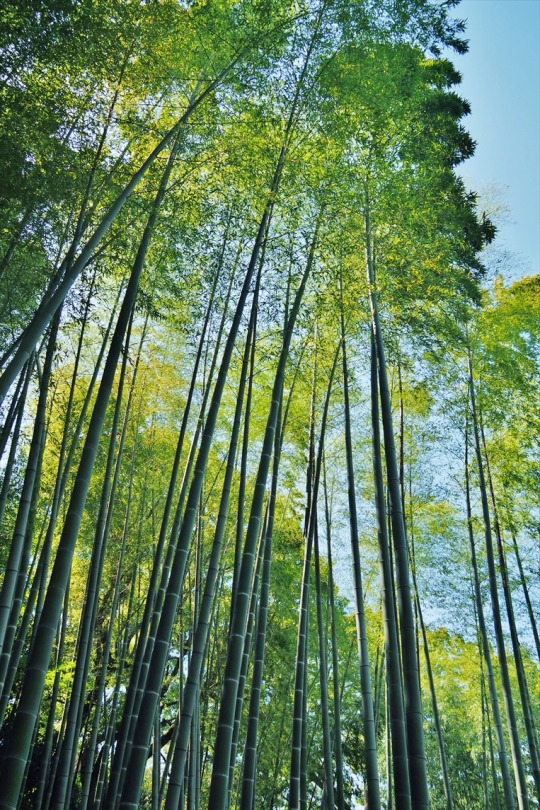
#imperial palace east garden
Text
Tokyo tour! Imperial Palace East Garden, Odaiba( manmade island), Love sign, Statue of Liberty, Shibuya Crossing, Takeshita street, rainbow cotton candy!
Tokyo car tour! Imperial Palace East Garden, Odaiba( manmade island), Love sign, Statue of Liberty, Shibuya Crossing, Takeshita street, rainbow cotton candy!
Hi I’m Nobu, I like traveling overseas and in Japan, visited 26 countries!
I’m a National Government Licensed Guide Interpreter of English for 10 years.
For the people who are interested in and planning trip to Japan ,I show you hidden…

View On WordPress
#imperial palace east garden#Odaiba seaside park#raimbow cotton candy#Shibuya crossing#Statue of Liberty#takeshita street#Tokyo travel tips
1 note
·
View note
Text

To Plant a Garden is to Believe in Tomorrow.
– Audrey Hepburn
#Azaleas#Pink#Flowers#Rhododendron#Shrub#Japanese Azalea#Imperial Family#Garden#Flower Bed#Petals#Spring#Tokyo Imperial Palace#Ninomaru Garden#Imperial Palace East Gardens#Tokyo#Japan
7 notes
·
View notes
Text

Regal Reverie: Imperial Tokyo Palace!
#Imperial Tokyo Palace#Japan#history#culture#architecture#royalty#gardens#traditional#elegance#heritage#landmarks#emperor#empress#Tokyo#East Asia#tourism#sightseeing#travel#Asian architecture#symbolic#regal#opulence#magnificent#serene#majestic#historic site#cherry blossoms#scenic#breathtaking#iconic
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo

