#nigerian cultural history
Text








The Igbo in the Atlantic slave trade
Bussa, Barbadian slave revolt leader of Igbo descent
Edward Blyden, Americo-Liberian educator, writer and politician of Igbo descent
Paul Robeson, American actor and writer whose father was of Igbo descent
Aimé Césaire, Martiniquais poet and politician who claimed Igbo descent) argues that many of the slaves taken from the Bight of Biafra across the Middle Passage would have been Igbo. These slaves were usually sold to Europeans by the Aro Confederacy, who kidnapped or bought slaves from Igbo villages in the hinterland. Igbo slaves may have not been victims of slave-raiding wars or expeditions but perhaps debtors or Igbo people who committed within their communities alleged crimes. With the goal for freedom, enslaved Igbo people were known to European planters as being rebellious and having a high rate of suicide to escape slavery. There is evidence that traders sought Igbo women. Igbo women were paired with Coromantee (Akan) men to subdue the men because of the belief that the women were bound to their first-born sons’ birthplace.
It is alleged that European slave traders were fairly well informed about various African ethnicities, leading to slavers targeting certain ethnic groups which plantation owners preferred. Particular desired ethnic groups consequently became fairly concentrated in certain parts of the Americas. The Igbo were dispersed to colonies such as Jamaica, Cuba, Saint-Domingue, Barbados, Colonial America, Belize and Trinidad and Tobago, among others.

Rihanna is also Igbo
Colonial Nigeria
The establishment of British colonial rule in present-day Nigeria and increased encounters between the Igbo and other ethnicities near the Niger River led to a deepening sense of a distinct Igbo ethnic identity. The Igbo proved decisive and enthusiastic in their embrace of Christianity and Western-style education. Because of the incompatibility of the Igbo decentralized style of government and the centralized system including the appointment of warrant chiefs required for British system of indirect rule, the period colonial rule was marked with numerous conflicts and tension. During the colonial era, the diversity within each of Nigeria's major ethnic groups slowly decreased, and distinctions between the Igbo and other large ethnic groups, such as the Hausa and the Yoruba, became sharper.
The establishment of British colonial rule transformed Igbo society, as portrayed in Chinua Achebe's novel Things Fall Apart. Colonial rule brought about changes in culture, such as the introduction of warrant chiefs as Eze (indigenous rulers) where there were no such monarchies. Christian missionaries introduced aspects of European ideology into Igbo society and culture, sometimes shunning parts of the culture. The rumours that the Igbo women were being assessed for taxation sparked off the 1929 Igbo Women's War in Aba (also known as the 1929 Aba Riots), a massive revolt of women never encountered before in Igbo history.
Aspects of Igbo culture such as construction of houses, education and religion changed following colonialism. The tradition of building houses out of mud walls and thatched roofs ended as the people shifted to materials such as concrete blocks for houses and metal roofs. Roads for vehicles were built. Buildings such as hospitals and schools were erected in many parts of Igboland. Along with these changes, electricity and running water were installed in the early 20th century. With electricity, new technology such as radios and televisions were adopted, and have become commonplace in most Igbo households.
A series of black and white, silent films about the Igbo people made by George Basden in the 1920s and 1930s are held in the British Empire and Commonwealth Collection at Bristol Archives

#african#afrakan#kemetic dreams#africans#brownskin#brown skin#afrakans#african culture#afrakan spirituality#igbo#nigerian#british empire#jamaica#jamaican#barbados#igbo culture#igbo history#rihanna
25 notes
·
View notes
Text
This month in Hoodoo History: The Igbo Freedom Landing March

In May of 1803, 75 Igbo men & women chose freedom in death over a life of hell, spurring one of the largest mass suicides in the history of Maafa.
• In May 1803, a British slave ship called, The Wanderer, captured over a hundred Igbo men/women & other West Afrikan Peoples from present-day Nigeria and taken to Savannah, GA.
In Savannah, they were resold into Slavery to be worked to death on plantations along the Georgia coast. The price for each of their lives? $100. They were forcibly transported onto a ship called, the York that set sail for St. Simon's Island.
• During this voyage from Savannah to St. Simon's Island, 75 Igbo men & women rose up against their captors. They drowned the slavers, took control of the ship - grounding it in the Dunbar Creek.
At some point, the Igbo fled the ship. Led by their High Chief, a subset of the Igbo sang as they marched into a salt marsh of Dunbar Creek. One by one, they returned home in the face of a fate worse than death.

• This event that became known as, the Igbo Freedom Landing March, spawned enormous symbolism & folklore in the Afrikan Peoples and their descendants on this land. Many believe that the Freedom Landing and the nearby salt marshes in Dunbar Creek are haunted by the Spirits of the Igbo Peoples who drowned there. It is heralded as the first recorded Freedom March in U.S. history and has long since been a staple in Gullah-Geechee folklore, as the story of the Igbo Peoples who chose death over Slavery.
• Today, Igbo Landing is a nationally recognized historical site. It is located at Dunbar Creek on St. Simon's Island in Glynn County, GA.
• In September 2002, the Afrikan descendant community of St. Simon's Island, GA held a two-day commemoration of this event, including a procession to the salt marshes along Dunbar Creek where the mass suicide took place. They were represented by 75 Afrikan descendants across the country, Haiti, Brazil, & Nigeria. The attendees consecrated the site and did the collective work to elevate the restless Igbo spirits into healing and peaceful transition.

#hoodoo#hoodoos#atr#atrs#the hoodoo calendar#juju#igbo culture#igbo history#igbo#afrikan#igbo freedom landing March#black history#Hoodoo Folklore#west Afrika#Nigeria#Nigerian history#Georgia#Georgia history#Savannah#st simons island#african american folklore#Hoodoo History
140 notes
·
View notes
Text
can African Americans please stop saying "black culture" in reference to the homogenised African black cultures in the United States please
#its extremely reductive even in America#there are so many black people internationally in different nations with different cultures#im Nigerian i have no idea what cultures are in Uganda#im Yoruba i have no idea what cultures go on in Igbo#im black British so i understand other like Ghanian and Jamaican cultures#im black British and i have so much knowledge about African American culture because it is exported to me and then posed as “my culture” as#a black person. That cant be right#black brit#black people#black culture#aave#i have so many takes on aave ans how other people should be able to use it as a black brit who knows white boys eho say wagwan. it's not as#big of an issue as most people think tbh#African#african american#black history#black cultures#please dont homogenise blackness.
17 notes
·
View notes
Text
New favorite thing: Ijaw owuamapu (water spirit) masks


