Photo
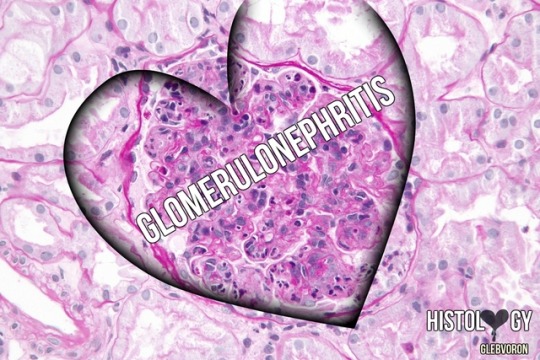
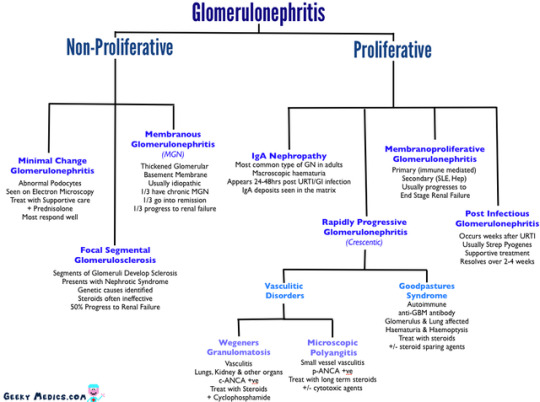
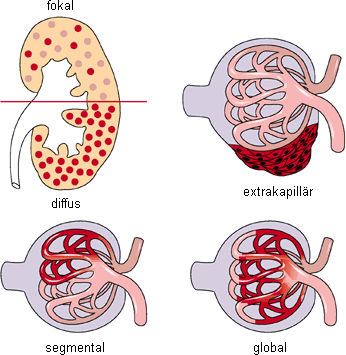
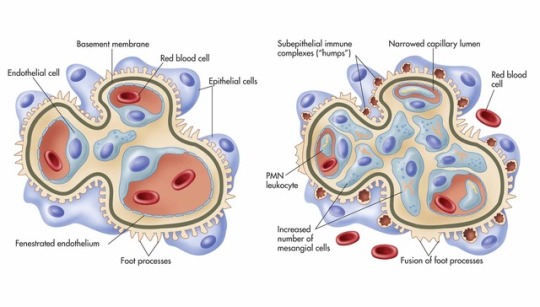
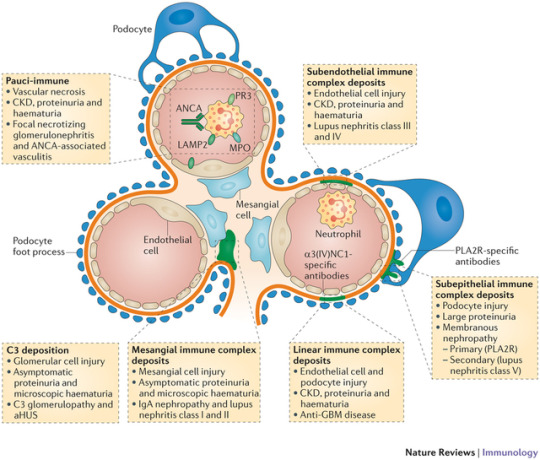
Glomerulonephritis.
Glomerulonephritis (GN), also known as glomerular nephritis, is a term used to refer to several kidney diseases (usually affecting both kidneys). Many of the diseases are characterised by inflammation either of the glomeruli or of the small blood vessels in the kidneys, hence the name, but not all diseases necessarily have an inflammatory component.
As it is not strictly a single disease, its presentation depends on the specific disease entity: it may present with isolated hematuria and/or proteinuria (blood or protein in the urine); or as a nephrotic syndrome, a nephritic syndrome, acute kidney injury, or chronic kidney disease.
They are categorized into several different pathological patterns, which are broadly grouped into non-proliferative or proliferative types. Diagnosing the pattern of GN is important because the outcome and treatment differs in different types. Primary causes are intrinsic to the kidney. Secondary causes are associated with certain infections (bacterial, viral or parasitic pathogens), drugs, systemic disorders (SLE, vasculitis), or diabetes.
#Histology#histo#patophisiology#biology#immunology#immunopathology#path#pathomorphology#pathohisto#pathtumblr#medicine#medstudent#medblr#phisiology#Illustration#study#pathology#histoblr#histoworld
29 notes
·
View notes
Photo
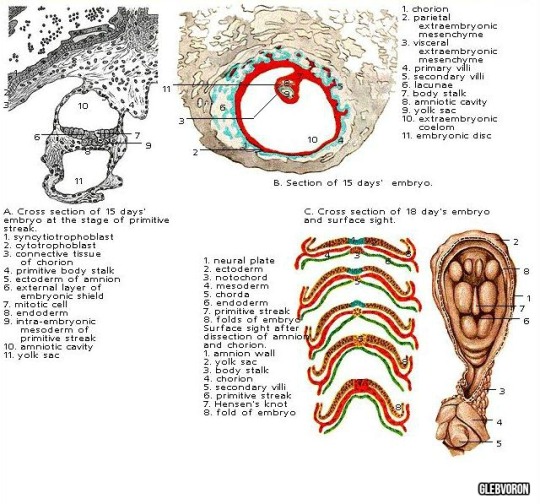
VI-VIII levels (13-18 days). The emergence of the primary node, the primitive streak, the yolk sac.
i♡embryo
#embryology#embryo#iheartembryo#embryotumblr#Histology#ihearthisto#histologyworld#biology#medicine#medstudent#Illustration#study#Bio#microscope#micro#histoblr#histotumblr
11 notes
·
View notes
Photo
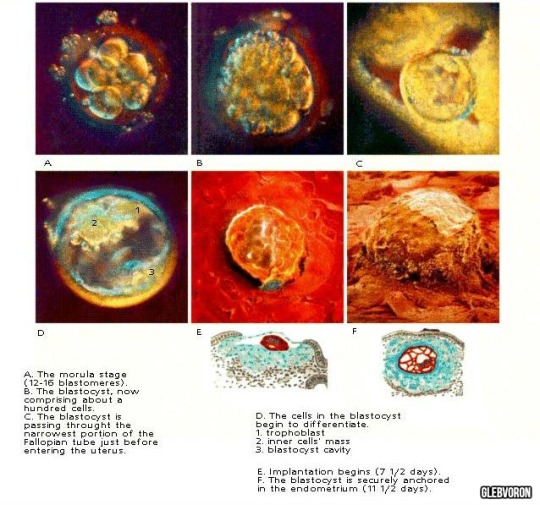
IV level (4-7 days) - V level (7-12 days): blastocyst.