3 notes
·
View notes
Text
in addition to being prone to an obvious naturalistic fallacy, the oft-repeated claim that various supplements / herbs / botanicals are being somehow suppressed by pharmaceutical interests seeking to protect their own profits ('they would rather sell you a pill') belies a clear misunderstanding of the relationship between 'industrial' pharmacology and plant matter. bioprospecting, the search for plants and molecular components of plants that can be developed into commercial products, has been one of the economic motivations and rationalisations for european colonialism and imperialism since the so-called 'age of exploration'. state-funded bioprospectors specifically sought 'exotic' plants that could be imported to europe and sold as food or materia medica—often both, as in the cases of coffee or chocolate—or, even better, cultivated in 'economic' botanical gardens attached to universities, medical schools, or royal palaces and scientific institutions.
this fundamental attitude toward the knowledge systems and medical practices of colonised people—the position, characterising eg much 'ethnobotany', that such knowledge is a resource for imperialist powers and pharmaceutical manufacturers to mine and profit from—is not some kind of bygone historical relic. for example, since the 1880s companies including pfizer, bristol-myers squibb, and unilever have sought to create pharmaceuticals from african medicinal plants, such as strophanthus, cryptolepis, and grains of paradise. in india, state-created databases of valuable 'traditional' medicines have appeared partly in response to a revival of bioprospecting since the 1980s, in an increasingly bureaucratised form characterised by profit-sharing agreements between scientists and local communities that has nonetheless been referred to as "biocapitalism". a 1990 paper published in the proceedings of the novartis foundation symposium (then the ciba foundation symposium) spelled out this form of epistemic colonialism quite bluntly:
Ethnobotany, ethnomedicine, folk medicine and traditional medicine can provide information that is useful as a 'pre-screen' to select plants for experimental pharmacological studies.
there is no inherent oppositional relationship between pharmaceutical industry and 'natural' or plant-based cures. there are of course plenty of examples of bioprospecting that failed to translate into consumer markets: ginseng, introduced to europe in the 17th century through the mercantile system and the east india company, found only limited success in european pharmacology. and there are cases in which knowledge with potential market value has actually been suppressed for other reasons: the peacock flower, used as an abortifacient in the west indies, was 'discovered' by colonial bioprospectors in the 18th century; the plant itself moved easily to europe, but knowledge of its use in reproductive medicine became the subject of a "culturally cultivated ignorance," resulting from a combination of funding priorities, national policies, colonial trade patterns, gender politics, and the functioning of scientific institutions. this form of knowledge suppression was never the result of a conflict wherein bioprospectors or pharmacists viewed the peacock flower as a threat to their own profits; on the contrary, they essentially sacrificed potential financial benefits as a result of the political and social factors that made abortifacient knowledge 'unknowable' in certain state and commercial contexts.
exploitation of plant matter in pharmacology is not a frictionless or infallible process. but the sort of conspiratorial thinking that attempts to position plant therapeutics and 'big pharma' as oppositional or competitive forces is an ahistorical and opportunistic example of appealing to nominally anti-capitalist rhetoric without any deeper understanding of the actual mechanisms of capitalism and colonialism at play. this is of course true whether or not the person making such claims has any personal financial stake in them, though it is of course also true that, often, they do hold such stakes.
537 notes
·
View notes
Text

Rome’s 'Lost' Imperial Palace 'Domus Tiberiana' Reopens
Until recently a crumbling and off-limits ruin near the famous Colosseum, the Domus Tiberiana palace — built in the first century AD and beloved by Nero — hopes to once again take its place as one of the city’s top tourist attractions.
The ancient palace sits on Palatine Hill — the city’s oldest hill, overhanging Rome —from where imperial dynasties ruled for centuries. But over the years, the site fell into disrepair and in the 1970s, the Domus Tiberiana site was shut due to the structural instability of some of the ruins. The closure left behind what many Romans described as a “black hole” in the capital’s archaeological heart.
Now, after a six-year makeover, the palace has reopened its doors as a “diffuse museum,” with findings and frescoes scattered across the site to provide visitors with an insight into the palace’s ancient grandeur.

And it was grand. The Domus Tiberiana was Rome’s first imperial palace, built by the emperor Tiberius who combined and incorporated the pre-existing noble mansions built on the hill. Occupying over four hectares, the palace featured residences alongside large gardens, places of worship and rooms for the emperor’s Praetorian guard.
As the seat of Rome’s power and politics, Domus Tiberiana held a prime location, high above the Palatine and Roman Forums, offering its occupants a “balcony view of the city.” Over time, the Domus was embellished and enlarged by other emperors including Nero, who was crowned on its steps aged just 16, in 54 AD.
Alfonsina Russo, director of the Colosseum’s archaeological park (in which Domus Tiberiana falls) and lead archaeologist on the renovation, said that ancient antiquities, many exceptionally well-preserved, were unearthed during the project.
The artifacts — bright stuccos, frescoes, amphorae, potteries, looms, terracotta, and divinity statues related to the cults of Isis, Dionysius and Mithras — offer visitors a trip through time, said Russo.
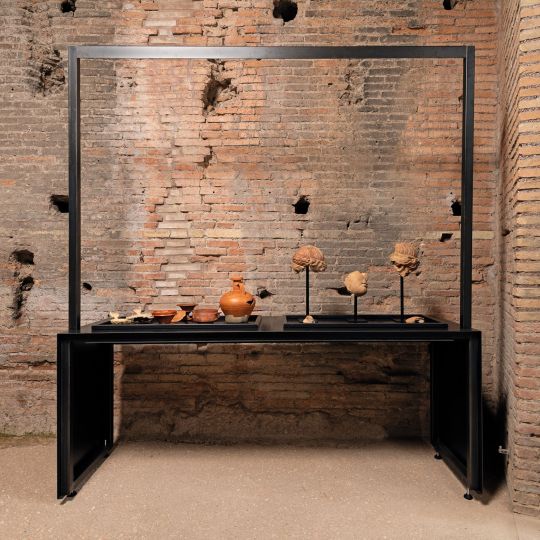

