#Edward Carpenter
Text
Queer history fact: feminist, socialist, and vegetarian Edward Carpenter bought and built a house on 7 acres of land in Millthorpe in 1881. The Millthorpe house was a place for Edward’s revolutionary ideas to develop and test themselves out in the real world. The place became a center for socialist thought, nudity, sandal-wearing, and homosexuality.
#queer history#queer#lgbt#lgbt history#gay history#lesbian history#making queer history#edward carpenter
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Sweet Moments Between Maurice and Alec That You Have Not Seen Before (From E.M. Forster's 1st Draft for Maurice)
Context: Forster's first version of Maurice, finished in 1914, has a rather different ending than the final published version (no hotel scene, and no boathouse reunion). See here.
Forster's first draft for Maurice is, in my opinion, the rawest in terms of boldly displaying the love shared between Maurice and Alec. This version shows much more of Alec's emotion and tenderness, as well as of Maurice's sentiments and affection towards Alec. It is definitely not as subtle as the final version, with quite a few straightforward declarations of love.
Hence, I'm disappointed that Forster did not manage to integrate at least some of these 1914 texts into the final version: it would've made the love between Maurice and Alec much more pronounced and convincing, as well as made Alec a character with more depth and feelings.
Having read Forster's first draft for Maurice, I share below some of these moments between Maurice and Alec that are not in the final version (ordered on how lovely I think each moment is. Bolded texts are the highlights).
1. After running into Mr. Ducie in the museum and Maurice bursting out to Alec.
M: "I'd possibly have blown out my own brains."
A: "Why?" he asked, stopping dead.
M: "I should have known by that time that I loved you."
A: "You can't, sir, you couldn't."
M: "I love you, sir be damned."
A: "Maurice"—never before had the word been spoken—"you're an angel."
M: "I don't want to hear that."
A: "Maurice, Maurice" his voice failed also; he had once said the rest to a woman. "Maurice - what you've said I feel. Understand?"
M: "I think so, but I want to be sure. Remember those rose bushes in the other rain? - Look at me hard - That's right. That'll do. It's settled." (Maurice is referring to the moment when Alec ran in the rain across the rose bushes at Penge just to see Maurice's face.)
2. The conversation after Maurice refuses to stay the night with Alec—a scenario that only happens in the first draft in 1914. Be prepared for tears.
A: "Come just for a little to me."
M: "If I came it would be for ever."
A: "Ever's the best."
M: "Why, man, you sail Thursday."
Alec found no answer.
...: here's when Maurice explains in a long paragraph why they can't be together because of their class difference and the fact that they're both men. But in this long paragraph Maurice pretty much brings up wanting to marry Alec—"We can't have the particular thing we want (which is roughly speaking marriage) unless we sacrifice something else"
M: I thought from that letter of yours you might want me to come. But, Alec, come where to?"
A: "I'd know if you weren't a gentleman," Alec said. "We'd a' found work together as mates."
M: "Yes, and if you were a gentleman, I'd take you this minute to my home.
A: "I'd a' been what young Clive was to you, then."
M: "He's a saint and we aren't. Leave out him."
A: "I'd a' been yours till death, then." ("I would've been yours till death, then")
M: "Out there if you get a chance to marry, take it. That's what I wish.
A: "Maurice, what'll you do without me, dear? Have you no other friends?"
Maurice dared not look forward to his own future. He rushed on the parting.
M: "And if there's ever a child, I shan't ever have that, so remember me."
A: "I'll remember you, child or none. God bless you. O God bless you, and be with you if I can't."
3. Right after Maurice puts his hand on Alec's back in the museum
"Yes, awfully serious," remarked Maurice, and rested his hand on Alec's shoulder, so that the fingers touched the back of the neck, doing this merely because he knew that he loved Alec, that he loved him not as a second Dickie Barry, but deeply, tenderly, for his own sake, beneath weakness and vulgarity.
4. In the museum, Alec in pain and acting cute
[Alec] had bitten his lip, his eyes were red too; face and body were cramped with pain.
M: "Alec -"
A: "Alec am I?"
M: "I'm sorry I used that other name of yours."
A: "Don't speak to me," he growled, "let me go, you calling me Alec when I"
M: "Did you give me away then on purpose?"
A: "You're correct.