i♡embryo
#embryology#iheartembryo#embryotumblr#embryo#Bio#biology#Histology#histo#medblr#medstudent#study#Illustration#ihearthisto#histologyworld#medtumblr#microscope#micro#histotumblr#histoblr
22 notes
·
View notes
Photo
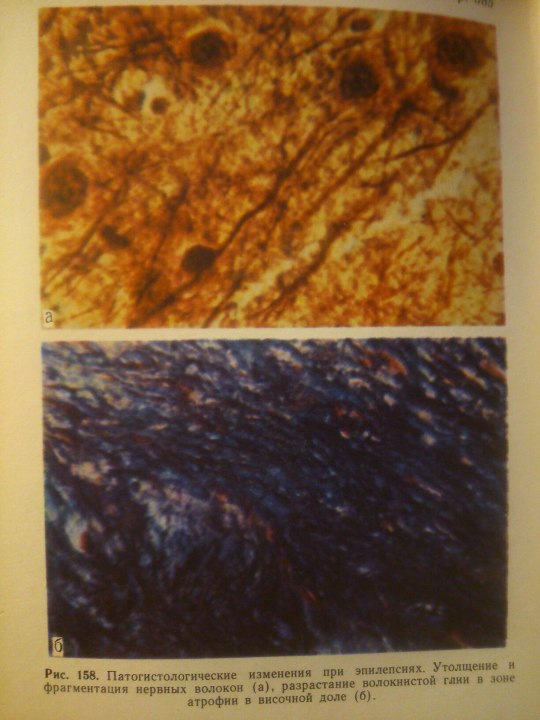
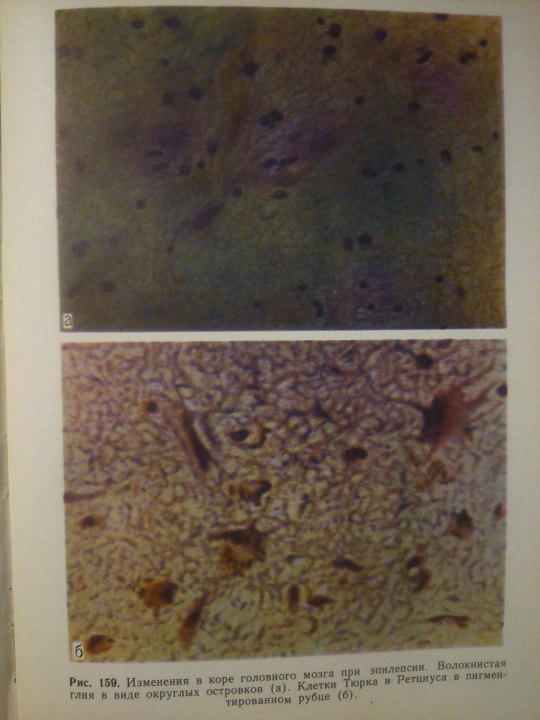
Epilepsy.
#Histology#histo#ihearthisto#path#pathology#pathomorphology#pathtumblr#Neuroscience#science#books#histologyworld#histotumblr#histoblr#neurology#morphology#medicine#medblr#medstudent#study#Illustration
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo
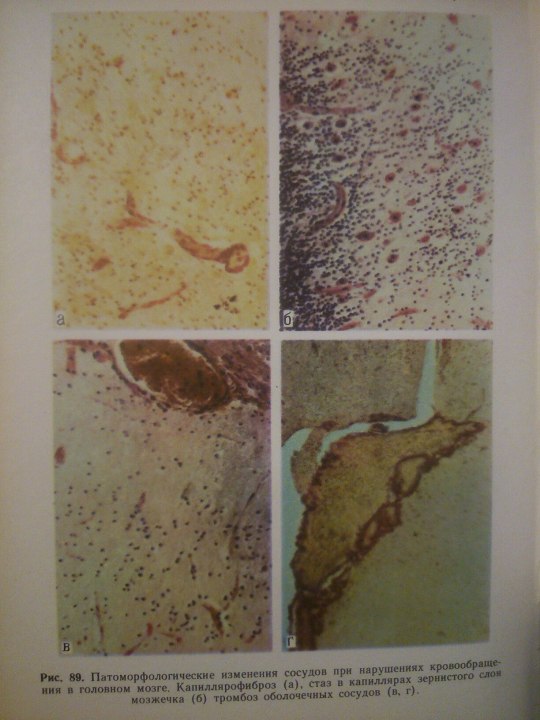
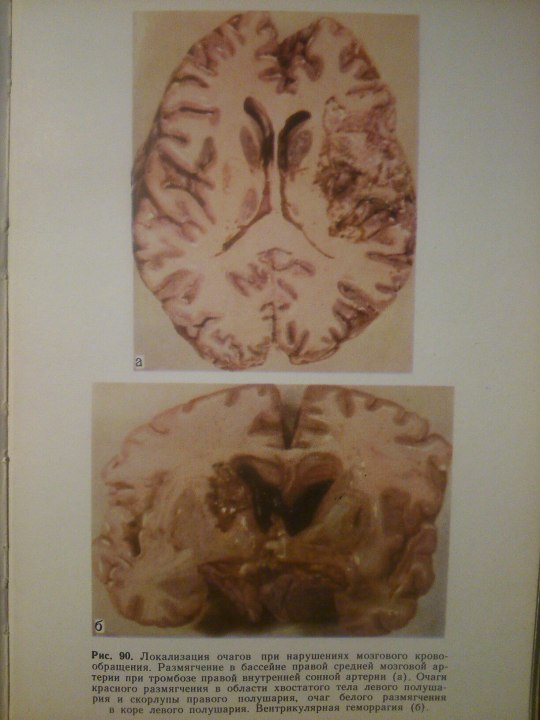
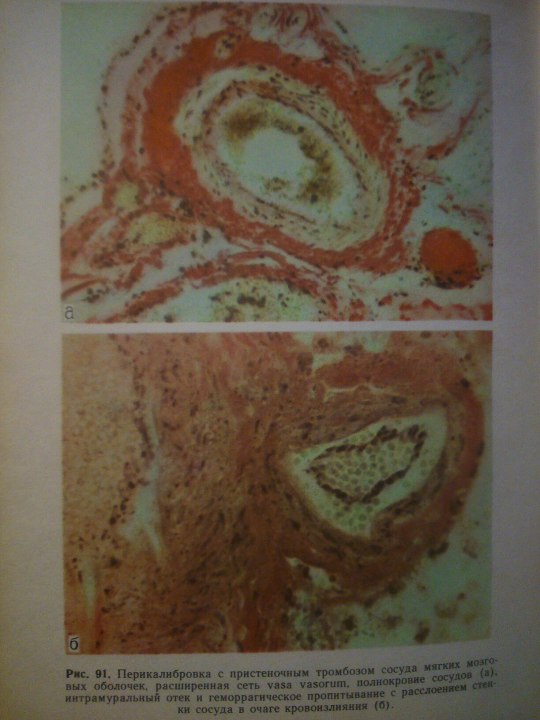
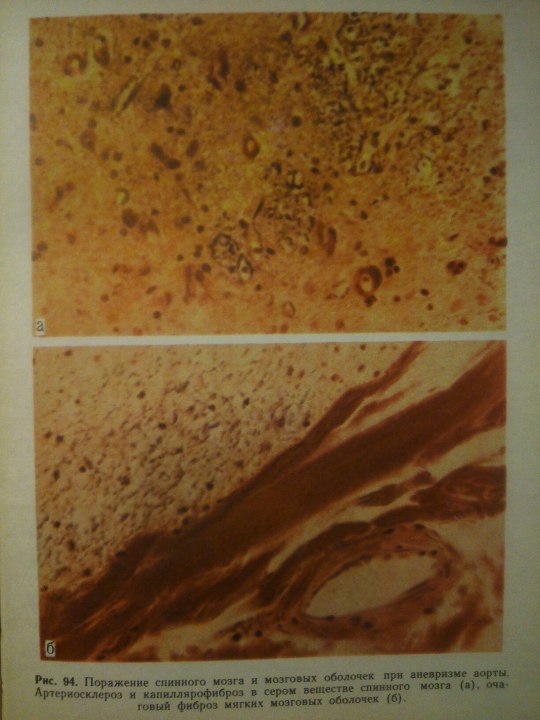
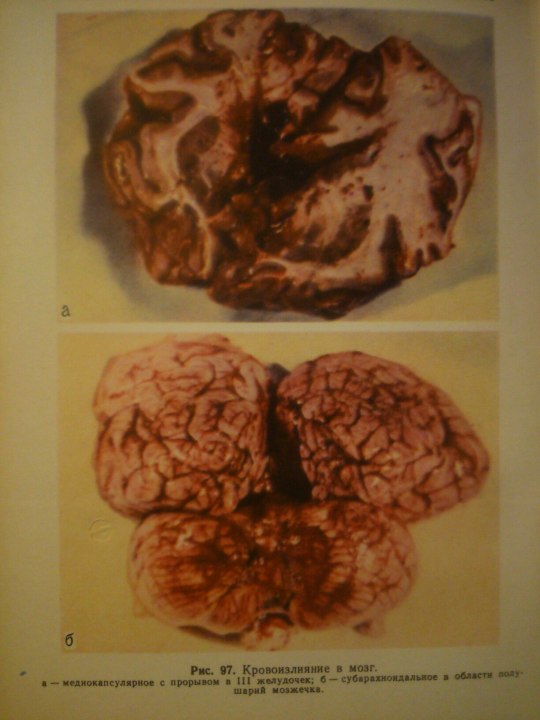
