Photo

Top 15 Interview Questions with Answers for Network Administrators
Q-1: What is Active Directory?
Active Directory provides a centralized control for network administration and security. Server computers configured with Active Directory are known as domain controllers. Active Directory stores all information and settings for a deployment in a central database, and allows administrators to assign policies and deploy and update software.
Q-2: What is NetBIOS protocol?
NetBIOS (Network Basic Input/Output System) Protocol allows applications on separate computers to communicate over a LAN. It runs over TCP/IP giving each computer in the network a NetBIOS name and IP address. E.g. It can be used for computers running Windows 2000 (or before) to join a computer network running Windows 2000 (or later).
Q-3: What are FMSO Roles?
Fsmo roles are server roles in a Forest
There are five types of FSMO roles
1-Schema master
2-Domain naming master
3-Rid master
4-PDC Emullator
5-Infrastructure master
Q-4: What is LMHOSTS file?
It’s a file stored on a host machine that is used to resolve NetBIOS to specific IP addresses.
Q-5: What is ARP?
ARP is used to resolve a known IP address to a MAC address. For a host to communicate with another host, it must know the MAC address of the destination host (if they are on the same network) or next-hop router. This is the reason for ARP.
Q-6: What is APIPA?
(Automatic Private IP Addressing) The Windows function that provides DHCP auto configuration addressing. APIPA assigns a class B IP address from 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255 to the client when a DHCP server is either permanently or temporarily unavailable. Designed for small non-routable networks, if a DHCP server becomes available later, the APIPA address is replaced with one from the DHCP server. For example, when a Windows Vista machine starts up, it waits only six seconds to find a DHCP server before assigning an IP from the APIPA range. It then continues to look for a DHCP server. Previous versions of Windows looked for a DHCP server for up to three minutes. See DHCP auto configuration addressing, DHCP and private IP address.
Q-7: What ports are used by DHCP and the DHCP clients?
Requests are on UDP port 68, Server replies on UDP 67
Q-8: DNS zones - describe the differences between the 4 types.
i)Forward Lookup Zones :-
This zone is responsible to resolve host name to ip.
ii)Reverse Lookup Zones :-
This zone is responsible to resolve ip to host name.
iii)Stub Zone :-
Stub zone is read only copy of primary zone. but it contains
only 3 records the SOA for the primary zone, NS record and a Host (A) record.
Q-9: DNS record types - describe the most important ones.
Type of Record What it does
A (Host) Classic resource record. Maps hostname to IP(ipv4)
PTR Maps IP to hostname (Reverse of A (Host)
AAAA Maps hostname to ip (ipv6)
Cname Canonical name, in plain English an alias. such as Web Server, FTP Server, Chat Server
NS Identifies DNS name servers. Important for forwarders
MX Mail servers, particularly for other domains.MX records
Q-10: What is Domain Controller?
A domain controller (DC) or network domain controller is a Windows-based computer system that is used for storing user account data in a central database. It is the center point of the Windows Active Directory service that authenticates users, stores user account information and enforces security policy for a Windows domain.
A domain controller allows system administrators to grant or deny users access to system resources, such as printers, documents, folders, network locations, etc., via a single username and password.
Q-11: What is Group Policy?
Group Policy allows you to implement specific configurations for users and computers. Group Policy settings are contained in Group Policy objects (GPOs), which are linked to the following Active Directory service containers: sites, domains, or organizational units (OUs).
Q-12: What are GPOs (Group Policy Objects)?
A Group Policy Object (GPO) is a collection of settings that control the working environment of user accounts and computer accounts. GPOs define registry-based policies, security options, software installation and maintenance options, script options, and folder redirection options.
Q-13: Where is the AD database stored?
The AD database is stored in C:\Windows\NTDS\NTDS.DIT.
Q-14: What is the SYSVOL folder?
The SYSVOL folder stores the server copy of the domain’s public files that must be shared for common access and replication throughout a domain.
