Text
1886-ban a montanai Madison völgyben Israel Ammon Hutchins egy reggel kutyaugatásra ébredt. A férfinak, mint minden telepes számára mindennapos lehetett a mostoha időjárással és a környéken élő nagy nagyragadozókkal folytatott harc. Azonnal kiment a ház elé, és meglátta, hogy a felesége libáit egy sötét bundájú, farkasra emlékeztető állat kergette.
Ammon a puskájáért nyúlt és az állatra lőtt, de a különös kutyaféle teremtmény megriadt a puska hangjától és berohant az erdőbe. Hutchins talán nem lepődött meg a teremtmény felbukkanásán, mivel halhatott a lény felbukkanásáról a szomszédos birtokok gazdáitól. A szemtanúk szetint a ragadozónak fekete bundája, erőteljes vállai és lejtős háta volt. Hutchins találkozása az állattal a férfi szempontjából már szerencsésebb volt Január végén a farm kutyái újra ugatással figyelmeztették a gazdájukat a behatolóra, mire a gazda már kirohant és egy pontos lövéssel leterítette a titokzatos teremtményt. Az elejtett ragadozót eladta a helyi vegyesbolt tulajának Joseph Sherwoodnak. Sherwood, aki egy múzeumot is működtetett az üzletében kitömette és "ringdocus" néven kiállította a teremtményt. Az 1980-as évekig volt megtekinthető a lény, míg egyszersmint el nem tűnt. 2007-ben került elő az Idaho-i Természettudományi Múzeum raktárából, mikor a ringdocust kilövő Hutchins unokája hosszú kutatás után rá nem talált az általa a családi legendáriumból ismert leletre. Jelenlegleg a Madison völgyi Helytörténeti Múzeumban tekinthető meg. Csak azért nem végeztek DNS vizsgálatot a kitömött kreatúrán, mivel az csak rontana a preparálás minőségén.

Tovább
0 notes
Text
Great Crossover

Allosaurus and its relatives were undoubtedly the apex predators of the Jurassic world. However, in the shadow of the sauropod-hunting carnosaurs came the first representatives of the Coelosauria theropodia, such as Ornitholestes, and even the small, mule-sized ancestors of Tyrannosaurus rex, such as Stokesaurus. However, these predators only hunted small vertebrates or fed on the carcasses left behind by large predators such as Allosaurus fragilis.
#animals#paleoart#dinosaur#wildlife#allosaurus#jurassicjune#jurassicjune2022#art#oc artwork#pencil#drawing
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
Holocene Dinosaurs Project - Leptocheirusauroidae Part 1
Leptocheirusauridae are large herbivores of the northern tundra, taiga and swamps. Their most important features are their developed forelegs, broad palms with curved claws. This helps them to dig out plants from under the snow and to pull branches closer to their beaks.
Their ancestors are omnivores of the Teschelosauridae, which lived in the Upper Cretaceous on the Asian and American continents. The thinning of the forests and the thinning and disappearance of the therizinosauroids, important plant eaters of the first Palaeocene and Eocene, played an important role in their rise to prominence.
While other Thescelosauroids evolved as quadrupedal and bipedal herbivores, the dinosaurs of the Leptoceheirusauridae retained the body plan of their ancestors. The true giant-sized representatives appeared in the Pleistocene. They evolved thick layers of fat and feathery stalks. Their powerful legs enabled them to migrate over vast areas in search of food.
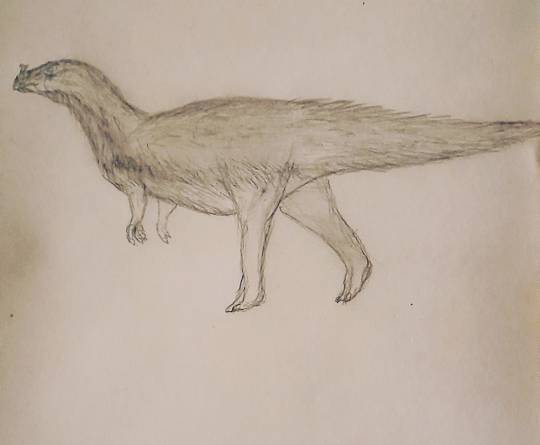
Leptocheirus palustris
A huge lepidopteran of the peatlands of Siberia and northern Europe. Their sloping legs help them avoid sinking in the mud, while their well-developed hands help them swim.
In winter they migrate to the drier interior forests from the frozen marshes. In summer they are often seen swarming to protect themselves from mosquitoes.
Solitary creatures, only during mating season do the male and q female meet, and the female shares her territory with her hatchlings.
Leptocheirus glaucos
Herds of Leptocheirus glaucos roam the frozen landscapes of Siberia in huge herds, alongside herds of Ludosaurus sibiricus. They warn other herbivores with their loud bellowing, in return for being led to rich pastures and shared by ludoceratops
0 notes
Text
Holocene Dinosaurs Project - Bauluroidae Part 2
Wyernraptor sicarius
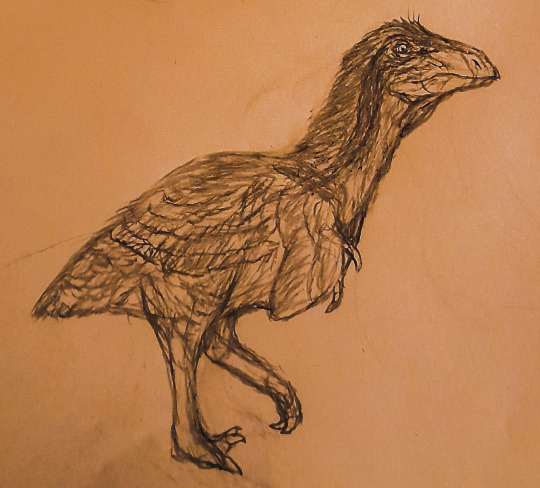
Another top predator of the African savannahs. However, unlike its relative W. coronatus, Wyernoraptor sicarius has sacrificed its speed. Its most important features that make it a formidable hunter are its powerful muscles, its well-developed jaw muscles and the raking claws on its wings.
It rushes down prey like a feathery cannonball, biting through the weak neck skin of its prey with its beak.
It roams the plains of Africa in solitude, feeding on its carrion alongside live prey.
Wyernraptor niloticus

