#internal controls
Text
Unlocking Clarity: Internal vs. External Audits Demystified | 10 Years of Expert Insight!
Unlocking Clarity: Internal vs. External Audits Demystified | 10 Years of Expert Insight!
Discover the nuances between internal and external audits. Gain valuable insights for a robust audit strategy. Your go-to guide! | Deciphering audits for success.

Internal Audit and External Audit: Understanding the Key Distinctions
In the realm of corporate governance and financial management, audits play a pivotal role in ensuring transparency, accuracy, and compliance with regulations. Two primary forms of audits, internal and external, serve distinct purposes within organizations. Understanding the differences between internal audit and external audit is essential for stakeholders, management, and regulatory bodies alike. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of both types of audits, exploring their scope, methodologies, and contributions to organizational governance.

1. Introduction to Internal and External Audit
1.1. Defining Internal Audit
Internal audit constitutes an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization’s operations. It helps an organization accomplish its objectives by bringing a systematic, disciplined approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes.
1.2. Defining External Audit
External audit, on the other hand, is an independent examination of financial information of any entity, whether profit-oriented or not, irrespective of its size or legal form, when such an examination is conducted with a view to expressing an opinion thereon. It is conducted by an external auditor, who is appointed by the shareholders or governing body of an organization.

2. Purpose and Scope
2.1. Internal Audit Purpose
Internal audits are conducted to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes within an organization. They provide insights into operational efficiency, compliance with policies and procedures, and the overall management of risk across various business functions.
Summary
Focus on Organizational Processes.
Delving into the intricacies of day-to-day operations.
Identifying inefficiencies and proposing enhancements.
Evaluating Internal Controls.
Scrutinizing the effectiveness of internal control mechanisms.
Mitigating the risk of fraud and operational lapses.
Risk Management.
Proactively managing risks inherent in business processes.
Developing strategies for risk mitigation and resilience.
2.2. External Audit Purpose
External audits primarily focus on providing assurance to stakeholders regarding the accuracy and reliability of financial statements. They verify the fairness of financial presentations and ensure compliance with relevant accounting standards and regulatory requirements.
Summary
Financial Statement Examination.
In-depth analysis of financial records and transactions.
Ensuring accuracy and reliability of financial reporting.
Compliance Verification.
Verifying adherence to legal and regulatory requirements.
Providing stakeholders with assurance on compliance.
Stakeholder Assurance.
Assuring external parties of the organization’s financial health.
Fostering trust among shareholders and investors.

3. Authority and Independence
3.1. Internal Audit Authority
Internal audit functions typically report to the highest levels of management within an organization, such as the board of directors or audit committee. They operate independently from operational areas to maintain objectivity and impartiality in their assessments.
Summary
Direct Reporting to Management.
Reporting directly to the organization’s management.
Facilitating immediate corrective actions.
Advisory Role.
Serving as an advisory body to improve internal processes.
Providing insights for strategic decision-making.
Employed by the Organization.
Internal auditors as part of the organizational structure.
Potential for internal biases and conflicts.
Potential Bias Concerns.
Navigating challenges associated with internal allegiances.
Striving for objectivity within the organizational context.
3.2. External Audit Authority
External auditors are appointed by shareholders or governing bodies and report directly to them. This independence from the organization ensures an unbiased evaluation of financial statements, enhancing the credibility of the audit process.
Summary
Independent Reporting to Shareholders.
Maintaining independence from internal biases.
Reporting findings directly to shareholders.
Regulatory Compliance Focus.
Emphasizing adherence to legal and regulatory standards.
Offering an objective assessment of compliance.
Independent from the Organization.
External auditors operate autonomously.
Minimizing biases and conflicts of interest.
Objective Evaluation.
Delivering an objective assessment of financial matters.
Prioritizing external stakeholders’ interests.
"Americans like to make money; Canadians like to audit it. I know no other country where accountants have a higher social and moral status." Northrop Frye
4. Focus Areas
4.1. Internal Audit Focus
Internal audits concentrate on evaluating operational efficiency, ensuring compliance with internal policies and procedures, and identifying areas of potential risk. They delve into the intricacies of day-to-day processes to enhance overall organizational performance.
Summary
Process Improvement.
Prioritizing the enhancement of internal processes.
Contributing to organizational efficiency and effectiveness.
Operational Efficiency.
Identifying opportunities for streamlining operations.
Addressing challenges that impact day-to-day efficiency.
4.2. External Audit Focus
External audits primarily focus on the accuracy of financial statements, compliance with accounting standards, and the detection of fraud or misstatements. The emphasis is on providing stakeholders with confidence in the financial information presented by the organization.
Summary
Financial Accuracy.
Ensuring precision in financial reporting.
Verifying the accuracy of financial statements.
Compliance Assurance.
Providing assurance on adherence to legal and regulatory standards.
Delivering confidence to external stakeholders.

