#mount vesuvius
Text

Herculaneum Scrolls Reveal Plato's Burial Place
Researchers used AI to decipher an ancient papyrus that includes details about where Greek philosopher is buried.
The decipherment of an ancient scroll has revealed where the Greek philosopher Plato is buried, Italian researchers suggest.
Graziano Ranocchia, a philosopher at the University of Pisa, and colleagues used artificial intelligence (AI) to decipher text preserved on charred pieces of papyrus recovered in Herculaneum, an ancient Roman town located near Pompeii, according to a translated statement from Italy's National Research Council.
Like Pompeii, Herculaneum was destroyed in A.D. 79 when Mount Vesuvius erupted, cloaking the region in ash and pyroclastic flows.
One of the scrolls carbonized by the eruption includes the writings of Philodemus of Gadara (lived circa 110 to 30 B.C.), an Epicurean philosopher who studied in Athens and later lived in Italy. This text, known as the "History of the Academy," details the academy that Plato founded in the fourth century B.C. and gives details about Plato's life, including his burial place.


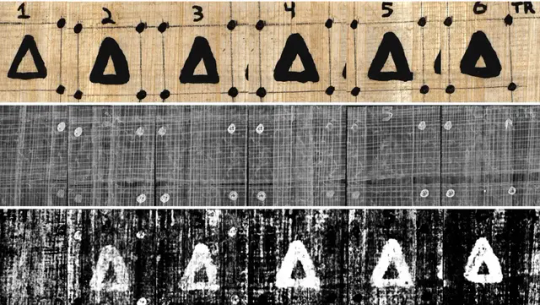

Historians already knew that Plato, the famous student of Socrates who wrote down his teacher's philosophies as well as his own, was buried at the Academy, which the Roman general Sulla destroyed in 86 B.C. But researchers weren't sure exactly where on the school's grounds that Plato, who died in Athens in 348 or 347 B.C., had been laid to rest.
However, with advances in technology, researchers were able to employ a variety of cutting-edge techniques including infrared and ultraviolet optical imaging, thermal imaging and tomography to read the ancient papyrus, which is now part of the collection at the National Library of Naples.
So far, researchers have identified 1,000 words, or roughly 30% of the text written by Philodemus.
"Among the most important news, we read that Plato was buried in the garden reserved for him (a private area intended for the Platonic school) of the Academy in Athens, near the so-called Museion or sacellum sacred to the Muses," researchers wrote in the statement. "Until now it was only known that he was buried generically in the Academy."




The text also detailed how Plato was "sold into slavery" sometime between 404 and 399 B.C. (It was previously thought that this occurred in 387 B.C.)
Another part of the translated text describes a dialogue between characters, in which Plato shows disdain for the musical and rhythmic abilities of a barbarian musician from Thrace, according to the statement.
This isn't the first time that researchers have used AI to read ancient scrolls that survived Mount Vesuvius's eruption. Earlier this year, researchers deciphered a different scroll that was charred during the volcanic eruption at a nearby villa that once belonged to Julius Caesar's father-in-law.
By Jennifer Nalewicki.


#Plato#Herculaneum Scrolls Reveal Plato's Burial Place#Herculaneum#Pompeii#Philodemus of Gadara#History of the Academy#The Academy#Plato's Academy#the Platonic Academy#the Academic School#athens greece#mount vesuvius#roman dictator sulla#ancient texts#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient greece#greek history#roman history#roman empire
47 notes
·
View notes
Text
ROUND 2: JERMA (vegas) VS MOUNT VESUVIUS (pompeii)


4K notes
·
View notes
Text

Vesuvius Eruption at Night overlooking the Scuola di Virgilio, 1822
by Josef Rebell
#josef rebell#joseph rebell#vesuvius#art#mount vesuvius#mt vesuvius#vesuvio#volcano#volcanoes#italy#mediterranean#europe#european#eruption#eruptions#night#sky#moon#clouds#sea#moonlit#moonlight#full moon#waves#landscape#romantic#virgil#roman#ruins#naples
893 notes
·
View notes
Text
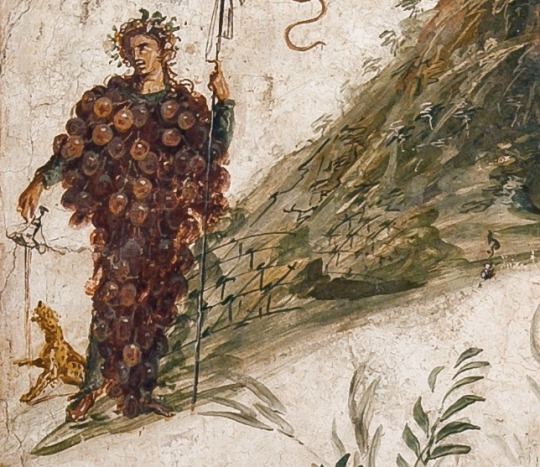