“They make this place — formerly (inhabited) by aristocratic families, then Roman emperors — feel alive again,” she said. “There are seven exhibition rooms full of extraordinary finds, starting with those preceding the original construction of the palace when aristocrats lived in mansions before Tiberius subsumed them into the Domus.”
Among the newly-exposed and frescoes are some of the earliest paintings of lemons (considered an exotic fruit in Ancient Rome, as they hailed from the Far East) and a depiction of a gladiator, proving that the era’s gladiatoral games were appreciated by rich families, explained Russo.
The imperial palace remained in use until the 7th century, when it became the papal residence of John VII. In the mid-16th century, the aristocratic Farnese family — who were powerful local landowners — built the lavish Orti Farnesiani gardens on the site, adorning it with ornaments and sculptures of nymphs, satyrs and fauns.
“This monument speaks of history,” Russo added. “We have restored (Domus Tiberiana) to its past splendor, but more work lies ahead.”
Indeed, painstaking efforts have been made to blend old and new. A series of majestic, reddish-brown vaulted arches that greet visitors having been carefully reconstructed with the same materials as ancient Romans used in the past.
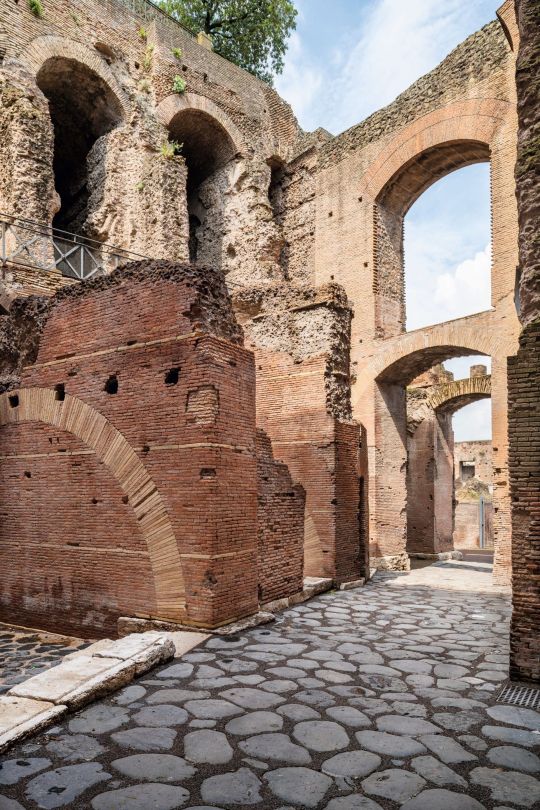


“What makes this revamped Domus unique is the architectural style,” said Russo. “We managed to use original materials to reinforce and strengthen the handmade 15-meter (50ft) tall front arches (which run alongside the palace’s) ancient paving.”
It has certainly caught the public’s attention. Since reopening at the end of September, Domus Tiberiana has attracted some 400,000 visitors, a “huge success,” said Russo, adding that she believes that this incarnation of the Domus Tiberiana offers visitors the most “evocative” visit in generations.
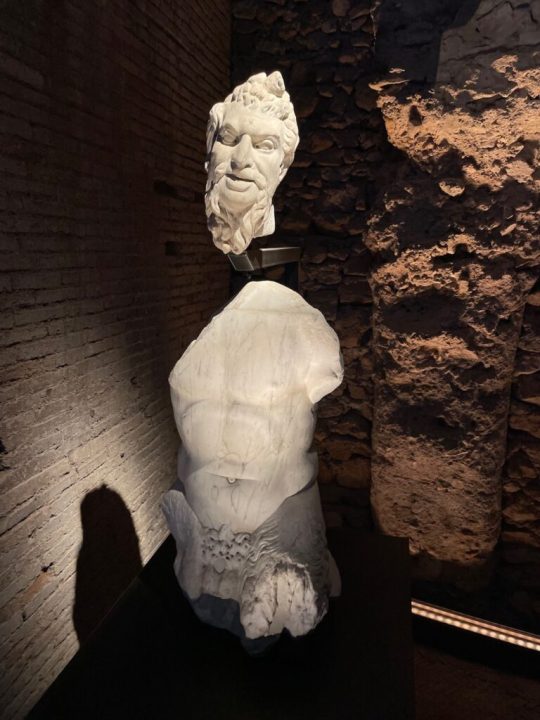


Archaeologist and scholar of ancient Rome Giorgio Franchetti saidN that, in the reopening of the Domus Tiberiana complex, Rome has “recovered a lost jewel.”
“The Palatine Hill has always been the stage of Rome’s power politics,” he said in an interview. “Tiberius likely chose this spot to build the palace as it was where his family residence stood. There aren’t many places like the Domus Tiberiana where you can really breathe the past.”
By Silvia Marchetti.



