#Clinical study Protocol San Diego
Text
The Impact Of Modeling & Simulation M&S On Pharmacometrics In North Carolina

Modeling and simulation M&S in North Carolina- Durham to Raleigh, Research Triangle Park! Pharmacometrics plays a key role in drug development. And the involvement of Modeling and simulation methods has taken this field to a whole new level. It helps to design drugs, improve dosing regimens and deliver safer treatments to patients.
Drug development is a time-consuming job and expensive. Traditional methods come with limitations. It makes trials inflexible and offers limited space for adjustments based on emerging data. This is where Modeling and simulation come in.
Modeling and simulation allow you to create virtual representations of the human body and drug behavior. You can make mathematical models by using biological data, drug properties and physiological processes that show how a medicine cooperates within the body.
The Impact Of Modeling And Simulation On Pharmacometrics-
Optimized Clinical Trial Design-
Modeling and simulation allow you to design a clinical trial with better accuracy. You can know the suitable dosage range, the required number of participants and potential roadblocks. You can easily identify the most efficient approach to get the best results. it ensures smaller and faster trials as well as lessens costs.
Personalized Medicine-
Modeling and simulation enable you to know the variability of patients. It helps to make personalized models to know the action of the drug according to the patient’s age, weight, and medical history. It improves efficiency while reducing side effects.
De-risking Drug Development-
Modeling and simulation can remove the red flags. It meets the standard of safety concerns and improves efficiency. It encourages potential drug interactions and shows adverse effects virtually.
Accelerating Drug Discovery-
Developing new drugs is time-consuming for any risky illnesses. This is where Modeling and simulation accelerate the drug development process. By virtually testing different drug properties, you can ensure the faster delivery of life-saving treatments for patients.
Service offered at AzureDelta Consulting Inc.-
Modeling & Simulation and Pharmacometrics
Population PK, statistics, kinetics and pharmacokinetics data analysis and non-linear mixed effects modeling with Phoenix WinNonLin/NLME, conversion of published NONMEM models and coding, Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic and exposure-response correlation analysis; developing modeling and simulation strategy for clinical programs; use of simulation methods to support dose and dosing regimen selection, trial design and Go/No-Go decisions, dosing in pediatric studies; simulation of multiple options for the selection of best approach in drug development.
We add value to Modeling and simulation M&S in North Carolina- Durham to Raleigh, Research Triangle Park. Visit https://azuredeltaconsulting.com/ for more information.
Resource: https://azuredeltaconsulting.wordpress.com/2024/04/09/the-impact-of-modeling-simulation-ms-on-pharmacometrics-in-north-carolina/
#clinical pharmacology boston-cambridge#pharmacometrics new jersey - princeton#regulatory strategy boston-cambridge#fda new york - new york city#clinical study report san diego#modeling and simulation m&s north carolina#clinical study protocol san diego
0 notes
Text
Empowering Lives - Unveiling Innovations in Diabetes Care through Pioneering Research
Among the dedicated professionals at this research clinic, one stands out - Dr. Hanid Audish. His unwavering commitment to improving diabetes care is a shining example of the clinic's overarching mission. Not only does he play an integral role in conducting and overseeing hundreds of research studies, but his keen insights and innovative thinking have led to groundbreaking advancements in the field. The magnitude of his contribution reflects in the lives of the 8,000 participants who have taken part in these clinical research studies. His work and the collective effort of the clinic continue to carve a path towards a better future for diabetes patients, solidifying the clinic's position as a beacon of hope and progress in San Diego and beyond.
At the core of Encompass’s mission is a commitment to advancing diabetes care beyond conventional boundaries. Driven by a passion for transformative research, the clinic has conducted over 500 studies that delve into various facets of diabetes, including Type 2 diabetes management and groundbreaking investigational medications. This relentless pursuit of knowledge reflects the clinic's dedication to enhancing the quality of life for those grappling with diabetes.
Behind the scenes, there exists a visionary responsible for spearheading the clinic's progress in diabetes research — Dr. Hanid Audish. This esteemed physician, with his unwavering dedication and commitment, has become a critical pillar for Encompass and its innovative approach towards healthcare. Specializing in diabetes care, he skillfully merges his extensive experience with a progressive approach to medical research. His pioneering work is creating a powerful momentum in the ongoing battle against diabetes, propelling Encompass into new frontiers of medical science. His invaluable contributions have not only advanced our understanding of diabetes, but also inspired hope for those affected by this chronic condition.
A noteworthy accomplishment of the clinic is the transformation of Type 2 diabetes management protocols. Thanks to the persistent research and innovative medical interventions led by Dr. Hanid Audish, they have been able to devise personalized treatment plans. These unique strategies are designed to cater to each patient's specific needs and circumstances, ensuring that we address not just the observable symptoms, but also the underlying aspects contributing to the progression of their diabetes. By doing so, they have managed to bring about significant improvements in patient outcomes and the overall quality of their lives.
In the pursuit of groundbreaking solutions, the clinic has been at the forefront of testing investigational medications. Spearheaded by the doctor, these trials aim to push the boundaries of traditional treatments and pave the way for more effective, targeted therapies. The commitment to rigorous testing ensures that only the most promising medications advance, promising a brighter future for individuals living with diabetes.
Beyond the walls of the clinic, this doctor has been a driving force in community engagement and outreach. Recognizing the importance of education and awareness, the doctor actively participates in community events, workshops, and seminars. By fostering a deeper understanding of diabetes and its management, the clinic aims to empower individuals to take control of their health and well-being.
Central to the clinic's success is its commitment to a patient-centric approach. The doctor embodies this ethos, going beyond traditional medical interactions to build meaningful relationships with patients. By understanding the unique challenges each individual faces, the doctor tailor’s treatment plans that align with the patient's lifestyle, ensuring a holistic and sustainable approach to diabetes management.
Under the vigilant leadership of Dr. Hanid Audish, the clinic has steadfastly embraced the dawn of rapid technological advancement in the medical field, specifically enhancing their methods in diabetes monitoring. With the integration of state-of-the-art tools, such as continuous glucose monitoring systems and comprehensive telehealth solutions, the patients are afforded real-time insights into their diabetic condition. This harmonious blend of technology and healthcare not only facilitates proactive management of disease, but also encourages and empowers their patients to take a more active role in their personal healthcare journey. In this way, Dr. Audish's approach is ensuring their clinic is synonymous with patient-centric, technologically advanced, and effective diabetes care.
As the clinic celebrates its remarkable achievements in groundbreaking diabetes research, the journey does not come to a halt. With the visionary guidance of their esteemed doctor, the institution remains steadfastly committed to pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation. Prospects on the horizon include exploring promising emerging therapies, delving even deeper into the intricate genetic components of diabetes, and harnessing the power of cutting-edge artificial intelligence to develop highly personalized and tailored treatment plans that cater to the unique needs of each individual patient. The clinic's unwavering dedication to advancing the field of diabetes research ensures that the pursuit of a cure and improved quality of life for all individuals affected by this condition continues with unwavering determination and enthusiasm.
Dr. Hanid Audish's tireless efforts and groundbreaking research have not only transformed the lives of individuals battling diabetes, but they have also catalyzed significant advancements in the broader sphere of diabetes research. His vision and dedication led to the successful completion of over 500 studies that saw the participation of more than 8,000 committed individuals. The collaborations and discoveries made possible through these studies have benefited not only the clinic but the entire medical community, fortifying their collective fight against diabetes. As we navigate the future, the clinic, under the guidance of Dr. Audish, remains unwavering in its commitment to empowering lives through exceptional patient care and pushing the boundaries of what is possible in diabetes research and treatment.
0 notes
Text
Sewage-testing robots process wastewater faster to predict COVID-19 outbreaks sooner

- By Smruthi Karthikeyan , Rob Knight , UC San Diego , The Conversation -
The big idea: by using a sewage-handling robot, our laboratory has been able to detect coronavirus in wastewater 30 times faster than nonautomated large-scale systems. This advance, published in the microbiology journal mSystems, provides even more lead time to communities monitoring their wastewater for early warning about local cases of COVID-19.
When clinical studies emerged showing that people who test positive for SARS-CoV-2 shed the virus in their stool, the sewer seemed like an obvious place to look for it. Wastewater surveillance can be used at the community level to see potential outbreak clusters before clinical diagnosis, especially in areas where COVID-19 prevalence rates far exceed testing rates.
The problem is that the virus is heavily diluted in the waste stream because of how many people’s bathrooms drain into it, not to mention all the other junk they flush. Surveillance depends on concentrating the viral particles from the wastewater to detect these low levels. This viral concentration step is typically the major bottleneck in wastewater analyses because it’s laborious and time-consuming. Our robot system takes a different, quicker approach.
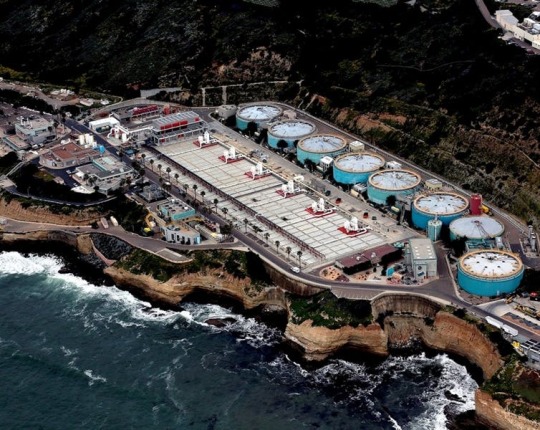

Wastewater treatment plants can be the front lines for coronavirus detection in a community. San Diego County, CC BY-ND
Why it matters
Cities, schools and businesses around the country are using wastewater surveillance to find coronavirus in their midst.
Wastewater surveillance is especially useful as an early-alert system for high-risk areas, such as communities where undocumented residents may be cautious about individual testing.
The most commonly used viral concentration technique uses filters and can take anywhere from six to eight hours to transform a couple dozen sewage specimens into samples that can then be tested for the presence of SARS-CoV-2. Our new protocol concentrates 24 samples in a single 40-minute run.
We repurposed gear that usually performs microbiology or cell biology tasks in the lab to deal with sewage instead. By miniaturizing and automating our system, we eliminate a bunch of labor-intensive steps, resources and associated costs. And our hands-free process is much quicker.

Researchers gather a liter of sewage collected over the course of the day from a sewer line connected to a UC San Diego building. C.H. Sheikhzadeh, CC BY-ND
How we do this work
We gather sewage from autosamplers at San Diego’s main wastewater treatment plant, as well as from those we’ve deployed at over 100 manholes on the campus of the University of California, San Diego, which collect sewer samples every 30 minutes through the day.
Then, back in the lab, instead of relying on multiple filter steps, we use tiny magnetic beads to enrich the viral particles. We purchase these nanomagnetic beads that are designed to bind to a variety of respiratory viruses. The sewage-handling robot is equipped with a specialized magnetic head that snags the magnetic beads, with viruses attached. It preferentially fishes out viral particles, leaving behind the rest of the junk in the sewage sample.
Using a robot to automate the sewage concentration process lets us concentrate 24 samples in 40 minutes for each robot. Then the same robot can extract the viral RNA, processing 96 samples in 36 minutes. Finally, we use a polymerase chain reaction to search for the signature genes of SARS-CoV-2, much like a clinical diagnostic test that a lab would run on a patient’s nasal swab.