Bacchus and Vesuvius.
950 notes
·
View notes
Text
No matter which one wins, everybody loses!
#I got polls this is how I am celebrating#disasters#the great fire of rome#mount vesuvius#pompeii#the black death#the plague#the donner party#cannabalism#earthquake#fire#titanic#the great molasses flood of 1919#boston molasses flood#hindenburg#the great smog#chernobyl
2K notes
·
View notes
Text

Vesuvius in Eruption, with a View over the Islands of the Bay of Naples, Joseph Wright of Derby, ca. 1776
#art#art history#Joseph Wright of Derby#landscape#landscape painting#landscape art#volcano#volcanic eruption#Mount Vesuvius#Bay of Naples#Italy#Italianate#British art#English art#18th century art#oil on canvas#Tate Britain
330 notes
·
View notes
Text
In the ruins of Pompeii, there is a room inside a house where two men were painting on the day Mt. Vesuvius erupted in AD 79.
The master painter was at work on the fresco itself, twining vines in green, men and women looking out of the image to one side. His partner, probably an apprentice or lesser, younger painter, was laying down fresh plaster nearby. We know it was fresh because the pumice left significant pockmarks in it as it dried that we can still see today.
There are holes where a shelf stood holding the different colors of paint, in the wall just below the unfinished fresco. We found jars of paint on the floor - red green blue white yellow black. We found his tools, the brushes and the pot of lime that kept the paint wet.
He spilled lime on the painting.
We can tell that, too. It is caked clear as day over the unfinished work.
In a documentary I am watching, an Italian anthropologist discussing the moment of eruption looks to the cameraman and says, with real sincerity, "We found their tools, but we didn't find them. We hope that they ran away, that they survived."
Next door, a baker left his livestock behind when he fled. We found the skeletal remains of the animals who helped to move the millstone, but we did not find the baker.
Not that we are certain of, anyway.
I just wanted to take a moment to think about a modern Italian anthropologist looking at unfinished paintings and bread turned to stone by ash and time, hoping to himself that those people made it out in time.
We are separated by almost two thousand years, but we still have empathy for lives facing terror beyond their understanding. We still hope against hope that two painters ran out of town and made a new life somewhere else, that they escaped before the final pyroclastic flows descended.
We hope the baker moved to another town.
We recognize ourselves in what was left behind, and hope that these people - who could have been us, but for a trick of time and place - had a fighting chance to survive.
I just.
Sometimes, I love people.
I love us.
423 notes
·
View notes
Text








— volcanic humanity
fagradalsfjall eruption, brian emfinger / autobiography of red, anne carson / dyke (geology), sabrina imbler / pahoehoe flow, grant ordelheide / chasing the lava flow in iceland, heidi julavits / vesuvius from posillipo, joseph wright of derby / thirteen ways of talking about a volcano, gina balibrera
#parallels#web weaving#science#geology#curators on tumblr#poetry#photography#greek mythology#anne carson#nature photography#nature#volcano#writing#art#vesuvius#mount vesuvius#my posts
209 notes
·
View notes
Text
AI is deciphering a 2,000-year-old 'lost book' describing life after Alexander the Great

A 2,000-year-old "lost book" discussing the dynasties that succeeded Alexander the Great may finally be deciphered nearly two millennia after the text was partially destroyed in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in A.D. 79 and, centuries later, handed off to Napoleon Bonaparte.
The reason for the breakthrough? Researchers are using machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence, to discern the faint ink on the rolled-up papyrus scroll.
"It's probably a lost work," Richard Janko, the Gerald F. Else distinguished university professor of classical studies at the University of Michigan, said during a presentation at the joint annual meeting of the Archaeological Institute of America and the Society for Classical Studies, held in New Orleans last month. The research is not yet published in a peer-reviewed journal.
Only small parts of the heavily damaged text can be read right now. "It contains the names of a number of Macedonian dynasts and generals of Alexander," Janko said, noting that it also includes "several mentions of Alexander himself." Read more.
410 notes
·
View notes
Text
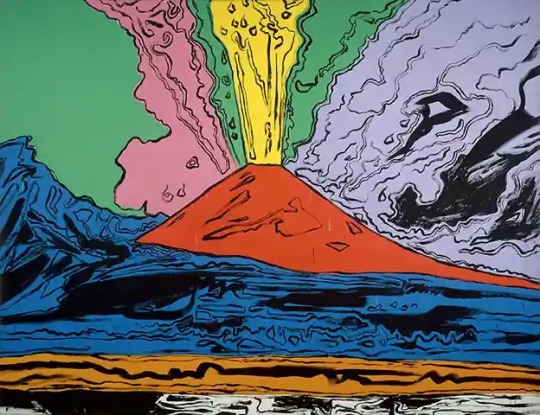