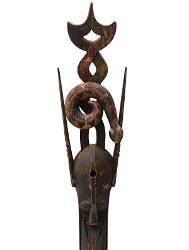

[Photo ID: 4 pictures of masks from the Ijaw tribe of Nligeria. The top left mask is a stylized fish with a human face on it's back. The top right mask is diamond shaped with a upside down human face on the upperportion of the mask and a rightside up human face on the lower portion. The lower left mask is a human face with horns and a snake coiled around the horns. The lower right mask is a stylized large fish (maybe a shark) with a human face on it's back. End photo ID]
#africa#african folklore#nigeria#nigerian artwork#nigerian culture#ijaw#ijo#izon#african masks#nigerian masks#catergory: aquatic chimera cubism#water spirit#merfolk#mermen#i think#black history month#blackblr
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
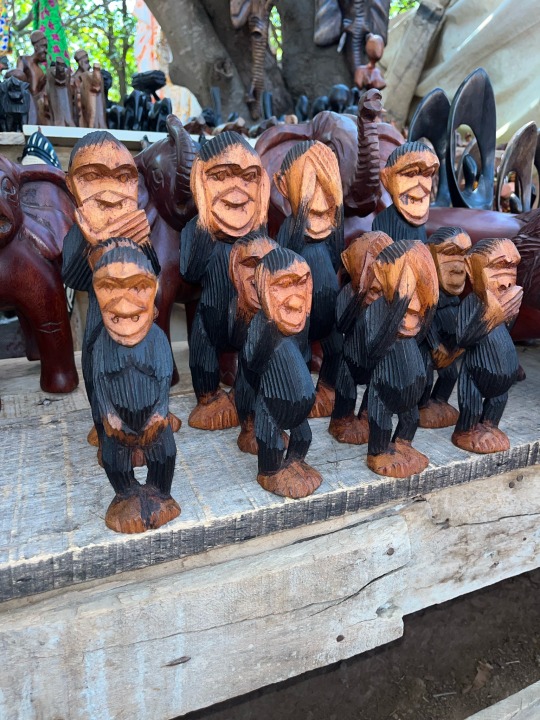




Hear no evil, see no evil, speak no evil
#photography#african culture#african history#chesspieces#chessboard#culture#artwork#traditional art#nigeria#nigerian
2 notes
·
View notes
Note
what are your hobbies?
Well other than writing, mmm...mmmm.....well I rlly like watching like...video essay/deep dives on YouTube? I watch a lot of cartoons and rlly like historical dramas. I had a history phase on YouTube too but I've forgotten a lot of it....
#like i luv fundie fridays currently.#they are the best youtube couple in MY opinion#exposing the insanity of christain fundamentalism#which i have never been apart of btw. my family is highly evangelical tho + culturally Nigerian so theres a lot of similarities tho#so i get the whys of why they believe or do what they do for the most part#i also rlly like history#im very boring;;;;;#i just like curling up in my room and consuming!!! media!!!
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Evolution of the Music Industry in Nigeria: A Journey Through Time
The Evolution of the Music Industry in Nigeria: A Journey Through Time