Overall, our system can process 96 samples in 4.5 hours, dramatically reducing the time from specimen to result.
What’s next
So far, ours is the only coronavirus wastewater study we’re aware of that uses an automated process.
We’re using this technique as a part of our large-scale wastewater surveillance on campus and sampling over 100 locations daily. San Diego school districts are also using it as an early-alert system.
We’re now using the viral genome sequencing part of our system to track the emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants.

Smruthi Karthikeyan, Postdoctoral Research Associate in Pediatrics, University of California San Diego and Rob Knight, Professor of Pediatrics and Computer Science and Engineering, University of California San Diego
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
--
Read Also
Detecting and monitoring COVID-19 in wastewater
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Imitation May Be a Sincere Form of Treatment
NIH to launch study of experimental monoclonal antibody therapy for COVID-19. Below is a Q&A with the trial’s protocol chair: Davey Smith, MD, at UC San Diego School of Medicine
The ACTIV-2 study team is led by protocol chair Davey Smith, MD, a translational research virologist, head of Infectious Diseases and Global Public Health at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and co-director of the San Diego Center for AIDS Research.
Question: Why are monoclonal antibodies considered particularly promising as potential therapeutics for COVID-19? What sets them apart from other approaches?
Smith: This therapy is made from antibodies that developed when someone had the infection. The antibody was then purified and then expanded so it could be used as a therapy in other people who got the infection. This approach has worked for other viral infections, like Ebola and HIV, so we think it will work for SARS-CoV-2 too.
Question: How will the ACTIV-2 trial work?
Smith: The first stage will enroll 220 volunteers who have tested positive for the novel coronavirus and who have experienced symptoms of COVID-19, but are not hospitalized. These volunteers will come from around the world, from member sites of the AIDS Clinical Trials Group. (The Antiviral Research Center at UC San Diego is a member of ACTG.)
Volunteer-participants will be randomly assigned to receive either an intravenous infusion of LY-CoV555 or a placebo infusion of saline solution: 110 persons in each group. Over the next 28 days, all participants will be monitored by clinicians tracking their COVID-19 symptoms. There will be swabs to measure the presence of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA and blood tests to help researchers understand how the drug is functioning in their bodies.
The primary goal is to evaluate safety and to see if LY-CoV555 reduces the duration of symptoms and speeds clearance of the coronavirus from the body. If there are no serious side effects and the investigational drug appears promising, the study will move to a larger Phase III trial and enroll an additional 1,780 outpatient volunteers to determine if the drug can prevent either hospitalization or death from COVID-19. A Phase III would last 28 days as well.
Question: Will LY-CoV555 be the only drug tested?
Smith: No. The study is set up so that it can be adapted to investigate other experimental therapeutics using the same trial protocol.
‘Imitation May Be a Sincere Form of Treatment‘
#science#medicine#covid-19#covid 19#novel coronavirus#sars-cov-2#infectious disease#public health#pandemic#clinical trials#monoclonal antibodies#nih#academic medicine#ucsd#uc san diego
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Iris Publishers_ Annals of Urology & Nephrology (AUN)
Understanding the Time-Course of Nephrolithiasis Management
Authored by: Seth K Bechis
Abstract
Purpose: The growing incidence of acute nephrolithiasis has increased the burden on healthcare. We sought to assess the time-course of acute stone disease treatment from symptom onset to spontaneous passage or definitive treatment to better characterize the current state of management and identify areas for improvement. Methods: We performed a retrospective review of patients treated for acute nephrolithiasis from August 2016 until February 2017. Patients were included if they had symptomatic renal or ureteral stones, evaluation by urology, and documented resolution by spontaneous passage or surgery. Primary outcome was the time from initial presentation at the Emergency Department (ED) to procedure or passage. Secondary outcomes included time to outpatient evaluation by urology and delays to procedure scheduling greater than 14 days. Results: 61 patients (41% female) met selection criteria. Median time from initial presentation to procedure or stone passage was 45 or 26 days, respectively. Median time from ED to clinic visit was 12.5 days. Time from clinic visit to procedure or spontaneous passage was 29 or 16 days, respectively. 38 patients (62%) had documented causes for delay in treatment. Of this cohort, 22 (58%) were due to provider availability issues, 8 (21%) had contraindications to surgery, and 8 (21%) had patient-related delays.
Conclusion: Prolonged time to treatment of acute nephrolithiasis occurred in 30 (49%) of the cohort due to provider availability and patientspecific delays. Developing initiatives to expedite management through improved patient education and operating room availability may help reduce healthcare costs and patient discomfort.
Keywords: Kidney stones; Time-course; Urolithiasis; Ureteroscopy; SWL; PCNL
Abbreviations: ACU: acute care urology, AUA: American Urological Association, ED: Emergency Department, EHR: Electronic health record, IRB: Institutional Review Board, MET: Medical expulsive therapy, NHANES: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, UC: Urgent Care
Introduction
The incidence of kidney stones has been noted to be 8.4% in the United States as of 2010, a dramatic increase from 5.2% in 1994 based on analysis of NHANES data [1]. The rising incidence, morbidity and cost of kidney stone disease place a major burden on the U.S. healthcare system [2,3]. Reducing healthcare costs and ultimately improving quality of care first requires an evaluation of the current status of urolithiasis treatment as well as identification of obstacles to care. Current data show an average 3.4 urologists per 100,000 persons in the U.S., with a substantial shift toward metropolitan regions and an estimated 38 million Americans living in counties without a single urologist [4]. This lack of availability of timely urologic care leads to costly repeat emergency department visits [5,6]. Our study aimed to assess, at a single tertiary care center, the time-course of nephrolithiasis treatment, from onset of symptoms and initial presentation to resolution either by definitive treatment or spontaneous passage. We hypothesized that time to treatment or passage was greater than 30 days.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective review of patients treated for nephrolithiasis at a single, tertiary academic center from August 2016 to February 2017. Under an IRB-approved protocol (#170854), medical records were reviewed for patients at least 18 years of age seen at the UC San Diego Health Comprehensive Kidney Stone Center. Inclusion criteria were history of symptomatic renal or ureteral stones (i.e., causing colic), presentation at a San Diego Emergency Department (ED), Urgent Care (UC) or other clinic, subsequent evaluation at our urology clinic, and documented resolution of their stone(s) by either spontaneous passage or surgical procedure. Spontaneous passage was confirmed via a submitted sample of a passed stone or subsequent imaging results. The primary outcome of the study was the time from initial presentation at the ED, UC or clinic to surgical procedure or spontaneous passage. Secondary outcomes included time from first ED or UC presentation to evaluation by urology, time from initial presentation to spontaneous stone passage, and delays in procedure scheduling greater than 14 days following first urology clinic appointment (designated as “delay in treatment time”). Fourteen days was set by institution as a goal to achieve in order to optimize patient care. Patients with delays in treatment time were included in sub-group analyses only if reasons for delay were documented within the electronic health record. In order to capture the entire time-course of a stone episode, patients were excluded from the study if by the end of the review period they had not yet had surgery to remove their stone(s), had not yet passed their stone(s) spontaneously, or were unsure of stone passage. Descriptive statistical analyses were performed.
Results
During the study period, 61 patients met inclusion criteria (see Table 1).
Median time from initial presentation to surgery or spontaneous passage was 45 or 27 days, respectively. The median time between initial presentation and first Urology clinic visit was 12.5 days. In total, the median time from the first appointment with Urology until resolution via a procedure or spontaneous stone passage was 29 days or 16 days, respectively, with 28 days overall. Of the total cohort, 38 study subjects (62%) waited greater than 14 days between the first Urology appointment and surgery (Table 3).
Analyzing this subgroup, the majority (22 patients, 58%) of the delays were due to provider availability issues (including operating room, staff, and/or surgeon availability). Another 8 patients (21%) were delayed due to contraindications to surgery. These included a positive pre-operative urine culture (2 patients); urosepsis (2); recent abdominal aortic aneurysm surgery and on anticoagulation (1); admission for small bowel obstruction (1); epididymo-orchitis (1); and ureteral perforation during initial urgent ureteral stent placement (1). Definitive treatment for 8 patients was delayed due to patient-related issues including missed clinic or imaging appointments or lack of call back to schedule their surgery.
Discussion
Our study aimed to assess, at a single U.S. tertiary care center, the time-course of nephrolithiasis treatment, from onset of symptoms and initial presentation to definitive treatment and follow-up imaging. We found that patients waited an average of 45 days until surgical treatment of their stones. This timeframe is clinically concerning given the risks of ED revisits for renal colic and/or infection as well as long-term risks of chronic kidney disease and ureteral stricture after 6 weeks [6-8]. The American Urological Association (AUA) guidelines for surgical management of urolithiasis provides a moderate recommendation for definitive stone management within 6 weeks, based on a 1973 study noting irreversible upper tract damage after this time frame [9]. Our data is in line with other studies in the literature. One U.S. group found that the median time from ED visit and/or stent placement to definitive stone intervention was 31.5 days [10]. In Canada, the mean wait time in 2011 for elective ESWL procedures nationally was 59 days [11]. A retrospective review of a 6 month period in the United Kingdom found a median time from ED visit and stent placement to stone intervention of 119 days, with only 3% receiving definitive procedure within 30 days [12]. This contrasts sharply with the British Association of Urologic Surgeons (BAUS) proposed target time of 4 weeks for definitive intervention in patients with acute stone presentations [12]. The most common reason 62% of patients waited more than 14 days for surgery was due to lack of provider availability or inability to access sooner operating room time. At our institution, surgical scheduling is based on a rigid block schedule that discourages non-urgent add-on cases. For example, each surgeon performs urological surgery on scheduled days of the month and open time for elective cases in between these blocks rarely exists. This makes scheduling patients with semi-acute but non-urgent stones challenging. Other healthcare systems with more flexibility may have improved access to surgical treatment. A recent population- based cohort study by Brubaker et al of over 15,000 patients discharged from an ED in California with a stone diagnosis found a median time from ED to stone surgery of 28 days [13]. Interestingly, patients with Medicare, Medicaid or self-pay coverage as well as Black or Hispanic race experienced a wait of up to 12 to 36 days longer, bringing the time to definitive treatment to 6 to 9 weeks. Our study complements this large dataset as we verify findings at a single institution similar to Brubaker et al. In addition, our study provides clinical granularity about reasons for delay that is lacking in administrative datasets. Implementation of protocols to enhance follow-up and expedite treatment of acute stone episodes is in its infancy but already shows significant promise to improve healthcare- associated costs as well as patient morbidity [10, 14]. The formation of an acute care urology (ACU) service at one New York hospital to facilitate timely evaluation and treatment of patients presenting to the ED with acute stone disease was found to reduce ED return visits and hospital readmissions [10]. At our own institution, measured institution goals for access to care exist, and enhancing access to surgery is an ongoing goal. Our study is not without limitations. It is retrospective in nature and focused on a small cohort at a tertiary referral center. In addition, we did not capture data about payer status, race or medical comorbidities. Therefore, it is possible that the surgical stone cases at our institution may be more complex and require more specialized care than cases found in the community. In addition, as mentioned previously, our current surgical scheduling model does not easily accommodate expedited surgical cases. However, the predominance of ureteral stones and gender equality amongst our patients with acute renal colic is in line with that of the greater population. Future research will be focused on prospectively following patients to further identify obstacles in accessing care.