Native to the papery marshes of the Nile, they are the largest of the Wyernraptors, standing 4 metres tall. These creatures prey mainly on sand fish in rivers. Their muscular necks shoot out like a harpoon as they wade into the water.
During high tides, they move upstream to their nesting grounds.
1 note
·
View note
Text
Holocene dinosaurs project Balauroidea Part 1
In Europe, then still isolated, the herbivorous relatives of the Ornothopoda, the rhabodontids, survive. The body size of these small herbivores decreased due to the insular effect, but when Europe becomes a continuous dryland in the Palaeocene, these herbivores will have more food sources. Therefore, their size starts to increase.
In turn, the massive, clawed predators that used to prey on them, such as Balaur, will have to adapt to larger prey to remain Europe's top predator. Their size is increasing.
With the movement of the plates, the Turgay Strait separating Europe from Asia is disappearing. The herbivores that have developed in North America and Asia flood Europe.
But the Balauridea predators take advantage of the situation and, as a counterattack, spread to Asia and North America, where they displace the last, ever smaller representatives of the Tyrannosauroids over millions of years.
Although they resemble dromaeosauroidean dinosaurs in appearance, they are not close relatives. These large-bodied predators belong to the Aviale dinosaurs. Their closest relatives are birds. Their main distinguishing features are their advanced wings and the two claws on their horns. They swoop down on prey and then flap their wings to distract and use their claws to inflict mortal wounds.
Hecatoraptor noctornus