View On WordPress
#2face Idibia#Afrobeat music#challenges facing the Nigerian music industry#Davido#development of Nigerian music industry#evolution of Nigerian music#evolution of Nigerian music from 1920s to present#Fela Kuti#history of Nigerian music#impact of Fela Kuti on Nigerian music#influence of Western music on Nigerian music#King Sunny Adé#music in Nigeria#music industry in Nigeria#Nigerian Afrobeats#Nigerian culture#Nigerian entertainment industry#Nigerian music and cultural identity#Nigerian music in the digital age#rise of Afrobeats in Nigeria#role of technology in Nigerian music industry#Tiwa savage#Wizkid
0 notes
Text
And people keep trying to justify Israel's existence on the basis that it is somehow a safe place for the preservation of Jewish people and their culture and not only is that an awful argument for establishing a Settler Colonist Apartheid State but it's not even true. Like the state is politically and economically dominated by Ashkenazi Jews from Northern Europe and their descendants. While not as severely mistreated as Palestinians, there is still a significant disparity between the European and Non-European Jews in terms of income and education. Non-European Jews are still regularly subject to interpersonal bigotry (hell earlier this year there was a news story about a viral video where Ashkenazi girls in a Purim made a skit mocking the Mizrahi) and Israel government policies towards non-Ashkenazi migrants have done severe damage to their social structure and cultural traditions. Not to mention the fact that the whole reason why many Mizrahi migrated in the first place was to escape the violence caused by European Jews committing atrocities in their name, tearing communities apart as neighbours that had peacefully co-existed for centuries found themselves on opposite sides of this new ethno-religious conflict
There have even been attempts in Israeli history at the forceful assimilation or even biological reduction of non-European Jews; the kidnapping and adoption of Yemeni Jewish children in the 1950s is significant example of the former while the forced contraception of Beta Israeli (Ethiopean Jewish migrants) with the explicit intention of reducing their population's birth rate is an example of the latter. There's also very clear favouritism when it comes to recent converts; white Afrikaner converts are given the right of Aliyah while Nigerian Igbos are not. Like the fact of the matter is that Israel's fundamental nature is as a European Settler Colony, incredibly racist not only towards the indigenous Palestinians but the many Non-European Jews it claims to represent. It's an outpost of Western Imperialism, not a haven for the Jewish people. If it was ever meant to be the latter than it has failed miserably
6K notes
·
View notes
Text
culture isn’t modular
I did a thread (actually several) on Twitter a few years ago about Christianity’s attempts to paint itself as modular, and I’ve been seeing them referenced here in the cultural christianity Discourse, and a few people have DMed me asking me to post it here, so here’s a rehash of several of those threads:
A big part of why Christian atheists have trouble seeing how culturally Christian they still are is that Christianity advertises itself as being modular, which is not how belief systems have worked for most of human history.
A selling point of Christianity has always been the idea that it's plug-and-play: you don't have to stop being Irish or Korean or Nigerian to be Christian, you don't have to learn a new language, you keep your culture.
And you’re just also Christian.
(You can see, then, why so many Christian atheists struggle with the idea that they’re still Christian--to them, Christianity is this modular belief in God and Jesus and a few other tenets, and everything else is... everything else. Which is, not to get ahead of myself, very compatible with some tacit white supremacy: the “everything else” is goes unexamined for its cultural specificity. It’s just Normal. Default. Neutral.)
Evangelicals in particular love to contrast this to Islam, to the idea that you have to learn Arabic and adopt elements of Arab culture to be Muslim, which helps fuel the image of Islam as a Foreign Ideology that's taking over the West.
The rest of us don’t have that particular jack
Meanwhile, Christians position Christianity as a modular component of your life. Keep your culture, your traditions, your language and just swap out your Other Religion Module for a Christianity Module.
The end game is, in theory, a rainbow of diverse people and cultures that are all one big happy family in Christ. We're going to come back to how Christianity isn't actually modular, but for the moment, let's talk about it as if it had succeeded in that design goal.
Even if Christianity were successfully modular, if it were something that you could just plug in to the Belief System Receptor in a culture and leave the rest of it undisturbed, the problem is most cultures don't have a modular Belief System Receptor. Spirituality has, for the entirety of human history, not been something that's modular. It's deeply interwoven with the rest of culture and society. You can't just pull it out and plug something else in and have the culture remain stable.
(And to be clear, even using the term “spirituality” here is a sop to Christianity. What cultures have are worldviews that deal with humanity’s place in the universe/reality; people’s relationships to other people; the idea of individual, societal, or human purpose; how the culture defines membership; etc. These may or may not deal with the supernatural or “spiritual.”)
And so OF COURSE attempting to pull out a culture's indigenous belief system and replace it with Christianity has almost always had destructive effects on that culture.
Not only is Christianity not representative of "religion" full stop, it's actually arguably *anomalous* in its attempt to be modular (and thus universal to all cultures) rather than inextricable from culture.
Now, of course, it hasn't actually succeeded in that--the US is a thoroughly Christian culture--but it does lead to the idea that one can somehow parse out which pieces of culture are "religious" versus which are "secular". That framing is antithetical to most cultures. E.g. you can't separate the development of a lot of cultural practices around what people eat and how they get it from elements of their worldview that Christians would probably label "religious." But that entire *framing* of religious vs. secular is a Christian one.
Is Passover a religious holiday or a secular one? The answer isn't one or the other, or neither, or both. It's that the framing of this question is wrong.
And Christianity isn’t a plugin, however much it wants to be
Moreover, Christianity isn't actually culture-neutral or modular.
It's easy for this to get obscured by seeing Christianity as a tool of particular cultures' colonialism (e.g. the British using Christianity to spread British culture) or of whiteness in general, and not seeing how Christianity itself is colonial. This helps protect the idea that “true” Christianity is good and innocent, and if priests or missionaries are converting people at swordpoint or claiming land for European powers or destroying indigenous cultures, that must be a misuse of Christianity, a “fake” or “corrupted” Christianity.
Never mind that for every other culture, that culture is what its members do. Christianity, uniquely, must be judged on what it says its ideals are, not what it actually is.
Mistaking the engine for the exhaust
But it’s not just an otherwise innocent tool of colonialism: it’s a driver of it.
At the end of the day, it’s really hard to construct a version of the Great Commission that isn’t inherently colonial. The end-goal of a world in which everyone is Christian is a world without non-Christian cultures. (As is the end goal of a world in which everyone is atheist by Christian definitions.)
Yet we focus on the way Christianity came with British or Spanish culture when they colonized a place--the churches are here because the Spaniards who conquered this area were Catholic--and miss how Christianity actually has its own cultural tropes that it brings with it. It's more subtle, of course, when Christianity didn't come in explicitly as the result of military conquest.
Or put another way, those cultures didn't just shape the Christianity they brought to places they colonized--they were shaped by it. How much of the commonality between European cultures is because of Christianity?
It’s not all a competition
A lot of Christians (cultural and practicing), if you push them, will eventually paint you a picture of a very Hobbesian world in which all religions, red in tooth and claw, are trying to take over the world. It's the "natural order" to attempt to eliminate all cultures but your own.
If you point out to them that belief and worldview are deeply personal, and proselytizing is objectifying, because you're basically telling the person you're proselytizing to that who they are is wrong, you often get some version of "that's how everyone is, though."
Like we all go through life seeing other humans as incomplete and fundamentally flawed and the only way to "fix" them is to get them to believe what we believe. And, like, that is not how everyone relates to others?
But it's definitely how both practicing Christians and Christian antitheists relate to others. If, for Christians, your lack of Jesus is a fundamental flaw in you that needs to be fixed, for New Atheists, your “religion” (that is, your non-Christian culture) is a fundamental flaw in you that needs to be fixed. Neither Christians nor New Atheists are able to relate to anyone else as fine as they are. It's all a Hobbesian zero-sum game. It's all a game of conversion with only win and loss conditions. You are, essentially, only an NPC worth points.
The idea of being any other way is not only wrong, but impossible to them. If you claim to exist in any other way, you are either deluded or lying.
So, we get Christian atheists claiming that if you identify as Jewish, you can’t really be an atheist. Or sometimes they’ll make an exception for someone who’s “only ethnically Jewish.” If the only way you relate to your Jewishness is as ancestry, then you can be an atheist. Otherwise, you’re lying.
Or, if you’re not lying, you’re deluded. You just don’t understand that there’s no need for you to keep any dietary practices or continue to engage in any form of ritual or celebrate any of those “religious” Jewish holidays, and by golly, this here “ex”-Christian atheist is here to separate out for you which parts of your culture are “religious” and which ones are “secular.”
Religious/secular is a Christian distinction
A lot of atheists from Christian backgrounds (whether or not they were raised explicitly Christian) have trouble seeing how Christian they are because they've accepted the Christian idea that “religion” is modular. (If we define “religion” the way Christians (whether practicing or cultural) define it, Christianity might be the only religion that actually exists. Maybe Islam?)
When people from non-Christian cultures talk about the hegemonically Christian and white supremacist nature of a lot of atheism, it reflects how outside of Christianity, spirituality/worldview isn't something you can just pull out of a culture.
Christian atheists tend to see the cultural practices of non-Christians as "religious" and think that they should give them up (talk to Jewish atheists who keep kosher about Christian atheist reactions to that). But because Christianity positions itself as modular, people from Christian backgrounds tend not to see how Christian the culture they imagine as "neutral" or "normal" actually is. In their minds, you just pull out the Christianity module and are left with a neutral, secular society.
So, if people from non-Christian backgrounds would just give up their superstitions, they'd look the same as Christian atheists.
Your secularism is specifically post-Christian
Of course, that culture with the Christianity module pulled out ISN'T neutral. So the idea that that's what "secular society" should look like ends up following the same pattern as Christian colonialism throughout history: the promise that you can keep your culture and just plug in a different belief system (or, purportedly, a lack of a belief system), which has always, always been a lie. The secular, "enlightened" life that most Christian atheists envision is one that's still built on white, western Christianity, and the idea that people should conform to it is still attempting to homogenize society to a white Christian ideal.
For people from cultures that don't see spirituality as modular, this is pretty obvious. It's obvious to a lot of people from non-white Christian cultures that have syncretized Christianity in a way that doesn't truck with the modularity illusion.
I also think, even though they're not conceptualizing it in these terms, that it's actually obvious to a lot of evangelicals. (The difference being that white evangelical Christianity enthusiastically embraces white supremacy, so they see the destruction of non-Christian culture as good.) But I think it's invisible to a lot of mainline non-evangelical Christians, and it's definitely invisible to a lot of people who leave Christianity.
And that inability to see culture outside a Christian framing means that American secularism is still shaped like Christianity. It's basically the same text with a few sentences deleted and some terms replaced.
Which, again, is by design. The idea that you can deconvert to (Christian) atheism and not have to change much besides your opinions about God is the mirror of how easy it’s supposed to be to convert to Christianity.
Human societies don’t follow evolutionary biology
The Victorian Christian framing underlying current Western ideas of enlightened secularism, that religious practice (and human culture in general) is subject to the same sort of unilateral, simple evolution toward a superior state to which they, at the time, largely reduced biological evolution, is deeply white supremacist.
It posits religious evolution as a constantly self-refining process from "primitive" animism and polytheism to monotheism to white European/American Christianity. For Christians, that's the height of human culture. For ex-Christians, the next step is Christian-derived secularism.
Maybe you’ve seen this comic?
The thing is, animism isn’t more “primitive” than polytheism, and polytheism isn’t more “primitive” than monotheism. Older doesn’t mean less advanced/sophisticated/complex. Hinduism isn’t more “primitive” than Judaism just because it’s polytheistic and Judaism is monotheistic.
Human cultures continue to change and adapt. (Arguably, older religions are more sophisticated than newer ones because they’ve had a lot more time to refine their practices and ideologies instead of having to define them.) Also, not all cultures are part of the same family tree. Christianity and Islam may be derived from Judaism, but Judaism and Hinduism have no real relationship to one another.
But in this worldview, Christianity is "normal" religion, which is still more primitive than enlightened secularism, but more advanced than all those other primitive, superstitious, irrational beliefs.
Just like Christians, when Christian atheists do try to make room for cultures that aren't white and European-derived, the tacit demand is "okay, but you have to separate out the parts of your culture that the Christian sacred-secular divide would deem 'religious.'"
