#medieval cooking
Text
How to cook in a medieval setting
Alright. As some of the people, who follow me for a longer while know... I do have opinions about cooking in historical settings. For everyone else a bit of backstory: When I was still LARPing, I would usually come to LARP as a camp cook, making somewhat historically accurate food and selling it for ingame coin. As such I know a bit about how to cook with a historical set up. And given I am getting so much into DnD and DnD stories right now, let me share a bit for those who might be interested (for example for stories and such).
🍲Cooking at Home
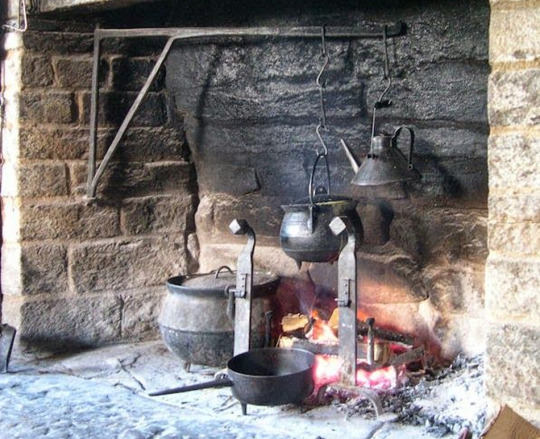

First things first: For the longest time in history most people did not have actual kitchens. Because actual kitchens were rather rare. Most people cooked their food over their one fireplace at home, which looked something like what you see above. There was something made of metal hanging over the fireplace. At times this was on hinges and movable, at times it was set in place. You could hang pots and kettles over it. When it came to pans, people either had a mount they would put over the fire or some kind of grid they could easily put into place there with some sourts of mounts (like the two metal thingies you can see above).
If you have a modern kitchen, you are obviously used to cook on several cooktops (for most people it is probably four of them), while in this historical you obviously only had one fire. Of course, as you can also see in the picture above, you could often put two smaller pots over the flames or put in a pan onto the fire additionally. But yes, the way we cook in modern times is very different.
Because of this a lot of people often ate stews and soups of sort. You could make those in just one pot - and often could eat from the same stew for days. In a lot of taverns the people had an "everything stew" going, which worked on the idea that everyone just brought their food leftovers, which were all put into one pot everyone would eat from.
Now, some alert readers might have also noticed something: What about bread and pastries? If you only have one fireplace and no oven, how did people make bread?
Well, there were usually three different methods for this. The most common one was communal ovens. Often people had one communal oven in a neighborhood. Especially in a village there might just be a communal oven everyone would just put their bread in to bake. (Though often this oven would only be fired up once or twice a week.)
The second version to deal with this some people used was a sort of what we today call a dutch oven. A pot made either of metal or clay with a lit you would put into the hot coals and then put bread or pastries into that, baking it like that.
There was also a version where people just baked bread in pans on the fire, rotating the bread during the baking process. At least some written accounts we have seem to imply. (Never tried this method, though. I have no idea how this might work. My camp bread was mostly done in dutch ovens or as stickbread.)
Keep in mind that the fireplace at home was very important for the people in historical times. Because it was their one source of warmth in the house.
🏕️ Cooking at Camp