M: "Was it to get money - or only to do me harm?"
A: "I couldn't say."
M: "Come, let's get away where we can finish our talk."
A: "What? What do you say?"
M: "Come along, Alec."
A: "Do you call me that still?"
M: "Come away, man, don't break down for God's sake...." He took hold of [Alec's] arm. The touch was not reminiscent; it hinted at a relation to come.
A: "Oh but you must, I want it." Alec yielded.
5. Maurice at night thinking about Alec's letter
He tried to forget the treacherous letter, but it stole back to his mind, and he suffered most during moments in bed, when it masqueraded as a real love letter, and offered him the completeness that Clive enjoyed with Anne.
(This is brilliant writing because we, as readers, know that Alec's letter is a love letter, yet Maurice's "muddles" prevent him from seeing it as a love letter, and it is only at night, when he's craving Alec's presence, that he's able to allow himself to see the truth and succumb to his feelings for Alec.
Here, again, is also a suggestion of Maurice wanting to marry Alec, like how Clive married Anne)
6. One version of Maurice's and Alec's first night together
A: "Good evening - sir, said the low voice. Was you wanting something? Couldn't you sleep?" It was the gamekeeper.
On your rounds? gasped Maurice, trying to sound natural, and felt corduroys. Their touch disconcerted him. Whither was he tending from Clive into what companionship?
A: "Just wait till I've set down my gun - eh aren't you trembling?"
M: "So are you - ah don't."
A: "Don't you like that?"
M: "I don't know."
A: "Christ you're fussy. Don't you like me to touch you."
M: "That's you lad."
A: "Yes."
Side notes: hopefully these will shut all the detractors (of the relationship between Maurice and Alec) up—namely Clive apologists, Clive+Maurice shippers, and all of those dark academia classist out there.
#em forster#maurice#maurice 1987#maurice em forster#maurice hall#alec scudder#em forster maurice#clive durham#edward carpenter#george merrill#dark academia#dark academism#dark acadamia aesthetic#dark acadamia quotes#gay novels#gay love#gay history#homosexuality#homosexual#m#mlm#gay literature#e.m. forster#edwardian era#happy ending#gay boots#gays#lgbt fiction#lgbt#lgbtq
419 notes
·
View notes
Text
British gay/bi male writers and their social circles
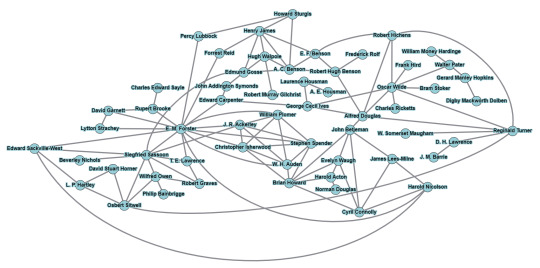
As a great admirer of gay literature, the social circles of gay and bisexual male writers is something that piques my interest. Due to the dangerousness of the matter in the past and also because it revolves around a relatively small niche, it seems that there was high level familiarity between these figures. The United Kingdom, a country whose literary input has abundant homoerotic tones, is a very adequate setting to analyze such a configuration.
I've been building a graph on this subject for some time, and now it seems mature enough for me to post it. It's a diagram based on friendship connections — deep or superficial —, although romantic and family-related connections are also included. Just a mutual recognition of existence isn't enough to justify a connection (otherwise most of them would be linked to Wilde!), and rivalries were not considered too. All the writers included were born during the Victorian and Edwardian eras (1837-1910), where this interconnectivity seemed particularly strong.
This is just an early version, as I imagine there is still a considerable amount of information that I missed. Therefore, I'm very open to suggestions and comments on it!