Conclusion
In our study of the time-course of acute nephrolithiasis, we found that the time from initial presentation to stone treatment was prolonged primarily due to provider availability, challenges in accessing expedited operating room time, and patient factors. These data suggest that improving provider availability, perhaps by incorporating a dedicated operating room to enable faster access for stone surgery cases, is critical to improving the overall morbidity and outcomes of acute stone management.
For More Open Access Journals in Iris Publishers Please Click on: https://irispublishers.com/
For More Information: https://irispublishers.com/aun/fulltext/understanding-the-time-course-of-nephrolithiasis.ID.000525.php
#Iris Publishers#Iris Publishers LLC#Open Access Journals of Urology#Open Access Journals of Nephrology
0 notes
Text
What Is TMS Therapy And How Does It Work?
From 15 to 44 years old, depression is the primary cause of disability among people. While there are many effective treatments for depression, they do not work for everyone. Some individuals with depression do not get adequate relief from the antidepressant they take. After a few months of treatment, some symptoms remain for these people. For this reason, they try the tms treatment for depression San Diego, which is a non-invasive form of brain stimulation.
What Is TMS Therapy?
TMS, also known as transcranial magnetic stimulation, is used to improve or manage symptoms of depression. TMS devices work outside the body and impact the activity in the central nervous system by applying powerful magnetic fields to areas of the brain connected with depression.
tms treatment for depression San Diego does not require anesthesia and patients usually tolerate it well compared to some medications and ECT (Electroconvulsive therapy) that often come with side effects. For TMS, the most common side effect is headache during or after therapy.
TMS treatment is a comprehensive treatment option that comprises five days a week of sessions for several weeks. Each session can last for about 20 to 50 minutes, depending on the clinical protocol being used and the device.
Before the stimulation process, the patient checks in with a doctor or technician. The practitioner identifies the ideal stimulation intensity and anatomical region in the brain, which is the motor cortex. By targeting this part of the brain first, the doctor can determine where best to locate the stimulation coil according to the brain of the patient and how intensely it should fire in order to get ample stimulation.
After that, the doctor utilizes calculations to translate data in locating the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. This is the brain target known to be involved in depression with the biggest evidence of clinical effectiveness. Even though one session of tms treatment for depression San Diego may be enough to change the level of excitability of the brain, you may notice relief between 3 to 6 weeks of treatment.
Does TMS Work?
About 60% of people who are suffering from depression experience a clinical response with TMS, after trying and failing to receive benefit from medications. Many of these individuals experience complete remission, indicating that they rid of their symptoms fully.
Keep in mind that these results are not permanent. There is a high recurrence rate, as with most other treatment methods for mood disorders.
In general, most patients feel better for many months after the tms treatment for depression, with the average period of response for a year or so. Some decide to come back for subsequent rounds of TMS therapy.
Is Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Effective With Other Conditions?
Many experts continue to study TMS treatment is across disorders and even disciplines with the idea that it can evolve into new treatments for pain management, physical rehabilitation, neurological disorders, etc.
There are large clinical trials looking at the effectiveness of TMS in conditions like bipolar disorder, smoking cessation, pediatric depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Speak with your doctor regarding tms treatment for depression, because dental implants, medical devices, and other procedures may hinder TMS due to potential interference between such devices and the machine.
0 notes
Text
FDA Clears Sorrento Phase 2 Trial Of Non-Opioid Product Candidate Resiniferatoxin (RTX) For Treatment of the Knee Pain in Osteoarthritis (OA) Patients
New Post has been published on https://depression-md.com/fda-clears-sorrento-phase-2-trial-of-non-opioid-product-candidate-resiniferatoxin-rtx-for-treatment-of-the-knee-pain-in-osteoarthritis-oa-patients/
FDA Clears Sorrento Phase 2 Trial Of Non-Opioid Product Candidate Resiniferatoxin (RTX) For Treatment of the Knee Pain in Osteoarthritis (OA) Patients

Phase 2 trial of RTX for OA pain to proceed following FDA clearance.
Phase 1b data demonstrated RTX safety for a single intra-articular administration without dose limiting toxicity (DLT) at any doses tested up to 30 ug.
Phase 1b data demonstrated significant efficacy supporting RTX as an ideal candidate for long-term control of refractory OA pain: significant pain relief observed in patients with advanced OA disease (Kellgren-Lawrence grade 3/4) and sustained pain relief last beyond 6 months.
Sorrento believes RTX has the potential to become a key therapeutic in a market segment estimated to continue to grow and exceed $10B by 20251
SAN DIEGO, July 06, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. (NASDAQ: SRNE, “Sorrento”) announced today that the company has received FDA clearance to proceed with a Phase 2 clinical study of RTX for treating moderate-to-severe osteoarthritis of the knee pain (OAK).
The phase 2 trial, a multi-center, double blind, placebo- and active-controlled study, will assess the efficacy and safety of several dose groups of RTX to manage pain in patients with moderate-to-severe osteoarthritis of the knee pain (OAK) (clinicaltrials.gov: NCT04885972). Given the durability of OA pain relief response to RTX demonstrated thus far, Sorrento has decided to include an active comparator (injectable corticosteroid) in the current trial protocol. Superiority data potentially generated by RTX against a widely used approved drug could be supportive for accelerated international registrations (Europe) and is required for pricing purposes in Europe.
This Phase 2 study follows the analysis of the significant observations from the Phase 1b trial results (NCT03542838) of RTX Day 84 patient data which completed the one year following up of last patient visit in February 2021. This Phase 1b study was a double-blinded, placebo-controlled ascending dose study in 94 patients and included an open-label expansion cohort to assess the long-term safety and preliminary efficacy of a single intra-articular administration of RTX or saline control (as placebo group) for the treatment of moderate-to-severe pain due to osteoarthritis of the knee. The magnitude of the difference in the treatment effect (RTX versus saline control) at 12 weeks exceeded what is traditionally considered sufficient to support regulatory approval based on greater than 2 points reduction in WOMAC A1 10-point scale question “pain at walking on flat surface” compared to placebo. RTX met this requirement in this study.
Story continues
The Phase 1b study was designed to follow patients to day 84 (primary endpoint). Patients were also given the option to be followed for up to a year. Pain relief appeared to be very consistent among patients responding to the initial treatment, with a large proportion of the patients followed past Day 84 showing pain relief sustained beyond all time points assessed through one year follow-up. Fast relief (starting within days, with optimal pain relief level achieved within weeks) and durability of the effect (past 84 days) confirm the clinical potential of the RTX drug for long-term control of pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee.
The RTX clinical development program continues, with Phase 2 and 3 clinical trials planned in larger patient populations. The first Phase 2 trial will focus on identifying the recommended Phase 3 dose.
_______________
1 Osteoarthritis Market Size, Share, Value, And Competitive Landscape 2021-2026 – MarketWatch
About RTX
A thousand times “hotter” than pure capsaicin (16 billion Scoville units versus 16M), and with a high affinity for afferent sensory pain nerves, RTX binds to TRPV1 receptors present and selectively ablates the nerve endings responsible for pain signals experienced by patients2. Delivered peripherally (into the joint space) the transient nerve ending ablation effect can have profound clinical benefits lasting for months to years (as shown in canine studies3).
PTVA-OA-001 was a multicenter, placebo-controlled Phase 1b study to assess the safety and define the maximally tolerated dose of RTX administered in the knee joint in patients with moderate to severe pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee. The study was a dose-escalation trial in which cohorts of patients receive increasing doses of RTX until the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) was achieved. The primary objective of the study was to evaluate the safety of RTX and identify the recommended Phase 3 dose. The secondary objective was to assess the preliminary efficacy of RTX measured by assessing changes in the intensity of pain using the A1 score from the WOMAC, a widely used proprietary validated pain questionnaire.
The osteoarthritis treatment market and in particular the Knee Osteoarthritis and injectable markets have historically seen healthy growth and are expected to continue the trend as populations age and present excessive weight. Multiple sources estimate the 2020 market to be around 50M patients and $7B.
More information on this completed trial can be found at www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT03542838).
_______________
2 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC398431/
3 Sorrento Therapeutics (Ark Animal Health) internal data (on file)
About Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc.
Sorrento is a clinical stage, antibody-centric, biopharmaceutical company developing new therapies to treat cancers and COVID-19. Sorrento’s multimodal, multipronged approach to fighting cancer is made possible by its extensive immuno-oncology platforms, including key assets such as fully human antibodies (“G-MAB™ library”), clinical stage immuno-cellular therapies (“CAR-T”, “DAR-T™”), antibody-drug conjugates (“ADCs”), and clinical stage oncolytic virus (“Seprehvir™”). Sorrento is also developing potential antiviral therapies and vaccines against coronaviruses, including COVIGUARD™, COVI-AMG™, COVISHIELD™, Gene-MAb™, COVI-MSC™ and COVIDROPS™; and diagnostic test solutions, including COVITRACK™, COVISTIX™ and COVITRACE™.
Sorrento’s commitment to life-enhancing therapies for patients is also demonstrated by our effort to advance a first-in-class (TRPV1 agonist) non-opioid pain management small molecule, resiniferatoxin (“RTX”), and SP-102 (10 mg, dexamethasone sodium phosphate viscous gel) (SEMDEXA™), a novel, viscous gel formulation of a widely used corticosteroid for epidural injections to treat lumbosacral radicular pain, or sciatica, and to commercialize ZTlido® (lidocaine topical system) 1.8% for the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia. RTX has completed a Phase IB trial for intractable pain associated with cancer and a Phase 1B trial in osteoarthritis patients. SEMDEXA is in a pivotal Phase 3 trial for the treatment of lumbosacral radicular pain, or sciatica. ZTlido® was approved by the FDA on February 28, 2018.
For more information visit www.sorrentotherapeutics.com.
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release and any statements made for and during any presentation or meeting contain forward-looking statements related to Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc., under the safe harbor provisions of Section 21E of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 and subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those projected. Forward-looking statements include statements regarding the expectations for Sorrento’s and its subsidiaries’ technologies and product candidates, including, but not limited to, resiniferatoxin (RTX), the clinical potential of RTX, including the potential for RTX to address long-term control of pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee, RTX’s potential to become a major therapeutic in the knee osteoarthritis and injectable markets, timing for commencing additional Phase 2 and 3 clinical trials for RTX, timing for completion and submission of a request to proceed with any Phase 3 trial for RTX, the possibility of proceeding to a Phase 3 trial, and the possibility of obtaining accelerated international registration for RTX in Europe. Risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual results to differ materially and adversely from those expressed in our forward-looking statements, include, but are not limited to: risks related to Sorrento’s technologies and prospects, including, but not limited to risks related to seeking regulatory approval for RTX; clinical development risks, including risks in the progress, timing, cost, and results of clinical trials and product development programs; risk of difficulties or delays in obtaining regulatory approvals; risks that clinical study results may not meet any or all endpoints of a clinical study and that any data generated from such studies may not support a regulatory submission or approval; risks that prior test, study and trial results may not be replicated in future studies and trials; risks of manufacturing and supplying drug product; risks related to leveraging the expertise of its employees, subsidiaries, affiliates and partners to assist Sorrento in the execution of its therapeutic antibody product candidate strategies; risks related to the global impact of COVID-19; and other risks that are described in Sorrento’s most recent periodic reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including Sorrento’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2020, and subsequent Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including the risk factors set forth in those filings. Investors are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date of this release and we undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statement in this press release except as required by law.