5. Reporting Structure
5.1. Internal Audit Reporting
Internal audit reports are directed to the management of the organization. These reports include recommendations for improvement in processes, controls, and risk management based on the findings of the audit.
Summary
Direct Reporting to Management.
Reporting directly to the organization’s management.
Facilitating immediate corrective actions.
Advisory Role.
Serving as an advisory body to improve internal processes.
Providing insights for strategic decision-making.
5.2. External Audit Reporting
External auditors provide reports directly to the shareholders or the board of directors. These reports contain opinions on the fairness of the financial statements and the adherence to accounting principles.
Summary
Independent Reporting to Shareholders.
Maintaining independence from internal biases.
Reporting findings directly to shareholders.
Regulatory Compliance Focus.
Emphasizing adherence to legal and regulatory standards.
Offering an objective assessment of compliance.

6. Frequency and Timing
6.1. Internal Audit Frequency
Internal audits can be conducted on an ongoing or periodic basis, depending on the organization’s needs. They are not limited to specific timeframes and can be scheduled throughout the year.
Summary
Continuous or Periodic.
A continuous process with ongoing assessments.
Periodic deep dives into specific operational areas.
Regular Assessments.
Ensuring ongoing alignment with organizational goals.
Real-time monitoring for effective risk management.
6.2. External Audit Frequency
External audits are typically an annual requirement, timed after the completion of financial periods. This ensures a comprehensive examination of the financial statements at the end of each fiscal year.
Summary
Annual or Periodic.
Typically conducted annually or periodically.
Focused on the financial year-end for comprehensive reviews.
Focused on Financial Year-End.
Ensuring the accuracy of year-end financial statements.
Aligning with regulatory reporting timelines.

7. Key Personnel and Teams
7.1. Internal Audit Team
Internal audit teams are usually employed by the organization itself. They report to the board or audit committee and are intimately familiar with the organization’s internal processes and controls.
7.2. External Audit Team
External audit teams, on the other hand, are independent audit firms hired by shareholders or the board. This independence ensures an unbiased evaluation of financial statements and internal controls.

8. Risk Management and Compliance
8.1. Internal Audit Role in Risk Management
Internal audits play a crucial role in identifying and mitigating risks associated with operational processes. They ensure compliance with internal policies and procedures, reducing the likelihood of financial and operational setbacks.
Summary
Operational Risks.
Identifying and mitigating risks associated with operations.
Enhancing operational resilience through proactive measures.
Internal Fraud.
Addressing the risk of internal fraud and misconduct.
Safeguarding organizational assets and resources.
8.2. External Audit Role in Risk Management
External audits focus on assessing financial risks and verifying compliance with accounting standards. While they may not delve as deeply into operational risks, they contribute significantly to overall risk management by ensuring financial accuracy.
Summary
Financial Misstatements.
Vigilantly assessing the risk of financial inaccuracies.
Providing assurance on the accuracy of financial records.
Non-Compliance Risks.
Identifying risks associated with non-compliance.
Assuring stakeholders of the organization’s commitment to compliance.

9. Documentation and Record Keeping
9.1. Internal Audit Documentation
Internal audit documentation is detailed and comprehensive, encompassing reports and findings, process flows, and control assessments. This documentation serves as a foundation for improving internal processes.
9.2. External Audit Documentation
External audit documentation primarily includes audited financial statements, working papers, and test documentation. These documents provide evidence of the audit process and support the auditor’s opinions on financial statements.

10. Confidentiality and Disclosure
10.1. Internal Audit Confidentiality
Internal audit findings are typically kept confidential within the organization. The focus is on improving internal processes, and disclosure is limited to the management or specific departments involved.
Summary
Internal Information Handling.
Safeguarding internal information with stringent confidentiality measures.
Balancing transparency with the need for confidentiality.
Limited External Disclosures.
Minimizing external disclosures of internal processes.
Prioritizing the security of sensitive organizational information.
10.2. External Audit Disclosure
External audits involve public disclosure of financial statements. The information provided in external audit reports is accessible to external stakeholders, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Summary
Public Disclosures.
Adhering to regulatory requirements for public disclosures.
Balancing transparency with legal obligations.
Limited Confidentiality.
Navigating constraints related to public disclosures.
Emphasizing the importance of transparency within legal bounds.

11. Regulatory Oversight and Compliance
11.1. Internal Audit Regulation
Internal audits may be conducted to ensure compliance with internal controls and policies, often voluntarily or as mandated by industry standards. Regulatory oversight is generally limited to specific sectors or industries.
Summary
Internal Policies.
Guided by internal policies and organizational guidelines.
Adhering to industry-specific standards.
Industry Guidelines.
Aligning with industry benchmarks and best practices.
Navigating sector-specific regulatory landscapes.
11.2. External Audit Regulation
External audits are mandated by government regulations, and regulatory bodies often oversee the auditing profession. Compliance with accounting standards is a critical aspect of external audit regulations.
Summary
Statutory Requirements.
Mandated by statutory regulations governing external audits.
Ensuring compliance with universally accepted accounting principles.
Compliance with Accounting Standards.
Adhering to international accounting standards.
Providing a standardized framework for financial reporting.

