#Louis-Philippe
Photo

The "Spring of Nations", Revolutionary Europe in 1848
A map illustrating the series of republican revolts and political upheavals against European monarchies in 1848, also known as the People's Spring or the Spring of Nations. The widespread violent unrest started in Sicily and, within a short time, spread to France, Germany, Italy, and the Austrian Habsburg Empire, only to simmer out at the western boundaries of Tsarist Russia.
Image by Simeon Netchev
95 notes
·
View notes
Text
Napoleon as a rallying cry during the revolutions in France during the 19th century
July Revolution (French Revolution of 1830):

French Revolution of 1848:

Source: The Pursuit of Power: Europe 1815-1914, Richard J. Evans
#The Pursuit of Power#Richard J. Evans#Evans#Napoleon#napoleon bonaparte#Talleyrand#Charles X#Thiers#Marmont#Lafitte#Jacques Lafitte#Louis-Philippe#Lafayette#Revolution#french revolution#July Revolution#1848 revolutions#Revolution of 1848#1848#napoleonic era#Blanc#first french empire#napoleonic#history#french history#my pics#book#book quotes#revolution of 1830#France
23 notes
·
View notes
Text

LES MIS LETTERS IN ADAPTATION - Louis Philippe, LM 4.1.3 (Les Miserables 1972)
The son of a father to whom history will accord certain attenuating circumstances, but also as worthy of esteem as that father had been of blame; possessing all private virtues and many public virtues; careful of his health, of his fortune, of his person, of his affairs, knowing the value of a minute and not always the value of a year; sober, serene, peaceable, patient; a good man and a good prince; sleeping with his wife, and having in his palace lackeys charged with the duty of showing the conjugal bed to the bourgeois, an ostentation of the regular sleeping-apartment which had become useful after the former illegitimate displays of the elder branch; knowing all the languages of Europe, and, what is more rare, all the languages of all interests, and speaking them; an admirable representative of the “middle class,” but outstripping it, and in every way greater than it; possessing excellent sense, while appreciating the blood from which he had sprung, counting most of all on his intrinsic worth, and, on the question of his race, very particular, declaring himself Orleans and not Bourbon; thoroughly the first Prince of the Blood Royal while he was still only a Serene Highness, but a frank bourgeois from the day he became king; diffuse in public, concise in private; reputed, but not proved to be a miser; at bottom, one of those economists who are readily prodigal at their own fancy or duty; lettered, but not very sensitive to letters; a gentleman, but not a chevalier; simple, calm, and strong; adored by his family and his household; a fascinating talker, an undeceived statesman, inwardly cold, dominated by immediate interest, always governing at the shortest range, incapable of rancor and of gratitude, making use without mercy of superiority on mediocrity, clever in getting parliamentary majorities to put in the wrong those mysterious unanimities which mutter dully under thrones; unreserved, sometimes imprudent in his lack of reserve, but with marvellous address in that imprudence; fertile in expedients, in countenances, in masks; making France fear Europe and Europe France!
Incontestably fond of his country, but preferring his family; assuming more domination than authority and more authority than dignity, a disposition which has this unfortunate property, that as it turns everything to success, it admits of ruse and does not absolutely repudiate baseness, but which has this valuable side, that it preserves politics from violent shocks, the state from fractures, and society from catastrophes; minute, correct, vigilant, attentive, sagacious, indefatigable; contradicting himself at times and giving himself the lie; bold against Austria at Ancona, obstinate against England in Spain, bombarding Antwerp, and paying off Pritchard; singing the Marseillaise with conviction, inaccessible to despondency, to lassitude, to the taste for the beautiful and the ideal, to daring generosity, to Utopia, to chimæras, to wrath, to vanity, to fear; possessing all the forms of personal intrepidity; a general at Valmy; a soldier at Jemappes; attacked eight times by regicides and always smiling. Brave as a grenadier, courageous as a thinker; uneasy only in the face of the chances of a European shaking up, and unfitted for great political adventures; always ready to risk his life, never his work; disguising his will in influence, in order that he might be obeyed as an intelligence rather than as a king; endowed with observation and not with divination; not very attentive to minds, but knowing men, that is to say requiring to see in order to judge; prompt and penetrating good sense, practical wisdom, easy speech, prodigious memory; drawing incessantly on this memory, his only point of resemblance with Cæsar, Alexander, and Napoleon; knowing deeds, facts, details, dates, proper names, ignorant of tendencies, passions, the diverse geniuses of the crowd, the interior aspirations, the hidden and obscure uprisings of souls, in a word, all that can be designated as the invisible currents of consciences; accepted by the surface, but little in accord with France lower down; extricating himself by dint of tact; governing too much and not enough; his own first minister; excellent at creating out of the pettiness of realities an obstacle to the immensity of ideas; mingling a genuine creative faculty of civilization, of order and organization, an indescribable spirit of proceedings and chicanery, the founder and lawyer of a dynasty; having something of Charlemagne and something of an attorney; in short, a lofty and original figure, a prince who understood how to create authority in spite of the uneasiness of France, and power in spite of the jealousy of Europe.