The ambush predator of the forests of Europe. The claw on its leg is receded, but the leg muscles and the claws on its wing are hardened.
When attacked, it leaps out of the bushes, knocks its prey off balance with a powerful kick, then flaps its wings to wound it and pin it to the ground.
Wyernraptor coronatus
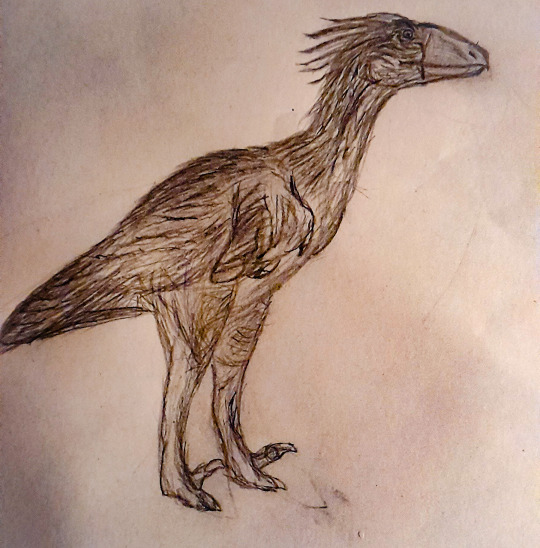
Representatives of the Balaurosauroidea native to the African savannah. They hunt in groups of three to four. They are usually a mother and her children. One of the fast-moving animals distracts its prey while its mates rush it, pinning it to the ground with their wings q and inflicting fatal wounds with their claws.
The female and male choose a mate for life. They lay their eggs in the tall grass and take turns to clutch at them.
#speculative evolution#animals#alternative history#speculative biology#holocene dinosaurs project#dinosaurs#dinosaur
0 notes
Text
Holocene Dinosaurs Project Ludoceratopsidea Part 2
Ludoceratops karkagan
This species of Ludoceratops lives in the Indian peninsula and the Middle East. This creature has the most impressive horn growth above the nose of any Old World member of the group.
The males fight fierce battles for females, driving off vanquished rivals as the males mature. Herds are thus the harems of alpha males.
Ludoceratops congoensis
It lives in the swampy region of the Congo Basin. It often dives into the water to graze on seaweed. The air sacs attached to its lungs help it to survive immersion for much longer.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Holocene Dinosaurs - Ludoceratopsidea Part 1
Large ceratopsid dinosaurs like Triceratops gradually disappeared in the late Cretaceous, but some of their representatives survived into the early Paleocene.
However, their smaller relatives in Asia and North America, the Leptoceratopsidae dinosaurs, appeared in the Late Cretaceous. In the closed forests of the Palaeocene, these dinosaurs evolved into cavity-dwelling omnivores. The vast forests became increasingly sparse. The undergrowth gained more light and became more richest, providing food for smaller herbivores. The Leptoceratopsidae dinosaurs grew in size over millions of years. By the end of the Eocene, the first Ludoceratopsidae dinosaurs appeared.
They spread across the ever-expanding plains of Asia to North America and the savannas of Africa in the Miocene.
Ludoceratops savannicus
When the African continent joined Eurasia in the Miocene period, it also closed the Mediterranean basin. The hitherto isolated region opened the way for many Eurasian animal groups. Like the Ludoceratops.
These dinosaurs had numerous advantages over the native herbivores Sauropoda and Iguanodontidea.
Primarily, they had a more efficient chewing ability and a more complex digestive system. This allowed them to extract more nutrients from the tough leaves of the increasingly proliferating grasses. As the savannah slowly became the dominant terrain in Africa, the legs of Ludoceratops became longer to allow them to roam the landscape more in search of food.
As the climate of the African continents is much drier and rainfall is seasonal, these herbivores have to migrate. The young grow much faster to keep up with the huge herds.
Ludoceratops sylvestris

The smallest species of ludoceratops. It lives in small family groups in temperate forests of Eurasia.
They are generally found around nesting sites. They migrate only when they migrate from nearby watering places.
Ludoceratops sibiricus

