#economic development
Text
“It is simply impossible to overstate both the importance of the buffalo to the Indian people and the damage that was done when the buffalo were nearly wiped out,” ITBC President Ervin Carlson said in a statement. “By helping tribes reestablish buffalo herds on our reservation lands, the Congress will help us reconnect with a keystone of our historic culture as well as create jobs and an important source of protein that our people truly need.”
#bison#buffalo#short grass prairie#conservation#sustainability#economic development#traditional ecological knowledge#ecological restoration#species conservation
213 notes
·
View notes
Note
Why do economists need to shut up about mercantilism, as you alluded to in your post about Louis XIV's chief ministers?
In part due to their supposed intellectual descent from Adam Smith and the other classical economists, contemporary economists are pretty uniformly hostile to mercantilism, seeing it as a wrong-headed political economy that held back human progress until it was replaced by that best of all ideas: capitalism.

As a student of economic history and the history of political economy, I find that economists generally have a pretty poor understanding of what mercantilists actually believed and what economic policies they actually supported. In reality, a lot of the things that economists see as key advances in the creation of capitalism - the invention of the joint-stock company, the creation of financial markets, etc. - were all accomplishments of mercantiism.
Rather than the crude stereotype of mercantilists as a bunch of monetary weirdos who thought the secret to prosperity was the hoarding of precious metals, mercantilists were actually lazer-focused on economic development. The whole business about trying to achieve a positive balance of trade and financial liquidity and restraining wages was all a means to an end of economic development. Trade surpluses could be invested in manufacturing and shipping, gold reserves played an important role in deepening capital pools and thus increasing levels of investment at lower interest rates that could support larger-scale and more capital intensive enterprises, and so forth.
Indeed, the arch-sin of mercantilism in the eyes of classical and contemporary economists, their interference in free trade through tariffs, monopolies, and other interventions, was all directed at the overriding economic goal of climbing the value-added ladder.
Thus, England (and later Britain) put a tariff on foreign textiles and an export tax on raw wool and forbade the emigration of skilled workers (while supporting the immigration of skilled workers to England) and other mercantilist policies to move up from being exporters of raw wool (which meant that most of the profits from the higher value-added part of the industry went to Burgundy) to being exporters of cheap wool cloth to being exporters of more advanced textiles. Hell, even Adam Smith saw the logic of the Navigation Acts!

And this is what brings me to the most devastating critique of the standard economist narrative about mercantilism: the majority of the countries that successfully industrialized did so using mercantilist principles rather than laissez-faire principles:
When England became the first industrial economy, it did so under strict protectionist policies and only converted to free trade once it had gained enough of a technological and economic advantage over its competitors that it didn't need protectionism any more.
When the United States industrialized in the 19th century and transformed itself into the largest economy in the world, it did so from behind high tariff walls.
When Germany made itself the leading industrial power on the Continent, it did so by rejecting English free trade economics and having the state invest heavily in coal, steel, and railroads. Free trade was only for within the Zollverein, not with the outside world.
And as Dani Rodrik, Ha-Joon Chang, and others have pointed out, you see the same thing with Japan, South Korea, China...everywhere you look, you see protectionism as the means of achieving economic development, and then free trade only working for already-developed economies.
#political economy#mercantilism#economic development#early modern state-building#early modern period#laissez-faire#classical liberalism#classical economics#economics#economic history
57 notes
·
View notes
Text
AN OPEN LETTER to THE U.S. CONGRESS
Put the Good Jobs for Good Airports standards in the FAA reauthorization bill!
104 so far! Help us get to 250 signers!
I’m calling on you to stand with working people, passengers and our communities by supporting Good Jobs for Good Airports standards (GJGA) in the FAA reauthorization bill. Airports should and can be strong, vibrant drivers of good jobs in every part of our country. The Good Jobs for Good Airports standards are central to that mission and our nation’s future prosperity. Billions of our public dollars are invested in our nation’s aviation system every year, and we must ensure that our public resources serve the public good. That includes ensuring airports better serve the needs of our families, our passengers, our communities and the airport service workers who make it all possible.