Either way, people from non-Christian cultures, if they’re to be equals, are supposed to get with the program and assimilate.
You’re not qualified to be a universal arbiter of what culture is good
Christian atheists usually want everyone to unplug that Religion module!
So, for example, you have ex-Christian atheists who are down with pluralism trying to get ex-Christian atheists who aren't to leave Jews alone by pointing out that you can be atheist and Jewish.
But some of us aren’t atheist. (I’m agnostic by Christian standards.) And the idea that Jews shouldn’t be targets for harassment because they can be atheists and therefore possibly have some common sense is still demanding that people from other cultures conform to one culture’s standard of what being “rational” is.
Which, like, is kind of galling when y’all don’t even understand what “belief in G-d” means to Jews, and people from a culture that took until the 1800s to figure out that washing their hands was good are setting themselves up as the Universal Arbiters of Rationality.
(BTW, most of this also holds true for non-white Christianity, too. I guarantee you most white Christian atheists don’t have a good sense of what role church plays in the lives of Black communities, so maybe shut up about it.)
In any case, reducing Christianity--a massive, ambient phenomenon inextricable from Western culture--to the specific manifestation of Christian practice that you grew up with is, frankly, absurd.
And you can’t be any help in deconstructing hegemony when you refuse to perceive it and understand that it isn’t something you can take off like a garment, and you probably won’t ever recognize and uproot all the ways in which it affects you, especially when you are continuing to live within it.
What hegemony doesn’t want you to know
One of the ways hegemony sustains and perpetuates itself is by reinforcing the idea not so much that other ways of being and knowing are evil (although that’s usually a stage in an ideology becoming hegemonic), but that they’re impossible. That they don’t actually exist.
See, again, the idea that anyone claiming to live differently is either lying or deluded.
There are few clearer examples of how pervasive Christian hegemony is than Christian atheists being certain every religion works like Christianity. Hegemonic Christianity wants you to think that all cultures work like Christianity because it wants their belief systems to be modular so you can just ...swap them. And it wants to pretend that culture/worldview is a free market where it can just outcompete other cultures.
But that’s... not how anything works.
And the truth of the matter is that white nationalist Christians shoot at synagogues and Sikh temples and mosques because those other ways of being can’t be allowed to exist.
They don’t shoot at atheist conventions because there’s room in hegemonic Christianity for Christian atheists precisely because Christian atheists are still culturally Christian. Their atheism is Christian-shaped.
They may not like you. They’re definitely going to try to convert you. They may not want you to be able to hold public office or teach their kids.
But the only challenge you’re providing is that of The Existence of Disbelief. And that’s fine. That makes you a really safe Other to have around. You can See The Light and not have to change much.
What you’re not doing is providing an example of a whole other way of being and knowing that (often) predates Christianity and is completely separate from it and has managed to survive it and continue to live and thrive (there’s a reason Christians like to speak of Jews and Judaism in the past tense, and it’s similar to the reason white people like to speak of indigenous peoples of the Americas in the past tense).
That’s not a criticism--it’s fine to just... be post-Christian. There’s not actually anything wrong with being culturally Christian. The problems come in when you start denying that it’s a thing, or insisting that you, unique among humankind, are above Having A Culture.
But it does mean that you don’t pose the same sort of threat to Christianity that other cultures do, and hence, less violence.
7K notes
·
View notes
Text
"In “Memory Voids and Role Reversals,” Palestinian political science professor Dana El Kurd writes of her jarring experience, hearing of the October 7th massacres by Hamas while visiting the Holocaust Tower at the Jewish Museum in Berlin. She notes the historic irony of Holocaust survivors seeking security from future oppression by expelling another people from their homeland by the hundreds of thousands, ghettoizing them in enclaves enforced by military checkpoints, and controlling them with collective punishment.
The irony of a state formed as the “antithesis” to the ghetto using ghettoization as a strategy of control is not lost on Palestinians. This infrastructure of coercion went hand in hand, of course, with ever-present physical violence — imprisonment, home demolitions, air strikes and more.
She quotes Aristide Zolberg’s observation that “formation of a new state can be a ‘refugee-generating process.’”
This is not only true of Palestinians. The Westphalian nation-state, which has been the normative component of the international system since the Treaty of Westphalia, necessarily entails (especially since the post-1789 identification of nationalism with the nation-state) the suppression of ethnic identity to a far greater extent than the expression of any such identity. Every constructed national identity associated with a “State of the X People” has necessarily involved the suppression and homogenization of countless ethnicities present in the territory claimed by that state. At the time of the French Revolution, barely half the “French” population spoke any of the many langue d’oil dialects of northern France, let alone the dialect of the Ile de France (the basis for the official “French” language). The rest spoke Occitan dialects like Provençal, or non-Romance languages like Breton (whose closest living relative is Welsh). The same is true of Catalan, Aragonese, Basque, and Galician in Spain, the low-German languages and now-extinct Wendish in Germany, the non-Javanese ethnicities of Indonesia, and so on. Heads of state issue sonorous pronouncements concerning the “Nigerian People” or “Zimbabwean People,” in reference to multi-ethnic populations whose entire “identity” centers on lines drawn on a map at the Berlin Conference.
When I say official national languages were established through the suppression of their rivals, I mean things like the residential schools of the United States and Canada punishing Native children for using their own languages. Or schools around the world shaming students with signs reading “I Spoke Welsh (or Breton, or Provencal, or Catalan, or Basque, or Ainu, or an African vernacular instead of the English, French, etc., lingua franca). And so on.
And when we consider the range of artificial national identities that were constructed by suppressing other real ethnicities, we can’t forget the “Jewish People” of Israel. Its construction occurred part and parcel with the suppression of diasporic Jewish ethnic identities all over Europe and the Middle East. The “New Jewish” identity constructed by modern Zionism was associated with the artificial revival of Hebrew, which had been almost entirely a liturgical language for 2300 years, as an official national language. And this, in turn, was associated with the suppression — both official and unofficial — of the actually existing Jewish ethnicities associated with the Yiddish, Ladino, and Arabic languages.
The centuries-old languages and cultures of actual Jewish ethnicities throughout Europe were treated as shameful relics of the past, to be submerged and amalgamated into a new artificially constructed Jewish identity centered on the Hebrew language.
Yiddish, the language spoken by the Ashkenazi Jews of Europe — derived from an archaic German dialect and written in the Hebrew alphabet — was stigmatized by Zionist leaders in Palestine and by the early Israeli government. According to Max Weinreich’s History of the Yiddish Language, the “very making of Hebrew into a spoken language derives from the will to separate from the Diaspora.” Diasporic Jewish identities, as viewed by Zionist settlers, were “a cultural morass to be purged.” The “New Jew” was an idealized superhuman construct, almost completely divorced from centuries worth of culture and traditions of actual Jews: “Yiddish began to represent diaspora and feebleness, said linguist Ghil’ad Zuckermann. ‘And Zionists wanted to be Dionysian: wild, strong, muscular and independent.’”
This “contempt for the Diaspora” was “manifested . . . in the fierce campaign against Yiddish in Palestine, which led not only to the banning of Yiddish newspapers and theaters but even to physical attacks against Yiddish speakers.” From the 1920s on, anyone in Palestine with the temerity to publish in Yiddish risked having their printing press destroyed by organizations with names like the “Battalion of the Defenders of the Hebrew Language,” “Organization for the Enforcement of Hebrew,” and “Central Council for the Enforcement of Hebrew.” The showing of the Yiddish-language film Mayn Yidishe Mame (“My Yiddish Mama”), in Tel Aviv in 1930, provoked a riot led by the above-mentioned Battalion. After the foundation of Israel, “every immigrant was required to study Hebrew and often to adopt a Hebrew surname.” In its early days Israel legally prohibited plays and periodicals in the Yiddish language. A recent defender of the early suppression of Yiddish, in the Jerusalem Post, argued that Diasporic languages threatened to “undermine the Zionist project”; in other words, an admission that actually existing ethnic identities threatened an identity manufactured by a nationalist ideology.
If this is true of Yiddish — the native language of the Ashkenazi Jews who dominated the Zionist settlement of Palestine — it’s even more so of the suppression of Jewish ethnic identities outside the dominant Sephardic minority. Golda Meir once dismissed Jews of non-Ashkenazi or non-Yiddish descent as “not Jews.”
Consider the roughly half of the Israeli population comprised of Mizrahi Jews from Middle Eastern communities (including those living in Palestine itself before European settlement). Although the Mizrahim are trotted out as worthy victims when they are convenient for purposes of Israeli propaganda — the majority of them were expelled from Arab countries like Iraq after 1948, in what was an undeniable atrocity — they are treated the rest of the time as an embarrassment or a joke, and have been heavily discriminated against, by the descendants of Ashkenazi settlers. For example former Prime Minister David Ben Gurion described Mizrahim
as lacking even “the most elementary knowledge” and “without a trace of Jewish or human education.” Ben Gurion repeatedly expressed contempt for the culture of the Oriental Jews: “We do not want Israelis to become Arabs. We are in duty bound to fight against the spirit of the Levant, which corrupts individuals and societies, and preserve the authentic Jewish values as they crystallized in the Diaspora.”
Current Prime Minister Netanyahu once joked about a “Mizrahi gene” as his excuse for tardiness. And an Israeli realtor ran a commercial appealing to “there goes the neighborhood” sentiments by depicting a light-skinned family having their Passover celebration disrupted by uncouth Mizrahi neighbors.
Nationalism and the nation-state are the enemies of true ethnicity and culture, and built on their graves. There’s no better illustration of this principle than the Zionist project itself."
-Kevin Carson, "Zionism and the Nation-State: Palestinians Are Not the Only Victims"
211 notes
·
View notes
Note
is it okay to learn gaeilge if you aren’t irish but most of your heritage actually is from ireland? i totally get what you were saying with your other post about barely having irish heritage and making it an aesthetic but if that’s not the case it’s not like a closed language right?
Ok so I’m going to go on a bit of a rant here and explain my post and my feelings about this.
First and foremost, it’s not a closed language.
More people learning Irish is always a good thing. However, I think you should ask yourself your intentions for learning Irish. This is where Irish people’s annoyance at US Americans can come in.
Firstly is regards to my posts about my frustrations at Americans making my post about Ireland and our relationship with Irish and efforts to preserve it, about themselves. Sometimes the best way to be and ally to a cultural group that you are not in, is to say nothing and to simply listen. This is something we deal with on the daily, and have dealt with for centuries. Having lived in the USA for centuries and now culturally being an American, you do not feel this.
I think because America is such a mish mash of DNA, you guys have a different idea of race than we do. We identify as nationalities rather than race. Yes we are black or white, but first and foremost we are Irish or Nigerian or Korean or whatever!
An Irish person is someone who lives in Ireland, who is immersed in our culture, who is affected by our laws and politics. Not someone who had a relative centuries ago that was Irish, but is now part of a different culture. You can have zero Irish ancestry and be Irish because you live on the island! Minimising a whole culture down to blood percentages is weird and not at all how it works.
Here is when the “celtiboo” (Celtic weaboo, ie, someone who is obsessed with and fetishises the Celtic nations such as Ireland) issue comes in. Someone could have ten different DNA percentages of different European countries, yet they focus in on Ireland. This is because of the fetishised idea that people have of us and our culture. People refuse to listen to Irish people, and will only believe their idea of what our culture and history is. I know this first hand living in a city that is inundated with tourists on the daily. My sister is a tour guide at a massive historical site here. US Americans won’t listen to us.
You don’t really see this with these same people who might have French DNA for example. And there is a massive difference between our Languages. French is a language that is far from endangered. It is itself a colonisers language. You learn French so you can go to French speaking countries and use your skills. With Irish, realistically you won’t get to use it. We only get to use it when studying in school or in Gaeltachts (Irish speaking areas), and they aren’t that common.
So you have to ask yourself why you do you want to learn it? Is it for a gimmick or party trick? Something you can pull out that other people in your country won’t have heard of?
When we say we want to preserve Irish, we mean that we want our people in Ireland to be able to speak it. We aren’t trying to spread that language around the world. We just want to restore things to the way they were before England colonised us.
Anyways, in conclusion, just please don’t claim to be a nationality that your aren’t and try to speak on our issues. Please be respectful of native languages and when people from the affected group speak on our troubles, just listen! Please don’t reply making it about yourself and your whatever percentage DNA that put you in “exactly the same position” as us, because it doesn’t.
#ireland#irish#hozier#unreal unearth#hozier unreal unearth#Gaeilge#celtiboo#usa#us american#America#American
320 notes
·
View notes
Text