Common herbivores of northern tundra and pine forests. They are protected from the cold of the Arctic by a thick layer of feathers and fat.
In the long winters they dig lichens and mosses out of the snow with their hooves, but in the short summer they pick up the fat by grazing continuously
After hatching, the chicks stay with the flock until the beginning of summer
They move in the middle of the flock.
#speculative evolution#animals#wildlife#dinosaurs#dinosaur#speculative zoology#speculative biology#alternative history
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
Hi, this is the Holocene Dinosaur Project.
Imagine a world where 66 million years ago the Chicxulub asteroid escaped the Earth and didn't wipe out the great minds of the species, including the non-bird dinosaurs.
Imagine dinosaurs continuing their evolution.
New species and families appear, while others disappear.
What is more likely to affect their evolution are changes in climate during the Tertiary. The initially tropical hot and humid climate became cooler and drier. And the rainforests of the Palaeocene became thinner and thinner, giving way to savannahs.
On the other hand, since no asteroid impacts occurred, dinosaur evolution could have continued. Palaeontologists believe that a kind of faunal shift began in the Late Cretaceous, with large herbivores slowly disappearing and giving way to other groups.
This shift was completed by the middle of the Palaeocene. This is when the last large ceratopsids and hadrosauroids disappeared. They were replaced by the large-clawed therizinosauroids and the diverse Oviraptosaurosids.
They were hunted by the still apex predators Tyrannosauroids and Dromaeosauroids.
As the Palaeocene forests thinned and the understorey became richer with the influx of sunlight, the small, hitherto cavernous Leptoceratopsids and the marsh-dwelling Thescelosauroids became more abundant. Their ability to chew and the development of a multipart digestive system accelerated their spread.
During the Eocene, the European continent, which had been an island continent, collided with Asia, and Ludoceratopsidea and other groups migrating from North America entered the new continent and displaced the extant Iguanodontidea and Titanosauroidea dinosaurs. But this mozzabat created the perfect situation for another character in the story to take the stage. Although the descendants of Balaur may look like Dromaeosauroids on the outside, this is merely the result of convergent evolution. In fact, the birds' relatives and ancestors may have arrived on the islands in flight and then become flightless due to lack of competition. Over millions of years, their descendants migrate further west and these terrormorphic predators become the food competitors of the Tyrannosauroids. They will then displace their last representatives.

This is what the world looks like. The savannahs are roamed by four-legged, parrot-beaked herbivores, resembling feathered gazelles, and stalked by bird-like predators.
I'm going to show you the corners of this alternative land in this article, with pictures
#speculative evolution#speculative zoology#speculative biology#dinosaur#dinosaurs#art#alternative history
5 notes
·
View notes
Text
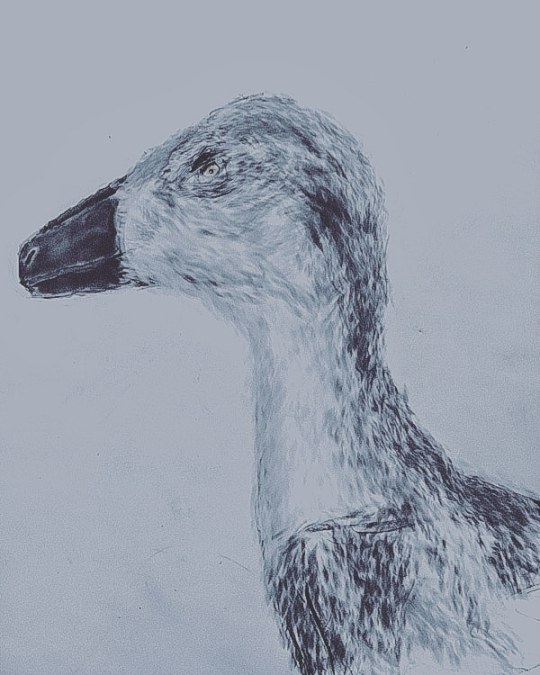

Alaskan big troodontidae portrai
This dinosaur lived 70 million years ago in Alaska. This creature was 4 metres long and 2 meters tall.
I think that it was bulk and string creature similar snow owls in present days. Their fossil teeth found in years 2017. Possible this creature was apex predator on beach of Mesosoic Artic Ocean.
0 notes
Text
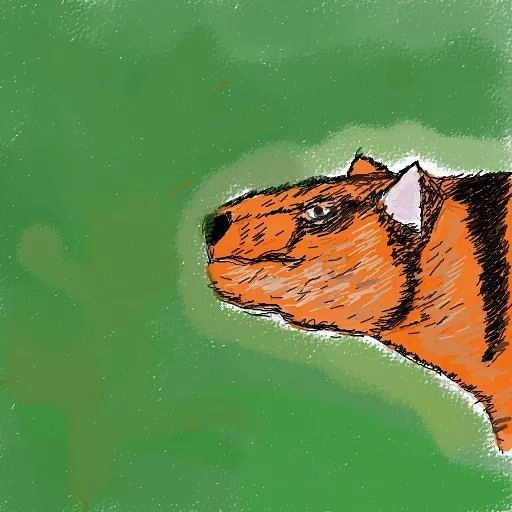