It is evident that our air travel industry is in crisis. From record flight cancellations during summer travel peaks to mountains of lost luggage during the holiday travel season. Airports are critical publicly-funded infrastructure vital to the health of our local communities and global economy, but right now airports aren't working the way they should for travelers or airport service workers — a largely Black, brown, multiracial and immigrant service workforce. These working people, including cleaners, wheelchair agents, baggage handlers, concessionaires and ramp workers, keep airports safe and running smoothly even through a global pandemic, climate disasters and busy travel seasons. Yet many are underpaid and underprotected--even as some major airlines rake in record profit and billions of our tax dollars are invested in our national air travel system.
Domestic passenger numbers increased by 80% between 2020 and 2021, total industry employment fell by nearly 14%, leaving airport service workers to sometimes clean entire airplanes in as little as five minutes as many take on additional responsibilities outside of their typical job duties. Meanwhile, wages have barely budged for airport service workers in 20 years. The Good Jobs for Good Airports standards has the power to transform workers’ lives by ensuring airport service workers have the pay and benefits they need to care for their families.
The Good Jobs for Good Airports standards would help build a stronger, safer, more resilient air travel industry by making airport service jobs good jobs with living wages and benefits like affordable healthcare for all airport workers. Airport service workers at more than 130 covered airports would be supported through established wage and benefit standards, putting money back into hundreds of local economies and helping families thrive. If passed over 73% of wage increases will go to workers making $20 or less, estimates show.
I urge you to include the Good Jobs for Good Airports standards in the FAA reauthorization bill, and help ensure our public money serves the public good.
▶ Created on September 20, 2023 by Jess Craven
📱 Text SIGN PNXUOF to 50409
🤯 Liked it? Text FOLLOW JESSCRAVEN101 to 50409
#JESSCRAVEN101#PNXUOF#resistbot#FAA reauthorization#Good Jobs for Good Airports#airport workers#aviation industry#public infrastructure#labor rights#economic justice#workers' rights#fair wages#benefits#community support#passenger rights#public investment#economic prosperity#airport service workers#living wages#healthcare#job security#labor standards#economic equity#social welfare#income equality#workplace conditions#economic development#local economies#financial stability#worker empowerment
5 notes
·
View notes
Link
Echoes throughout the world
#physical economy#progress#economic development#ICJ#Gaza#genocide#crimes against humanity#Nixon#destabilization#Africa#Palestine#Brazil
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The belt and road initiative has brought prosperity to many nations and it the future it will bring it to many more!
The post is machine translated
Translation is at the bottom
The collective is on telegram
😘 CELEBRARE GLI OBIETTIVI RAGGIUNTI, PIANTARE NUOVI SEMI PER LA CRESCITA DEL FUTURO 🥰
🇨🇳 Il Compagno Chen Wenjun, Direttore dell'Iniziativa di Pubblicazione del Libro Bianco "La Belt and Road Initiative: un Pilastro-Chiave di una Comunità dal Futuro Condiviso per l'Umanità", ha dichiarato - durante una conferenza stampa, che l'Opera mira a fornire alla Comunità Internazionale una migliore comprensione del valore di questa iniziativa e del Concetto di Cooperazione a Mutuo Vantaggio (合作共赢):
💬 «Il Libro Bianco, guidato dal Pensiero di Xi Jinping sul Socialismo con Caratteristiche Cinesi per una Nuova Era, ha esposto sistematicamente l'Origine Storica, la Mentalità, la Visione, l'approccio per la realizzazione e i risultati pragmatici della Cooperazione tramite la Nuova Via della Seta» 😍
👉 Statistiche sulla BRI rilasciate dalla Compagna Guo Tingting - Vice-Ministro del Commercio ⭐️
📊 10 anni dopo la Presentazione della BRI, sono stati organizzati 3000 progetti di cooperazione, investiti quasi 1 Trilione di Dollari e sono stati creati 420.000 posti di lavoro per i Paesi che hanno partecipato al Progetto 😍
🇨🇳 Come prossimo passo, il Ministero del Commercio della Repubblica Popolare Cinese si concentrerà su quattro aspetti per promuovere ulteriormente la Cooperazione a Mutuo Vantaggio:
一 Rafforzare l'Apertura verso il Mondo, espandendo e facilitando l'importazione e l'esportazione di beni di alta qualità, organizzando sempre più eventi, fiere e mostre per approfondire la Cooperazione Commerciale con i Paesi interessati 😍