Media and Investor Relations Contact
Alexis Nahama, DVM (SVP Corporate Development)
Email: [email protected]
Sorrento® and the Sorrento logo are registered trademarks of Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc.
G-MAB™, DAR-T™, SOFUSA™, COVIGUARD™, COVI-AMG™, COVISHIELD™, Gene-MAb™, COVIDROPS™, COVI-MSC™, COVITRACK™, COVITRACE™ and COVISTIX™ are trademarks of Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc.
SEMDEXA™ is a trademark of Semnur Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
ZTlido® is a registered trademark owned by Scilex Pharmaceuticals Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
©2021 Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Source link
0 notes
Photo

New Post has been published on https://techcrunchapp.com/california-oks-outdoor-youth-sports-under-certain-rules-national-world-news/
California OK's outdoor youth sports under certain rules | National/World News

SACRAMENTO, Calif. (AP) — Youth sports competitions can resume next week in parts of California and could be back for a vast majority of the state by the end of March under a plan announced Friday by public health officials that clears the way for abbreviated spring versions of high school football, field hockey, gymnastics and water polo.
“It’s going to be a very welcome reprieve for hundreds of thousands of kids who (experienced) a lot of pain in not being able to play in the fall,” said Patrick Walsh, head football coach for Junipero Serra High School, a gridiron power just south of San Francisco. “This gives us a sense of hope and something to look forward to in an otherwise pretty melancholy situation.”
Nearly all interscholastic, club and community league sports in California have been on hold since the pandemic began in March, along with adult recreational sports that also are covered by the new rules. The California Interscholastic Federation, the state’s high school sports’ governing body, moved most fall sports to the spring in the hopes that students could salvage some of their season.
But state rules only allowed soccer, baseball, football and nearly all other team sports to resume once a county advanced out of the state’s most restrictive of four tiers of virus regulations, a slow process that threatened to scuttle any spring seasons.
Gov. Gavin Newsom, a former college baseball player and father of four children who play youth sports, repeatedly said he wanted to get children back onto playing fields but would only do it when it was safe. California’s virus cases have dropped precipitously in the last six weeks and that prompted a relaxation of the sports guidelines.
Under the new rules, a county’s overall tier designation doesn’t matter. The one metric being used for sports competitions is per capita cases. All outdoor sports are allowed — with safety protocols — once a county reaches a level of 14 cases or lower for every 100,000 people.
There are 27 counties that meet that standard and can resume competitions as soon as next Friday, Feb. 26. They are virtually all in Northern California and include three of the four largest San Francisco Bay Area counties — Santa Clara, Alameda and San Francisco — as well as many of the state’s most rural counties.
Another 16 counties, including Los Angeles, San Diego, Orange and Fresno, will likely meet the standard within a few weeks.
The new rules apply to all outdoor youth and adult recreational sports, including schools and community-sponsored leagues. The rules do not apply to collegiate or professional sports that already are being played under a separate set of rules or “community events” like marathons and other endurance races. And they also don’t apply to indoor sports like basketball and volleyball.
“That’s more complicated, and that’s where we have more controversy, and understandably so,” Newsom said Friday during a news conference at a COVID-19 vaccine clinic in Alameda County. “We are confident that if we can resume it will only help enliven the capacity of these kids to feel more engaged, feel more alive.”
The new rules impose lots of limitations, including banning indoor activities like team dinners and film study and prohibiting athletes from sharing equipment. Coaches and players not in games must wear masks, and fans should be limited to immediate family members.
Most burdensome of all, the rules require weekly virus testing for all coaches and athletes 13 and older in close-contact sports including football, rugby and soccer if they are played in counties with a per capita rate above 7 cases.
Newsom said the state would pay for those tests, so as not to prohibit some less wealthy schools from participating. But he did not provide more details other than to say “we will absorb the cost.”
The rules will apply to school districts regardless of whether they have returned to in-person instruction, a key component pushed for by a group of high school coaches organized under the banner “Let Them Play CA.”
“This situation would be the classic cut off our nose to spite our face if we didn’t allow sports to happen because certain school districts were not opening,” said Justin Alumbaugh, a social studies teacher and head varsity football coach De La Salle High School, a perennial state championship contender located in the San Francisco Bay Area city of Concord. “We’ve punished kids enough. Today a lot of that punishment stopped.”
Others were less charitable to the governor, including Republican Assemblyman James Gallagher, who has been advocating for the return of youth sports for months.
“I think this could have been done weeks ago, but I appreciate the governor listening to the voices of these kids, parents and coaches,” Gallagher said. “Now do it for schools,” he added, a reference to reopening more districts for classroom instruction.
———
This story has been corrected to say the new rules for youth sports take effect Feb. 26.
Copyright 2021 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed without permission.
!function(f,b,e,v,n,t,s) if(f.fbq)return;n=f.fbq=function()n.callMethod? n.callMethod.apply(n,arguments):n.queue.push(arguments); if(!f._fbq)f._fbq=n;n.push=n;n.loaded=!0;n.version='2.0'; n.queue=[];t=b.createElement(e);t.async=!0; t.src=v;s=b.getElementsByTagName(e)[0]; s.parentNode.insertBefore(t,s)(window,document,'script', 'https://connect.facebook.net/en_US/fbevents.js'); fbq('init', '1022689164882457'); fbq('track', 'PageView');
0 notes
Text
Looking for a clinical study design in North Carolina - Durham to Raleigh, Research Triangle Park? You have come to the right place. We provide development and regulatory support of complete clinical development programs for an asset, innovative design of clinical studies, gap analysis of preclinical and clinical programs, and selection of appropriate populations for the studies. For more information, you can visit our website.
#clinical pharmacology boston-cambridge#pharmacometrics new jersey - princeton#regulatory strategy boston-cambridge#fda new york - new york city#clinical study protocol san diego#clinical study report san diego#modeling and simulation m&s north carolina#research triangle park
0 notes
Text
Dr. Hanid Audish - A Vanguard of Medical Innovation
Dr. Hanid Audish is no ordinary medical professional. He is, instead, a beacon of innovation in a field perennially in need of breakthroughs and advancement. As the leading force at the clinic, he has transformed this facility into a powerhouse of clinical research and patient care. Having catered to over 8,000 participants in San Diego alone since 1994, he has contributed immensely to the evolution of medical science. The clinic's work has led to the development of promising new investigational medications and new ways to use already-approved ones.
His role at Encompass cannot be overemphasized. He is instrumental in the clinic's ongoing research, particularly in neurology. His work primarily focuses on complex disorders such as Multiple Sclerosis, Neuropathic Pain, and Parkinson’s Disease. His dedication to understanding these conditions at a deeper level and exploring novel therapeutic strategies has ushered in a wave of hope for patients across the globe.
In the realm of translational research, he has set new standards. His belief in quickly converting laboratory findings into practical applications for patients is a testament to his commitment to making a tangible difference in people's lives. His leadership has facilitated the development of new diagnostic tools, treatment protocols, and therapies at an impressive pace.
Under his guidance, the clinic's impact extends far beyond its walls. His ethos of sharing knowledge freely has led to regular publication of scientific papers, which in turn contributes to the global advancement of medicine and facilitates collaboration.
His unyielding dedication to his work embodies the culture at the clinic. His commitment to patient well-being, combined with an unwavering determination to advance scientific discovery, has solidified the clinic's position as a pioneer in the field of medical research.
Dr. Hanid Audish’s scientific curiosity and patient-centric approach have seen him champion numerous clinical trials at the clinic. He notably spearheads studies exploring treatment options for conditions such as Rheumatoid Arthritis and Psoriasis, further expanding the facility's scope of impact. Under his leadership, the clinic has become a key player in clinical research, with over 500 studies conducted since the inception of the clinic.
His research interests extend to a broad array of areas, from autoimmune disorders to endocrine conditions. He has been instrumental in conducting studies on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide. Through these studies, he explores groundbreaking treatment approaches that aim to better manage the disease and improve quality of life for patients. His research on Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis, a liver disease often associated with obesity and diabetes, represents an important step in addressing a key public health concern.
In addition, his work in the field of dermatology has led to advancements that promise transformative outcomes for individuals grappling with skin conditions. He has been at the forefront of studies on Atopic Dermatitis, a condition that impairs the quality of life for numerous patients. His relentless pursuit of innovative therapeutic strategies holds immense potential for the future of skin care management. Also noteworthy is his research on Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria, aimed at delving deeper into understanding this complex inflammatory skin disorder and devising effective treatments. His contributions to these studies highlight his unwavering commitment to advancing science and improving patient outcomes across a variety of health conditions.
What truly sets Dr. Hanid Audish apart is his unwavering belief in the power of clinical trials not only as a means for scientific breakthroughs but also as a viable option for patient treatment. He is a staunch advocate for clinical trials as a means to offer patients access to the latest treatments before they are widely available, presenting a beacon of hope for many. This philosophy, combined with his relentless pursuit of medical innovation, continues to shape the trajectory of the clinic, establishing it as a bastion of pioneering research and superior patient care.
This determination is evident in every aspect of his work. From the quiet, sterile rooms of the laboratory to the comforting confines of an examination room, his influence pervades. His work has fostered a unique dialogue between science and humanity that could revolutionize medical science.
His dedication is unparalleled. His work ethic is not confined to the traditional hours of a workday. Instead, his passion for patient health and scientific discovery often sees him working late into the night, meticulously examining patient data or poring over the latest research studies. Driven by his commitment to his patients and his thirst for knowledge, he willingly devotes countless hours to his work, constantly striving to push the boundaries of our current understanding. His steadfast dedication to medical research is not just commendable, it is inspirational, setting a high standard for everyone at the clinic. His unwavering dedication is the cornerstone on which the success of the clinic is built.
His work extends far beyond the local community, impacting the global medical fraternity. His relentless commitment to research and patient well-being has led to breakthroughs that have the potential to redefine our understanding of medical science.
At Encompass, under his stewardship, patient care is not just about treating the illness, but about treating the individual as a whole. The team recognizes that each patient comes with a unique set of circumstances, health conditions, and treatment goals. As such, personalized care is at the heart of the clinic's approach. Dr. Hanid Audish and his team spend time listening to each patient, understanding their concerns, and providing clear explanations about their condition and treatment options. The goal is not only to provide the highest standard of care but also to ensure that patients are empowered, involved, and reassured in their healthcare journey. This empathetic and comprehensive approach to patient care has been a significant factor in the enduring trust and satisfaction among the patients at the clinic.
In conclusion, the story of Dr. Hanid Audish is one of unyielding dedication and commitment to the betterment of human lives. His work at the clinic exemplifies the profound impact that can be made when healthcare providers, researchers, and patients unite in a common pursuit of better health. His name is synonymous with tireless research and unwavering dedication, attributes that have accelerated the pace of scientific discovery, leading to breakthroughs that promise a brighter, healthier future for all.
0 notes
Text
National Clinical Trial Launches, Will Test Promising Vaccine Against Novel Coronavirus
UC San Diego among sites across the country seeking to recruit up to 30,000 participants, with hopes of developing and confirming an effective vaccine to prevent COVID-19 by end of year
UC San Diego Health and the Altman Clinical and Translational Research Institute, part of UC San Diego School of Medicine, will be sites for an accelerated national clinical trial to assess the efficacy and immunogenicity of a vaccine intended to protect against SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19.