Long before it arose in New York City and became an influential style of music around the world, salsa music has its seeds in African rhythms and traditions that came to the Caribbean through the slave trade. Centuries of enslavement caused many cultural changes in Cuba, including the music that led to salsa.

Some people know Bobby Day’s 1958 “Rockin’ Robin” or Michael Jackson’s remake but the origin of the song goes back to the days of slavery.
The majority of the Africans that were enslaved and brought to the Americas were of West African descent where the drum was used as a form of communication. In the Americas, enslaved Africans used the drum in the same way — communicating with the enslaved on distant plantations and ultimately planning uprising.
The enslavers caught wind of this and enacted a ban.
It is absolutely necessary to the safety of this Province, that all due care be taken to restrain Negroes from using or keeping of drums, which may call together or give sign or notice to one another of their wicked designs and purposes.
— Slave Code of South Carolina, Article 36
That ban went down in 1740 and soon spread throughout Colonial America.
But the beat is in the heart of the African.
We soon found other ways to imitate the sound of the drum; stomping, playing spoons, washboards, or anything other household item. We also “slapped Juba” or played “hambone” where the body became an instrument where the player slaps their thighs and chest for the drum beat. (How did young boys in 1980s Park Hill, Denver know “Hambone?”)
Although we kept the beat, we lost the tradition, a cultural marker snatched away from us.