二 Rafforzare la Cooperazione nelle catene di produzione e approvvigionamento, migliorando ulteriormente l'efficienza dei trasporti e accelerando la formazione di nuovi corridoi commerciali tramite la costruzione di infrastrutture di alta qualità 😍
三 Piantare i semi, annaffiare e far germogliare nuovi progetti atti a promuovere ulteriormente la crescita economica, pianificando progetti infrastrutturali e costruendo nuove Zone di Cooperazione 🤝
四 Promuovere l'adesione all'Accordo Globale e Progressivo del Partenariato Trans-Pacifico e sostenere le imprese della Regioni Amministrative Speciali di Hong Kong e Macao, dove vige il Principio 一国两制 - Un Paese, Due Sistemi, affinché partecipino alla Costruzione della Nuova Via della Seta 💕
🌸 Iscriviti 👉 @collettivoshaoshan 😘
😘 CELEBRATING WHAT HAS BEEN ACHIEVED, PLANTING NEW SEEDS FOR THE GROWTH OF THE FUTURE 🥰
🇨🇳 Comrade Chen Wenjun, Director of the White Paper Publishing Initiative "The Belt and Road Initiative: a Key Pillar of a Community with a Shared Future for Humanity", declared - during a press conference, that the Opera aims to provide the International Community with a better understanding of the value of this initiative and the Concept of Cooperation for Mutual Benefit (合作共赢):
💬 «The White Paper, guided by Xi Jinping Thought of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era, systematically laid out the Historical Origin, Mindset, Vision, approach to implementation and pragmatic results of Cooperation through the New Silk Road" 😍
👉 BRI Statistics Released by Comrade Guo Tingting - Vice-Minister of Commerce ⭐️
📊 10 years after the Presentation of the BRI, 3000 cooperation projects have been organized, almost 1 Trillion Dollars have been invested and 420,000 jobs have been created for the countries that participated in the Project 😍
🇨🇳 As the next step, the Ministry of Commerce of the People's Republic of China will focus on four aspects to further promote Mutual Benefit Cooperation:
一 Strengthen Openness to the World, expanding and facilitating the import and export of high quality goods, organizing more and more events, fairs and exhibitions to deepen Commercial Cooperation with interested countries 😍
二 Strengthen Cooperation in production and supply chains, further improving transportation efficiency and accelerating the formation of new trade corridors through the construction of high-quality infrastructure 😍
三 Planting seeds, watering and sprouting new projects to further promote economic growth, planning infrastructure projects and building new Cooperation Zones 🤝
四 Promote adherence to the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement of the Trans-Pacific Partnership and support enterprises in the Special Administrative Regions of Hong Kong and Macao, where the 一国两制 Principle - One Country, Two Systems applies, to participate in the Construction of the New Way of Silk 💕
🌸 Subscribe 👉 @collectivoshaoshan 😘
#socialism#china#italian#translated#collettivoshaoshan#china news#communism#marxism leninism#marxist leninist#marxist#marxismo#marxism#chinese economy#belt and road initiative#news#economic news#world news#asia news#economic development#Chen Wenjun#xi jinping#Guo Tingting#socialismo#socialist#multipolar world#multipolarity
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
"Beijing has long known what must be done to alleviate this crisis. An obvious step would be to initiate redistributive reform to boost household income and hence household consumption – which, as a share of GDP, has been among the lowest in the world. Since the late 90s, there have been calls to rebalance the Chinese economy in favour of a more sustainable growth model, by reducing its reliance on exports and fixed asset investment like infrastructure construction. This led to some reformist, redistributive policies under the Hu Jintao and Wen Jiabao government of 2003–13, such as the New Labour Contract Law, the abolition of agriculture tax, and the redirection of government investment to inland rural regions. But the weight of vested interests (state enterprises, as well as local governments thriving on construction contracts and state bank loans fuelling those projects), and the powerlessness of social groups who stand to benefit from such rebalancing policy (workers, peasants and middle-class households), meant that reformism did not take root. The minimal gains in inequality reduction in the Hu–Wen period were duly reversed after the mid-2010s. More recently, Xi has made clear that his ‘common prosperity programme’ is not a return to the egalitarianism of the Mao era, nor even a restoration of welfarism. It is, rather, an assertion of the state’s paternalistic role vis-à-vis capital: increasing its presence in the tech and real estate sectors, and aligning private entrepreneurship with the broader interests of the nation."