#Rome’s 'Lost' Imperial Palace 'Domus Tiberiana' Reopens#Domus Tiberiana palace#Palatine Hill#Emperor Tiberius#Emperor Nero#ancient artifacts#archeology#archeolgst#history#history news#ancient history#ancient culture#ancient civilizations#ancient rome#roman history#roman empire#roman emperor#roman art
264 notes
·
View notes
Text
A walk through Bengal's architecture
Bengali architecture has a long and rich history, fusing indigenous elements from the Indian subcontinent with influences from other areas of the world. Present-day Bengal architecture includes the nation of Bangladesh as well as the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura, and Assam's Barak Valley. West Bengal’s architecture is an amalgamation of ancient urban architecture, religious architecture, rural vernacular architecture, colonial townhouses and country houses, and modern urban styles. Bengal architecture is the architecture of Wind, Water, and Clay. The Pala Empire (750–1120), which was founded in Bengal and was the final Buddhist imperial force on the Indian subcontinent, saw the apex of ancient Bengali architecture. The majority of donations went to Buddhist stupas, temples, and viharas. Southeast Asian and Tibetan architecture was influenced by Pala architecture. The Grand Vihara of Somapura, which is now a UNESCO World Heritage Site, was the most well-known structure erected by the Pala rulers.

The Grand Vihara of Somapura
According to historians, the builders of Angkor Wat in Cambodia may have taken inspiration from Somapura. Bengal architecture became known for its use of terracotta due to the scarcity of stone in the area. Clay from the Bengal Delta was used to make bricks.
The temple architecture has distinct features like the rich wall decoration, often known as the terracotta temples, which was one of the remarkable elements of Bengali temple architecture. The double-roofed architecture of thatched huts was replicated by Bengali temples. Square platforms were used to construct the temples. Burnt brick panels with figures in geometric patterns or substantial sculptural compositions served as the temples' adornment.

Dochala style
These served as models for many temples that were built in undivided Bengal. Construction materials used in ancient times included wood and bamboo. Bengal has alluvial soil, so there isn't a lot of stone there. The bricks that were utilized to build the architectural components were made from stone, wood, black salt, and granite. Bengal has two different types of temples: the Rekha type, which is smooth or ridged curvilinear, and the Bhadra form, which has horizontal tiers that gradually get smaller and is made up of the amalaka sila. Mughal architecture, including forts, havelis, gardens, caravanserais, hammams, and fountains, spread throughout the area during the Mughal era in Bengal. Mosques built by the Mughals in Bengal also took on a distinctive regional look. The two major centers of Mughal architecture were Dhaka and Murshidabad. The do-chala roof custom from North India was imitated by the Mughals.

Jorasako thakurbari

The Rasmancha is a heritage building located at Bishnupur, Bankura district, West Bengal.
Influence of the world on Bengal architecture: Although the Indo-Saracenic architectural style predominated in the area, Neo-Classical buildings from Europe were also present, particularly in or close to trading centers. While the majority of country estates had a stately country house, Calcutta, Dacca, Panam, and Chittagong all had extensive 19th and early 20th-century urban architecture that was equivalent to that of London, Sydney, or other British Empire towns. Calcutta experienced the onset of art deco in the 1930s. Indo-Saracenic architecture can be seen in Ahsan Manzil and Curzon Hall in Dhaka, Chittagong Court Building in Chittagong, and Hazarduari Palace in Murshidabad.

Hazarduari Palace in Murshidabad
The Victoria Memorial in Kolkata, designed by Vincent Esch also has Indo-Saracenic features, possibly inspired by the Taj Mahal. Additionally, Kolkata's bungalows, which are being demolished to make way for high-rise structures, have elements of art deco. The 1950s in Chittagong saw a continuation of Art Deco influences. The Bengali modernist movement, spearheaded by Muzharul Islam, was centered in East Pakistan. In the 1960s, many well-known international architects, such as Louis Kahn, Richard Neutra, Stanley Tigerman, Paul Rudolph, Robert Boughey, and Konstantinos Doxiadis, worked in the area.

The Jatiyo Sangshad Bhaban
This iconic piece of contemporary Bangladeshi architecture, was created by Louis Kahn. Midsized skyscrapers dominate the cityscapes of contemporary Bengali cities, which are frequently referred to as "concrete jungles." With well-known architects like Rafiq Azam, architecture services play a key role in the urban economies of the area. Overall Bengal architecture was influenced by various contemporaries of their time and continues to evolve.

Gothic architectural style seen in St. Paul's Cathedral in Kolkata.

Zamindar era buildings in ruin.