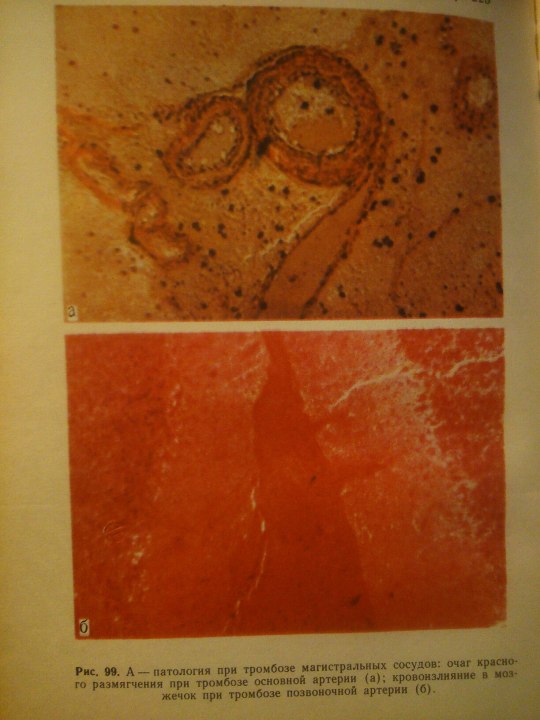
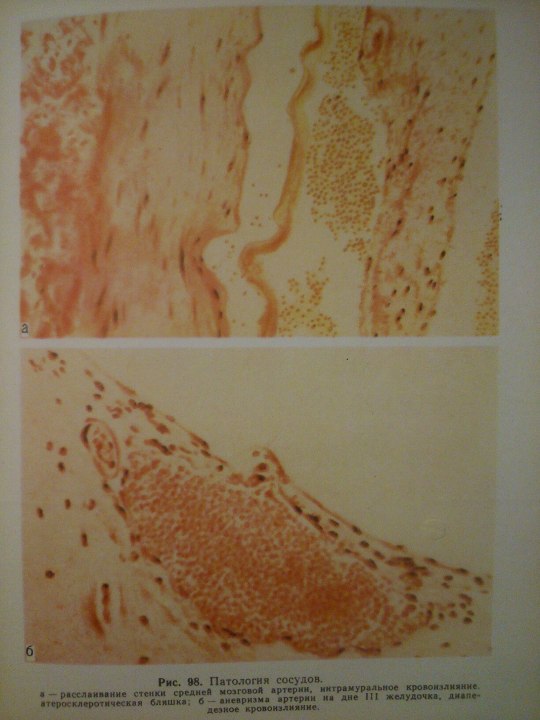
Cerebrovascular Diseases.
From: Н.К.Боголепов - Клинические лекции по невропатологии.
#Histology#histo#ihearthisto#pathology#pathtumblr#medicine#medstudent#medtumblr#medblr#histoworld#pathomorphology#morphology#Neuroscience#science#books#Blood#histolove#pathohisto#path#neurology
14 notes
·
View notes
Photo
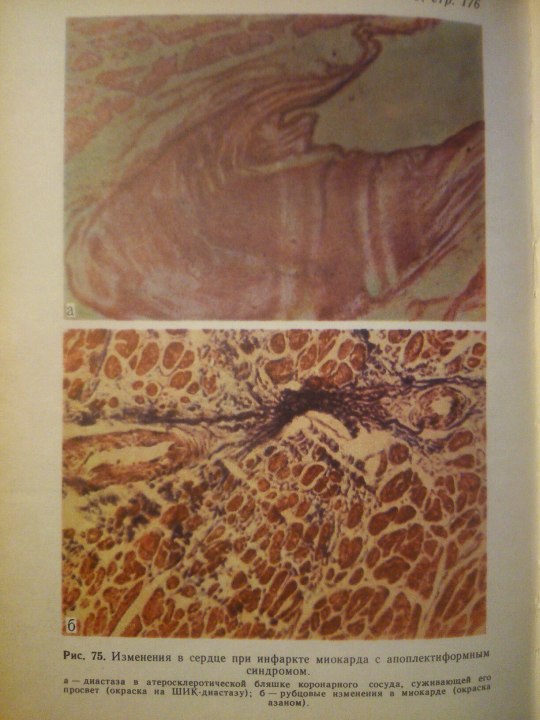
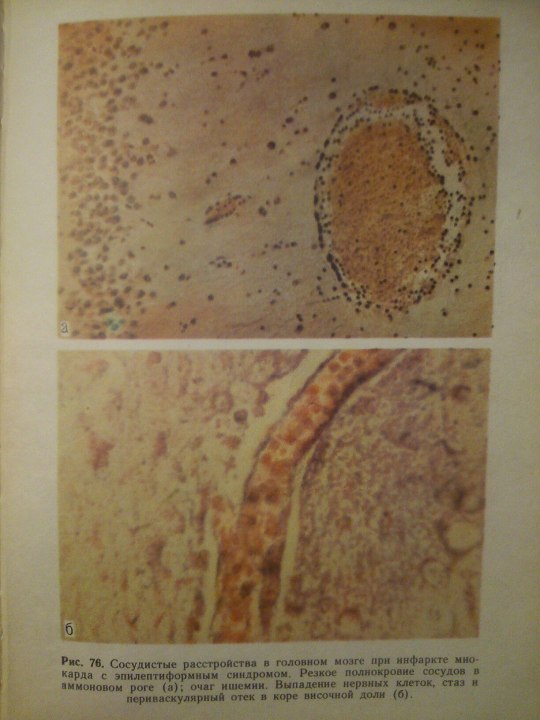
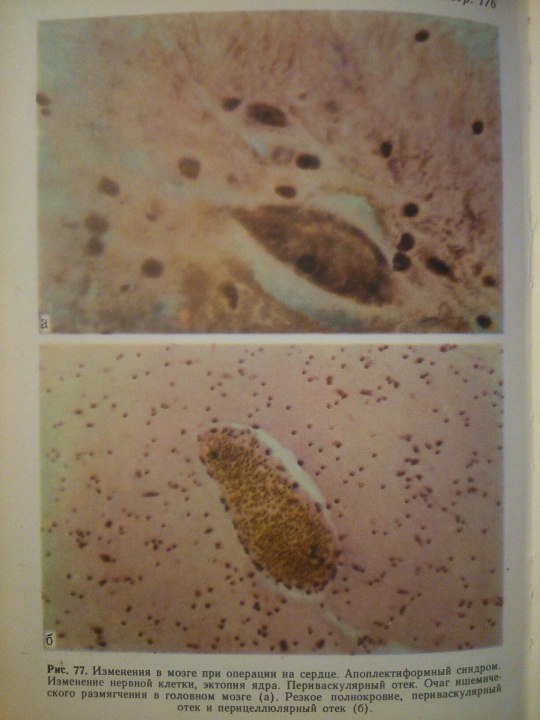
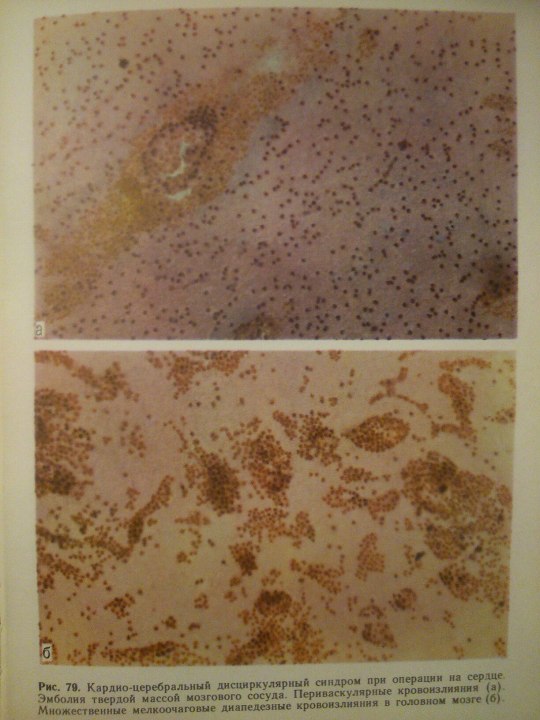
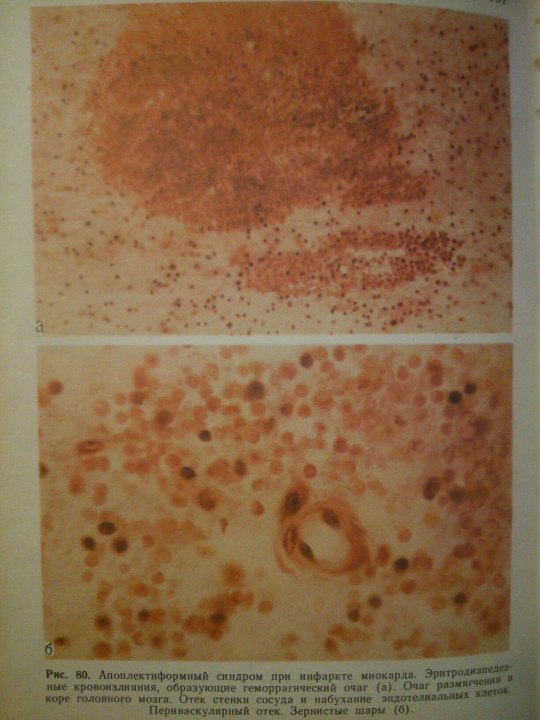
Эпилептиформный синдром (syndromum epileptiforme) — общее название пароксизмальных расстройств (припадков), являющихся одним из проявлений органического процесса в головном мозге. Развивается при