12. Cost and Resource Allocation
12.1. Internal Audit Costs
Internal audit costs are typically incorporated into the operational budgets of organizations. The allocation of resources depends on the size and complexity of the organization.
Summary
In-House Expenses.
Involving internal personnel and resources.
Managing costs associated with internal audits.
Resource Allocation.
Allocating internal resources for audit activities.
Balancing costs with the benefits of continuous internal oversight.
12.2. External Audit Costs
External audit costs involve contractual fees paid to audit firms. The fees are based on the complexity and scope of the audit, reflecting the level of effort required by the external audit team.
Summary
External Firm Fees.
Engaging external audit firms for independent reviews.
Incurring fees for external expertise.
Cost of Compliance.
Balancing the costs associated with ensuring compliance.
Weighing the benefits of external assurance against financial outlays.

13. Value Addition and Benefit
13.1. Internal Audit Value Addition
Internal audits add value by identifying process improvements, strengthening internal controls, and providing insights into operational efficiency. Their focus on internal processes enhances overall organizational effectiveness.
13.2. External Audit Value Addition
External audits enhance financial transparency by ensuring the accuracy of financial statements. Their opinions provide assurance to stakeholders and investors, contributing to the overall credibility of the organization.

14. Challenges and Limitations
14.1. Internal Audit Challenges
Internal audits may face challenges such as limited resources and budgets. Ensuring independence from management while working closely with operational areas can also pose challenges.
14.2. External Audit Challenges
External audits encounter challenges related to the complexity of financial transactions and the evolving landscape of regulatory requirements. Staying abreast of changes is crucial for maintaining audit effectiveness.

15. Collaboration and Communication
15.1. Internal Audit Collaboration
Internal audits involve collaboration with various departments and levels of management. They play a key role in facilitating process improvement initiatives by working closely with operational areas.
Summary
Immediate Corrections.
Implementing swift corrective actions based on findings.
Addressing identified weaknesses promptly.
Continuous Improvement Plans.
Developing long-term strategies for ongoing improvement.
Fostering a culture of continuous enhancement.
15.2. External Audit Communication
External audits require effective communication with management and audit committees. Providing feedback and recommendations based on audit findings is essential for ensuring continuous improvement.
Summary
Compliance Recommendations.
Offering recommendations for addressing compliance gaps.
Providing a roadmap for achieving and maintaining compliance.
Legal Consequences.
Highlighting potential legal consequences of non-compliance.
Emphasizing the importance of proactive adherence to regulations.

16. Continuous Improvement and Evolution
16.1. Internal Audit Evolution
Internal audits evolve by embracing technology and automation. The incorporation of data analytics and artificial intelligence enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of internal audit processes.
Summary
Iterative Assessments.
Conducting iterative assessments for ongoing improvement.
Adapting audit methodologies based on lessons learned.
Adaptive Strategies.
Developing adaptive strategies for dynamic organizational environments.
Embracing change as a catalyst for improvement.
16.2. External Audit Evolution
External audits adapt to changes in accounting standards and regulations. Leveraging technology for audit efficiency, they stay at the forefront of industry best practices to ensure thorough and accurate evaluations.
Summary
Yearly Reflections.
Reflecting on annual audit processes for improvement.
Incorporating lessons learned into future audit engagements.
Industry Benchmarking.
Benchmarking against industry standards and best practices.
Contributing to the evolution of external audit practices.

17. Industry Best Practices
17.1 Internal Audit Best Practices
Internal audit best practices include adopting COSO frameworks for internal controls and implementing risk-based auditing approaches. These practices ensure a systematic and effective audit process.
17.2. External Audit Best Practices
External audit best practices involve adhering to Generally Accepted Auditing Standards (GAAS) and Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Upholding professional ethics and independence is paramount.

18. Training and Professional Development
18.1. Internal Audit Training
Internal audit professionals undergo continuous professional education. Certification programs such as Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) and Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) contribute to their expertise.
18.2. External Audit Training
External audit professionals obtain certifications such as Certified Public Accountant (CPA). Ongoing professional development requirements ensure they stay current with industry standards and regulations.

19. Emerging Trends and Technologies
19.1. Internal Audit Trends
Emerging trends in internal audit include the use of data analytics and artificial intelligence. Internal audits are increasingly focusing on cybersecurity audits to address evolving threats.
19.2 External Audit Trends
External audit trends encompass the integration of blockchain technology and the use of data analytics for fraud detection. These advancements enhance the accuracy and efficiency of external audit processes.