#Les Mis#Les Miserables#Les Mis Letters#Les Mis Letters in Adaptation#Louis-Philippe#pureanonedits#lesmiserablesedit#lesmisedit#lesmiserables1972edit#LM 9.1.3#TUMBLR WOULDN'T LET ME POST THIS WITHOUT THE BREAK LMAO#long post
19 notes
·
View notes
Text
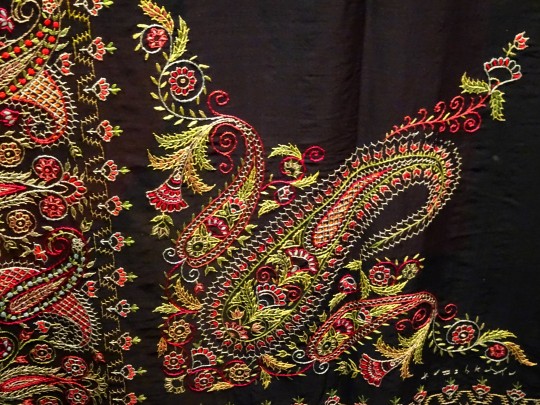
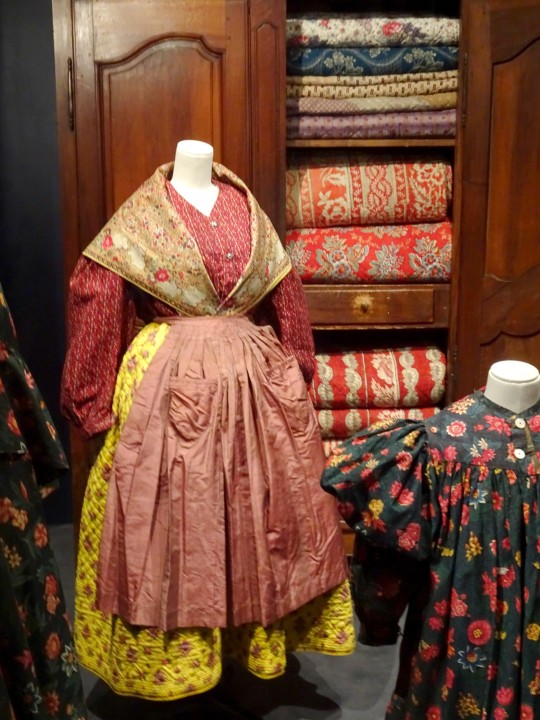





Marseille. Au musée Borély, musée des Arts Décoratifs, de la Faïence et de la Mode, il y a actuellement une expo très intéressante : "L'Asie Fantasmée", montrant comment , au XVIIIe et au XIXe s. , la France (et l'Europe), voyaient et surtout imaginaient les empires d'Orient, Chine, Japon et Empire Ottoman entre autres, avec parfois une réciprocité étonnante.
châle double-pointe Louis-Philippe
châle Louis-Philippe; châle des Indes 1860; robe en soie 1880 avec châle "tapis", mi XIXe s.
Devant : tissus "Bonnes Herbes'": mantelet de visite avec jupon de travail début XIX; robe de fillette 1830; robes à manches "gigot" avec fichu et tablier début XIXe. Derrière : ...
...caraco, jupon, fichu, tablier - Marseille, vers 1850 ; dans la penderie : couvertures XVIII et XIXe s.
châle Amli-Shall - Cachemire, milieu XIXe s.
#marseille#musée borély#musée des arts décoratifs de la faïence et de la mode#expo#l'asie fantasmée#mode#indienne#indiennes#tissus#louis-philippe#châle#cachemire#châle tapis#bonnes herbes#mantelet#mantelet de visite#jupon#jupon de travail#manches gigot#fichu#couverture#caraco#amli-shall
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

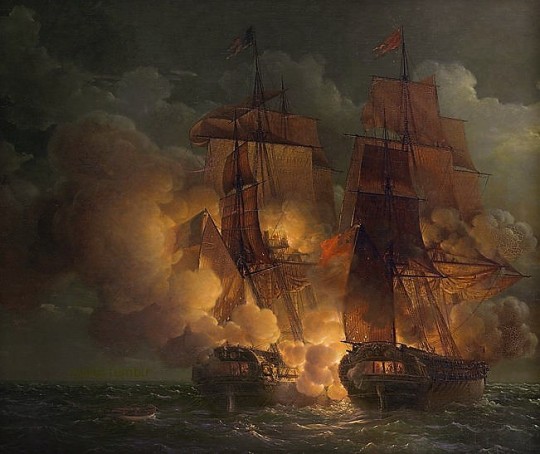
Honoré Daumier. [Honest reward, decreed, in 1800, to Louis Philippe of Orleans, surgeon and immigrant, but always French, by the not very delicate savages of North America.] Published in La Caricature, 19 February 1835.
This caricature alludes to the exile of Louis-Philippe Duke of Orleans (who became Louis-Philippe I King of the French in 1830) in North America from 1797 to 1799.