(Three Irishmen were also included in the diagram: Stoker, Wilde and Reid)
#literature#gay literature#lgbt literature#lgbtq literature#gay history#lgbt history#british literature#english literature#booklr#victorian#edwardian#henry james#edward carpenter#bram stoker#oscar wilde#a. e. housman#j. m. barrie#e. f. benson#george cecil ives#alfred douglas#somerset maugham#e. m. forster#d. h. lawrence#siegfried sassoon#rupert brooke#wilfred owen#robert graves#evelyn waugh#christopher isherwood#w. h. auden
76 notes
·
View notes
Text


Interview with the Vampire S01E06 (Like Angels Put in Hell by God)
Book title: Marriage in a Free Society (1894) by Edward Carpenter
#louis de pointe du lac#interview with the vampire#interview with the vampire season 1#like angels put in hell by god#edward carpenter#english literature#marriage in a free society#books in tv shows#jacob anderson
106 notes
·
View notes
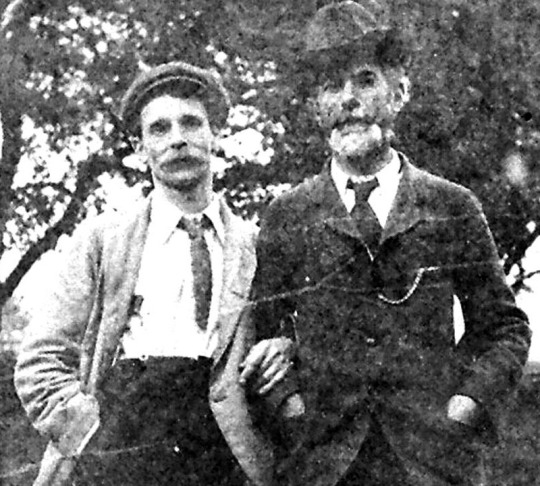
Text

Edward Carpenter (center)
George Merrill (right) his life-partner
George Hukin (left) his occasional partner
#we were always there#gay couple#vintage photo#affectionate men#Edward carpenter#George Miller#gay icons
40 notes
·
View notes
Text

Thanks to @rstabbert for his post about Countee Cullen. Cullen was a poet who was a part of the African American cultural revival of the 1920s and 1930s called the Harlem Renaissance.
Cullen attended New York University and won an award for his book of poems "The Ballad of the Brown Girl". When he graduated from NYU in 1925, he was one of eleven students selected to Phi Beta Kappa.
He continued on to Harvard towards a Masters Degree and published “Color”, his book of poetry that “celebrated black beauty and deplored the effects of racism.”
Although Cullen was married twice, like other men of his era, he had to hide his true feelings about men. His friend Alain Locke introduced Cullen to the works of British poet Edward Carpenter who was an early advocate for Gay Rights. (Carpenter had maintain a same sex relationship for nearly 40 years.)
Cullen wrote about the impact Carpenter’s work had on him:
“It opened up for me soul windows which had been closed; it threw a noble and evident light on what I had begun to believe, because of what the world believes, ignoble and unnatural"
Of course some historians deny Cullen was homosexual, as is usually the case of straight society trying to deny Gay men exist.
For more about Cullen, read Rstabbert’s post.
To read about Edward Carpenter, check my post about him here:
#gay icons#gay rights#gay man#Countee Cullen#African American poet#harlem renaissance#Edward Carpenter#Harvard#black beauty#the effects of racism
31 notes
·
View notes
Text

downton abbey (2010-2015) // excerpt from 'o child of uranus' by edward carpenter (1883)
screencap credit to @juwonah
#shoutout to michael bedwell's lgbtq nation article for drawing this comparison first#downton abbey#downton abbey film#downton abbey movie#thomas barrow#edward carpenter#poetry
63 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kissing, embraces and touching were rarely described, and may have been rare in life, as in letters. Frances Wilder, a young woman, wrote a searingly honest letter to Edward Carpenter for his advice on her sexual desire for women, describing a relationship for another woman that 'never went further than a handshake': 'I was 28 when I again fell in love with a girl about my own age. I made it my business to cultivate her, but soon found that tho' she was quite friendly and admirable, she cared less for me than I did for her. Often when alone with her, I had a strong desire to caress & fondle her; but I am naturally reserved & restrained and we never advanced further than the formal handshake. I had no sexual desire in connexion with her & I couldn't quite understand my feelings towards her . . . but my attachment for this girl was quite emotional. I loved to be with her, to hear her talk, even though I seldom agreed with her.'
"Normal Women: 900 Years of Making History" - Philippa Gregory
#book quote#normal women#philippa gregory#nonfiction#kiss#embrace#touch#rare#letters#frances wilder#edward carpenter#wlw#lesbian#handshake#infatuation#love#cultivation#caress#fondle#reserved#restrained#desire
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Forster's jungle
And yet the wonder of the novel was that it had been written when it had been written; the wonder was Forster himself, imprisoned within the jungle of pre-war prejudice, putting these unthinkable thoughts into words. Perhaps listening from time to time, to give himself courage, to the faraway chop-chop of those pioneer heroes, Edward Carpenter and George Merrill, boldly enlarging their clearing in the jungle.