Belur Math in Howrah
#bengali#bangla#west bengal#bangladesh#tripura#assam#desi#বাংলা#india#architecture#tales#bengal architecture#history#kolkata#international#technology#information#temple#asia#bricks
171 notes
·
View notes
Text
British presence in the Straits Settlements […] (Penang, Singapore and Melaka) as a whole opened the way […]. Governor Andrew Clarke [...] clearly intended that economic botany should follow the quest for tin. Hardly three months after the [signing of the treaty legitimising British control in Malaya] [...] the Governor pressed Lord Carnarvon, Secretary of State for the Colonies, himself a keen botanist and collector, for the services of a ‘scientific botanist’. [...] Intimate plant knowledge among local [people] [...] assisted the discovery of many [plants valuable to European empire] [...] and the absorption of a number of vernacular names such as kempas (Koompassia), pandan (Pandanus) and nipah (Nypa) into scientific nomenclature. Equally, indigenous names for timbers, pre-eminently meranti and cengal, attained the status of trade names on the international market. Malay knowledge [...] proved also invaluable for commerce and [...] industries.
The Great Exhibition of 1851 at the Crystal Palace in Hyde Park, which displayed representative samples of colonial resources, was a microcosm of empire. Empire [...] co-sponsored the surveying, mapping and inventorying of people, lands and products for the ends of imperial power. Tropical nature, once a source [...] of wonderment, was brought to the domestic market place.
High on the imperial economic agenda were the Malayan territories, the source of gutta percha (from Palaquium gutta). Ingeniously adapted by the Malays [...], the plastic qualities of gutta percha were investigated for medical and industrial use by the [English East India] Company surgeons, T. Mongtomerie (1819-43) and T. Oxley (1846-57). [...] At the same time Oxley successfully pioneered the use of gutta percha for plastering fractures and preserving vaccine, the latter hitherto unable to be kept even for a few days. When a Prussian artillery Officer [...] then perfected its use for insulating telegraph cables, the product immediately gained strategic importance for the empire. Similar adaptations of other indigenous uses of plants paid dividends to industry and agriculture. [...]
---
The emergence of Hevea rubber in the Peninsula, superseding gutta percha as an industrial product was, again, the result of scientific exchange within the close-knit colonial botanical network [...] [following] [t]he illegal exportation by Kew [Royal Botanic Gardens in London] of the seedlings from South America to Ceylon and the Singapore Botanic Gardens [...]. Out of the seedlings sent in 1877 to Singapore, seven were planted by Hugh Low in the Perak Residency Garden. These and those raised in the Botanic Gardens furnished the seeds for the first plantations.
Though an introduced species, indigenous knowledge [...] of a wide variety of gums and exudates [...] benefited the plantation industry.
This [...] scored a major triumph for the colonial plantation industry. [...]
Large areas of Melaka had already been laid to waste by [...] a fast-growing variety of Brazilian cassava introduced in 1886 by Cantley.
The same cultivators soon turned the Imperata grasslands to rubber, but its rapid spread meant that a number of native plant species either became very rare or were entirely exterminated. The wild ancestor of the domestic mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) is a likely example. [...] During his visit to Singapore in 1854 Wallace identified, within just a square mile, some 700 species of beetles [...].
---
All text above by: Jeyamalar Kathirithamby-Wells. "Peninsular Malaysia in the context of natural history and colonial science." New Zealand Journal of Asian Studies Volume 11 Number 1. 2009. [Bold emphasis and some paragraph breaks/contractions added by me.]
56 notes
·
View notes
Text
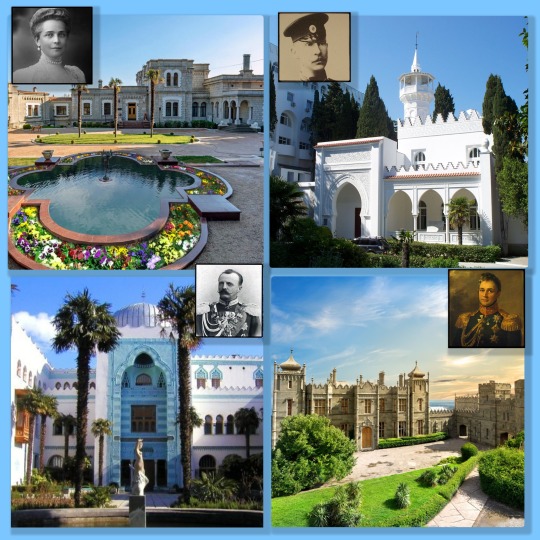