Andy Warhol, Vesuvius, Naples, ca. 1985
Joseph Wright, Vesuvius in Eruption, 1774
Andy Warhol, Vesuvius 365, 1985
#joseph wright#andy warhol#american art#american artist#english art#english artist#english painter#English painting#american painter#american painting#pop art#pop artist#volcano#volcanic eruption#mount vesuvius#italy#naples#aesthetic#beauty#modern art#art history#aesthetictumblr#tumblraesthetic#tumblrpic#tumblrpictures#tumblr art#tumblrstyle#artists on tumblr
139 notes
·
View notes
Photo



i ended up drawing more stained glass inspired puppet history art
#puppet history#watcher#watcher entertainment#shane madej#ryan bergara#beef boy#olympic torch#spool#gay oars#vesuvius#mount vesuvius#puppet history art#puppet history fanart#my art#polycarpa#snitch on the rich#i had a lot of fun with these#especially the gay oars
458 notes
·
View notes
Text


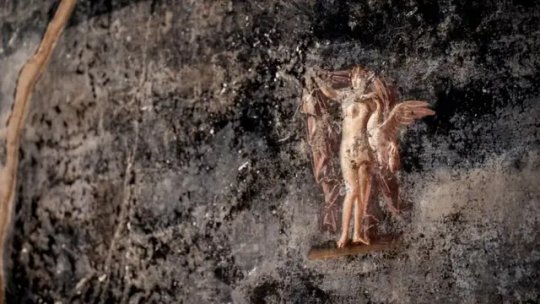
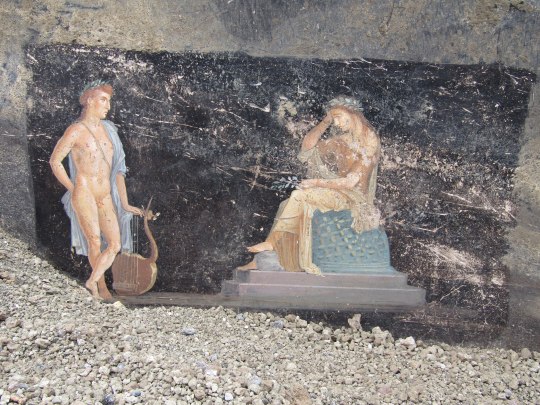
Breathtaking New Frescoes Found at Pompeii
Stunning Roman frescoes have been uncovered by archeologists in Pompeii, the ancient city destroyed by an eruption of the volcano Mount Vesuvius in the year 79 AD. Experts say the newly discovered frescoes are among the finest ever to emerge at the renowned archeological site.
The works of art line the high walls of what was once a large banquet hall. The walls themselves were painted mostly black, and the figures on the frescoes appear to emerge from the shadows. Site director Dr. Gabriel Zuchtriegel told CBS News partner network BBC News that the dark color was likely used to hide stains from the lamps that lit the hall after the sun went down.
"In the shimmering light, the paintings would have almost come to life," Zuchtriegel said.
Two pieces dominate the hall; one depicts the Greek god Apollo trying to seduce the priestess Cassandra. The second piece shows Prince Paris meeting Helen of Troy.