While the American enslaver worked feverishly to destroy any vestige of African culture, the Spanish enslaver of Cuba felt that it was in his best interest to allow the enslaved African to maintain his culture. In support of that, the Spanish allowed the Africans to organize Cabildos (or social groups) based on their nation of origin. Thus you had the Abakua (or Ekpe) from the nations known as Nigeria and Cameroon, the Madinga (or Malinke) from Sierre Leone, etc.
Our focus is primarily on the Lucumi, the Cabildo founded for the Yoruba of Benin and Nigeria. This lineage would be the cornerstone and origin point for what is now called “Salsa.” And what is this “Salsa?”

When we spoke of the drum being forbidden among the enslaved Africans in America, we forgot to mention that there was one place that didn’t enact that ban. That place was the port city of New Orleans, Louisiana — some even call New Orleans the Northernmost Caribbean city.
Similar in the way that the Spanish allowed for Cabildos in Cuba, the Louisiana enslavers permitted Sundays off and were okay with the dance and celebration so long as the enslaved African did so outside of the city limits in a place called Place des Negres (eventually known as Congo Square).
After the Civil War, Africans in America were able to get a hold of surplus brass instruments and shortly thereafter began composing music based on the popular music in the Caribbean at the time, the Cuban Habanero. Many say that this is one of the foundations of jazz music itself and the basis of the habanero, the tressilo, can be heard in second lines. Self-proclaimed jazz inventor, Jelly Roll Morton had this to say:
Now take the habanero “La Paloma”, which I transformed in New Orleans style. You leave the left hand just the same. The difference comes in the right hand — in the syncopation, which gives it an entirely different color that really changes the color from red to blue.
Now in one of my earliest tunes, “New Orleans Blues”, you can notice the Spanish tinge. In fact, if you can’t manage to put tinges of Spanish in your tunes, you will never be able to get the right seasoning, I call it, for jazz. Jelly Roll Morton
Because of those qualities, a young musical prodigy from Cuba, Mario Bauzá recognized the similarities between jazz and Cuban music straightaway. Bauzá fell in love with jazz having heard it on Cuban radio but it was his trip to Harlem, NYC in 1927 that convinced him that New York was where he wanted to be and jazz was the music that he wanted to play.
Bauzá returned to New York in 1930, immediately found work, eventually landing a gig in the Cab Calloway band. Here he brought on the legend in the making, Dizzy Gillespie, and the two became fast friends. Bauzá attempted to play his “native” music to many in the band but they dismissed it as “country” music. Gillespie, on the other hand, embraced it.
For the next eight years Bauzá played in predominately African jazz bands having seen discrimination from white Cubans. Yet he longed to start a group that incorporated the music from his home and his second love, jazz. He shot this idea to his childhood friend/brother-in-law and in 1939 at the Park Palace Ballroom the Machito Afro-Cubans would debut.
“I am Black, which means my roots are in Africa. Why should I be ashamed of that?” Bauzá said in reference to the name.
Bauzá replaced the drum kit, which at that time had only been around for 20 years, with the hard to find congas, timbales, and toms. “The timbales play the bell pattern, the congas play the supportive drum part, and the bongos improvise, simulating a lead drum”. In the 40s these drums could only be found at Simon Jou’s bakery, La Moderna, locally known in East Harlem simply as Simon’s.
Next, the Afro-Cubans needed a home and they would find that not in Harlem nor the Bronx, but instead in Midtown Manhattan, a club called the Palladium.