3 notes
·
View notes
Photo

An homage to Charles Philipon in le Journal Amusant, 1919
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Uses of History, 7 – From France 1812 to Russia, 1917, 4
The Uses of History, 7 – From France 1812 to Russia, 1917, 4
(Image credit: Web Gallery of Art)
Following the failure of the Decembrist Revolt in 1825 and the accession of Tsar Nicholas I, the vast Russian Empire was locked into extreme reactionarianism. The reformist elements were suppressed and no license was permitted in expressing contrary views to Divine Right for the Tsar under God’s anointing, aristocratic privilege as its corollary, as well as the…

View On WordPress
#July Monarchy#King Charles X#Louis-Philippe#Marmont#Revolution of 1830#Russian émigrés in France#Swiss Guard
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Roerig Frankrijk: over pensioenen en een misplaatste keizer
De Franse politieke cultuur heeft veel merkwaardigs. De quasi-revolutionaire stemming waarin het land nu al maanden verkeert, naar aanleiding van zoiets onbenulligs als de geleidelijke verhoging van de pensioengerechtigde leeftijd van 62 naar 64 in het jaar 2030, is daarvan een goed voorbeeld. Wie de luide tegenstanders van deze ‘hervorming’ hoort – parlementariërs van ‘La France Insoumise’,…

View On WordPress
#Adolphe Thiere#Élysée#Bourbons#Commune#De Gaulle#Disderi#Edgar Quinet#Empire#Guernesey#Hugo#Jersey#Koning van Holland#Krimoorlog#La France Insoumise#Le Pen#Louis-Philippe#Macron#Manet#Maximiliaan#Melenchon#Mexico#Mitterrand#Napoleon Bonaparte#Napoleon III#Nice#Rassemblement National#Saint-Simon#Savoie#Schoelcher#Second Empire
0 notes
Text

The Accursed Kings in 1314
#mine#the accursed kings#les rois maudits#philippe le bel#louis X le hutin#philippe V le long#Charles V le Bel#Isabelle de France#Mahaut d’Artois#14th century#medieval#middle ages
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
if you're wondering what the big deal is about the louis-philippe sentence in les misérables, it is, in the original french, 760 words long. the subject of the sentence doesn't appear until 95% of the way through, at word #711; the main verb is word #712. the sentence contains 91 commas and 49 semicolons and is almost entirely a list of laudatory adjectival phrases describing the erstwhile king of france. this is perhaps especially notable because les mis is, shall we say, not known for being particularly gung-ho about the monarchy.
this sentence copied and pasted into Word takes up more than one page single-spaced. in the 1800-page folio classique edition, it is fully two and a half of those 1800 pages. that means that les mis is 0.14% this single sentence. more of les mis is made up of this sentence than earth's atmosphere is made up of carbon dioxide (0.04%). if the page count of les mis stayed the same but every sentence was the length of this one, les mis would consist of only 720 sentences total.
incidentally, guess who named hugo a peer of france 17 years before the publication of les mis?
#he also goes on for another six pages after this but by then he has remembered the existence of the full stop#the endnotes say that hugo 'se devait de faire [ce portrait] aussi favorable que possible à la personnalité de l'homme#qui avait favorisé sa carrière' (had to make this portrait as favorable as possible to the character of the man who had favored his career)#in fairness to hugo it's not like louis-philippe was alive to read this. so he wasn't just sucking up to get something out of it#he says at the end of the chapter that this description is 'entirely disinterested'. which like on the one hand i get#bc like i said louis-philippe was not in power and reading this. but otoh victor 'ancien pair de france' hugo u r not exactly unbiased. lol#les mis#lm 4.1.3#i just looked up the english translation and gasp! hapgood turned it into four separate sentences!!!!#so i think y'all who are reading it via les mis letters (which uses hapgood i think?) are gonna miss out on the full experience :/#my posts#linked to#syntax#idk if i got this across but the worst part is that the subject of the sentence - the beginning of the independent clause -#doesn't occur until the very end. so for the first 95% of the sentence you're just waiting for the bass to drop!!!#like reading it out loud you have to raise your pitch at the end of every dependent clause because you haven't gotten to the subject yet#AND THERE ARE SO MANY CLAUSES!! 49 SEMICOLONS PEOPLE!!! FORTY-NINE!!!!#victor hugo would be TERRIBLE as a hype man. he would take so long that the crowd would tear him to pieces with their fingernails#before louis-philippe could come out on stage. and then they'd be so mad at louis-philippe for inspiring him that they'd tear LP apart too#actually i think i'm using hype man wrong. i'm thinking of the guy that gets the crowd hyped up for the main guy before the main guy#makes an appearance. a hype man is the guy who makes interjections during a song. victor hugo would be bad at both of these#like just imagine the announcer at the beginning of a basketball game. and now...your starting lineup...at power forward...#and then he just says the 760-word louis-philippe sentence.#dead. murdered at the hands of the fans. microphone shoved down his trachea.
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
"that you could be so cruel" ok correct me if i'm wrong but does penelope featherington not run a gossip rag that exist solely to publish unsubstantiated rumors about women she doesn't like for various reasons that have profoundly negative repercussions on those women (didn't the publication of marina's pregnancy lead to marina almost dying in her quest to terminate said pregnancy??????) and has in fact used that same rag to put not just colin's entire family but also specifically colin's sister, her best friend, through a significant amount of grief and strife that came as a direct result of that rag?
but colin's the cruel one? because she happened to eavesdrop on a conversation where he said he doesn't wanna date her? that's cruelty but all the other stuff isn't?