20. Conclusion
In conclusion, the differences between internal audit and external audit are multifaceted, each serving a unique purpose within the realm of organizational governance. While internal audits focus on operational efficiency, risk management, and compliance, external audits provide assurance regarding the accuracy of financial statements and adherence to accounting standards. It is crucial to recognize the complementary nature of these audits, with each contributing significantly to the overall health and credibility of an organization.

#accounting#banking#finance#investment#cfo#financial accounting#personal finance#financial literacy#financial modeling#financial planning#Internal Audit#External Audit#auditing#risk management#Internal Controls
0 notes
Text
https://www.illumeo.com/courses/segregation-duties-core-business-processes

'Segregation of Duties' (SOD) within essential business processes, a linchpin for risk management and regulatory compliance, notably Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX). SOD ensures robust internal controls by delineating distinct roles to mitigate conflicts of interest. It elucidates SOD principles, dissects specific process intricacies, and empowers participants to pinpoint vulnerabilities, enact effective SOD strategies, and comprehend control mechanisms. By mastering SOD, individuals fortify organizations against financial improprieties and regulatory breaches, safeguarding integrity and compliance.
#e-learning#enhancement#finance#certification#accounting#business#courses#Segregation of Duties#Risk Management#Regulatory Compliance#Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX)#Internal Controls#Conflict Mitigation#Financial Integrity#Compliance Strategies#Role Delineation#Control Mechanisms
0 notes
Text
The Role of Fraud and Investigation Support in Safeguarding Organizations against Financial Deception
In today's complex and interconnected business landscape, organizations face an ever-present threat of financial deception and fraud. To mitigate these risks, companies must have robust fraud and investigation support systems in place. This article delves into the vital role played by fraud investigation support in safeguarding organizations against financial deception, highlighting the importance of prevention, detection, and response strategies.
Prevention Strategies:
Preventing fraud requires a proactive approach that focuses on creating a strong internal control environment. Fraud and investigation support aids organizations in establishing and implementing preventive measures, including:
a. Fraud Risk Assessments: Conducting regular assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and areas of exposure to fraud risks. This allows organizations to implement targeted preventive measures and allocate resources efficiently.
b. Fraud Awareness Training: Educating employees about various forms of fraud, warning signs, and the importance of reporting suspicious activities. By fostering a culture of awareness, organizations empower their workforce to act as the first line of defense against fraudulent activities.
c. Internal Controls: Establishing robust internal controls, such as segregation of duties, authorization procedures, and access controls, to minimize the opportunities for fraudulent behavior. Fraud and investigation support professionals assist in evaluating and strengthening these controls.
Detection Mechanisms:
While preventive measures are crucial, no system can eliminate the risk of fraud. Effective detection mechanisms are essential for identifying fraudulent activities promptly. Fraud and investigation support provides organizations with the following detection strategies:
a. Data Analytics and Forensic Accounting: Utilizing advanced data analytics techniques and forensic accounting expertise to identify irregularities, anomalies, and patterns indicative of fraudulent activities. By analyzing financial data, transaction records, and other relevant information, fraud investigators can detect suspicious activities that might go unnoticed through traditional methods.
b. Whistleblower Hotlines: Establishing confidential reporting channels, such as whistleblower hotlines, where employees, customers, and stakeholders can report suspicions or evidence of fraudulent behavior. Fraud and investigation support plays a critical role in managing these reports, conducting thorough investigations, and protecting whistleblowers.
c. Regular Audits and Reviews: Conducting periodic internal and external audits, along with independent reviews, to assess the effectiveness of existing control mechanisms and identify any gaps or weaknesses that may be exploited by fraudsters.
Response and Investigation:
When fraud is suspected or detected, organizations must respond swiftly and conduct thorough investigations. Fraud and investigation support offers specialized expertise to handle these situations effectively:
a. Incident Response Planning: Developing comprehensive incident response plans that outline the necessary steps to be taken when fraud is suspected or detected. These plans help organizations react swiftly and minimize the impact of fraud incidents on their operations, reputation, and financial stability.
b. Forensic Investigations: Engaging forensic experts who possess in-depth knowledge of fraud investigation techniques, digital forensics, and evidence collection. These professionals assist in gathering and analyzing evidence, conducting interviews, and preparing reports that can be used for legal actions, if necessary.
c. Collaboration with Law Enforcement: Coordinating with law enforcement agencies and legal counsel to ensure proper reporting, evidence preservation, and assistance in prosecuting fraudsters. Fraud and investigation support professionals often possess valuable relationships with law enforcement authorities, enabling seamless collaboration.Conclusion:
In the face of escalating financial deception threats, organizations must prioritize the implementation of comprehensive fraud and investigation support systems. By focusing on prevention, detection, and effective response strategies, companies can safeguard themselves against fraud, protecting their finances, reputation, and stakeholders. The role of fraud and investigation support in this endeavor cannot be overstated, as it provides the expertise and tools necessary to combat the ever-evolving landscape of financial deception.
#fraud#fraud investigation#investigation support#ca firm in delhi#internal audits#business#internal controls#accounting#finance
0 notes
Text
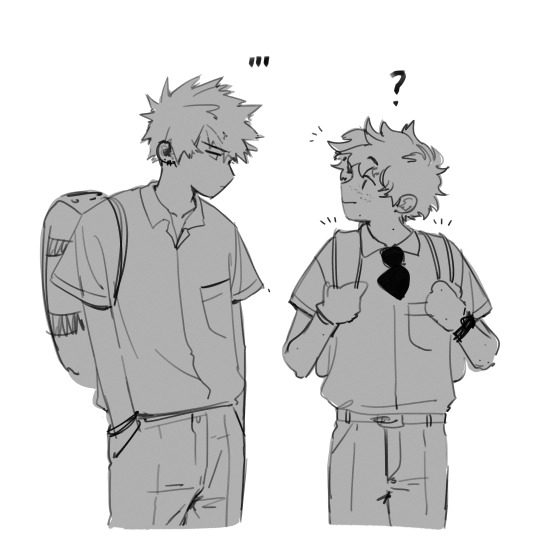