Ho-Fun Hung, Zombie Economy
4 notes
·
View notes
Quote
Examples of the developmental state are familiar in East Asia: Japan and the four Asian Tigers (Hong Kong, South Korea, Taiwan, and Singapore), plus post-Mao China. But the East Asians borrowed the developmentalist model from Germany and the United States, which in their successful attempts to catch up with industrial Britain in the 19th century had used their own variants of the tradition, associated with Friedrich List in Germany and Alexander Hamilton and Henry Clay in the U.S. The roots of developmentalist economics can be traced back to mercantilism and cameralism in early modern Europe and even further back to Renaissance Italy. (There was no “fascist model” of economics. Mussolini’s regime might be classified as an authoritarian developmentalist state, but the short-lived Nazi economy was based first on preparation for war and then on plunder and slavery.)
Ironically, during the Cold War, when the U.S. supposedly illustrated the virtues of free enterprise, the U.S. had its own successful developmental-state industrial policy, orchestrated by the Defense Department through the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and other agencies. In the 1990s, libertarians and neoliberals claimed that the information technology revolution proved the superiority of the free market to government when it comes to innovation. But the major tools of the computer age, from digitization to the global internet to the computer mouse were developed by government contractors reliant on U.S. taxpayer money. It is no coincidence that U.S. productivity and innovation sputtered in this century, when neoliberal Democrats and libertarian Republicans decided to let the free market develop the next wave of technologies. It turns out that venture capitalists and advertisers are more interested in addictive online sites like Facebook and Twitter than in robots and cures for cancer. Without exception the major advances in basic technology during the post-1980s era of free market utopianism have been largely funded by the federal government.
Michael Lind, “Cold War II” (January 3rd 2023).
#America#American Civilization#Economic Development#National Development#Developmental State#Globalization#Current State of Affairs
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cryptocurrency: The Game-Changing Force Transforming the Future of Money

I. preface :
Since the creation of Bitcoin, multitudinous cryptocurrencies have been developed, each with their own unique features and functions. Cryptocurrencies operate on a decentralized network, using technology called blockchain to record deals and help fraud.
The use of cryptocurrency has grown in fashionability over the times, with further individualities and businesses starting to borrow it as a means of exchange. While cryptocurrency is still in its early stages, it has the implicit to revise the way we suppose about and use plutocrat.
2. The Benefits of Cryptocurrency:
One of the main benefits of cryptocurrency is the capability to make faster, cheaper deals. Traditional fiscal institutions frequently charge freights for services similar as line transfers and currency exchanges, which can be time- consuming and precious. Cryptocurrency allows for near-immediate deals at a much lower cost.
Cryptocurrency can also increase fiscal addition by furnishing access to fiscal services to individualities who may not have access through traditional means. This is especially important in developing countries where access to banks and other fiscal institutions may be limited.
Cryptocurrency deals are also more secure and private compared to traditional styles. Blockchain technology, which underlies utmost cryptocurrencies, uses advanced cryptography to cover against fraud and insure the confidentiality of deals.
3. The Impact of Cryptocurrency on Traditional Finance
Cryptocurrency has the implicit to disrupt traditional payment systems by offering a briskly, cheaper, and more secure volition. As further individualities and businesses borrow cryptocurrency, traditional payment systems may be forced to acclimatize or risk getting obsolete.