Technically speaking cooking at camp is not that different - with the exception of course that you have to drag all your supplies along. And while in Baldur's Gate 3 and most other videogames you can carry around several sets of full-plate armor and several pounds of ingredients so that dear Gale can whip something up... In real life as an adventurer running around you need to make decisions on what to take along.
If you have read Lord of the Rings, you might remember how many people have criticized Sam for actually dragging all his cooking supplies along and how sad he was for not being able to cook for most of the time, because they were very limited in taking ingredients along.
So, yes, if you are an adventurer who is camping out in the open, you will probably need to do a lot of hunting and gathering to eat during your travels. You can take food for a couple of days along, but not for a lot.
A special challenge is of course, that while you can cook food for several days when you are at homes, you do not want to drag along a prepared stew for several days. So usually you will cook in smaller batches.
A lot of people who were journeying would often just take along one or two pots along.
So, what would you eat as an adventurer travelling around while trying to save the world from some evil forces? Well, it would depend on the time of the year of course. You would probably hunt yourself some food. For example hares, birds or squirrels. Mostly small things you can eat within one or two days. You do not want to drag along half a dead deer. In the warm months you might also forrage for all sorts of greens. You also can cook with many sorts of roots. Of course you can also always look into berries and other fruits you might find.
Things you might bring with you might be salt and some spices. A good thing to bring along would be herbs for tea, too, because I can tell you from experience that water you might have gotten from a river does not always taste very well - and springs with fresh water are often not accessible.
Now, other than what you can access the basic ideas of camping fires and cooking with them has not changed in the last few thousand years. While modern people camping usually have a car nearby and hence will have access to a lot of ingredients. But the general ideas of how to build a fire and put a pot over it... has not really changed.
So, yeah.
Just keep in mind that for the most part in historical settings until fairly recently, there was not much terms of proper kitchens. People cooked over an open fire and hence had to get at times ingenius about it.
#dungeons & dragons#baldurs gate 3#lord of the rings#medieval europe#medieval#cooking#medieval cooking#food history#historical settings#history#european history#writing#fantasy#writing resources
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
Why We Can't Have Medieval Food
I noted in a previous post that I'd "expand on my thinking on efforts to reproduce period food and how we’re just never going to know if we have it right or not." Well, now I have 2am sleep?-never-heard-of-it insomnia, so let's go.
At the fundamental level, this is the idea that you can't step in the same river twice. You can put your foot down at the same point in space, and it'll go into water, but that's different water, and the bed of the river has inevitably changed, even a little, from the last time you did so.
Our ingredients have changed. This is not just because we can't get the fat from fat-tailed sheep in Ireland, or silphium at all anywhere, although both of those are true. But the aubergine you buy today is markedly different to the aubergine that was available even 40 years ago. You no longer need to salt aubergine slices and draw out the bitter fluids, which was necessary for pretty much all of the thing's existence before (except in those cultures that liked the bitter taste). The bitterness has been bred out of them. And the old bitter aubergine is gone. Possibly there are a few plants of it preserved in some archive garden, or a seed bank, or something, but I can't get to those.
We don't really have a good idea of the plant called worts in medieval English recipes. I mean, we know (or we're fairly sure) it was brassica oleracea. But that one species has cultivars as distinct as cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, kale, Brussels sprouts, collard greens, Savoy cabbage, kohlrabi, and gai lan (list swiped from Wikipedia). And even within "cabbage" or "kale", you have literally dozens of varieties. If you plant the seeds from a brassica, unless you've been moderately careful with pollination, you won't get the same plant as the seeds are from. You can crossbreed brassicas just by planting them near each other and letting them flower. And of course there is no way to determine what varietal any medieval village had, a very high likelihood that it was different to the village next door, and an exceedingly high chance that that varietal no longer exists. Further, it only ever existed for a few tens of years - before it went on cross-breeding into something different. So our access to medieval worts (or indeed, cabbage, kale, etc) is just non-existant.
Some other species within the brassica genus are as varied. Brassica rapa includes oilseed rape, field mustard, turnip, Chinese cabbage, and pak choi.
We have an off-chance, as it happens, of getting almost the same kind of apple as some medieval varieties, because apples can only be reproduced for orchard use by grafting, which is essentially cloning. Identification through paintings, DNA analysis, and archaeobotany sometimes let us pin down exactly which apple was there. But the conditions under which we grow those apples are probably not the same as the medieval orchard. Were they thinned? When were they harvested? How were they stored? And apples are pretty much the best case.
Medieval wheat was practically a different plant. It was far pickier about where it would grow, and frequently produced 2-4 grains per stalk. A really good year had 6-8. In modern conditions, any wheat variety with less than 30 grains per stalk would be considered a flop.
Meats are worse. Selective breeding in the last century has absolutely and completely changed every single species of livestock, and if you follow that back another five centuries, some of them would be almost unrecognisable. Even our heritage breeds are mostly only about 200 years old.
Cheese, well. Cheese is dependent on very specific bacteria, and there are plenty of conditions where the resulting cheese is different depending on whether it was stored at the back or front of the cave. Yogurts, quarks, skyrs, etc, are also live cultures, and almost certainly vary massively. (I have a theory about British cheese here, too, which I'll expand on in a future post)
So, even before you go near the different cooking conditions (wood, burnables like camel and cow dung, smoke, the material and condition of cooking pots), we just can't say with any reliability that the food we're making now is anything like medieval people produced from the same recipe. We can't even say that with much reliability over a century.
Under very controlled conditions, you could make an argument for very specific dishes. If you track down a wild mountain sheep in Afghanistan, and use water from a local spring, and salt from some local salt mine, then you can make a case that you can produce something fairly close to the original ma wa milh, the water-and-salt stew that forms the most basic dish in Arabic cookery. But once you start introducing domestic livestock, vegetables, or even water from newer wells, you're now adrift.
It is possible that some dishes taste exactly the same, by coincidence. But we can't determine that. We can't compare the taste of a dish from five years ago, let alone five hundred, because we're only just getting to a state where we can "record" a taste accurately. Otherwise it's memory and chance.
We've got to be at peace with this. We can put in the best efforts we can, and produce things that are, in spirit, like the medieval dishes we're reading about. But that's as good as it gets.
#medieval cookery#medieval cooking#food history#historical cookery#historical cuisine#medieval arabic cookery#horticulture#genetics
1K notes
·
View notes
Text
I don't know who needs to hear this, but Auntie Arwen's doesn't just sell some of the most incredible spice blends (Ultimate Garlic Insanity will water your crops, clear your skin, and heal your grandma), but they also sell supplies for natural fabric and fibre dyeing.
#support small business#fabric dyeing#spices#medieval cooking#natural dyes#auntie arwen#mySCA#SCA#society for creative anachronism
60 notes
·
View notes
Video
youtube
Here’s a dish from French Cooking Academy, another of my subscribed YouTube channels.
I like the business of stuffing each chunk of beef with a bit of garlic and bacon; I’ve done this with lamb, using garlic and lemon. Another interesting detail is the use of cinnamon, suggesting a way-back-when influence either from the Moors or having access to spices as they passed through from Dpain Spain or North Africa on the way to somewhere else.
Kokkinisto (Greek) and Tajine (Morocco) also use cinnamon - and cloves, and nutmeg, and ginger etc. etc. depending on recipe. I’ve made both, they’re really excellent.
@dduane and I got Very Interested because the use of what Mum used to call “cake spices” is also quite medieval and, in DD’s case, adaptable for the Middle Kingdoms project.
The Corsican one recommends rigatoni, cannelloni or similar large hollow pasta (presumably to hold lots of sauce!) For a more medieval approach I’d try Loseyns from late-1300s cookbook “The Forme of Cury” (that’s “cookery” without the k, so “coo’rey” not “curry”.)
*****
These are often regarded as Richard II-era ”lasagne”, though I wonder if there’s also an association with heraldic “lozenges”, easily created by cutting a sheet of pasta dough slantwise...