All AD databases are stored in a SYSVOL folder and it’s only created in an NTFS partition. The Active Directory Database is stored in the %SYSTEM ROOT%NDTS folder.
Q-15: What do Forests, Trees, and Domains mean?
Forests, trees, and domains are the logical divisions in an Active Directory network.
A domain is defined as a logical group of network objects (computers, users, devices) that share the same active directory database.
A tree is a collection of one or more domains and domain trees in a contiguous namespace linked in a transitive trust hierarchy.
At the top of the structure is the forest. A forest is a collection of trees that share a common global catalog, directory schema, logical structure, and directory configuration. The forest represents the security boundary within which users, computers, groups, and other objects are accessible.
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
Securing A Wireless Network
Modern wireless networking products are inexpensive, easy to install and very convenient. They are also full of holes ... security holes, that is.
The reason for this, can be traced to the popularity of wireless. The wireless network is firmly anchored in the computer market at home, and that means that people who buy the products can not be assumed to have any type of computer expertise; therefore, the products had better be extremely easy to configure and use.

The ease of use and security tend to be out of the other. So for wireless manufacturers, the reasoning is that, while the average Joe or Jane Smith house is nothing they really want to hide from the world, or the world would really care to learn about them, they will be very angry when obtaining they can practice their new wireless router quickly and without help does not work.
Unfortunately, the only way to make such a router without wireless idiot proof a default device settings complex that the user needs to use a parameter to one of the other wireless hardware change. By extension, this means that each wireless device can connect with said router with the default settings.
Again, this means that all wireless devices within range can connect to the new Smith router. Now, if you're Joe Smith, do you have something you want to hide?
There are a few reasons why wireless networks are less secure than their wired counterparts. First, there is the fact of their physical nature. They are wireless, transmission of a signal over an area. Each computer in this field with the right equipment can be considered "connected" to the network.
No similar access easier son to the network for everyone. This also makes it one of the most popular hacking tactics lot easier: packet sniffing or capturing network traffic for analysis for more information. Anyone coming within range can receive all traffic on the wireless network.
Second, the current methods of security technology without most available wireless, 802.11b, or easy to beat or difficult to implement.
The two most common methods for secure 802.11b WEP (Wireless Encryption Protocol) and MAC address filtering. WEP (64-bit or 128-bit) to protect wireless traffic using a key to encrypt the data shared between all computers that need access. WPA (WiFi Protected Access), which is now just beginning to emerge, treat all Weps gaps, so we'll go into a little later in the guide.
Unfortunately, WEP is quite easy to crack with the right software (freely available) and nature of wireless, it is easy for intruders enough encrypted traffic to a cracking software to capture something to work with.
11 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Difference between SAN and NAS:
SAN and NAS are two different storage systems; difference between them is the cost and complexity to use and operate the storage system.
• Network-attached storage is less costly than Storage area networks for its users to handle and operate.
• Network-attached storage uses TCP/IP network protocol and applications such as NFS or CIFS for file access.
• Managing Network-attached storage is a lot easier than Storage area networks.
• Storage area networks can cater to a large scale of users but Network-attached storage cannot but the change is coming.
• Network-attached storages are efficient for organizing and delivering data to clients over the network and data can be transferred over long distances efficiently.
• The major difference between the two storage networks is the cost and complexity to use and operate the storage system.
92 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Why CCNP Certification is the key to success in Networking Industry?
Here are 8 reasons why CCNP Certification is the key to success in Networking Industry:
1. Job availability is high
CCNP certification qualifies you for many different jobs such as IT manager; computers and information systems manager; network engineer; computer systems and network administrators; computer network architect or engineer projects, just to name a few.
2. Salary potential is high
Getting a CCNP certification will qualify you for an array of employment opportunities and the chance to earn a higher salary. According to research conducted by Cisco, individuals that are CCNP certified are earning at the least ten percent more than those employed at the same position, but without the certification.
