenings in its history. The resulting government became more complex overtime as institutions became increasingly fragmented in their size, scope and duties, some almost obsolete but still retained and others not fully defined. Yet, the republic managed to function quite well for most of its history. It incorporated elements of oligarchy, monarchy & limited democracy.
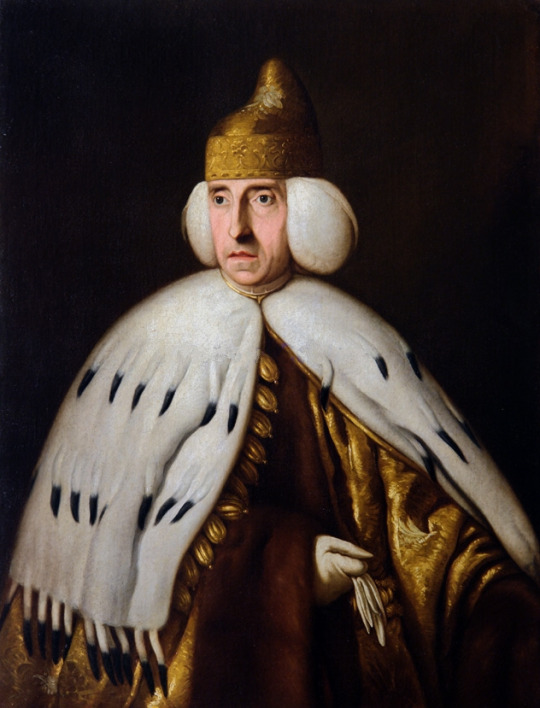
It's head of state and government was known as the Doge which is akin to the term of Duke. Though this similarity of name ends there. The Doge was neither similar to a duke in the modern sense nor was it meant as a hereditary position. The doge was rather a lifetime appointment much like the Pope for the Roman Catholic Church. Furthermore, doges were elected by the ruling elite of Venice, namely its wealthy oligarchy merchant class. The doge didn't have well defined & precise powers throughout the republic's 1,100-year history. It varied from great autocracy in the early parts of the republic to increasing regulation and restriction by the late 13th century onward. Though the doge always maintained a symbolic and ceremonial role throughout the republic's history. Some doges were forcibly removed from power and post-1268 until a new doge could be elected, the republic's rule transferred to the most senior ducal counsellor with the style of "vicedoge". After a doge's death following a commission was formed to study the doge's life and review it for moral and ethical transgressions and placed judgment upon him posthumously. If the commission found the deceased doge to have transgressed, his estate could be found liable and subject to fines. The doge was given plenty of ceremonial roles such as heading the symbolic marriage of Venice to the sea by casting a marriage ring into the sea from the doge's barge (similar to a royal yacht). Additionally, the doge was treated in foreign relations akin to a prince. It's titles and styles include "My Lord the Doge", "Most Serene Prince" and "His Serenity". The doge resided in the ducal palace (Palazzo Ducale) or Doge's Palace on the lagoonfront in Venice next St. Mark's Basilica and St. Mark's Square.
While the doge remained the symbolic and nominal head of the government, the oligarchy remained supreme overall. The supreme political organ was the 480-member Great Council. This assembly elected many of the office holders within the republic (including the doge) and the various senior councils tasked with administration, passing laws and judicial oversight. The Great Council's membership post 1297 was restricted to an inheritance by members of the patrician elite of the city of Venice's most noble families recorded in the famed Golden Book. This was divided between the old houses of the republic's earliest days and newer mercantile families if their fortunes should attain them property ownership and wealth. These families usually ranged between 20-30 total. They were socially forbidden from marrying outside their class & usually intermarried for political and economic reasons. Their economic concerns were chief to the whole of the republic and most centered on Eurasian & African trade throughout the Mediterranean Sea's basin. Members of these families served in the military and eventually rose to prominent positions of administration throughout the republic.