Banks and other fiscal institutions may also face challenges as a result of the growing fashionability of cryptocurrency. While some institutions have started to offer cryptocurrency- related services, they may struggle to keep up with the rapid-fire pace of change in the cryptocurrency request.
There’s also the eventuality for central banks to borrow cryptocurrency, either by issuing their own digital currencies or by integrating cryptocurrency into being fiscal systems. This could potentially bring further stability and oversight to the cryptocurrency request, but it may also raise enterprises about government control and the loss of the decentralized nature of cryptocurrency.
4. The Future of Cryptocurrency:
There are numerous prognostications about the future of cryptocurrency and its implicit for mainstream relinquishment. Some experts believe that cryptocurrency could ultimately replace traditional edict currency, while others are more skeptical about its long- term prospects.
It’s possible that cryptocurrency could come more extensively accepted as a means of exchange and a store of value, particularly if it can address some of the challenges and limitations it presently faces. These challenges include scalability issues, volatility, and nonsupervisory query.
Despite these challenges, cryptocurrency has the implicit to bring significant benefits to individualities and businesses, similar as briskly, cheaper deals and bettered fiscal addition. As similar, it’s likely that the use of cryptocurrency will continue to grow and evolve in the coming times.
5. Conclusion:
In conclusion, cryptocurrency has the implicit to revise the way we suppose about and use plutocrat. It offers briskly, cheaper deals and bettered security and sequestration compared to traditional fiscal systems. Cryptocurrency has the implicit to disrupt traditional payment systems and challenge banks and fiscal institutions, and it may also be espoused by central banks in the future.
While there are challenges and limitations to the wide relinquishment of cryptocurrency, it has the implicit to bring significant benefits to individualities and businesses. As similar, it’s likely that we will see the uninterrupted growth and elaboration of cryptocurrency in the future.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
"While accepting that latecomer countries do not have to spend as much time as the pioneer countries had done in developing new institutions, we should not forget that it took the [Developed Countries] typically decades, and sometimes even generations, to establish certain institutions whose need had already been perceived. It usually took them another few decades to make them work properly by improving administration, closing various loopholes and strengthening enforcement. ...Given this, it may be unreasonable to ask them to raise the quality of their institutions dramatically in a short time span."
- Kicking Away the Ladder (2002), p. 139, by Ha-Joon Chang
#economics#least developed countries#economic development#developing countries#global wealth inequality#bretton woods instituions#washington consensus#kicking away the ladder#ha-joon chang#like... is this not obvious to people at WB or IMF...?
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Autocracy on the advance
What have Russia, China, India, Pakistan and Venezuela in common? They all repress democratic expression by their populations, be it in general or as part of recent or upcoming elections. In Russia Vladimir Putin’s reelection at 87% of the population’s vote following the death of Alexei Navalny in an arctic penal colony in February is more than circumspect. Even more so in light of the passive…
View On WordPress
0 notes
Text
How international law significantly changed its scope and depth over the past decades.

This chapter introduces the role of international law in development. It explains that international law and the rule of law are the foundations of the international system, where the rules are essential preconditions for lasting peace, security, economic development, and social progress. The sustainable development goals (SDGs) and social and environmental frameworks of key institutions determine the degree of influence international law has within development. The chapter considers how international law significantly changed its scope and depth over the past decades. It clarifies that SDGs are not legally binding, but they are soft laws intended to change behaviours through implementation in policies and activities and increase international trade.
Read the publication on The Role of International Law in Development: An Introduction
#rule of law#development policy#sustainable development#applicable law#treaty provisions#international law#Public International Law#foundations of the international system#lasting peace#internationasecurity#economic development#social progress.#international trade
0 notes
Text
Tax Benefits and Incentives: Why Foreign Investors Choose India

Tax benefits and incentives play a pivotal role in attracting foreign investors to India. The country offers various tax advantages and schemes designed to encourage foreign investment. Understanding these benefits is crucial for investors seeking to maximize returns and minimize tax liabilities. Tax benefits for investing in India are-
Tax Holidays and Concessions:
India provides tax holidays and concessions in specific sectors to promote investment. For instance, Special Economic Zones (SEZs) offer tax exemptions on income generated from business operations within these designated zones for a specified period. Similarly, certain industries, such as infrastructure, renewable energy, and startups, enjoy tax holidays aimed at fostering growth and development.