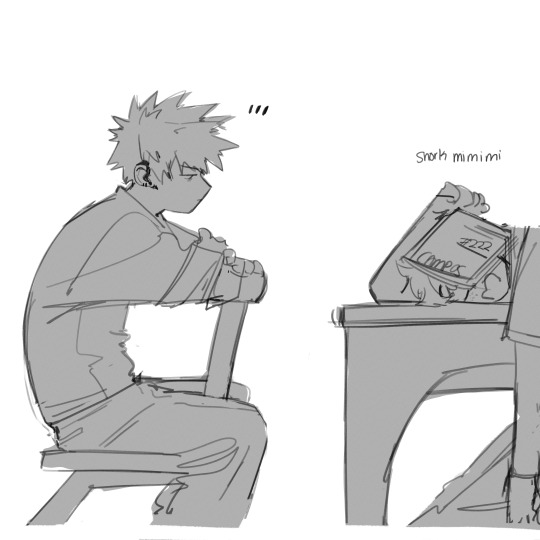
that time period when bakugo is worried sick about deku & the implications of being an ofa vessel but he’s still too proud to verbalize his worries so he just silently watches deku like a helicopter parent and nags like yea bakugo!!!! burying the hatchet won’t magically make you guys understand each other you actually have to verbalize your thoughts!!!! Deku doesn’t know you’re that worried you have to tell him!!!! Maybe that will make him less reckless!!!!friendship is magic but friendship is also so much work!!!!!
(I like to think that bakugo just stares at deku while fighting his demons (vulnerability) and deku is clueless and everyone else is a bit scared that this weird prolonged eye contact means that we’re gonna have a bkdk fight act IV)
#kind of related I love how most of that fic is dedicated to bakugo and deku realizing that they can’t just assume thing you have to#sit down and talkkkk#anyway these sketches are for the manga but yeah I like to observe bakugo’s internal struggle#and I get ittttt it can be so hard to just say the words it’s so much easier to nag and try to control others#I think bakugo would love to be a little control freak when it comes to deku like stop going doing everything by yourselfffffd#crazyyyy how that’s how he basically dies like he rlly shouldn’t be there but he has to this is bakugo after all
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
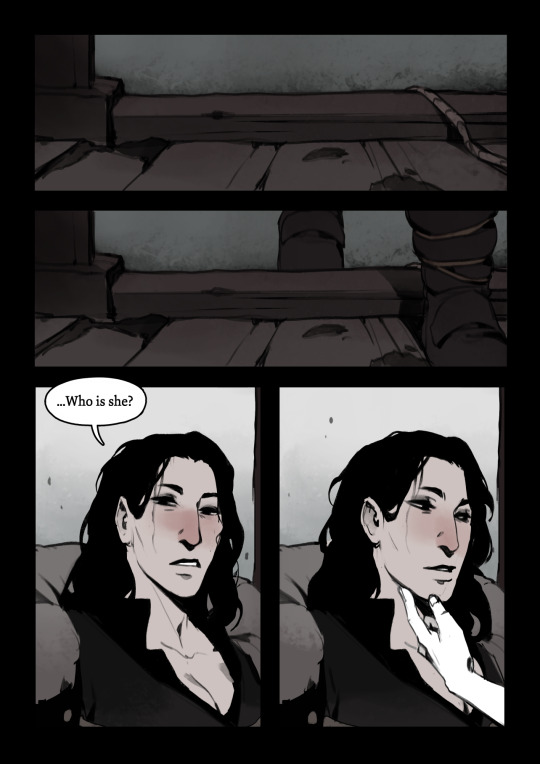
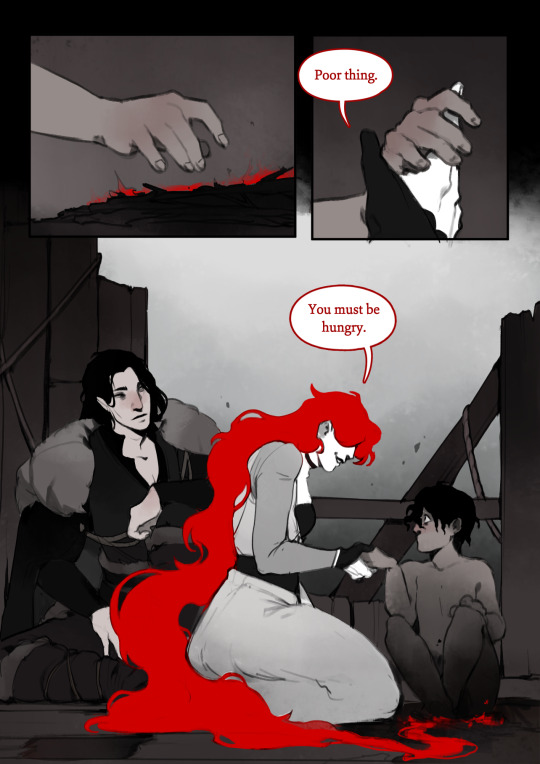