Christopher Isherwood, Christopher and his Kind.
#christopher and heinz#em forster#christopher isherwood#edward carpenter#george merrill#lgbt history#queer history#queer books#queer love#queer representation
40 notes
·
View notes
Text

Edward Carpenter, son compagnon George Merrill en tailleur à ses pieds et deux amis (c. 1900)
J’avance avec plaisir dans « La vie nouvelle » de Tom Crewe. J’y ai retrouvé Edward Carpenter et son compagnon Georges Merrill, croisé dans « L’été arctique » écrit par Damon Galgut, une biographie romancée d'E. M. Forster.
Pour écrire son roman, Tom Crewe a largement et librement puisé dans ce que l’on sait de la vie des deux personnages principaux, John Addington et Havelock Hellis qui ont écrit ensemble, sans jamais se rencontrer, « l’inversion sexuelle », publié en Allemagne en 1896, 4 ans après la mort de John Addington.

John Addington Symonds, à droite, et Havelock Ellis
En toile de fond de leur rencontre et du roman, les deux procès d’Oscar Wilde, dont le dernier en 1895 le condamnera à deux ans de travaux forcés pour « grossières indécences ».
#edward carpenter#George Merrill#culture gay#grande-bretagne#tom crewe#livres#oscar wilde#procès#reading#damon galgut#em forster
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Thing Which Lay Still Was Marriage


18 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Edward Carpenter
Support Making Queer History on Patreon
Send in a One-Time Donation
Email Making Queer History: [email protected]
Follow us on:
Pinterest, Twitter, Instagram, Facebook
178 notes
·
View notes
Text
Edward Carpenter's full response letter to E.M. Forster after reading Maurice in 1914.
(The images of the letter can be found here at King's College's archive. Below is my transcription followed by photocopies of the letter. )
PS: 1) "MS" is the abbreviation for "manuscript".
23 Aug. [1914?]
My dear & blessed E.M.,
(I wish you had a name. Why do you always hide behind initials? What do your friends call you? My name is Edward, or ‘chips’!)
I have read your ‘Maurice’ after all, and am very much pleased with it. I don’t always like your rather hesitating tantalizing impressionist style - though it has subtleties - but I think the story has many fine points. You succeed in joining the atmosphere with the various characters, and there are plenty of happenings which is a good thing. Maurice’s love affairs are all interesting, and I have a mind to read them again, if I can find time - so I won’t send the MS back for a day or two. I am so glad you end up on a major chord. I was so afraid you were going to let Scudder go at the last - but you saved him and saved the story, because the end though improbable is not impossible and is the one bit of real romance - which those who understand will love.
I wish I could write more, but I am devoured just now by innumerable things. I expect to be in and about London from the 1st to 8th Sep. - so give me a cue to see you.
Your Edward C.
Transcription of vertical writings on the second page of the letter:
I am sending my birthday reply to the papers on Sep. 1 with a lot about the war in it.


Only a small part of the letter has been transcribed then included in reviews, or different Maurice editions. Which is why I wanted to transcribe the whole response from the real-life Maurice to the author of fictional Maurice after he read Maurice. The entirety is far more interesting.
Below: Edward Carpenter in 1886 and 1897.