The other palaces in the Crimea
The Palace of Koreiz was owned by the Yousupov Family, and the inside photos show an exquisite place. It is worth taking the time to check them out.
The Palace of Kichkine was built by Grand Duke Dmitry Konstantinovich as a place he could enjoy with his nephews.
Dulber means "beautiful" or "heart stealing" in Tartar. This palace was built by Grand Duke Pyotr Nikolaievich. Design and construction were based on his sketches. The Grand Duke had great knowledge of Middle Eastern Architecture and history. The palace has more than 100 rooms.
The Vorontzov Palace (built by Prince Mikhail Vorontzov) is one of the oldest palaces in the Crimea. It has 150 rooms and is surrounded by gardens and parks. Vorontsov's palace started a tradition of imperial residency in the area. Many Russian elite were attracted to build villas and palaces in the Crimea.
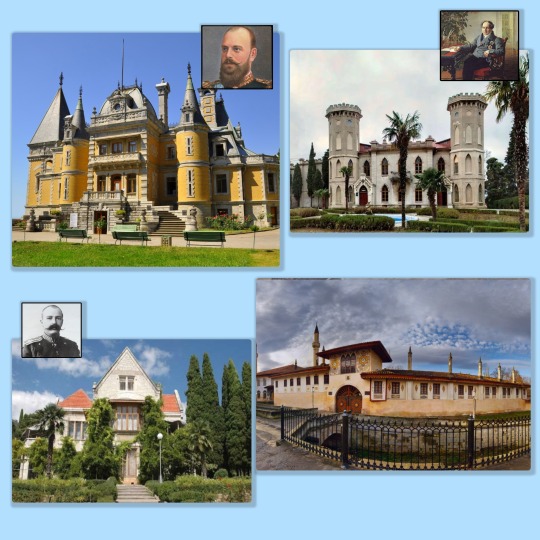
Massandra: This palace was initially being built for the Vorontzovs, but a death in the family caused the project to halt. Alexander III bought the palace and had it redesigned. The family never stayed in the palace, preferring their other palace at Livadia (the old Livadia palace, not the beautiful white heaven we all know and love.
The Golytzin Palace: This palace can only be seen on the outside. It has a long and turbulent story. The Golytzin who built it only lived in it for one year.
Harax: Grand Duke George Mikhailovich's wife, Grand Duchess Marie Georgievna, wanted an English country house in the middle of the Middle East. Everybody thought it could not be done but it was. George and Marie spent the best years of their very troubled marriage living at Harax.
Bagçesaray Palace of the Crimean Khans is a compact architectural ensemble consisting of 17 buildings and 9 inner closed courtyards. I have included a photo here because it is a source of much controversy. The palace is said to be magically beautiful and, in 2013, was listed by UNESCO as a potential addition to its World Heritage List. It was the administrative capital of the Crimean Khanate from 1532 to 1783. Apparently, the renovations have been botched. The issues regarding this historic treasure will have to be picked up again once the region has restored peace. Right now, they are not the priority.
The nobility in the Crimea
By the end of the Russian Empire, Crimea had become the most coveted "vacation spot" for the Russian elites. Palaces continued to sprout up. The sun, sea, mountains, flowers...and nobility had each other. Summers in Crimea became almost like an informal season, with teas, picnics, the occasional balls, dinners, etc. And protocol was eased. The Tsar was a frequent visitor to Harax and Dulber (at one point.) He enjoyed sitting outside and smoking. When he was there, the cossacks were there for musical entertainment.
.
#russian history#imperial russia#romanov family#Princess Zenaida Yusupova#Koreiz#Harax#Dulber#Golytzin Pa;ace#Vorontsov Palace#Dulber Palace#Kichkine#Bagçesaray Palace#Massandra Palace
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
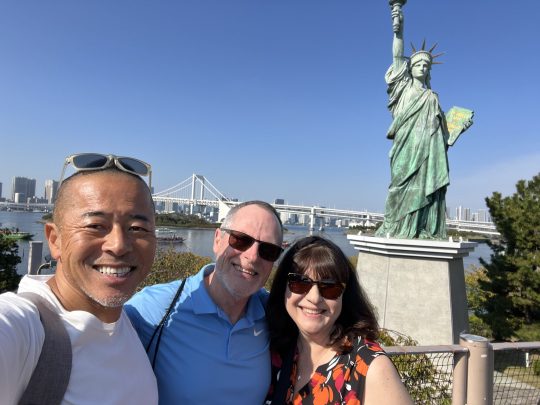
Tokyo 1 day tour! Imperial palace east garden, Odaiba seaside park, Okonomiyaki lunch,Gundam robot, Statue of Liberty ,Tokyo cruise,Asakusa,Akihabara and plushy!
Tokyo 1 day tour! Imperial palace east garden, Odaiba seaside park, Okonomiyaki lunch,Gundam robot, Statue of Liberty ,Tokyo cruise,Asakusa,Akihabara and plushy!
Hi I’m Nobu, I like traveling overseas and in Japan, visited 25 countries!
I’m a National Government Licensed Guide Interpreter of English for 8 years.
For the people who are interested in and planning trip to Japan ,
I show you…

View On WordPress
#Asakusa#gundam statue#imperial palace east garden#Odaiba seaside park#okonomiyaki#Statue of Liberty#Tokyo cruise#Tokyo travel tips#Yurikamome
1 note
·
View note
Text
Japanese Azaleas ❁ཻུ۪✾⚘༉ (Rhododendron Japonicum)