Either way, here’s “Tasting History with Max Miller” (subscribed of course!) having a go at Loseyns, which turn out like mac & cheese with extra spices.

Max ended up eating them with a stick because forks hadn’t been introduced yet, but IMO a better utensil would be the historical eating pick, like one of these.

...or even a spoon, especially if the loseyns were cut small with that in mind.
However eating pasta with the fingers - like many other foods - may have been done in the 1300s; it was certainly recorded in paintings from the 1600s...

...right up to the 1800s...

...though I don’t think these were dressed with anything more than oil or butter and some grated cheese, and the potential for messy eating was still pretty high. Eating small pasta rather than dangly strands with the fingers was probably much tidier, especially if diners knew the proper etiquette for doing it...
Finally, here’s something from our own store-cupboard, bought out of curiosity during a recent visit to Polonez in Dublin.
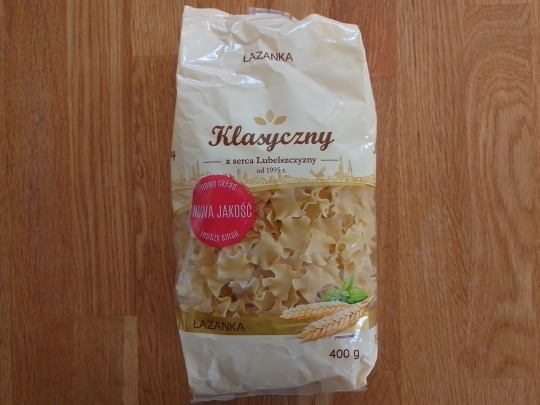

This is pasta cut into little squares; both the front and the back of the pack calls them łazanka...

...and according to Google Translate, this just means “pasta noodles”.
However...
Can any followers tell me if "łazanka” has any relationship to “lasagna” or “lozenge”? An enquiring mind wants to know! :->
ETA: @seriously-mike says “...łazanki were brought to Poland in 16th century by queen Bona Sforza (so) the relationship with lasagna might be there.” See his Reply for more info.
ETA (2): A little bell went off in my head about the shapes in the bag and I suddenly remembered seeing them as something call “torn pasta” - the Italian word is “maltagliati“ - which were made using re-rolled scraps of dough from “formal” shapes; more info at that link.
#food and drink#corsican beef ragout#spices in cooking#medieval cooking#food and cooking of the middle kingdoms#French Cooking Academy#Tasting History#lasagne#pasta
154 notes
·
View notes
Text
Gaylede
"I mean, yes, we do have a gay lead, but I'm not sure what that has to do with this bowl."
youtube