3. Skill recognition
Obtaining CCNP certification is a way to have your advanced knowledge and skills in computer networking showcased. Being certified from a reputable organization like Cisco means that you will be recognized as a person that has received best training available in the industry.
4. You get an opportunity to keep up with the technology
We are all surrounded by technology. The best way to keep your career growing is to keep up with the current technology, which is exactly what a CCNA certified professional does.
5. You make your resume mouthwatering
Your resume speaks volumes about your education, skills and work experience. Once you see a CCNP certification on the resume you can expect the potential employers to believe that you are the kind of person who will carry on with the organization and will be an asset to it. Having such certifications in your resume also demonstrates your interest in learning and education.
6. You build up self confidence
A CCNP certification can work as a confidence and morale builder. As opposed to being afraid of applying for the job due to less education, you build up a confidence of knowing that you have a top-notch certification of an industry that is constantly growing.
7. Excellent job growth
Apart from helping you to find a very good job in computer networking, earning a CCNP certification puts you on the top of the list when it is time for promotions and career advancements. In case you want to switch the company, this certification will help you obtain a better job without having to start from entry level and working your way up gradually.
8. You make yourself eligible for more advanced certifications
Many Cisco certifications work as stepping stones for more advanced certifications, or at least provide the additional training necessary for acquiring additional certifications. This is certainly the truth with the CCNP certification. Obtaining a CCNP Certification prepares you for further education.
155 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Compare Windows 10 Editions
Here they are:
• Windows 10 Home, which is the most basic PC version.
• Windows 10 Pro, which has touch features and is meant to work on two-in-one devices like laptop/tablet combinations, as well as some additional features to control how software updates get installed — important in the workplace.
• Windows 10 Enterprise, which will have extra management features. We have some ideas of pricing here, as Microsoft is touting a $7/month Windows 10 Enterprise subscription for businesses that also includes a bunch of juicy, lucrative cloud services.
• Windows 10 Mobile for Smartphone’s.
• Windows 10 Mobile Enterprise, which is like the one above, but with more business management features.
• Windows 10 Education, which is optimized for schools.
• Windows 10 IoT Core, which is for robots, smart sensors, and — well, if you need it, you'll know it.
80 notes
·
View notes
Photo

How to disable Telnet on Cisco Switches and Routers?
Telnet protocol enables users to remotely connect to Cisco devices and it is enabled by default on most Cisco device. However it is not very secure to enable Telnet on your Cisco device as the login information and commands are sent in clear text and can be easily hacked. It is recommended to use SSH for remote access as this gives you secure, encrypted connection to your Cisco device.
To disable Telnet and enable only SSH connections:
First login to the Cisco Switch or Router and enter configuration mode
Router# config t
Router1(config)# line vty 0 4
Router1(config-line)# transport input ssh
This disables telnet and enables ssh on all the five VTYs (Virtual Terminal Lines)
On earlier platforms five simultaneous remote connections are allowed and these are vty 0 to 4. On IOS 12.2 and up 16 simultaneous connections are allowed. On these
Router1(config)# line vty 0 15
Router1(config-line)# transport input ssh
This disables telnet and enables ssh on all the 16 VTYs.
Sometimes you want to disable all forms of remote access (Telnet and SSH). For this
Router1(config)# line vty 0 4
Router1(config-line)# transport input none
Or
Router1(config)# line vty 0 15
Router1(config-line)# transport input none
After this you can only connect to your Cisco device by direct console connection.
To enable Telnet and SSH back
Router1(config)# line vty 0 4
Router1(config-line)# transport input telnet ssh
155 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Traditionally, enterprises prefer to tunnel all the wireless traffic from branch offices back to the central controller at the headquarters, in order to maintain unified security and access policies. However, this also increases bandwidth consumption and latency, decreasing overall network performance.
You now have a compromise. Different tunnel types can be configured independently for each SSID, providing maximum deployment flexibility.
For instance, the employee SSID can continue to tunnel all the traffic back to the controller, while the guest SSID can be configured with split tunnel – tunneling only authentication, management, and accounting traffic back to the controller, and allowing user data traffic to exit locally to the Internet.