#Azaleas#Flowers#Rhododendron#Shrub#Japanese Azalea#Imperial Family#Garden#Flower Bed#Petals#Spring#Tokyo Imperial Palace#Ninomaru Garden#Imperial Palace East Gardens#Tokyo#Japan
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
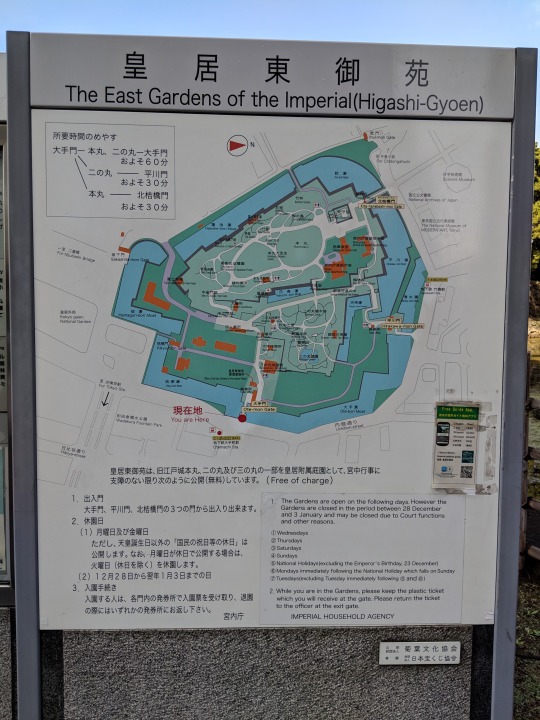
皇居東御苑
The East Gardens of the Imperial (HIgashi-Gyoen)
所要時間
大手本 → 本丸、二の丸ーー大手門
およそ60分
→二の丸、ーーー平川門
およそ30分
→本丸ーーーー北桔橋門
およそ30分
乾門 Inui-mon Gate
至千鳥ヶ淵 For Chidorigafuchi
科学技術館 Science Museum
国立公文書館 National Archives of Japan
東京国立近代武術間 The National Museum of MODERN ART, Tokyo
乾濠 Inui-bori Moat
発券所 Ticket office
北桔橋門 Kita-hanebashi-mon Gate
平川濠 Hirakawa-bori Moat
1a出口 (Exit)
地下鉄 竹橋駅 Takebashi Sta.
清水濠 Shimizu-bori Moat
平川門 Hirakawa-mon Gate
天守台 Tenshudai (Tenshukaku Dunjon Base)
宮内庁書陵部庁舎 Shoryobu (Archives and Mausolea Department Bldg.)
桃華楽堂 Gakubu (Music Department Bldg.)
梅林坂 Bairin-zaka Slope
都道府県の木 Symbolic Prefectural Tree Emblems
天神濠 Tenjin-bori Moat
発券所 Ticket office
大手濠 Ote-bori Moat
内堀通り Uchibori-street
諏訪の茶屋 Suwano-chaya Tea House
竹林 Bamboo Garden
石室 Ishimuro (Stone Cellar)
桜の島 Sakura Blossom Island
富士見多門 Fujimi-tamon Defence-house
バラ園 Rose Garden
茶畑 Tea Garden
ユーロッパアカマツ Scots Pine
本丸 Honmaru
本丸大芝生 Honmaru Oshibafu (Lawn)
本丸休憩所 Honmaru Rest House
汐見坂 Shiomizaka Slope
白鳥濠 Hakucho-bori Moat
展望台 Observatory
二の丸休憩所 Ninomaru Rest House
二の丸雑木林 Ninomaru Grove
秋の七草 The Seven Flowers of Autumn
新雑木林 Renewed Grove
菖蒲田 Iris Garden
二の丸庭園 Ninomaru Garden
蓮池濠 Hausike-bori Moat
松の大廊下跡 Site of Matsuno-o-roka Corridor
果樹古品種園 Orchard (Old Species of Japanese Fruits)
野草の島 Wild Grass Island
緑の泉 Green Fountain
中雀門跡 Site of Chujaku-mon Gate
大番所 O-bansho Guardhouse
中之門跡 Site of Nakano-mon Gate
百人番所 Hyakunin-bansho Guardhouse
同心番所 Doshin-bansho Guardhouse
大手休憩所 Ote Rest House
三の丸尚蔵館 Sannomaru Shozokan The museum of the Imperial Collections
皇居東御苑管理事務所 Office of the East Gardens of the Imperial Palace
発券所 Ticket Office
大手門 Ote-mon Gate
現在地 You are Here
C13b出口 (Exit) Otemachi Sta.
坂下門 Sakashita-mon Gate
富士見櫓 Fujimi-yagura (Mt. Fuji View Keep
蛤濠 Hamaguri-bori Moat
桔梗門 Kikyo-mon Gate
桔梗濠 Kikyo-bori Moat
←至 二重橋 For Nijubashi Bridge
皇居外苑 Kokyi gaien National garden
至 JR東京駅 For Tokyo Sta.
和田倉噴水公園 Wadakura Fountain Park
日比谷通り Hibiya-street
皇居東御苑は、旧江戸城本丸、二の丸及び三の丸の一部を皇居付属庭園として、宮中行事に支障のない限り次のように公開(無量)しています。(Free of charge)
1.出入門
大手門、平川門、北桔橋門の3つの門から出入り出来ます。
2.休園日
(1)月曜日及び金曜日
ただし、天皇誕生日以外の「国民の祝日等の休日」は公開します。なお、月曜日が休日で公開する場合は、火曜日(休日を除く)を休園します。
(2)12月28日から翌年1月3日までの日
3.入園手続き
入園するは、各門内の発券所で入園票を受け取り、退園の際にはいずれかの発券所にお返し下さい。
宮内庁
