#Apollo Program
Text
Cancelled Missions: Skylab Rescue Mission (SL-R)

Mission patch for rescue mission for SL-3
Spacecraft: CSM-119
Launch Vehicle: Saturn IB AS-208, later AS-209
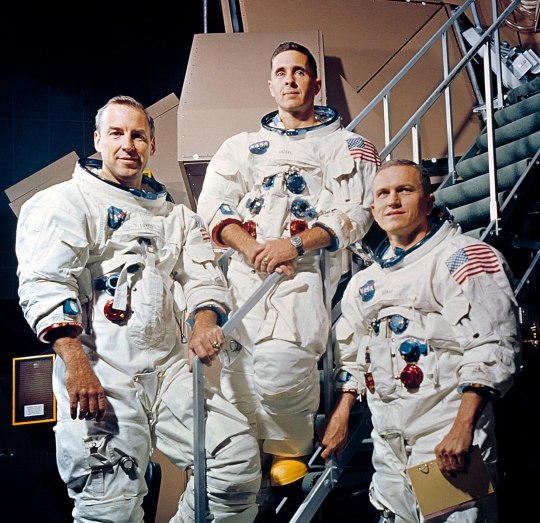
Commander: Vance D. Brand
Command Module Pilot: Don L. Lind
Intended launch date: September 1973, (on standby from August 1973 - February 1974)
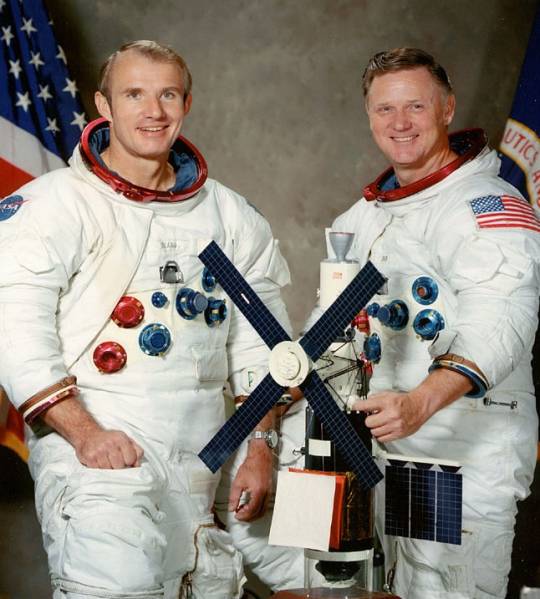

Skylab rescue mission crewmen Vance Brand (left) and Don Lind.
"Influenced by the stranded Skylab crew portrayed in the book and movie 'Marooned', NASA provided a crew rescue capability for the only time in its history." Prepared for launch during Skylab 3."
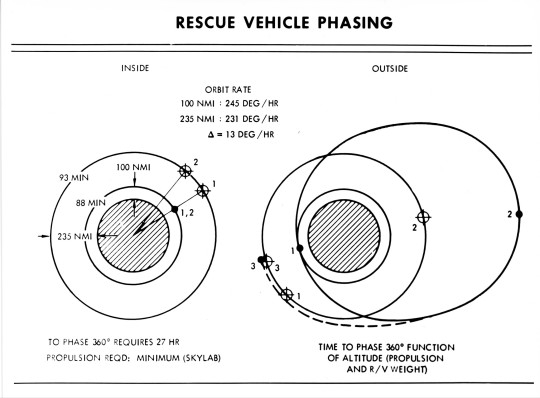
"Skylab rescue vehicle phasing - NAR Space Division drawing illustrates phasing of 5-seater Skylab rescue vehicle for a Skylab mission."
Date: April 5, 1971
"A kit was developed to fit out an Apollo command module with a total of five crew couches. In the event a Skylab crew developed trouble with its Apollo CSM return craft, a rescue CSM would be prepared and launched to rendezvous with the station. It would dock with the spare second side docking port of the Skylab docking module."
- information from Astronautix.com: link
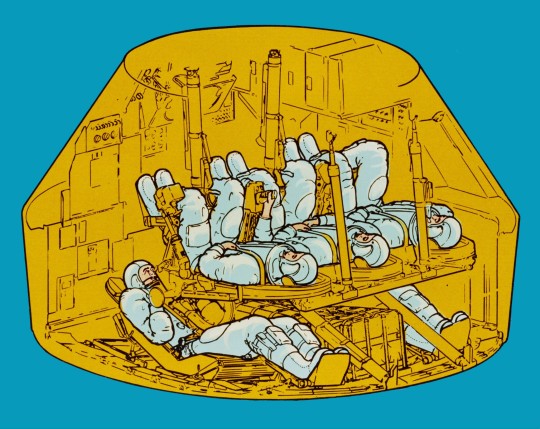
"The Apollo Command Module as modified to rescue stranded crews for the Skylab program. Two crew + three rescuees packed like sardines...."
"Skylab 3 astronauts Alan Bean and Jack Lousma helped design the "field modification kit" to use a standard CSM for rescue, and would have flown the CSM for their mission to rescue Skylab 2 if necessary. The standard Skylab Command Module accommodated a crew of three with storage lockers on the aft bulkhead for resupply of experiment film and other equipment, as well as the return of exposed film, data tapes and experiment samples. To convert the standard CSM to a rescue vehicle, the storage lockers were removed and replaced with two crew couches to seat a total of five crewmen."