The Great Council overtime circumscribed the doge's power by creating councils devoted to oversight of the doge or executive and administrative functions (similar to modern executive cabinets or departments) whereas the doge became more and more a ceremonial role. The also created a senate which handled daily legislation. They also created a Council of Ten set to have authority over all government action. Other bodies were formed from this Great Council and others overtime. This resulted in intricate and overlapping yet separate bodies which found themselves subject to limitations with various checks on virtually each other's power. Essentially running as committees or sub-committees with checks on another committee's powers. These bodies weren't always completely defined in their scope and overtime their complexity led to battles to limit other's power (with limited success) along with gradual obsolescence and sometimes slow grinding administration.
Military: The military of Venice consisted of a relatively small army and a powerful navy. The famed Venetian Arsenal in Venice proper was essentially a complex of armories and shipyards to build and arm Venice's navy. The arsenal in Venice has the capacity to mass produce ships and weapons in the Middle Ages, centuries before the Industrial Revolution allowed for modern mass production in economic and military applications. Venice's military was designed towards protecting it possessions both in Italy and its overseas territories. The primary concern was to secure Venice's trade routes to the rest of Europe as well as Asia & Africa. It faced opponents' overtime ranging from the Franks, the Byzantine Empire, Bulgarians to other Italian city-states, France, Austria, the Ottoman Empire and Barbary Corsairs along with European pirates in the Adriatic and Mediterranean. It played key roles as a naval transport in other powers including throughout the Crusades. It also played a key role in the infamous Fourth Crusade which culminated in the Sack of Constantinople in 1204 AD, an event which fractured the Byzantine Empire into a half-century of civil war between successor states before a weakened revival in the mid 13th century. The Byzantine Empire would linger until the 15th century when the Ottoman Empire finally conquered its last remaining portions. Many attribute this loss to in part to its weakness still resulting from that 1204 sack lead by Venice. The Venetian military would exist until the republic's end when The French Republic's Army of Italy under Napoleon Bonaparte conquered the republic, a conquest in which the Venetians surrendered without a proper fight.
Economy: Venice's economy was based largely in trade. Namely control over the salt trade. Venice was to control salt (preservative of food) production and trade throughout the Mediterranean. It also traded in commodities associated with the salt trade routes to Eurasia and Africa. These commodities could include other foodstuffs (grains, meats & cheeses), textiles & glassware among other items.
Lifespan: 697AD-1797AD. Though the exact founding of Venice itself hasn't been determined. It is traditionally said to have taken place in the year 421 AD. At a time when Roman citizens in northeast Italy were escaping waves of Germanic & Hunnic barbarian invasions that contributed to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. The going theory is that these Romans evaded barbarian attacks by building their homes in the Venetian Lagoon by hammering wood stakes to form a foundation which sunk into the muddy shallows and petrified. Upon which they built their homes and created a cityscape marked by streets and canals interlaced. Venice remained a community of fishermen and merchants and was nominally under the control of the surviving Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire). It avoided barbarians overrunning the land but also was removed enough from Constantinople that it was relatively autonomous and became strategically important as a port. Other islands in the lagoon also banded together with Venice in a loose confederation of sorts by the 6th and 7th centuries which increased economic productivity and security for the city. The first doge was said to have been elected in 697 AD under the name Paolo Lucio Anafesto, though there is dispute about his historicity. Anafesto supposedly ruled until 717 AD. This is traditionally regarded as the foundation of the Republic of Venice.
Venice's third doge was Orso Ipato who reigned from 726-737 and he is the first undisputed historically recorded doge whose existence was confirmed. Orso also known as Ursus was known to strengthen the city's navy and army to protect it from the Lombard Germanic invaders who had overrun and ruled Italy by that time. Though nominally part of the Byzantine Empire, by 803, the Byzantine Emperors are said to have recognized Venice's de-facto independence. Though this view is disputed somewhat, it nevertheless remained virtually independent until its collapse in 1797.
Venice also partook in the slave trade of non-Christian European populations from Eastern Europe and transferred them to North Africa, selling them to the Arab and Berber (Moors) of the Islamic world.
As the 9th century progressed, the Venetian navy secured the Adriatic and various trade routes by defeating Slavic and Muslim pirates in the region. The Venetians also went onto battle the Normans who settled in southern Italy and Sicily in the 11th century.