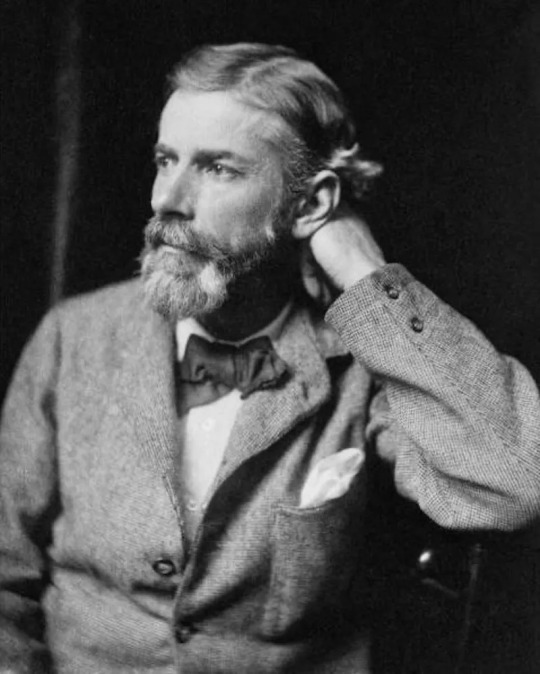


Some contexts: based on Forster's diaries, Maurice was first finished in June/July, 1914, so Carpenter did read the first complete MS—with or without the epilogue is unclear since there's no solid proof for when the epilogue was written (though it appeared in the novel by February 1915 at the latest.)
However, since Carpenter said he liked the happy ending he read (and fun fact: the first complete MS which he read actually had a fairly different ending between Maurice and Alec than the published version's), we know that even from the first draft, Forster remained unwavering about how a happy ending is imperative.

More contexts: according to a letter from Forster to a friend, he thought Carpenter was "too unliterary to be helpful"—meaning Carpenter probably wasn't much interested in reading literature. And Carpenter sort of confirmed that in writing "I read your 'Maurice' after all", implying he was indeed reluctant to read at first.
Still, it made absolute sense for Forster to send the story back to the man who, in a manner of speaking, held the copyright of Maurice in flesh before Forster even finished it.
So the question is: did Carpenter know that Maurice was inspired by him and his lover George Merrill? Did he know that he was the real-life Maurice and Merrill was the real-life Alec? Perhaps that was why he was reluctant to read the novel at first?
#edward carpenter#em forster maurice#maurice em forster#em forster#edward morgan forster#maurice#maurice 1987#maurice hall#maurice 1914#maurice 1971#alec scudder#george merrill#clive durham#1914#1910s
697 notes
·
View notes
Text




For anyone else curious as to what Louis is attempting to read while recovering in 106, while Narrator!Louis asks us if any crimes are truly unforgivable, I think this is the chapter he’s reading from the book ‘Love’s Coming of Age’ by Edward Carpenter. Interestingly, Carpenter is described as being “an English socialist poet, socialist philosopher, anthologist, and early gay activist.”
I’m not articulate enough to make any points here I just think the book choice is interesting. The rest of it is publicly available at https://wellcomecollection.org/works/vwq8vzye/items
#iwtv#iwtv meta#louis meta#for all my girlies who like to read stuff 'for context'#this show does nothing by mistake#edward carpenter
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
'The horse and the cow, the rabbit and the cat, the deer and the hare, the pheasant and the lark, please us better as friends than as meat. We wish to preserve them either as respected fellow-workers, or simply as companions in the joy of life and friendship.'
Men of such high standing in hygiene and biology having made a profound study of questions relating to normal food, I shall take good care not to display my incompetence by expressing an opinion as to animal and vegetable nourishment. Let the cobbler stick to his last. As I am neither chemist nor doctor, I shall not mention either azote or albumen, nor reproduce the formulas of analysts, but shall content myself simply with giving my own personal impressions, which, at all events, coincide with those of many vegetarians. I shall move within the circle of my own experiences, stopping here and there to set down some observation suggested by the petty incidents of life.
First of all I should say that the search for truth had nothing to do with the early impressions which made me a potential vegetarian while still a small boy wearing baby-frocks. I have a distinct remembrance of horror at the sight of blood. One of the family had sent me, plate in hand, to the village butcher, with the injunction to bring back some gory fragment or other. In all innocence I set out cheerfully to do as I was bid, and entered the yard where the slaughtermen were. I still remember this gloomy yard where terrifying men went to and fro with great knives, which they wiped on blood-besprinkled smocks. Hanging from a porch an enormous carcase seemed to me to occupy an extraordinary amount of space; from its white flesh a reddish liquid was trickling into the gutters. Trembling and silent I stood in this blood-stained yard incapable of going forward and too much terrified to run away. I do not know what happened to me; it has passed from my memory. I seem to have heard that I fainted, and that the kind-hearted butcher carried roe into his own house; I did not weigh more than one of those lambs he slaughtered every morning.