1.The Gardens are open on the following days. However the Gardens are closed in the period between 28 December and 3 January and may be closed due to Court functions and other reasons.
① Wednesdays
② Thursdays
③ Saturdays
④ Sundays
⑤ National Holidays (excluding the Emperor’s Birthday, 23 December)
⑥ Mondays immediately following the National Holiday which falls on Sunday
⑦ Tuesdays (excluding Tuesday immediately following ⑤ and ⑥)
2.While you are in the Gardens, please keep the plastic ticket which you will receive at the gate. Please return the ticket to the officer at the exit gate.
IMPERIAL HOUSEHOLD AGENCY
公益財団法人菊葉文化協会
寄贈 財団法人日本宝くじ協会
Vocab
皇居(こうきょ)imperial
御苑(ぎょえん)imperial garden
所要時間(しょようじかん)time required, time taken
至(し)to
科学時術(かがくじじゅつ)science and technology
近代美術館(きんだいびじゅつかん)museum of modern art
濠(ほり)moat, canal
発券(はっけん)issuing (a ticket, etc.)
宮内庁(くないちょう)Imperial Household Agency
書陵部(しょりょうぶ)agency that takes care of records and the tombs
庁舎(ちょうしゃ)government office building
梅林(ばいりん)plum grove
都道府県(とどうふけん)prefectures of Japan
竹林(ちくりん)bamboo grove
茶畑(ちゃばたけ)tea field
ユーロッパアカマツ Scots/Scotch pine, Pinus slyvestris
芝生(しばふ)lawn, grass
休憩所(きゅうけいしょ)rest area, rest stop
展望台(てんぼうだい)observation deck
雑木林(ぞうきばやし)thicket; grove of miscellaneous trees
秋の七草(あきのななくさ)seven flowers of autumn: bush clover, Chinese silvergrass, kudzu, fringed pink, golden lace, thoroughwort, and balloon flower
菖蒲(しょうぶ)Japanese iris (Iris ensata var. ensata) [coll.]
果樹(かじゅ)fruit tree
品種(ひんしゅ)breed variety, cultivar
野草(のぐさ)wild grasses
泉(いずみ)fountain
番所(ばんしょ)guardhouse
桔梗(ききょう)Chinese bellflower (Platycodon grandiflorus)
外苑(がいえん)outer garden
噴水(ふんすい)water fountain
付属(ふぞく)being attached (to), belonging (to)
宮中(きゅうちゅう)imperial court
行事(ぎょうじ)event, function
支障(ししょう)obstacle, hindrance
休園日(きゅうえんび)day on which a park (or kindergarten or zoo) is closed
祝日(しゅくじつ)national holiday
なお furthermore
除く(のぞく)to exclude, except
手続き(てつづき)procedure, process
票(ひょう)ticket, stub (suffix)
公益財団法人(こうえきざいだんほうじん)public interest incorporated foundation
文化協会(ぶんかきょうかい)cultural association
公益財団法人菊葉文化協会(こうえきざいだんほうじんきくようぶんかきょうかい)a cultural association that focuses its research on making artifacts of the imperial household available to the public.
寄贈(きぞう)donation, gift
宝くじ(たからくじ)lottery ticket
#日本語#日本#japanese language#japanese langblr#japanese vocabulary#japan#東京#Tokyo#Tokyo imperial gardens#皇居東御苑
12 notes
·
View notes
Photo

2 notes
·
View notes
Text





2023年 11月 22日
Buildings in Imperial Palace East Gardens
Fujifilm X-T20 + 35mm
11 notes
·
View notes