Posted on Flickr by Mike Acs. NASA ID: 108-KSC-70P-69
"Soon after Skylab 3's launch the crew's CSM developed a problem with Quad B, one of its four reaction control system thrusters. On August 2, 1973, six days later, a snowstorm-like effect outside the station startled the crew during breakfast. What appeared to be 'a real blizzard' was fuel leaking from Quad D, opposite from Quad B. The malfunctions left two available quads, and while the spacecraft could operate with just one, the leaks posed a possible risk to other systems. The fuel for all quads and the main service propulsion system (SPS) engine were from the same batch; if the SPS fuel was contaminated, the CSM might not be able to deorbit.
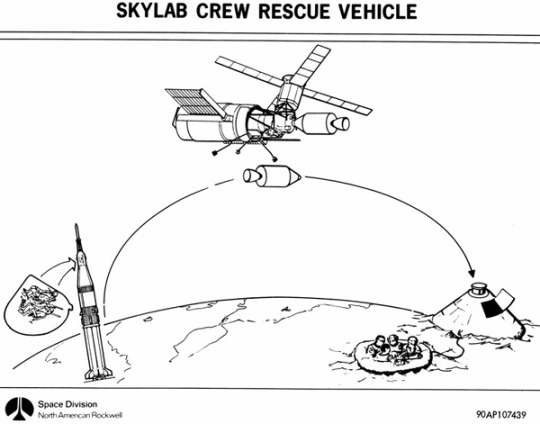

source
NASA considered bringing the crew home immediately, but because the astronauts were safe on the station with ample supplies and because plans for a rescue flight existed, the mission continued while the Saturn IB rocket AS-208 with CSM-119 was assembled in the Vehicle Assembly Building at Launch Complex 39 for possible use. It was at one point rolled out to LC-39B.
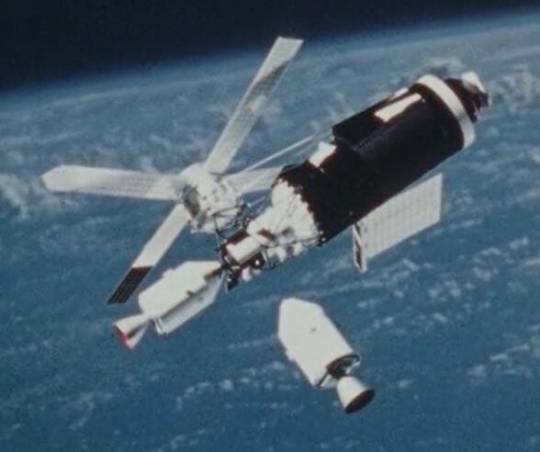