#personal#bridgerton#anti penelope featherington#i'm gonna be honest i skim the absolute fuck out of this show whenever i force myself to watch it#but from what i remember that is literally what penelope does as lady whistledown#but yeah sure a guy who'd never shown any interest in her continuing to not show interest is the worst thing ever done to a human woman#like girl fix yourself!!!#it's you you're the problem!#(also typing that just led me to a horrible realization that at some low point for penelope in the show)#(we're gonna get a vitamin string quartet cover of antihero by taylor swift)#anyway eloise should be allowed to slap girlie across the face once an episode until she begs forgiveness#i'm only interested in that and if jonathan bailey's character has more sad scenes i can use in gifsets about louis philippe of france
214 notes
·
View notes
Text










Le grand chariot (Philippe Garrel, 2023)
#films watched in 2024#Le grand chariot#The Plough#Philippe Garrel#Garrel#2023#quote#resistence#life#philosophy#Esther Garrel#Lena Garrel#Louis Garrel#siete#Damien Mongin#Francine Bergé#Mathilde Weil#Asma Messaoudene#drama#family#art#puppet
161 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Louis-Philippe Crépin (detail)
1K notes
·
View notes
Photo
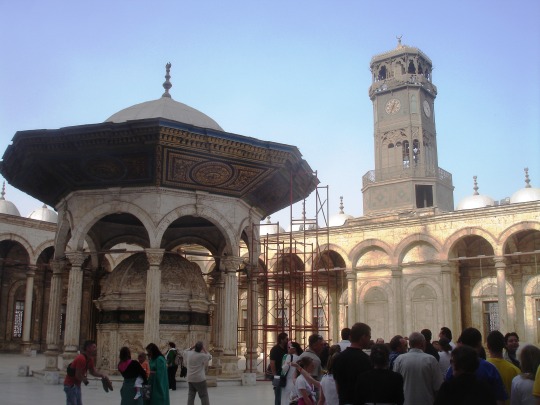
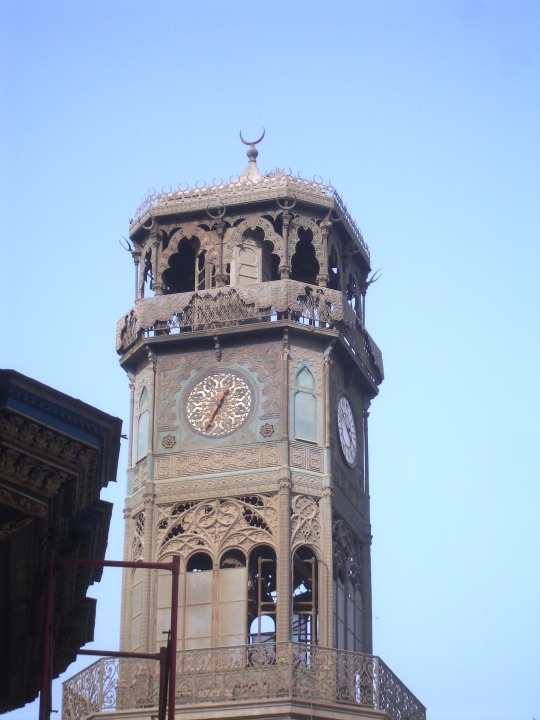







Retour à mon projet de présenter la plupart de mes 52825 photos
2010. Ma mère avait toujours rêvé d’aller en Egypte. On concrétise ce rêve !
La Citadelle du Caire : la Mosquée de Mohammed Ali (sur les 2 dernières, on voit l’horloge de Louis-Philippe)
#souvenirs#égypte#citadelle#citadelle du caire#le caire#mosquée#mosquée de mohammed ali#mohammed ali#tombeau#horloge#louis-philippe#horloge de louis-philippe
18 notes
·
View notes
Text











"On the field, I saw a man, young like we were. He carried his brother in a sack over his shoulder. He told me he had promised their mother to take him home. Would you do that for me? I would, but you? I do not know."
#i thought about this show yesterday and while i think the script and acting are bad...it's somewhat entertaining to watch idk#it's just drama after drama...although this scene is actually great though...#versaillesedit#versailles#philippe d'orléans#periodedit#periodedits#perioddramaedit#cinemapix#tvarchive#tvedit#perioddramacentral#alex vlahos#george blagden#louis xiv#dailytvfilmgifs#tvfilmcentral#userstream#tvfilmdaily#by jen
93 notes
·
View notes
Text
Frev Friendships — Saint-Just and Robespierre

You who supports the tottering fatherland against the torrent of despotism and intrigue, you whom I only know, like God, through his miracles; I speak to you, monsieur, to ask you to unite with me in order to save my sad fatherland. The city of Gouci has relocated (this rumour goes around here) the free markets from the town of Blérancourt. Why do the cities devour the privileges of the countryside? Will there remain no more of them to the latter than size and taxes? Support, please, with all your talent, an address that I make for the same letter, in which I request the reunion of my heritage with the national areas of the canton, so that one lets to my country a privilege without which it has to die of hunger. I do not know you, but you are a great man. You are not only the deputy of a province, you are one of humanity and of the Republic. Please, make it that my request be not despised. I have the honour to be, monsieur, your most humble, most obedient servant.
Saint-Just, constituent of the department of Aisne.
To Monsieur de Robespierre in the National Assembly in Paris.
Blérancourt, near Noyon, August 19, 1790.
Saint-Just’s first letter ever written to Robespierre, dated August 19 1790
Citizens, you are aware that, to dispel the errors with which Roland has covered the entire Republic, the Society has decided that it will have Robespierre's speech printed and distributed. We viewed it as an eternal lesson for the French people, as a sure way of unmasking the Brissotin faction and of opening the eyes of the French to the virtues too long unknown of the minority that sits with the Mountain. I remind you that a subscription office is open at the secretariat. It is enough for me to point it out to you to excite your patriotic zeal, and, by imitating the patriots who each deposited fifty écus to have Robespierre's excellent speech printed, you will have done well for the fatherland.
Saint-Just at the Jacobins, January 1 1793
Patriots with more or less talent […] Jacquier, Saint-Just’s brother-in-law.
Robespierre in a private list, written sometime during his time on the Committee of Public Safety
Saint-Just doesn’t have time to write to you. He gives you his compliments.
Lebas in a letter to Robespierre October 25 1793
Trust no longer has a price when we share it with corrupt men, then we do our duty out of love for our fatherland alone, and this feeling is purer. I embrace you, my friend.