With split tunnel, users get the best network experience, while the company can also reduce unnecessary bandwidth consumption from users that do not need such tight security policies.
345 notes
·
View notes
Photo
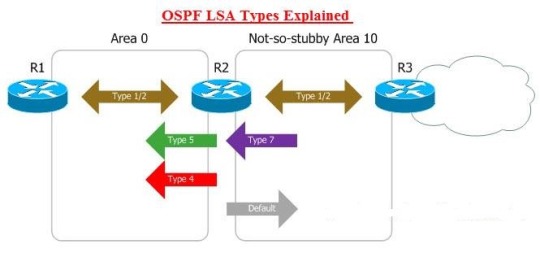
OSPF LSA Types Explained
• Router LSA (Type 1)— This LSA contains information about a router and the links that it has in an area. LSA type 1s are flooded only in that area. The LSA also tells whether the router is a stub or ASBR, or whether it has one end of a virtual link. OSPF represents these routes in the forwarding table with an O.
• Network LSA (Type 2)— This LSA is used for transit networks within an area. It describes the set of routers attached to a network. LSA Type 2s are not flooded outside an area. OSPF represents these routes in the forwarding table with an O.
• Summary LSAs for ABRs (Type 3)— These LSAs advertise internal networks to routers in other areas, called OSPF interarea routes. The LSA might contain a summary network or a single network. ABRs are the only router type that generates this LSA type. OSPF represents these routes in the forwarding table with an O IA.
• Summary LSA for ASBRs (Type 4)— These LSAs are used to advertise the location of an ASBR. Routers searching for a path to an external network use LSA Type 4 to determine the best next hop. OSPF represents these routes in the forwarding table with an O IA. This LSA type is hard to remember, so you can think of it as the "how do I get out here LSA."
• Autonomous system external LSAs (Type 5)— Type 5 LSAs are used to advertise routes redistributed into OSPF. These routes are called OSPF external routes, and they are flooded throughout the entire OSPF autonomous system, except for stub, totally stubby, and NSSA areas. OSPF represents these routes in the forwarding table with an O E1 or O E2, depending on the route.
• NSSA external LSA (Type 7)— This type of LSA is generated for the external routes redistributed into a not-so-stubby area. They are flooded throughout the NSSA area. When they hit an ABR, the ABR advertises them as Type 5 LSAs into Area 0. Type 7 LSAs never leave the NSSA area. OSPF represents these routes in the forwarding table with an O N1 or O N2, depending on how the route was redistributed.
100 notes
·
View notes
Photo

TOP 15 CCNP Job Interview Questions & Answers
Q1. Define the criteria for best path selection of a router?
Ans. A router’s routing table contains only best route. To select a route as best, a router considers the following parameters;
• Longest prefix match
• Minimum AD (administrative distance)
• Lowest metric value
Q2. Can we use OSPF without backbone area?
Ans. Yes, but it will be limited to intra-area (same area) communication. By default, Inter-area communication is not possible without backbone area.
Q3. What do you mean by OSPF transit area?
Ans. A transit area is the area that has a virtual link connecting two or more ABRs attached to this area.
Q4. What is the difference between an OPPF neighbor and an adjacent neighbor?
Ans. Neighbors are the routers that are in the same area and exchange hello packets, but not LSA information. Adjacent routers are routers that have fully exchanged their LSA information and are stable.
If OSPF state is in 2WAY/DROTHER, it means a neighbor relationship and, if the state is FULL/DR or FULL/BDR, it means that the adjacency is formed.
Q5. What is the difference between standard and extended ACL?
Ans. Standard ACLs are source-based, whereas extended ACLs are source- and destination-based. Standard ACLs can only filter layer 3 network traffic, while extended ACLs can be used to filter layer 3 and layer 4, as well.
Q6. What is the use of distribute-list?