Of course I had to try some for myself. I looked up the recipe:
Take Almaunde Mylke & Flowre of Rys, & do there-to Sugre or Hony, & Powder Gyngere & Galyngale; then take figys, an kerue hem a-to, or Roysonys y-hole, or hard Wastel y-diced and coloure it with Saunderys, & seethe it & dresse hem yn.
I soon found a much easier to follow recipe by SCA member Lady Bronwyn ni Mhathain:
Simple enough! Here's my own process
4 cups/1 litre almaunde mylke (mine was sweetened)
Half cup flowre of rys (I used glutinous rice flour, ymmv)
As much hony as fits on a wooden spoon
1 1/4 teaspoons powder gyngere
bit over half a teaspoon galyngale
1 cinnamon stick
dash of cinnamon powder
1/4 teaspoon vanilla paste
Step 1: Procure the ingredients. Do your usual shopping and realise you forgot the almond milk in the line. Rush back to the dairy section. Buy some bread at the bakery, and some galengal powder and rice flour at the asian supermarket.
Step 2: Pour the almond milk into a pot with a cinnamon stick because you like cinnamon and the shops don't have sandalwood. Add in some more cinnamon and the vanilla paste because it tastes nice.
Step 3: Wait for the almond milk to simmer. Get frustrated that it's taking too long and just add in all the other ingredients after about 10 minutes
Step 4: Notice the glutinous rice flour is forming clumps and realise you should have used regular rice flour or added it in more slowly. Break it up with a fork for a while until it looks more manageable
Step 5: Give it a taste, decide it needs a bit more ginger
Step 6: Finally it starts to boil. Keep stirring it until the texture seems about right

Step 7: Put it in a big mug. Chop up a bunch of bread for yours. Watch @kitstacean put progressively more fruits in hers


Step 8: Delicious
All in all, a great success! I like the texture the glutinous rice gave it, but you might prefer it with regular rice flour. The big problem is my gas stove is a bit crap.
36 notes
·
View notes
Text



⊱ɱε∂เεѵαℓ-ƭɦყɱεร⊰
#medieval#medieval cooking#medieval food#medieval times#medievaltimes#rustic food#rustic#rustic cooking#primitive#primitive cooking#outdoor cooking
21 notes
·
View notes
Text
I have now received the 14th century cook book i was talking about!

tadaa! and it is so pretty on the inside


so it has the modern english translations to the original, with illustrations and stuff. it is so cute
i already talked my medieval friend into trying things out when i am back home after the holidays
49 notes
·
View notes
Text

Welcome to another installment of the chronically ill breakfast club: Medieval cooking edition. Poached eggs in mustard sauce on brown bread with broccoli and lemon butter on the side. When I’m cooking, I forget my symptoms. Instead, I feel a great influx of joy and relaxation so yes to more of this. And it wasn’t that difficult to make either. Thanks, chef ancestors!
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo


Barley and buckwheat stew with wild garlic, patty-pan squash, parsnips, onions and leeks, for a delicious dinner.
#original photography#medieval cooking#reenactment#food#cottagecore#stew#adventures in Scandinavia#my pictures
23 notes
·
View notes
Text
Medieval Food - Let's Talk

You know what? One week later and I am still fairly annoyed.
First of all: Yes, I am very much aware that technically one should not take MatPat too seriously and that for the most part if anything the “XY Theory” channels are just mild entertainment… But let’s face it: There are thousands of kids watching this, who are gonna take it seriously. And even a lot of adults, who do not know better.
So, as this is a topic near and dear to my heart and also a topic that the internet just throws around so much misinformation around on, let me talk a bit about Medieval Cuisine.
The Offense
Let me start with the thing that annoyed me so much, even though the issue is not so much about the issue at hand and more about the missing context in this one. Last week the @gametheoreoy sister channel Food Theory uploaded a video on Medieval Cuisine. While some of the information in there was good and included some important stuff that a lot of folks get wrong (like the fact that tomatoes, potatoes and maize were foods that came from the Americas and hence were not around in medieval Europe), the thing that annoyed me most about the video was… that MatPat and team absolutely ignored the fact that the place in question, medieval "Spain", was in that timeframe under under Black Muslim rule. In fact, there was technically no “Spain” at the time in question. Not as we imagine it today. Instead there was Al-Andalus (or Andalusia, how we know it today) and Leon-Castille. While the latter was Catholic, yes, the former was Muslim.
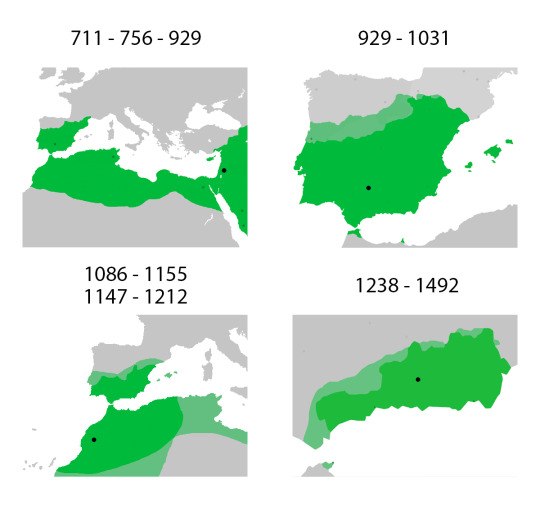
This really makes me angry, as it once again just plays into the misconception that medieval Europe was all white and Christian. Which it was not. For most of the medieval period, large chunks of the Iberian peninsula were under Muslim rule, which was also a reason that a lot of persecuted minorities – for example Jews, some Sinti and Romani people and also followers of Christian sects, that were not Catholic – fled there, as at that time Muslim rulers tended to not persecute those minorities, while the Catholic church did.
Now, it should be said that under Muslim rule, nobody who was not Muslim was forced to follow Muslim religious law, as not eating pork. But from what we know there was a lot less pork consumed on the Iberian peninsula at the time, than elsewhere in Europe. Instead, lamp, veal, dear and poultry were the more popular meats.
And I am sorry, MatPat, but talking about this part of Europe in the medieval times without speaking about Muslim rule is just a super bad look. Because it erases some important history.
While we are on it
But while we are on it, allow me to talk about Medieval cuisine, because bow, howdy, do people get this topic wrong.
For reference: No, I am no historian. But I am an autistic person, who spend a couple years hyperfixating on the history of food and henceforth getting annoyed with a lot of books, movies and the like, whenever they are depicting food in the medieval times.