опухолях, абсцессе, туберкуломе, гумме головного мозга, нарушении мозгового кровообращения, паразитарных болезнях, менингоэнцефалитах, арахноидите, а также при последствиях перинатальных поражений головного мозга, ранних нейроинфекциях и травмах (резидуально-органический Э. с.). Возникновение Эпилептиформного синдрома свидетельствует об утяжелении основного заболевания. Особенности клинических проявлений судорожного припадка нередко отражают локализацию очага поражения в головном мозге.
From: Н.К.Боголепов - Клинические лекции по невропатологии.
#Histology#histo#Neuroscience#neurophisiology#morphology#pathology#path#neurology#book#books#science#ihearthisto#histoblr#medstudent#medicine#medtumblr#medblr#histotumblr#pathomorphology#pathohisto#study
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo
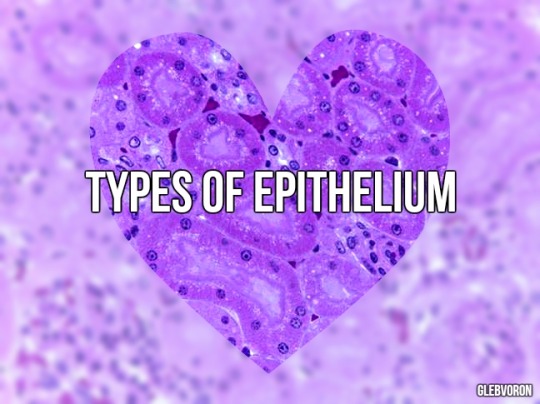
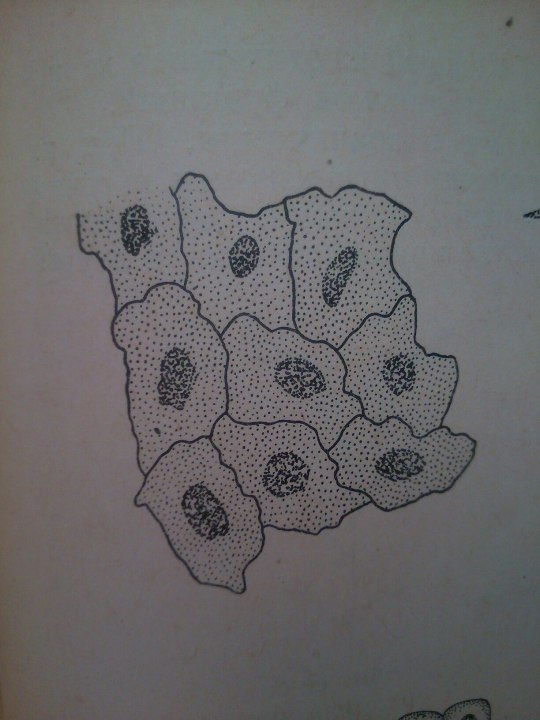
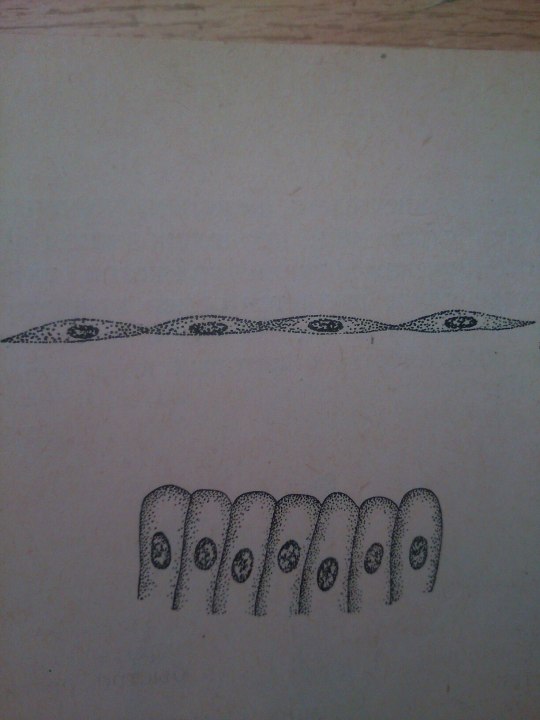
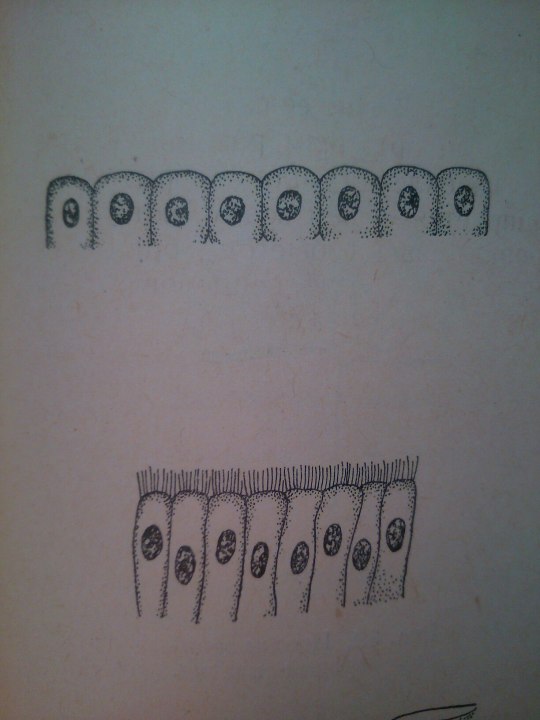
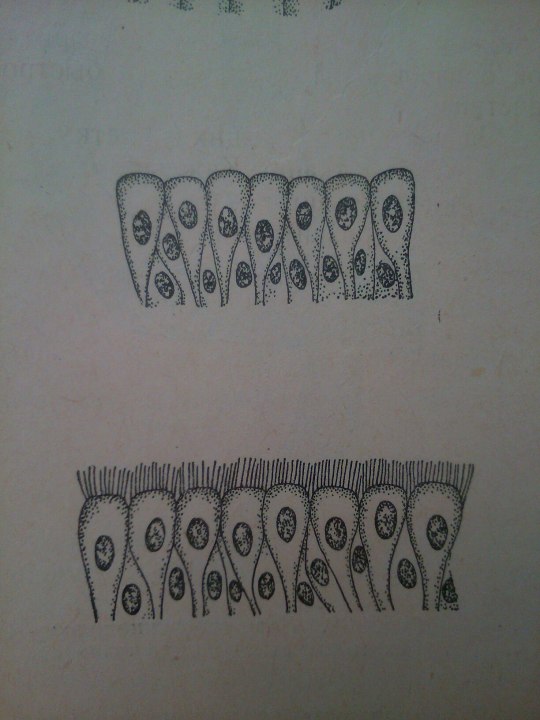
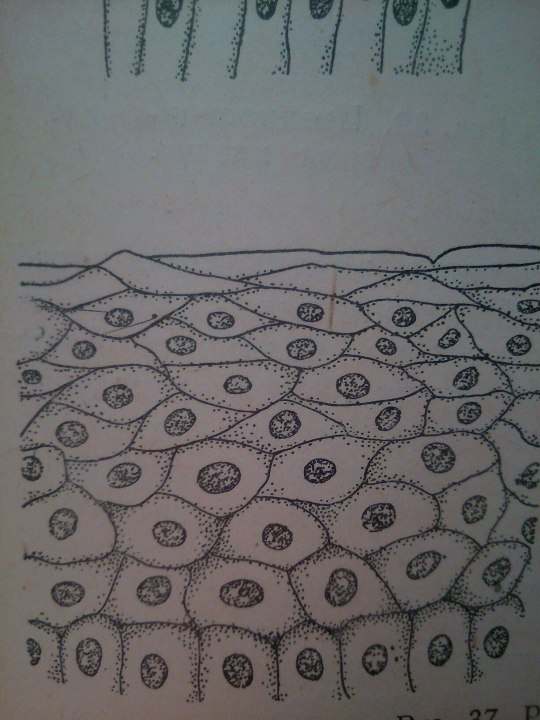
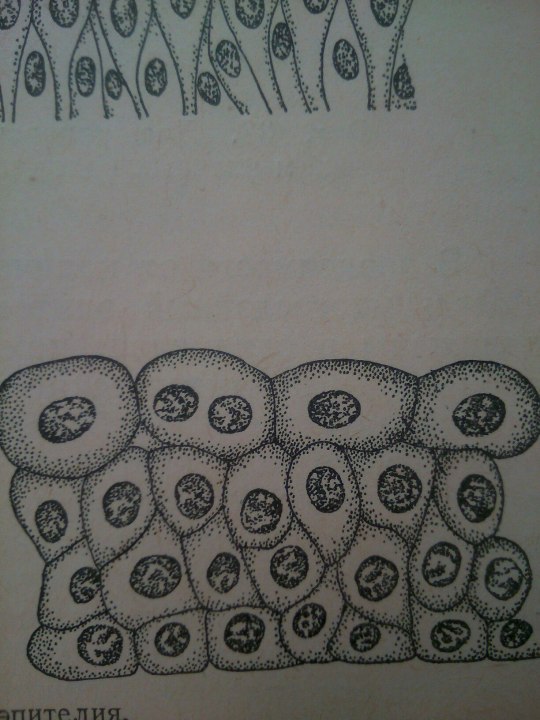
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue. The other three types are connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of blood vessels and organs throughout the body.
From: Общая биология под ред. Маховко В.В. (1950).
#Histology#histo#ihearthisto#histologyworld#histoworld#histolove#medicine#medstudent#study#book#books#histoblr#histotumblr#medblr#medtumblr
27 notes
·
View notes
Photo
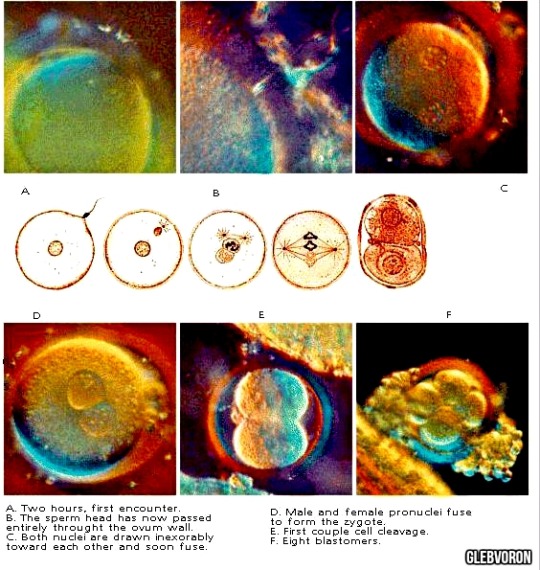
I-III levels. Fertilization and germ cells of humans.