Venice provided naval transports for Crusaders from Western Europe starting with the successful First Crusade.
The High Middle Ages (1000AD-1350AD) saw the wealth and expansion Venice increase dramatically. However, over this period Venice gradually came into mixed relations with its former ruler the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantine Empire endured corruption, civil war and foreign invasion which saw it alternate between periods of waning power and restored power. Venice provided the Byzantines with an increased naval force when needed and many trading commodities. In exchange for this, Venice was granted trading rights within Byzantine territory and a place within the "Latin Quarter" for Western Europeans in Constantinople. The Byzantine populace though calling themselves "Romans" having taken on the political & cultural institutions of the Roman Empire which lived on in the East long after the Western half's collapse, were in fact mostly Greek by ethnicity, language and culture. Their religion was the Eastern Orthodox or Greek Orthodox branch of Christianity which was often at odds with Roman Catholics of Western Europe. Resentment at the religious and cultural differences along with the economic displacement the Venetians and other Italian merchants from Genoa & Pisa had caused in Constantinople's maritime & financial sectors contributed to the 1182 "Massacre of the Latins" in which the Byzantine Greek majority of the city rioted and slaughtered much of the 60,000 mostly Italian Catholics living within the city. Thousands were also sold into slavery to the Anatolian Seljuk Turks.
This event lingered in Venice's memory as its trade in the city was reduced for awhile. Though trade resumed between the Byzantines and the West again shortly thereafter, the event soured the perception of the Greeks to Western Europeans. This along with a subsequent power struggle for the throne of the Eastern Roman Emperor fell into Venice & Western Crusader's hands in 1202. Looking to originally ferry Western Crusaders to the Levant against the Islamic Ayyubid Sultanate of Egypt & Syria. Events transpired that devolved into Venice conspiring under its doge Enrico Dandalo along with other Western leaders and a Byzantine claimant to the throne that resulted in the first successful sacking of Constantinople in 1204. The city was ransacked, some Greek citizens murdered by the Crusaders & classical works of art destroyed or looted (most famously the four bronze horses of St. Marks in Venice) and politically, the Byzantine Empire would be temporarily fractured between competing Greek dynasties while the Crusaders along with Venice created the short-lived Latin Empire, which controlled Constantinople and its environs while Venice also acquired Greek territories which it was to hold for centuries. Venice also came into conflict with the Second Bulgarian Empire at this time as its support of the Latin Empire of Constantinople encroached on the Bulgarian's land. Eventually by the mid 13th century the Latin Empire (never fully stable) collapsed, and the Byzantine Empire was restored until the mid-15th century but forever weakened as a result of the 1204 sacking of its capital.
Venice reached trade deals with the Mongol Empire in 1221. As the century wore on, it also engaged its rival in Western Italy Genoa in some warfare.
The 14th century is generally regarded as Venice at its peak as it faced down Genoa in a number of battles and came to be the most dominant trading power in the Mediterranean, though it was impacted by the Black Death plague. Nevertheless, into the 15th and even 16th centuries, it partook in a number of wars which saw it gain territory on the Italian mainland, establishing its terraferma domain.
By the 16th late 15th and into the 16th century new threats had emerged such as the Turkish Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman capture of Constantinople in 1453 is seen as the end of the Middle Ages as the last political vestiges of the Roman Empire vanished from the world stage. However, a number of Byzantine Greeks escaped on Italian ships during the conquest of the city and others escaped Greece in subsequent years. These refugees brought with them artistic and cultural heritages that reemphasized the classical forms of Ancient Greece and Rome and lead to the Italian Rennaisance in art & other forms of culture. Ideas which emphasized humanism and spread to elsewhere in Europe overtime.
While there was a cultural flourishing in Venice and elsewhere due to the Rennaisance. There was also the first signs of economic and political decline as well from the 16th century onwards. The Ottoman dominance in the Eastern Mediterranean meant the traditional trade routes to the East were cut off by an often-hostile Muslim power. Additionally, other maritime powers in the West namely Spain & Portugal had recently begun exploring the continents of South & North America and in time France, England & the Netherlands would join in them. This decline in Eastern trade and the newfound trade routes dominated by other European states in the Americas and Asia (by way of rounding Africa) would render trade with Venice gradually obsolete. Venice would still maintain what trade it could in the Mediterranean, but it also focused on production and placed increasing importance on its Italian mainland possessions rather than just its declining position overseas in Greek territories, including the loss of Cyprus to the Ottomans in 1571. Though the Venetian navy with other Christian powers won the notable naval victory against the Ottomans in 1570 at Lepanto.