Some things that I have seen in those contexts are, obviously, the tomatoes, potatoes and maize. But especially potatoes. Oh, boy, howdy, do people love depicting medieval folks eating potatoes. Maybe not surprising, given that the potato is in fact a main stay in modern day European cuisine. Also, obviously, the potato has still the reputation of a pauper’s food, which then easily combines with the common misconception of “people in medieval times were very poor and ate very poorly”. But, again, the potato would not reach Europe until probably 1519, though it would still be a while until people figured out how to eat potatoes (given that the green parts of the plants are in fact poisonous). Same goes for tomatoes, all sorts of peppers and again maize (corn, for the Americans).
Meanwhile people would go up to me and tell me seriously that “people in the medieval times did not have noodles”, which is… ridiculous, given that noodles and all sorts of pasta were around in Europe since ancient times. Even the old Greeks and Romans ate noodles, just not in those many fancy forms we know today. For the most part in medieval times people ate some sort of ribbon noodle, something we might call ravioli today, just noodles cut into square and something that was called lasagna, though it did not resemble today’s lasagna much. But noodles there were.

Another food that people do not associate with the medieval times, even though it was very much around in Southern European places, was rice. Other than the Americas, people kinda always knew about Asia and were trading with them. Even in Roman times. Which lead to the Romans actually cultivating a strain of rice, that did well enough in Europe. Now, while rice was not a common food in medieval Europe, it was certainly around.
Probably the weirdest thing, someone claimed about medieval food, was, that there was no “stew” around in medieval times, because it was “too complicated for the people back then”. You know, stew, the food where you basically just put a lot of different stuff into one pot and cook it… “Too complicated”. Honestly, I do not know what to say about that. Stew was not only around, but also very common. Especially as a lot of people did not have actual kitchens and were instead cooking their food over their fireplace, that often enough would only allow for one pot.
The thing about meat
One thing that MatPat gets mostly right – though, again not for Al-Andalus/Spain, because things were different there – is the bit about meat in the middle ages, though while he says the right thing here, he kinda misses a bit of context.

Meat was expensive in medieval times. Why? Because in a time before factory farming it was expensive to raise an animal. Some of you might’ve heard about “economy of scale”, which basically just says, that the more of a thing you produce, the cheaper it will become. And yes, this very much is true for factory farming. (Note: Factory farming is evil, simple as that. No living being should be treated the way, we treat those animals on factory farms.)
So, yes, without factory farms it was just more expensive to make the meat. Which was especially true for smaller animals like chicken. Especially as medieval chicken breeds were smaller than those chickens we see today.
Hence, for a lot of people, meat was just not a thing that they could eat more than once or twice a week. Or, more realistically, a lot of meat was eaten at once, when an animal was slaughtered, while only parts of the animal that could be conserved would then be served over a longer period of time.
It should also be noted that at least Christians tended to use all parts of the animal upon death, including blood and organs. (Muslims did not, as stuff like the blood is not halal.)