Ans. To filter a routing database, we use distribute-list, which can be applied over most routing protocols. This means that, If you don’t want any specific network in your routing table, then you can use distribute-list
Q7. What are broadcast domains?
Ans. A broadcast domain defines a group of devices that receive each others' broadcast messages. As with collisions, the more broadcasts that occur on the network, the slower your network will be. This is because every device that receives a broadcast must process it to see if the broadcast is intended for it.
Q8. What is the difference between a routing protocol and a routed protocol?
Ans. Routing protocols determine how to route traffic to the best location of a routed protocol. Examples of routing protocols are RIP, EIGRP, OSFP, and BGP. Examples of routed protocols are IP and IPX.
Q9. What is the destination address of broadcast frames?
Ans. The destination address of broadcast frames (Layer 2 broadcast addresses) is FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF, or all 1s in binary.
Q10. What is the Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP)?
Ans. STP is a loop-prevention bridge-to-bridge protocol. Its main purpose is to dynamically maintain a loop-free network. It does this by sending out Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs), discovering any loops in the topology, and blocking one or more redundant links.
Q11. In spanning tree, what is a Bridge ID (BID)?
Ans. A BID is an 8-byte field that is composed of the bridge's 6-byte MAC address and a 2-byte bridge priority.
Q12. In.In spanning tree, what is path cost?
Ans. Path cost is a calculation to determine the link's bandwidth. It is a value assigned to each port that is based on the port's speed.
Q13. What is the STP blocking state?
Ans. When a switch starts, all ports are in the blocking state. This is to prevent any loops in the network. If there is a better path to the root bridge, the port remains in the blocked state. Ports in the blocked state cannot send or receive traffic, but they can receive BPDUs.
Q14. What is the STP listening state?
Ans. Ports transition from a blocked state to a listening state. In this state, no user data is passed. The port only listens for BPDUs. After listening for 15 seconds (if the bridge does not find a better path), the port moves to the next state, the learning state.
Q15. What is the hello time in STP timers?
Ans. The hello time is the time interval between the sending of BPDUs. The default time is 2 seconds.
160 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Common Inter-VLAN Routing Problems
• Missing VLAN
o VLAN might not be defined across all the switches.
o VLAN might not be enabled on the trunk ports.
o Ports might not be in the right VLANs
• Layer 3 interface misconfiguration
o Virtual interface might have the wrong IP address or subnet mask
o Virtual interface might not be up
o Virtual interface number might not be matched with the VLAN number
o Routing has to be enabled to route frames between VLAN.
o Routing might not be enabled
• Routing protocol misconfiguration
o Every interface or network needs to be added in the routing protocol. The new interface might not be added to the routing protocol. Routing protocol configuration is needed only if VLAN subnets need to communicate to the other routers.
• Host misconfiguration
o Host might not have the right IP or subnet mask
57 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Top 15 Interview Questions with Answers for Network Administrators
Q-1: What is Active Directory?
Active Directory provides a centralized control for network administration and security. Server computers configured with Active Directory are known as domain controllers. Active Directory stores all information and settings for a deployment in a central database, and allows administrators to assign policies and deploy and update software.
Q-2: What is NetBIOS protocol?
NetBIOS (Network Basic Input/Output System) Protocol allows applications on separate computers to communicate over a LAN. It runs over TCP/IP giving each computer in the network a NetBIOS name and IP address. E.g. It can be used for computers running Windows 2000 (or before) to join a computer network running Windows 2000 (or later).
Q-3: What are FMSO Roles?
Fsmo roles are server roles in a Forest
There are five types of FSMO roles
1-Schema master
2-Domain naming master
3-Rid master
4-PDC Emullator
5-Infrastructure master
Q-4: What is LMHOSTS file?
It’s a file stored on a host machine that is used to resolve NetBIOS to specific IP addresses.
Q-5: What is ARP?
ARP is used to resolve a known IP address to a MAC address. For a host to communicate with another host, it must know the MAC address of the destination host (if they are on the same network) or next-hop router. This is the reason for ARP.