It was also involved in the Italian Wars between various rival city states and the power struggle between the Papacy, France and the Hapsburg realms of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain.
Other factors that impacted the declining trade in the 17th century included an inability to keep up in the textile trade elsewhere in Europe, closure of the spice trade to all but the Spanish, Dutch, Portuguese, French and English and the Thirty Years War (1618-1648) which impacted Venice's trade partners.
Ongoing wars including a 21-year siege of Crete by the Ottomans saw further losses. Although Venice partook in the Holy League headed by the Holy Roman Empire (under Hapsburg Austria) which saw some minor temporary gains from the Ottomans in southern Greece before losing them again in the early 18th century.
War and loss of overseas territories along with a stagnant economy was slightly offset by a somewhat strong position in northern Italy. Nevertheless, its maritime fleet was reduced to a mere shadow of its former glory and it found itself sandwiched still between Austria and France. Over the rest of the 18th century, economic stagnation and social stratification remained prevalent while Venice remained in a quiet peace. However, the French Revolution reignited war in Italy and while Venice remained neutral, it would soon get caught up in events.
The Austrians and the Piedmontese (Italian) allies were beaten by the French Republic's Army of Italy headed by an up-and-coming general named Napoleon Bonaparte. Bonaparte and the French army crossed the borders of northern Italy into Venetian neutral territory to pursue the Austrians. Eventually half of Venice's territory was occupied by France and the remainder of the mainland was occupied by Austria. By secret treaty the French and Austrians were to divide the territory between themselves (Venice was consulted in the matter). Bonaparte gave orders to Venetian doge Ludovico Manin to surrender the city to French occupation to which he abdicated his power. The republic's Major Council met one last time to officially declare an end to republic on May 12th, 1797, after 1,100 years. Venice was placed under a provisional government and ironically the French looted Venice stripping it of artworks to grace the Louvre Museum in Paris along with the Arc d'Triomphe, taking the famed four bronze horses of St. Mark's to adorn the triumphal arch in Paris, the very same horses Venice had confiscated from Constantinople in 1204. It was a symbolic end to the republic, the irony of which did not escape commentators at the time. Following Napoleonic France's final defeat in 1815 the horses were returned to Venice and St. Mark's where they remain today. Venice itself was given over to the Austrian Empire.
The Republic of Venice has a historical legacy in terms of its economic accomplishments through control of trade and its innovative mass production of ships, armaments & trade commodities. It also holds a political legacy worthy of study given it was a unique and enduring polity for 1,100 years. One that maintained a complex and at times chaotic form of government that still managed to function and endure for centuries.



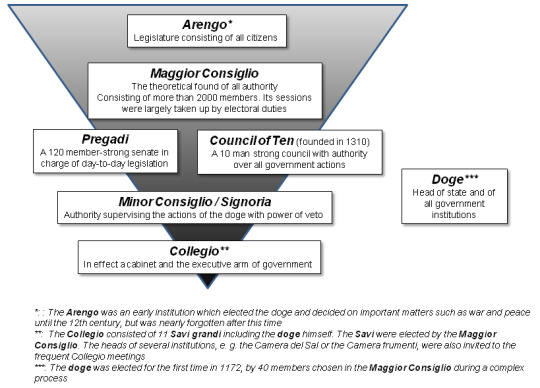






#military history#middle ages#venice#venetian republic#italy#politics#political history#trade#economics#governance#commerce#ottoman empire#spain#byzantine empire#napoleon#doge#republic
67 notes
·
View notes
Text

“This book presents a brilliant analysis of the neoliberal policies imposed on Haiti by international institutions. Dupuy skillfully connects decades of extractive foreign interventions in Haiti, from the US occupation to the aftermath of Jovenel Moïse’s assassination. Haiti since 1804 points the way toward a future in which Haitians might finally regain sovereignty over their own economy and government."