ashes to ashes.
a short comic about the day Ash was born.
Ash's story
Red and Wolf's story
notes:


--
all my other comics
store
#we love a family with a storied history of loving women and committing mass murder#wolf is a couple years older than she was in her original comic but still just as smitten with red#i dont intend on making it a habit to connect my comics together into a shared universe#but i did make ash with the internal headcanon that she was the kid of red and wolf#if only to justify elements of her design#the gravity defying hair - the control over fire - the commitment to a black/white/red colour scheme#i wont be doing a backstory for snow btw since she's kind of just. a human being who grew up very entitled and spoiled#although maybe during her undead journey she unknowingly comes across her mothers-in-law in the mountains#(they like to live in remote snowy areas)#red would like her#thats all!#thank you for reading#sapphic art#comic art#stillindigo art#hearteaters#stillindigo comics
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
How The Behavioral Risk Team Is Innovating The Internal Audit Function At NatWest
How The Behavioral Risk Team Is Innovating The Internal Audit Function At NatWest
The internal audit (IA) function is a largely unseen and unsung one compared to ones like sales and marketing, operations, and finance. But it is an essential one. Recently its role has been expanding beyond the traditional internal controls focus to a broader one getting into more complex issues like corporate culture. In order to do so, the IA function is adding new capabilities, such as in…

View On WordPress
#Alex Chesterfield#behavioral risk#Chris Spedding#corporate cultures#Featured#Financial Services#internal audit#internal controls#NatWest Group#outcomes#Sustainability
0 notes
Text
I really enjoy the contrast between the attitude towards killing in PJO and MCGA. Percy doesn't like killing and only does it when he has to, while feeling very tortured that he is quite good at violence despite wanting to avoid it. then Magnus shows up and his first resort is killing and he is so so bad at it. his sword is swinging him for god's sake, this boy is so cringefail at fighting and it is his first instinct, which goes entirely unquestioned. really a beautiful, beautiful contrast.
#HES SO FUNNY LIKE BABYGIRL WHAT ARE YOU DOING!!! WHY ARE YOU SO FULL OF RAGE!!!!#percy scares himself and hates it but magnus. he scares neither himself nor others but would like to! very muchly#and i love percy dearly as well bevause hes such a compelling and complex character so i love that internal conflict#but the contrast. gorgeous.#also in tkc. its like having those two fighting each other for control.#carter: what if we didnt kill everyone now#sadie: what if we did. that would be so cool and easier.#carter: nO-#percy jackson#magnus chase#pjo#mcga
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