Saint-Just.
To Robespierre the older.
Saint-Just in a post-scriptum note added to a letter written by Lebas to Robespierre, November 5 1793. Saint-Just uses tutoiement with Robespierre here, while Lebas used vouvoiement.
We have made too many laws and too few examples: you punish but the salient crimes, the hypocritical crimes go unpunished. Punish a slight abuse in each part, it is the way to frighten the wicked, and to make them see that the government has its eye on everything. No sooner do we turn our backs than the aristocracy rises in the tone of the day, and commits evils under the colors of liberty.
Engage the committee to give much pomp to the punishment of all faults in government. Before a month has passed you will have illuminated this maze in which counter-revolution and revolution march haphazardly. Call, my friend, the attention of the Jacobin Club to the strong maxims of the public good; let it concern itself with the great means of governing a free state. I invite you to take measures to find out if all the manufactures and factories of France are in activity, and to favor them, because our troops would within a year find themselves without clothes; manufacturers are not patriots, they do not want to work, they must be forced to do so, and not let down any useful establishment. We will do our best here. I embrace you and our mutual friends.
Saint-Just
To Robespierre the older.
Saint-Just in a letter to Robespierre, December 14 1793
Paris, 9 nivôse, year 2 of the Republic.
Friends.
I feared, in the midst of our successes, and on the eve of a decisive victory, the disastrous consequences of a misunderstanding or of a ridiculous intrigue. Your principles and your virtues reassured me. I have supported them as much as I could. The letter that the Committee of Public Safety sent you at the same time as mine will tell you the rest. I embrace you with all my soul.
Robespierre.
Robespierre in a letter to Saint-Just and Lebas, December 29 1793
Why should I not say that this (the dantonist purge) was a meditated assassination, prepared for a long time, when two days after this session where the crime was taking place, the representative Vadier told me that Saint-Just, through his stubbornness, had almost caused the downfall of the members of the two committees, because he had wanted that the accused to be present when he read the report at the National Convention; and such was his obstinacy that, seeing our formal opposition, he threw his hat into the fire in rage, and left us there. Robespierre was also of this opinion; he believed that by having these deputies arrested beforehand, this approach would sooner or later be reprehensible; but, as fear was an irresistible argument with him, I used this weapon to fight him: You can take the chance of being guillotined, if that is what you want; For my part, I want to avoid this danger by having them arrested immediately, because we must not have any illusions about the course we must take; everything is reduced to these bits: If we do not have them guillotined, we will be that ourselves.
À Maximilien Robespierre aux enfers (1794) by Taschereau de Fargues and Paul-Auguste-Jacques. Robespierre and Saint-Just had also worked out the dantonists’ indictment together.
…As far from the insensibility of your Saint-Just as from his base jealousies, [Camille] recoiled in front if the idea of accusing a college comrade, a companion in arms. […] Robespierre, can you really complete the fatal projects which the vile souls that surround you no doubt have inspired you to? […] Had I been Saint-Just’s wife I would tell him this: the sake of Camille is yours, it’s the sake of all the friends of Robespierre!
Lucile Desmoulins in an unsent letter to Robespierre, written somewhere between March 31 and April 4 1794. Lucile seems to have believed it was Saint-Just’s ”bad influence” in particular that got Robespierre to abandon Camille.
In the beginning of floréal (somewhere between April 20 and 30) during an evening session (at the Committee of Public Safety), a brusque fight erupted between Saint-Just and Carnot, on the subject of the administration of portable weapons, of which it wasn’t Carnot, but Prieur de la Côte-d’Or, who was in charge. Saint-Just put big interest in the brother-in-law of Sijas, Luxembourg workshop accounting officer, that one thought had been oppressed and threatened with arbitrary arrest, because he had experienced some difficulties for the purpose of his service with the weapon administration. In this quarrel caused unexpectedly by Saint-Just, one saw clearly his goal, which was to attack the members of the committee who occupied themselves with arms, and to lose their cooperateurs. He also tried to include our collegue Prieur in the inculpation, by accusing him of wanting to lose and imprison this agent. But Prieur denied these malicious claims so well, that Saint-Just didn’t dare to insist on it more. Instead, he turned again towards Carnot, whom he attacked with cruelty; several members of the Committee of General Security assisted. Niou was present for this scandalous scene: dismayed, he retired and feared to accept a pouder mission, a mission that could become, he said, a subject of accusation, since the patriots were busy destroying themselves in this way. We undoubtedly complained about this indecent attack, but was it necessary, at a time when there was not a grain of powder manufactured in Paris, to proclaim a division within the Committee of Public Safety, rather than to make known this fatal secret? In the midst of the most vague indictments and the most atrocious expressions uttered by Saint-Just, Carnot was obliged to repel them by treating him and his friends as aspiring to dictatorship and successively attacking all patriots to remain alone and gain supreme power with his supporters. It was then that Saint-Just showed an excessive fury; he cried out that the Republic was lost if the men in charge of defending it were treated like dictators; that yesterday he saw the project to attack him but that he defended himself. ”It’s you,” he added, ”who is allied with the enemies of the patriots. And understand that I only need a few lines to write for an act of accusation and have you guillotined in two days.”