Yarry, or Quennsland tiger
My favourite cryptid in Australia. I think that this creature isn't survival marsupial lion or marsupial wolf. The yarri is species of Dasyuromorphia belike distant relative of Thylacinidae.
1 note
·
View note
Text
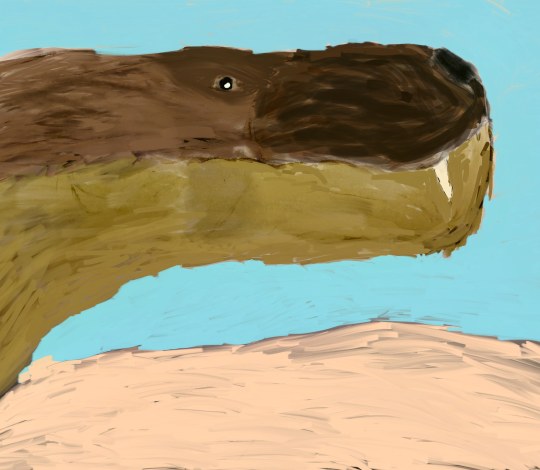

Kings of the Pangea
Gorgonops whaiti
Late Perm 255-250 million years ago. South Africa, Karoo formation.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Name: Titanus Mafune
Monarch Outpost 75
Length: 50 meter
Behavior: Herbivore, friendly
Shinzo Mafune japanese monarch scientist discovered this titan after battle of Boston. The Titanosaur lives in Japanese trench. This titan marine now, the continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column.
This titan is friendly. The Japanese specimen is male animal. Mafune find female Titanosaur in Atlantic ocean.
0 notes
Text
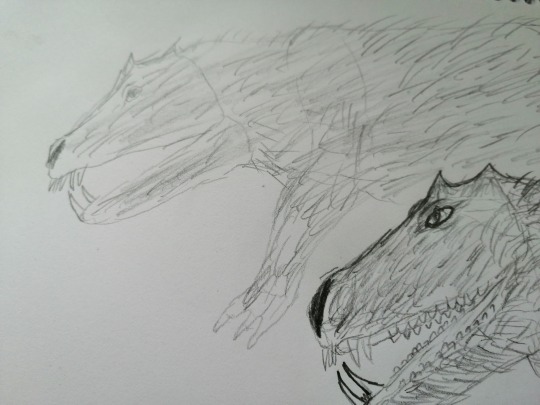
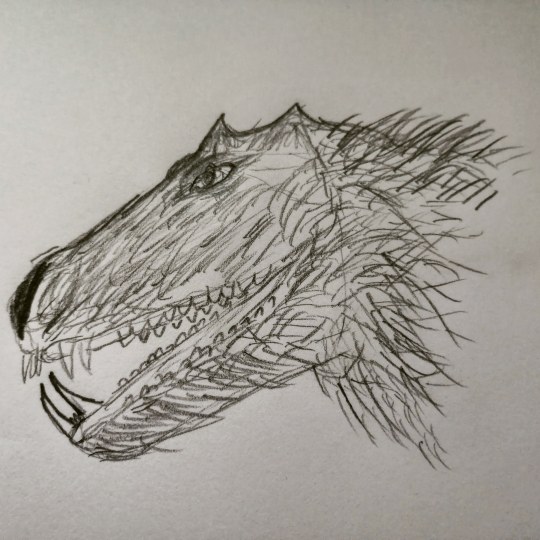


Hippotamus was apex predator is Holocene Africa. This animal chrus bones of giant herbivore like the elephant.
0 notes
Text
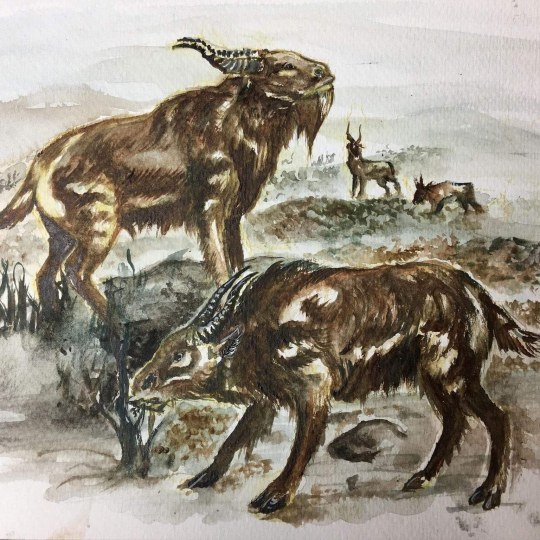