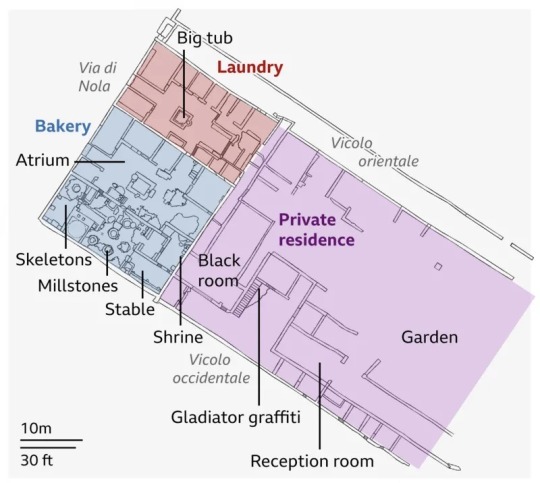
About a third of the "lost city" of Pompeii remains obscured by volcanic debris from the eruption almost two millennia ago. As scientists make new finds, they quickly move them to a storeroom to protect them from the elements.
The newly discovered frescoes, however, cannot be moved, so they have been protected with temporary roofing. Plaster glue is also being injected into the walls behind the artwork to stop them from falling down.



"We have a passion and a deep love for what we're doing, because what we're uncovering and protecting is for the joy also of the generations that come after us," chief restorer Dr. Roberta Prisco told the BBC, adding that the work was very stressful.
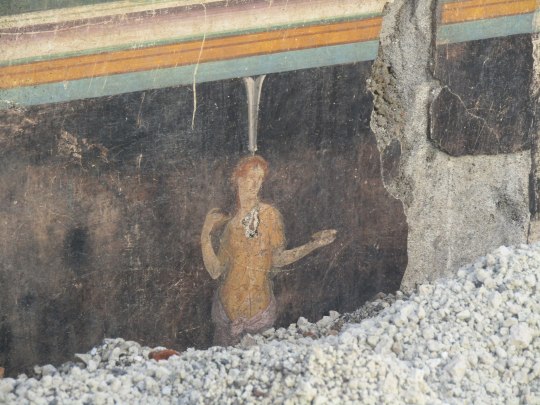
The dig site is much bigger than just the banquet hall.
Another fresco recovered from what was once one of Pompeii's grand properties had been on a ceiling, but it was smashed by the eruption that destroyed the city. Archeologists were able to lay out the pieces like a puzzle and recreate landscapes, theatrical masks, and Egyptian characters.



"This is my favorite discovery in this excavation because it is complex and rare," Dr. Alessandro Russo, co-lead archeologist on the dig, told the BBC. "It is high-quality, for a high-status individual."
In a bakery next to the grand property, the skeletons of two adults and a child were discovered.
Archeologists believe they may have been slaves who were trapped and couldn't flee the eruption, and were killed by falling stones.



"When we excavate, we wonder what we're looking at," co-lead archeologist Dr. Gennaro Iovino told the BBC. "Much like a theater stage, you have the scenery, the backdrop, and the culprit, which is Mount Vesuvius. The archeologist has to be good at filling in the gaps — telling the story of the missing cast, the families and children, the people who are not there anymore."
The team's discovery was just one of a number of recent revelations from the site, after they found other mythological-themed frescoes in early March and then, just weeks later, a construction site that was being worked on right up until the eruption.
The archeologists said near the end of March that they'd found a home construction project that was frozen in time by the eruption, with materials such as bricks and tools still piled up in the reception area of the home.
By Haley Ott.



#Breathtaking New Frescoes Found at Pompeii#Roman frescoes#Mount Vesuvius#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#roman history#roman empire#roman art
325 notes
·
View notes
Text
ROUND 1: CONAN O'BRIEN (funny) VS MOUNT VESUVIUS (pompeii)


#conan#conan o'brien#pompeii#mount vesuvius#tournament#now kill#f1#rome#ancient rome#volcano#volconan#volcanal
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

The eruption of Vesuvius, 1794 — Circle of Camillo de Vito
#vesuvius#vesuvio#mount vesuvius#volcano#volcanoes#art#camillo de vito#camillo di vito#eruption#eruptions#volcanic#lava#fire#clouds#mediterranean#southern italy#italy#europe#european
245 notes
·
View notes
Text
Me reading Pliny the Elder's Natural History: You silly man, that's not how eels work! Stop judging my drink choices lol!
Me reading about how Pliny the Elder had the opportunity to escape Vesuvius' eruption, but went back and lost his life trying to rescue people who were trapped:

#i might make fun of him but i really do respect him for that#it's vesuvius eruption day and i'm having Emotions#pliny the elder#pompeii#mount vesuvius
90 notes
·
View notes
Text
Archaeologists from the University of Tokyo might have just confirmed a historical gem near Mount Vesuvius – the possible Villa of Augustus, where the legendary first Roman emperor, Augustus Caesar, is believed to have spent his final days.
45 notes
·
View notes