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
Historical context of Britain's role in the imperialist occupation of Palestine : taking land that wasn't theirs for their own interests and following their previously used models of two faced colonisation, messing everything up and creating intentional instability amongst a once stable region : aka the beginnings of this whole situation
youtube
#Britain#Imperialism#Colonisation#Ottoman empire#Palestine#Free Palestine#They obviously had no right to take land that wasn't theirs#Imperialist Britain#Accountability#Responsibility#Israel#Truth#The truth#History#Historical context#Political History#Global History#Educate yourselves#Educate#Education#Important#Psa#Genocide#Indigenous Palestine#Watermelon#🍉 🇵🇸#Youtube
24 notes
·
View notes
Text




A collection of four gay liberation papers, demonstrating the close ties between left-wing organising and the Australian gay lib movement. The top two come from the 1976 Manifesto of the Socialist Homosexuals, the bottom two are from a queer anarchist paper and satire Marxist groups by painting them as bourgeois intellectuals who would rather talk politics than engage in praxis.
(Photos my own, taken at the Australian Queer Archives. You can find a substantial collection of gay lib material on the site Reason in Revolt).
#history#historyblr#queer history#australian history#gay history#lgbtq history#political history#gay liberation#20th century
83 notes
·
View notes
Text
Please please please prioritize Tibetan, Vietnamese, Indian and Iranian voices & narratives when talking about self immolation and its history.
Dr Tenzin M Paldron has a brilliant thesis on this with so maybe references: Tibet, China, and the United States: Self-immolation and the limits of understanding
As well:
Tsering Shakya has an essay called Self-Immolation: the Changing Language of Protest in Tibet
Nicholas Michelsen wrote The Political Subject of Self-Immolation which is available in Occupying Subjectivity (available for free on annas-archive.org)
Michelle Murray Yang published Still Burning: Self-Immolation as Photographic Protest.
There are tons more! There is no shame in not knowing or understanding this intense action BUT! It is so easy for academics, reporters, and theorists living within western-colonial systems to completely disregard the incredibly powerful and horrific act that self-immolation is. Please don’t be a part of that!
*** all these links should be free & accessible - if they’re not & you want to read them reach out & let me know!
#protest#political protest#political history#politics#free palestine#tibetan buddhism#free tibet#colonialism#readings#resources#essays#to read#info dump#essay#copyleft#academia
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
The fact that the pseudonym for the guy who leaked Watergate to the Washington Post was "Deep Throat" is honestly so fucking funny to me
Like imagine the next big American political scandal is broken in the NY Times or something and they're like "yeah we got it from our informants Fuck Nasty and Sloppy Dome"
28 notes
·
View notes
Text

"It hurt to lose to Ronald Reagan. But after the election, I tried to make the transition as smooth as possible. Later, from my experience in trying to brief him on matters of supreme importance, I was very disturbed at his lack of interest. The issues were the 15 or 20 most important subjects that I as President could possibly pass on to him. His only reaction of substance was to express admiration for the political circumstances in South Korea that let President Park close all the colleges and draft all the demonstrators. That was the only issue on which he came alive."
-- Former President Jimmy Carter, on losing the 1980 election and the transition leading to the inauguration of Ronald Reagan, interview with TIME Magazine, October 11, 1982.
#History#Presidents#Jimmy Carter#President Carter#Carter Administration#Ronald Reagan#President Reagan#Reagan Administration#1980 Election#Presidential History#Presidency#Presidential Elections#Presidential Transitions#Inauguration of Ronald Reagan#Presidential Rivals#Presidential Rivalries#Presidential Relationships#Quotes#Presidential Quotes#Quotes by Presidents#Presidents on Presidents#Politics#Political History
5K notes
·
View notes
Text
The British government in the 1790s was constantly going Wow a political situation where the end result might be something we don't like we should purposefully inflame it until it's well past the breaking point & absolutely beyond anyone's control. just to see what happens
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
#tiktok#schoolhousecaulk#us politics#politicians#political history#2000 presidential election#president#presidential election#us presidential election#us presidential race#democrats#republicans#presidential race#history
9 notes
·
View notes
Note
is lobbying just basically legalized bribing, or is there any other difference?