Now, one thing that should be noted, is, that most animals that were kept, were kept for multi purposes. Chicken lay eggs. Cows, sheep and goats give milk, with sheep obviously additionally providing wool, making them a very well-beloved animal in medieval times indeed. Horses you can ride. And yes, the pigs were useful, too, as they disposed of garbage, which was why in a lot of places you would just have pigs roaming the streets to take care of that.
Which brings me to the thing, a lot of folks do not want to hear, but… yeah, no, we have sources that tell us that medieval folks did at least also eat their dogs, when those were too old to help on the farm. We do not know how common this was, but we know that it happened. (Just as a note to the white folks getting all snooty about some Asian cultures eating dog meat.)
Of course, game was not kept but hunted. And yes, some people might go out to hunt when they were hungry for meat, but technically speaking it was illegal in many parts of Europe, based on the fact that game living in an area would belong to the nobility owning the land. Now, how those laws were enforced depended a lot on the area and how much game there was. But technically it was considered as such.
About vegetables
Having established that tomatoes, bell peppers, chilies and potatoes were not around in medieval times, this leaves the question: But what was around?

Well, two stable foods we still eat a lot today were definitely around: Carrots and peas. Especially peas were rather cheap and hence were eaten a lot. There was also at least one type of bean around in medieval Europe. Yes, only one. But horse beans were around in medieval Europe and were in fact eaten. Lentils were also quite popular.
Other than that, we also know of turnips, beets, cabbage, kohlrabi, onions and garlic being eaten. But that is not all, as there were several other types of vegetables, that are not around today that much, having been eaten. Especially a lot of root vegetables, like celeriac and parsnip for example.
But also fennel, that tends to be rather unpopular with modern people, was very much around and eaten.
One other vegetable that had some types around in Europe, was the pumpkin. Specifically, the gourd, that originated from Africa, but was cultivated in Europe rather early on.
Also there was a lot of salads and herbs, that also might be eaten as a form of salads.
But how do we know about medieval cuisine?
Another big thing that people tend to be kinda confused about, is, how we know what medieval people ate. Because, yes, at the time books were very expensive and a lot of folks could not read or write. While I will always harp on about the point that we greatly overestimate the number of completely illiterate folks in medieval times, as a lot of people were at least able to read a bit and write down the results of the harvest. But… written language was definitely not the main method of conserving information. Hence, there are only a handful of books around, that are primary texts and are collections of recipes. Most of them originate from noble or royal households, where the chefs would write down what the lord and lady of the house favored.

Other than that, we have a couple of letters, in which people shared their recipes.
But a lot of what we know “existed” is more from mentions within letters and diaries of “today I ate this and that” and historians then trying to figure out what that could have been, based around what we know about the foods that we know were available to the people. At times we also have findings of preserved foods. Now, of course those foods did not preserve for hundreds of years, but we can do chemical testing on what remained and hence figure out what originally had been preserved.
And of course there are pictures we have, that depict foods.
What we thankfully do have, is well documented harvests and things like ledgers from the likes of butchers and farmers based on the stuff they might have sold or given off as a form of taxes (which were often paid in goods, not coin). So, we know at least the raw materials and what might have been available.
And yes, there are also those kind of food that we know where around at ancient times and that are around in some form today. So, we can gather that they have been around the entire time. A good example for this are garlic bread and a version of pizza. We know that even in ancient times people baked bread with garlic butter and bread with vegetables, meat if available and cheese on them. It does not take a genius to figure out that bread with molten cheese on it, is pretty awesome.
Something I want to note as well is, that those recipe books we do have basically all originate from France, Germany and England, with two also originating in Italy. Medieval Europe was more than those four places. Which leads to my issue that a lot of folks tend to ignore that there were cultural differences and that, yes, we kinda are forced to rely on finds and maybe letters. (Believe me, as someone who writes about medieval Wallachia for my fics, it is a pain in the butt.)
But what did medieval people eat?
So, let me overgeneralize a bit. Because again, what you would eat in those times was dependent on where you were living and how wealthy you were. Richer people and nobility would eat meat a lot more often than less wealthy folks.
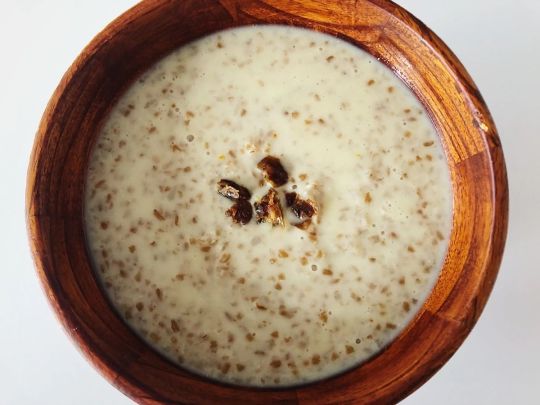