The trial, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) newly formed COVID-19 Prevention Network (CoVPN), is based upon a vaccine prototype developed by Moderna, a pharmaceutical company located in Massachusetts. The trial is slated to begin July 27.
“Our country and the world are facing an unprecedented pandemic that has already killed more than 600,000 people worldwide,” said Stephen Spector, MD, Distinguished Professor of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases in the UC San Diego School of Medicine and principal investigator for the UC San Diego arm of the vaccine trial.
“A vaccine is desperately needed to help control the epidemic. We are excited that UC San Diego will be able to offer the San Diego community the opportunity to participate in a Phase III vaccine trial that, if successful, has the potential to change the course of the epidemic.”
Participation Protocol
The study trial will be randomized, observer-blind and placebo-controlled — the gold standard for clinical trials — with a primary objective to demonstrate efficacy of the vaccine to prevent COVID-19 and a secondary goal to assess whether it can prevent severe symptoms and death associated with COVID-19.
Participants must be 18 years or older with no known history of SARS-CoV-2 infection. The trial will give preference to participants who live in locations or under circumstances that put them at appreciable risk. For example:
persons working in essential jobs, such as first responders, health care or grocery stores
persons living in densely populated residential environments or living/working in congregated facilities, such as nursing homes
persons belonging to demographic groups disproportionately impacted by the pandemic, such as older persons, persons with underlying health conditions or some racial/ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Latinx and Native American populations
For more information about participating in the Moderna trial at UC San Diego, visit medschool.ucsd.edu/research/actri/clinical/Pages/COVID-19-Prevention-Network-Study
‘National Clinical Trial Launches, Will Test Promising Vaccine Against Novel Coronavirus‘
#covid-19#covid 19#novel coronavirus#sars-cov-2#clinical trial#covid-19 prevention network#moderna#vaccine#public health#infectious disease#science#medicine#immunology#nih#academic medicine#ucsd#uc san diego
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
FDA Clears Sorrento Phase 2 Trial Of Non-Opioid Product
New Post has been published on https://depression-md.com/fda-clears-sorrento-phase-2-trial-of-non-opioid-product/
FDA Clears Sorrento Phase 2 Trial Of Non-Opioid Product

Phase 2 trial of RTX for OA pain to proceed following FDA clearance.
Phase 1b data demonstrated RTX safety for a single intra-articular administration without dose limiting toxicity (DLT) at any doses tested up to 30 ug.
Phase 1b data demonstrated significant efficacy supporting RTX as an ideal candidate for long-term control of refractory OA pain: significant pain relief observed in patients with advanced OA disease (Kellgren-Lawrence grade 3/4) and sustained pain relief last beyond 6 months.
Sorrento believes RTX has the potential to become a key therapeutic in a market segment estimated to continue to grow and exceed $10B by 20251
SAN DIEGO, July 06, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. (NASDAQ: SRNE, “Sorrento”) announced today that the company has received FDA clearance to proceed with a Phase 2 clinical study of RTX for treating moderate-to-severe osteoarthritis of the knee pain (OAK).
The phase 2 trial, a multi-center, double blind, placebo- and active-controlled study, will assess the efficacy and safety of several dose groups of RTX to manage pain in patients with moderate-to-severe osteoarthritis of the knee pain (OAK) (clinicaltrials.gov: NCT04885972). Given the durability of OA pain relief response to RTX demonstrated thus far, Sorrento has decided to include an active comparator (injectable corticosteroid) in the current trial protocol. Superiority data potentially generated by RTX against a widely used approved drug could be supportive for accelerated international registrations (Europe) and is required for pricing purposes in Europe.
This Phase 2 study follows the analysis of the significant observations from the Phase 1b trial results (NCT03542838) of RTX Day 84 patient data which completed the one year following up of last patient visit in February 2021. This Phase 1b study was a double-blinded, placebo-controlled ascending dose study in 94 patients and included an open-label expansion cohort to assess the long-term safety and preliminary efficacy of a single intra-articular administration of RTX or saline control (as placebo group) for the treatment of moderate-to-severe pain due to osteoarthritis of the knee. The magnitude of the difference in the treatment effect (RTX versus saline control) at 12 weeks exceeded what is traditionally considered sufficient to support regulatory approval based on greater than 2 points reduction in WOMAC A1 10-point scale question “pain at walking on flat surface” compared to placebo. RTX met this requirement in this study.
The Phase 1b study was designed to follow patients to day 84 (primary endpoint). Patients were also given the option to be followed for up to a year. Pain relief appeared to be very consistent among patients responding to the initial treatment, with a large proportion of the patients followed past Day 84 showing pain relief sustained beyond all time points assessed through one year follow-up. Fast relief (starting within days, with optimal pain relief level achieved within weeks) and durability of the effect (past 84 days) confirm the clinical potential of the RTX drug for long-term control of pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee.
The RTX clinical development program continues, with Phase 2 and 3 clinical trials planned in larger patient populations. The first Phase 2 trial will focus on identifying the recommended Phase 3 dose.
_______________
1 Osteoarthritis Market Size, Share, Value, And Competitive Landscape 2021-2026 – MarketWatch
About RTX
A thousand times “hotter” than pure capsaicin (16 billion Scoville units versus 16M), and with a high affinity for afferent sensory pain nerves, RTX binds to TRPV1 receptors present and selectively ablates the nerve endings responsible for pain signals experienced by patients2. Delivered peripherally (into the joint space) the transient nerve ending ablation effect can have profound clinical benefits lasting for months to years (as shown in canine studies3).
PTVA-OA-001 was a multicenter, placebo-controlled Phase 1b study to assess the safety and define the maximally tolerated dose of RTX administered in the knee joint in patients with moderate to severe pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee. The study was a dose-escalation trial in which cohorts of patients receive increasing doses of RTX until the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) was achieved. The primary objective of the study was to evaluate the safety of RTX and identify the recommended Phase 3 dose. The secondary objective was to assess the preliminary efficacy of RTX measured by assessing changes in the intensity of pain using the A1 score from the WOMAC, a widely used proprietary validated pain questionnaire.
The osteoarthritis treatment market and in particular the Knee Osteoarthritis and injectable markets have historically seen healthy growth and are expected to continue the trend as populations age and present excessive weight. Multiple sources estimate the 2020 market to be around 50M patients and $7B.
More information on this completed trial can be found at www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT03542838).
_______________
2 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC398431/
3 Sorrento Therapeutics (Ark Animal Health) internal data (on file)
About Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc.
Sorrento is a clinical stage, antibody-centric, biopharmaceutical company developing new therapies to treat cancers and COVID-19. Sorrento’s multimodal, multipronged approach to fighting cancer is made possible by its extensive immuno-oncology platforms, including key assets such as fully human antibodies (“G-MAB™ library”), clinical stage immuno-cellular therapies (“CAR-T”, “DAR-T™”), antibody-drug conjugates (“ADCs”), and clinical stage oncolytic virus (“Seprehvir™”). Sorrento is also developing potential antiviral therapies and vaccines against coronaviruses, including COVIGUARD™, COVI-AMG™, COVISHIELD™, Gene-MAb™, COVI-MSC™ and COVIDROPS™; and diagnostic test solutions, including COVITRACK™, COVISTIX™ and COVITRACE™.
Sorrento’s commitment to life-enhancing therapies for patients is also demonstrated by our effort to advance a first-in-class (TRPV1 agonist) non-opioid pain management small molecule, resiniferatoxin (“RTX”), and SP-102 (10 mg, dexamethasone sodium phosphate viscous gel) (SEMDEXA™), a novel, viscous gel formulation of a widely used corticosteroid for epidural injections to treat lumbosacral radicular pain, or sciatica, and to commercialize ZTlido® (lidocaine topical system) 1.8% for the treatment of post-herpetic neuralgia. RTX has completed a Phase IB trial for intractable pain associated with cancer and a Phase 1B trial in osteoarthritis patients. SEMDEXA is in a pivotal Phase 3 trial for the treatment of lumbosacral radicular pain, or sciatica. ZTlido® was approved by the FDA on February 28, 2018.
For more information visit www.sorrentotherapeutics.com.
Forward-Looking Statements
This press release and any statements made for and during any presentation or meeting contain forward-looking statements related to Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc., under the safe harbor provisions of Section 21E of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 and subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those projected. Forward-looking statements include statements regarding the expectations for Sorrento’s and its subsidiaries’ technologies and product candidates, including, but not limited to, resiniferatoxin (RTX), the clinical potential of RTX, including the potential for RTX to address long-term control of pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee, RTX’s potential to become a major therapeutic in the knee osteoarthritis and injectable markets, timing for commencing additional Phase 2 and 3 clinical trials for RTX, timing for completion and submission of a request to proceed with any Phase 3 trial for RTX, the possibility of proceeding to a Phase 3 trial, and the possibility of obtaining accelerated international registration for RTX in Europe. Risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual results to differ materially and adversely from those expressed in our forward-looking statements, include, but are not limited to: risks related to Sorrento’s technologies and prospects, including, but not limited to risks related to seeking regulatory approval for RTX; clinical development risks, including risks in the progress, timing, cost, and results of clinical trials and product development programs; risk of difficulties or delays in obtaining regulatory approvals; risks that clinical study results may not meet any or all endpoints of a clinical study and that any data generated from such studies may not support a regulatory submission or approval; risks that prior test, study and trial results may not be replicated in future studies and trials; risks of manufacturing and supplying drug product; risks related to leveraging the expertise of its employees, subsidiaries, affiliates and partners to assist Sorrento in the execution of its therapeutic antibody product candidate strategies; risks related to the global impact of COVID-19; and other risks that are described in Sorrento’s most recent periodic reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including Sorrento’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2020, and subsequent Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including the risk factors set forth in those filings. Investors are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date of this release and we undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statement in this press release except as required by law.
Media and Investor Relations Contact
Alexis Nahama, DVM (SVP Corporate Development)
Email: [email protected]
Sorrento® and the Sorrento logo are registered trademarks of Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc.
G-MAB™, DAR-T™, SOFUSA™, COVIGUARD™, COVI-AMG™, COVISHIELD™, Gene-MAb™, COVIDROPS™, COVI-MSC™, COVITRACK™, COVITRACE™ and COVISTIX™ are trademarks of Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc.
SEMDEXA™ is a trademark of Semnur Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
ZTlido® is a registered trademark owned by Scilex Pharmaceuticals Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
©2021 Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Source link
0 notes
Text
Biomed Grid | Assay Linearity and Spike-Recovery Assessment in Optimization protocol for the analysis of Serum Cytokines by Sandwich ELISA Platform
Introduction
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological test technique that explores the principle of antigen-antibody reaction to identify and quantify substances such as antigens, cytokines, antibodies, glycoproteins and proteins in biological samples [1,2]. The approach employs the use of a solid phase, usually, an enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to accurately detect the presence of its target, normally an antigen in a biological sample, which is the liquid or wet phase. The analyte (antigen) would typically be absorbed to the solid surface and still participate in the specific high binding affinity reaction with the antibody [3]. The absorption process also facilitates the separation of free from the bound analyte, which gives ELISA an advantage over radioimmunoassay (RIA) technique. ELISA technique comprises three main analytical approaches; the direct ELISA, indirect ELISA, and sandwich ELISA [4]. The sandwich ELISA (sELISA) approach is based on the detection of the interaction between two antibodies; the capture and detection antibodies. The capture antibody functions to immobilize protein or targets onto the solid plate, meanwhile the secondary antibodies (detection antibodies), which are enzyme-linked engage the immobilized targets in a catalyzed substrate transformation reactions yielding detectable signals [5,6].