Other pictures cast their shadows over my childish years, and, like that glimpse of the slaughter-house, mark so many epochs in my life. I can see the sow belonging to some peasants, amateur butchers, and therefore all the more cruel. I remember one of them bleeding the animal slowly, so that the blood fell drop by drop; for, in order to make really good black puddings, it appears essential that the victim should have suffered proportionately. She cried without ceasing, now and then uttering groans and sounds of despair almost human; it seemed like listening to a child.
And in fact the domesticated pig is for a year or so a child of the house; pampered that he may grow fat, and returning a sincere affection for all the care lavished on him, which has but one aim — so many inches of bacon. But when the affection is reciprocated by the good woman who takes care of the pig, fondling him and speaking in terms of endearment to him, is she not considered ridiculous — as if it were absurd, even degrading, to love an animal that loves us?
One of the strongest impressions of my childhood is that of having witnessed one of those rural dramas, the forcible killing of a pig by a party of villagers in revolt against a dear old woman who would not consent to the murder of her fat friend. The village crowd burst into the pigstye and dragged the beast to the slaughter place where all the apparatus for the deed stood waiting, whilst the unhappy dame sank down upon a stool weeping quiet tears. I stood beside her and saw those tears without knowing whether I should sympathise with her grief, or think with the crowd that the killing of the pig was just, legitimate, decreed by common sense as well as by destiny.
Each of us, especially those who have lived in a provincial spot, far away from vulgar ordinary towns, where everything is methodically classed and disguised — each of us has seen something of these barbarous acts committed by flesh-eaters against the beasts they eat. There is no need to go into some Porcopolis of North America, or into a saladero of La Plata, to contemplate the horrors of the massacres which constitute the primary condition of our daily food. But these impressions wear off in time; they yield before the baneful influence of daily education, which tends to drive the individual towards mediocrity, and takes out of him anything that goes to the making of an original personality. Parents, teachers, official or friendly, doctors, not to speak of the powerful individual whom we call “everybody,” all work together to harden the character of the child with respect to this “four-footed food,” which, nevertheless, loves as we do, feels as we do, and, under our influence, progresses or retrogresses as we do.
It is just one of the sorriest results of our flesh-eating habits that the animals sacrificed to man’s appetite have been systematically and methodically made hideous, shapeless, and debased in intelligence and moral worth. The name even of the animal into which the boar has been transformed is used as the grossest of insults; the mass of flesh we see wallowing in noisome pools is so loathsome to look at that we agree to avoid all similarity of name between the beast and the dishes we make out of it. What a difference there is between the moufflon’s appearance and habits as he skips about upon the mountain rocks, and that of the sheep which has lost all individual initiative and becomes mere debased flesh — so timid that it dares not leave the flock, running headlong into the jaws of the dog that pursues it. A similar degradation has befallen the ox, whom now-a-days we see moving with difficulty in the pastures, transformed by stock-breeders into an enormous ambulating mass of geometrical forms, as if designed beforehand for the knife of the butcher. And it is to the production of such monstrosities we apply the term “breeding”! This is how man fulfils his mission as educator with respect to his brethren, the animals.
For the matter of that, do we not act in like manner towards all Nature? Turn loose a pack of engineers into a charming valley, in the midst of fields and trees, or on the banks of some beautiful river, and you will soon see what they would do. They would do everything in their power to put their own work in evidence, and to mask Nature under their heaps of broken stones and coal. All of them would be proud, at least, to see their locomotives streaking the sky with a network of dirty yellow or black smoke. Sometimes these engineers even take it upon themselves to improve Nature. Thus, when the Belgian artists protested recently to the Minister of Railroads against his desecration of the most beautiful parts of the Meuse by blowing up the picturesque rocks along its banks, the Minister hastened to assure them that henceforth they should have nothing to complain about, as he would pledge himself to build all the new workshops with Gothic turrets!
In a similar spirit the butchers display before the eyes of the public, even in the most frequented streets, disjointed carcasses, gory lumps of meat, and think to conciliate our æstheticism by boldly decorating the flesh they hang out with garlands of roses!