Tax holidays and concessions are incentives provided by governments to specific businesses, industries, or geographical areas, exempting them from certain taxes or offering reduced tax rates for a specified period. In the context of India, these measures are crucial in attracting investments, stimulating economic growth, and fostering development in targeted sectors or regions.
Features of Tax Holidays and Concessions:
1. Duration and Period: Tax holidays typically have a predefined duration during which businesses or entities enjoy exemptions or reduced tax rates. This period can range from a few years to more extended periods, encouraging businesses to make long-term investments.
2. Sector-Specific Benefits: These benefits are often sector-specific, targeting industries crucial for economic development. Sectors such as manufacturing, exports, technology, infrastructure, and startups commonly receive tax holidays to promote growth and innovation.
3. Geographical Focus: Tax holidays may also be geographically focused, aiming to promote development in specific regions or areas. Special Economic Zones (SEZs) and backward areas might be designated for tax concessions, encouraging investments and job creation in those regions.
4. Eligibility Criteria: Businesses or entities eligible for tax holidays usually need to fulfill specific criteria or comply with certain conditions set by the government. These criteria may include minimum investment thresholds, job creation targets, or adherence to prescribed regulations.5. Types of Taxes Covered: Tax holidays and concessions can apply to various taxes such as corporate income tax, property tax, sales tax, or customs duties. The exemptions or reduced rates aim to alleviate the tax burden on businesses, fostering an environment conducive to investments and growth.
Importance and Benefits:
1. Encouragement for Investments: Tax holidays and concessions serve as powerful tools to attract investments. By offering reduced tax liabilities or exemptions, governments encourage businesses to invest in specific sectors or regions, boosting economic activities.
2. Promotion of Priority Sectors: These incentives target priority sectors critical for economic development. Industries such as manufacturing, infrastructure, renewable energy, and technology receive support through tax benefits, fostering their growth and competitiveness.
3. Stimulation of Employment: Tax holidays often come with requirements for job creation. By incentivizing businesses to expand or establish operations, these measures contribute to employment generation, alleviating unemployment concerns in targeted areas.
4. Boost to Export-Oriented Activities: Tax concessions in export-oriented industries or SEZs stimulate exports, as businesses enjoy tax advantages while producing goods for international markets, promoting trade and enhancing foreign exchange earnings.
5. Regional Development: Geographically focused tax holidays aim to reduce regional disparities by promoting investments in underdeveloped or backward areas. This leads to infrastructure development and overall socio-economic upliftment in those regions.
6. Attraction for Foreign Investors: Tax holidays and concessions enhance the attractiveness of a country or region for foreign investors. These incentives, along with a conducive business environment, act as catalysts for foreign direct investment (FDI), attracting capital inflows into the country.
Lower Corporate Tax Rates:
To enhance competitiveness and attract foreign capital, India has reduced corporate tax rates. The government introduced a significant cut in corporate tax rates for domestic companies and new manufacturing units, providing a reduced rate of taxation, making India more attractive for investments in manufacturing and other sectors.
Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAA):
DTAA is a crucial feature for foreign investors as it prevents the same income from being taxed twice in both the investor's home country and India. India has signed DTAA agreements with various countries, allowing foreign investors to claim tax credits or exemptions in their home countries for taxes paid in India.
Capital Gains Tax Exemption:
In an effort to promote long-term investments, India offers capital gains tax exemptions under specific conditions. For instance, investments made in listed equity shares and specified funds through recognized stock exchanges may be exempt from long-term capital gains tax if held for a stipulated period.
Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT) Reforms:
Previously, India levied DDT on companies distributing dividends to shareholders, resulting in double taxation. To align with international practices and boost investor sentiment, India abolished DDT, thereby enabling shareholders to receive dividends tax-free, leading to increased post-tax returns for investors.