Illustration of the rescue Apollo spacecraft preparing to dock at Skylab’s lateral port. source
NASA announced on August 4 that Skylab 3 and Skylab 4 backup crewmen Vance Brand and Don Lind would fly any rescue mission; they had immediately begun training for the flight once the second quad had failed on August 2. After engineers found that the leaks would not disable the spacecraft, the two men used simulators to test reentry using two quads. If ground personnel worked 24 hours a day and skipped some tests, the mission could launch on September 10, and would last no more than five days. The astronauts would attempt to prepare Skylab for further use but returning experimental data and diagnosing the cause of the problem were more important, with Lind choosing what would be brought back. Human urine and feces samples and Apollo Telescope Mount and other film were the priorities. Although Skylab had two docking ports the primary one would be used if possible, jettisoning the Skylab crew's CSM if necessary.
Posted on Flickr by Drew Granston: link
While many within NASA believed that the rescue mission would occur, within hours of the failure of the second quad the agency canceled the rescue mission. Beyond NASA's conclusion that the failed quads would not disable the Skylab 3 CSM and the SPS fuel was uncontaminated, Brand and Lind had already shown during their training as backup Skylab crewmen that a reentry with failed quads was safe. They also devised a method to deorbit with the command module's attitude control system. Later joking that they were 'very efficient but perfectly stupid, because we have literally worked ourselves out of the mission', Brand and Lind continued to train for a rescue mission, as well as for their backup roles, but the Skylab 3 crew was able to complete its full 59-day mission on the station and safely return to Earth using the two functional RCS thruster quads, using the SPS engine once instead of twice as precaution."
- Information from Wikipedia: link

Posted on Flickr by Ed Dempsey: link
Saturn IB SA-208 was used for Skylab 4 and SA-209 was assigned to the standby rescue mission. At one point, CSM-119/SA-209 was slated for the Skylab 5 mission but it was cancelled when SL-4 was extended and completed all of it objectives.

Mission patch for rescue mission for SL-4
Later, CSM-119/SA-209 was the backup launch vehicle for Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission and standby rescue vehicle. After the Apollo program ended, the surplus rocket and spacecraft were displayed at the Kennedy Space Center, Florida.
NASA ID: 71-H-662, S73-31922
source, source
#Skylab Rescue#SL-R#Apollo CSM Block II#CSM-119#Saturn IB#SA-208#SA-209#Rocket#NASA#Apollo Program#Apollo Applications Program#Cancelled#Cancelled Mission#September#1973#my post
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
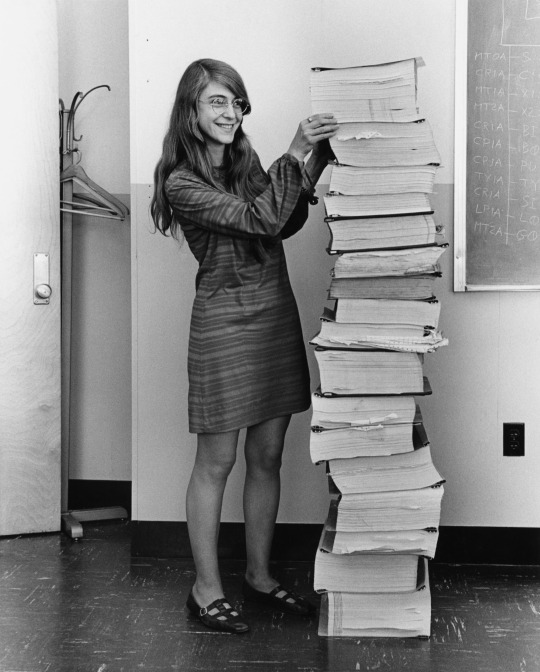