Q-6: What is APIPA?
(Automatic Private IP Addressing) The Windows function that provides DHCP auto configuration addressing. APIPA assigns a class B IP address from 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255 to the client when a DHCP server is either permanently or temporarily unavailable. Designed for small non-routable networks, if a DHCP server becomes available later, the APIPA address is replaced with one from the DHCP server. For example, when a Windows Vista machine starts up, it waits only six seconds to find a DHCP server before assigning an IP from the APIPA range. It then continues to look for a DHCP server. Previous versions of Windows looked for a DHCP server for up to three minutes. See DHCP auto configuration addressing, DHCP and private IP address.
Q-7: What ports are used by DHCP and the DHCP clients?
Requests are on UDP port 68, Server replies on UDP 67
Q-8: DNS zones - describe the differences between the 4 types.
i)Forward Lookup Zones :-
This zone is responsible to resolve host name to ip.
ii)Reverse Lookup Zones :-
This zone is responsible to resolve ip to host name.
iii)Stub Zone :-
Stubzone is read only copy of primary zone.but it contains
only 3 records the SOA for the primary zone, NS record and a Host (A) record.
Q-9: DNS record types - describe the most important ones.
Type of Record What it does
A (Host) Classic resource record. Maps hostname to IP(ipv4)
PTR Maps IP to hostname (Reverse of A (Host)
AAAA Maps hostname to ip (ipv6)
Cname Canonical name, in plain English an alias.such as Web Server,FTP Server, Chat Server
NS Identifies DNS name servers. Important for forwarders
MX Mail servers, particularly for other domains.MX records
Q-10: What is Domain Controller?
A domain controller (DC) or network domain controller is a Windows-based computer system that is used for storing user account data in a central database. It is the center point of the Windows Active Directory service that authenticates users, stores user account information and enforces security policy for a Windows domain.
A domain controller allows system administrators to grant or deny users access to system resources, such as printers, documents, folders, network locations, etc., via a single username and password.
Q-11: What is Group Policy?
Group Policy allows you to implement specific configurations for users and computers. Group Policy settings are contained in Group Policy objects (GPOs), which are linked to the following Active Directory service containers: sites, domains, or organizational units (OUs).
Q-12: What are GPOs (Group Policy Objects)?
A Group Policy Object (GPO) is a collection of settings that control the working environment of user accounts and computer accounts. GPOs define registry-based policies, security options, software installation and maintenance options, script options, and folder redirection options.
Q-13: Where is the AD database stored?
The AD database is stored in C:\Windows\NTDS\NTDS.DIT.
Q-14: What is the SYSVOL folder?
The SYSVOL folder stores the server copy of the domain’s public files that must be shared for common access and replication throughout a domain.
All AD databases are stored in a SYSVOL folder and it’s only created in an NTFS partition. The Active Directory Database is stored in the %SYSTEM ROOT%NDTS folder.
Q-15: What do Forests, Trees, and Domains mean?
Forests, trees, and domains are the logical divisions in an Active Directory network.
A domain is defined as a logical group of network objects (computers, users, devices) that share the same active directory database.
A tree is a collection of one or more domains and domain trees in a contiguous namespace linked in a transitive trust hierarchy.
At the top of the structure is the forest. A forest is a collection of trees that share a common global catalog, directory schema, logical structure, and directory configuration. The forest represents the security boundary within which users, computers, groups, and other objects are accessible.
94 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Switch VS Router
106 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Cisco Delivers One of World's Largest Wi-Fi Networks at 2014 Mobile World Congress
Network Supported Nearly 81,000 Connections and Carried 19 Terabytes of High-Speed Data in Four Days, Emphasizing the Growing Importance of Wi-Fi to Cellular
SAN JOSE, Calif. – March 12, 2014 – Cisco today announced it worked with Fira de Barcelona and the GSMA to successfully provide one of the world's largest carrier-grade Wi-Fi networks at the GSMA's recent Mobile World Congress 2014 at Fira Gran Via in Barcelona.