i♡embryo
#embryology#cytology#cell#cells#study#medicine#medblr#medtumblr#biology#Bio#embryo#ihearthisto#iheartembryo#embryotumblr#science#beauty#beautiful#illustration#medstudent#Histology
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo
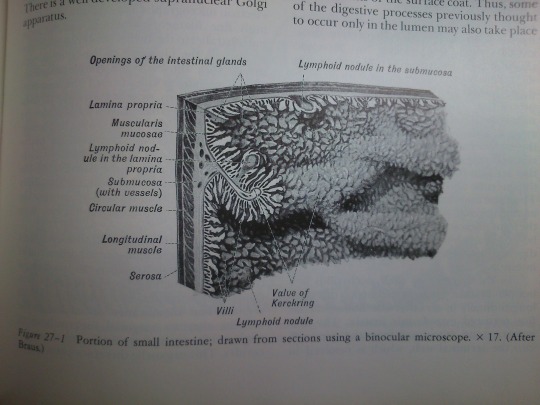
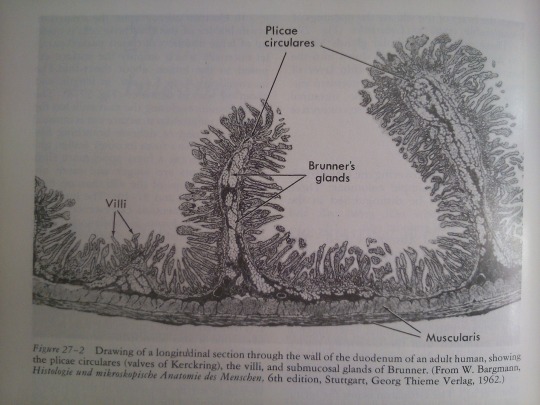
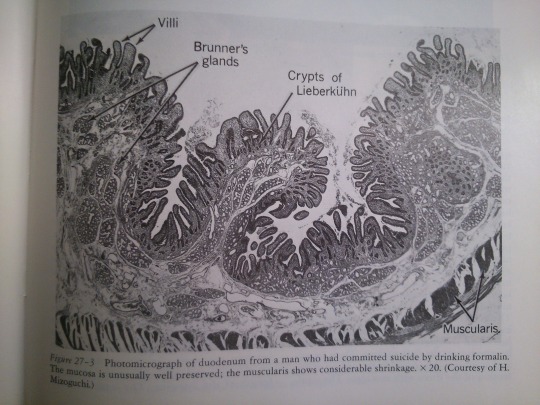
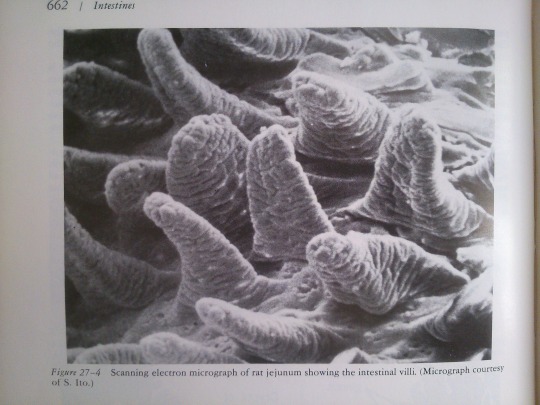
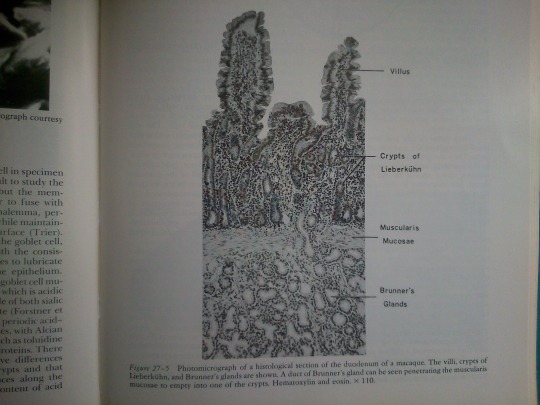
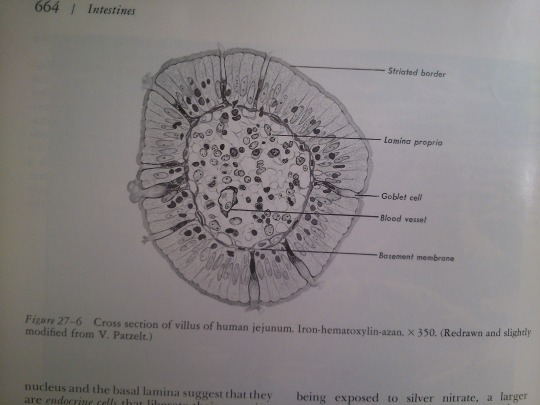
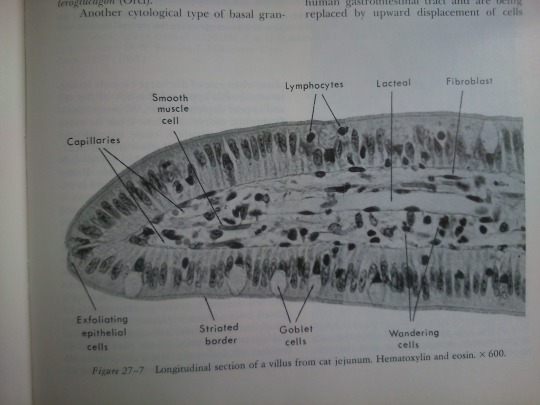
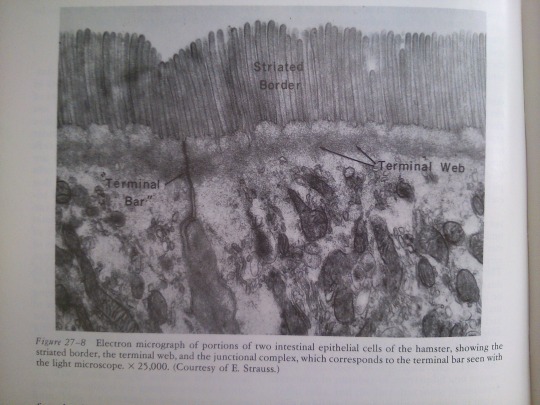
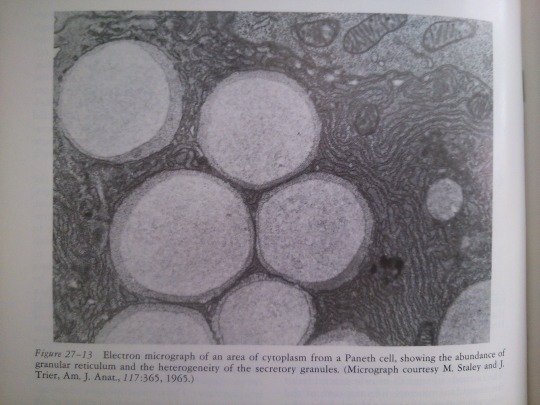
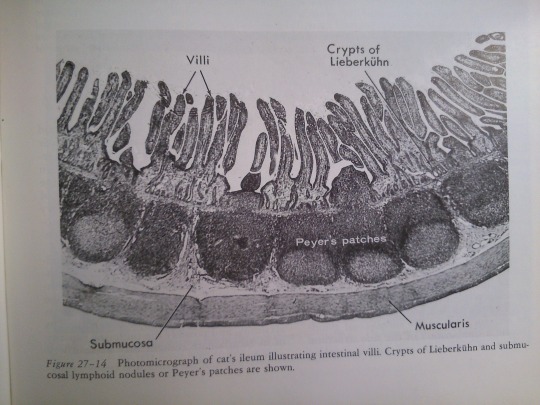
Part 27: Intestines.