Margaret Hamilton, Director of the Apollo project Software Engineering Division, with a stack of papers containing the code to the Apollo Guidance Computer navigation software. The software that on this day, in 1969, guided Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin when they landed on the Moon.
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
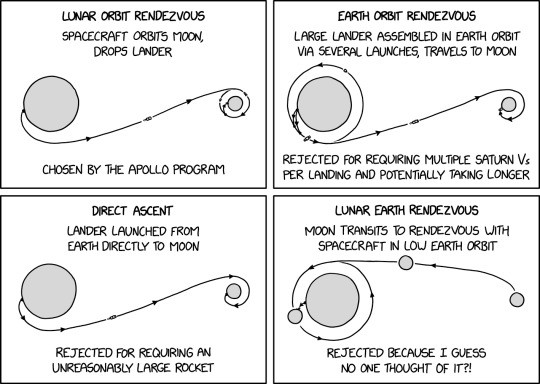
If you pick a low enough orbit, it gives you a lot of freedom to use a lightweight launch vehicle such as a stepladder.
Moon Landing Mission Profiles [Explained]
Transcript Under the Cut
[Four diagrams of potential ways to achieve a moon landing shown.]
Lunar orbit rendezvous
Spacecraft orbits Moon, drops lander
Chosen by the Apollo program
Earth orbit rendezvous
Large lander assembled in Earth orbit via several launches, travels to Moon
Rejected for requiring multiple Saturn Vs per landing and potentially taking longer
Direct ascent
Lander launched from Earth directly to Moon
Rejected for requiring an unreasonably large rocket
Lunar Earth rendezvous Moon transits to rendezvous with spacecraft in low Earth orbit
Rejected because I guess no one thought of it?!
446 notes
·
View notes
Text

Apollo 16 rollout attracts a crowd at the Vehicle Assembly Building, 9 February 1972.
875 notes
·
View notes
Text
I love Apollo 8 because not only was it like a monumental human achievement to orbit the moon but also they took like 800 photos and they’re all absolutely stunning
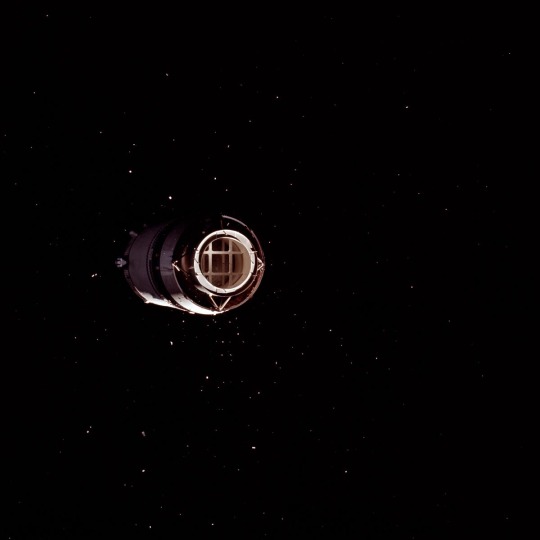
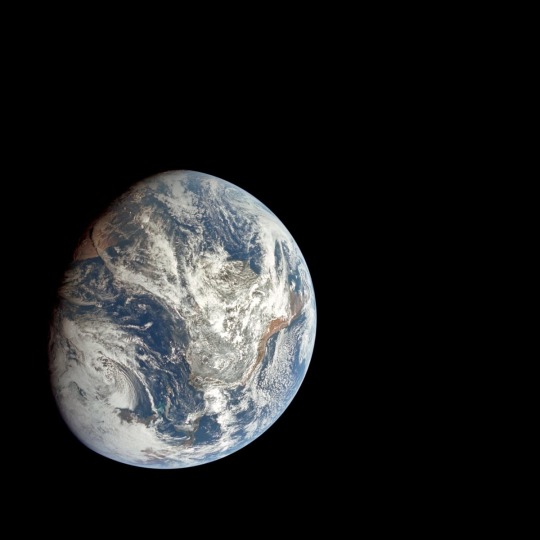
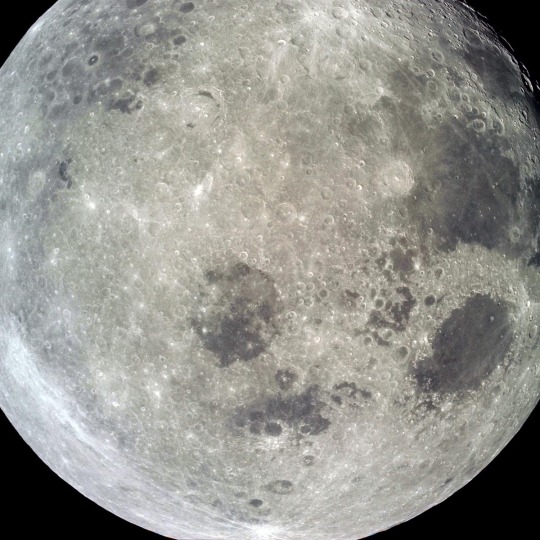
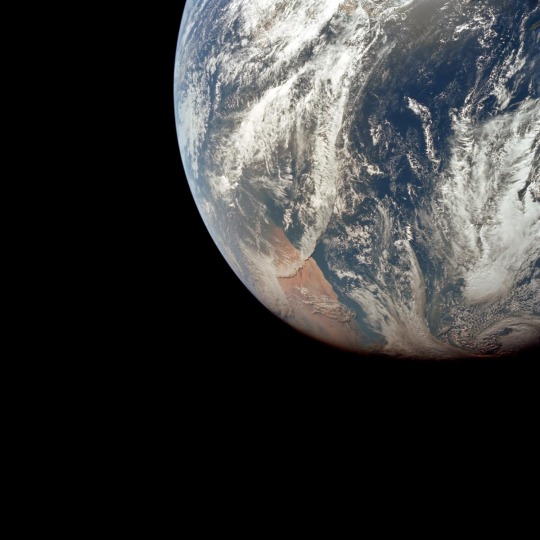