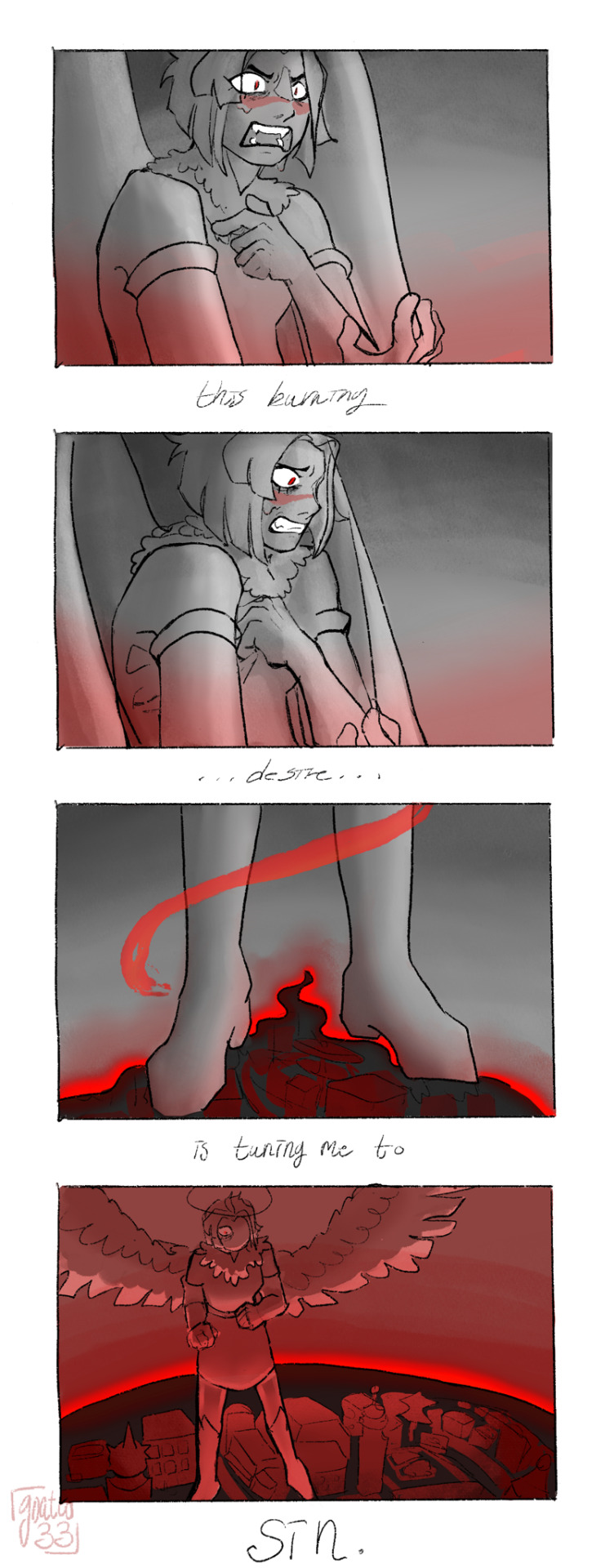
It’s not my fault! I’m not to blame. It is that wretched girl, the witch who sent this flame!
Inspired by @sharkscene ‘s tags
#to be clear it’s not her going to hell it’s her being terrified of it#heaven isn’t threatening her either she’s just breaking down from fear#vaggies the one ending up in hell after this#this was supposed to be a shitty sketch. again. I need self control I need restraint#ten productive and healthy ways to deal with your severe internalized homophobia! one: Kill Her#[my art]#hazbin hotel#hazbin hotel spoilers#(vaguely)#lute#vaggie x lute#lute x vaggie#fallenwings#…..#luggie#it’s only implied but that Is what it is#Ik what the songs about but it’s real funny to imagine that she had (1) romantic thought about her sparring partner#and immediately freaked out like this#not the cover I initially had in mind but it’s the only fem one I can find that doesn’t. slur#(use a slur. I mean)
237 notes
·
View notes
Text
Someone called Ozai "temper tantrum man", and I was going to comment on that with some sort of "Yes, but"...but then I realized that there is no "yes" to that.
He's not a tantrum person.
He has a temper, yes, but the guy doesn't freak out. Ever. Not even once. And it's a trait I hadn't considered about him, but it's so terrifyingly brilliant.
-Zuko speaks out. He just drags him off to the disciplinary Agni-Kai
-Zuko tells him Azula lied and the Avatar's alive. He just snarls at Zuko and tells him to get out, then starts goading the kid to attack him with swords while he doesn't have his own firebending
-Aang blows up his airship, and he just flies down and starts gloating about how favored he is by the universe
-Aang unlocks the Avatar State and grabs Ozai's beard, and Ozai counterattacks in the blink of an eye
-Aang nearly kills him and Ozai scoffs about how Aang is weak
-Aang takes his bending and Ozai throws punches until he realizes he's exhausted
-A bunch of teenagers start making fun of him and Ozai (still exhausted) pathetically protests before falling over
-Zuko comes to see him in jail and Ozai hits him with snark
The writing on that man is insane when you think about how cold he is.
#firelord ozai#the phoenix king#phoenix king ozai#atla#avatar: the last airbender#OBVIOUSLY he's kind of doing little internal tantrums every time#but he keeps himself controlled#heck it's probably one of the reasons why he despises zuko#because he's always just as angry as zuko but HE'S mature enough not to show it#gotta make daddy proud after all#be a respectable adult leader of a nation and all that
155 notes
·
View notes
Text