During the event, more than 80,000 attendees had access to free Wi-Fi at Fira Gran Via and over the four days nearly 81,000 Internet-connected devices generated a total of 19.1 terabytes of traffic.
A preliminary breakdown of the unprecedented volume of data exchanged revealed a 300 per cent year on year increase in the amount of traffic at the event, reflecting the performance and reliability of the high-density Wi-Fi network enabled by Cisco.
Attendees predominantly used the Wi-Fi network to enable productivity and to stay in touch with their social networks; 33 percent of the traffic was used for highly-secure connections to business services such as email, closely followed by web browsing, Skype, Google Services and Facebook.
Fast Facts on the Cisco-based Mobile World Congress Wi-Fi network
• 80,880 Internet-enabled devices were connected, doubling the number from the 2013 Mobile World Congress;
• 1.2 gigabytes per second of peak Internet traffic;
• 19.1 terabytes of data – offloading 3G/4G traffic from mobile networks to provide an improved, integrated mobile experience for attendees;
• Five gigahertz (GHz) to 2.4 GHz ratio was 58 percent to 42 percent -- indicating a shift to higher adoption of five GHz devices;
• 280 gigabytes uploaded and transmitted via a single access point in the Mobile World Congress Media Village on Monday, Feb. 24, 2014; and
• By 10:00 a.m. on Feb. 24, 2014, the number of connections had surpassed the total number of connections on last year's network, ultimately reaching 22,126 peak-concurrent connections.
Key Highlights
• Cisco worked with Fira de Barcelona to install a permanent Wi-Fi network covering 240,000 square meters of the Fira's Gran Via venue, the site of the annual Mobile World Congress.
• The Cisco Service Provider Wi-Fi solution allowed the GSMA to offer free high-speed Wi-Fi service to Mobile World Congress attendees at Fira Gran Via and allowed Fira to offer exhibitors Wi-Fi services in the eight exhibit halls.
• High-performance results demonstrate that carrier-grade Wi-Fi can complement cellular services in even the toughest environments. Delivering high-density Wi-Fi service in a venue as large as the Fira requires precise planning, monitoring and management. Cisco worked closely with the Fira in the months prior to the event to prepare the network for the four-day conference and exhibition.
• Cisco also worked with AT&T and Accuris Networks to provide highly-secure and seamless authentication on the Wi-Fi network with a Hotspot 2.0 next-generation network allowing show attendees to securely roam onto the Wi-Fi network as easily as they do on the cellular network.
138 notes
·
View notes
Photo

PRI vs. SIP Trunking
What are the advantages of PRI versus SIP Trunks?
1. Relatively little equipment between the PTSN and the PBX. Less to break or go wrong.
2. Simple to set up. No need for QoS, routing, authentication, etc. Of course if you only know IP, SIP is easier, but if you learn both, ISDN is easier.
3. If compared to SIP over internet, PRI has guaranteed quality. Granted, SIP *can* have just as good (and better) quality, just not guaranteed if done over the internet (it can be guaranteed over a private circuit).
4. Less latency/delay so there is less "talk-over".
5. FAX, high speed modem, TTY, etc, pass-through actually works. (it *can* work over SIP, but Asterisk just isn't quite there yet)
What are the advantages of SIP Trunks versus PRI?
1. Cost - Inexpensive. (at least SIP-over-internet)
2. Easy and quick to scale if you have bandwidth.
3. Great for disaster recovery if using SIP over internet.
4. Very cheap to get "local" numbers from all around the world.
5. If using SIP over internet, easy to compare provider.
60 notes
·
View notes
Photo

BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Basics
• The current version of BGP is BGP version 4, based on RFC4271.
• BGP is the path-vector protocol that provides routing information for autonomous systems on the Internet via its AS-Path attribute.
• BGP is a Layer 4 protocol that sits on top of TCP. It is much simpler than OSPF, because it doesn’t have to worry about the things TCP will handle.