Tax Incentives for Research & Development (R&D):
The government offers tax incentives to encourage R&D activities. Companies investing in research and development initiatives receive deductions or tax credits on eligible expenses, fostering innovation and technological advancements.
Goods and Services Tax (GST) Reform:
India implemented the Goods and Services Tax, unifying various indirect taxes and simplifying the tax structure. GST streamlines the tax regime, reduces logistical complexities, and enhances ease of doing business for both domestic and foreign investors.
One-Time Settlement Schemes:
To alleviate tax-related disputes and provide relief to taxpayers, the government introduces one-time settlement schemes. These schemes allow taxpayers to settle pending tax disputes by paying a defined amount, often with reduced penalties or interest, promoting certainty and stability for investors.
Investment Linked Deductions:
Specific sectors like infrastructure, affordable housing, and certain manufacturing activities enjoy investment-linked deductions under the Income Tax Act. Investments in these sectors qualify for deductions, stimulating investments and growth in critical areas.
Incentives refer to various inducements, rewards, or advantages offered to individuals, organizations, or entities to encourage specific actions, behaviors, or investments. These incentives are designed to stimulate desired activities, foster growth, and attract participation in particular sectors or initiatives. Understanding their features and importance is crucial in comprehending their role in influencing decisions and outcomes across various domains.
Features of Incentives:
1. Purposeful Design: Incentives are deliberately crafted to influence behavior or actions toward a predefined goal. They are tailored to address specific objectives, whether it's stimulating economic growth, encouraging investments, fostering innovation, or promoting certain industries.
2. Variety and Customization: Incentives come in various forms, such as tax breaks, subsidies, grants, rebates, preferential treatment, or non-monetary rewards. They can be customized based on the target audience, sector, or desired outcomes.
3. Targeted Application: Incentives are often sector-specific or directed towards particular demographics, industries, geographical regions, or developmental areas. This targeted approach ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, maximizing the impact of the incentive programs.
4. Time-Bound Nature: Many incentives have predefined timeframes or expiration dates. They might be offered for a limited period to create a sense of urgency or to prompt immediate action from individuals or businesses.
5. Measurement and Evaluation: Effective incentive programs include mechanisms for measuring their impact and evaluating their success. This assessment aids in determining the effectiveness of the incentives and whether they achieve the intended objectives.
Importance of Incentives:
1. Stimulating Economic Growth: Incentives play a vital role in spurring economic activities, attracting investments, and driving growth in specific sectors. They encourage businesses to expand, innovate, and invest in new technologies or markets, contributing to overall economic development.
2. Attracting Investments: Incentives are instrumental in attracting foreign direct investment (FDI) or domestic investments by offering favorable conditions, tax breaks, or other benefits. These incentives create a competitive edge, making a country or region more appealing for investors.
3. Encouraging Innovation and Research: Incentives promoting research and development (R&D) activities foster innovation and technological advancements. They encourage companies to invest in R&D initiatives, leading to the creation of new products, services, and processes.
4. Supporting Key Industries: Incentives are deployed to support vital industries, especially those crucial for a country's development. They provide financial aid, tax advantages, or policy support to sectors like healthcare, infrastructure, renewable energy, and manufacturing, contributing to their growth and sustainability.
5. Promoting Regional Development: Incentives directed at specific regions or underdeveloped areas aim to reduce regional disparities and promote balanced regional development. They attract investments to areas that require economic stimulation, creating job opportunities and improving infrastructure.
6. Enhancing Competitiveness: Incentives improve the competitiveness of businesses by reducing costs, providing access to resources, or incentivizing adoption of best practices. This fosters a conducive environment for growth and sustainability.
7. Driving Behavioral Changes: Incentives can influence behaviors by encouraging certain actions or discouraging others. For instance, incentives for adopting sustainable practices or energy-efficient technologies promote environmentally conscious behaviors.
In essence, incentives serve as catalysts for desired behaviors, investments, and development. Their strategic design and implementation contribute significantly to economic progress, innovation, and societal well-being by aligning individual and organizational actions with broader developmental goals.