”I invite you, said Carnot with the firmness that only appartient to virtue: I provoke all your severity against me, I do not fear you, you are ridiculous dictators.” The other members of the Committee insisted in vain several times to extinguish this ferment of disorder in the committee, to remind Saint-Just of the fairer ideas of his colleague and of more decency in the committee; they wanted to call people back to public affairs, but everything was useless: Saint-Just went out as if enraged, flying into a rage and threatening his colleagues. Saint-Just probably had nothing more urgent than to go and warn Robespierre the next day of the scene that had just happened, because we saw them return together the next day to the committee, around one o'clock: barely had they entered when Saint-Just, taking Robespierre by the hand, addressed Carnot saying: ”Well, here you have my friends, here are the ones you attacked yesterday!” Robespierre tried to speak of the respective wrongs with a very hypocritical tone: Saint-Just wanted to speak again and excite his colleagues to take his side. The coldness which reigned in this session, disheartened them, and they left the committee very early and in a good mood.
Réponse des membres des deux anciens Comités de salut public et de sûreté générale (Barère, Collot, Billaud, Vadier), aux imputations renouvellées contre eux, par Laurent Lecointre et declarées calomnieuses par décret du 13 fructidor dernier; à la Convention Nationale (1795), page 103-105
My friends, the committee has taken all the measures within its control at this time to support your zeal. It has asked me to write to you to explain the reasons for some of its provisions. It believed that the main cause of the last failure was the shortage of skilled generals, it will send you all the patriotic and educated soldiers that can be found. It thought it necessary at this time to re-use Stetenhofen, whom it is sending to you, because he has military merit, and because the objections made against him seem at least to be balanced by proofs of loyalty. He also relies on your wisdom and your energy. Salut et amitié.
Paris, 15 floréal, year 2 of the Republic.
Robespierre.
Robespierre to Saint-Just and Lebas, May 4 1793
Dear collegue,
Liberty is exposed to new dangers; the factions arise with a character more alarming than ever. The lines to get butter are more numerous and more turbulent than ever when they have the least pretexts, an insurrection in the prisons which was to break out yesterday and the intrigues which manifested themselves in the time of Hébert are combined with assassination attemps on several occasions against members of the Committee of Public Safety; the remnants of the factions, or rather the factions still alive, are redoubled in audacity and perfidy. There is fear of an aristocratic uprising, fatal to liberty. The greatest peril that threatens it is in Paris. The Committee needs to bring together the lights and energy of all its members. Calculate whether the army of the North, which you have powerfully contributed to putting on the path to victory, can do without your presence for a few days. We will replace you, until you return, with a patriotic representative.
The members composing the Committee of Public Safety.
Robespierre, Prieur, Carnot, Billaud-Varennes, Barère.
Letter to Saint-Just from the CPS, May 25 1794, written by Robespierre. It was penned down just two days after the alleged attempt on Robespierre’s life by Cécile Renault.
Robespierre returned to the Committee a few days later to denounce new conspiracies in the Convention, saying that, within a short time, these conspirators who had lined up and frequently dined together would succeed in destroying public liberty, if their maneuvers were allowed to continue unpunished. The committee refused to take any further measures, citing the necessity of not weakening and attacking the Convention, which was the target of all the enemies of the Republic. Robespierre did not lose sight of his project: he only saw conspiracies and plots: he asked that Saint-Just returned from the Army of the North and that one write to him so that he may come and strengthen the committee. Having arrived, Saint-Just asked Robespierre one day the purpose of his return in the presence of the other members of the Committee; Robespierre told him that he was to make a report on the new factions which threatened to destroy the National Convention; Robespierre was the only speaker during this session. He was met by the deepest silence from the Committee, and he leaves with horrible anger. Soon after, Saint-Just returned to the Army of the North, since called Sambre-et-Mouse. Some time passes; Robespierre calls for Saint-Just to return in vain: finally, he returns, no doubt after his instigations; he returned at the moment when he was most needed by the army and when he was least expected: he returned the day after the battle of Fleurus. From that moment, it was no longer possible to get him to leave, although Gillet, representative of the people to the army, continued to ask for him.
Réponse de Barère, Billaud-Varennes, Collot d’Herbois et Vadier aux imputations de Laurent Lecointre (1795)
On 10 messidor (June 28) I was at the Committee of Public Safety. There, I witnessed those who one accuses today (Billaud-Varenne, Barère, Collot-d'Herbois, Vadier, Vouland, Amar and David) treat Robespierre like a dictator. Robespierre flew into an incredible fury. The other members of the Committee looked on with contempt. Saint-Just went out with him.
Levasseur at the Convention, August 30 1794. If this scene actually took place, it must have done so one day later, 11 messidor (June 29), considering Saint-Just was still away on a mission on the tenth.
Isn’t it around the same time (a few days before thermidor) that Saint-Just and Lebas would dine at your father’s house with Robespierre?
Lebas often dined there, having married one of my sisters. Saint-Just rarely there, but he frequently went to Robespierre’s and climbed the stairs to his office without speaking to anyone.
During the dinner which I’m talking about, did you hear Saint-Just propose to Robespierre to reconcile with some members of the Convention and Committees who appeared to be opposed to him?
No. I only know that they appeared to be very devided.
Do you have any ideas what these divisions were about?
I only learned about it through the discussions which took place on this subject at the Jacobins and through the altercation which was said to have taken place at the Committee of Public Safety between Robespierre older and Carnot.
Robespierre’s host’s son Jacques-Maurice Duplay in an interrogation held January 1 1795
Saint-Just then fell back on his report, and said that he would join the committee the next day (9 thermidor) and that if it did not approve it, he would not read it. Collot continued to unmask Saint-Just; but as he focused more on depicting the dangers praying on the fatherland than on attacking the perfesy of Saint-Just and his accomplices, he gradually reassured himself of his confusion; he listened with composure, returning to his honeyed and hypocritical tone. Some time later, he told Collot d'Herbois that he could be reproached for having made some remarks against Robespierre in a café, and establishing this assertion as a positive fact, he admitted that he had made it the basis of an indictment against Collot, in the speech he had prepared.