Generally poor folks would most of the time have some form of porridge for breakfast. That was: Oats cooked in water. If they could afford it, those might be cooked in milk. Maybe with honey. When it was the season, there might’ve been some fruits or nuts in there, too. But most of the times just oats in water. As oats were one of the cheapest forms of corn, they were good for that. Some people might use other corn like rye or barley softened in water as well.
If you could afford it, you might have head bread as well. For most folks it was a rye bread or rye sour dough, because rye was cheaper than wheat. This bread would not be eaten in slices, but rather eaten together with whatever was available. Maybe together with cheese. Maybe dunked in stew or soup. (Which, by the way, leads me to the fact that most taverns only served stew or soup with bread. Not “nice pork grilled over a fire” as we so often see it depicted in media.)
And yes, as a main warm meal there was stew and soup – vegetable soup for the most parts, because again: Meat was expensive. When there was meat in the soup, chances were, that It was all sorts of meats and in fact it was more likely that it would be hare or sheep, rather than pork or poultry. At times the same stew would be eaten for more than a week, with just new stuff being added, whenever it was half-empty, so you might actually get a mix of meats in there. (This was, again, also quite common in taverns, where people might just bring some stuff they had lying around and add it to the so called “everything stew”.) While it might sound disgusting to us today, it actually allowed for pretty deep flavor profiles.

Again, poor folks would often not have a dedicated kitchen or stove and rather would prepare their food over the fire place that was also used to heat the house. Which would lead to a lot of “one pot meals” as we would call it these days. And if there was meat, it often would be prepared as a larger chunk, instead of small cuts being prepared in a pan.
Of course, those were things that rich people could afford more easily. Though this did not necessarily mean nobility, but also folks like tradesmen and the likes. Who not only might have a dedicated kitchen, but also some maid to cook for them.
And there was of course the thing about spices: Medieval cuisine for the most part did not use spices, but only herbs. Because spices mostly originated in North Africa and South Asia and hence had to be traded over long distances. This would make them rather expensive, so many folks were not able to afford them. (Again: the entire colonialism affair started, because everyone wanted spices, while the Ottoman Empire controlled the spice trade.) This does, however, not mean that spice heavy recipes were unknown to medieval folks. They were expensive, yes, but we have both archeological and written evidence from meals, we would today call “curry” being prepared both in England and France.
Milk, no matter what animal it came from, would often be turned into some form of cheese, because most animals would only give milk, when it was season for their young. So, making the milk into cheese was a good way of making the milk last for longer. And yes, lots of folks knew how to make cheese. So, cheese was something that was often enough served to the side. Though dairy as well was not as common as it is today.
Wheat, again, was expensive. So, bread and other food based around wheat was more expensive than rye. Often wheat would only be enjoyed by rich folks and men of the cloth (meaning church folks). And only very rich people could afford white flour based food, while everyone else was eating food based around whole grain flour.
And yes, for the observant ones it should be obvious: Poor folks were eating a lot more healthy, than rich people were. Which led to interesting stuff like the fact that poor people often did not suffer from dental problems, even though dental hygiene was not yet a thing. Simply because they were eating better and less sweet.
Oh, and also: Most people would in fact drink alcoholic beverages (though with a lot less alcohol content than what we know today) instead of just pure water. Why? Well, because chances were, it made you less sick. And yes, also it tasted a lot better than stale water you got from a well. For most folks that was beer or ale, for richer folks wine or at least thinned wine. Except, again, in areas where there was a Muslim majority, because those obviously would not drink alcohol, so there would often be fewer breweries.
Medieval people did not eat badly
Now, let me make one thing clear, because it is a thing I tend to get annoyed by a lot: No, medieval people did not eat badly. Which was the other thing that annoyed me about MatPat’s video, given that the title card was “Medieval Food SUCKS!”, which… no, it doesn’t. It didn’t. It was different, from what we eat today, yes, but it was not bad food.

See, it is something that a lot of modern first world folks (especially white folks) are just too picky eaters and with that also kinda wasteful. We will only eat certain bits of dead animals, will not eat a lot of dead animals that are gonna die either way (heck, we have laws against eating certain animals, that are not based in any other reason but people’s emotional attachment to those animals), will not eat many vegetables that would be easier to grow and so on.
And sure, the fact that there was so little spice in medieval food, that makes it kinda… meh. But herbs can be used for those purposes, too. And yes, they can make things rather tasty indeed.
And yeah, I kinda bemoan the way we consume food today. Part of it has a lot to do with capitalism, of course. With the fact that we just do not have the time and means to grow our own food and the fact that of course, that to keep food prices low (which is necessary) but also keep the profits high, food production is plagued by all sorts of inhumanities. Be it slave labor, violence again humans (just look into the history of Chiquita or Dole) and of course the inhumane ways we keep animals.
A lot of folks do not even know how to prepare their own food properly. And do not know where it comes from. And as someone who identifies with the solarpunk culture, I just wish we could change away from that.
So, yeah, Let me just say: The MatPat video was just not that good and ignored an important part of history. Also, a lot of media depicts medieval food culture wrong, leading people to have all sorts of misconceptions about it.