Salsa is a set of Afro-Caribbean rhythms fused with jazz and other styles. The truth is that its origins have always been much debated, although as a general rule it is mentioned that it comes from a fusion that came from Africa in the Caribbean when they heard European music and wanted to mix it with their drums
These origins focus especially on mambo, danzó, cha cha chá, guaracha and son montuno, later enriched with instruments such as saxophone, trumpet or trombone.
It was the Cuban exiles and those from Puerto Rico who popularized salsa in New York back in the 1950s. But it wasn't until the last third of this century that salsa dancing began to take off all over the world.
Cuba played a leading role in the origin of salsa. Already in the 1930s, melodies and rhythms from Africa were playing on the Caribbean island. Among them was the danzón, a musical piece acquired by the French who had fled Haiti.
History tells us that it was these first rhythms that were then mixed with rumbas such as guagancó and sonero to begin to create their own Afro-Cuban rhythms, including Afro-Cuban jazz, mambo, guaracha, Cuban son and montuno.
The exquisite melody of these new rhythms soon set in other Latin American countries. Puerto Rico and Colombia were the first to welcome these new sounds from the Cuban country.
However, it was not until their appearance in the United States, and more specifically in the Bronx neighborhood of New York, when these rhythms acquired a greater impact. It was the moment in which new musical instruments were added that today form an indissoluble part of salsa.
The great Cuban musicians who moved to New York along with the wave of these new rhythms created the famous tumbadoras, congas or son montuno, and were responsible for introducing trombones and guaracha.
The Origin of the Salsa Dance Steps
Once salsa was defined as a musical genre in the 1970s, the movements and steps of its dance were collected through a fusion of the African with the European.
These steps and movements of salsa fundamentally reflect the influence of the dances that the Africans brought to the Caribbean and the European dances that have been danced in Cuba since the 1930s.
So much so that the basic steps of salsa are precisely the same steps as the Cuban son, just as it also includes steps that can be seen in rumba, danzón and mambo.
The origin of these variants is in the regions where this style comes from, which are the ones that developed each dance, always under the same umbrella of the term salsa.
It is not surprising, then, that salsa is defined as the result of a series of social conditions and the evolution of a series of rhythms and melodies from Cuba, which were developed and achieved repercussion in the United States.
There are those who assure against this mixture that salsa is neither a rhythm nor a style, but rather a term that serves to represent all the music of Afro-Cuban origin that emerged in the first decades of the twentieth century.
In short, the origin of salsa has always been, and will continue to be, much discussed. American musician Tito Puente was right when he said, "Salsa doesn't exist. What they now call salsa is what I have played for many years, and this is mambo, guaracha, cha cha chá and guagancó".
#salsa#cuba#congo#nigeria#african#afrakan#kemetic dreams#brownskin#africans#afrakans#brown skin#african culture#afrakan spirituality#nigerian#nigerians#ghana#niger#cameroon#senegal#west africa#afro cuban#american#african american#african american history#american history#dance#african dance#congo dance#ekik#yoruba
11 notes
·
View notes
Text