Réponse des membres des deux anciens Comités de salut public et de sûrété générale… (1795) page 107.
I attest that Robespierre declared himself a firm supporter of the Convention and never spoke but gently in the Committee so as not to undermine any of its members. […] Billaud-Varenne said to Robespierre, “We are your friends, we have always walked together.” This dishonesty made my heart shudder. The next day, he called him Peisistratos and had written his act of accusation. […] If you reflect carefully on what happened during your last session, you will find the application of everything I said: a man alienated from the Committee due to the bitterest treatments, when this Committee was, in fact, no longer made up of more than the two or three members present, justified himself before you; he did not explain himself clearly enough, to tell the truth, but his alienation and the bitterness in his soul can excuse him somewhat: he does not know why he is being persecuted, he knows nothing except his misfortune. He has been called a tyrant of opinion: here I must explain myself and shine light on a sophism that tends to proscribe merit. And what exclusive right do you have to opinion, you who find that it is a crime to touch souls? Do you find it wrong that a man should be tenderhearted? Are you thus from the court of Philip, you who make war on eloquence? A tyrant of opinion? Who is stopping you from competing for the esteem of the fatherland, you who find it so wrong that someone should captivate it? There is no despot in the world, save Richelieu, who would be insulted by the fame of a writer. Is it a more disinterested triumph? Cato is said to have chased from Rome the bad citizen who had called eloquence at the tribune of harangues, the tyrant of opinion. No one has the right to claim that; it gives itself to reason and its empire is not the in the power of governments. […] The member who spoke for a long time yesterday at this tribune did not seem to have distinguished clearly enough who he was accusing. He had no complaints and has not complained either about the Committees; because the Committees still seem to me to be dignified of your estime, and the misfortunes that I have spoken to you of were born of isolation and the extreme authority of several members left alone.
Saint-Just defending Robespierre in his last, undelivered speech, July 27 1794
One brings St. Just, Dumas and Payan, all of them shackled, they are escorted by policemen. They stay a good quarter of an hour standing in front of the door of the Committee’s room; one makes them sit down onto a windowsill; they have still not uttered a single word, pleasant people make the persons who surround these three men step aside, and say move back, let these gentlemen see their King sleep on a table, just like a man. Saint-Just moves his head in order to see Robespierre. Saint-Just’s figure appeared dejected and humiliated, his swollen eyes expressed chagrin.
Faits recueillis aux derniers instants de Robespierre et de sa saction, du 9 au 10 thermidor (1794) by anonymous.
The Committee of General Security was being spied on by Héron, D…, Lebas: Robespierre knew, through them, word for word, everything that was happening at said committee. This espionage gave rise to more intimate connections between Couthon, Saint-Just and Robespierre. The fierce and ambitious character of the latter gave him the idea of establishing the general police bureau, which, barely conceived, was immediately decreed.
Révélations puisées dans les cartons des comités de Salut public et de Sûreté générale ou mémoires (inédits) (1824) by Gabriel Jérôme Sénart.
Intimately linked with Robespierre, [Saint-Just] had become necessary to him, and he had made himself feared perhaps even more than he had desired to be loved. One never saw them divided in opinion, and if the personal ideas of one had to bow to those of the other, it is certain that Saint-Just never gave in. Robespierre had a bit of that vanity which comes from selfishness; Saint-Just was full of the pride that springs from well-established beliefs; without physical courage, and weak in body, to the point of fearing the whistling of bullets, he had the courage of reflection which makes one wait for certain death, so as not to sacrifice an idea.
Memoirs of René Levasseur (1829) volume 2, page 324-325.
Often [Robespierre] said to me that Camille was perhaps the one among all the key revolutionaries whom he liked best, after our younger brother and Saint-Just.
Mémoires de Charlotte Robespierre sur ses deux frères (1834) page 139.
After the month of March, 1794, Robespierre's conduct appeared to me to change. Saint-Just was to a great degree the cause of this, and this leader was too youthful ; he urged him into the vain and dangerous path of dictatorship which he haughtily proclaimed. From that time all confidences in the two committees were at an end, and the misfortunes that followed the division in the government became inevitable. […] We did not hide from [Robespierre] that Saint-Just, who was formed of more dictatorial stuff, would have ended by overturning him and occupying his place ; we knew too that he would have us guillotined because of our opposition to his plans; so we overthrew him.
Memoirs of Bertrand Barère (1896), volume 1, page 103-104.
About this time Robespierre felt his ambition growing, and he thought that the moment had come to employ his influence and take part in the government. He took steps with certain members of the committee and the Convention, asking them to show a desire that he, Robespierre, should become a member of the Committee of Public Safety. He told the Jacobins it would be useful to observe the work and conduct of the members of the committee, and he told the members of the Convention that there would be more harmony between the Convention and the committee if he entered it. Several deputies spoke to me about it, and the proposal was made to the committee by Couthon and Saint-Just. To ask was to obtain, for a refusal would have been a sort of accusation, and it was necessary to avoid any split during that winter which was inaugurated in such a sinister manner. The committee agreed to his admission, and Robespierre was proposed.