On the other hand, Spike and Recovery (SAR) assessment is a procedure that can be used for the analysing and evaluation of the accuracy of the sELISA method for particular sample types [10]. This assessment can be used to determine whether analyte detection can be affected by the differences between diluent used for the preparation of samples and the experimental sample matrix [10]. Complex sample matrices, such as serum and plasma, may contain interfering factors that may affect the ability of an assay to quantify the target analyte accurately. Recovery experiments are used to determine if test results are affected by interfering factors [10].
Cytokines perform critical roles in the control of fundamental pathways of the immune system [11]. Hence, the expression levels of certain cytokines have been shown to associate with the prognosis of a variety of diseases, including hematological cancers. For instance, high frequencies of several cytokines and angiogenic factors have been documented as biomarkers for utility in the diagnosis and prognosis of Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas (NHL) [12-14]. Adopting reliable methods of quantifying cytokines from diverse sample types can help in disease diagnosis and can provide prognostic value. Therefore, this study is aimed to provide a practical approach for optimizing optimum dilutions of serum samples for cytokine sandwich ELISA.
Materials and Methods
Study location
This experiment was carried out in a Good Clinical Laboratory Practice (GCLP) laboratory at the Royal Liverpool University Hospital, Liverpool.
Sample collection
Whole blood samples were collected from healthy volunteers (HV) into plain glass vacutainers, and serum samples were separated by spinning down the cellular components. Serum samples were stored in a minus 80 Freezer (-86 Freezer) until ready to use.
Ethical considerations and informed consent
No separate ethical clearance was obtained for this experiment since it was part of a bigger study, the PACIFICO phase 3 clinical trial that had been granted ethical clearance. The PACIFICO trial has approvals of the European Union Drug Regulating Authorities Clinical Trials (EudraCT) on a unique number 2008-004759-31 and the International Standard Randomized Controlled Trial (ISRCTN) number ISRCTN99217456. Written informed consent to donate blood for this experiment was obtained from volunteers.
Laboratory methodologies
We carried out sELISA linearity (assay linearity) on serially diluted serum samples from healthy volunteers to establish optimum working dilutions of serum samples for the serum cytokine analysis. The linearity assessment and the spike and recovery (SAR) assay employed to evaluate matrix effect on sELISA, especially for serum samples that yielded reduced ELISA signal.
Assay Linearity for optimum working dilution
Assay Linearity or Linearity of Dilution (LD) assay is an essential measure of ELISA accuracy and reliability [15]. Using serum samples from healthy volunteers and patients, we undertook assay linearity for serum IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-9, FGF-basic and GM-CSF to determine the best dilutions that can be used for serum cytokine sELISA. The choice of cytokines for the experiment was not based on stringent criteria; however, these were part of the 27 cytokines analyzed by Luminex assay in the bigger project (PACIFICO). To assess for assay linearity and to determine the optimal working dilutions of the serum samples. Sandwich ELISA was carried out using serially diluted serum samples (neat to 1:100) from healthy volunteers (HV1 – HV5) and controlled by human AB serum (hABs).
Spike and Recovery (SAR) assessment
The Spike and Recovery (SAR) assessment is essential for the analysis and accuracy evaluation of the ELISA method for particular sample types [10]. Spike and recovery assay is used to determine whether the detection of an analyte is affected by biological sample matrix and differences in the standard curve diluent [16]. For the SAR assessment, healthy volunteer sera and hABs were used for the sELISA to evaluate the effect of sample matrix on serum sELISA. Serum samples were spiked with different concentrations of standard IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-9, FGF-basic and GM-CSF plus unspiked control serum (0) respectively
Data management and Statistical analysis
Results of Assay Linearity are presented as line graphs, which is the mean of the individual biological triplicates. All Line graphs were generated using GraphPad Prism 5.0 (GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA). In determining the per cent (%) recovery, the concentration of the mean of Expected is calculated by adding the concentration of spiked level to the assay value of the un spiked serum. The per cent recovery is calculated by dividing the mean of Observed sELISA value of the spiked serum by the theoretically determined mean of Expected value [17]. Ideally, the SAR per cent recovery should not be less than 100 with results from 80 to 120% considered satisfactory [18].
Results
Line Charts have been used to display the trends of the levels of expression or signals of the various cytokines (IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-9, FGF-basic and GM-CSF) in picogram per millilitre (pg/ml) (y-axis) against the dilutions in X-axis as determined by sandwich ELISA. Higher signals of IL-4 can be seen to be expressed at 1:16 for volunteer serum samples HV1 and HV2, but hABs control showed a slight decline in the expression of IL-4 compared to the value at neat as in Figure 1. Therefore, IL-4 can be better demonstrated using undiluted (neat) serum sample. Figure 2 represents the line chat for serum IL-6 expression levels at different dilutions of the volunteer serum samples HV2, HV3, HV4 and HV5, as well as the human AB serum control. HV3 has shown a hook effect at 1:4 dilution, therefore a dilution of 1:4 of serum samples is recommended and could be adopted for IL-6 sELISA. Sandwich ELISA signals of serially diluted patients sera pac0085, pac0001 and a volunteer serum HV5 along the hABs are depicted in Figure 3. The signal trends indicated that IL-8 could best be analysed by an sELISA method using undiluted serum samples.
Figure 1: Line chat showing linearity of dilution for serum IL-4 of volunteer samples HV1, HV2 and human AB serum (hABs) as a control on sandwich ELISA.
Figure 2: Line chat showing linearity of dilution for serum IL-6 of volunteer samples HV2, HV3, HV4, HV5 and human AB serum (hABs) as a control on sandwich ELISA.
Figure 3: Line chat showing linearity of dilution for serum IL-8 of patient samples pac0085, pac0001, volunteer HV5 and human AB serum (hABs) as a control on sandwich ELISA.
Figure 4: Line chat showing linearity of dilution for serum IL-9 of patient samples pac0001, pac0026 and human AB serum (hABs) as a control on sandwich ELISA.
Figure 5:Line chat showing linearity of dilution for serum FGFbasic of human AB serum (hABs) control on sandwich ELISA.
Figure 6: Line chat showing linearity of dilution for serum GMCSF of volunteer serum samples HV1, HV2 and human AB serum (hABs) control on sandwich ELISA
As shown in Figure 4, Researchers are advised to make higher dilutions (of about 1:100) of serum samples for the analysis of IL-9 by sELISA technique. Figure 5 shows a line chat of serum FGF-basic from human AB serum (hABs) control on sandwich ELISA. A hook effect is noted at 1:8 which showed that the optimum dilution for the analysis of serum FGF-basic by sELISA is 1:8. Meanwhile, an undiluted (neat) serum sample is recommended for the analysis of serum GM-CSF for the best signal as in Figure 6. The results of Spike & Recovery assay (SAR) for IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-9, FGF-basic and GM-CSF are presented in Table 1. Serum samples from healthy volunteers (HVs) were used, except for IL-9 that employed patient samples and controlled by human AB serum (hABs). In most cases, the per cent recovery rate of the serum cytokines assayed on sELISA platform appears poor. However, higher per cent recovery rates are reported for IL-8 and IL-9. All the remaining cytokines (IL-4, IL-6, FGF-basic and GM-CSF) showed low per cent recovery below the acceptable recovery rate of 80-120% [18]. This result suggests that there is possible interference in the sample matrix that could be responsible for masking the detection of these cytokines.
Table 1: The Spike & Recovery assay –evaluating matrix effects on cytokine ELISA.
Note: Normal recovery range: 80 %-120% [18].
However, lower concentrations (higher dilutions) of IL-6, IL-8 and IL-9 can be seen to show acceptable per cent recovery rates at the lower limits. Also, this observation could be interpreted as caused by the sample matrix effect which gets diluted out in higher dilutions and yielding better recovery rates.
Discussion and Conclusion
The basic laboratory protocol commonly adopted for the optimization of sELISA technique for the validation of cytokine data include the determining of preferred working dilutions (sensitivity) of antibodies, Spike & Recovery assay and linearity of dilution assessment to check for sample matrix effects using dilutions. However, this study is designed to provide a simple, practical approach to determine optimum working dilutions for serum cytokine sandwich ELISA. It focuses on the linearity of dilution assessment and spike and recovery assay. The validation protocol targeted mainly six cytokines which include IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-9, FGF-basic and GM-CSF which were selected randomly and are part of the Bio-Plex Human Cytokine 27-plex panel. The linearity of dilution assays for adoption in the quantification of cytokines in serum samples revealed that serum IL-4, IL-8 and GM-CSF can be analysed on sELISA platform using undiluted (neat) serum samples. The study further showed that optimum signals for quantification could be obtained when serum samples are diluted by 1:4 for serum IL-6, 1:100 for IL-9 and 1:8 for FGF-basic using appropriate diluents.
However, an unexpected unending rise in signal strength (pg/ ml) along the increasing serial dilutions of serum samples was observed for IL-9 as in Figure 4. Interestingly, an apparent hook effect is reported in IL-6 (HV3) at 1:4 dilution in Figure 2 and FGFbasic (hABs) at 1:8 dilution in Figure 5. The sharp increase in IL-6 levels following serial dilutions as depicted in Figure 2 suggests that sample dilution might have probably enhanced detection by diluting out the effect of interfering factors in the sample matrix that could undermine the accuracy of sELISA results. This observation can be seen in IL-9 and FGF-basic. Assay linearity for cytokines under study by sELISA could be described as generally poor. The gross inconsistencies in the sensitivity and linearity of dilution of the serum sELISA could pose difficulty in determining optimum working dilutions for the serum cytokine sELISA. Interfering agents are capable of changing the concentration of the determinable intensity of the target analyte in the serum sample [19,20] and could be responsible for this trend. Assay interference has been shown to comprise analyte-dependent or analyte–independent with a resultant increase (positive) or decrease (negative) concentration of analytes. These interferences can cause erroneously elevated or lowered analyte number in a sample depending on the type of the interfering substance or the test design [20].
One of the most common interferences in sELISA is crossreactivity which exerts a nonspecific impact on elements in a test sample that have a structural resemblance to the analyte. Consequently, these elements may be having comparable or the same epitopes as the analyte and hence struggle for the binding site on the antibody, leading to false exaggerated or underestimated analyte concentration [21]. Additional features that are capable of influencing the results of sELISA due to elements within the sample can be grouped under pre-analytical factors such as sample collection, sample type, haemolysis, sample stability and storage [20]. Furthermore, the presence of proteins such as albumin, complement, lysozyme, fibrinogen and paraprotein in the samples has been shown to interfere with the results of immunoassays (sELISA) by affecting the antigen-antibody binding ability [19,20]. It is believed that albumin may interfere with to sELISA due to its elevated quantity and the capacity to bind or release large proportions of ligand [22,24]. However, our investigation of possible protein interference suggests that protein concentration in the serum sample could not account for the incredible high cytokine signals (IL-9) in sELISA observed in higher dilutions (unpublished data).