What a beautiful world we share
393 notes
·
View notes
Text
So considering that it’s the 54 anniversary of the moon landing I thought I’d share one of my favorite bits of trivia about the mission (along with a bit of a shitpost). So the first every liquid to be poured on the moon was actually whine as Buzz Aldrin took communion in the lunar module (the bread and whine were blessed a few days beforehand by a priest). Buzz wanted to broadcast the ceremony back to earth but decided not to at the request of Deke Slayton because of the controversy surrounding the reading of the book of genesis on Apollo 8.
Here’s where the shitposting comes in: According to Catholics (and other religions sects that believe in transubstantiation) believe that during communion the bread and whine literally becomes the body and blood of Christ. Which is why imho (despite not being religious in any way) it is perfectly accurate to say that Jesus Christ has landed on the moon
#shitpost#apollo program#space#moon landing#please do not take this seriously#Buzz Aldrin is a presbyterian iirc#it’s still funny tho imho#checkmate atheists
468 notes
·
View notes
Text

The view ain’t all that bad. Apollo 9 astronaut David Scott takes it all in in this epic photograph by crewmate Rusty Schweickart, March 1969. The 10-day mission commanded by James McDivitt saw the first crewed flight of the Lunar Module.
#apollo 9#astronauts#nasa#space travel#the earth#astronaut#space exploration#vintage space#space age#apollo program#historic#space#space race#nasa astronauts#nasa photos#nasa picture of the day#space program#1960s#1969#outer space
208 notes
·
View notes
Text
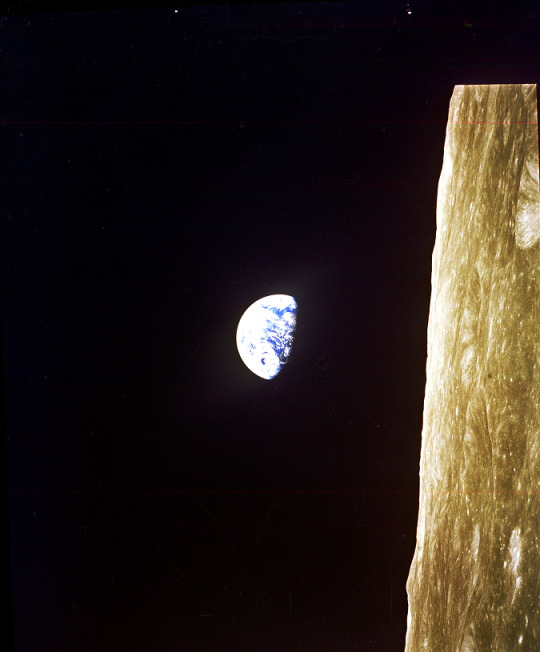