Africa has been very rich even before colonialism
The truth you should know about African
Blacks know your history and divinity
They gave us the Bible and stole our natural resources
Community and Social Cohesion: Traditional African religions often emphasized communal values, fostering a sense of belonging and mutual support within the community. Rituals and ceremonies were communal events that strengthened social ties.
Respect for Nature: Many African traditional religions were deeply connected to nature, promoting a harmonious relationship with the environment. This connection often led to sustainable practices and a respect for the natural world.
Ethical Guidelines: These religions often included moral and ethical guidelines that governed interpersonal relationships. Concepts such as honesty, hospitality, and respect for elders were commonly emphasized.
Cultural Identity: Traditional African religions played a crucial role in shaping cultural identity. They provided a framework for understanding the world, explaining origins, and passing down cultural practices through rituals, myths, and oral traditions.
Islam reached Nigeria through a combination of trade, migration, and cultural interactions. The trans-Saharan trade routes were crucial in bringing Islam to the region. Muslim traders from North Africa and the Middle East ventured into West Africa, establishing economic ties and introducing Islam to local communities.
The city-states along the trade routes, such as Kano and Katsina, became significant centers for Islamic influence. Merchants not only engaged in commercial activities but also played a role in spreading Islamic teachings. Over time, rulers and elites in these city-states embraced Islam, contributing to its gradual acceptance.
Additionally, the spread of Islam in Nigeria was facilitated by the activities of Islamic scholars and missionaries. Scholars known as clerics or Mallams played a key role in teaching Islamic principles and converting people to Islam. They often established Quranic schools and engaged in educational activities that promoted the understanding of Islamic teachings.
Military conquests also played a part in the expansion of Islam in Nigeria. Islamic empires, such as the Sokoto Caliphate in the 19th century, emerged through conquest and warfare, bringing Islam to new territories. The Sokoto Caliphate, led by Usman dan Fodio, sought to establish a strict Islamic state based on Sharia law.
Overall, the spread of Islam in Nigeria was a gradual process influenced by trade networks, migration, the activities of scholars, and, at times, military expansion. The interplay of these factors contributed to the integration of Islam into Nigerian society, shaping its cultural and religious landscape.
In the vast tapestry of Africa's rich cultural heritage, herbal traditional healing stands out as a profound and time-honored practice. African herbal traditional healers, often known as traditional or indigenous healers, play a vital role in the healthcare systems of many communities across the continent. Their practices are deeply rooted in the natural world, drawing on centuries-old wisdom and an intimate understanding of local flora.
African herbal traditional healers are custodians of ancient knowledge, passing down their expertise through generations. They serve as primary healthcare providers in many communities, addressing a wide range of physical, mental, and spiritual ailments. The healing process involves a holistic approach, considering the interconnectedness of the individual with their community and environment.
One of the hallmark features of African herbal traditional healers is their profound knowledge of medicinal plants. These healers have an intricate understanding of the properties, uses, and combinations of various herbs. Passed down through oral traditions, this knowledge is often a well-guarded family secret or shared within the apprentice-master relationship.
The methods employed by herbal traditional healers encompass diverse approaches. Herbal remedies, administered as infusions, decoctions, or ointments, form a significant part of their treatment. These remedies are carefully crafted based on the healer's understanding of the patient's symptoms, lifestyle, and spiritual condition. Additionally, rituals, ceremonies, and prayers are often incorporated into the healing process, acknowledging the interconnectedness of physical and spiritual well-being.
African herbal traditional healers frequently integrate spiritual elements into their practice. They believe that illness can be a manifestation of spiritual imbalances or disharmony. Through rituals and consultations with ancestors or spirits, healers seek to restore balance and harmony within the individual and the community.
Herbal traditional healers are integral to the social fabric of their communities. They often serve not only as healers but also as counselors, mediators, and keepers of cultural traditions. Their practices are deeply intertwined with community life, contributing to the resilience and cohesion of African societies.
While herbal traditional healing holds immense value, it faces challenges in the modern era. The encroachment of Western medicine, issues related to regulation and standardization, and the potential exploitation of traditional knowledge pose threats to this practice. However, there is also a growing recognition of the importance of integrating traditional healing into mainstream healthcare systems, leading to collaborative efforts to preserve and promote this valuable heritage.
African herbal traditional healers are bearers of an ancient legacy, embodying a profound connection between humanity and the natural world. Their healing practices, rooted in herbal wisdom and spiritual insights, offer a unique perspective on healthcare that complements modern medical approaches. Preserving and respecting the knowledge of these healers is not only crucial for the well-being of local communities but also for the broader appreciation of the diverse cultural tapestry that defines Africa.
#life#animals#culture#aesthetic#black history#history#blm blacklivesmatter#anime and manga#architecture#black community
124 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’m going to be speaking to some primary and secondary school kids this week. They’re having a huge performance and arts competition based on Nigerian culture, and the school is having difficulty because no one really has a research practice imaginative enough when dealing with the archives of our history. They’ve been treating it quite binary and the school wants me to encourage the kids to reach beyond!!!! I’m so excited, honored and nervous. Imagine me, a whole chi, talking to children about culture and art 🌀
51 notes
·
View notes
Text
blows my mind there's not even a Chinese coven in The Twilight Saga. no Indian coven. only ONE coven in the Middle East/Africa: EGYPTIAN. no Greek coven, no Iranian coven, no Afghan coven, no Ethiopian coven, no Nigerian coven; FUCK ancient civilizations i guess! no one in South or Central America but the AMAZONS???? for real?????? the POTENTIAL to incorporate LEGENDS and HISTORY and CULTURE — wasted! i CANNOT with this author thinking the only vampire civilizations exist in Europe & America!! fuck off directly into the sun!!!
#you know what the worst part of this is????#it's actually better off they don't exist because you KNOW Meyer will just depict them as RACIST CARICATURES#this tag is sponsored by Maria 'her features were clearly Mexican' [NO LAST NAME GIVEN]#and of course the 'wild' 'feral' Amazons#oh and lest we forget Amun 'all Egyptians look the same' [last name]#OH AND LEST WE FORGET#THE ENTIRE NATIVE TRIBE MEYER APPROPRIATED & COLORED W/ RACIST TROPES & STEREOTYPES JUST TO PROFIT OFF OF W/O GIVING BACK ANYTHING TO THEM#yeah it's such a shame actually this author is so ignorant bc this series could have been batshit insane with coolness#whatever you won't hear me complaining too much - that's what this fandom is for#saddle up twilight bitches we ride at dawn#twilight#twilight renaissance#the twilight saga#twilight saga
196 notes
·
View notes
Text
With white actors, their stereotypes are clear satire, while their authentic portrayals of accents are taken seriously—African accents are not afforded that luxury. Part of the authenticity and grit we’ve come to love in Good Will Hunting (1997) owes to the fact that both Matt Damon and Ben Affleck speak in accents native to South Boston—which successfully shows the importance of class distinctions, Will’s intellectual ability despite his “rough” surroundings, and rooting him in his neighborhood and background even as he progresses to new places and opportunities. Part of the joy of watching Mary Poppins (1964), is the grating sound of Dick Van Dyke’s bizarre “Cockney” accent. Often noted as one of the worst accents in film history, Van Dyke’s character sounded like he came from New Jersey, Australia, but Poppins is a children’s comfort film filled with magic, so audiences are already prepared to suspend their disbelief. Language, voice, and tone are vital parts of storytelling, but somehow caricature-like portrayals of African accents still manage to win Oscars, while Dick Van Dyke’s “Cockney” failure is an actor’s cautionary tale.
This speaks to a larger issue: the hierarchy of occidental languages over languages from the global south, the (lack of) knowledge of African dialects, and a general laziness toward the research required to thoughtfully and effectively learn regional African accents. Alongside my research for this article, I also spoke to Djeneba Bagayoko, a linguist who specializes in African languages and is currently working on a book exploring the similarities in Ebonics and continental languages. When we discussed Beasts of No Nation—no nation indeed, as the film is set in an “unspecified” West African country—Djeneba pointed out the prevalence of guttural sounds and line delivery in a lower vocal pitch.
While having a lower-pitched voice is completely within the rights of directors and actors to be a stylistic choice for a character, its unfortunate prevalence goes beyond artistic prerogative and seems closer to laziness or ignorance. Viola Davis’s accent in The Woman King is also delivered in a lower register, with an emphasis on guttural sounds and a sprinkling of that American English rhotic R that would not be present in a West African accent during the 1820s. Winston Duke’s accent in Black Panther (2018) also features guttural sounds, a low pitch, and even Nigerian facets of speech (adding “o” as a standalone sound at the end of sentences), despite the fact that the fictional nation of Wakanda is supposedly located in southeast Africa. Bagayoko rightly asked, “Why, when it comes to Africa, are we all lumped together?” Reducing Western and Southern African accents down to hard, low-pitched noises positioned at the back of the throat perpetuates the idea that African languages are too “other” for any attention to detail. The frequency with which we see this technique reiterates the view of Africans as homogenized and underdeveloped—a colonial perspective.
114 notes
·
View notes