it's strange, knowing now who it was this whole time...
#stranger things#stranger things art#will byers#will byers fanart#byler#< target audience#obv <3#my art#are we ready to talk about how reeeeealy creepy vecna/henry is targeting kids or has this been discussed already...#or huge ramifications him possessing and controlling will has had on will's mental health#i'm still pissed about the fact that duffers started to explore more about will's internal conflict at the beginning of the 3rd season#(him not being able to move on and grow up)#and then they JUST DROPPED IT LIKE WHAT THE FUCK#AND THEN THEY JUST oh the conflict is resolved everything is cool now :)))#thank god we have fanfics otherwise this show is unwatchable
762 notes
·
View notes
Text
Anonymous asked:
What is the best about being mission control?
#FlightDirectorAT#answertime#NASA#flight director#mission control#International Space Station#Orion#artemis#space shuttle#Starliner
210 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sample Fraud Examination Report
Are you concerned about fraud in your business? Take a look at a hypothetical fraud examination report I prepared based on a real-life employee theft, criminal investigation, and prosecution. This case highlights the importance of proper internal controls and sound oversight in any organization. If you have similar concerns for your small or medium-sized business, feel free to reach out to me to discuss.
Link to the report: https://www.academia.edu/112496146/Sample_FRAUD_EXAMINATION_REPORT
NV PILB# 4253
0 notes
Text

Bartolomeo
#one piece#crezztellations#bartolomeo#he just like me fr fr#like bro fangirling over ur faves. i felt that#we are both hopeless nerds#literally collects all stuff / merch of our faves#becoming a weirdo when around the people u admire is near#but also wanting to look cool infront of them#its a constant internal struggle to control ur weirdo side and mature side#bartolomeo my boi
185 notes
·
View notes
Text
✨Manifesting a daily life of Eclipse✨
#I just want to see him struggle with the directives#I want to see his internal war#is that too much to ask??#headcanon that he was banging his head against the wall because he was losing control#sun and moon show#sams#the sun and moon show#tsams#sams eclipse#tsams eclipse
76 notes
·
View notes
Text
it is pretty fascinating redbull who is unbeatable on track is going through an internal implosion of absolute power corrupting like straight out of a moral fable. lol
#let it burn!#max gets paid 60 mil a year and has 4 championships in the bag#i promise you don't need to worry about him#when things are out of your control like this just let the chips fall where they may#imagine remembering 2024 in the future and going on i spent the first half worrying about a billion dollar corporation's internal managemen
62 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hey, yanno how Climate Change is a real thing that is tangibly, at this moment, affecting our world?
Well it turns out, the wealthy and their investment firms have been seeing the mounting evidence that oil companies have had for decades and are slowly starting to think more long-term about their portfolios in the face of rising sea levels, more extreme weather, and the myriad of ways climate crises are affecting...well. Everything. Maybe this means they invest more into sustainability, green energy, building more resilient infrastructure, or carbon offsets. Some of it, of course, is simple corporate greenwashing, but there are those that are taking this trend and packaging it into something called ESG (Environmental, Social, and corporate Governance).
Now some people would say this is predictable, even sensible. Just the good ol’ Free Market(tm) rationally responding to market forces and a changing world.
But those people would be fools! Insidious fools! For conservative sorcerers have come out with a new cursed phrase to explain this new market trend: Woke Investing.
What makes this investing “woke?” Well, much like how conservatives normally flounder when trying to define a word they stole from black people, “Woke Investing” essentially just means any kind of capital investment that they, the fossil fuel billionaire class and their sycophants, don’t personally profit from.
One of these aforementioned sycophants is Andy Puzder, conservative commentator, fellow at The Heritage Foundation, and former fast-food CEO. He calls this kind of so-called woke investing “socialism in sheep’s clothing,” further explaining in leaked audio of a closed-door meeting:
“My father's generation's challenge was the Nazis, who, by the way, were, of course, very proud socialists[citation fucking needed]. The challenge of my generation was the communists, who were, of course, very committed socialists. The challenge of your generation is ESG investing, and it's more insidious than communism or the Nazis.”(source)
You heard it here first, folks. Not investing as much in fossil fuels is more insidious than the Third Fucking Reich.
As usual, the Heritage Foundation is putting their petro-chemical donor’s money where their mouth is. Bills are being proposed to blacklist banks that don’t invest in key state industries, such as West Virginia coal or Texas oil. Fourteen states have already passed bills to restrict ESG-type investing, with Florida Governor Ron “Bullies Kids for Wearing Masks” Desantis leading the charge.
In other words, Climate Denial has reached such a point that so-called Free Market Conservatives who claim to hate big government are trying to make it illegal for banks, investment firms, and financial institutions to make any financial decisions that acknowledges Climate Change is real.
#of course ESG has also been used to describe any kind of internal corporate action#to increase diversity in the work place or implementing new anti-discrimination policies#(which are usually more performative than actually meaningful but that's a separate issue)#a Republican Presidential candidate#Vivek Ramaswamy#has even made ESG investing his personal bugbear#writing such books as 'Woke Inc' and warning of socially conscious investors ''forcing'' companies they invest in#to devote resources to environmental and social policies that are anathema to the right#which is just...a brand new invented crisis by a political movement#in constant need of a crisis to rally their base and justify for draconian legal controls#to favor certain industries and undercut their competition#all under the guise of red scare-type moral and economic panic#ESG#Woke Politics#Climate Change#Capitalism#Republicans#Investment
112 notes
·
View notes