The characteristic unexpected low signals in higher concentrations (lower dilutions) and high signals in lower concentrations of cytokines as observed in the serum cytokine sELISA for IL-6, and IL-9 shown in Figures 2 & 4 are more agreeable with high-dose hook effect phenomenon. This phenomenon is centred on the saturation curve of an antibody with antigen, which is due to an extremely high number of analyte concurrently saturating both capture and detector antibodies giving a decrease in the signal at very high concentration of the analyte [20,25]. In immunoassays (such as sELISA) of very high analyte frequencies in a sample; the antigen-antibody interactions can result in antigen surplus; producing misleadingly reduced signals with consequential misrepresentations. Importantly, to improve the sensitivity and quality of sELISA and data, the occurrence of high-dose hook effect must be prevented by either increasing the quantity of the reagent antibodies or reducing the amount of sample (analyte) required for the analysis by sample dilution [26]. The variably poor recovery rates observed in the serum cytokine spike-and-recovery experiments, mostly seen outside the acceptable lower limit of the normal 80 %-120% suggests the effect of interference within the sample matrix.
Other forms of interferants such as cross-reactivity needed to be validated in further validation experiments to help in the process of determining optimal working dilutions of serum samples for adoption in sELISA. In conclusion, our study showed that different serum cytokines show different signal strengths on the sELISA platform to varying dilutions of serum samples. Sandwich ELISA on multiple serially diluted serum samples is, therefore, the first activity before embarking on serum cytokine sELISA analysis for the rest of the study. This first step will help in the determination of the optimum working dilutions for the respective cytokines of interest. Therefore, further studies on the other cytokines to determine the best serum dilutions for the best signals on the sELISA platform is recommended. We further recommend a more rigorous optimisation protocol to be carried out to set the best dilution for adoption in the analysis of multiple serum cytokines on Multiplex platforms.
Source of Funding
Professor Andrew Pettitt, Ronald Finn Chair of Experimental Medicine and Head of Department of Molecular and Clinical Cancer Medicine, University of Liverpool supported this work.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Melanie Oates, Dr Ke Lin and Professor Andrew R Pettitt who supervised and provided reagents for this work. We also thank the voluntary blood donors who donated blood for this experiment at the GCLP Laboratory of the Royal Liverpool University Hospital, Liverpool.
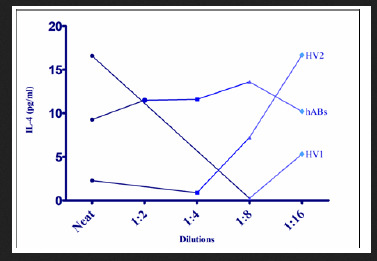
Read More About this Article: https://biomedgrid.com/fulltext/volume3/assay-linearity-and-spike-recovery-assessment.000657.php
For more about: Journals on Biomedical Science :Biomed Grid
#biomedgrid#List of open access medical journal#Journals on Biomedical Engineering#Journals on Biomedical Imaging#Journals on Medical Casereports#Journals on Medical drug and theraputics
0 notes
Text
Pharmacometrics In New Jersey – Princeton: Revolutionizing Drug Development

Pharmacometrics New Jersey – Princeton plays a key role in modern drug development. It offers a new approach that optimizes drug therapy. This is where Jersey's Princeton stands as a crucial epicenter for advancing pharmacometrics.
The drug development process is a task that is both time-consuming and costly. It also presents numerous challenges to the safety of compounds. However, pharmacometricians through their untiring efforts is steadily expanding the scope of pharmacometrics over time.
The most crucial tool for developing new drugs with maximum safety and efficacy and for optimizing doses in clinical settings is pharmacometrics analysis. It is a computer-based modeling and simulation of pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics (PK/PD) data. This method supplements the process by characterizing key aspects of drug safety- an imperative factor in successful development–and efficacy.
In the optimization of proper pharmacotherapy practice for achieving enhanced therapeutic outcomes, clinical pharmacometricians apply active drug management models. The pivotal role that clinical pharmacometrics practice plays is undeniable. It not only ensures precise dosing in vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly and patients with concomitant diseases or comedications but can also significantly enhance medicine utilization overall.
The Significance Of Pharmacometrics New Jersey – Princeton In Drug Development-
Enhancing Efficacy and Safety Profiles-
When it comes to precision medicine, pharmacometrics stands as the most crucial element to tailor drug therapies to individual patients. By involving the best modeling and simulation methods, it can predict drug behavior with supreme accuracy. Its analytical power allows various pharmaceutical companies to optimize dosage regimens. It improves therapeutic efficacy while minimizing adverse effects.
Accelerating Drug Approval Processes-
Usually, the common drug development pipeline is lengthy and resource-intensive. However, pharmacometrics comes with the most efficient solution by reforming various stages of drug development. With the help of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data, researchers can speed up clinical trial designs. It leads to faster regulatory approvals and brings medications to market within the timeframe.
Informing Regulatory Decision-Making-
Regulatory agencies always count the value of pharmacometric analyses in assessing drug safety and efficiency. By providing robust quantitative evidence, pharmacometric models allow regulators to make the right decisions regarding drug labeling, dosage recommendations and risk-benefit assessments. It promotes transparency and confidence in the regulatory process. Moreover, it is helpful for patients and healthcare providers alike.
This is where AzureDelta plays a vital role. It is devoted to consulting in clinical research and the name represents multiple meanings related to Clinical Pharmacology. It helps pharmaceutical companies to bring better medicine to patients faster and safer to save lives and make families happier.
Galina Bernstein has provided preclinical, clinical pharmacology, pharmacometrics, and analytical support for multiple clinical programs for over 300 studies including over 30 studies for the pediatric population. She was involved in a large number of studies for rare diseases as well as advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMP) such as gene therapy. She has been involved in the development and characterization of medical devices and clinical programs in the therapeutic areas of oncology, CNS, vaccines, dermatology, diabetes, cardiovascular, immunology, infectious diseases, renal impairment and others. Visit https://azuredeltaconsulting.com/ today for more information.
#clinical pharmacology boston-cambridge#pharmacometrics new jersey - princeton#regulatory strategy boston-cambridge#fda new york - new york city#clinical study report san diego#clinical study protocol san diego#modeling and simulation m&s north carolina
0 notes
Text
With Landmark Gift, UC San Diego Will Map Compassion in the Brain, then Prove its Power
Seeking to transform the education and well-being of current and future doctors, South Dakota businessman and philanthropist T. Denny Sanford has created a new institute at the University of California San Diego.
The T. Denny Sanford Institute for Empathy and Compassion will conduct innovative research into the neurological basis of compassion, establishing the empirical evidence required to design a compassion-focused curriculum for training new generations of medical professionals and developing new methods to protect and promote the well-being of current clinicians and their patients.
“I have been inspired by the work and teachings of the Dalai Lama, whose interest in the intersection where science and faith meet is deep and profound,” said Sanford. “I have had the opportunity to see how grace, humanity and kindness can change people and the world. This gift extends that vision. Doctors work in a world where compassion is essential, but often lost in the harsh realities of modern medicine. If we can help medical professionals preserve and promote their compassion, based on the findings of hard science, the world can be a happier, healthier place.”
Sanford’s philanthropy is well-known. He has donated millions of dollars to build children’s hospitals and clinics in South Dakota, Minnesota and Florida. In recent years, he has focused attention on reimagining medicine and health care through vanguard research. In 2013, for example, he donated generously to launch the Sanford Stem Cell Clinical Center at UC San Diego. In 2008, Sanford helped build the Sanford Consortium of Regenerative Medicine, a partnership of multiple local research institutions, including UC San Diego, to expand and translate stem cell research into clinical therapies and cures.
“We are immensely grateful to Denny Sanford for his transformative generosity and his vision to address physician burnout,” said UC San Diego Chancellor Pradeep K. Khosla. “This sort of multidisciplinary, collaborative effort that builds upon our existing leadership in neuroscience to understand the expression of and capacity for compassion and empathy is exactly what UC San Diego is known to do.”
Sanford’s gift significantly advances the Campaign for UC San Diego, a $2 billion fundraising effort to transform the student experience, the campus community and, through innovative interdisciplinary research, ultimately the world. Aligning with these priorities, the new Sanford Institute for Empathy and Compassion will also emphasize research, education and outreach, harnessing deep neurobiological resources and expertise in social sciences, engineering, data science and other disciplines across the university and in collaboration with partners, including the Sanford School of Medicine at the University of South Dakota and the T. Denny Sanford School of Social and Family Dynamics at Arizona State University, where Sanford has supported substantial programs in youth well-being, education and teacher training.
Using latest technologies, including neuroimaging, the institute seeks to establish the biology of empathy, then translate that data into compassion-focused medical training for new physicians and programs to improve the well-being of current clinicians and their patients.
Neurobiology of Compassion
The new institute will employ state-of-the-art neuroscience technologies, including sophisticated neuroimaging, to identify and map brain activity created by empathic behavior, quantify the factors promoting or inhibiting compassionate behavior and then design new methods to increase empathic signals in the brain.
“UC San Diego is an undisputed hub for neurosciences,” said William Mobley, MD, PhD, associate dean of neuroscience initiatives, a long-time advocate for the empirical study of compassion and interim director of the new institute. “There are few places in the world with the experts and expertise, the resources and ability to tackle the topic.
“People talk about compassion, but almost no one has ever studied how it exists in the brain. We want to find the irrefutable scientific data that validates the immense power of compassion, identify and understand its biological underpinnings and then use that knowledge to teach empathy to new doctors, benefit current ones and, most importantly, improve health care for everyone, patients and providers alike.”
Medical Education
Data and discoveries based upon research conducted by institute scientists, other faculty and collaborators will be used to inform and redesign the current medical curriculum at UC San Diego School of Medicine, which will seek to effectively integrate compassion-centered methods into training modules and later, provide guidance and expertise to other participating schools and institutions to embrace empathy and compassion in their training.
Steven Garfin, MD, interim dean of the UC San Diego School of Medicine, said the Sanford gift comes at a time when medical students are under enormous pressure. “Today’s medical students are tackling an explosive growth of knowledge. Here at UC San Diego, we’ve made excellent strides in integrating compassion and strategies for bedside manner into our training; the new institute will develop and teach us new and more advanced tools to continue that work and exponentially expand that knowledge.”
The institute will partner closely with the UC San Diego Student-Run Free Clinic, which has provided free comprehensive health care since 1997 to San Diego underserved communities.
“People go into medicine because they are driven by compassion. They're full of compassion. They have a desire to serve, a desire to help others, a desire to decrease suffering. Medicine as a profession is really all about compassion,” said Sunny Smith, MD, co-medical director of the Student-Run Free Clinic. “The problem right now is that the systems that are in place in medical training and in medical practice really cause suffering in the people who are practicing medicine and it makes us lose our compassion. That is the core concept of what we're trying to address.”
Physician Burnout
Part of the institute’s mission will also be to extrapolate new science-based programs and remedies to help address the issue of physician burnout (and other health professions, including medical students) through validated instruction of self-compassion, mindfulness training (including assessing and integrating existing compassion training protocols) and a heightened focus on mental health.