Mammothtelope
Biggest herbivore of North. Its ancestor is gnu. This antilop domesticated of human. This animals is escape from its pen after missing of the humanity.
African continent climate is wetter. Savannahs got smaller. Gnus descendants got little forest animals become dominant herbivorus mammals on planet.
The gnus descendants spread savannahs, forest and tundras after global impact event.
The mammothlope is Biggest antelope species in the future age. Height is 1.4 meters its body defemd stuffed brown-white spotted furcoat. They live big herds. They stay tundra every year.
1 note
·
View note
Text

Leaf bullock.
Little sized cattle species from Southeast Asia. It lives little family groups in umdergrows.
They are build nest for their little claves.
1 note
·
View note
Photo
I think that sasquatch is descendants Sivatpithecine monkey. This primates lived Tibetian plateu before 3.6 million years.
They grown biggest and they had stuffed furr. This giant monkeys migrante.
Some populaton stay in Himalaya. They are descendants of yeti. Other giant monkeys migrante China and Japan (Yeren and Hibagon)
Acentors of the Sasquatch migrante tNoeth America circa 1 million years ago. The clovis people hunting them After extintincion of American megafauna for they meat.
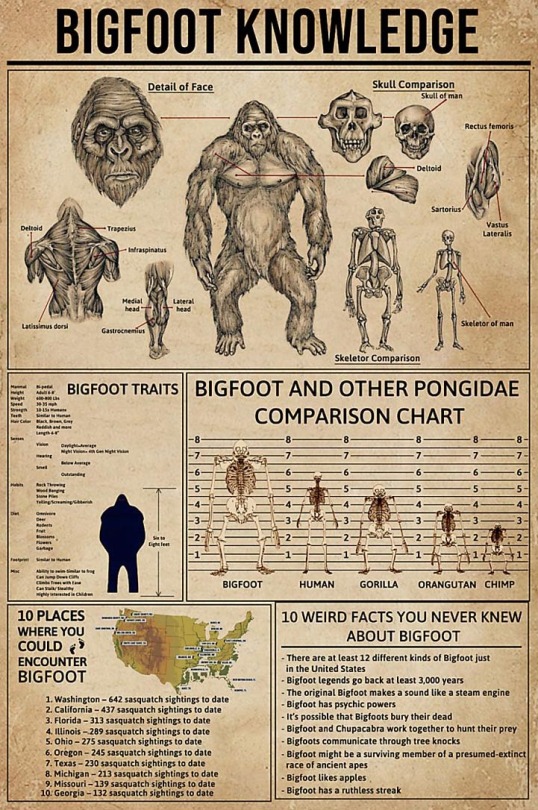
Bigfoot knowledge
260 notes
·
View notes
Text
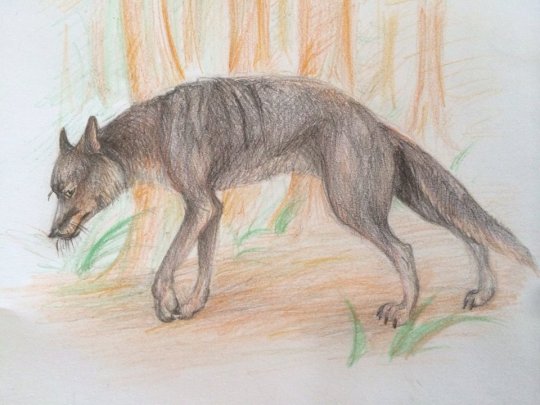