• Peers that have been manually configured to exchange routing information will form a TCP connection and begin speaking BGP. There is no discovery in BGP.
• Medium-sized businesses usually get into BGP for the purpose of true multi-homing for their entire network.
• An important aspect of BGP is that the AS-Path itself is an anti-loop mechanism. Routers will not import any routes that contain themselves in the AS-Path.
91 notes
·
View notes
Photo

10 Things You Should Do Right After Installing Windows 10
1. Turn on System Restore
If it’s off, turn it back on right away. System Restore is the most effective way to save your day when it turns bad to you.
2. Reduce notifications
Being notified what’s going on is nice but having too much will get you distracted. Heading over to Settings → System → Notification & actions to turn off those unnecessary ones.
3. Declutter your taskbar
If you are like me, you would need all the space you can get on the Taskbar as you will be pinning apps down there as much as you can. If Search box takes too much space, let’s make it either smaller or disappear for good, along with the Taskview icon.
4. Decide what to sync
By default, windows 10 syncs all of your settings, themes, passwords, and other preferences with your Microsoft Account to bring a consistent environment for you if you log in the same account on different computers. But if this is not your thing or you just don’t want everything sync’d across board, Settings → Accounts → Sync your settings is the place to go.
5. Decide which browser to use
If Microsoft Edge is yet good enough to be your primary browser for internet, it’s time to install Chrome or Firefox on your Windows 10. Otherwise, let’s customize your Edge a little to make it more personal and easy to use, things like theme, default search engine, start page, home page, bookmarks, etc.
6. Set default apps
If you decided to keep using Chrome or Firefox as your browser or Adobe as default PDF reader, you need to set them as default apps in Settings → System → Default apps.
7. Check Windows Defender
To make sure 1) real-time protection is on; and 2) version info is up to date. It’s the built-in anti-virus system that comes with Windows 10 so you save money on something else. Keep it running in good shape is important to your system.
8. Setting up OneDrive
Since OneDrive is no longer using Online-Only mode, it’s important to know that if you have a large OneDrive you need to pay attention to your Internet usage. You don’t want to throttle your network just because you are downloading your whole OneDrive onto your new Windows 10 computer. Check the following post for more details.
9. Sign-in options
Windows 10 has more sign-in options than any previous Windows. In addition to Password, Pin, Picture Password, you now can use your face to sign in using Microsoft’s Hello face recognition technology. It’s pretty cool but it also requires a 3-D depth camera to be functional. Unfortunately, not all laptops or tablets have that equipped at the moment.
10. Decided how Windows Updates delivers
Unless you are behind a WSUS inside a corporate network, your default Windows Update is set to Updates from more than one place, meaning that you are not only getting the updates from Microsoft, computers on the local network, and on the internet, but also are acting as part of Windows Update network sending updates to other computers on the local network or on the internet.
148 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Following are Some of the Most Common SHOW commands:
• show version—Displays the configuration of the system hardware, the software version, the names and sources of configuration files, and the boot images.
• show running-config—Displays the router configuration currently running.
• show startup-config—Displays the router configuration stored in NVRAM.
• show interfaces—Displays statistics for all interfaces configured on the router or access server. The resulting output varies, depending on the network for which an interface has been configured.
• show controllers—Displays statistics for interface card controllers.
• show flash—Displays the layout and contents of flash memory.
• show buffers—Displays statistics for the buffer pools on the router.
• show memory summary—Displays memory pool statistics and summary information about the activities of the system memory allocator, and gives a block-by-block listing of memory use.
• show process cpu—Displays information about the active processes on the router.
• show stacks—Displays information about the stack utilization of processes and interrupt routines, and the reason for the last system reboot.
• show cdp neighbors—Provides reachability information for directly connected Cisco devices. This is an extremely useful tool for determining the operational status of the physical and data link layers. Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) is a proprietary data link layer protocol.
• show debugging—Displays information about the type of debugging that is enabled for your router.
84 notes
·
View notes