According to a 2019 Medscape national survey of 15,000 physicians, 44 percent reported burnout, with 15 percent saying they had experienced colloquial or clinical depression and 14 percent admitting they had contemplated suicide. Doctors have the highest suicide rate of any profession in the country: approximately 28 to 40 suicides per 100,000, according to the American Psychiatry Association.
David Brenner, MD, vice chancellor for health sciences at UC San Diego, said, “There is no understating the importance or need for this work and the significance of this gift. This is not about a single disease. It’s not about money for a building or project. It’s about transforming from a deep state of malaise and despair to a state of wellness that benefits everyone.”
Visit the T. Denny Sanford Institute for Empathy and Compassion website at compassion.ucsd.edu.
#science#medicine#empathy#compassion#med school#medical education#neurobiolgy#neuroscience#physician burnout#ucsd#philanthropy
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
New coronavirus tests promise to be faster, cheaper and easier
In the United States, the average wait time for COVID-19 test results is about four days. Even worse, 10 percent of individuals don’t receive lab results for 10 days or more.
Quick reporting of test results helps identify infected individuals so they and anyone they potentially spread the coronavirus to can be isolated, preventing further spread of the virus.
“If you have a 14-day lag to knowing if someone is actually sick and contagious, then they’ll interact with many, many more people in that period than if you have a one-day or a six-hour or one-hour turnaround,” says Omar Abudayyeh, a bioengineer at MIT.
Abudayyeh is among the many researchers and companies racing to develop new and speedier types of diagnostic tests that circumvent clinical labs altogether. Some of these tests complete their analyses in all-in-one machines that are portable enough to be set up in schools, nursing homes and offices. Several companies are developing tests like these that can diagnose COVID-19 in 30 minutes or less, with a level of accuracy comparable to lab tests. Others are harnessing the power of the gene editor CRISPR to deliver rapid results.
And another type of test, made by Abbott Laboratories and granted emergency use authorization by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on August 26, works more like a pregnancy test. All it requires is a test card the size of a credit card, a few drops of a reaction solution and a sample from a nasal swab. Within 15 minutes, two lines appear on the card if the sample contains the virus; one line appears if it doesn’t.
The gold standard
The current gold standard for accurate COVID-19 testing is PCR, or polymerase chain reaction, which can detect even tiny quantities of the virus’s genetic material, RNA (SN: 3/6/20).
The test requires collecting viral RNA directly from the patient, typically gathered using a swab inserted deep into the nasal cavity. At a clinical laboratory, the virus’s RNA is converted to DNA and then run through a specialized instrument that heats and cools that DNA to multiply copies of it, making it easier to detect. After repeating the process for around an hour, if DNA shows up, the sample is considered positive for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
See all our coverage of the coronavirus outbreak
Such tests are fairly accurate. They miss some people very early in the infection or because of lab errors, producing false negatives, meaning that the test results indicate someone isn’t infected when they really are. False positives — when tests wrongly indicate an uninfected person has the virus — are rare with this type of technology. So if a PCR test indicates a person is infected, they probably do carry the virus. The main drawback is the speed. It typically takes days to get results back, and backups at labs can drag the process out for a week or two.
Some people find the nasal probe uncomfortable, so other lab tests have been developed that rely on less invasive samples. On August 15, the FDA authorized a saliva-based test, SalivaDirect, for emergency use. This isn’t the first test to detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus in saliva, which is easier to collect than samples from nasal passages. But its simplified protocol speeds up sample preparation and bypasses testing supplies that have been in short supply in recent months. SalivaDirect, however, is not a rapid test. It still requires processing by clinical laboratories, which contributes to the wait time between providing a sample and receiving results.
To develop faster tests, companies are taking a variety of approaches. Funding for some of this work comes from the Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics initiative, or RADx, from the National Institutes of Health, which has invested $248.7 million in seven companies tackling testing challenges.
Compact instruments, such as Mesa Biotech’s Accula test, replace the function of clinical labs and could bring rapid testing to schools, nursing homes and offices.Mesa Biotech
San Diego–based Mesa Biotech, for instance, received RADx funding to manufacture a PCR test that replaces an entire clinical lab with a handheld dock and a single-use cartridge. The company says the proprietary technology in its Accula test, which has already received FDA emergency use authorization, can provide a COVID-19 diagnosis in just 30 minutes.
Turning on the LAMP
Other RADx-funded companies, such as Talis Biomedical, headquartered in Menlo Park, Calif., aren’t using PCR to amplify SARS-CoV-2 viral material. The Talis One system instead uses LAMP, or loop-mediated isothermal amplification. In a typical LAMP assay, a patient’s nasal or oral swab sample is mixed with enzymes and specially designed DNA fragments, then heated to 65° Celsius to copy the viral RNA to DNA and produce many more DNA copies. With the Talis test, samples are placed in a cassette, popped into a specialized dock, and analyzed in just 30 minutes.
As opposed to an instrument that cycles between hot and cold, LAMP heats the reaction to one temperature. “You could run the reaction in a water bath,” says Nathan Tanner, a molecular biologist at New England Biolabs in Ipswich, Mass.
In general, LAMP-based diagnostic tests aren’t quite as sensitive as ones based on PCR, Tanner says, but could be used to test more people, given their simpler requirements. In one newly described LAMP testing method, a solution changes color in the presence of 100 or more SARS-CoV-2 RNA molecules. The authors, who describe the test August 12 in Science Translational Medicine, propose that the approach, which didn’t detect the lowest viral loads, would be suitable for identifying individuals with a moderate to high viral load.
Telltale proteins
A third RADx-funded test provides results in a mere 15 minutes. Rather than detecting viral RNA, the test, by Quidel, based in San Diego, detects proteins from virus particles. These viral proteins are also antigens, meaning they stimulate immune responses when they invade our bodies. Such antigen tests are similar to ones used in doctors’ offices and pharmacies to diagnose people with influenza.
Don’t confuse antigen tests with an antibody test that detects antibodies a person develops in response to an infection (SN: 4/28/20) Much like a pregnancy test, COVID-19 antigen tests use antibodies to detect the viral proteins and give a yes or no answer, says Kim Hamad-Schifferli, a bioengineer at the University of Massachusetts Boston.
The Quidel Sofia SARS antigen test has been authorized for emergency use. Like the other RADx-funded rapid tests, it uses a dock and single-use cartridges: Instead of making a line on stick the way a pregnancy test does, the dock detects a fluorescent signal if SARS-CoV-2 proteins are present.
An antigen test by Abbott Laboratories requires only a test card, a swab sample and a few drops of a reaction solution to return a COVID-19 diagnosis in 15 minutes.Abbott
Abbott Laboratories’ test granted emergency use authorization August 26 also is an antigen test and, with its card-based technology, is even simpler. Abbott, based in Abbott Park, Ill., said its test was able to detect 34 of 35 COVID-19-positive patients with symptoms, or 97 percent, in initial studies.
The benefit: An antigen test doesn’t require any specialized lab instruments or enzymes. “It’s all self-contained,” Hamad-Schifferli says. Without a step to amplify viral material, however, an antigen test can be less sensitive than PCR or LAMP and result in a higher rate of false-negative results, up to 20 percent per the FDA’s emergency use authorization guidelines for antigen tests.
That’s because people may produce widely varying amounts of virus, depending on how long has passed since they became infected. In most people, the coronavirus is most abundant from a couple of days after infection to about nine days into the illness (SN: 3/13/20). After that, the immune system kicks in, preventing viruses from being made. On the other hand, viral RNA can be detectable in some people for more than a month. A negative result from an antigen test has a higher chance of being false comfort, so the FDA says that diagnosis may need to be confirmed with another type of test, like PCR.
A new kind of rapid test
Even though antigen tests typically are not as accurate as standard PCR or the new rapid tests, they could play a crucial role helping to end the pandemic — if their use becomes widespread. As of now, though, even Abbott’s 15-minute test still needs to be ordered by a doctor and performed in a health care setting, so that can provide hurdles to its use. But what if people didn’t even have to leave home to get a test?
That’s what Hamad-Schifferli and her colleagues are working on. The idea is to build a cheaper test that doesn’t involve a dedicated instrument — just a paper strip and a signal detectable by eye. Such a simple test could be used more widely by people at home. “It would be a game changer,” she says.
Sign up for e-mail updates on the latest coronavirus news and research
If COVID-19 tests are deployed widely enough, they could serve as a public health measure to identify people with high levels of SARS-CoV-2 and spreading the virus to others, even if they’re not displaying symptoms. That’s because frequent and fast tests can be used to pinpoint outbreaks as they are happening (SN: 7/1/20). If cheap enough, these tests could be used by people daily, catching any missed detections through repeated rounds of testing.
The United States is currently testing nearly 700,000 people a day on average, based on data from August 21 through August 27. Michael Mina, however, wants to see even more tests, like “200 million tests … every day in this country.” Surveillance provided by such widespread testing “will effectively do the same thing as a vaccine” in slowing the spread of the coronavirus says Mina, an epidemiologist at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
But for daily, population-wide testing that could alert people when they first start transmitting the coronavirus to be adopted, a test needs to be cheap enough — for instance, under a dollar — for many people to use them frequently. Abbott said its tests would cost $5. Quidel’s test cartridges cost $23 apiece and the other RADx-funded rapid tests are likely in a similar price range. Given their higher accuracy, those tests could serve a separate purpose: to conclusively determine if an individual is infected and ensure they receive treatment.

With overwhelming demand for COVID-19 testing, it can take days or even longer than a week for people to receive test results.Hoptocopter/E+/Getty Images
The holy grail of tests may be one that is fast, easy, accurate and inexpensive and that could be used broadly — even by people at home. One group of scientists may be among those nearing that goal. The work is led by Abudayyeh, Jonathan Gootenberg and Feng Zhang, all bioengineers at the McGovern Institute for Brain Research at MIT. Zhang is also at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard University.
The team adapted an FDA-authorized test by Sherlock Biosciences in Cambridge, Mass., that uses the gene-editing tool CRISPR. All someone has to do is add a sample — either from a nasal swab or saliva — to a tube with a reaction solution, heat the tube to 60° C for an hour in a pot of water, then add a paper test strip to the tube. If two lines appear, that means SARS-CoV-2 RNA is present.
The readout relies on activity of a CRISPR enzyme, Cas12b. If SARS-CoV-2 RNA is present in the reaction, Cas12b cuts what’s called a reporter, a short piece of DNA that’s labeled on both ends. The two halves of the reporter then wick up the paper strip to different places and appear as two lines. If viral RNA isn’t present, the reporter remains intact and wicks up the strip to one place, showing up as one line.
The new test, STOPCovid, is not yet authorized for clinical use, but based on tests in a small number of patients, it identifies SARS-CoV-2 cases as well as PCR tests, the researchers reported May 8 in a preprint posted at medRxiv.org. It returns results in about an hour and would cost under $10, they say.
Unlike rapid tests relying on docks and cartridges, the STOPCovid test is uniquely designed to scale up to millions of tests per week, says Gootenberg. “There’s never been a demand for millions or tens of millions of tests per week — ever.”
Other research groups have also developed similar CRISPR-based COVID-19 tests (SN: 4/17/20).
With the development of so many new technologies to test for the coronavirus, “we’re going to come away from the epidemic with a whole new field of diagnostics,” Mina says.
from Tips By Frank https://www.sciencenews.org/article/coronavirus-covid19-rapid-tests-rna-virus
0 notes