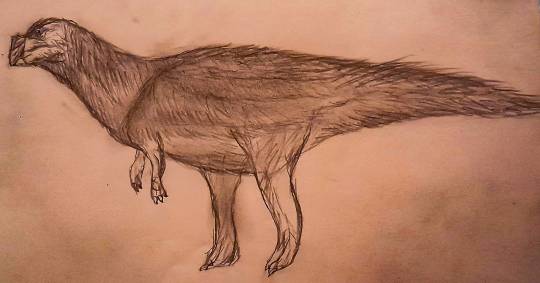
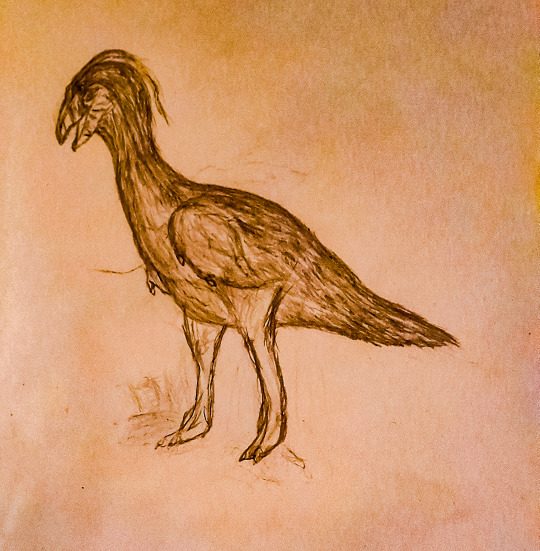
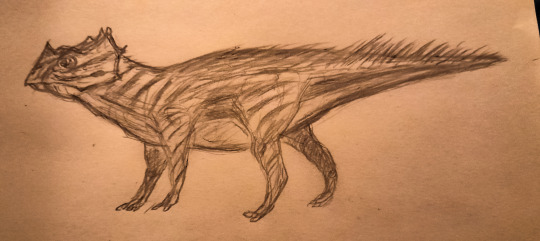
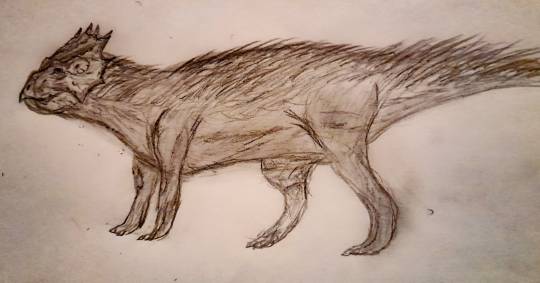
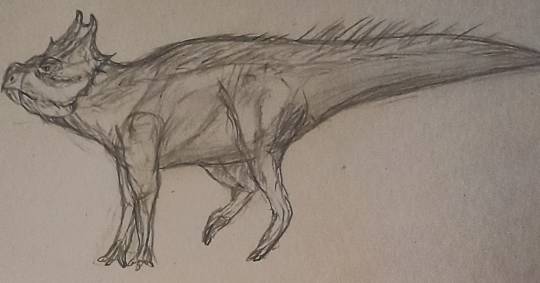
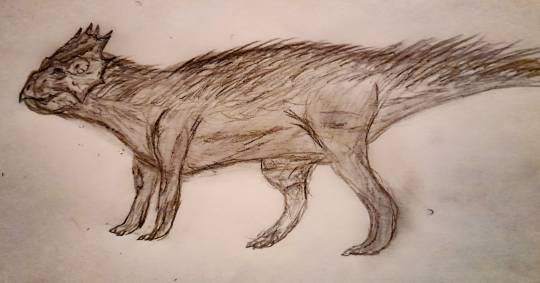
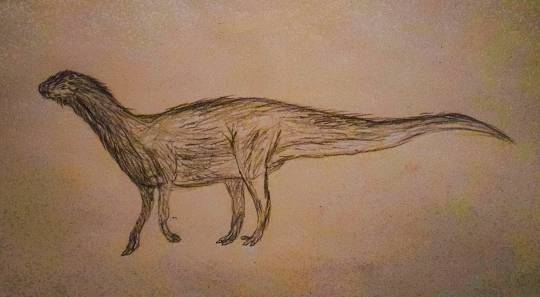
Name: North American laughing fox (Urocyon ringdocus)
First sighting: 1885. Montana, Madison Valley
Habitat: North American forest
Nutrition: Little mammals and carcass. This animal hunts in night. This animal, with its long forelegs, digs its prey out of its cavity
Family life. Lonely predator. The female gives birth to 3-4 puppies in winter.
Paiting by Nemes Boglárka.
3 notes
·
View notes