Rising Earth Greets Apollo VIII Astronauts
Record Group 306: Records of the U.S. Information AgencySeries: Master File Photographs of U.S. and Foreign Personalities, World Events, and American Economic, Social, and Cultural Life
This image is a color photograph of earth from lunar orbit. The surface of the moon appears on the right edge of the image. To the left, the earth appears to be floating in the blackness of space. Just over half of the earth is visible, the rest is in shadow.
#archivesgov#December 29#1968#Apollo 8#apollo program#nasa#nasa photos#space#space exploration#moon#1960s
163 notes
·
View notes
Text
does it ever drive you crazy

just how fast the night changes

#nasa#space#science#astronomy#moon mission#moon#lunar mission#space exploration#apollo#apollo program#artemis#artemis 2#apollo 8#artemis II#jim lovell#bill anders#frank borman#christina koch#reid wiseman#victor glover#jeremy hansen
604 notes
·
View notes
Text

The picture of earth from space that we will rarely be shown
#earth#nasa#space#spcae program#apollo program#vieformidable#design#architecture#interior design#photography#art#fashion#foodporn#interiordesign#israel#solar system#planets#3rd rock from the sun#water planet#hubble#hubble space telescope#hubble telescope#edwin hubble#astrophotography#color photos#color photography#nature#natural
126 notes
·
View notes
Text
Happy Earth Day from the Moon
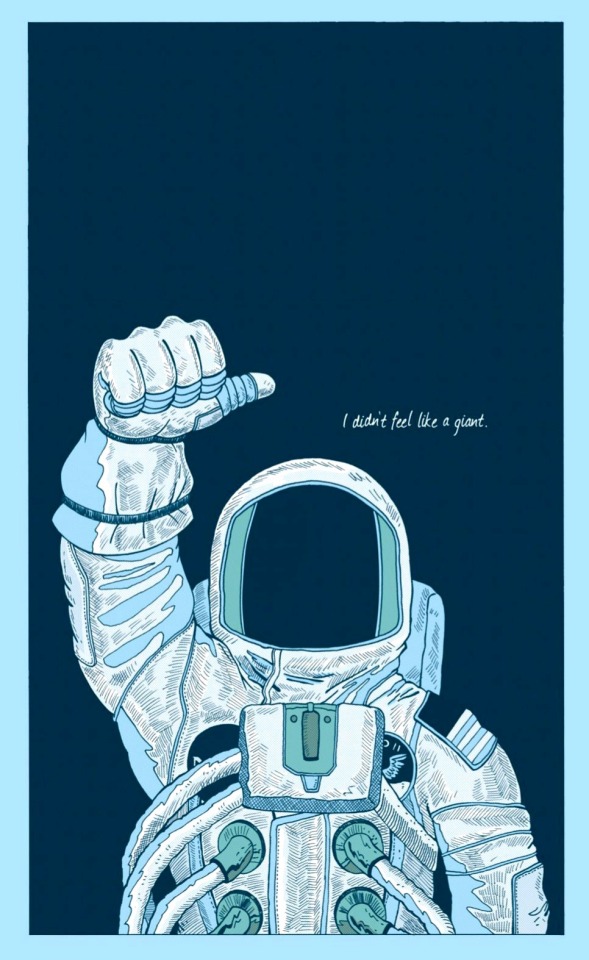



comic by zen pencils: "Neil Armstrong: A giant among men"
"It suddenly struck me that that tiny pea, pretty and blue, was the Earth. I put up my thumb and shut one eye, and my thumb blotted out the planet Earth. I didn’t feel like a giant. I felt very, very small."
- Neil Armstrong
60 notes
·
View notes
Text
The original Moon landing sites