The difficulty is that lobbying is simultaneously "legalized bribery" and "influence peddling," and the core of the First Amendment's guarantee of "the right of the people...to petition the Government for a redress of grievances."
Whether it's done by an environmental group trying to preserve endangered species or a deeply corrupt corporation that wants to strip-mine public lands for pennies on the dollar while poisoning the planet, or by a civil rights group trying to achieve equal rights or a hate group trying to legalize oppression of minorities, it's all lobbying.
Now, professionalized lobbying is actually a fairly recent phenomenon. Back in the 19th century, wealthy elites simply just bought elected officials or entire branches of government outright, but during the Progressive Era this was uncovered by muck-raking journalists and led to a lot of people going to jail, so something had to take its place - and that was lobbying.

Even as late as 1945, there were barely 400 lobbying groups in the U.S compared to 17,000 today. The cause of the explosion of lobbying as an industry was a combination of the post-war expansion of the U.S government and changes to campaign finance law in the wake of Watergate. The Federal Election Campaign Act (FECA) sought to regulate campaign spending and campaign finance in response to perceived corruption in Federal elections, and was further strengthened by major amendments in 1974 that set hard limits on contributions and spending and created the Federal Elections Commission to enforce FECA.
The Supreme Court, which had begun its slide to the right thanks to LBJ massively fumbling the ball with his Supreme Court nominations and letting Nixon get a bunch of Justices on the Court, struck down a lot of those limits in Buckley v. Valeo in 1976 - which started us down the road to Citizens United. Corporate lobbies very quickly realized that they could expand their influence enormously by acting as the middle-men between corporate cash and elected officials, which now meant that they could wield enormous carrots and sticks to get elected officials to comply with their wishes.

Now, I think there will always be problems with lobbying that come down to the issue of concentrated vs. diffuse interests. There are all kinds of political issues where the majority of the people are on one side of a debate, but where they aren't particularly aware of or engaged with that debate, and even though they have a stake in the outcome, it's rather vague and abstract not something they care about very much. But a lobbying group for a particular "special interest" that is on the other side of that debate and is very aware and engaged and cares about the outcome very much because they stand to gain or lose a lot of money from the outcome. So that lobbying group, which represents a minority position and should lose in the democratic process, will invest the necessary resources in order to win.
The only way to fight this, sadly, is for social movements to be just as organized as lobbyists. For the longest time, it was the labor movement that acted as the "countervailing power" in American politics, because they had the manpower and the money to effectively lobby the Federal government not just on behalf of unions but also on behalf of low-wage workers or racial minorities or consumers and so forth. The problem is that the labor movement doesn't really have that manpower and money any more, but nothing has really replaced it in American politics, in no small part because the left is not immune to America's instinctive hatred of politics and institutions.
And yes, the other major thing that we could do to fight "legalized bribery" is to break up the nexus between campaign finance and lobbying, but in order to do that, we'd have to overrule about fifty years of Supreme Court precedents, and that's not going to happen without the Democratic Party successfully taking back control of the Supreme Court.
#u.s politics#u.s history#political history#political science#lobbying#political economy#labor history#campaign finance
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Instead of imagining a world without work that will never come to pass, we should examine the ways historical struggles posited an alternative relationship to work and liberation, where control over the labor process leads to greater control over other social processes, and where the ends of work are human enrichment rather than abstract productivity. furthermore, these struggles point toward the only vehicle for a liberation from capitalism: the composition of a militant struggling class that attacks capital in all its manifold domination, including the technological".
Breaking Things at Work: The Luddites Are Right About Why You Hate Your Job by Gavin Mueller
#book quotes#currently reading#capitalism#luddism#political economy#breaking things at work#gavin mueller#history#political history#labor#labor relations#class struggle#marxism#technology#politics#verso books#book rec#nonfiction#r/#book recommendations#writings
38 notes
·
View notes