From: Bloom’s Histology (1975).
i♡histo
#Histology#medicine#ihearthisto#histo#cytology#science#gastroenterology#histoworld#book#books#illustration#histolove#histoblr#histotumblr#medstudent#medtumblr#medblr
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo
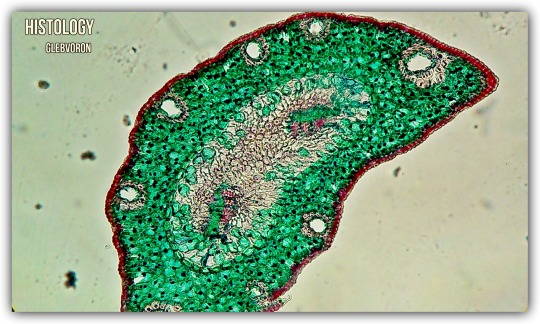
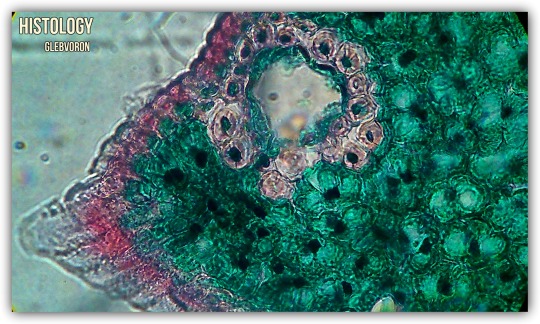

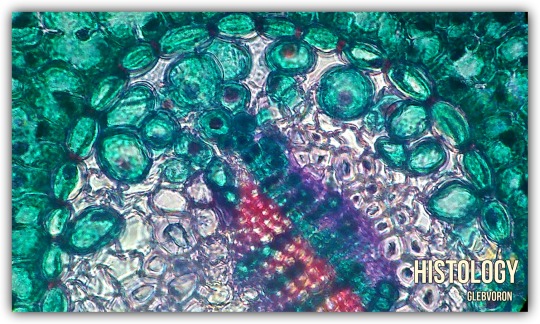
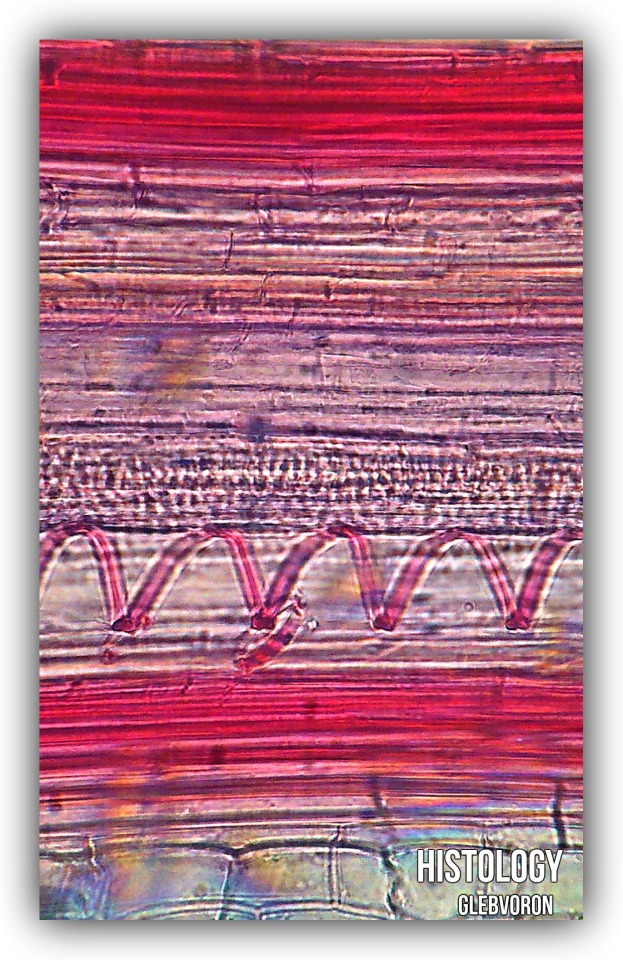
Needle of the pine.
Paint: saftanin-green.
#histochemistry#histo#histolove#histoworld#histoblr#histotumblr#botanique#botany#botanica#Histology#study#biology#Bio#micro#microscope#green#beauty
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Tilia.
#Histology#histo#ihearthisto#biology#Bio#histolove#histologyworld#botanique#botany#botanica#histotumblr#beauty
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo
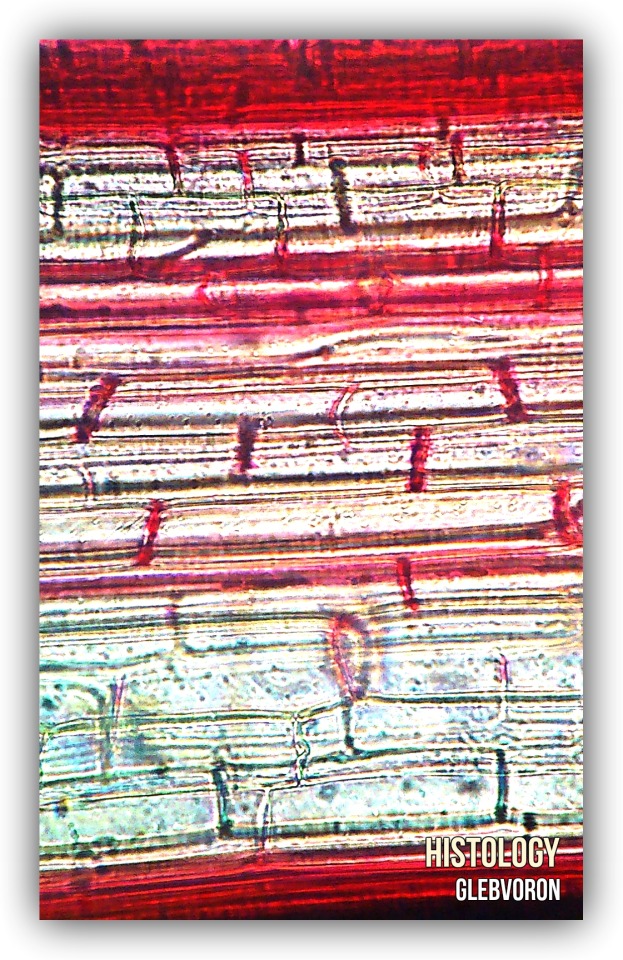

Cornstalk. Zea Mays.