This post was originally published on: Foxnangel
#investing in india#renewable energy#tax holidays#foreign investors#double taxation avoidance agreements#dtaa agreement#goods and services tax#economic development#foreign direct investment#fdi direct investment#foxnangel
1 note
·
View note
Note
Many of your economic development plans call for the LPs to climb the "value-added chain". In a late medieval context, what value-added product would give you the most bang for your buck when it comes to timber?
Timber is a bit trickier than the classic case of textiles (where there are more links in the value-added chain from raw wool to carded wool to spun thread to plain woven cloth to dyed cloth to higher-end fabrics).
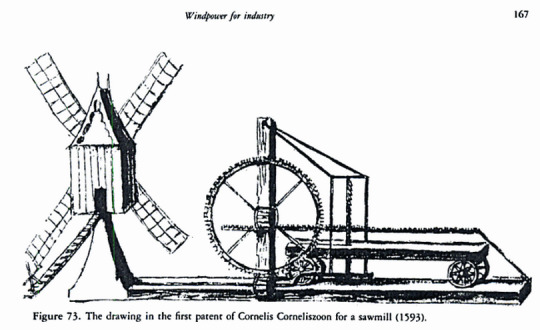
The first place to start is to shift from timber (i.e, the harvesting of raw, unprocessed logs from trees) to lumber (treating and seasoning, and sawing the logs into standardized boards, planks, beams, posts, and the like that can be used by carpenters to make furniture, housing, etc.). This requires the construction of sawmills (usually water- or wind-powered), usually downstream from the timberland so that logs can be easily floated down to the sawmill rather than going to the effort and expense of carting them overland.
The next step is to encourage the development of associated industries like furniture-making, construction...and most prized of all, ship-building. These industries continue to climb the value-added chain, because there's more money to be made from selling artisan furniture than selling raw logs and more money to be made in real estate than selling planks retail, and thus they allow you to maximize your profits from your natural resources. More importantly, if you can get into ship-building, you not only make money from selling and repairing the ships, but it's a pretty easy step from there to branch out into commerce on your own account (since you are already producing the main capital investment that seaborn commerce requires).
This is why various forms of Navigation Acts were often a key strategy of mercantilist policy during the Commercial Revolution, because if you could make sure that foreign trade was carried out by your nation's ships crewed by your sailors and your pilots and financed by your merchants, that the profits from trade would be more likely to be re-invested at home rather than exported to someone else's country.
#asoiaf#asoiaf meta#economic development#early modern economic development#mercantilism#early modern state-building#commercial revolution
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
Business, government and education leaders share vision for the future during Northeastern’s Global Leadership Summit in Singapore
Northeastern President Joseph Aoun welcomed U.S. Ambassador to Singapore Jonathan Kaplan, Indonesia’s Tourism Minister Sandiaga Uno and others to discuss topics ranging from entrepreneurship to the Asian music industry.
Share this story
Copy Link
Link Copied!
Email
Facebook
LinkedIn
Twitter
WhatsApp
Reddit
Hundreds of people participated in Northeastern University’s Global Leadership…

View On WordPress
#ai#alumni#artificial intelligence#cultural awareness#economic development#entrepreneur#Entrepreneurism#global#graduates#leadership#mentoring#singapore#Women who empower
0 notes
Link
Hillary Clinton's bad hair day
#Larouche#Oasis Plan#economic development#physical economy#Gaza#Israel#ceasefire#genocide#ethnic cleansing#ICJ ruling#Palestine#reason#morality
2 notes
·
View notes
Text

Representation in commercial real estate is not just about filling spaces; it is about reflecting the diversity of the communities we serve. Prioritizing representation can lead to better investments and vibrant spaces. It reflects a good business sense, as different perspectives often lead to better decision-making and more successful outcomes. From tenants to investors, everyone benefits from a well-thought-out approach to commercial real estate. #RepresentationMatters #SmartSpaces
Nicole Jones Commercial Real Estate
Dr. Nicole Jones
(256) 886-7700
#alabama#nicole jones alabama#nicole jones#nicole jones wadsworth#Commercial real estate#dr nicole jones wadsworth#Rep tim wadsworth#AL#representation#economic development
0 notes