Ibid, volume 2, page 96-97
The continued victories of our fourteen armies were as a cloud of glory over our frontiers, hiding from allied Europe our internecine struggles, and that unhappy side of our national character which acts and reacts so deplorably as much on the whole population as on our nghts and our manners. The enthusiasm with which I announced these victories from the tnbune was so easily seen that Saint- Just and Robespierre, being in the committee at three in the morning, and learning of the taking of Namur and some other Belgian towns, insisted for the future that the letters alone of the generals should be read, without any comments which might exaggerate their contents. I saw at once at whom this reproach was directed, and I took up the gauntlet with the deasion of a man willing to once more merit the hatred of the enemies of our national glory, and the bravery of our armies. Then Samt-Just cried, “ I beg to move that Barère be no longer allowed to add froth to our victories.” […] While Saint-Just was reproving me, Robespierre supported the longsightedness of his friend… […] The next day my report on the taking of Namur was somewhat more carefully drawn up, and I alluded to the observation of my critics, who were envious of the power of public opinion in favour of our troops, then busied in saving the country. This phrase in my report was much commented on, although its meaning was only clear to those who had heard the debate in the committee on the previous evening “Sad are the tunes, sad is the period, when the recital of the triumphs and glories of the armies of the Repubhc is coldly hastened to in this place! Henceforth liberty will be no longer defended by the country, it will be handed over to its enemies!”This pronouncement was not of a nature to be forgiven by Saint-Just and Robespierre, so they determined to supplant me with regard to these reports. They forced that idiot Couthon to attend the Committee of Public Safety at eleven in the morning, before I got there Couthon asked for the letters of the generals that had come in during the night, and took his usual seat at the back of the hall, waiting until the assembly was sufficiently full for him to announce the victones. About one, Couthon, being paralysed and unable to stand up in the tribune, coldly read the news from the armies from his place. This time, no effect was produced in the Assembly, or upon the public. This attempt, authorised by Robespierre and Saint-Just, having missed fire completely, the committee signified its dissatisfaction at the innovation.
Ibid, volume 2, page 123-125
After his return from Fleurus, Saint-Just remained some time in Paris, although his mission as representative to the armies of the Sambre and Meuse and the Rhine and Moselle was unfinished. The campaign was only beginning, but he had several projects in hand, and he stayed in committee, or rather his office, where he was always absorbed and thoughtful. Robespierre, in speaking of him at the committee, said familiarly, as if speaking of an intimate friend: ”Saint-Just is silent and observant, but I have noticed, in his personality, he has a great likeness to Charles IX.” This did not flatter Saint-Just, who was a deeper and cleverer revolutionist than Robespierre. One day, when the former was angry about several legislative propositions or decrees that did not please him, Saint-Just said to him, “Be calm, it is the phlegmatic who govern.”
Ibid, volume 2, page 139
This tyrannical law was the work of Saint-Just Consult the Momteuv of the 22nd of Germinal, where it is reported with the explanation of his motives, and you will see that, if there had been no committee, SamtJust would have used his power with as much dictatorial fanaticism as did Manus, that great enemy of the Roman anstocracy. Robespierre’s fnend never forgave me for having dimmished the force of this blow. Whilst I was at the tnbune of the Convention, he came, with someone unknown, and perused my register of requisitions. He took down certain names, and some days after, towards midnight, Robespierre and Saint-Just entered the committee, where they did not usually come (for they worked in a private office, under pretext that their duties were completely private) A few moments after their entry Saint-Just complained of the abuse I had made of the requisitions, which had been granted, said he, in such profusion that the law of the 21st of Germinal had become null and void.
Ibid, volume 2, page 146
Robespierre, Saint-Just and Couthon were inseparable. The first two had a dark and duplicitous character; they pushed away with a kind of disdainful pride any familiarity or affectionate relationship with their colleagues. The third, a legless man with a pale appearance, affected good-nature, but was no less perfidious than the other two. All three of them had a cold heart, without pity, they interacted only with each other, holding mysterious meetings outside, having a large number of protégés and agents, impenetrable in their designs.
Révélations sur le Comité de salut public by Prieur-Duvernois
Robespierre, who had great confidence in Le Bas because he knew his wise and prudent character well, had chosen him to accompany Saint-Just, whose burning love of the fatherland sometimes led to too much severity, and who had a tendency to get carried away. […] [Saint-Just] also had friendship for me and came often enough to our house. […] Finally our providence, our good friend Robespierre, spoke to Saint-Just to engage him to let me depart with them, along with my sister-in-law Henriette. He consented, but with some conditions.
Memoirs of Élisabeth Lebas (1901)
Volume 8 — page 153. ”Saint-Just, his (Robespierre’s) only confident.” His only confident?
Élisabeth Lebas corrects a passage in Alphonse de Lamartine’s Histoire des Girondins (1847)
The Lamenths and Péthion in the early days, quite rarely Legendre, Merlin de Thionville and Fouché, often Taschereau, Desmoulins and Teault, always Lebas, Saint-Just, David, Couthon and Buonarotti.
Élisabeth Lebas regarding visitors to the Duplay’s during the revolution
—
When arriving in Paris in September 1792, Saint-Just first lived on No. 7 rue de Gaillon up until March 1794, and then on No. 3 rue de Caumartin (today’s No. 5) up until his death. Both those places were within a ten minute walking distance from Robespierre’s home on 398 Rue Saint-Honoré.
Saint-Just was away from Paris (and therefore Robespierre) on missions between March 9 to March 31, October 17 to December 4, December 10 to December 30, January 22 to February 13, April 30 to May 31 and June 10 to June 29.
#sj and max holding hands 🤗💓#robespierre#saint-just#maximilien robespierre#louis antoine de saint just#barère#élisabeth lebas#philippe lebas#frev#frev friendships#long post#saintspierre
197 notes
·
View notes