Currently I am writing a fanfic about medieval cooking based around the Castlevania fandom. You can find it on Ao3! Though, yeah, the characters here are rich enough to eat spices.
And if you liked this little rant essay, maybe consider leaving me a little something on Ko-Fi!
#History#medieval cooking#medieval food#food theory#historical cooking#medieval europe#learning#education#middle ages#spain did not exist in the middle ages#white washed#white washed history#long reads#rant post#food history
114 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cooking in Stoneware Pots
For my elevation, Órlaith and Gytha got me a stoneware cooking pot. This is a pot made of actual stone - soapstone - and of a kind widely used in the Middle East in the era in which al-Warraq was writing. I have finally gotten a chance to try it out, since Pen & Sword provided me with an event where I had room on the fire and wasn't under any pressure to produce food (I was cooking a couple of Arabic stews, but they're things I know well).
The most immediate thing, which is completely obvious once it's pointed out, but which I didn't know before, is that a thick stone pot (the walls are not quite an inch thick) retains far more heat than a cast iron pot, which retains a good bit more heat itself than a stainless steel one. Nonetheless, if you take a cast iron pot off the heat, it will stop boiling in seconds. The stoneware one just keeps on boiling, and will do so for a good 2-3 minutes.
This makes sense of a number of instructions in period texts where pots are removed from the heat, and also makes sense in the context of serving the food in the cooking pot - the food will stay hot for much longer than it could in any serving dish. There's usually an instruction to wipe down the pot to remove soot and so on, so there's no doubt that it's the actual cooking pot.
Second, and this will need more trials, the food tasted different - the sweetness of the onions was far more evident. Also, there's a separation that happens when the stew is ready; you can see oil and other liquids apart from each other at the edges of the pot. This happened sooner, by far, in the stone pot. That might be because it's smaller, of course. Further experimentation needed.
#sca#medieval food#medieval cookery#medieval cooking#medieval arabic food#al warraq#soapstone#stoneware#more research necessary
22 notes
·
View notes
Text
favorite sekanjabin
I grew up on the classic cold mint and apple cider, but I know some people will use different vinegar and will also add other stuff. What's your favorite and do you drink it hot or cold?
My sister and I are now on a mission to find a couple of combinations for a thing we're doing in our household, so I need your recommendations. Yes, I realize I can just google suggestions, but that's not what I want. I want to know what YOU personally have tried and liked and recommend.
If you have no idea what I'm talking about, BOY HAVE I GOT A TREAT FOR YOU.
#mysca#society for creative anachronism#sca#sekenjabin#medieval cooking#medieval recipes#middle eastern
46 notes
·
View notes
Text

⊱ɱε∂เεѵαℓ-ƭɦყɱεร⊰
#medieval#medieval cooking#medieval kitchen#primitive#primitive cooking#rustic#bread#breadmaking#breadcore#sourdough#baker#bakery#bread oven#rye bread
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
discovered a german medieval cook book from 1350 (Das Buoch von guoter Spise)! with way more reasonable recipes than the forme of cury. still sometimes rather fancy, but it looks like also having more 'common people' dishes. the forme of cury puts in almonds and saffron into EVERYTHING! that what you get for buying a cook book made for a king
#personal#medievalcore#medieval cooking#i dont have a physical copy but it is all online#also while writing this post fireworks started to go off outside#very loud
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
HARLEIAN MS. 279 (AB 1430) - .XXIIJ. Nomblys of Þe Venyson- Numbles of the Venison

Numbles of Venison - A delightfully archaic term referring to the offal of an animal, including heart, liver, lungs, etc. This dish is similar to garbage, which is made of chicken offal. Not pleasant to look at, however, this sweet and sour dish is fit for a king.
https://giveitforth.wixsite.com/giveitforth/post/harleian-ms-279-ab-1430-xxiij-nomblys-of-%C3%BEe-venyson-numbles-of-the-venison
#food history#medieval food#cooking#recipes#ediblehistory#culinary history#culinaryhistory#eatlikeaking#giveitforth#food#foodblogger#food network#medieval cooking#medieval manuscripts#medieval history
3 notes
·
View notes