"NASA contracted to have 15 flight-worthy Saturn V rockets produced. Apollo 11 achieved the first landing with the sixth Saturn V, leaving nine for follow-on landings. The following landing sites were chosen for these missions, planned to occur at intervals of approximately four months through July 1972."
Note: I've updated this list with the original tentative planned launch dates.
G-type Mission
Apollo 11: (G) Mare Tranquillitatis, July 1969
H-type missions
Apollo 12: (H1) Ocean of Storms (Surveyor 3 site), November 1969
Apollo 13: (H2) Fra Mauro Highlands, March 1970
Apollo 14: (H3) Littrow Crater, July 1970
Apollo 15: (H4) Censorinus Crater, November 1970
J-type missions, the extended stay missions
Apollo 16: (J1) Descartes Highlands or Tycho Crater (Surveyor 7 site), April 1971
Apollo 17: (J2) Marius Hills or Marius Hills volcanic domes, September 1971
Apollo 18: (J3) Copernicus crater or Schröter's Valley or Gassendi crater, February 1972, later July 1973
Apollo 19: (J4) Hadley Rille, July 1972, later December 1973
Apollo 20: (J5) Tycho Crater or Copernicus Crater or Marius Hills, December 1972, later July 1974
As we all know, plans were changed and missions were cancelled. But it's nice to see what was initially planned.

To compare with the actual landing sites and dates:
Apollo 12: (H1) Ocean of Storms (Surveyor 3 site), November 1969
Apollo 13: (H2) never landed, April 1970
Apollo 14: (H3) Fra Mauro, January-February 1971
Apollo 15: (J1) Hadley–Apennine, July-August 1971
Apollo 16: (J2) Descartes Highlands, April 1972
Apollo 17: (J3) Taurus–Littrow, December 1972
NASA ID: link, link
Information from Astronautix: link
Information from Wikipedia: link
#Apollo 11#Apollo 12#Apollo 13#Apollo 14#Apollo 15#Apollo 16#Apollo 17#Apollo 18#Apollo 19#Apollo 20#NASA#Apollo Program#Moon#Moon landing#Lunar Module#cancelled#G-type Mission#H-type mission#J-type mission#Cancelled Mission#my post
436 notes
·
View notes
Text

Apollo 16: back side of the Moon (April 18, 1972)
#apollo missions#apollo program#apollo 16#astronomy#krakenmare#solar system#astrophotography#outer space#thank you nasa#nasa#space#moon
122 notes
·
View notes
Text
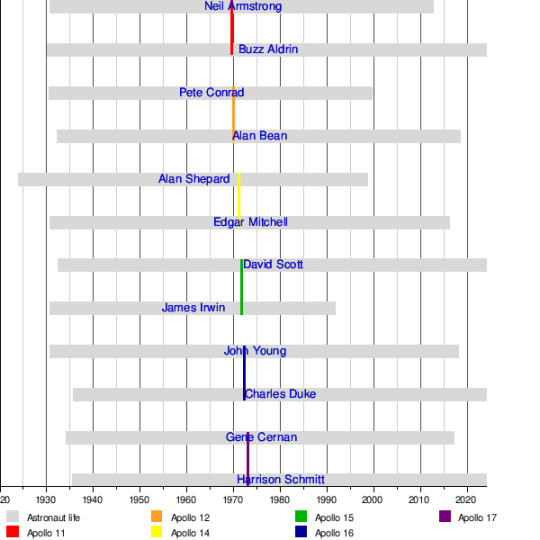
Timeline of the lives of everyone who has walked on the moon.
by u/emsot
57 notes
·
View notes
Text

Boys in Virginia watch the Apollo 8 broadcast from the Moon, December 24, 1968.
520 notes
·
View notes
Text

Margaret Hamilton, Apollo Guidance Computer source code, 1969
VS
Bruno Rainaldi, Sapiens, Sintesi | BBB Italia, 2003
#Margaret Hamilton#nasa#code#apollo 11#moon#apollo program#spaceflight#moon landing#sintesi#sapiens#bruno rainaldi#book#bookcase#bookshelf#bookshelves#design#made in italy#italian design#BBB Italia
108 notes
·
View notes