When reading the papers, one wonders if all the atrocities of the war in China are not a bad dream instead of a lamentable reality. How can it be that men having had the happiness of being caressed by their mother, and taught in school the words “justice” and “kindness,” how can it be that these wild beasts with human faces take pleasure in tying Chinese together by their garments and their pigtails before throwing them into a river? How is it that they kill off the wounded, and make the prisoners dig their own graves before shooting them? And who are these frightful assassins? They are men like ourselves, who study and read as we do, who have brothers, friends, a wife or a sweetheart; sooner or later we run the chance of meeting them, of taking them by the hand without seeing any traces of blood there.
But is there not some direct relation of cause and effect between the food of these executioners, who call themselves “agents of civilisation,” and their ferocious deeds? They, too, are in the habit of praising the bleeding flesh as a generator of health, strength, and intelligence. They, too, enter without repugnance the slaughter house, where the pavement is red and slippery, and where one breathes the sickly sweet odour of blood. Is there then so much difference between the dead body of a bullock and that of a man? The dissevered limbs, the entrails mingling one with the other, are very much alike : the slaughter of the first makes easy the murder of the second, especially when a leader’s order rings out, or from afar comes the word of the crowned master, “Be pitiless.”
A French proverb says that “every bad case can be defended.” This saying had a certain amount of truth in it so long as the soldiers of each nation committed their barbarities separately, for the atrocities attributed to them could afterwards be put down to jealousy and national hatred. But in China, now, the Russians, French, English, and Germans have not the modesty to attempt to screen each other. Eyewitnesses, and even the authors themselves, have sent us information in every language, some cynically, and others with reserve. The truth is no longer denied, but a new morality has been created to explain it. This morality says there are two laws for mankind, one applies to the yellow races and the other is the privilege of the white. To assassinate or torture the first named is, it seems, henceforth permissible, whilst it is wrong to do so to the second.
Is not our morality, as applied to animals, equally elastic? Harking on dogs to tear a fox to pieces teaches a gentleman how to make his men pursue the fugitive Chinese. The two kinds of hunt belong to one and the same “sport”; only, when the victim is a man, the excitement and pleasure are probably all the keener. Need we ask the opinion of him who recently invoked the name of Attila, quoting this monster as a model for his soldiers?
It is not a digression to mention the horrors of war in connection with the massacre of cattle and carnivorous banquets. The diet of individuals corresponds closely to their manners. Blood demands blood. On this point any one who searches among his recollections of the people whom he has known will find there can be no possible doubt as to the contrast which exists between vegetarians and coarse eaters of flesh, greedy drinkers of blood, in amenity of manner, gentleness of disposition and regularity of life.
It is true these are qualities not highly esteemed by those “superior persons,” who, without being in any way better than other mortals, are always more arrogant, and imagine they add to their own importance by depreciating the humble and exalting the strong. According to them, mildness signifies feebleness : the sick are only in the way, and it would be a charity to get rid of them. If they are not killed, they should at least be allowed to die. But it is just these delicate people who resist disease better than the robust. Full-blooded and high-coloured men are not always those who live longest : the really strong are not necessarily those who carry their strength on the surface, in a ruddy complexion, distended muscle, or a sleek and oily stoutness. Statistics could give us positive information on this point, and would have done so already, but for the numerous interested persons who devote so much time to grouping, in battle array, figures, whether true or false, to defend their respective theories.
But, however this may be, we say simply that, for the great majority of vegetarians, the question is not whether their biceps and triceps are more solid than those of the flesh-eaters, nor whether their organism is better able to resist the risks of life and the chances of death, which is even more important : for them the important point is the recognition of the bond of affection and goodwill that links man to the so-called lower animals, and the extension to these our brothers of the sentiment which has already put a stop to cannibalism among men. The reasons which might be pleaded by anthropophagists against the disuse of human flesh in their customary diet would be as well-founded as those urged by ordinary flesh-eaters today. The arguments that were opposed to that monstrous habit are precisely those we vegetarians employ now. The horse and the cow, the rabbit and the cat, the deer and the hare, the pheasant and the lark, please us better as friends than as meat. We wish to preserve them either as respected fellow-workers, or simply as companions in the joy of life and friendship.