#Histology#histo#histolove#botanique#botany#ihearthisto#histoworld#histoblr#histotumblr#science#beauty#beautiful#micro#microscope
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo
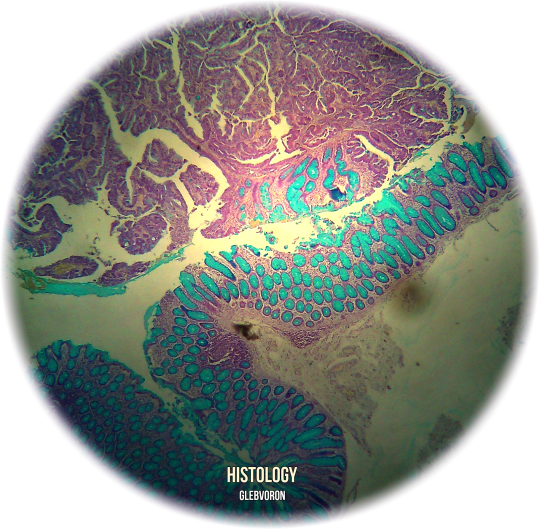
Mucinous Adenocarcinoma of the small intestine.
Schiff (PAS) reaction.
#Histology#histo#histolove#histoworld#histoblr#histotumblr#medicine#pathology#path#cancer#microscope#micro#biology#Bio#medtumblr#pathtumblr#beauty#histochemistry#medstudent#study#ihearthisto#iheartpath#medblr
4 notes
·
View notes
Photo
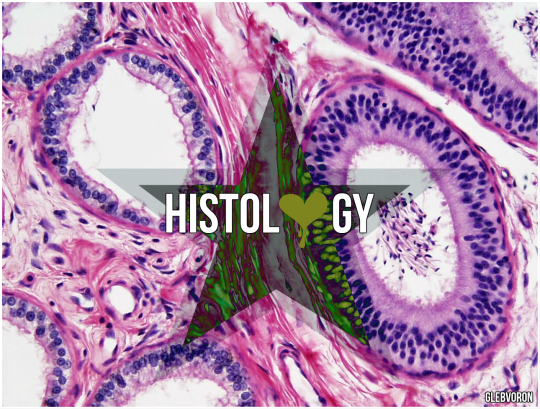
The epididymis is covered by a two layered pseudostratified epithelium. The epithelium is separated by a basement membrane from the connective tissue wall which has smooth muscle cells. The major cell types in the epithelium are:
Main cells: columnar cells that, with the basal cells, form the majority of the epithelium. These cells extend from the lumen to the basal lamina, They also have non-motile stereocilia, which are long and branching in the head region and shorter in the tail region. They also secrete carnitine, sialic acid, glycoproteins, and glycerylphosphorylcholine into the lumen.
Basal cells: shorter, pyramid-shaped cells which contact the basal lamina but taper off before their apical surfaces reach the lumen. These are thought to be undifferentiated precursors of principal cells.
Apical cells: predominantly found in the head region.
Clear cells: predominant in the tail region.
Intraepithelial lymphocytes: distributed throughout the tissue.
Intraepithelial macrophages.
From: wikipedia.
#Histology#histo#histoblr#histologyworld#ihearthisto#testis#epididymis#medicine#Bio#biology#science#medtumblr#medstudent#medblr
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo
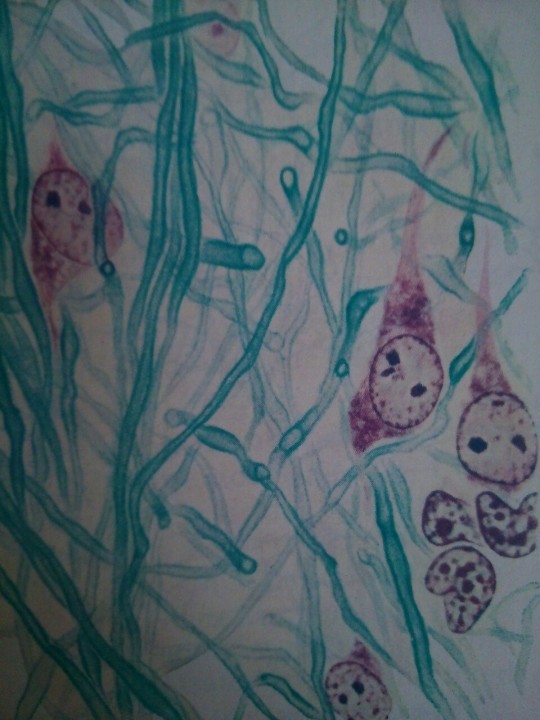

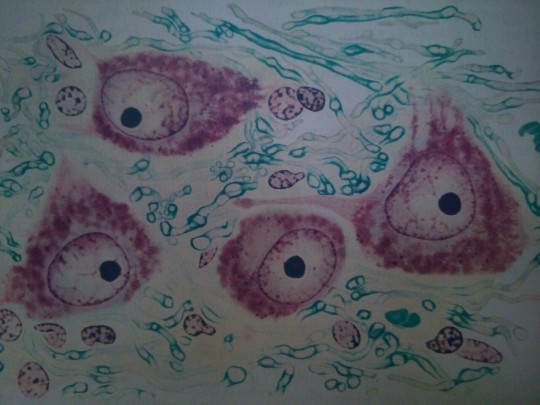
1, 2) Two areas of section through the optic tectum of a leopard frog, showing blue-stained myelin sheaths and the nerve cell bodies. The small dark nuclei are supporting cells. 3) Section from pons of man, showing myelin sheaths, nerve cell bodies, and glial cells. (Drawn by Esther Bohlman.) From Bloom's histology.
5 notes
·
View notes
Photo
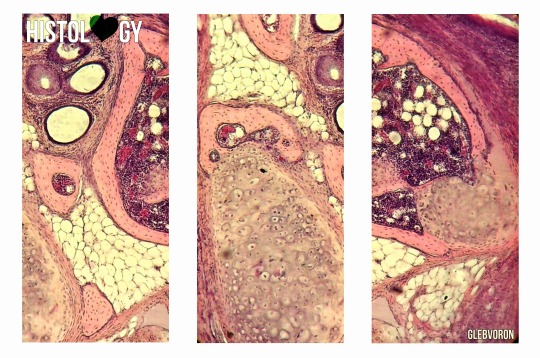
Limb growth
i♡histo
#Histology#histotumblr#histo#histoworld#medicine#medblr#histoblr#bone#muscle#blood#cell#microscope#micro#medtumblr#embryo#embryology
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo
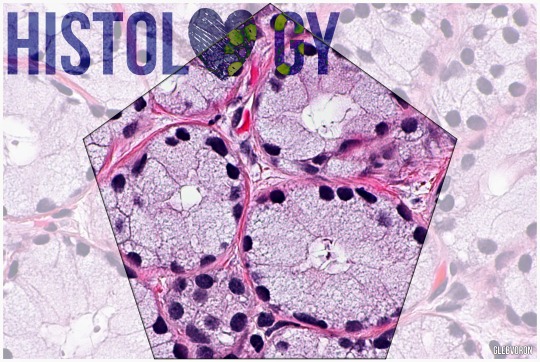
A bulbourethral gland, also called a Cowper gland for English anatomist William Cowper, is one of two small exocrine glands in the reproductive system of many male mammals (of all domesticated animals, they are only absent in the dog).They are homologous to Bartholin's glands in females.
The bulbourethral gland contributes about 0.1 to 0.2 ml or 5% of the ejaculate. The secretion is a clear fluid that is rich in mucoproteins. The secretion also helps to lubricate the distal urethra, and neutralize acidic urine which remains in urethra.
From: wikipedia
1 note
·
View note