“But,” you will say, “if you abstain from the flesh of animals, other flesh-eaters, men or beasts, will eat them instead of you, or else hunger and the elements will combine to destroy them.” Without doubt the balance of the species will be maintained, as formerly, in conformity with the chances of life and the inter-struggle of appetites; but at least in the conflict of the races the profession of destroyer shall not be ours. We will so deal with the part of the earth which belongs to us as to make it as pleasant as possible, not only for ourselves, but also for the beasts of our household. We shall take up seriously the educational rôle which has been claimed by man since prehistoric times. Our share of responsibility in the transformation of the existing order of things does not extend beyond ourselves and our immediate neighbourhood. If we do but little, this little will at least be our work.
One thing is certain, that if we held the chimerical idea of pushing the practice of our theory to its ultimate and logical consequences, without caring for considerations of another kind, we should fall into simple absurdity. In this respect the principle of vegetarianism does not differ from any other principle; it must be suited to the ordinary conditions of life. It is clear that we have no intention of subordinating all our practices and actions, of every hour and every minute, to a respect for the life of the infinitely little; we shall not let ourselves die of hunger and thirst, like some Buddhist, when the microscope has shown us a drop of water swarming with animalculæ. We shall not hesitate now and then to cut ourselves a stick in the forest, or to pick a flower in a garden; we shall even go so far as to take a lettuce, or cut cabbages and asparagus for our food, although we fully recognise the life in the plant as well as in animals. But it is not for us to found a new religion, and to hamper ourselves with a sectarian dogma; it is a question of making our existence as beautiful as possible, and in harmony, so far as in us lies, with the æsthetic conditions of our surroundings.
Just as our ancestors, becoming disgusted with eating their fellow-creatures, one fine day left off serving them up to their tables; just as now, among flesh-eaters, there are many who refuse to eat the flesh of man’s noble companion, the horse, or of our fireside pets, the dog and cat — so is it distasteful to us to drink the blood and chew the muscle of the ox, whose labour helps to grow our corn. We no longer want to hear the bleating of sheep, the bellowing of bullocks, the groans and piercing shrieks of the pigs, as they are led to the slaughter. We aspire to the time when we shall not have to walk swiftly to shorten that hideous minute of passing the haunts of butchery with their rivulets of blood and rows of sharp hooks, whereon carcasses are hung up by blood-stained men, armed with horrible knives. We want some day to live in a city where we shall no longer see butchers’ shops full of dead bodies side by side with drapers’ or jewellers’, and facing a druggist’s, or hard by a window filled with choice fruits, or with beautiful books, engravings or statuettes, and works of art. We want an environment pleasant to the eye and in harmony with beauty.
And since physiologists, or better still, since our own experience tells us that these ugly joints of meat are not a form of nutrition necessary for our existence, we put aside all these hideous foods which our ancestors found agreeable, and the majority of our contemporaries still enjoy. We hope before long that flesh-eaters will at least have the politeness to hide their food. Slaughter houses are relegated to distant suburbs; let the butchers’ shops be placed there too, where, like stables, they shall be concealed in obscure corners.
It is on account of the ugliness of it that we also abhor vivisection and all dangerous experiments, except when they are practised by the man of science on his own person. It is the ugliness of the deed which fills us with disgust when we see a naturalist pinning live butterflies into his box, or destroying an ant-hill in order to count the ants. We turn with dislike from the engineer who robs Nature of her beauty by imprisoning a cascade in conduit-pipes, and from the Californian woodsman who cuts down a tree, four thousand years old and three hundred feet high, to show its rings at fairs and exhibitions. Ugliness in persons, in deeds, in life, in surrounding Nature — this is our worst foe. Let us become beautiful ourselves, and let our life be beautiful!
What then are the foods which seem to correspond better with our ideal of beauty both in their nature and in their needful methods of preparation? They are precisely those which from all time have been appreciated by men of simple life; the foods which can do best without the lying artifices of the kitchen. They are eggs, grains, fruits; that is to say, the products of animal and vegetable life which represent in their organisms both the temporary arrest of vitality and the concentration of the elements necessary to the formation of new lives. The egg of the animal, the seed of the plant, the fruits of the tree, are the end of an organism which is no more, and the beginning of an organism which does not yet exist. Man gets them for his food without killing the being that provides them, since they are formed at the point of contact between two generations. Do not our men of science who study organic chemistry tell us, too, that the egg of the animal or plant is the best storehouse of every vital element? Omne vivum ex ovo.
Elisée Reclus / On Vegetarianism *1901
(translation Edward Carpenter)
2 notes
·
View notes





